Rapid Resolution of Large Bowel Diarrhea after the Administration of a Combination of a High-Fiber Diet and a Probiotic Mixture in 30 Dogs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion Criteria for Dogs and Diagnostic Work-Up
2.2. Therapeutic Intervention
2.3. Fecal Score
2.4. CCECAI Score
2.5. Dysbiosis Index
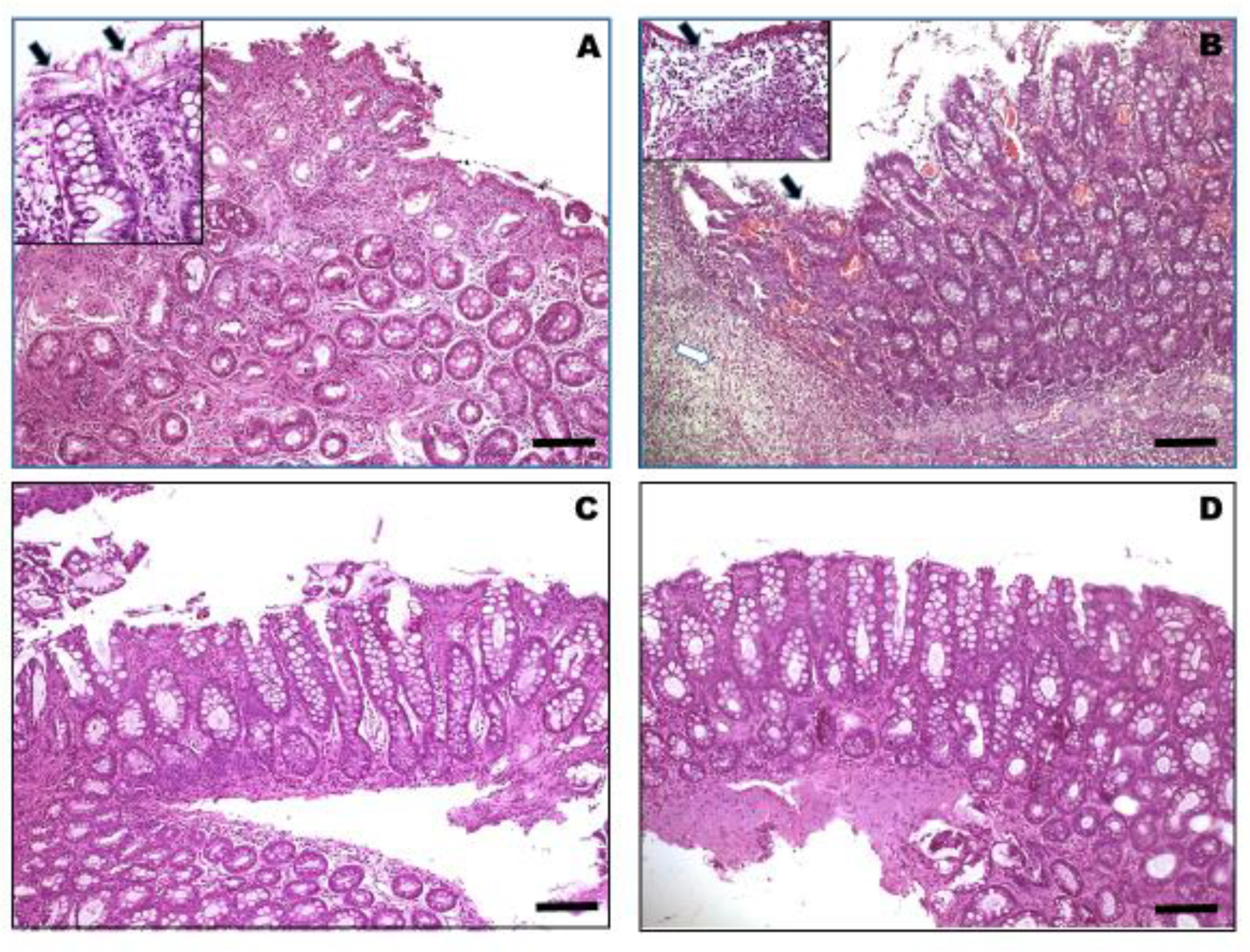
2.6. Histopathology
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cerquetella, M.; Rossi, G.; Spaterna, A.; Tesei, B.; Gavazza, A.; Pengo, G.; Pucciarelli, S.; Scortichini, L.; Sagratini, G.; Ricciutelli, M.; et al. Fecal Proteomic Analysis in Healthy Dogs and in Dogs Suffering from Food Responsive Diarrhea. Sci. World J. 2019, 2019, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalenyak, K.; Isaiah, A.; Heilmann, R.M.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Burgener, I.A. Comparison of the intestinal mucosal microbiota in dogs diagnosed with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease and dogs with food-responsive diarrhea before and after treatment. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattasathuchana, P.; Allenspach, K.; Lopes, R.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M. Evaluation of serum 3-bromotyrosine concentrations in dogs with steroid-responsive diarrhea and food-responsive diarrhea. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 1056–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilley, L.P.; Smith, F.W.K. Fiber-responsive large bowel diarrhea. In Blackwell’s Five-Minute Veterinary Consult: Canine and Feline, 6th ed.; Tilley, L.P., Smith, F.W.K., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Ames, IA, USA, 2016; p. 514. [Google Scholar]
- Cerquetella, M.; Rossi, G.; Spaterna, A.; Tesei, B.; Jergens, A.E.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Bassotti, G. Is irritable bowel syndrome also present in dogs? Tierarztl. Prax. Ausg. K Kleintiere Heimtiere 2018, 46, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecoindre, P.; Gaschen, F.P. Chronic idiopathic large bowel diarrhea in the dog. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2011, 41, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leib, M.S. Treatment of chronic idiopathic large-bowel diarrhea in dogs with a highly digestible diet and soluble fiber: A retrospective review of 37 cases. J. Vet. Int. Med. 2000, 14, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, S.; Glanemann, B.; Garden, O.A.; Brooks, H.; Chang, Y.M.; Werling, D.; Allenspach, K. A prospective, randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled pilot study on the effect of enterococcus faecium on clinical activity and intestinal gene expression in canine food-responsive chronic enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2015, 29, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.; Atherly, T.; Guard, B.; Rossi, G.; Wang, C.; Mosher, C.; Webb, C.; Hill, S.; Ackermann, M.; Sciabarra, P.; et al. Randomized, controlled trial evaluating the effect of multi-strain