Epidemiology and National Surveillance System for Foot and Mouth Disease in Cattle in Thailand during 2008–2019
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Outbreak Definitions
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
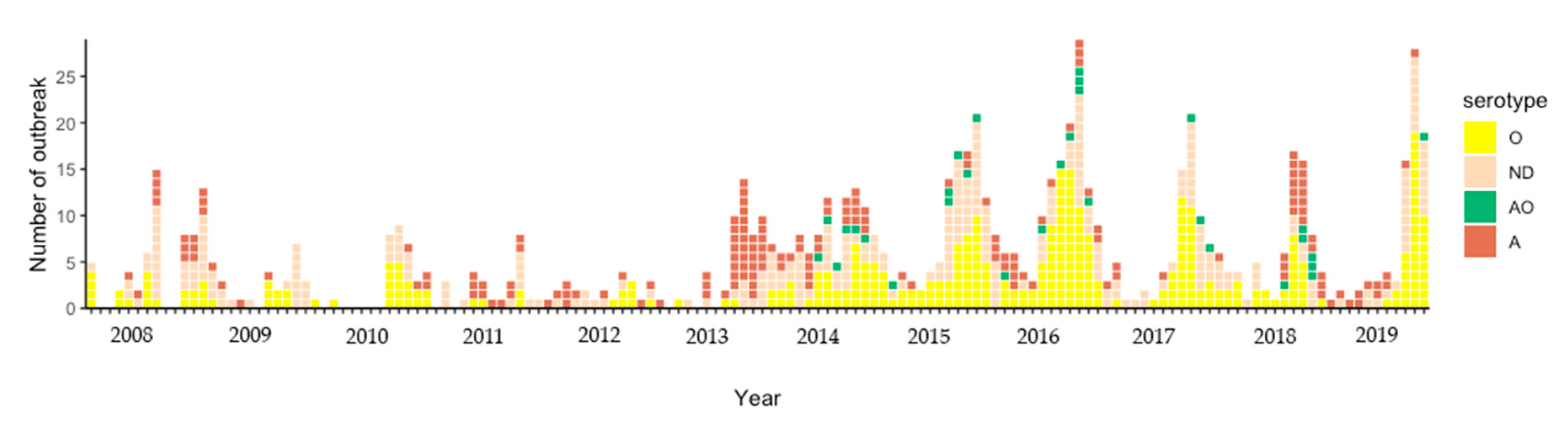
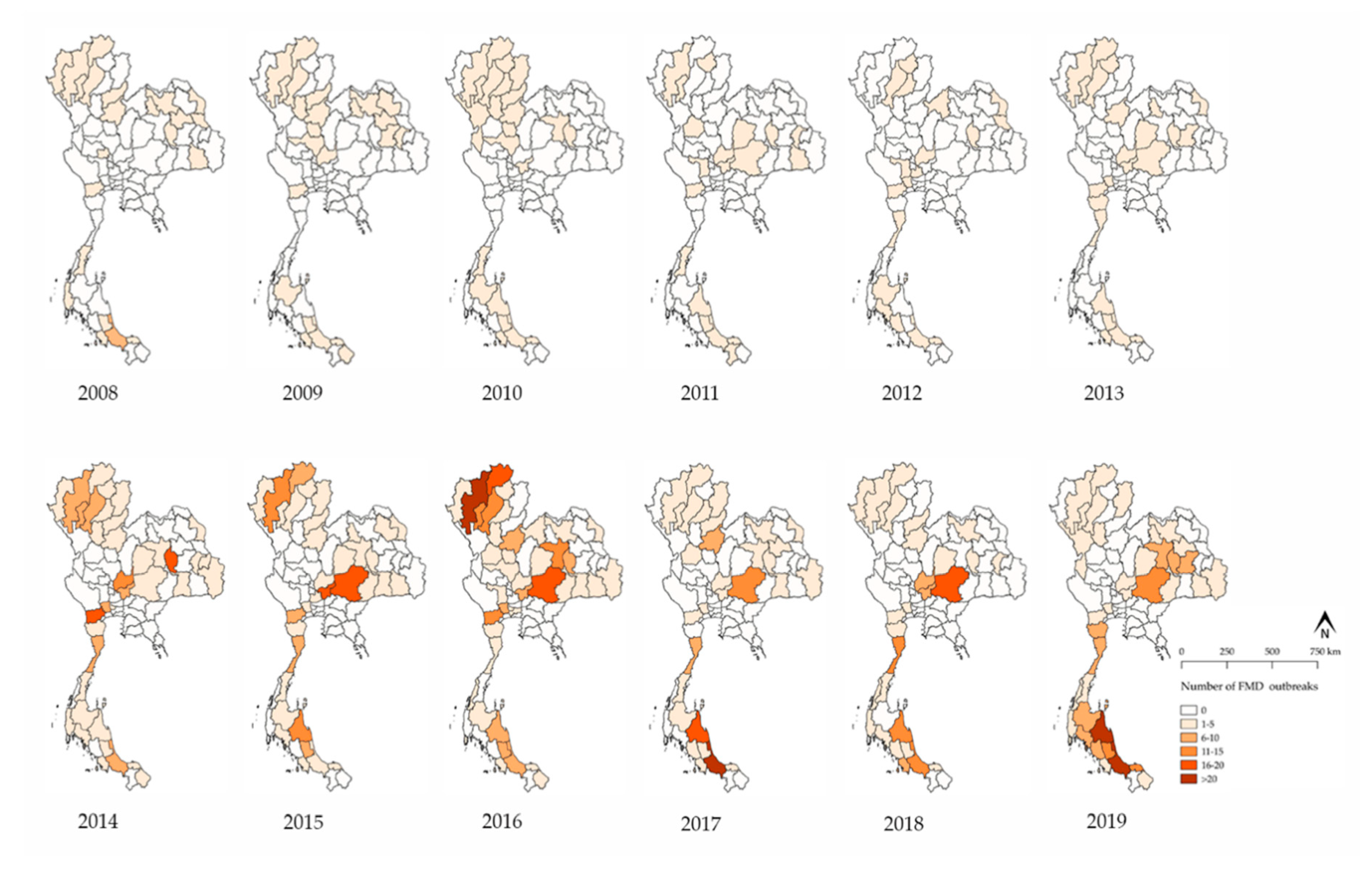
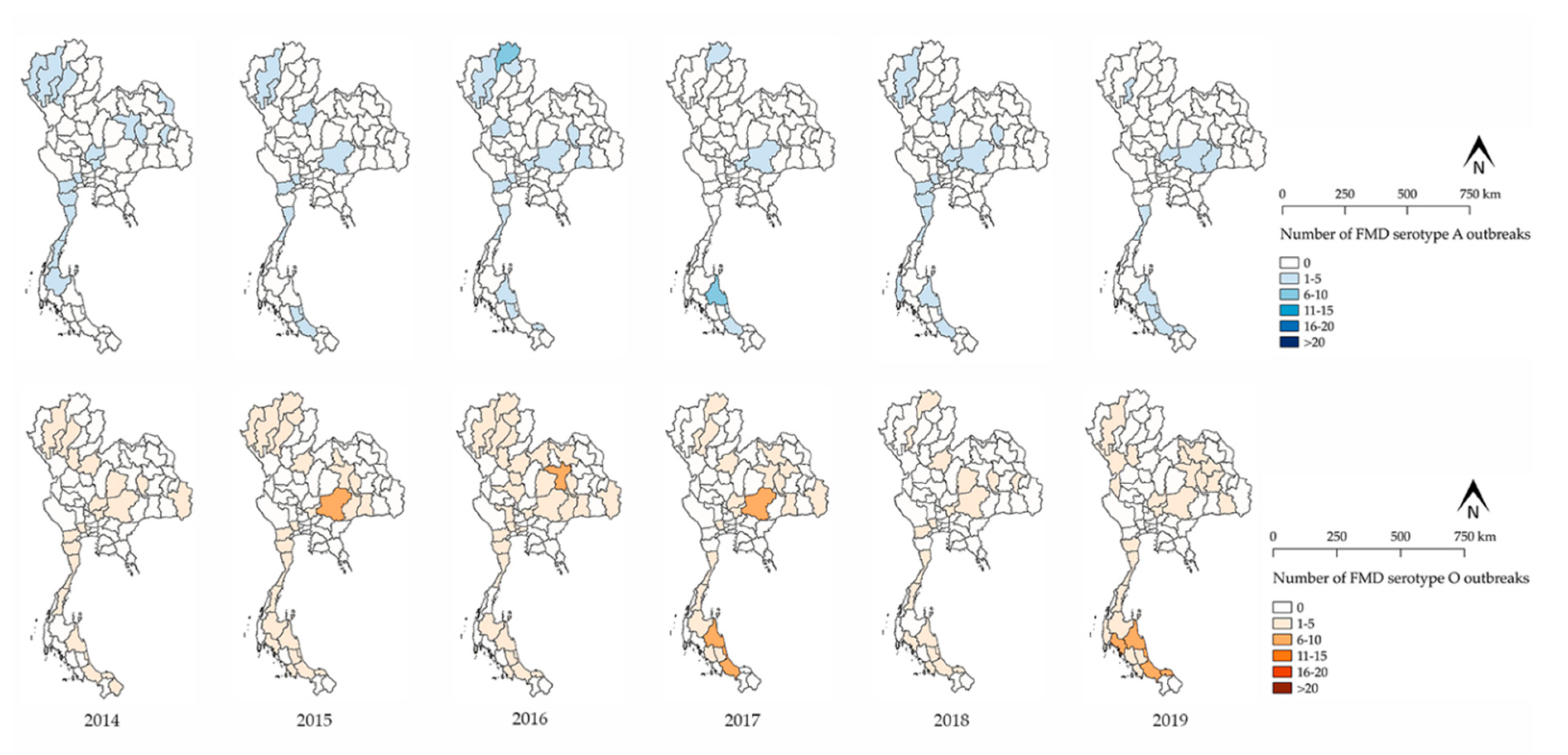
3.1. FMD Outbreak
3.2. FMD National Strategic Plan
3.3. Structure of FMD Surveillance by DLD Authority
3.4. FMD Vaccination and Control Measures
3.5. Seroprevalence Survey of FMD and Nucleotide Sequencing
3.6. Epidemiological Study for FMD
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foot & Mouth Disease (FMD). Available online: https://www.oie.int/en/animal-health-in-the-world/animal-diseases/Foot-and-mouth-disease/ (accessed on 7 March 2020).
- Kitching, R. Clinical variation in foot-and-mouth disease: Cattle. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2002, 21, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, N.J.; Samuel, A.R. Molecular epidemiology of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Virus Res. 2003, 91, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemberu, W.T.; Mourits, M.C.M.; Sahle, M.; Siraw, B.; Vernooij, J.C.M.; Hogeveen, H. Epidemiology of foot and mouth disease in Ethiopia: A retrospective analysis of district level outbreaks, 2007–2012. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, e246–e259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, S.M.; Belsham, G.J. Foot and mouth disease: Past, present and future. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blacksell, S.D.; Siengsanan-Lamont, J.; Kamolsiripichaiporn, S.; Gleeson, L.J.; Windsor, P.A. A history of FMD research and control programmes in Southeast Asia: Lessons from the past informing the future. Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Global Foot and Mouth Disease Control Strategy: Strengthening Animal Health Systems Through Improved Control of Major Diseases. Available online: https://www.oie.int/doc/ged/D11886.PDF (accessed on 7 March 2020).
