Infectious Bronchitis Virus (Gammacoronavirus) in Poultry Farming: Vaccination, Immune Response and Measures for Mitigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology of IBV
3. Vaccination
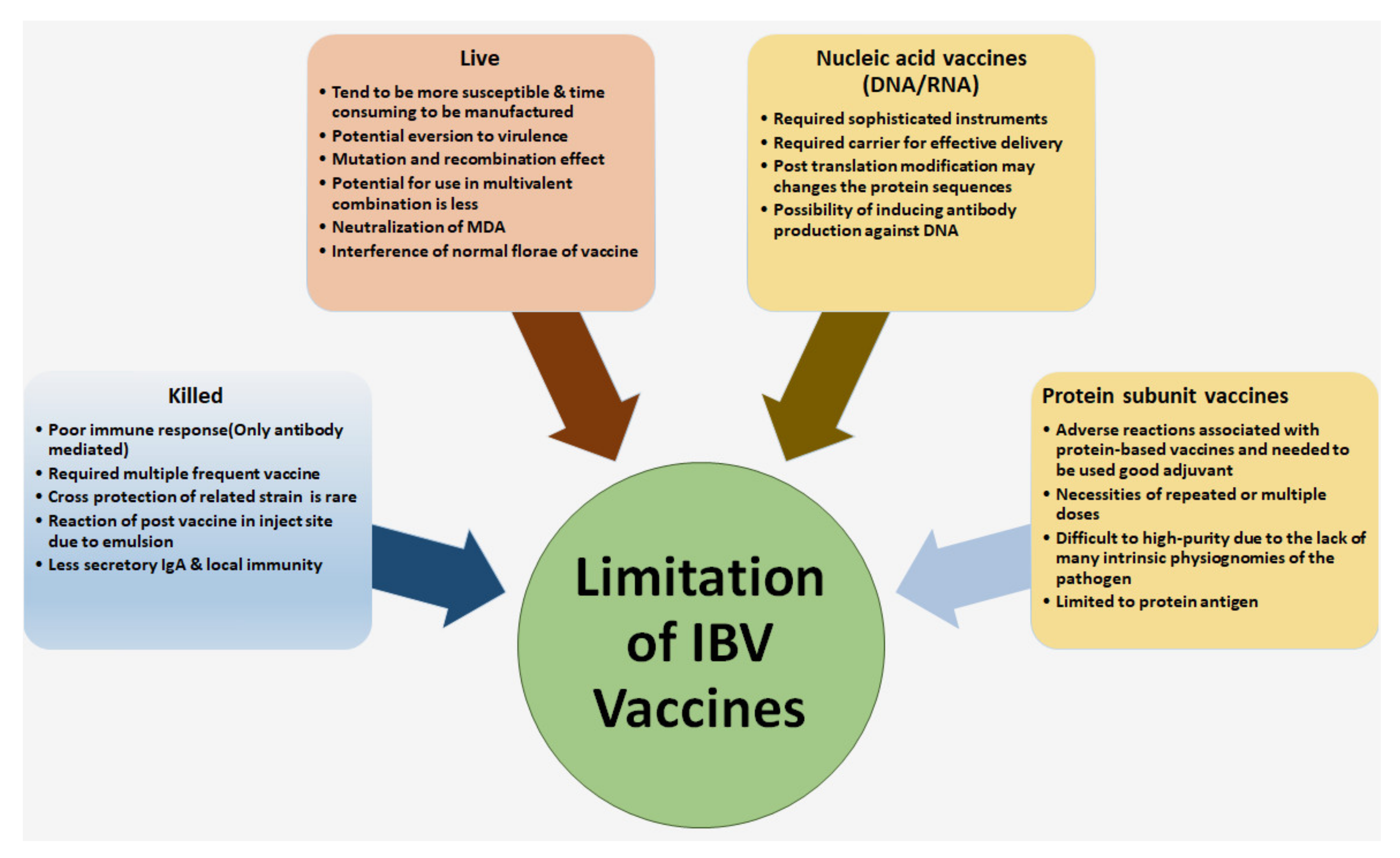
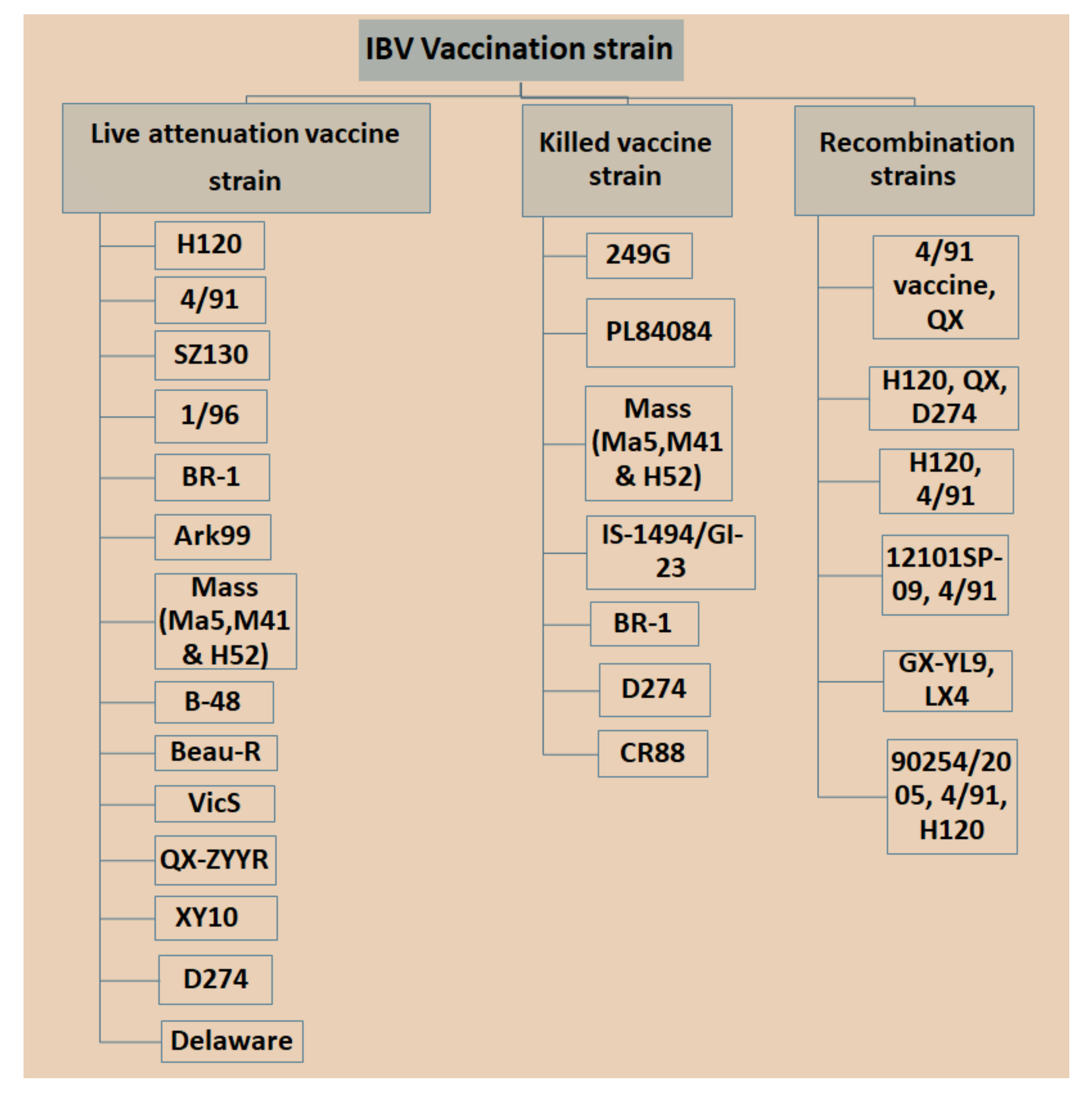
3.1. Live Attenuated IBV Vaccine
3.2. Inactivated or Killed Vaccines
3.3. Recombinant Vaccines
3.3.1. Viral Vector-Based Vaccines
3.3.2. Subunit and Peptide-Based Vaccines
3.3.3. Plasmid DNA Vaccine
3.3.4. Reverse Genetic Vaccines (RGV)
3.4. Vaccine Development against IBV
4. Immune Response against IBV
4.1. Local Immune System
4.1.1. Passive Immunity
4.1.2. Active Immunity/Innate Immune Responses
4.2. Adaptive Immune System
4.2.1. Humoral Immunity
4.2.2. Cell-Mediated Immunity (CMI)
4.2.3. Mucosal Immunity
5. Potential Mitigation Approaches in Controlling IBV
5.1. Limitation for Controlling of IBV in the Poultry Farm
5.2. Issues Related to Antiviral Therapy
5.3. Biosecurity and Control of Disease
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Liao, K.; Chen, S.; Yan, K.; Du, X.; Zhang, C.; Guo, M.; Wu, Y. Evaluation of the reproductive system development and egg-laying performance of hens infected with TW I-type infectious bronchitis virus. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Li, M.; Wei, P.; Mo, M.L.; Wei, T.C.; Li, K.R. Complete genome sequence of an infectious bronchitis virus chimera between cocirculating heterotypic strains. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 13887–13888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, D. Coronavirus avian infectious bronchitis virus. Vet. Res. 2007, 38, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.K.A.; Jackwood, M.; Jones, R.C. The long view: 40 years of infectious bronchitis research. Avian Pathol. 2012, 41, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, K. Infectious Bronchitis Virus Detection and Persistence in Experimentally Infected Chickens. Master’s Thesis, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Legnardi, M.; Tucciarone, C.M.; Franzo, G.; Cecchinato, M. Infectious Bronchitis Virus Evolution, Diagnosis and Control. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brian, D.; Baric, R. Coronavirus genome structure and replication. In Coronavirus Replication and Reverse Genetics; Brian, D.A., Baric, R.S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh, D.; Mawditt, K.; Welchman, D.d.B.; Britton, P.; Gough, R. Coronaviruses from pheasants (Phasianus colchicus) are genetically closely related to coronaviruses of domestic fowl (infectious bronchitis virus) and turkeys. Avian Pathol. 2002, 31, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papineau, A.; Berhane, Y.; Wylie, T.N.; Wylie, K.M.; Sharpe, S.; Lung, O. Genome organization of Canada Goose Coronavirus, a novel species identified in a mass die-off of Canada Geese. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, e5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehr, A.R.; Perlman, S. Coronaviruses: An overview of their replication and pathogenesis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1282, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Alluwaimi, A.M.; Alshubaith, I.H.; Al-Ali, A.M.; Abohelaika, S. The Coronaviruses of Animals and Birds: Their Zoonosis, Vaccines, and Models for SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV2. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 582287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elengoe, A. COVID-19 Outbreak in Malaysia. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2020, 11, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.-L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Siddique, R.; Shereen, M.A.; Ali, A.; Liu, J.; Bai, Q.; Bashir, N.; Xue, M. Emergence of a Novel Coronavirus, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2: Biology and Therapeutic Options. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00187-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddell, S.; Snijder, E.J. An introduction to Nidoviruses. In Nidoviruses; Perlman, S., Gallagher, T., Snijder, E., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wickramasinghe, I.N.; van Beurden, S.J.; Weerts, E.A.; Verheije, M.H. The avian coronavirus spike protein. Virus Res. 2014, 194, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bande, F.; Arshad, S.S.; Bejo, M.H.; Moeini, H.; Omar, A.R. Progress and challenges toward the development of vaccines against avian infectious bronchitis. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 424860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinley, E.T.; Hilt, D.A.; Jackwood, M.W. Avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis attenuated live vaccines undergo selection of subpopulations and mutations following vaccination. Vaccine 2008, 26, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, J.J.; Cook, J.K.A. Spotlight on avian pathology. Avian Pathol. 2020, 49, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cao, Y. Host Antiviral Responses against Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus (IBV): Focus on Innate Immunity. Viruses 2021, 13, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalk, A.E.; Hawn, M.C. An apparently new respiratory disease of baby chicks. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1931, 78, 413–422. [Google Scholar]
