A Preliminary Assessment of HTST Processing on Donkey Milk
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
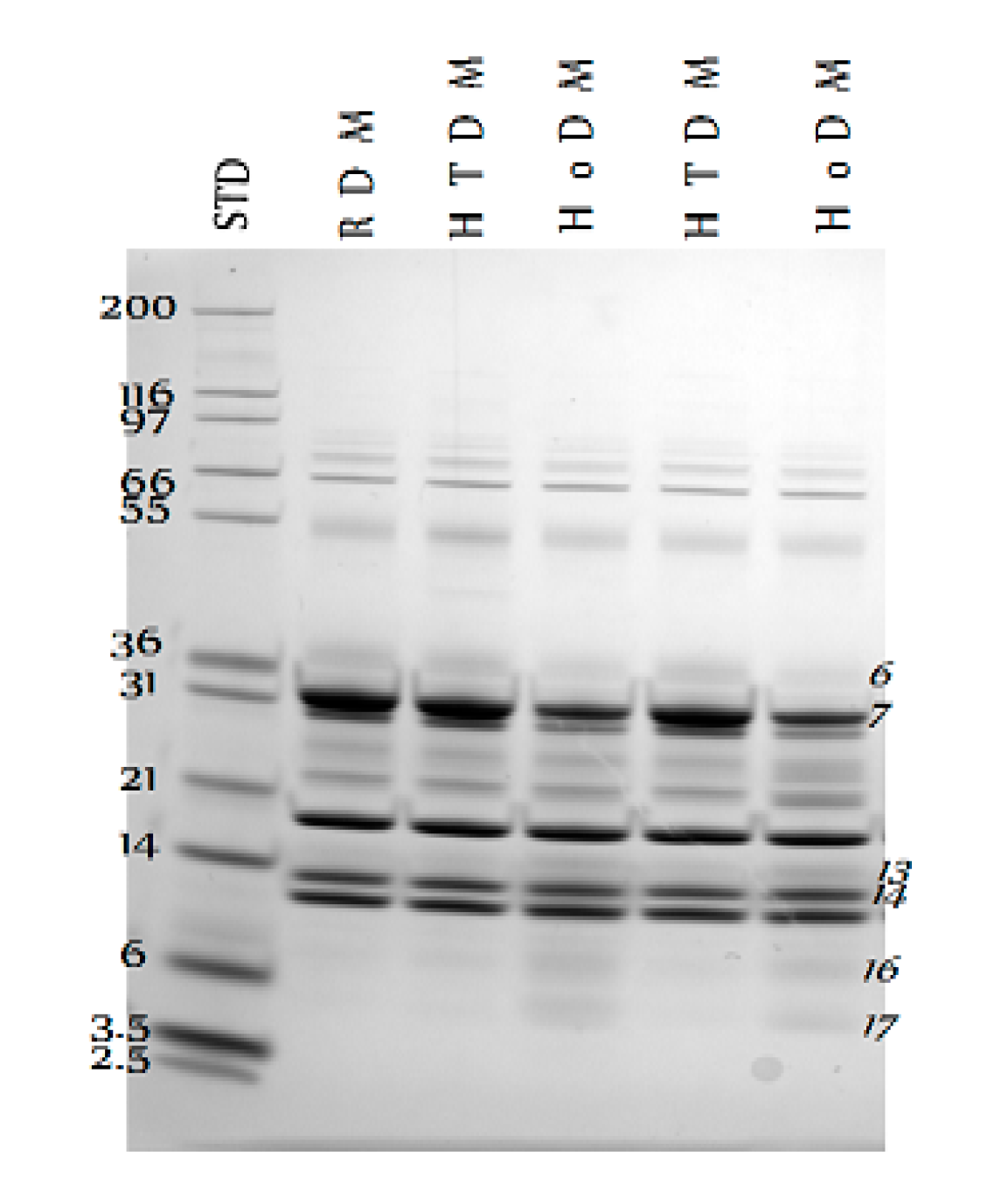
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, L.; Dong, M.-L.; Ren, F.-Z. The antimicrobial activity of donkey milk and its microflora changes during storage. Food Control 2008, 19, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, F.; Foti, M.; Malvisi, M.; Giacopello, C.; Piccinini, R. Valutazione dell’azione antibatterica del lisozima del latte d’asina. Considerazioni igienico—Sanitarie. Large Anim. Rev. 2012, 18, 13–16. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- El-Agamy, E.I. The challenge of cow milk protein allergy. Small Rumin. Res. 2007, 68, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, G.; Bertino, E.; Muratore Cristina, M.; Coscia, A.; Cresi, F.; Silvestro, L.; Fabris, C.; Fortunato, D.; Giuffrida Gabriella, M.; Conti, A. Efficacy of donkey’s milk in treating highly problematic cow’s milk allergic children: An in vivo and in vitro study. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2008, 19, 90–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesse, R.; Paglialunga, C.; Braccio, S.; Armenio, L. Adequacy and tolerance to ass’s milk in an Italian cohort of children with cow’s milk allergy. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2009, 35, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, G.; Viola, S.; Baro, C.; Cresi, F.; Tovo, P.A.; Moro, G.; Ferrero, M.P.; Conti, A.; Bertino, E. Tolerability of donkey’s milk in 92 highly-problematic cow’s milk allergic children. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2012, 26, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amati, L.; Marzulli, G.; Martulli, M.; Tafaro, A.; Jirillo, F.; Pugliese, V.; Martemucci, G.; D’Alessandro, A.G.; Jirillo, E. Donkey and goat milk intake and modulation of the human aged immune response. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simos, Y.; Metsios, A.; Verginadis, I.; D’Alessandro, A.G.; Loiudice, P.; Jirillo, E.; Charalampidis, P.; Kouimanis, V.; Boulaka, A.; Martemucci, G.; et al. Antioxidant and anti-platelet properties of milk from goat, donkey and cow: An in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo study. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetti, L.; Cavaliere, G.; Bergamo, P.; Trinchese, G.; De Filippo, C.; Gifuni, G.; Gaita, M.; Pignalosa, A.; Donizzetti, I.; Putti, R.; et al. Diet supplementation with donkey milk upregulates liver mitochondrial uncoupling, reduces energy efficiency and improves antioxidant and antiinflammatory defences in rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 1596–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirillo, F.; Magrone, T. Anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic properties of donkey’s and goat’s milk. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 14, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinchese, G.; Cavaliere, G.; Canani, R.B.; Matamoros, S.; Bergamo, P.; De Filippo, C.; Aceto, S.; Gaita, M.; Cerino, P.; Negri, R.; et al. Human, donkey and cow milk differently affects energy efficiency and inflammatory state by modulating mitochondrial function and gut microbiota. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aspri, M.; Economou, N.; Papademas, P. Donkey milk: An overview on functionality, technology, and future prospects. Food Rev. Int. 2017, 33, 316–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavari, C.; Coloretti, F.; Nanni, M.; Sorrentino, E.; Grazia, L. Use of donkey’s milk for a fermented beverage with lactobacilli. Lait 2005, 85, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzaro, F.; Fratianni, F.; Orlando, P.; Coppola, R. The use of probiotic strains in the production of a donkey milk-based functional beverage. Int. J. Probiotics Prebiotics 2010, 5, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Vincenzetti, S.; Savini, M.; Cecchini, C.; Micozzi, D.; Carpi, F.; Vita, A.; Polidori, P. Effects of lyophilization and use of probiotics on donkey's milk nutritional characteristics. Int. J. Food Eng. 2011, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidona, F.; Charfi, I.; Povolo, M.; Pelizzola, V.; Carminati, D.; Contarini, G.; Giraffa, G. Fermented beverage emulsion based on donkey milk with sunflower oil. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 2644–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchi, B.; Pedonese, F.; Torracca, B.; Fratini, F.; Mancini, S.; Galiero, A.; Montalbano, B.; Cerri, D.; Nuvoloni, R. Lactobacillus plantarum and Streptococcus thermophilus as starter cultures for a donkey milk fermented beverage. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 256, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polidori, P.; Vincenzetti, S. Differences of protein fractions among fresh, frozen and powdered donkey milk. Recent Pat. Food Nutr. Agric. 2010, 2, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polidori, P.; Vincenzetti, S. Effects of thermal treatments on donkey milk nutritional characteristics. Recent Pat. Food Nutr. Agric. 2013, 5, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturkoglu-Budak, S. Effect of different treatments on the stability of lysozyme, lactoferrin and β-lactoglobulin in donkey’s milk. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacometti, F.; Bardasi, L.; Merialdi, G.; Morbarigazzi, M.; Federici, S.; Piva, S.; Serraino, A. Shelf life of donkey milk subjected to different treatment and storage conditions. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4291–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino, C.; Labella, C.; Elshafie, H.S.; Camele, I.; Musto, M.; Paolino, R.; D’Adamo, C.; Freschi, P. Effects of different heat treatments on lysozyme quantity and antimicrobial activity of jenny milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 5173–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Renzo, G.C.; Altieri, G.; Genovese, F. Donkey milk powder production and properties compared to other milk powders. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2013, 93, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo, C.N.A.; Ferragut, V. Evaluating the Ultra-High Pressure Homogenization (UHPH) and Pasteurization effects on the quality and shelf life of donkey milk. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 4, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giribaldi, M.; Coscia, A.; Peila, C.; Antoniazzi, S.; Lamberti, C.; Ortoffi, M.; Moro, G.E.; Bertino, E.; Civera, T.; Cavallarin, L. Pasteurization of human milk by a benchtop High-Temperature Short-Time device. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 36, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallarin, L.; Giribaldi, M.; Soto-Del Rio, M.; Valle, E.; Barbarino, G.; Gennero, M.S.; Civera, T. A survey on the milk chemical and microbiological quality in dairy donkey farms located in northwestern Italy. Food Control 2015, 50, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, R.; Daprà, V.; Zecconi, A.; Piccinini, R. Hygienic and health characteristics of donkey milk during a follow-up study. J. Dairy Res. 2010, 77, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fratini, F.; Turchi, B.; Pedonese, F.; Pizzurro, F.; Ragaglini, P.; Torracca, B.; Tozzi, B.; Galiero, A.; Nuvoloni, R. Does the addition of donkey milk inhibit the replication of pathogen microorganisms in goat milk at refrigerated condition? Dairy Sci. Technol. 2016, 96, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragona, G.; Corrias, F.; Benedetti, M.; Paladini, M.; Salari, F.; Altomonte, l.; Martini, M. Amiata donkey milk chain: Animal health evaluation and milk quality. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2016, 5, 5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, R.; Salimei, E.; Sorrentino, E.; Nanni, M.; Ranieri, P.; Belli Blanes, R.; Grazia, L. Behaviour of Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains in ass’ milk. Ann. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Papademas, P.; Parmaxi, I.; Aspri, M. Probiotic, antimicrobial, antioxidant and sensory properties of fermented donkey milk with Lactobacillus fermentum ME-3 and Lactobacillus acidophilus (ATCC 4356). BAOJ Microbiol. 2015, 1, 004. [Google Scholar]
| PCA | VRBGA | PEMBA | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RDM | 99 ± 5 | 20 ± 6 | 7 ± 3 |
| HTDM | 8 ± 3 | - | 1 ± 1 |
| RDM | HoDM | HTDM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative Intensity | SD | Relative Intensity | SD | Relative Intensity | SD | Significance |
| 0.848 | 0.009 | 0.775 | 0.094 | 0.947 | 0.113 | NS |
| 0.788 | 0.100 | 0.969 | 0.169 | 0.851 | 0.054 | NS |
| 1.91 | 0.117 | 1.92 | 0.219 | 1.93 | 0.052 | NS |
| 1.92 | 0.016 | 1.84 | 0.044 | 1.86 | 0.134 | NS |
| 2.98 | 0.644 | 3.14 | 0.178 | 3.34 | 0.190 | NS |
| 3.66 A | 0.087 | 2.74 B | 0.555 | 3.08 AB | 0.483 | * |
| 5.01 B | 0.068 | 4.11 A | 0.263 | 5.46 C | 0.226 | *** |
| 2.33 | 0.056 | 2.20 | 0.113 | 2.53 | 0.112 | * |
| 2.60 | 0.097 | 2.42 | 0.347 | 2.26 | 0.210 | NS |
| 1.16 | 0.161 | 1.38 | 0.245 | 1.36 | 0.143 | NS |
| 3.37 | 0.036 | 3.39 | 0.66 | 2.88 | 0.122 | NS |
| 4.93 | 0.384 | 4.53 | 0.397 | 4.95 | 0.051 | NS |
| 1.91 A | 0.025 | 2.87 B | 0.164 | 2.12 A | 0.286 | * |
| 3.12 A | 0.291 | 3.95 B | 0.225 | 3.62 AB | 0.359 | * |
| 3.60 | 0.132 | 3.92 | 0.157 | 4.08 | 0.265 | * |
| 2.07 A | 0.681 | 3.40 B | 0.615 | 2.27 A | 0.337 | * |
| 2.49 AB | 0.631 | 3.48 B | 0.581 | 2.20 A | 0.528 | * |
| Sample | Enzyme Activity | SD |
|---|---|---|
| RDM | 86.7 | 6.9 |
| HoDM | 81.9 | 3.5 |
| HTDM | 81.0 | 0.7 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giribaldi, M.; Antoniazzi, S.; Gariglio, G.M.; Coscia, A.; Bertino, E.; Cavallarin, L. A Preliminary Assessment of HTST Processing on Donkey Milk. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci4040050
Giribaldi M, Antoniazzi S, Gariglio GM, Coscia A, Bertino E, Cavallarin L. A Preliminary Assessment of HTST Processing on Donkey Milk. Veterinary Sciences. 2017; 4(4):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci4040050
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiribaldi, Marzia, Sara Antoniazzi, Gian Marco Gariglio, Alessandra Coscia, Enrico Bertino, and Laura Cavallarin. 2017. "A Preliminary Assessment of HTST Processing on Donkey Milk" Veterinary Sciences 4, no. 4: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci4040050