probiotic on the mucosal microbiota in canine idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. Microbes 2017, 8, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Cerquetella, M.; Scarpona, S.; Pengo, G.; Fettucciari, K.; Bassotti, G.; Jergens, A.E.; Suchodolski, J.S. Effects of probiotic bacteria on mucosal polyamines levels in dogs with IBD and colonic polyps: A preliminary study. Benef. Microbes 2018, 9, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Jergens, A.; Cerquetella, M.; Berardi, S.; Di Cicco, E.; Bassotti, G.; Pengo, G.; Suchodolski, J.S. Effects of a probiotic (SLAB51™) on clinical and histologic variables and microbiota of cats with chronic constipation/megacolon: A pilot study. Benef. Microbes 2018, 9, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Pengo, G.; Caldin, M.; Palumbo Piccionello, A.; Steiner, J.M.; Cohen, N.D.; Jergens, A.E.; Suchodolski, J.S. Comparison of microbiological, histological, and immunomodulatory parameters in response to treatment with either combination therapy with prednisone and metronidazole or probiotic VSL#3 strains in dogs with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, F. Do All Types of Human Research Need Ethics Committee Approval? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, G.; Gioacchini, G.; Pengo, G.; Suchodolski, J.; Jergens, A.E.; Allenspac, K.; Gavazza, A.; Scarpona, S.; Berardi, S.; Galosi, L.; et al. Enterocolic increase of cannabinoid receptor type 1 and type 2 and clinical improvement after probiotic administration in dogs with chronic signs of colonic dysmotility without mucosal inflammatory changes. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 8, e13717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moxham, G. Waltham feces scoring system—A tool for veterinarians and pet owners: How does your pet rate? WALTHAM® Focus 2001, 11, 24–25. [Google Scholar]
- Allenspach, K.; Wieland, B.; Gröne, A.; Gaschen, F. Chronic enteropathies in dogs: Evaluation of risk factors for negative outcome. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2007, 21, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlShawaqfeh, M.K.; Wajid, B.; Minamoto, Y.; Markel, M.; Lidbury, J.A.; Steiner, J.M.; Serpedin, E.; Suchodolski, J.S. A dysbiosis index to assess microbial changes in fecal samples of dogs with chronic inflammatory enteropathy. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, M.J.; Bilzer, T.; Mansell, J.; Wilcock, B.; Hall, E.J.; Jergens, A.; Minami, T.; Willard, M.; Washabau, R.; World Small Animal Veterinary Association Gastrointestinal Standardization Group. Histopathological standards for the diagnosis of gastrointestinal inflammation in endoscopic biopsy samples from the dog and cat: A report from the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Gastrointestinal Standardization Group. J. Comp. Pathol. 2008, 138, S1–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.forza10.com/index.php/prodotto/intestinal-colitis-fase-1/ (accessed on 14 August 2019).