- Beach, J.R.; Schalm, O.W. A Filterable Virus, Distinct from That of Laryngorracheitis, the Cause of a Respiratory Disease of Chicks. Poult. Sci. J. 1936, 15, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignjatovic, J.; Gould, G.; Sapats, S. Isolation of a variant infectious bronchitis virus in Australia that further illustrates diversity among emerging strains. Arch. Virol. 2006, 151, 1567–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Youn, H.N.; Kwon, J.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.B.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, S.; Song, C.S. Characterization of a novel live attenuated infectious bronchitis virus vaccine candidate derived from a Korean nephropathogenic strain. Vaccine 2010, 28, 2887–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valastro, V.; Holmes, E.C.; Britton, P.; Fusaro, A.; Jackwood, M.W.; Cattoli, G.; Monne, I. S1 gene-based phylogeny of infectious bronchitis virus: An attempt to harmonize virus classification. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 39, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackwood, M.W. Review of infectious bronchitis virus around the world. Avian Dis. 2012, 56, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Jiang, Y.H.; Low, S.; Wang, Z.L.; Nam, S.J.; Liu, W.; Kwang, J. Characterization of three infectious bronchitis virus isolates from China associated with proventriculus in vaccinated chickens. Avian Dis. 2001, 45, 416–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasipreeyajan, J.; Pohuang, T.; Sirikobkul, N. Efficacy of different vaccination programs against Thai QX-like infectious bronchitis virus. Thai J. Vet. Med. 2012, 42, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Jang, J.H.; Lim, T.H.; Choi, S.W.; Youn, H.N.; Park, J.K.; Lee, J.B.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, I.S.; et al. Cross-protective immune responses elicited by a Korean variant of infectious bronchitis virus. Avian Dis. 2013, 57, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Low, S.; Kwang, J. Molecular epidemiology of infectious bronchitis virus isolates from China and Southeast Asia. Avian Dis. 2001, 45, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulperi, Z.M.; Omar, A.R.; Arshad, S.S. Sequence and phylogenetic analysis of S1, S2, M, and N genes of infectious bronchitis virus isolates from Malaysia. Virus Genes 2009, 38, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, H.A.; Ali, A.; El Feil, W.K.; Bazid, A.H.I.; El-Abideen, M.A.Z.; Kilany, W.H. Protective Efficacy of Different Live Attenuated Infectious Bronchitis Virus Vaccination Regimes Against Challenge With IBV Variant-2 Circulating in the Middle East. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 9, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, M.; Hidalgo, H. Live Attenuated Infectious Bronchitis Virus Vaccines in Poultry: Modifying Local Viral Populations Dynamics. Animals 2020, 10, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackwood, M.W.; Hilt, D.A.; Sellers, H.S.; Williams, S.M.; Lasher, H.N. Rapid heat-treatment attenuation of infectious bronchitis virus. Avian Pathol. 2010, 39, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvani, E.; Samal, S.K. Comparative Protective Efficacies of Novel Avian Paramyxovirus-Vectored Vaccines against Virulent Infectious Bronchitis Virus in Chickens. Viruses 2020, 12, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babapoor, S.; Almeida, D.d.O.; Fabis, J.J.; Helal, Z.H.; Wang, X.; Girshick, T.; Khan, M.I. Protective effect of In ovo vaccination with IBV-spike-recombinant DNA and chicken interferon as an adjuvant. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2009, 11, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Yuan, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Qui, X.; Meng, C.; Song, C.; Ding, C. Infectious bronchitis virus poly-epitope-based vaccine protects chickens from acute infection. Vaccine 2016, 34, 5209–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Yan, W.; Song, Z.; Li, H.; Xie, X.; Gu, K.; Ma, P.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Design and Characterization of a DNA Vaccine Based on Spike with Consensus Nucleotide Sequence against Infectious Bronchitis Virus. Vaccines 2021, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Qiu, J.; Lei, W.; Ji, W.; Li, X.; Wu, Q.; Shi, X.; Li, Z. Protection of chickens against infectious bronchitis virus with a multivalent DNA vaccine and boosting with an inactivated Vaccine. J. Vet. Sci. 2013, 14, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldemery, F.; Joiner, K.S.; Toro, H.; van Santen, V.L. Protection against infectious bronchitis virus by spike ectodomain subunit Vaccine. Vaccine 2017, 35, 5864–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Helal, Z.H.; Karch, C.P.; Mishra, N.; Girshick, T.; Garmendia, A.; Burkhard, P.; Khan, M.I. A self-adjuvanted nanoparticle based vaccine against infectious bronchitis virus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203771. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, H.; Pan, Z.; Yin, Y.; Geng, S.; Sun, L.; Jiao, X. Oral and nasal DNA vaccines delivered by attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium induce a protective immune response against infectious bronchitis in chickens. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2011, 18, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.P.; Wang, H.N.; Yang, X.; Zhang, A.Y.; Li, X.; Ding, M.D.; Liu, S.T.; Zhang, Z.K.; Yang, F. Lactococcus lactis anchoring avian infectious bronchitis virus multi-epitope peptide EpiC induced specific immune responses in chickens. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, R.; Forrester, A.; Lemiere, S.; Awad, F.; Chantrey, J.; Ganapathy, K. Mucosal, Cellular, and Humoral Immune Responses Induced by Different Live Infectious Bronchitis Virus Vaccination Regimes and Protection Conferred against Infectious Bronchitis Virus Q1 Strain. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2015, 22, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, J.J.; Cook, J.K.; van der Heijden, H.M. Infectious bronchitis virus variants: A review of the history, current situation and control measures. Avian Pathol. 2011, 40, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Y.; Chen, H.W. Infectious Bronchitis Virus Variants: Molecular Analysis and Pathogenicity Investigation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, D.; Naqi, S.A. Infectious Bronchitis, Diseases of Poultry, 10th ed.; Calnek, B.W., Barnes, H.J., Beard, C.W., McDougald, L.R., Saif, Y.M., Eds.; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2003; pp. 511–526. [Google Scholar]
