Estimation of Nitrite—Nitric Oxide Derivative—In Horses with Intestinal Colic by ESR Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Legal Requirements
2.2. Animals
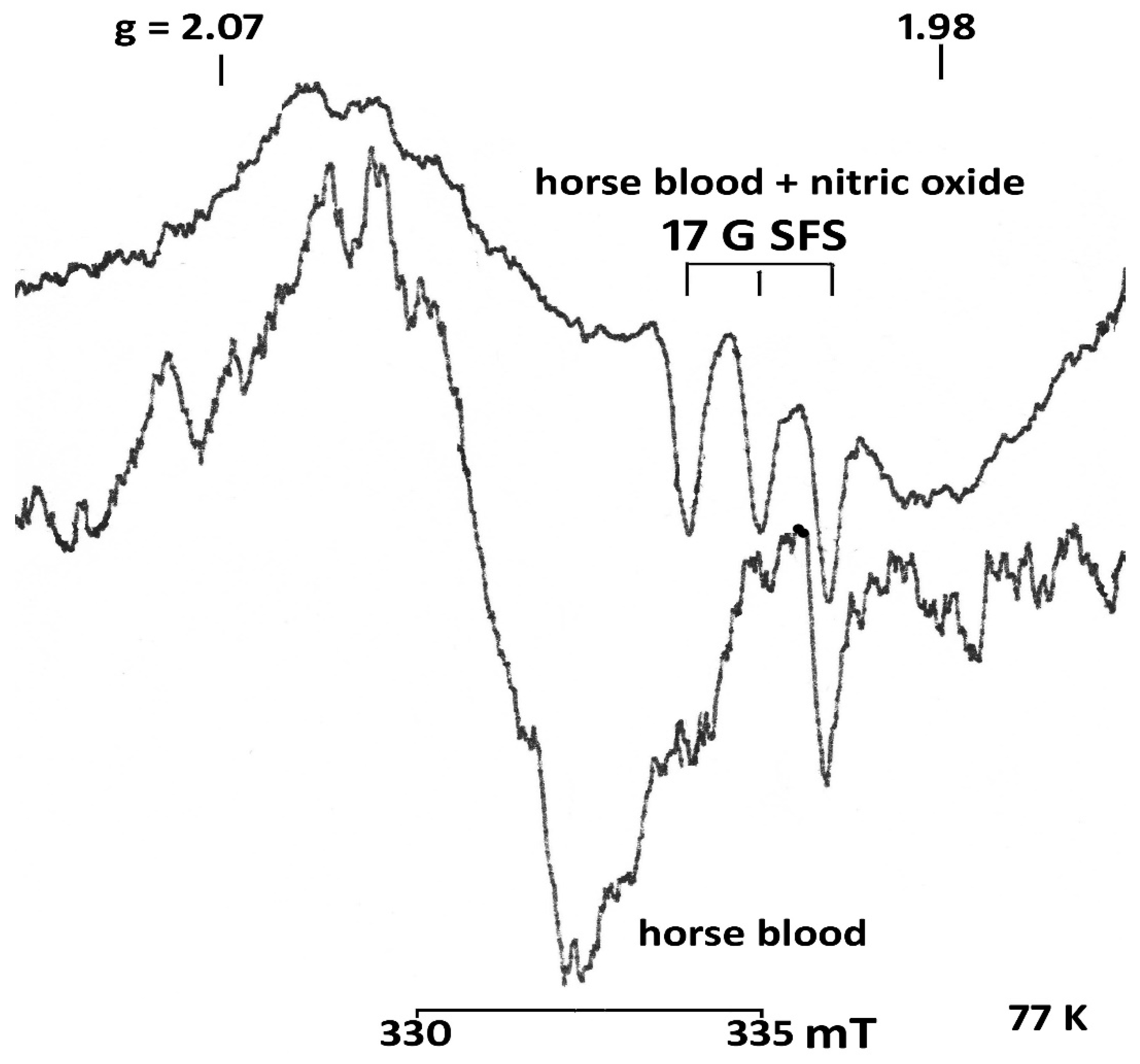
2.3. Determining Nitric Oxide (NO)
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
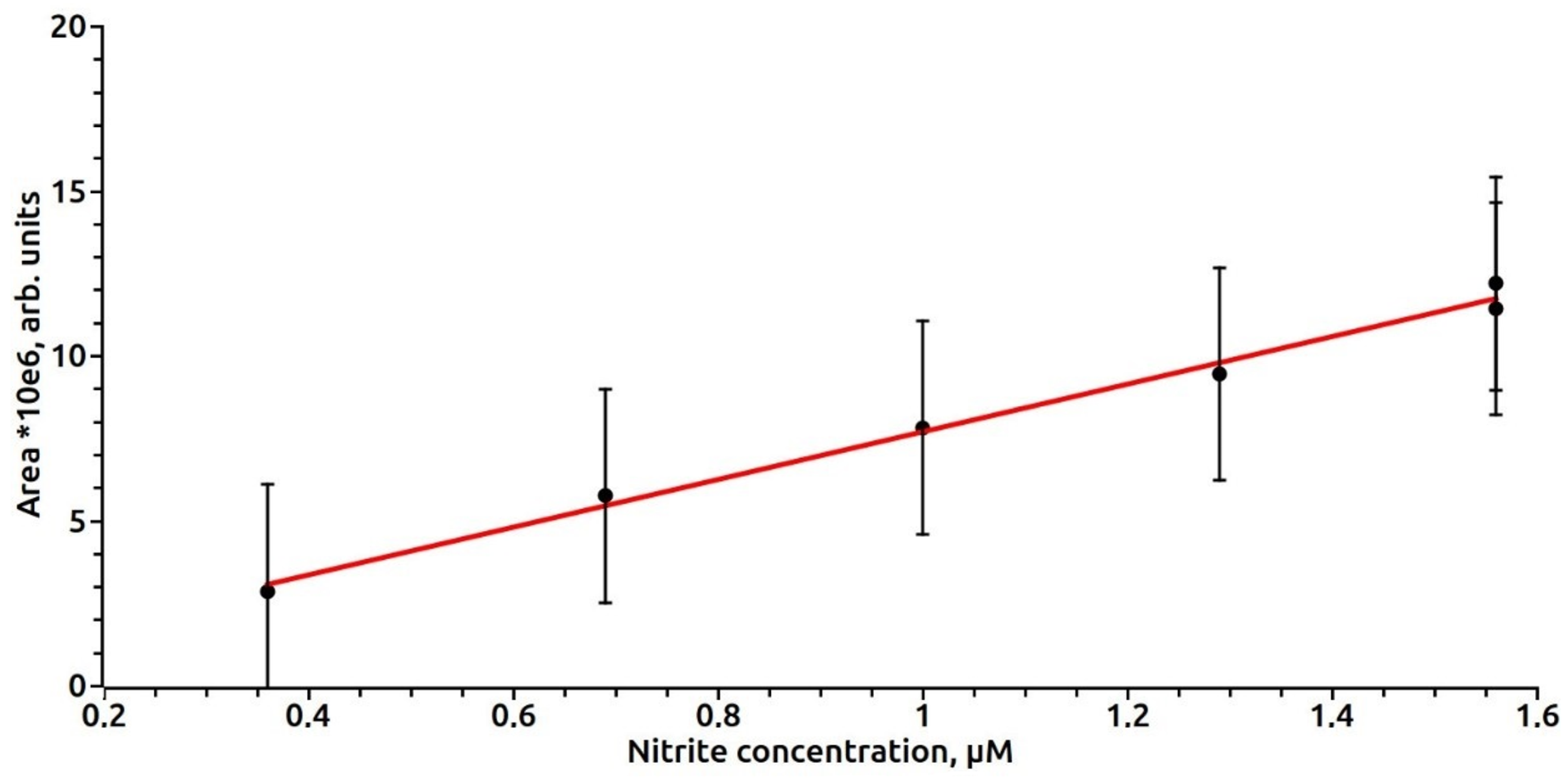
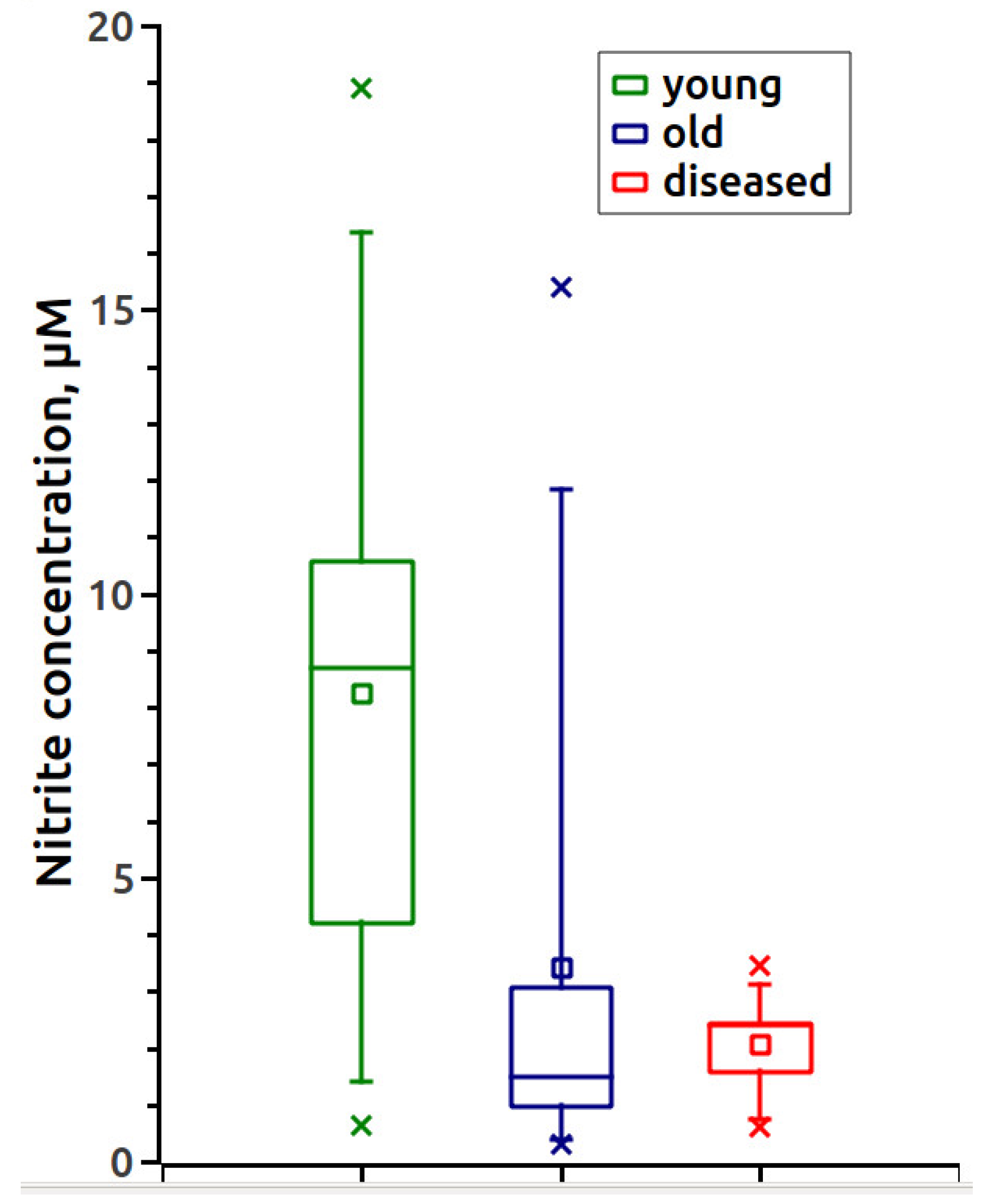
3. Results
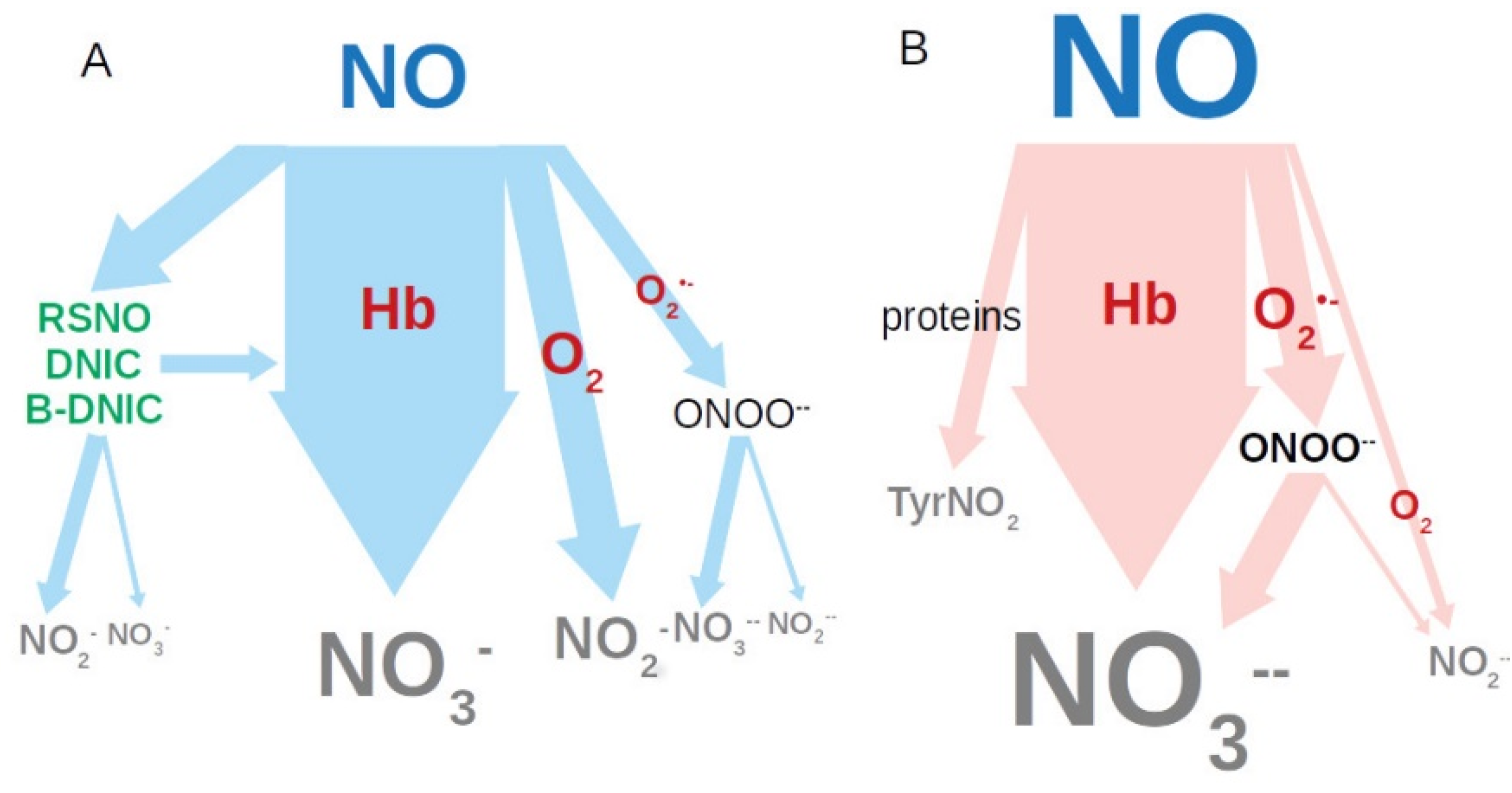
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barko, P.C.; McMichael, M.A.; Swanson, K.S.; Williams, D. The Gastrointestinal Microbiome: A Review. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, N.D. Right dorsal colitis. Equine Vet. Educ. 2002, 14, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, H.; Mohajeri, M.H.; La Fata, G. Toll-Like Receptors. Regulators of the Immune Response in the Human Gut. Nutrients 2018, 10, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, E. TLR2 and TLR4 Expression during Bacterial Infections. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 4185–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, H.M.M. Oxidative stress associated with spasmodic, flatulent, and impaction colic in draft horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2014, 34, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Deeb, W.; Iacob, O.; Fayez, M.; Elgioushy, M.; Shawaf, T.; Ibrahim, A. Acute phase proteins, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor, nitric oxide and oxidative stress markers in horses with cutaneous habronemosis under field condition. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 255, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slivka, A.; Chuttani, R.; Carr-Locke, D.L.; Kobzik, L.; Bredt, D.S.; Loscalzo, J.; Stamler, J.S. Inhibition of sphincter of Oddi function by the nitric oxide carrier S-nitroso-N-acetylcysteine in rabbits and humans. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 94, 1792–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E. Biology of nitrogen oxides in the gastrointestinal tract. Gut 2013, 62, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzal, F.A.; Diab, S.S. Gastritis, Enteritis, and Colitis in Horses. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2015, 31, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokshi, N.K.; Guner, Y.S.; Hunter, C.J.; Upperman, J.S.; Grishin, A.; Ford, H.R. The role of nitric oxide in intestinal epithelial injury and restitution in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin. Perinatol. 2008, 32, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herulf, M.; Svenungsson, B.; Lagergren, A.; Ljung, T.; Morcos, E.; Wiklund, N.P.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E. Increased nitric oxide in infective gastroenteritis. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 180, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmström, R.E.; Björne, H.; Oldner, A.; Wanecek, M.; Fredriksson, M.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E. Intestinal nitric oxide in the normal and endotoxemic pig. Shock 2002, 18, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachmilewitz, D.; Stamler, J.S.; Bachwich, D.; Karmeli, F.; Ackerman, Z.; Podolsky, D.K. Enhanced colonic nitric oxide generation and nitric oxide synthase activity in ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Gut 1995, 36, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisham, M.B.; Pavlick, K.P.; Laroux, F.S.; Hoffman, J.; Bharwani, S.S.; Wolf, R.E. Nitric oxide and chronic gut inflammation: Controversies in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Investig. Med. 2002, 50, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCafferty, D.M.; Mudgett, J.S.; Swain, M.G.; Kubes, P. Inducible nitric oxide synthase plays a critical role in resolving intestinal inflammation. Gastroenterology 1997, 112, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokh, V.P.; Poltorakov, A.P.; Serezhenkov, V.A.; Vanin, A.F. On the nature of a compound formed from dinitrosyl-iron complexes with cysteine and responsible for a long-lasting vasorelaxation. Nitric Oxide 2010, 22, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanin, A.F.; Serezhenkov, V.A.; Mikoyan, V.D.; Genkin, M.V. The 2.03 signal as an indicator of dinitrosyl-iron complexes with thiol-containing ligands. Nitric Oxide 1998, 2, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serezhenkov, V.A.; Borunova, S.M.; Kuznetsova, M.I.; Tkachev, N.A. Therapeutic effect of dinitrosyl iron complexes with glutathione in cattle endometritis. Disinfect. Antiseptic 2014, 5, 50–53. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Rocks, S.A.; Davies, C.A.; Hicks, S.L.; Webb, A.J.; Klocke, R.; Timmins, G.S.; Johnston, A.; Jawad, A.S.; Blake, D.R.; Benjamin, N.; et al. Measurement of S-nitrosothiols in extracellular fluids from healthy human volunteers and rheumatoid arthritis patients, using electron paramagnetic resonance spectrometry. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 39, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D. A critcal review and discussion of analytical methods in the L-arginine/nitric oxide area of basic and clinical research. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 379, 139–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, N.; Dillon, H.; McGovern, F. Right dorsal colitis in the horse: Minireview and reports on three cases in Ireland. Ir. Vet. J. 2004, 57, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.H.; Oliver, J.L.; Seahorn, T.L.; Hosgood, G.; Moore, R.M. Detection