- Medcalf, D.G.; Larsen, B. Fucose-containing polysaccharides in the brown algae Ascophyllum nodosum and Fucus vesiculosus. Carbohydr. Res. 1977, 59, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, F.; Wei, X.; Zhao, R. Fucoidan: Structure and bioactivity. Molecules 2008, 13, 1671–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh-Sang, V.; Se-Kwon, K. Fucoidans as a natural bioactive ingredient for functional foods. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallman, J.; Moxley, R.; Reinhart, G.; Wallace, G.A.; Clemens, E.T. Cellulose, beet pulp, and pectin/gum arabic effects on canine colonic microstructure and histopathology. Vet. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 2, 137–142. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, K.L.; Yamka, R.M.; Khoo, C.; Friesen, K.G.; Jewell, D.E; Schoenherr, W.D.; Debraekeleer, J.; Zicker, S.C. Macronutrients. In Small Animal Clinical Nutrition, 5th ed.; Hand, M.S., Thatcher, C.D., Remillard, R.L., Roudebush, P., Novotny, B.J., Eds.; Mark Morris Institute: Topeka, KS, USA, 2010; pp. 49–105. [Google Scholar]
- Heyman, M.; Darmon, N.; Dupont, C.; Dugas, B.; Hirribaren, A.; Blaton, M.A.; Desjeux, J.F. Mononuclear cells from infants allergic to cow’s milk secrete tumor necrosis factor alpha, altering intestinal function. Gastroenterology 1994, 106, 1514–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanuytsel, T.; van Wanrooy, S.; Vanheel, H.; Vanormelingen, C.; Verschueren, S.; Houben, E.; Salim Rasoel, S.; Tόth, J.; Holvoet, L.; Farré, R.; et al. Psychological stress and corticotropin-releasing hormone increase intestinal permeability in humans by a mast cell-dependent mechanism. Gut 2014, 63, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfili, L.; Cecarini, V.; Cuccioloni, M.; Angeletti, M.; Berardi, S.; Scarpona, S.; Rossi, G.; Eleuteri, A.M. SLAB51 probiotic formulation activates SIRT1 pathway promoting antioxidant and neuroprotective effects in an AD mouse model. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 7987–8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peran, L.; Sierra, S.; Comalada, M.; Lara-Villoslada, F.; Bailón, E.; Nieto, A.; Concha, A.; Olivares, M.; Zarzuelo, A.; Xaus, J.; et al. A comparative study of the preventative effects exerted by two probiotics, Lactobacillus reuteri and Lactobacillus fermentum, in the trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid model of rat colitis. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 97, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisham, M.B. Oxidants and free radicals in inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet 1994, 344, 859–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálvez, J.; Garrido, M.; Rodriguez-Cabezas, M.E.; Ramis, I.; Sanchez de Medina, F.; Merlos, M.; Zarzuelo, A. The intestinal anti-inflammatory activity of UR-12746S on reactivated experimental colitis is mediated through downregulation of cytokine production. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2003, 9, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camuesco, D.; Comalada, M.; Rodriguez-Cabezas, M.E.; Nieto, A.; Lorente, M.D.; Concha, A.; Zarzuelo, A.; Galvez, J. The intestinal anti-inflammatory effect of quercitrin is associated with an inhibition in iNOS expression. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 143, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peran, L.; Camuesco, D.; Comalada, M.; Nieto, A.; Concha, A.; Adrio, J.L.; Olivares, M.; Xaus, J.; Zarzuelo, A.; Galvez, J. Lactobacillus fermentum, a probiotic capable to release glutathione, prevents colonic inflammation in the TNBS model of rat colitis. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2006, 21, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borruel, N.; Carol, M.; Casellas, F.; Antolin, M.; de Lara, F.; Espin, E.; Naval, J.; Guarner, F.; Malagelada, J.R. Increased mucosal tumour necrosis factor alpha production in Crohn’s disease can be downregulated ex vivo by probiotic bacteria. Gut 2002, 51, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutgeerts, P.; Van Assche, G.; Vermeire, S. Optimizing anti-TNF treatment in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1593–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, A.; Xie, K.; Yu, Y. Dietary Supplementation with High Fiber Alleviates Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Responses Caused by Severe Sepsis in Mice Without Altering Microbiome Diversity. Front. Physiol. 2019, 9, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, D.; Knuchel-Takano, A.; McCutchan, A.; Chang, Y.M.; Downes, C.; Miller, S.; Stevens, K.; Verheyen, K.; Phillips, A.D.; Miah, S.; et al. Comprehensive pathological survey of duodenal biopsies from dogs with diet-responsive chronic enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2013, 27, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Dogs | Breed | Sex | Age | Days until Stool Normalization (Mean Value: 8.5) | Fecal Score * | CCECAI * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 (Median Value: 4) | T1 (Median Value: 2) | T0 (Median Value: 8) | T1 (Median Value: 2) | |||||
| 1 | German Shepherd | M | 2.5 years | 6 | 4 | 2 | 9 | 2 |
| 2 | Crossbreed | F | 6 years | 5 | 5 | 2 | 8 | 3 |
| 3 | Border Collie | M | 1.5 years | 11 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 3 |
| 4 | Boxer | M | 2.5 years | 10 | 5 | 3 | 9 | 3 |
| 5 | Dobermann | F | 2 years | 7 | 4 | 1 | 9 | 1 |
| 6 | Cocker Spaniel | F | 10 years | 9 | 3 | 2 | 7 | 0 |
| 7 | Boston Terrier | M | 6.5 years | 11 | 4 | 3 | 8 | 2 |
| 8 | Sussex Spaniel | M | 8.5 years | 15 | 5 | 3 | 10 | 4 |
| 9 | Amstaff | M | 12 years | 9 | 4 | 2 | 8 | 5 |
| 10 | Labrador Retriever | F | 10 years | 8 | 4 | 1 | 7 | 0 |
| 11 | Boxer | M | 1 year | 7 | 5 | 3 | 7 | 3 |
| 12 | German Shepherd | M | 3.5 years | 4 | 5 | 3 | 10 | 4 |
| 13 | Crossbreed | M | 11 years | 5 | 4 | 1 | 8 | 1 |
| 14 | German Shepherd Crossbreed | F | 12 years | 5 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 0 |
| 15 | Magyar Vizsla | M | 6 years | 8 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 2 |
| 16 | Wire-haired Dachshund | F | 7.5 years | 11 | 3 | 2 | 8 | 2 |
| 17 | Crossbreed | M | 3 years | 9 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
| 18 | Poodle | M | 3 years | 8 | 4 | 3 | 8 | 4 |
| 19 | Boxer | M | 2 years | 13 | 5 | 3 | 8 | 3 |
| 20 | Bernese Mountain Dog | M | < 1 year | 10 | 5 | 2 | 9 | 0 |
| 21 | Yorkshire Terrier | F | 7.5 years | 5 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 3 |
| 22 | German Shepherd | M | 1 year | 8 | 4 | 2 | 9 | 4 |
| 23 | Dobermann | F | < 1 year | 10 | 5 | 3 | 11 | 5 |
| 24 | Pinscher | M | 2 years | 4 | 4 | 2 | 8 | 2 |
| 25 | Jack Russel Terrier | M | 11 years | 11 | 5 | 3 | 9 | 3 |
| 26 | Rhodesian Ridgback | F | 4 years | 5 | 4 | 2 | 9 | 0 |
| 27 | Italian Greyhound | M | < 1 year | 14 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 0 |
| 28 | Akita Inu | F | 3 years | 6 | 3 | 2 | 8 | 4 |
| 29 | French Bulldog | M | 2 years | 15 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| 30 | English Setter | M | 3 years | 7 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 0 |
| Patient Number | T0 * | T1 * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Score by Variable § | Total | Score by Variable § | Total | |