- Dhama, K.; Singh, S.D.; Barathidasan, R.; Desingu, P.A.; Chakraborty, S.; Tiwari, R.; Kumar, M.A. Emergence of avian infectious bronchitis virus and its variants need better diagnosis, prevention and control strategies: A global perspective. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 17, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijlenga, G.; Cook, J.K.A.; Gelb, J., Jr.; de Wit, J.J. Development and use of the H strain of avian infectious bronchitis virus from the Netherlands as a vaccine: A review. Avian Pathol. 2004, 33, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.P.; Naqi, S.A. Maternal antibody to infectious bronchitis virus: Its role in protection against infection and development of active immunity to Vaccine. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2001, 79, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurjar, R.S.; Gulley, S.L.; van Ginkel, F.W. Cell-mediated immune responses in the head-associated lymphoid tissues induced to a live attenuated avian coronavirus Vaccine. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 41, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.H.; Song, C.S. Live attenuated nephropathogenic infectious bronchitis virus vaccine provides broad cross protection against new variant strains. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.J.; Wang, H.N.; Zhou, S.; Huang, Y.; Liu, P. Potent immune responses elicited by a bicistronic IBV DNA vaccine expressing S1 and IL-2 gene. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 2007, 47, 1055–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.; Li, H.; Qian, J.; Yang, J.; Lu, Y.; Yi, Q. Optimizing dendritic cell vaccine for immunotherapy in multiple myeloma: Tumour lysates are more potent tumour antigens than idiotype protein to promote anti-tumour immunity. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2012, 170, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladman, B.S.; Pope, C.R.; Ziegler, A.F.; Swieczkowski, T.; Callahan, C.J.; Davison, S.; Gelb, J. Protection of chickens after live and inactivated virus vaccination against challenge with nephropathogenic infectious bronchitis virus PA/Wolgemuth/98. Avian Dis. 2002, 46, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collisson, E.W.; Pei, J.; Dzielawa, J.; Seo, S.H. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes are critical in the control of infectious bronchitis virus in poultry. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2000, 24, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinley, E.T.; Jackwood, M.W.; Hilt, D.A.; Kissinger, J.C.; Robertson, J.S.; Lemke, C.; Paterson, A.H. Attenuated live vaccine usage affects accurate measures of virus diversity and mutation rates in avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus. Virus Res. 2011, 158, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vriese, J.; Steensels, M.; Palya, V.; Gardin, Y.; Dorsey, K.M.; Lambrecht, B.; Van Borm, S.; van den Berg, T. Passive protection afforded by maternally-derived antibodies in chickens and the antibodies’ interference with the protection elicited by avian influenza-inactivated vaccines in progeny. Avian Dis. 2010, 54, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblatt, A.E.; Stein, S.L. Cutaneous reactions to vaccinations. Clin. Dermatol. 2015, 33, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haan, C.A.M.; Rottier, P.J.M. Molecular interactions in the assembly of coronaviruses. Adv. Virus. Res. 2005, 64, 165–230. [Google Scholar]
- Rauch, S.; Jasny, E.; Schmidt, K.E.; Petsch, B. New Vaccine Technologies to Combat Outbreak Situations. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsis, N.; Ertl, H.C.J. Adenoviruses as vaccine vectors. Mol. Ther. 2004, 10, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.A.; Pooley, C.; Ignjatovic, J.; Tyack, S.G. A recombinant fowl adenovirus expressing the S1 gene of infectious bronchitis virus protects against challenge with infectious bronchitis virus. Vaccine 2003, 21, 2730–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, O.B.; Estevez, C.; Yu, Q.; Suarez, D.L. Passive antibody transfer in chickens to model maternal antibody after avian influenza vaccination. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2013, 152, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dertzbaugh, M.T. Genetically engineered vaccines: An overview. Plasmid 1998, 39, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.M.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, H.B.; Jing, Z.; Wang, M.; Cui, H.Y.; Tong, G.Z.; Wang, Y.F. Evaluation of recombinant fowlpox virus expressing infectious bronchitis virus S1 gene and chicken interferon-γ gene for immune protection against heterologous strains. Vaccine 2011, 29, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Yang, M.F.; Cui, B.A.; Cui, P.; Sheng, M.; Chen, G.; Wang, S.-J.; Geng, J.