and comparison of nitric oxide in clinically normal horses and those with naturally acquired small intestinal strangulation obstruction. Can. J. Vet. Res. 1999, 63, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mirza, M.H.; Seahorn, T.L.; Oliver, J.L.; Hosgood, G.; Moore, R.M. Detection and comparison of nitric oxide in clinically healthy horses and those with naturally acquired strangulating large colon volvulus. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2005, 69, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kleinbongard, P.; Dejam, A.; Lauer, T.; Rassaf, T.; Schindler, A.; Picker, O.; Scheeren, T.; Goedecke, A.; Schrader, J.; Schulz, R.; et al. Plasma nitrite reflects constitutive nitric oxide synthase activity in mammals. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 35, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D. Analysis of nitrite and nitrate in biological fluids by assays based on the Griess reaction: Appraisal of the Griess reaction in the L-arginine/nitric oxide area of research. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007, 851, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.K.; Thomas, M.P.; Smith, S.; Madhani, M.; Rogers, S.C.; James, P.E. In vivo EPR spectroscopy: Biomedical and potential diagnostic applications. Faraday Discuss. 2004, 126, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikoyan, V.D.; Kubrina, L.N.; Serezhenkov, V.A.; Stukan, R.A.; Vanin, A.F. Complexes of Fe2+ with diethyldithiocarbamate or N-methyl-D-glucamine dithiocarbamate as traps of nitric oxide in animal tissues: Comparative investigations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1997, 1336, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, G.; van Goor, H.; Jansen, P.L.; Moshage, H. Targeting nitric oxide in the gastrointestinal tract. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2004, 5, 529–536. [Google Scholar]