- The Progressive Control Pathway for Foot and Mouth Disease (PCP-FMD). Available online: http://www.fao.org/eufmd/global-situation/pcp-fmd/en/ (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Quah, S.R. Infectious disease surveillance. In International Encyclopedia of Public Health, 2nd ed.; Murray, J., Cohen, A.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soehadji, M.M.; Setyaningsih, H. The experience of Indonesia in the control and eradication of foot-and-mouth disease. Diagnosis and epidemiology of foot-and-mouth disease in Southeast Asia. In Proceedings of the an International Workshop Held at Lampang, Lampang, Thailand, 6–9 September 1993; Copland, J.W., Gleeson, L.J., Chamnanpood, C., Eds.; Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research Proceedings: Canberra, Australia, 1994; Volume 51, pp. 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Windsor, P.A.; Freeman, P.G.; Abila, R.; Benigno, C.; Verin, B.; Nim, V.; Cameron, A. Foot-and-mouth disease control and eradication in the Bicol surveillance buffer zone of the Philippines: FMD control and eradication in the Bicol surveillance buffer zone. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2011, 58, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisrisongkram, W. An overview of foot and mouth disease control in Thailand. In Diagnosis and Epidemiology of Foot and Mouth Disease in Southeast Asia: ACIAR Proceeding Series No. 51; Copland, J.W., Gleeson, L.J., Chamnanpood, C., Eds.; Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research: Canberra, Australia, 1993; pp. 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Premashthira, S. Overview of foot and mouth disease control in Thailand and Southeast Asia. In Proceedings of the 20th FAVA and the 15th KIVNAS PDHI 2018, Bali, Indonesia, 1–3 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson, L.J. A review of the status of foot and mouth disease in South-East Asia and approaches to control and eradication. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz. 2002, 21, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojanasthien, S.; Padungtod, P.; Yamsakul, P.; Kongkeaw, S.; Yano, T. Cross-sectional study of foot and mouth diseases in cattle farms in northern Thailand. In Global Response and Emerging Disease. In Proceedings of the 11th International Symposium on Veterinary Epidemiology and Economics, Cairns, Australia, 7–11 August 2006; ISVEE: Queensland, Australia. [Google Scholar]
- Rojanasthien, S.; Padungtod, P.; Yamsakul, P.; Kongkeaw, S.; Yano, T. Cross-sectional study of foot and mouth diseases in pig farms in northern Thailand. In Global Response and Emerging Disease. In Proceedings of the 11th International Symposium on Veterinary Epidemiology and Economics, Cairns, Australia, 7–11 August 2006; ISVEE: Queensland, Australia. [Google Scholar]
- National FMD Strategic Plan of Thailand. Available online: http://aqi.dld.go.th/th/index.php? option=com_content&view=article&id=212:fmdcontrol&catid=73:document-aqi&Itemid=119 (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Department of Livestock Development (DLD). National FMD Plan for OIE Endorsement; DLD: Bangkok, Thailand, 2015; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Animal Health Situation. Available online: https://www.oie.int/wahis_2/public/ wahid.php/Countryinformation/Animalsituation (accessed on 7 March 2020).
- Arjkumpa, O.; Sansamur, C.; Sutthipankul, P.; Inchaisri, C.; Na Lampang, K.; Charoenpanyanet, A.; Punyapornwithaya, V. Spatiotemporal analyses of foot and mouth disease outbreaks in cattle farms in Chiang Mai and Lamphun, Thailand. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing: R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. Available online: https://www.gbif.org/tool/81287/r-a-language-and-environment-for- statistical-computing (accessed on 8 June 2020).
- EpiCurve: Plot an Epidemic Curve version 2.3.1. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/EpiCurve/index.html (accessed on 3 June 2020).
- QGIS: A Free and Open Source Geographic Information System. Available online: https://qgis.org/en/site/ (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Yano, T.; Premashthira, S.; Dejyong, T.; Tangtrongsup, S.; Salman, M.D. The effectiveness of a foot and mouth disease outbreak control programme in Thailand 2008–2015: Case studies and lessons learned. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaosuancharoen, T. Experience of FMD control in Thailand: The continual attempts and foresight. In key elements in the prevention and control of FMD and in implementing the strategy. In Proceedings of the FAO/OIE global conference on foot and mouth disease control ensuring excellence and ethics of the veterinary profession, Bangkok, Thailand, 27–29 June 2012; FAO and OIE: Bangkok, Thailand, 2012; pp. 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- SEACFMD Roadmap 2016–2020. Available online: https://rr-asia.oie.int/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/seacfmd-roadmap_2016-2020.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- National Animal Disease Surveillance System (NADSS). Available online: http://en.dld.go.th/index.php/en/focus-menu/animal-health-menu/over-all-of-animal-health/national-animal-disease-surveillance-system-nadss (accessed on 23 March 2020).
- Linchongsubongkoch, W.; Seeyo, K.B.; Petvanichakul, S.; Samanit, J. Vaccine matching strain characterization of foot and mouth disease virus in South East Asia during 2010–2012. In Proceedings of the Thailand-Japan Joint Conference on Animal Health, Bangkok, Thailand; 2012; pp. 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Regional Reference Laboratory for FMD in South East Asia (RRLSEA) Activity. In Proceedings of the 12th SEACFMD Laboratory Network Meeting, Pakchong, Thailand, 4–5 November 2019; Available online: https://rr-asia.oie.int/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/1-4-udon_rrl-pak-chong.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2020).