-W. Construction and immunogenicity of a recombinant fowlpox vaccine coexpressing S1 glycoprotein of infectious bronchitis virus and chicken IL-18. Vaccine 2010, 28, 8112–8119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Z.; Gao, G.; Reyes-Sandoval, A.; Li, Y.; Wilson, J.; Ertl, H. Oral vaccination of mice with adenoviral vectors is not impaired by preexisting immunity to the vaccine carrier. Virol. J. 2005, 79, 3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ura, T.; Okuda, K.; Shimada, M. Developments in Viral Vector-Based Vaccines. Vaccines 2014, 2, 624–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackwood, M.W. Current and future recombinant viral vaccines for poultry. Adv.Vet. Med. 1999, 41, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Z.P.; He, Y.N.; Fan, W.S.; Dong, Z.H.; Zhang, L.H.; Sun, X.K.; Song, L.L.; Wei, T.C.; Mo, M.L. Protection against virulent infectious bronchitis virus challenge conferred by a recombinant baculovirus co-expressing S1 and N proteins. Viruses 2018, 10, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Lin, Z.; Wu, J.; Qian, K.; Shao, H.; Ye, J.; Qin, A. Peptide enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (pELISA) as a possible alternative to the neutralization test for evaluating the immune response to IBV Vaccine . BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, H.N.; Wang, X.; Tang, J.N.; Gao, R.; Li, J.; Guo, Z.-C.; Li, Y.-L. Multivalent DNA vaccine enhanced protection efficacy against infectious bronchitis virus in chickens. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2009, 71, 1585–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Parr, R.L.; King, D.J.; Collisson, E.W. A highly conserved epitope on the spike protein of infectious bronchitis virus. Arch. Virol. 1995, 140, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promkuntod, N.; van Eijndhoven, R.E.W.; Vrieze, G.; de Gr¨one, A.; Verheije, M.H. Mapping of the receptorbinding domain and amino acids critical for attachment in the spike protein of avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus. Virology 2014, 448, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, S.; Timon, M. DNA vaccination: An immunological perspective. Inmunologia 2004, 23, 41–55. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.A. DNA vaccines: An historical perspective and view to the future. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 239, 62–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bande, F.; Arshad, S.S.; Bejo, M.H.; Omar, A.R.; Moeini, H.; Khadkodaei, S.; Wei, T.S.; Keong, Y.S.; Abba, Y.; Anka, I.A. Development and immunogenic potentials of chitosan-saponin encapsulated DNA vaccine against avian infectious bronchitis coronavirus. Microb Pathog. 2020, 149, 104560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Sung, H.W.; Yoon, B.I.; Kwon, H.M. Protection of chicken against very virulent IBDV provided by in ovo priming with DNA vaccine and boosting with killed vaccine and the adjuvant effects of plasmid-encoded chicken interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma. J. Vet. Sci. 2009, 10, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapczynski, D.R.; Hilt, D.A.; Shapiro, D.; Sellers, H.S.; Jackwood, M.W. Protection of chickens from infectious bronchitis by in ovo and intramuscular vaccination with a DNA vaccine expressing the S1 glycoprotein. Avian Dis. 2003, 47, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Wang, H.; Zhou, S.; Tian, G. Enhancement of the immunogenicity of an infectious bronchitis virus DNA vaccine by a bicistronic plasmid encoding nucleocapsid protein and interleukin-2. J. Virol. Met. 2008, 149, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Wang, H.; Shang, L.; Yang, T. Coadministration of chicken GM-CSF with a DNA vaccine expressing infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) S1 glycoprotein enhances the specific immune response and protects against IBV infection. Arch.Virol. 2009, 154, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prompetchara, E.; Ketloy, C.; Tharakhet, K.; Kaewpang, P.; Buranapraditkun, S.; Techawiwattanaboon, T.; Sathean-Anan-Kun, S.; Pitakpolrat, P.; Watcharaplueksadee, S.; Phumiamorn, S.; et al. DNA vaccine candidate encoding SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins elicited potent humoral and Th1 cell-mediated immune responses in mice. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotoran, W.L.; Santangelo, R.; de Miranda, B.N.M.; Irvine, D.J.; Wunderlich, G. DNA-Loaded Cationic Liposomes Efficiently Function as a Vaccine against Malarial Proteins. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, P.; Armesto, M.; Cavanagh, D.; Keep, S. Modification of the avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus for vaccine development. Bioeng. Bugs 2012, 3, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogales, A.; Martínez-Sobrido, L. Reverse Genetics Approaches for the Development of Influenza Vaccines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armesto, M.; Evans, S.; Cavanagh, D.; Abu-Median, A.B.; Keep, S.; Britton, P. A recombinant Avian infectious bronchitis virus expressing a heterologous spike gene belonging to the 4/91 serotype. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.N.; Fan, W.Q.; Yang, X.; Zhang, A.Y.; Zeng, F.Y.; Zhang, Z.K.; Cao, H.P.; Zeng, C. Establishment of reverse genetics system for infectious bronchitis virus attenuated vaccine strain H120. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 162, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapczynski, D.R.; King, D.J. Protection of chickens against overt clinical disease and determination of viral shedding following vaccination with commercially available Newcastle disease virus vaccines upon challenge with highly virulent virus from the California 2002 exotic Newcastle disease outbreak. Vaccine 2005, 23, 3424–3433. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, K.E.; El-Kady, M.F.; El-Sawah, A.A.A.; Luttermann, C.; Parvin, R.; Shany, S.; Beer, M.; Harder, T. Respiratory disease due to mixed viral infections in poultry flocks in Egypt between 2017 and 2018: Upsurge of highly pathogenic avian influenza virus subtype H5N8 since 2018. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 68, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, C.; Bennett, S.; Forrester, A.; Ganapathy, K. Genetic mutations in live infectious bronchitis vaccine viruses following single or dual in vitro infection of tracheal organ cultures. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 3232–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, P.D.; Okino, C.H.; Fernando, F.S.; Pavani, C.; Casagrande, V.M.; Lopez, R.F.V.; Montassier, M.d.F.S.; Montassier, H.J. Inactivated infectious bronchitis virus vaccine encapsulated in chitosan nanoparticles induces mucosal immune responses and effective protection against challenge. Vaccine 2018, 36, 2630–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, B. Vaccination against infectious bronchitis virus: A continuous challenge. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 206, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.K.A.; Orbell, S.J.; Woods, M.A.; Huggins, M.B. Breadth of protection of the respiratory tract provided by different live-attenuated infectious bronchitis vaccines against challenge with infectious bronchitis viruses of heterologous serotypes. Avian Pathol. 1999, 28, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.C.; Worthington, K.J.; Capua, I.; Naylor, C.J. Efficacy of live infectious bronchitis vaccines against a novel European genotype, Italy 02. Vet. Rec. 2005, 156, 646–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, J.J.; Van de Sande, H.; Prandini, F. Enhanced efficacy of the use of a monovalent infectious bronchitis virus inactivated vaccine in layers primed with H120 and 793B live IBV vaccines to increase the protection against challenge with 3 European serotypes of IBV. In Proceedings of the VI International Symposium on Corona- and Pneumoviruses and Complicating Pathogens, Rauischholzhausen, Germany, 14–17 June 2009; pp. 159–167. [Google Scholar]
- Tarpey, I.; Orbell, S.J.; Britton, P.; Casais, R.; Hodgson, T.; Lin, F.; Hogan, E.; Cavanagh, D. Safety and efficacy of an infectious bronchitis virus used for chicken embryo vaccination. Vaccine 2006, 24, 6830–6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.S.A.; Amin, Z.; Bakar, A.M.S.A.; Saallah, S.; Yusuf, N.H.M.; Shaarani, S.M.; Siddiquee, S. Factor Influences for Diagnosis and Vaccination of Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus (Gammacoronavirus) in Chickens. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohjola, L.K.; Ek-Kommonen, S.C.; Tammiranta, N.E.; Kaukonen, E.S.; Rossow, L.M.; Huovilainen, T.A. Emergence of avian infectious bronchitis in a non-vaccinating country. Avian Pathol. 2014, 43, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscox, T.; Wurm, L.; Wilson, P.; Britton, D.; Cavanagh, G.; Brooks, G. The coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus nucleoprotein localizes to the nucleolus. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erf, G.F. Cell-mediated immunity in poultry. Poult. Sci. 2004, 83, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, M.A.; Heggen, C.L.; Hussain, I. Avian macrophage: Effector functions in health and disease. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2000, 24, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghman, L.R. Immune responses to improving welfare. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 2216–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, C.A.; van de Haar, P.M.; van Haarlem, D.; van Kooten, P.; de Wit, S.; van Eden, W.; Viertlböck, B.C.; Göbel, T.W.; Vervelde, L. Identification of new populations of chicken natural killer (NK) cells. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Yolcu, E.S.; Srivastava, A.K.; Shirwan, H. CD4+ T cells play a critical role in the generation of primary and memory antitumor immune responses elicited by SA-4-1BBL and TAA-based vaccines in mouse tumor models. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niewiesk, S. Maternal antibodies: Clinical significance, mechanism of interference with immune responses, and possible vaccination strategies. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumińska, E.; Koncicki, A.; Stenzel, T. Structure and function of the avian immune system in birds. Medycyna Wet. 2008, 64, 265–268. [Google Scholar]
- Grindstaff, J.L.; Brodie, E.D., 3rd; Ketterson, E.D. Immune function acrossgenerations: Integrating mechanism and evolutionary process inmaternal antibody transmission. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 2309–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmer-Franco, A.M.; Cherian, G.; Quezada, N.; Fasenco, G.M.; MacMullen, L.M. Hatching egg and newly hatched chick yolk sac total IgY content at 3 broiler breeder flock ages. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, A.T.; El-Kafrawy, S.A.; Sohrab, S.S.; Azhar, E.I.A. IgY antibodies for the immunoprophylaxis and therapy of respiratory infections. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2019, 15, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, N.C.; Khan, M.S.R.; Islam, S.; Akhter, A.T.; Shil, N.K. Maternally-derived antibody and seroconversion to infectious bronchitis virus in chicken. Bangladesh J. Microbiol. 2008, 25, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclachlan, N.; Dubovi, E.J. Fenner’s Veterinary Virology, 5th ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 259–268. [Google Scholar]
