Differentiation of Antibodies against Selected Simbu Serogroup Viruses by a Glycoprotein Gc-Based Triplex ELISA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blood Samples
2.2. Production of Recombinant Proteins
2.2.1. Cloning
2.2.2. Expression and Purification in Drosophila S2 Cells
2.2.3. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot
2.3. ELISA Procedure
2.4. Data Analyses and Cut-off Determination
2.5. Repeatability and Reproducibility
3. Results
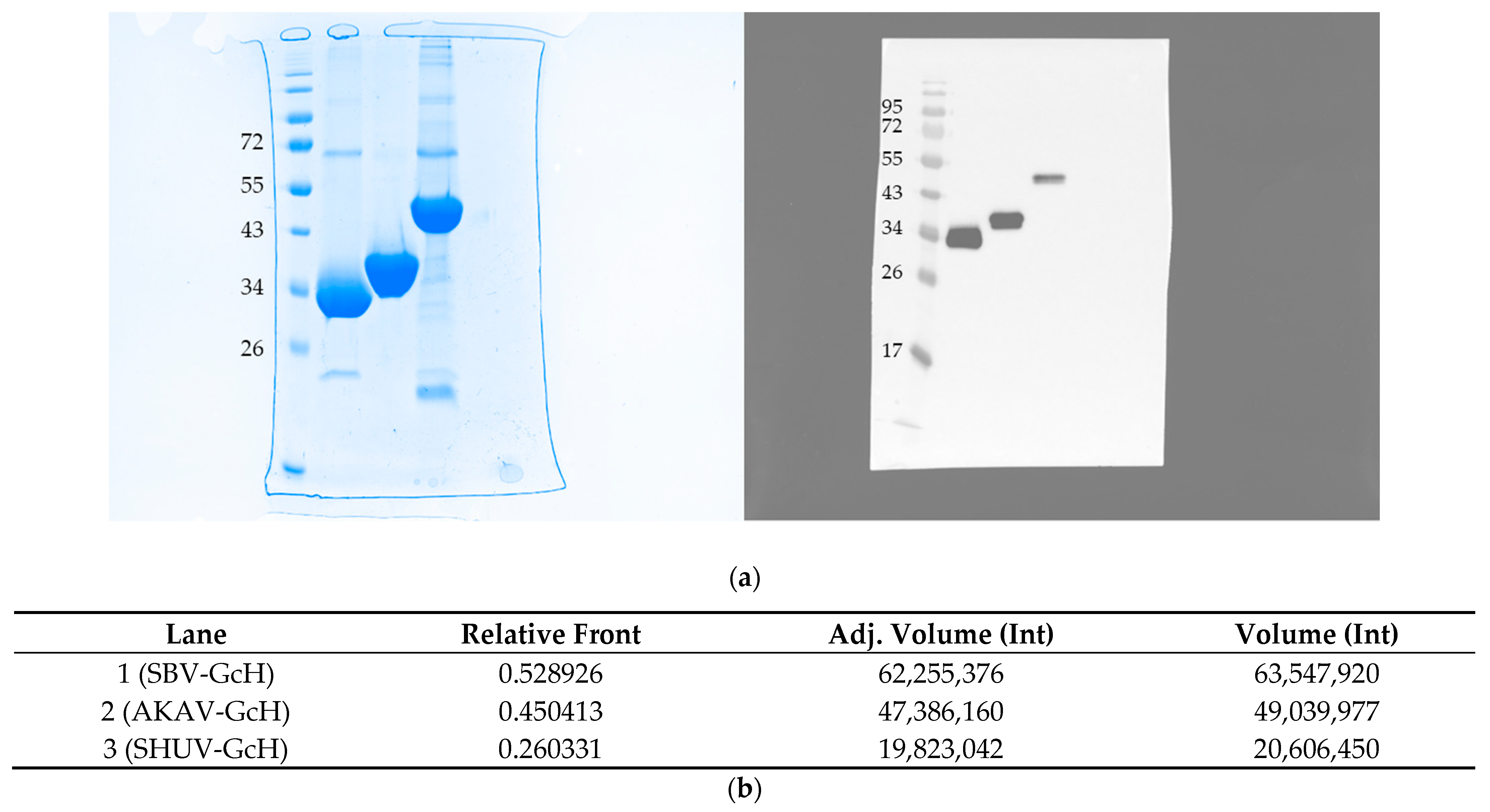
3.1. Expression and Purification of Proteins
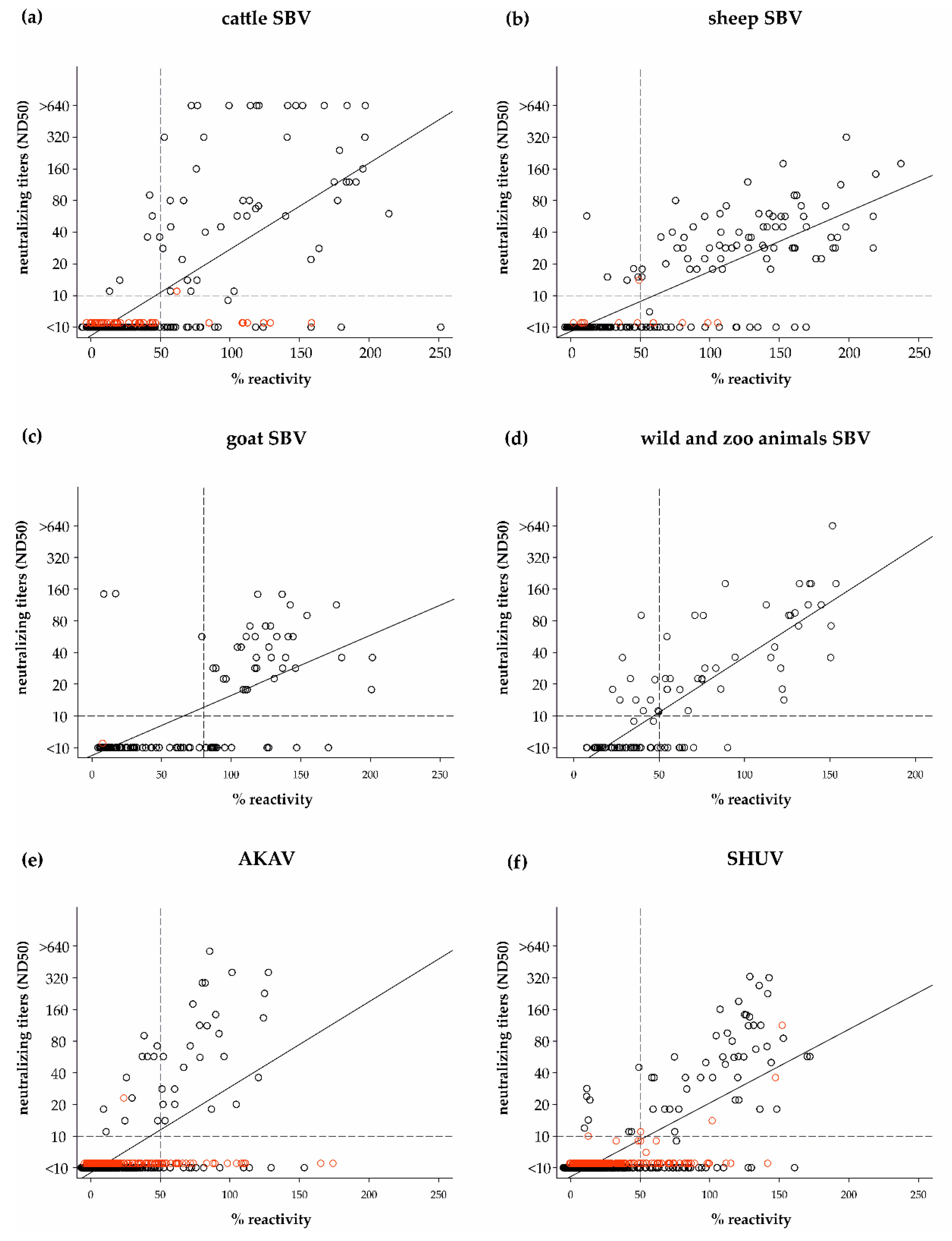
3.2. Cut-off Determination and Diagnostic Characteristics
3.3. Repeatability and Reproducibility
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Sick, F.; Beer, M.; Kampen, H.; Wernike, K. Culicoides biting midges—Underestimated vectors for arboviruses of public health and veterinary importance. Viruses 2019, 11, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.F.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Weaver, S.C.; Barrett, A.D. Phylogeny of the simbu serogroup of the genus bunyavirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, P.; Adkins, S.; Alkhovsky, S.V.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Ballinger, M.J.; Bente, D.A.; Beer, M.; Bergeron, E.; Blair, C.D.; Briese, T.; et al. Taxonomy of the order bunyavirales: Second update 2018. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, R.M.; Calisher, C.H. Antigenic relationships among simbu serogroup (Bunyaviridae) viruses. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 30, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causey, O.R.; Kemp, G.E.; Causey, C.E.; Lee, V.H. Isolations of simbu-group viruses in Ibadan, Nigeria 1964–69, including the new types Sango, Shamonda, Sabo and Shuni. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1972, 66, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, C.T.W.a.J.N. Recent advances in the molecular and cellular biology of bunyaviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2467–2484. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, R.M. Orthobunyaviruses: Recent genetic and structural insights. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Lappin, D.F.; Elliott, R.M. Mapping the Golgi targeting and retention signal of bunyamwera virus glycoproteins. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 10793–10802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; van Mierlo, J.T.; French, A.; Elliott, R.M. Visualizing the replication cycle of bunyamwera orthobunyavirus expressing fluorescent protein-tagged gc glycoprotein. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 8460–8469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Goli, J.; Clark, G.; Brauburger, K.; Elliott, R.M. Functional analysis of the bunyamwera orthobunyavirus gc glycoprotein. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2483–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellert, J.; Aebischer, A.; Wernike, K.; Haouz, A.; Brocchi, E.; Reiche, S.; Guardado-Calvo, P.; Beer, M.; Rey, F.A. Orthobunyavirus spike architecture and recognition by neutralizing antibodies. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman-Sosa, G.; Brocchi, E.; Schirrmeier, H.; Wernike, K.; Schelp, C.; Beer, M. Analysis of the humoral immune response against the envelope glycoprotein gc of Schmallenberg virus reveals a domain located at the amino terminus targeted by mabs with neutralizing activity. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Beer, M. Schmallenberg virus: A novel virus of veterinary importance. Adv. Virus Res. 2017, 99, 39–60. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, T.; Shirafuji, H.; Tanaka, S.; Sato, M.; Yamakawa, M.; Tsuda, T.; Yanase, T. Bovine arboviruses in culicoides biting midges and sentinel cattle in Southern Japan from 2003 to 2013. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, e160–e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Yanase, T.; Suzuki, M.; Katagiri, Y.; Ikemiyagi, K.; Takayoshi, K.; Shirafuji, H.; Ohashi, S.; Yoshida, K.; Yamakawa, M.; et al. Monitoring for bovine arboviruses in the most southwestern islands in Japan between 1994 and 2014. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayama, Y.; Yanase, T.; Suzuki, M.; Unten, K.; Tomochi, H.; Kakehi, M.; Shono, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Murai, K.; et al. Meteorological factors affecting seroconversion of akabane disease in sentinel calves in the subtropical Okinawa islands of Japan. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2018, 50, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Holsteg, M.; Szillat, K.P.; Beer, M. Development of within-herd immunity and long-term persistence of antibodies against Schmallenberg virus in naturally infected cattle. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoghegan, J.L.; Walker, P.J.; Duchemin, J.B.; Jeanne, I.; Holmes, E.C. Seasonal drivers of the epidemiology of arthropod-borne viruses in Australia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Beer, M. Re-Circulation of Schmallenberg virus, Germany, 2019. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 2290–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golender, N.; Bumbarov, V.Y.; Erster, O.; Beer, M.; Khinich, Y.; Wernike, K. Development and validation of a universal S-segment-based real-time RT-PCR assay for the detection of simbu serogroup viruses. J. Virol. Methods 2018, 261, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, C.; Klevar, S.; Elbers, A.R.; van der Poel, W.H.; Kirkland, P.D.; Godfroid, J.; Mdegela, R.H.; Mwamengele, G.; Stokstad, M. Detection of serum neutralizing antibodies to Simbu sero-group viruses in cattle in Tanzania. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Firth, C.; Amos-Ritchie, R.; Davis, S.S.; Yin, H.; Holmes, E.C.; Blasdell, K.R.; Walker, P.J. Evolutionary history of simbu serogroup orthobunyaviruses in the Australian episystem. Virology 2019, 535, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, K.; Yanaka, T.; Lee, K.K.; Lee, J.B. Seroprevalence of bovine arboviruses belonging to genus orthobunyavirus in South Korea. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 1619–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, M.; Wernike, K. Akabane virus and Schmallenberg virus. Ref. Mod. Life Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sick, F.; Breithaupt, A.; Golender, N.; Bumbarov, V.; Beer, M.; Wernike, K. Shuni virus-induced meningoencephalitis after experimental infection of cattle. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, P.D. Akabane virus infection. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2015, 34, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, B.; Scheuch, M.; Höper, D.; Jungblut, R.; Holsteg, M.; Schirrmeier, H.; Eschbaumer, M.; Goller, K.V.; Wernike, K.; Fischer, M.; et al. Novel orthobunyavirus in cattle, Europe, 2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golender, N.; Bumbarov, V.; Assis, I.; Beer, M.; Khinich, Y.; Koren, O.; Edery, N.; Eldar, A.; Wernike, K. Shuni virus in Israel: Neurological disease and fatalities in cattle. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Elbers, A.; Beer, M. Schmallenberg virus infection. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2015, 34, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golender, N.; Brenner, J.; Valdman, M.; Khinich, Y.; Bumbarov, V.; Panshin, A.; Edery, N.; Pismanik, S.; Behar, A. Malformations caused by Shuni virus in ruminants, Israel, 2014–2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 2267–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Huang, T.S.; Deng, M.C.; Jong, M.H.; Lin, S.Y. Natural infections of pigs with Akabane virus. Vet. microbiol. 2003, 94, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eeden, C.; Williams, J.H.; Gerdes, T.G.; van Wilpe, E.; Viljoen, A.; Swanepoel, R.; Venter, M. Shuni virus as cause of neurologic disease in horses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmecht, D.; Garigliany, M.M.; Beer, M.; Schirrmeier, H.; Paternostre, J.; Volpe, R.; Linden, A. Detection of antibodies against Schmallenberg virus in wild boars, Belgium, 2010–2012. In Proceedings of the 31th Congress of the International Union Game Biologists, Brussels, Belgium, 27–29 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mouchantat, S.; Wernike, K.; Lutz, W.; Hoffmann, B.; Ulrich, R.G.; Borner, K.; Wittstatt, U.; Beer, M. A broad spectrum screening of Schmallenberg virus antibodies in wildlife animals in Germany. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wensman, J.J.; Blomqvist, G.; Hjort, M.; Holst, B.S. Presence of antibodies to Schmallenberg virus in a dog in Sweden. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2802–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sailleau, C.; Boogaerts, C.; Meyrueix, A.; Laloy, E.; Bréard, E.; Viarouge, C.; Desprat, A.; Vitour, D.; Doceul, V.; Boucher, C.; et al. Schmallenberg virus infection in dogs, France, 2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1896–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Eschbaumer, M.; Schirrmeier, H.; Blohm, U.; Breithaupt, A.; Hoffmann, B.; Beer, M. Oral exposure, reinfection and cellular immunity to Schmallenberg virus in cattle. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 165, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Hoffmann, B.; Bréard, E.; Bøtner, A.; Ponsart, C.; Zientara, S.; Lohse, L.; Pozzi, N.; Viarouge, C.; Sarradin, P.; et al. Schmallenberg virus experimental infection of sheep. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laloy, E.; Riou, M.; Barc, C.; Belbis, G.; Bréard, E.; Breton, S.; Cordonnier, N.; Crochet, D.; Delaunay, R.; Moreau, J.; et al. Schmallenberg virus: Experimental infection in goats and bucks. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurogi, H.; Inaba, Y.; Takahashi, E.; Sato, K.; Goto, Y. Experimental infection of pregnant goats with Akabane virus. Nat. Inst. Anim. Health Quart. 