- Sakrasaer, P.; Polratana, K. Serological Study of FMD in Imported Cattle and Buffaloes from Myanmar during 2006–2007. Available online: http://dcontrol.dld.go.th/dcontrol/images/km/research/10.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2020).
- Noourai, P. Outbreak Investigation of Foot and Mouth Disease in Ruminant at Risk Area. In Proceedings of the 14th Academic National Conference, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Western University, Thailand, 27–28 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pisek, S.; Srisai, P.; Arjkumpa, O.; Sirikanok, I.; Wongsathapornchai, K.; Chanachai, K. Investigation of foot and mouth disease outbreak in Nakhon Ratchasima province, Thailand, July, 2011. In Field Epidemiology in Veterinary Reports: 2009–2013 Yearly Book Reports, Field Epidemiology Training Program for Veterinarians (FETPV); Department of Livestock Development: Bangkok, Thailand, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 74–75. ISBN 978-616-358-083-2. [Google Scholar]
- Yano, T.; Rojanasthien, S.; Yamsakul, P.; Kongkeaw, S.; Patchanee, P.; Suppawilai, C.; Pornwisetsirikul, S.; Sutthipunkul, P. A case study of foot and mouth disease in Chiang Mai and Lamphun, 2007–2011(In Thai). Chiang. Mai. Vet. J. 2013, 11, 277–287. [Google Scholar]
- Prakotcheo, R.; Premashthira, S. Seroprevalence and Risk Factors of Foot and Mouth Disease Virus Infection in Cloven-Hoofed Animals in the Eastern Part of Thailand. Available online: http://dcontrol.dld.go.th/dcontrol/images/km/research/22.pdf (accessed on 23 March 2020).
- Thongtha, P.; Linchongsubongkoch, W. Molecular epidemiology analysis of foot and mouth disease virus type A field outbreaks in Thailand during 2004–2005. Thai NIAH J. 2006, 1, 44–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cleland, P.C.; Chamnanpood, P.; Baldock, F.C.; Gleeson, L.J. Questionnaire survey of foot and mouth disease (FMD) and of FMD control by vaccination in villages in northern Thailand. Rev. Sci. Tech. 1995, 14, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noimoh, T.; Thanopongtharm, W. Epidemiology of Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) in Thailand from Animal Disease Reporting System (e-Smart Surveillance) during 2014–2016. Available online: http://dcontrol.dld.go.th/dcontrol/images/km/FMD_esmart2017_31102017.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Polratana, K.; Hongchumpon, N.; Jenpanich, C. Studying the Foot and Mouth Disease in Thailand during 2005–2009 using GIS and Descriptive Statistical Methods. Available online: http://dcontrol.dld.go.th/ dcontrol/images/km/research/15.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Sansamur, C.; Arjkumpa, O.; Charoenpanyanet, A.; Punyapornwithaya, V. Determination of risk factors associated with foot and mouth disease outbreaks in dairy farms in Chiang Mai province, Northern Thailand. Animals 2020, 10, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangrat, W.; Poolkhet, C. Spatial-temporal analysis of foot-and-mouth disease in Thailand during 2014–2016. Proccedings of the 14th KU-KPS Conference, Nakhon Pathom, Thailand, 7–8 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Penghiran, K. Risk Factors of Foot and Mouth Disease Occurrence on Social Network of Smallholder Dairy Frmers, Nongpho Dairy Co-Operative Ltd. (Under the Royal Patronage). Master’s Thesis, Graduate School, Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rojanasthien, S.; Padungtod, P.; Yamsakul, P.; Kongkaew, S.; Yano, T. Risk factors for foot and mouth disease in ruminants in Chiang Mai, Lumphun and Nan. In Proceedings of the 44th Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand, 30 January–2 February 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cleland, P.C.; Baldock, F.C.; Chamnanpood, P.; Gleeson, L.J. Village level risk factors for foot and mouth disease in Northern Thailand. Prev. Vet. Med. 1996, 26, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prueksakorn, K.; Kasemsuwan, S.; Pamaranon, N.; Swe, H.; Nguyen, H.A.T. Risk assessment of foot-and-mouth disease in cattle farms in Saraburi province from remote transmission using WRF/CALPUFF modeling system. Khon. Kaen. Agri. J. 2019, 47, 307–316. [Google Scholar]
- Pamaranon, N.; Ruksupap, N. Quantitative Risk Assessment of the Introduction of Foot and Mouth Disease Virus Through Importation of Cattle and Buffaloes into Thailand. Available online: https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B7E7iFEFocNjMDVkSS14SUl6VFk/view (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Onnum, W. The Level of Knowledge and Understanding of Farmers in Changwat Kamphaeng Phet towards the Foot and Mouth Disease of Cattle. Available online: https://dric.nrct.go.th/ Search/SearchDetail/73861 (accessed on 23 March 2020).