- Dunkelberger, J.; Song, W.C. Complement and its role in innate and adaptive immune responses. Cell Res. 2017, 20, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarante-Mendes, G.P.; Adjemian, S.; Branco, L.M.; Zanetti, L.C.; Weinlich, R.; Bortoluci, K.R. Pattern recognition receptors and the host cell death molecular machinery. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catani, L.; Fagioli, M.E.; Tazzari, P.L.; Ricci, F.; Curti, A.; Rovito, M.; Preda, P.; Chirumbolo, G.; Amabile, M.; Lemoli, R.M.; et al. Dendritic cells of immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) show increased capacity to present apoptotic platelets to T cells. Exp. Hematol. 2006, 7, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariaans, M.P.; Matthijs, M.G.R.; Van Harlen, D.; Van de Haar, P.; van Eck, J.H.H.; Hensen, E.J.; Vervelde, L. The role of phagocytic cells in enhanced susceptibility of broilers to colibacillosis after infectious bronchitis virus infection. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 123, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Rosa, A.J.M.; Chen, D.G.; Wang, X. Molecular mechanisms of primary and secondary mucosal immunity using avian infectious bronchitis virus as a model system. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 121, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervelde, L.; Matthijs, M.G.; van Haarlem, D.A.; de Wit, J.J.; Jansen, C.A. Rapid NK-cell activation in chicken after infection with infectious bronchitis virus M41. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2013, 151, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ike, A.C.; Ononugbo, C.M.; Obi, O.J.; Onu, C.J.; Olovo, C.V.; Muo, S.O.; Chukwu, O.S.; Reward, E.E.; Omeke, O.P. Towards Improved Use of Vaccination in the Control of Infectious Bronchitis and Newcastle Disease in Poultry: Understanding the Immunological Mechanisms. Vaccines 2021, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.P.; Bilousova, T.; Escande-Beillard, N.; Dang, H.; Hsieh, T.; Tian, J.; Kaufman, D.L. Major histocompatibility complex class I-mediated inhibition of neurite outgrowth from peripheral nerves. Immunol. Lett. 2011, 135, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallet, S.; Puri, V.; Gibson, F. Linkage of infection to adverse systemic complications: Periodontal disease, toll-like receptors, and other pattern recognition systems. Vaccines 2018, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hug, H.; Mohajeri, M.H.; La, G.F. Toll-like receptors: Regulators of the immune response in the human gut. Nutrients 2018, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.K.; Kakker, N.K.; Bhadouriya, S.; Chhabra, R. Effect of TLR agonist on infections bronchitis virus replication and cytokine expression in embryonated chicken eggs. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 120, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okabayashi, T.; Kariwa, H.; Yokota, S.; Iki, S.; Indoh, T.; Yokosawa, N.; Takashima, I.; Tsutsumi, H.; Fujii, N. Cytokine regulation in SARS coronavirus infection compared to other respiratory virus infections. J. Med. Virol. 2006, 78, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, X.; Wu, T.; Su, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ruan, B.; Niu, X.; Wu, Y. Avian infectious bronchitis virus disrupts the melanoma differentiation associated gene 5 (MDA5) signaling pathway by cleavage of the adaptor protein MAVS. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Sekellick, M.J.; Marcus, P.I.; Choi, I.-S.; Collisson, E.W. Chicken interferon type I inhibits infectious bronchitis virus replication and associated respiratory illness. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2001, 21, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiemstra, P.S.; McCray, P.B., Jr.; Bals, R. The innate immune function of airway epithelial cells in inflammatory lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1150–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, M.D.; Pickett, D.L.; van Rooijen, N.; Brooks, A.G.; Reading, P.C. Critical role of airway macrophages in modulating disease severity during influenza virus infection of mice. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7569–7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delamarre, L.; Pack, M.; Chang, H.; Mellman, I.; Trombetta, E.S. Differential lysosomal proteolysis in antigen-presenting cells determines antigen fate. Science 2005, 307, 1630–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscic-Mrkic, B.; Schwendener, R.A.; Odermatt, B.; Zuniga, A.; Pavlovic, J.; Billeter, M.A.; Cattaneo, R. Roles of macrophages in measles virus infection of genetically modified mice. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 3343–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinet, W.; Verheye, S.; De Meyer, G.R. Selective depletion of macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques via macrophage-specific initiation of cell death. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2001, 17, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mahajan, D.; Tay, Y.C.; Bao, S.; Spicer, T.; Kairaitis, L.; Rangan, G.K.; Harris, D.C. Partial depletion of macrophages by ED7 reduces renal injury in Adriamycin nephropathy. Nephrology 2005, 10, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Tan, Y.W.; Liu, D.X. Recent progress in studies of arterivirus– and coronavirus–host interactions. Viruses 2012, 4, 980–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, T.S.; Liao, Y.; Liu, D.X. The endoplasmic reticulum stress sensor IRE1alpha protects cells from apoptosis induced by the coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 12752–12764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruano, M.; El-Attrache, J.; Villegas, P. A rapid-plate hemagglutination assay for the detection of infectious bronchitis virus. Avian Dis. 2000, 44, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, L.N.; Jiang, W.; Bhamidipati, K.; Millican, M.; Macaubas, C.; Hung, S.C.; Mellins, E.D. The Other Function: Class II-Restricted Antigen Presentation by B Cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najimudeen, S.M.; Hassan, M.S.H.; Cork, S.C.; Abdul-Careem, M.F. Infectious Bronchitis Coronavirus Infection in Chickens: Multiple System Disease with Immune Suppression. Pathogens 2020, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadakchi, H.; Dadras, H.; Pourbakhsh, S.A.; Hosseini, S.M.H. Standardization of an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Detection of Infectious Bronchitis Virus Antibody. Arch. Razi Inst. 2005, 59, 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- De Wit, J.J.; Swart, W.A.J.M.; Fabri, T.H.F. Efficacy of infectious bronchitis virus vaccinations in the field: Association between the α-IBV IgM response, protection and vaccine application parameters. Avian Pathol. 