1977, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kurogi, H.; Inaba, Y.; Takahashi, E.; Sato, K.; Goto, Y.; Satoda, K.; Omori, T.; Hatakeyama, H. Development of inactivated vaccine for Akabane disease. Nat. Inst. Anim. Health Quart. 1978, 18, 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Wernike, K.; Nikolin, V.M.; Hechinger, S.; Hoffmann, B.; Beer, M. Inactivated Schmallenberg virus prototype vaccines. Vaccine 2013, 31, 3558–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Holsteg, M.; Schirrmeier, H.; Hoffmann, B.; Beer, M. Natural infection of pregnant cows with Schmallenberg virus—A follow-up study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Regge, N.; van den Berg, T.; Georges, L.; Cay, B. Diagnosis of Schmallenberg virus infection in malformed lambs and calves and first indications for virus clearance in the fetus. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goller, K.V.; Höper, D.; Schirrmeier, H.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Beer, M. Schmallenberg virus as possible ancestor of Shamonda virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1644–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernike, K.; Beer, M.; Hoffmann, B. Schmallenberg virus infection diagnosis: Results of a German proficiency trial. Transbound. emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oluwayelu, D.; Wernike, K.; Adebiyi, A.; Cadmus, S.; Beer, M. Neutralizing antibodies against Simbu serogroup viruses in cattle and sheep, Nigeria, 2012–2014. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Scarano, F.; Shope, R.E.; Calisher, C.E.; Nathanson, N. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against the G1 and N proteins of Lacrosse and Tahyna, two California serogroup bunyaviruses. Virology 1982, 120, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Aebischer, A.; Roman-Sosa, G.; Beer, M. The n-terminal domain of Schmallenberg virus envelope protein gc is highly immunogenic and can provide protection from infection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Brocchi, E.; Cordioli, P.; Senechal, Y.; Schelp, C.; Wegelt, A.; Aebischer, A.; Roman-Sosa, G.; Reimann, I.; Beer, M. A novel panel of monoclonal antibodies against Schmallenberg virus nucleoprotein and glycoprotein Gc allows specific orthobunyavirus detection and reveals antigenic differences. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Mundt, A.; Link, E.K.; Aebischer, A.; Schlotthauer, F.; Sutter, G.; Fux, R.; Beer, M. N-Terminal domain of Schmallenberg virus envelope protein Gc delivered by recombinant equine herpesvirus type 1 and modified vaccinia virus Ankara: Immunogenicity and protective efficacy in cattle. Vaccine 2018, 36, 5116–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechinger, S.; Wernike, K.; Beer, M. Single immunization with an inactivated vaccine protects sheep from Schmallenberg virus infection. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hechinger, S.; Wernike, K.; Beer, M. Evaluating the protective efficacy of a trivalent vaccine containing Akabane virus, Aino virus and Chuzan virus against Schmallenberg virus infection. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.J.; Liang, M.F.; Zhang, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.D.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.F.; Popov, V.L.; Li, C.; et al. Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marklewitz, M.; Zirkel, F.; Rwego, I.B.; Heidemann, H.; Trippner, P.; Kurth, A.; Kallies, R.; Briese, T.; Lipkin, W.I.; Drosten, C.; et al. Discovery of a unique novel clade of mosquito-associated bunyaviruses. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 12850–12865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edridge, A.W.D.; Deijs, M.; Namazzi, R.; Cristella, C.; Jebbink, M.F.; Maurer, I.; Kootstra, N.A.; Buluma, L.R.; van Woensel, J.B.M.; de Jong, M.D.; et al. Novel orthobunyavirus identified in the cerebrospinal fluid of a Ugandan child with severe Encephalopathy. Clin. Infect. 2018, 68, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abutarbush, S.M.; La Rocca, A.; Wernike, K.; Beer, M.; Al Zuraikat, K.; Al Sheyab, O.M.; Talafha, A.Q.; Steinbach, F. Circulation of a Simbu serogroup virus, causing Schmallenberg virus-like clinical signs in Northern Jordan. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussien, M.O.; Alfaki, S.H.; Enan, K.A.; Gafar, R.A.; Elhassan, A.M.; Taha, K.M.; El Hussein, A.R.M. Prevalence of antibodies to Simbu serogroup viruses in cattle in Sudan. Vet. Med. Int. 2020, 2020, 8858742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbers, A.R.; Stockhofe, N.; van der Poel, W.H. Schmallenberg virus antibodies in adult cows and maternal antibodies in calves. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 901–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbers, A.R.