- Rand, M.J.; Li, C.G. Nitric oxide as a neurotransmitter in peripheral nerves: Nature of transmitter and mechanism of transmission. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1995, 57, 659–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamper, N.; Ooi, L. Redox and nitric oxide-mediated regulation of sensory neuron ion channel function. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 486–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittle, B. Nitric oxide-modulating agents for gastrointestinal disorders. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2005, 14, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinders, C.A.; Jonkers, D.; Janson, E.A.; Stockbrügger, R.W.; Stobberingh, E.E.; Hellström, P.M.; Lundberg, J.O. Rectal nitric oxide and fecal calprotectin in inflammatory bowel disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 42, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, C.; Shiloh, M.U. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates in the relationship between mammalian hosts and microbial pathogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8841–8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, R.P.; Josephy, P.D. An electron spin resonance investigation of the iron-catalyzed reaction of metronidazole with cysteine. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1985, 24, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borniquel, S.; Jansson, E.A.; Cole, M.P.; Freeman, B.A.; Lundberg, J.O. Nitrated oleic acid up-regulates PPARgamma and attenuates experimental inflammatory bowel disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Lim, J.Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, E.S.; Keum, B.; Seo, Y.S.; Jeen, Y.T.; Lee, H.S.; et al. Benexate hydrochloride betadex modulates nitric oxide synthesis and cytokine expression in gastric ulcers. Exp. Med. 2016, 12, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickok, J.R.; Vasudevan, D.; Thatcher, G.R.; Thomas, D.D. Is S-nitrosocysteine a true surrogate for nitric oxide? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 17, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ischiropoulos, H. Biological tyrosine nitration: A pathophysiological function of nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1998, 356, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marañón, G.; Manley, W.; Cayado, P.; García, C.; de la Muela, M.S.; Vara, E. Alterations in the glutathione metabolism could be implicated in the ischemia-induced small intestinal cell damage in horses. BMC Vet. Res. 2009, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Animal Groups | Nitrosylhemoglobin Concentration, μM, Mean ± SD | Serum Nitrite Concentration μM, Mean ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy horses Aged 1 to 5 years, n = 11 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | min 0.6 ± 0.3 max 18.9 ± 0.6 |
| Healthy horses Aged 6 to 25 years, n = 19 | 0.15 ± 0.1 | min 0.30 ± 0.2 max 15.4 ± 0.5 |
| Ventral colon obstruction, 13.5 years | * | 2.4 ± 0.7 |
| Tympanic caecum, 7 years | * | 0.6 ± 0.4 |
| Cecal impaction, 14 years | * | 2.4 ± 0.7 |
| Large colon displacement, 8 years | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 2.4 ± 1.3 |
| Colitis, 18 years | * | 2.5 ± 0.6 |
| Seasonal colic of pelvic flexure, 3.5 years | * | 2.3 ± 0.6 |
| Spasmodic colic 6.5 years | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 1.8 ± 0.5 |
| Recurrent colic 3 years | * | 6.1 ± 2.1 |