2010, 39, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, L.F. Etiology and immunology of infectious bronchitis virus. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Avic. 2010, 12, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Koo, B.S.; Jeon, E.O.; Lee, H.-R.; Lee, S.-M.; Mo, I.-P. Altered pro-inflammatory cytokine mRNA levels in chickens infected with infectious bronchitis virus. Poult. Sci. 2013, 9, 2290–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mockett, A.P.; Darbyshire, J.H. Comparative studies with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for antibodies to avian infectious bronchitis virus. Avian Pathol. 1981, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, S.; Kappala, D. Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus. Recent Adv. Anim. Virol. 2019, 6, 301–319. [Google Scholar]
- Toro, H.; van Santen, V.L.; Li, L.; Lockaby, S.B.; van Santen, E.; Hoerr, F.J. Epidemiological and experimental evidence for immunodeficiency affecting avian infectious bronchitis. Avian Pathol. 2006, 35, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okino, C.H.; dos Santos, I.L.; Fernando, F.S.; Alessi, A.C.; Wang, X.; Montassier, H.J. Inflammatory and cell-mediated immune responses in the respiratory tract of chickens to infection with avian infectious bronchitis virus. Viral Immunol. 2014, 27, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chubb, R.C.; Huynh, V.; Bradley, R. The induction and control of delayed type hypersensitivity reactions induced in chickens by infectious bronchitis virus. Avian Pathol. 1988, 17, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubb, R.C.; Huynh, V.; Law, R. The detection of cytotoxic lymphocyte activity in chickens infected with infectious bronchitis virus or fowlpox virus. Avian Pathol. 1987, 16, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.; Naqi, S. Cytotoxic activity of cells recovered from the respiratory tracts of chickens inoculated with infectious bronchitis virus. Avian Dis. 1997, 41, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okino, C.H.; Mores, M.A.Z.; Trevisol, I.M.; Coldebella, A.; Montassier, H.J.; Brentano, L. Early immune responses and development of pathogenesis of avian infectious bronchitis viruses with different virulence profiles. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.D.; Fraire, A.E.; Joris, I.; Welsh, R.M.; Selin, L.K. Specific history of heterologous virus infections determines antiviral immunity and immunopathology in the lung. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 1341–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.S.; Pei, J.; Briles, W.E.; Dzielawa, J.; Collisson, E.W. Adoptive transfer of infectious bronchitis virus primed alphabeta T cells bearing CD8 antigen protects chicks from acute infection. Virology 2000, 32, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Samanta, D.; Park, Y.; Ni, X.; Li, H.; Zahnow, C.A.; Gabrielson, E.; Pan, F.; Semenza, G.L. Chemotherapy induces enrichment of CD47+ /CD73+ /PDL1+ immune evasive triple-negative breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1239–E1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meir, R.; Krispel, S.; Simanov, L.; Pitcovski, J. Immune Responses to Mucosal Vaccination by the Recombinant S1 and N Proteins of Infectious Bronchitis Virus. Viral Immunol. 2012, 25, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, T.; Wang, X.; Lu, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Priming with a DNA vaccine and boosting with an inactivated vaccine enhance the immune response against infectious bronchitis virus. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 167, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Briles, W.E.; Collisson, E.W. Memory T cells protect chicks from acute infectious bronchitis virus infection. Virology 2003, 306, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, L.; Gage, P.; Ewart, G. Hexamethylene amiloride blocks E protein ion channels and inhibits coronavirus replication. Virology 2006, 353, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, F.; Hutton, S.; Forrester, A.; Baylis, M.; Ganapathy, K. Heterologous live infectious bronchitis virus vaccination in day-old commercial broiler chicks: Clinical signs, ciliary health, immune responses and protection against variant infectious bronchitis viruses. Avian Pathol. 2016, 45, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, T.; Wada, S.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Kuwamura, M.; Yamate, J.; Sakuma, S. Kinetics of lymphocytic subsets in chicken tracheal lesions infected with infectious bronchitis virus. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2000, 62, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhinakar Raj, G.; Jones, R.C. An in vitro comparison of the virulence of seven strains of infectious bronchitis virus using tracheal and oviduct organ cultures. Avian Pathol. 1996, 25, 649–662. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, R.M.D.; Fernando, F.S.; Montassier, M.F.S.; Silva, K.R.; Lopes, P.D.; Pavani, C.; Borzi, M.M.; Okino, C.H.; Montassier, H.J. Memory immune responses and protection of chickens against a nephropathogenic infectious bronchitis virus strain by combining live heterologous and inactivated homologous vaccines. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 81, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nochi, T.; Jansen, C.A.; Toyomizu, M.; van Eden, W. The well-developed mucosal immune systems of birds and mammals allow for similar approaches of mucosal vaccination in both types of animals. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, E.J.; McNeela, E.; Pizza, M.; Rappuoli, R.; O’Neill, L.; Mills, K.H.G. Modulation of innate and acquired immune responses by Escherichiacoli heat-labile toxin: Distinct pro- and anti-inflammatory effects of thenontoxic AB complex and the enzyme activity. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 5750–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Ginkel, F.W.; Jackson, R.J.; Yuki, Y.; McGhee, J.R. Cutting edge: Themucosal adjuvant cholera toxin redirects vaccine proteins into olfactorytissues. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 4778–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ginkel, F.W.; Van Santen, V.L.; Gulley, S.L.; Toro, H. Infectious bronchitis virus in the chicken harderian gland and lachrymal fluid: Viral load, infectivity, immune cell responses, and effects of viral immunodeficiency. Avian Dis. 2008, 52, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Rosa, A.J.; Oliverira, H.N.; Rosa, G.J.; Guo, X.; Travnicek, M.; Girshick, T. Transcriptome of local innate and adaptive immunity during early phase of infectious bronchitis viral infection. Viral Immunol. 2006, 19, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrubia, S.C.; Escarmis, C.; Domingo, E.; Lazaro, E. High mutation rates, bottlenecks, and robustness of RNA viral quasispecies. Gene 2005, 347, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biebricher, C.K.; Eigen, M. What is a quasispecies? Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2006, 299, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vignuzzi, M.; Stone, J.K.; Arnold, J.J.; Cameron, C.E.; Andino, R. Quasispecies diversity determines pathogenesis through cooperative interactions in a viral population. Nature 2006, 439, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casais, R.; Dove, B.; Cavanagh, D.; Britton, P. Recombinant avian infectious bronchitis virus expressing a heterologous spike gene demonstrates that the spike protein is a determinant of cell tropism. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 9084–9089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackwood, M.W.; Hilt, D.A.; McCall, A.W.; Polizzi, C.N.; McKinley, E.T.; Williams, S.M. Infectious bronchitis virus field vaccination coverage and persistence of Arkansas-type viruses in commercial broilers. Avian Dis. 2009, 53, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattnaik, G.P.; Chakraborty, H. Entry Inhibitors: Efficient Means to Block Viral Infection. J. Membr. Biol. 2020, 253, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.K.A.; Williams Smith, H.; Huggins, M.B. Infectious bronchitis immunity: Its study in chickens experimentally infected with mixtures of infectious bronchitis virus and Escherichia coli. J. Gen. Virol. 1986, 67, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.K.A. Coronaviridae. In Poultry Diseases, 6th ed.; Pattison, M., Bradbury, A., Eds.; Saunders Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 340–349. ISBN 9780702037269. [Google Scholar]



| Name of the Vaccine | Route of Delivery | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Live attenuated IBV or | Aero nasal spray | Serial attenuation of virulent IB strain for weakened |
| Live IBV vaccines | In Ovo route | virulence [32,33]. |
| Orally | ||
| Subcutaneous (S/C) | ||
| 2. Killed or inactivated | IM injection | Inactivated by chemical treatment or heat treat to kill the |
| IB vaccines | S/C | virulence of strain [34]. |
| 3. Viral Vector vaccine | In ovo route | Recombinant rNDV/APMV-2 expressing the S protein of |
| IBV strain Mass-41 (rNDV/APMV-2/IBV-S) [35]. | ||
| 4. DNA vaccine | Mucosal/Orally | IBV-DNA vaccine carrying S1-protein and/or N-protein constructs |
| IM injection | the respective vector [36,37,38,39]. | |
| Intranasal | ||
| In ovo route | ||
| 5. Recombinant protein (sub-unit) | Intraocular-nasally IM injection | Water-in-oil emulsified recombinant S-ectodomain protein [40]. |
| Second heptad repeat (HR2) region of S protein were | ||
| repeatedly co-displayed in the Self-assembling | ||
| Protein Nanoparticle (SAPN) [41]. | ||
| 6. Multi-epitope-based | Oral | Using attenuated S enterica serovar Typhimurium strain [42]. |
| peptide vaccine | Mucosal | Recombinant DNA: The EpiC gene was presented in |
| (Lactococcus lactis bacterial system) | Intranasal | Lactococcus lactis NZ3900 with 3 recombinant strains expressing EpiC gene [43]. |
| 7. VLP-based IBV vaccine or | IM immunized | Efficient mucosal immune response [44] |
| chimeric VLP vaccine |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhuiyan, M.S.A.; Amin, Z.; Rodrigues, K.F.; Saallah, S.; Shaarani, S.M.; Sarker, S.; Siddiquee, S. Infectious Bronchitis Virus (Gammacoronavirus) in Poultry Farming: Vaccination, Immune Response and Measures for Mitigation. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8110273
Bhuiyan MSA, Amin Z, Rodrigues KF, Saallah S, Shaarani SM, Sarker S, Siddiquee S. Infectious Bronchitis Virus (Gammacoronavirus) in Poultry Farming: Vaccination, Immune Response and Measures for Mitigation. Veterinary Sciences. 2021; 8(11):273. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8110273
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhuiyan, Md. Safiul Alam, Zarina Amin, Kenneth Francis Rodrigues, Suryani Saallah, Sharifudin Md. Shaarani, Subir Sarker, and Shafiquzzaman Siddiquee. 2021. "Infectious Bronchitis Virus (Gammacoronavirus) in Poultry Farming: Vaccination, Immune Response and Measures for Mitigation" Veterinary Sciences 8, no. 11: 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8110273
APA StyleBhuiyan, M. S. A., Amin, Z., Rodrigues, K. F., Saallah, S., Shaarani, S. M., Sarker, S., & Siddiquee, S. (2021). Infectious Bronchitis Virus (Gammacoronavirus) in Poultry Farming: Vaccination, Immune Response and Measures for Mitigation. Veterinary Sciences, 8(11), 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8110273






