Inquiring into the Gaps of Campylobacter Surveillance Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Gaps in Campylobacter spp. Identification
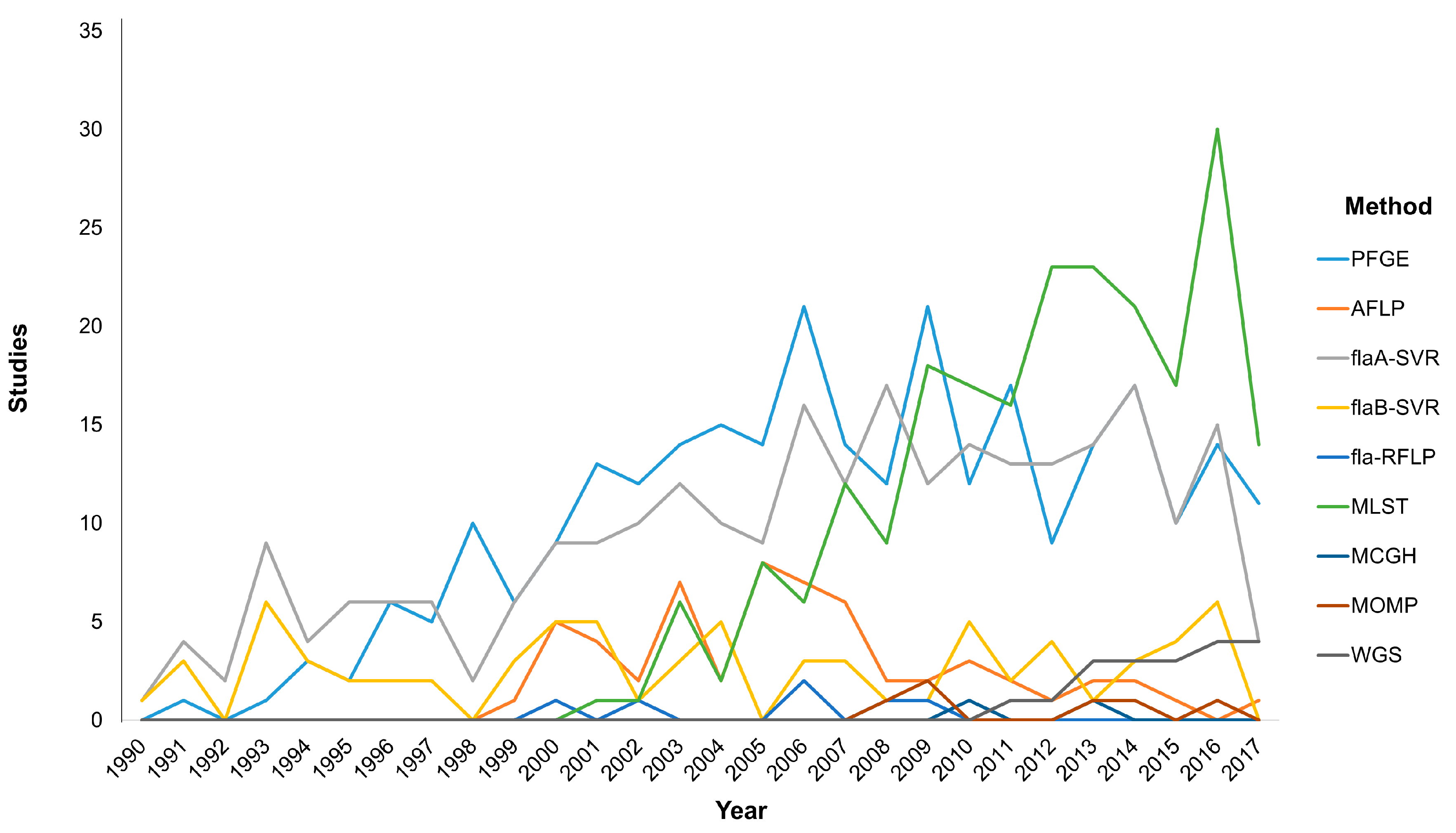
3. Molecular Typing Tools: Getting to Know Each Other
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolton, D.J. Campylobacter virulence and survival factors. Food Microbiol. 2015, 48, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaakoush, N.O.; Castano-Rodriguez, N.; Mitchell, H.M.; Man, S.M. Global epidemiology of Campylobacter infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 687–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allos, B.M. Campylobacter jejuni Infections: Update on emerging issues and trends. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luangtongkum, T.; Jeon, B.; Han, J.; Plummer, P.; Logue, C.M.; Zhang, Q. Antibiotic resistance in Campylobacter: Emergence, transmission and persistence. Future Microbiol. 2009, 4, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Campylobacter . Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/foodsafety/diseases/campylobacter/ (accessed on 4 May 2017).