| Young 1–5 Years | Aged 6–25 Years | Diseased | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD, μM | 8.24 ± 5.42 | 3.42 ± 4.22 | 2.07 ± 0.90 |
| Median, μM | 8.7 | 1.5 | 2.4 |
| Distribution normality Shapiro–Wilk test, p | 0.79 | 7 × 10−5 | 0.4274 |
| Distribution function Kolmogorov–Smirnov test, p | 0.0484 | 0.007 a | 0.654 |
| Median Mann–Whitney U-test, p | 0.010 | 0.039 b | 0.250 |
| Mean Student’s t-test, p | 0.021 | 0.003 c | 0.1990 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borunova, S.-F.; Tkachev, N.; Iolchiev, B.; Artyushina, Z.; Abramov, P.; Nikitina, M.; Silanteva, A.; Khusnetdinova, N.; Serezhenkov, V. Estimation of Nitrite—Nitric Oxide Derivative—In Horses with Intestinal Colic by ESR Spectroscopy. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7040191
Borunova S-F, Tkachev N, Iolchiev B, Artyushina Z, Abramov P, Nikitina M, Silanteva A, Khusnetdinova N, Serezhenkov V. Estimation of Nitrite—Nitric Oxide Derivative—In Horses with Intestinal Colic by ESR Spectroscopy. Veterinary Sciences. 2020; 7(4):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7040191
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorunova, Seid-Fatima, Nikolay Tkachev, Baylar Iolchiev, Zinaida Artyushina, Pavel Abramov, Marina Nikitina, Anastasia Silanteva, Neilia Khusnetdinova, and Vladimir Serezhenkov. 2020. "Estimation of Nitrite—Nitric Oxide Derivative—In Horses with Intestinal Colic by ESR Spectroscopy" Veterinary Sciences 7, no. 4: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7040191
APA StyleBorunova, S.-F., Tkachev, N., Iolchiev, B., Artyushina, Z., Abramov, P., Nikitina, M., Silanteva, A., Khusnetdinova, N., & Serezhenkov, V. (2020). Estimation of Nitrite—Nitric Oxide Derivative—In Horses with Intestinal Colic by ESR Spectroscopy. Veterinary Sciences, 7(4), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7040191