- Premashthira, S.; Prakotcheo, R. Survey on Knowledge, Attitude and Practice on Foot and Mouth Disease Control of Farmers in the Eastern Region of Thailand. Available online: http://dcontrol.dld.go.th/ dcontrol/images/km/research/2015_3_16KAPFMDR2-2.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Onmueang, S.; Charoenpanyanet, A. Geo-Information techniques for analysis of foot and mouth disease in cattle, Maeon District, Chiang Mai Province. J. Mahanakorn. Vet. Med. 2018, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Ramasoota, P.; Sariya, L.; Masrinoul, P.; Pitaksatjakul, P.; Lekcharoensuk, P.; Srimahasombat, W.; Linchongsubongkoch, W.; Lekcharoensuk, C. Enhancement of Diagnostic Efficacy for ControllingF and Mouth Disease in Cattle and Pigs; Full report of research project of National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT): Bangkok, Thailand, 2010.
- Patchimasiri, T.; Rodtian, P. Using of Immunohistochemistry Technique for Detection of Foot and Mouth Disease Virus (FMDV) Type O in Cattle Tissues. Available online: http://niah.dld.go.th/th/ files/ejournal/v11n2t03.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Immak, N.; Teeyasuksaet, N. Seroprevalence and Antibody Titer of Foot and Mouth Disease of Cattle and Water Buffalo in Upper Northern Part of Thailand, 2015–2017. Available online: http://region5.dld.go.th/webnew/ images/stories/2562/paper/paper1_072562.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Immak, N.; Kongsook, P.; Sriboonruang, C. Antibody Titer of Foot and Mouth Disease of Dairy Cattle in Chiang Mai Province, Thailand. Available online: http://region5.dld.go.th/webnew/ images/stories/2561/paper61/paper%20fmd1.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Seekhaow, S.; Chinson, P. Food and Mouth Disease: Seroprevalence in Cattle and Buffaloes at the Kanchanaburi Animal Quarantine Station by 3ABC ELISA. Available online: http://dcontrol.dld.go.th/ dcontrol/images/km/research/8.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Jithlang, W.; Sirimongkolrat, C. Serological Survey for Foot and Mouth Disease of Beef Cattle in Thailand, 2006. Available online: http://dcontrol.dld.go.th/dcontrol/images/km/research/37.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Tisdell, C.A.; Kehren, T. An overview of the occurrence of FMD in Thailand and policies for its control. In Research Papers and Reports in Animal Health Economics, An Aciar Thai-Australian Project; University of Queensland: St. Lucia, Australia, 1997; ISSN 1322-624X. [Google Scholar]
- German, R.R. Sensitivity and predictive value positive measurements for public health surveillance systems. Epidemiology 2000, 11, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, R.R.; Lee, L.M.; Horan, J.M.; Milstein, R.L.; Pertowski, C.A.; Waller, M.N. Updated guidelines for evaluating public health surveillance systems: Recommendations from the guidelines working group. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2001, 50, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrikx, P.; Gay, E.; Chazel, M.; Moutou, F.; Danan, C.; Richomme, C.; Boue, F.; Souillard, R.; Gauchard, F.; Dufour, B.; et al. OASIS: An assessment tool of epidemiological surveillance systems in animal health and food safety. Epidemiol. Infect. 2011, 139, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewe, J.; Hoinville, L.; Cook, A.; Floyd, T.; Stärk, K. Evaluation of animal and public health surveillance systems: A systematic review. Epidemiol. Infect. 2012, 140, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewe, J.A.; Hoinville, L.J.; Cook, A.J.; Floyd, T.; Gunn, G.; Stärk, K. SERVAL: A new framework for the evaluation of animal health surveillance. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2013, 62, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabarro, D. Global disease surveillance and response: Incentives and disincentives to timely disease reporting and response–lessons from the influenza campaign. In Infectious Disease Movement in a Borderless World; Relman, D.A., Choffnes, E.R., Mack, A., Eds.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; pp. 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- Alexanderson, S.; Zhang, Z.; Donaldson, A.I.; Garland, J.M. The pathogenesis and diagnosis of foot-and-mouth disease. J. Comp. Pathol. 2003, 129, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center of Disease Control and Prevention. Principles of Epidemiology in Public Health Practice: An Introduction to Applied Epidemiology and Biostatistics, 3rd ed.; CDC: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2012. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/csels/dsepd/ss1978/lesson6/section2.html (accessed on 2 June 2020).