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; van der Poel, W.H. Schmallenberg virus antibody persistence in adult cattle after natural infection and decay of maternal antibodies in calves. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wernike, K.; Holsteg, M.; Saßerath, M.; Beer, M. Schmallenberg virus antibody development and decline in a naturally infected dairy cattle herd in Germany, 2011–2014. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 181, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, Y.; Matumoto, M. Chapter 43: Akabane virus. In Virus Infections of Vertebrates, Virus Infections of Ruminants; Dinter, S., Morien, B., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publishers, B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; Volume 3, pp. 467–480. [Google Scholar]
- Blomström, A.L.; Stenberg, H.; Scharin, I.; Figueiredo, J.; Nhambirre, O.; Abilio, A.P.; Fafetine, J.; Berg, M. Serological screening suggests presence of Schmallenberg virus in cattle, sheep and goat in the Zambezia Province, Mozambique. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2014, 61, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasekh, M.; Sarani, A.; Hashemi, S.H. Detection of Schmallenberg virus antibody in equine population of Northern and Northeast of Iran. Vet. World 2018, 11, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman-Sosa, G.; Karger, A.; Kraatz, F.; Aebischer, A.; Wernike, K.; Maksimov, P.; Lillig, C.H.; Reimann, I.; Brocchi, E.; Keller, M.; et al. The amino terminal subdomain of glycoprotein gc of Schmallenberg virus: Disulfide bonding and structural determinants of neutralization. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1259–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jongh, W.A.; Salgueiro, S.; Dyring, C. The use of Drosophila S2 cells in R&D and bioprocessing. Pharma. Bioprocess. 2013, 1, 197–213. [Google Scholar]
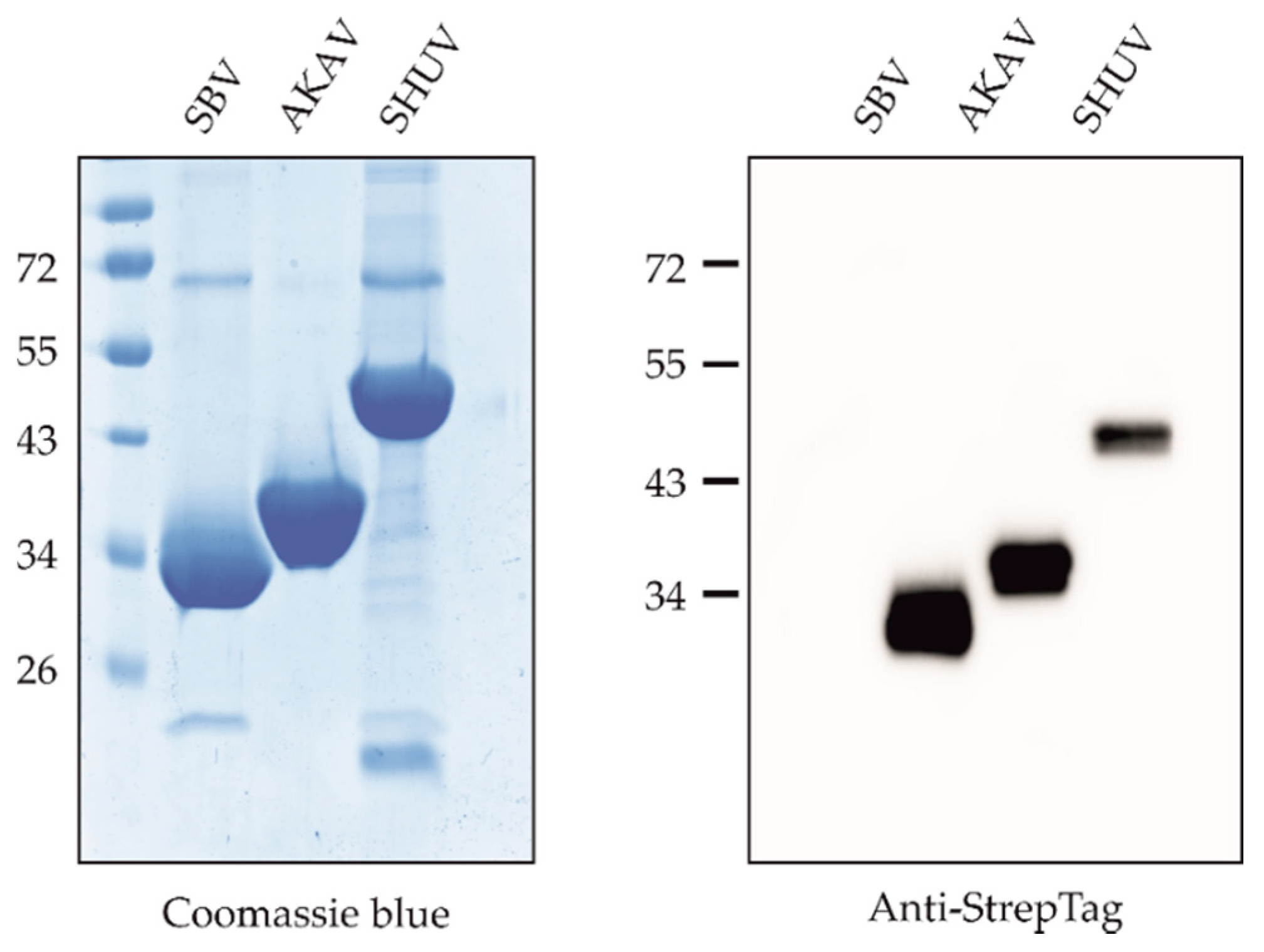


| Animal Species | No. Negative | No. Positive against SBV | No. Positive against AKAV | No. Positive against SHUV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cattle | 192 | 76 | 30 | 42 |
| sheep | 159 | 76 | 5 | 11 |
| goat | 78 | 37 | 1 | 0 |
| wild and zoo animals | 48 | 49 | 0 | 0 |
| total | 477 | 238 | 36 | 53 |
| Antigen | Animal Species | AUC | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBV | cattle-1 | 0.9519 (CI: 0.9259 to 0.9779) | 92.11% (CI: 83.60% to 97.05%) | 89.58% (CI: 84.37% to 93.52%) |
| cattle-2 | 0.9418 (CI: 0.9149 to 0.9686) | 92.11% (CI: 83.60% to 97.05%) | 87.98% (CI: 83.10% to 91.86%) | |
