Treatment of Harvest Mite Infestation in Dogs Using a Permethrin 54.5% and Fipronil 6.1% (Effitix®) Topical Spot-On Formulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Animal Population
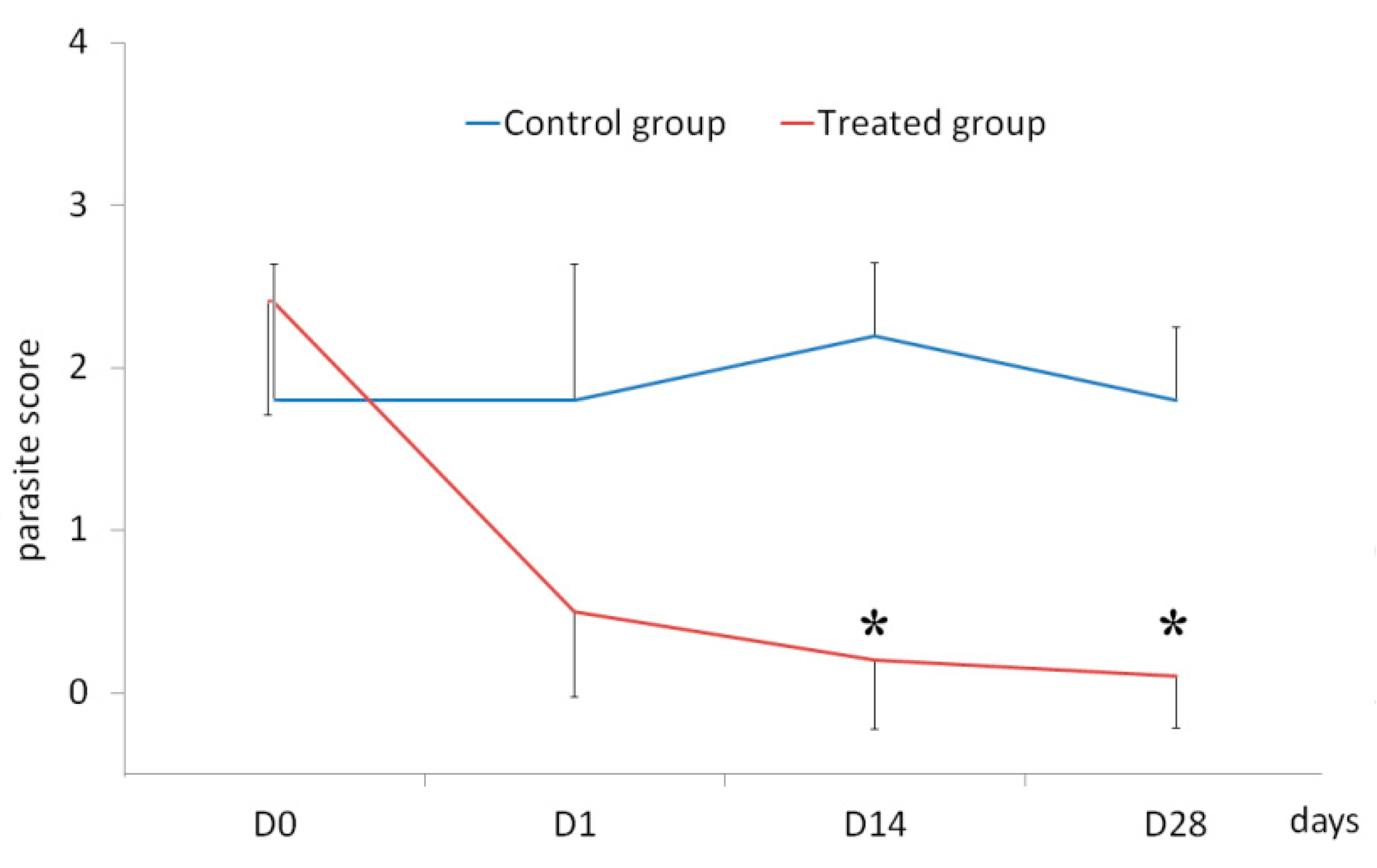
3.2. Parasite Score
3.3. Other Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Score | Administration | Tolerance | Efficacy |
| 1 | The treatment was very difficult to administer | The treatment was very poorly tolerated | The treatment did not work at all |
| 2 | The treatment was difficult to administer | The treatment was poorly tolerated | The treatment was only marginally effective |
| 3 | The treatment was reasonably straightforward to administer | The treatment was reasonably tolerated | The treatment partially resolved the skin problem |
| 4 | The treatment was easy to administer | The treatment was well tolerated | The treatment worked quite well |
| 5 | The treatment was very easy to administer | The treatment was very well tolerated | The treatment cleared up the skin problem |
References
- Guarneri, F.; Pugliese, A.; Giudice, E.; Guarneri, C.; Giannetto, S.; Guarneri, B. Trombiculiasis: Clinical contribution. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2005, 15, 495–496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hohenberger, M.E.; Elston, D.M. What’s eating you? chiggers. Cutis 2017, 99, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.H., Jr.; Griffin, C.E.; Campbell, K.L. Parasitic skin disease. In Muller and Kirk’s Small Animal Dermatology, 7th ed.; Mosby, E., Ed.; Saunders: St Louis, MO, USA, 2012; pp. 284–342. [Google Scholar]
- Parcell, B.J.; Sharpe, G.; Jones, B.; Alexander, C.L. Conjunctivitis induced by a red bodied mite, Neotrombicula autumnalis. Parasite 2013, 20, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Soulsby, E. Helminths, Arthropods and Protozoa of Domesticated Animals, 7th ed.; Bailliere Tindall: London, UK, 1982; p. 809. [Google Scholar]
- Stekolnikov, A.A.; Waap, H.; Gomes, J.; Antunes, T. Chigger mites of the genus Ericotrombidium (Acariformes: Trombiculidae) attacking pets in Europe. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 221, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholer, A.; Maier, W.A.; Kampen, H. Multiple environmental factor analysis in habitats of the harvest mite Neotrombicula autumnalis (Acari: Trombiculidae) suggests extraordinarily high euryoecious biology. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2006, 39, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosl, H.; Rabitsch, A.; Brabenetz, J. Trombiculid mite—Neotrombicula autumnalis (Shaw 1790)--in veterinary medicine. Nervous systems in dogs following massive infestation. Tierarztl. Prax. 1985, 13, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Soto, P.; Perez-Sanchez, R.; Encinas-Grandes, A. Molecular detection of Ehrlichia phagocytophila genogroup organisms in larvae of Neotrombicula autumnalis (Acari: Trombiculidae) captured in Spain. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 1482–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampen, H.; Scholer, A.; Metzen, M.; Oehme, R.; Hartelt, K.; Kimmig, P.; Maier, W.A. Neotrombicula autumnalis (Acari, Trombiculidae) as a vector for Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato? Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2004, 33, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Literak, I.; Stekolnikov, A.A.; Sychra, O.; Dubska, L.; Taragelova, V. Larvae of chigger mites Neotrombicula spp. (Acari: Trombiculidae) exhibited Borrelia but no Anaplasma infections: A field study including birds from the Czech Carpathians as hosts of chiggers. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2008, 44, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuttall, T.J.; French, A.T.; Cheetham, H.C.; Proctor, F.J. Treatment of Trombicula autumnalis infestation in dogs and cats with a 0.25 per cent fipronil pump spray. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1998, 39, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smal, D.; Jasmin, P.; Mercier, P. Treatment of Neotrombicula autumnalis dermatitis in dogs using two topical permethrin-pyriproxyfen combinations. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2004, 45, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, L. Fipronil and permethrin combination: A novel ectoparasiticide for dogs. Parasit Vectors 2015, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzis, M.K.; Psemmas, D.; Papadopoulos, E.; Navarro, C.; Saridomichelakis, M.N. A field trial of a fixed combination of permethrin and fipronil (Effitix(R)) for the treatment and prevention of flea infestation in dogs living with sheep. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonneau, S.; Reymond, N.; Gupta, S.; Navarro, C. Efficacy of a fixed combination of permethrin 54.5% and fipronil 6.1% (Effitix) in dogs experimentally infested with Ixodes ricinus. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Navarro, C.; Reymond, N.; Crastes, N.; Bonneau, S. Efficacy and Safety of a Permethrin-Fipronil Spot-On Solution (Effitix(R)) in Dogs Naturally Infested by Ticks in Europe. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 9498604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franc, M.; Lienard, E.; Jacquiet, P.; Bonneau, S.; Navarro, C.; Bouhsira, E. Efficacy of a new combination of fipronil and permethrin (Effitix(R)) against Phlebotomus perniciosus in dogs. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 212, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franc, M.; Lienard, E.; Jacquiet, P.; Bonneau, S.; Bouhsira, E. Efficacy of fipronil combined with permethrin commercial spot on (Effitix) preventing Culex pipiens from feeding on dogs. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 2093–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ucan-Mezquita, A.; Jimenez-Coello, M.; Guzman-Marin, E.; Gutierrez-Blanco, E.; Chan-Perez, J.I.; Travi, B.L.; Hernandez-Cortazar, I.; Ortega-Pacheco, A. Efficacy of a topical combination of fipronil-permethrin against Rhodnius prolixus on dogs. Vet. Parasitol. 2019, 276, 108978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadiergues, M.C.; Navarro, C.; Castilla-Castano, E.; Lecru, L.A.; Pressanti, C. Treatment of Neotrombicula species infestation in cats using a 10% (w/v) fipronil topical spot-on formulation: A pilot study. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2017, 20, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, M.A.; Shanks, D.J. A review of the off-label use of selamectin (Stronghold/Revolution) in dogs and cats. Acta Vet. Scand. 2008, 50, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Lesion Score | IPS | GAS | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D0 | D1 | D14 | D28 | D0 | D1 | D14 | D28 | D28 | |
| Treated dogs 1 | 2.9 ± 0.9 | 2.9 ± 0.9 | 0.6 ± 0.5 | 0.1 ± 0.3 | 2.2 ± 0.8 | 2 ± 0.7 | 0.4 ± 0.5 | 0.2 ± 0.4 | 4.8 ± 0.4 |
| Control dogs | 0.4 ± 0.5 | 0.4 ± 0.5 | 0 ± 0 | 0.2 ± 0.4 | 0.6 ± 0.9 | 0.6 ± 0.9 | 0.4 ± 0.9 | 0.4 ± 0.5 | / |
| Percentage of reduction/D0 2 | / | 0% | 79% | 97% | / | 9% | 82% | 91% | / |
| p-value | / | / | 0.002 | 0.002 | / | 0.5 | 0.004 | 0.002 | / |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lecru, L.-A.; Combarros, D.; Castilla-Castaño, E.; Navarro, C.; Cadiergues, M.C. Treatment of Harvest Mite Infestation in Dogs Using a Permethrin 54.5% and Fipronil 6.1% (Effitix®) Topical Spot-On Formulation. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci6040100
Lecru L-A, Combarros D, Castilla-Castaño E, Navarro C, Cadiergues MC. Treatment of Harvest Mite Infestation in Dogs Using a Permethrin 54.5% and Fipronil 6.1% (Effitix®) Topical Spot-On Formulation. Veterinary Sciences. 2019; 6(4):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci6040100
Chicago/Turabian StyleLecru, Line-Alice, Daniel Combarros, Eloy Castilla-Castaño, Christelle Navarro, and Marie Christine Cadiergues. 2019. "Treatment of Harvest Mite Infestation in Dogs Using a Permethrin 54.5% and Fipronil 6.1% (Effitix®) Topical Spot-On Formulation" Veterinary Sciences 6, no. 4: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci6040100
APA StyleLecru, L.-A., Combarros, D., Castilla-Castaño, E., Navarro, C., & Cadiergues, M. C. (2019). Treatment of Harvest Mite Infestation in Dogs Using a Permethrin 54.5% and Fipronil 6.1% (Effitix®) Topical Spot-On Formulation. Veterinary Sciences, 6(4), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci6040100