- Caporale, V.; Giovannini, A.; Zepeda, C. Surveillance strategies for foot and mouth disease to prove absence of disease and absence of viral circulation. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2012, 31, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunasekera, U.C.; Sivasothy, A.; Wedasingha, N.; Thayaparanb, S.; Rotewewac, B.; Muralithasa, M.; Baumannd, M.P.O.; Punyapornwithaya, V. Analyzing the foot and mouth disease outbreak as from 2008 to 2014 in cattle and buffaloes in Sri Lanka. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 148, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunarathne, A.; Kubota, S.; Kumarawadu, P.; Karunagoda, K.; Kon, H. Is hiding foot and mouth disease sensitive behavior for farmers? A survey study in Sri Lanka. Asian Aust. J. Ani. Sci. 2016, 29, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazerooni, P.A.; Fararouei, M.; Nejat, M.; Akbarpoor, M.; Sedaghat, Z. Under-ascertainment, under-reporting and timeliness of Iranian communicable disease surveillance system for zoonotic diseases. Public Health 2018, 154, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergne, T.; Grosbois, V.; Durand, B.; Goutard, F.; Bellet, C.; Holl, D.; Roger, F.; Dufour, B. A capture–recapture analysis in a challenging environment: Assessing the epidemiological situation of foot-and-mouth disease in Cambodia. Prev. Vet. Med. 2012, 105, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, G. The selection from multiple data sources in epidemiological capture-recapture studies. Statistician 1997, 46, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, P.K.; Chao, A. Population size estimation for capture-recapture model with applications to epidemiological data. J. Appl. Stat. 2001, 28, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergne, T.; Del Rio Vilas, V.J.; Cameron, A.; Dufour, B.; Grosbois, V. Capture–recapture approaches and the surveillance of livestock diseases: A review. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 120, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, A.C.A.; Lwambo, N.J.S.; Blair, L.; Nyandindi, U.; Kaatano, G.; Kinung’hi, S.; Webster, J.P.; Fenwick, A.; Brooker, S. Bayesian spatial analysis and disease mapping: Tools to enhance planning and implementation of a schistosomiasis control programme in Tanzania. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2006, 11, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Period | Estimate | Standard Error | Z-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period * 1 | Reference class | |||
| Period 2 | 0.526 | 0.140 | 3.75 | <0.001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arjkumpa, O.; Yano, T.; Prakotcheo, R.; Sansamur, C.; Punyapornwithaya, V. Epidemiology and National Surveillance System for Foot and Mouth Disease in Cattle in Thailand during 2008–2019. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7030099
Arjkumpa O, Yano T, Prakotcheo R, Sansamur C, Punyapornwithaya V. Epidemiology and National Surveillance System for Foot and Mouth Disease in Cattle in Thailand during 2008–2019. Veterinary Sciences. 2020; 7(3):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7030099
Chicago/Turabian StyleArjkumpa, Orapun, Tedsak Yano, Rotchana Prakotcheo, Chalutwan Sansamur, and Veerasak Punyapornwithaya. 2020. "Epidemiology and National Surveillance System for Foot and Mouth Disease in Cattle in Thailand during 2008–2019" Veterinary Sciences 7, no. 3: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7030099
APA StyleArjkumpa, O., Yano, T., Prakotcheo, R., Sansamur, C., & Punyapornwithaya, V. (2020). Epidemiology and National Surveillance System for Foot and Mouth Disease in Cattle in Thailand during 2008–2019. Veterinary Sciences, 7(3), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7030099