| sheep-1 | 0.9566 (CI: 0.9326 to 0.9806) | 93.42% (CI: 85.31% to 97.83%) | 86.79% (CI: 80.52% to 91.63%) | |
| sheep-2 | 0.9532 (CI: 0.9289 to 0.9775) | 93.42% (CI: 85.31% to 97.83%) | 84.80% (CI: 78.52% to 89.82%) | |
| goat-1 | 0.9186 (CI: 0.8553 to 0.9818) | 94.59% (CI: 81.81% to 99.34%) | 76.92% (CI: 66.00% to 85.71%) | |
| goat-2 | 0.9196 (CI: 0.8571 to 0.9821) | 94.59% (CI: 81.81% to 99.34%) | 77.22% (CI: 66.40% to 85.90%) | |
| wild/zoo animals-1 | 0.8835 (CI: 0.8199 to 0.9471) | 73.47% (CI: 58.92% to 85.05%) | 79.17% (CI: 65.01% to 89.53%) | |
| wild/zoo animals-2 | 0.8835 (CI: 0.8199 to 0.9471) | 73.47% (CI: 58.92% to 85.05%) | 79.17% (CI: 65.01% to 89.53%) | |
| overall-1 | 0.9339 (CI: 0.9159 to 0.9520) | 89.08% (CI: 84.40% to 92.74%) | 85.53% (CI: 82.05% to 88.57%) | |
| overall-2 | 0.9292 (CI: 0.9110 to 0.9474) | 89.08% (CI: 84.40% to 92.74%) | 84.56% (CI: 81.20% to 87.53%) | |
| AKAV | overall-1 | 0.9536 (CI: 0.9247 to 0.9825) | 69.44% (CI: 51.89% to 83.65%) | 97.06% (CI: 95.12% to 98.39%) |
| overall-2 | 0.9386 (CI: 0.9079 to 0.9692) | 69.44% (CI: 51.89% to 83.65%) | 94.68% (CI: 92.80% to 96.19%) | |
| SHUV | overall-1 | 0.9384 (CI: 0.8997 to 0.9771) | 84.91% (CI: 72.41% to 93.25%) | 93.29% (CI: 90.66% to 95.37%) |
| overall-2 | 0.9234 (CI: 0.8792 to 0.9676) | 84.91% (CI: 72.41% to 93.25%) | 89.39% (CI: 86.89% to 91.55%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wernike, K.; Aebischer, A.; Sick, F.; Szillat, K.P.; Beer, M. Differentiation of Antibodies against Selected Simbu Serogroup Viruses by a Glycoprotein Gc-Based Triplex ELISA. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8010012
Wernike K, Aebischer A, Sick F, Szillat KP, Beer M. Differentiation of Antibodies against Selected Simbu Serogroup Viruses by a Glycoprotein Gc-Based Triplex ELISA. Veterinary Sciences. 2021; 8(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleWernike, Kerstin, Andrea Aebischer, Franziska Sick, Kevin P. Szillat, and Martin Beer. 2021. "Differentiation of Antibodies against Selected Simbu Serogroup Viruses by a Glycoprotein Gc-Based Triplex ELISA" Veterinary Sciences 8, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8010012
APA StyleWernike, K., Aebischer, A., Sick, F., Szillat, K. P., & Beer, M. (2021). Differentiation of Antibodies against Selected Simbu Serogroup Viruses by a Glycoprotein Gc-Based Triplex ELISA. Veterinary Sciences, 8(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8010012