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2015. EFSA J. 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Campylobacter . Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs255/en/ (accessed on 4 May 2017).
- Crim, S.M.; Griffin, P.M.; Tauxe, R.; Marder, E.P.; Gilliss, D.; Cronquist, A.B.; Cartter, M.; Tobin-D’Angelo, M.; Blythe, D.; Smith, K.; et al. Preliminary incidence and trends of infection with pathogens transmitted commonly through food—Foodborne diseases active surveillance network, 10 U.S. sites, 2006–2014. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2015, 64, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority. The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2013. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrackin, M.A.; Helke, K.L.; Galloway, A.M.; Poole, A.Z.; Salgado, C.D.; Marriott, B.P. Effect of antimicrobial use in agricultural animals on drug-resistant foodborne campylobacteriosis in humans: A systematic literature review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2115–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, S.M. The clinical importance of emerging Campylobacter species. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojanic, K.; Midwinter, A.C.; Marshall, J.C.; Rogers, L.E.; Biggs, P.J.; Acke, E. Variation in the limit-of-detection of the ProSpecT Campylobacter microplate enzyme immunoassay in stools spiked with emerging Campylobacter species. J. Microbiol. Methods 2016, 127, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasti, J.I.; Tareen, A.M.; Lugert, R.; Zautner, A.E.; Gross, U. Campylobacter jejuni: A brief overview on pathogenicity-associated factors and disease-mediating mechanisms. Int. J. Med. Microbiol.: IJMM 2010, 300, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.; Leite, D.; Fernandes, M.; Mena, C.; Gibbs, P.A.; Teixeira, P. Campylobacter spp. as a foodborne pathogen: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van, T.T.; Elshagmani, E.; Gor, M.C.; Scott, P.C.; Moore, R.J. Campylobacter hepaticus sp. nov., isolated from chickens with spotty liver disease. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 4518–4524. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vandamme, P.; Falsen, E.; Rossau, R.; Hoste, B.; Segers, P.; Tytgat, R.; De Ley, J. Revision of Campylobacter, Helicobacter, and Wolinella taxonomy: Emendation of generic descriptions and proposal of Arcobacter gen. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1991, 41, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, K.F.; Kiehlbauch, J.A.; Anderson, D.C.; McClure, H.M.; Wachsmuth, I.K. Arcobacter (Campylobacter) butzleri-associated diarrheal illness in a nonhuman primate population. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 2220–2223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Romaniuk, P.J.; Zoltowska, B.; Trust, T.J.; Lane, D.J.; Olsen, G.J.; Pace, N.R.; Stahl, D.A. Campylobacter pylori, the spiral bacterium associated with human gastritis, is not a true Campylobacter sp. J. Bacteriol. 1987, 169, 2137–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandamme, P.; Harrington, C.S.; Jalava, K.; On, S.L. Misidentifying helicobacters: The Helicobacter cinaedi example. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 2261–2266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Achtman, M.; Wagner, M. Microbial diversity and the genetic nature of microbial species. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patton, C.M.; Shaffer, N.; Edmonds, P.; Barrett, T.J.; Lambert, M.A.; Baker, C.; Perlman, D.M.; Brenner, D.J. Human disease associated with “Campylobacter upsaliensis” (catalase-negative or weakly positive Campylobacter species) in the United States. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salama, S.M.; Tabor, H.; Richter, M.; Taylor, D.E. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for epidemiologic studies of Campylobacter hyointestinalis isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 1982–1984. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lindblom, G.B.; Sjogren, E.; Hansson-Westerberg, J.; Kaijser, B. Campylobacter upsaliensis, C. sputorum sputorum and C. concisus as common causes of diarrhoea in Swedish children. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 27, 187–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichiyama, S.; Hirai, S.; Minami, T.; Nishiyama, Y.; Shimizu, S.; Shimokata, K.; Ohta, M. Campylobacter fetus subspecies fetus cellulitis associated with bacteremia in debilitated hosts. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 27, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- On, S.L.; Atabay, H.I.; Corry, J.E.; Harrington, C.S.; Vandamme, P. Emended description of Campylobacter sputorum and revision of its infrasubspecific (biovar) divisions, including C. sputorum biovar paraureolyticus, a urease-producing variant from cattle and humans. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, J.M.; Burnens, A.; Linton, D.; Lawson, A.J.; Stanley, J. Campylobacter lanienae sp. nov., a new species isolated from workers in an abattoir. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorkiewicz, G.; Feierl, G.; Zechner, R.; Zechner, E.L. Transmission of Campylobacter hyointestinalis from a pig to a human. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 2601–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, R.F.; Harrington, C.S.; Kortegaard, H.E.; On, S.L. A PCR-DGGE method for detection and identification of Campylobacter, Helicobacter, Arcobacter and related Epsilobacteria and its application to saliva samples from humans and domestic pets. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 2601–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debruyne, L.; On, S.L.; De Brandt, E.; Vandamme, P. Novel Campylobacter lari-like bacteria from humans and molluscs: Description of Campylobacter peloridis sp. nov., Campylobacter lari subsp. concheus subsp. nov. and Campylobacter lari subsp. lari subsp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Man, S.M.; Day, A.S.; Leach, S.T.; Lemberg, D.A.; Dutt, S.; Stormon, M.; Otley, A.; O’Loughlin, E.V.; Magoffin, A.; et al. Detection and isolation of Campylobacter species other than C. jejuni from children with Crohn’s disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, S.M.; Kaakoush, N.O.; Octavia, S.; Mitchell, H. The internal transcribed spacer region, a new tool for use in species differentiation and delineation of systematic relationships within the Campylobacter genus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3071–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, S.M.; Zhang, L.; Day, A.S.; Leach, S.T.; Lemberg, D.A.; Mitchell, H. Campylobacter concisus and other Campylobacter species in children with newly diagnosed Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglis, G.D.; Boras, V.F.; Houde, A. Enteric campylobacteria and RNA viruses associated with healthy and diarrheic humans in the Chinook health region of southwestern Alberta, Canada. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, C.N.; Scully, B.; Garvey, G.J. Campylobacter lari associated with permanent pacemaker infection and bacteremia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 27, 220–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tee, W.; Luppino, M.; Rambaldo, S. Bacteremia due to Campylobacter sputorum biovar sputorum. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1998, 27, 1544–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linscott, A.J.; Flamholtz, R.B.; Shukla, D.; Song, Y.; Liu, C.; Finegold, S.M. Fatal septicemia due to Clostridium hathewayi and Campylobacter hominis. Anaerobe 2005, 11, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louwen, R.; van Baarlen, P.; van Vliet, A.H.; van Belkum, A.; Hays, J.P.; Endtz, H.P. Campylobacter bacteremia: A rare and under-reported event? Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2012, 2, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- On, S.L.; Ridgwell, F.; Cryan, B.; Azadian, B.S. Isolation of Campylobacter sputorum biovar sputorum from an axillary abscess. J. Infect. 1992, 24, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herve, J.; Aissa, N.; Legrand, P.; Sorkine, M.; Calmette, M.J.; Santin, A.; Roupie, E.; Renaud, B. Campylobacter fetus meningitis in a diabetic adult cured by imipenem. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2004, 23, 722–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetsch, N.M.; Somani, K.; Tyrrell, G.J.; Gebhart, C.; Bailey, R.J.; Taylor, D.E. Campylobacter curvus-associated hepatic abscesses: A case report. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1909–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanayama, S.; Ohnishi, K.; Yamaura, T.; Katayama, M.; Makino, J.; Takemura, N.; Hamabe, Y. Case of bilateral subdural empyema complicating Campylobacter fetus subspecies fetus meningitis. Brain Nerve 2008, 60, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shimakha Ia, A.; Pozdeev, O.K.; Ibragimova, A.A.; Minullina, N.K.; Fedorova Zh, P.; Khasanov, A.A.; Il’inskaia, O.N. Isolation of Campylobacter fetus from persons with obstetric-gynecological infections. Zh. Mikrobiol. Epidemiol. Immunobiol. 2009, 80–83. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, J.Y.; Wu, A.K.; Ngai, D.C.; Teng, J.L.; Wong, E.S.; Lau, S.K.; Lee, R.A.; Woo, P.C. Three cases of severe invasive infections caused by Campylobacter rectus and first report of fatal C. rectus infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 1687–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajene, A.N.; Fischer Walker, C.L.; Black, R.E. Enteric pathogens and reactive arthritis: A systematic review of Campylobacter, Salmonella and Shigella-associated reactive arthritis. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2013, 31, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, J.J.; Arents, N.L.; Manson, W.L. Campylobacter species isolated from extra-oro-intestinal abscesses: A report of four cases and literature review. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 27, 1119–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uotila, T.; Korpela, M.; Vuento, R.; Laine, J.; Lumio, J.; Kuusi, M.; Virtanen, M.J.; Mustonen, J.; Antonen, J.; Pirkanmaa Waterborne Outbreak Study Group. Joint symptoms after a faecal culture positive Campylobacter infection associated with a waterborne gastroenteritis outbreak: A questionnaire study. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 43, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiguchi, S.; Sekine, I.; Kuroda, S.; Sato, M.; Kitagawa, I. Myositis Ossificans of the Hip Due to Pyogenic Arthritis Caused by Campylobacter fetus Subspecies fetus. Intern. Med. 2017, 56, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglis, G.D.; Hoar, B.M.; Whiteside, D.P.; Morck, D.W. Campylobacter canadensis sp. nov., from captive whooping cranes in Canada. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, M.; Debruyne, L.; Zanoni, R.G.; Manfreda, G.; Revez, J.; Vandamme, P. Campylobacter avium sp. nov., a hippurate-positive species isolated from poultry. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2364–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoni, R.G.; Debruyne, L.; Rossi, M.; Revez, J.; Vandamme, P. Campylobacter cuniculorum sp. nov., from rabbits. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 1666–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debruyne, L.; Broman, T.; Bergstrom, S.; Olsen, B.; On, S.L.; Vandamme, P. Campylobacter volucris sp. nov., isolated from black-headed gulls (Larus ridibundus). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 1870–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debruyne, L.; Broman, T.; Bergstrom, S.; Olsen, B.; On, S.L.; Vandamme, P. Campylobacter subantarcticus sp. nov., isolated from birds in the sub-Antarctic region. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, T.; Singh, J.; Huffman, M.A.; Petrzelkova, K.J.; Taylor, N.S.; Xu, S.; Dewhirst, F.E.; Paster, B.J.; Debruyne, L.; Vandamme, P.; et al. Campylobacter troglodytis sp. nov., isolated from feces of human-habituated wild chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii) in Tanzania. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2366–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platts-Mills, J.A.; Liu, J.; Gratz, J.; Mduma, E.; Amour, C.; Swai, N.; Taniuchi, M.; Begum, S.; Penataro Yori, P.; Tilley, D.H.; et al. Detection of Campylobacter in stool and determination of significance by culture, enzyme immunoassay, and PCR in developing countries. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweon, O.J.; Lim, Y.K.; Yoo, B.; Kim, H.R.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, M.K. First Case Report of Campylobacter volucris Bacteremia in an Immunocompromised Patient. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1976–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llarena, A.K.; Taboada, E.; Rossi, M. Whole-Genome Sequencing in Epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni Infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Belkum, A.; Tassios, P.T.; Dijkshoorn, L.; Haeggman, S.; Cookson, B.; Fry, N.K.; Fussing, V.; Green, J.; Feil, E.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; et al. Guidelines for the validation and application of typing methods for use in bacterial epidemiology. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13 Suppl. 3, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maziero, M.T.; de Oliveira, T.C. Effect of refrigeration and frozen storage on the Campylobacter jejuni recovery from naturally contaminated broiler carcasses. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2010, 41, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, T.K.; Knabel, S.J.; Kwan, B.W. Bacterial persister cell formation and dormancy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7116–7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Mendis, N.; Trigui, H.; Oliver, J.D.; Faucher, S.P. The importance of the viable but non-culturable state in human bacterial pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayrapetyan, M.; Oliver, J.D. The viable but non-culturable state and its relevance in food safety. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 8, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakruddin, M.; Mannan, K.S.; Andrews, S. Viable but nonculturable bacteria: Food safety and public health perspective. ISRN Microbiol. 2013, 2013, 703813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO. Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuff—Horizontal Method for Detection and Enumeration of Campylobacter spp. Part 1: Detection Method; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuff—Horizontal Method for Detection and Enumeration of Campylobacter spp. Part 2: Colony Count Technique; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Linton, D.; Lawson, A.J.; Owen, R.J.; Stanley, J. PCR detection, identification to species level, and fingerprinting of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli direct from diarrheic samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 2568–2572. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, M.; Huang, J.Y.; Cronquist, A.B.; Medus, C.; Hurd, S.; Zansky, S.; Dunn, J.; Woron, A.M.; Oosmanally, N.; Griffin, P.M.; et al. Bacterial enteric infections detected by culture-independent diagnostic tests—FoodNet, United States, 2012–2014. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2015, 64, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maher, M.; Finnegan, C.; Collins, E.; Ward, B.; Carroll, C.; Cormican, M. Evaluation of culture methods and a DNA probe-based PCR assay for detection of Campylobacter species in clinical specimens of feces. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 2980–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, S.P.; Lever, S.; Logan, J.M.; Lawson, A.J.; Stanley, J.; Shafi, M.S. Detection of Campylobacter species: A comparison of culture and polymerase chain reaction based methods. J. Clin. Pathol. 2002, 55, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Belkum, A.; Chatellier, S.; Girard, V.; Pincus, D.; Deol, P.; Dunne, W.M., Jr. Progress in proteomics for clinical microbiology: MALDI-TOF MS for microbial species identification and more. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2015, 12, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandrell, R.E.; Harden, L.A.; Bates, A.; Miller, W.G.; Haddon, W.F.; Fagerquist, C.K. Speciation of Campylobacter coli, C. jejuni, C. helveticus, C. lari, C. sputorum, and C. upsaliensis by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 6292–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.E.; Kaleta, E.J.; Arora, A.; Wolk, D.M. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry: Afundamental shift in the routine practice of clinical microbiology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 547–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, C.; Tu, Z.C.; Patrick, M.; Stiles, T.; Lawson, A.J.; Santovenia, M.; Gilbert, M.J.; van Bergen, M.; Joyce, K.; Pruckler, J.; et al. Campylobacter fetus subsp. testudinum subsp. nov., isolated from humans and reptiles. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 2944–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccia, S.; Pasquarella, C.; Colotto, M.; Barchitta, M.; Quattrocchi, A.; Agodi, A.; the Public Health Genomics and GISIO Working Groups of the Italian Society of Hygiene, Preventive Medicine and Public Health (SItI). Molecular epidemiology tools in the management of healthcare-associated infections: Towards the definition of recommendations. Epidemiol. Prev. 2015, 39, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mossong, J.; Mughini-Gras, L.; Penny, C.; Devaux, A.; Olinger, C.; Losch, S.; Cauchie, H.M.; van Pelt, W.; Ragimbeau, C. Human campylobacteriosis in Luxembourg, 2010–2013: A case-control study combined with multilocus sequence typing for source attribution and risk factor analysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabat, A.J.; Budimir, A.; Nashev, D.; Sa-Leao, R.; van Dijl, J.; Laurent, F.; Grundmann, H.; Friedrich, A.W.; Markers, E.S.G.o.E. Overview of molecular typing methods for outbreak detection and epidemiological surveillance. Euro Surveill. 2013, 18, 20380. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taboada, E.N.; Clark, C.G.; Sproston, E.L.; Carrillo, C.D. Current methods for molecular typing of Campylobacter species. J. Microbiol. Methods. 2013, 95, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newell, D.G.; Fearnley, C. Sources of Campylobacter colonization in broiler chickens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4343–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colles, F.M.; Maiden, M.C. Campylobacter sequence typing databases: Applications and future prospects. Microbiology 2012, 158, 2695–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struelens, M.J. Consensus guidelines for appropriate use and evaluation of microbial epidemiologic typing systems. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 1996, 2, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenover, F.C.; Arbeit, R.D.; Goering, R.V.; Mickelsen, P.A.; Murray, B.E.; Persing, D.H.; Swaminathan, B. Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: Criteria for bacterial strain typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, B.; Barrett, T.J.; Hunter, S.B.; Tauxe, R.V.; CDC PulseNet Task Force. PulseNet: The molecular subtyping network for foodborne bacterial disease surveillance, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lajhar, S.A.; Jennison, A.V.; Patel, B.; Duffy, L.L. Comparison of epidemiologically linked Campylobacter jejuni isolated from human and poultry sources. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 3498–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, E.M.; Engberg, J.; Fussing, V.; Petersen, L.; Brogren, C.H.; On, S.L. Evaluation of phenotypic and genotypic methods for subtyping Campylobacter jejuni isolates from humans, poultry, and cattle. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 3800–3810. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nachamkin, I.; Bohachick, K.; Patton, C.M. Flagellin gene typing of Campylobacter jejuni by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meinersmann, R.J.; Helsel, L.O.; Fields, P.I.; Hiett, K.L. Discrimination of Campylobacter jejuni isolates by fla gene sequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 2810–2814. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Taylor, D.E. Natural transformation in Campylobacter species. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingle, K.E.; Colles, F.M.; Falush, D.; Maiden, M.C. Sequence typing and comparison of population biology of Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingle, K.E.; Colles, F.M.; Wareing, D.R.; Ure, R.; Fox, A.J.; Bolton, F.E.; Bootsma, H.J.; Willems, R.J.; Urwin, R.; Maiden, M.C. Multilocus sequence typing system for Campylobacter jejuni. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingle, K.E.; Colles, F.M.; Ure, R.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Duim, B.; Bolton, F.J.; Fox, A.J.; Wareing, D.R.; Maiden, M.C. Molecular characterization of Campylobacter jejuni clones: A basis for epidemiologic investigation. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.G.; On, S.L.; Wang, G.; Fontanoz, S.; Lastovica, A.J.; Mandrell, R.E. Extended multilocus sequence typing system for Campylobacter coli, C. lari, C. upsaliensis, and C. helveticus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 2315–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bliss, C.M.; Bennett, J.S.; Bratcher, H.B.; Brehony, C.; Colles, F.M.; Wimalarathna, H.; Harrison, O.B.; Sheppard, S.K.; Cody, A.J.; et al. Ribosomal multilocus sequence typing: Universal characterization of bacteria from domain to strain. Microbiology 2012, 158, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feil, E.J.; Li, B.C.; Aanensen, D.M.; Hanage, W.P.; Spratt, B.G. eBURST: Inferring patterns of evolutionary descent among clusters of related bacterial genotypes from multilocus sequence typing data. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 1518–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, A.P.; Bugalho, M.; Ramirez, M.; Carrico, J.A. Global optimal eBURST analysis of multilocus typing data using a graphic matroid approach. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cody, A.J.; Colles, F.M.; Sheppard, S.K.; Maiden, M.C. Where does Campylobacter come from? A molecular odyssey. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 659, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Adawy, H.; Hotzel, H.; Tomaso, H.; Neubauer, H.; Taboada, E.N.; Ehricht, R.; Hafez, H.M. Detection of genetic diversity in Campylobacter jejuni isolated from a commercial turkey flock using flaA typing, MLST analysis and microarray assay. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e51582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidou, V.; Ioannidis, A.; Magiorkinis, E.; Bagos, P.; Nicolaou, C.; Legakis, N.; Chatzipanagiotou, S. Multilocus sequence typing (and phylogenetic analysis) of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli strains isolated from clinical cases in Greece. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escher, R.; Brunner, C.; von Steiger, N.; Brodard, I.; Droz, S.; Abril, C.; Kuhnert, P. Clinical and epidemiological analysis of Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus infections in humans and comparative genetic analysis with strains isolated from cattle. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cody, A.J.; Maiden, M.J.; Dingle, K.E. Genetic diversity and stability of the porA allele as a genetic marker in human Campylobacter infection. Microbiology 2009, 155, 4145–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jay-Russell, M.T.; Mandrell, R.E.; Yuan, J.; Bates, A.; Manalac, R.; Mohle-Boetani, J.; Kimura, A.; Lidgard, J.; Miller, W.G. Using major outer membrane protein typing as an epidemiological tool to investigate outbreaks caused by milk-borne Campylobacter jejuni isolates in California. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Luangtongkum, T.; Morishita, T.Y.; Zhang, Q. Molecular typing of Campylobacter strains using the cmp gene encoding the major outer membrane protein. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2005, 2, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleihauf, E.; Mutschall, S.; Billard, B.; Taboada, E.N.; Haldane, D. Comparative genomic fingerprinting of Campylobacter: Application in routine public health surveillance and epidemiological investigations. Epidemiol. Infect. 2017, 145, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, C.G.; Taboada, E.; Grant, C.C.; Blakeston, C.; Pollari, F.; Marshall, B.; Rahn, K.; Mackinnon, J.; Daignault, D.; Pillai, D.; et al. Comparison of molecular typing methods useful for detecting clusters of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli isolates through routine surveillance. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiden, M.C.; Jansen van Rensburg, M.J.; Bray, J.E.; Earle, S.G.; Ford, S.A.; Jolley, K.A.; McCarthy, N.D. MLST revisited: The gene-by-gene approach to bacterial genomics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carleton, H.A.; Gerner-Smidt, P. Whole-genome sequencing is taking over foodborne disease surveillance. Microbe 2016, 11, 311–317. [Google Scholar]
- Koser, C.U.; Ellington, M.J.; Cartwright, E.J.; Gillespie, S.H.; Brown, N.M.; Farrington, M.; Holden, M.T.; Dougan, G.; Bentley, S.D.; Parkhill, J.; et al. Routine use of microbial whole genome sequencing in diagnostic and public health microbiology. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Sanchez, S.; Hanning, I.; Pendleton, S.; D’Souza, D. Next-generation sequencing: The future of molecular genetics in poultry production and food safety. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, K.T.; Clark, T.A.; Muppirala, U.K.; Severin, A.J.; Plummer, P.J. Methods for genome-wide methylome profiling of Campylobacter jejuni. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1512, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Loughlin, J.L.; Eucker, T.P.; Chavez, J.D.; Samuelson, D.R.; Neal-McKinney, J.; Gourley, C.R.; Bruce, J.E.; Konkel, M.E. Analysis of the Campylobacter jejuni genome by SMRT DNA sequencing identifies restriction-modification motifs. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.G.; DiRita, V.J. Generation and screening of an insertion sequencing-compatible mutant library of Campylobacter jejuni. Methods Mol. Med. 2017, 1512, 257–272. [Google Scholar]
- Didelot, X.; Maiden, M.C. Impact of recombination on bacterial evolution. Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schouls, L.M.; Reulen, S.; Duim, B.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Willems, R.J.; Dingle, K.E.; Colles, F.M.; Van Embden, J.D. Comparative genotyping of Campylobacter jejuni by amplified fragment length polymorphism, multilocus sequence typing, and short repeat sequencing: Strain diversity, host range, and recombination. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suerbaum, S.; Lohrengel, M.; Sonnevend, A.; Ruberg, F.; Kist, M. Allelic diversity and recombination in Campylobacter jejuni. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 2553–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelius, A.J.; Vandenberg, O.; Robson, B.; Gilpin, B.J.; Brandt, S.M.; Scholes, P.; Martiny, D.; Carter, P.E.; van Vught, P.; Schouten, J.; et al. Same-day subtyping of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli isolates by use of multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification-binary typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 3345–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taboada, E.N.; Mackinnon, J.M.; Luebbert, C.C.; Gannon, V.P.; Nash, J.H.; Rahn, K. Comparative genomic assessment of Multi-Locus Sequence Typing: Rapid accumulation of genomic heterogeneity among clonal isolates of Campylobacter jejuni. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Magana, M.; Chatzipanagiotou, S.; Burriel, A.R.; Ioannidis, A. Inquiring into the Gaps of Campylobacter Surveillance Methods. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci4030036
Magana M, Chatzipanagiotou S, Burriel AR, Ioannidis A. Inquiring into the Gaps of Campylobacter Surveillance Methods. Veterinary Sciences. 2017; 4(3):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci4030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleMagana, Maria, Stylianos Chatzipanagiotou, Angeliki R. Burriel, and Anastasios Ioannidis. 2017. "Inquiring into the Gaps of Campylobacter Surveillance Methods" Veterinary Sciences 4, no. 3: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci4030036
APA StyleMagana, M., Chatzipanagiotou, S., Burriel, A. R., & Ioannidis, A. (2017). Inquiring into the Gaps of Campylobacter Surveillance Methods. Veterinary Sciences, 4(3), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci4030036