| 1 | 3 + 2 + 3 + 4 | 12 | 1 + 1 + 0 + 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 3 | 9 | 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 | 4 |
| 3 | 2 + 2 + 1 + 2 | 7 | 1 + 1 + 0 + 1 | 3 |
| 4 | 3 + 3 + 4 + 4 | 14 | 1 + 2 + 0 + 1 | 4 |
| 5 | 3 + 2 + 4 + 4 | 13 | 1 + 1 + 0 + 3 | 5 |
| 6 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 | 8 | 2 + 1 + 2 + 2 | 7 |
| 7 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 3 | 9 | 1 + 1 + 0 + 3 | 5 |
| 8 | 3 + 3 + 4 + 4 | 14 | 1 + 1 + 0 + 1 | 3 |
| 9 | 2 + 3 + 3 + 3 | 11 | 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 | 4 |
| 10 | 3 + 2 + 4 + 4 | 13 | 1 + 1 + 0 + 3 | 5 |
| 11 | 3 + 3 + 4 + 4 | 14 | 1 + 1 + 0 + 1 | 3 |
| 12 | 3 + 2 + 4 + 4 | 13 | 1 + 1 + 0 + 3 | 5 |
| 13 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 3 | 9 | 1 + 1 + 0 + 1 | 3 |
| 14 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 | 8 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 3 | 9 |
| 15 | 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 | 4 | 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 | 4 |
| 16 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 | 8 | 0 + 0 + 0 + 0 | 0 |
| 17 | 1 + 1 + 0 + 1 | 3 | 0 + 0 + 0 + 0 | 0 |
| 18 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 3 | 9 | 0 + 0 + 0 + 0 | 0 |
| 19 | 3 + 2 + 4 + 4 | 13 | 1 + 1 + 0 + 0 | 2 |
| 20 | 3 + 3 + 4 + 4 | 14 | 1 + 1 + 0 + 1 | 3 |
| 21 | 2 + 2 + 2 + 3 | 9 | 1 + 1 + 0 + 1 | 3 |
| 22 | 3 + 2 + 3 + 4 | 12 | 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 | 4 |
| 23 | 3 + 3 + 4 + 4 | 14 | 1 + 1 + 0 + 1 | 3 |
| 24 | 2 + 2 + 1 + 2 | 7 | 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 | 4 |
| 25 | 3 + 2 + 3 + 3 | 11 | 1 + 1 + 0 + 1 | 3 |
| 26 | 3 + 2 + 3 + 4 | 12 | 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 | 4 |
| 27 | 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 | 4 | 0 + 0 + 0 + 0 | 0 |
| 28 | 3 + 2 + 2 + 2 | 9 | 1 + 1 + 0 + 1 | 3 |
| 29 | 1 + 1 + 0 + 1 | 3 | 0 + 0 + 0 + 0 | 0 |
| 30 | 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 | 4 | 1 + 1 + 0 + 0 | 2 |
| Median value 9 | Median value 3 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rossi, G.; Cerquetella, M.; Gavazza, A.; Galosi, L.; Berardi, S.; Mangiaterra, S.; Mari, S.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Lidbury, J.A.; Steiner, J.M.; et al. Rapid Resolution of Large Bowel Diarrhea after the Administration of a Combination of a High-Fiber Diet and a Probiotic Mixture in 30 Dogs. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7010021
Rossi G, Cerquetella M, Gavazza A, Galosi L, Berardi S, Mangiaterra S, Mari S, Suchodolski JS, Lidbury JA, Steiner JM, et al. Rapid Resolution of Large Bowel Diarrhea after the Administration of a Combination of a High-Fiber Diet and a Probiotic Mixture in 30 Dogs. Veterinary Sciences. 2020; 7(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleRossi, Giacomo, Matteo Cerquetella, Alessandra Gavazza, Livio Galosi, Sara Berardi, Sara Mangiaterra, Subeide Mari, Jan S. Suchodolski, Jonathan A. Lidbury, Joerg M. Steiner, and et al. 2020. "Rapid Resolution of Large Bowel Diarrhea after the Administration of a Combination of a High-Fiber Diet and a Probiotic Mixture in 30 Dogs" Veterinary Sciences 7, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7010021
APA StyleRossi, G., Cerquetella, M., Gavazza, A., Galosi, L., Berardi, S., Mangiaterra, S., Mari, S., Suchodolski, J. S., Lidbury, J. A., Steiner, J. M., & Pengo, G. (2020). Rapid Resolution of Large Bowel Diarrhea after the Administration of a Combination of a High-Fiber Diet and a Probiotic Mixture in 30 Dogs. Veterinary Sciences, 7(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7010021







