A Review of the Sentinel Role of Erinaceus europaeus in Zoonotic Diseases Across Urban and Rural Environments: A One Health Perspective
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Erinaceus europaeus: Ecology, Behavior and Habitat
1.2. Zoonotic Threats
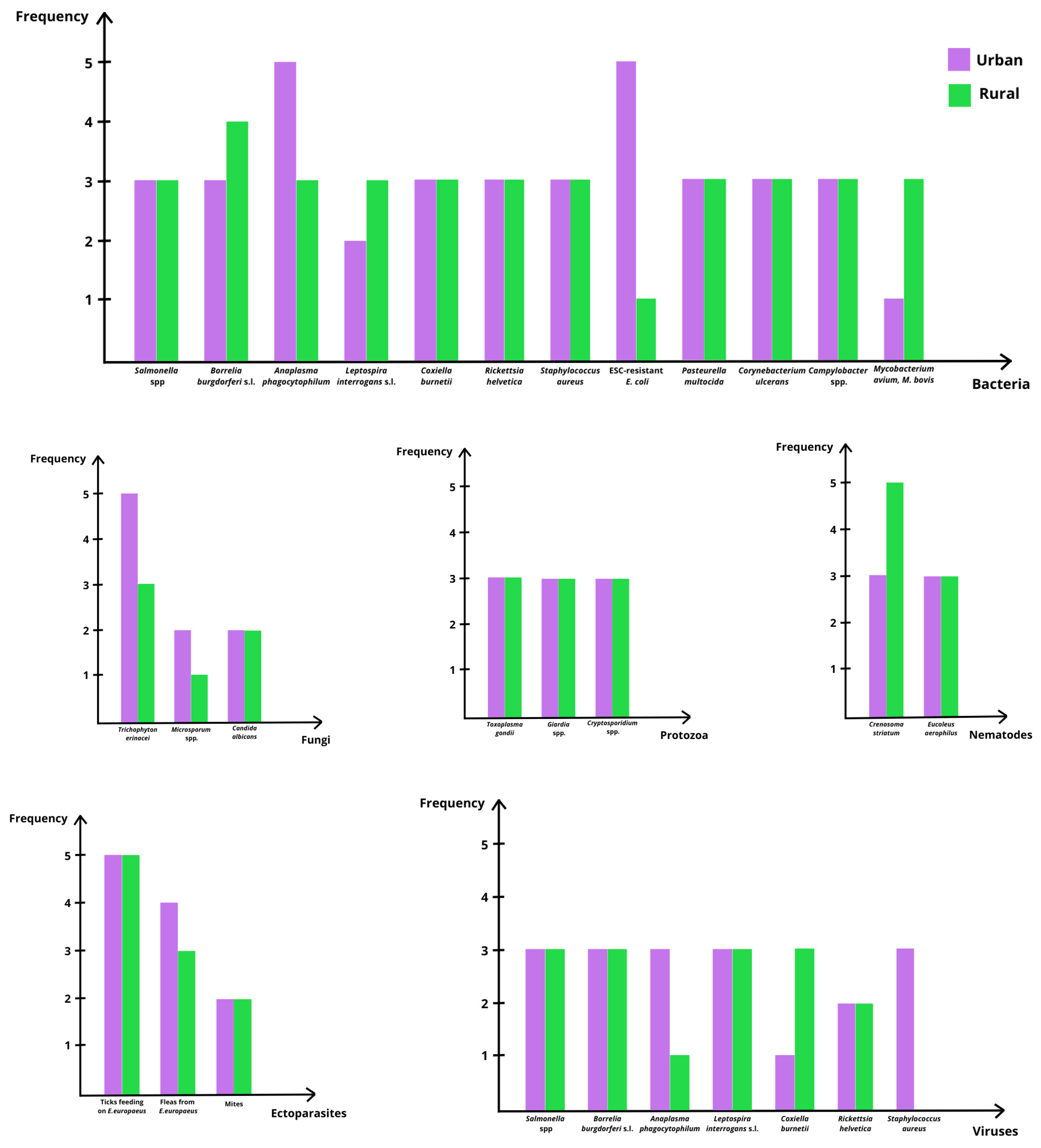
| Group | Agent Detected in E. europaeus | Urban | Rural | Transmission Route | Zoonotic Relevance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | Salmonella spp. (S. Enteritidis, S. Typhimurium) | Yes | Yes (low frequency) | Fecal–oral; environmental | High | [10,28,35,36] |
| Borrelia burgdorferi s.l. | Yes | Yes (frequent) | Tick bites | Moderate to high | [27,30,31] | |
| Anaplasma phagocytophilum | Yes (common) | Yes | Tick bites | Moderate to high | [30,32] | |
| Leptospira interrogans s.l. | Occasional | Present | Urine; environment | Moderate | [27] | |
| Coxiella burnetii | Yes | Yes | Aerosols, environmental | Moderate | [27,28,37] | |
| Rickettsia helvetica | Yes | Yes | Tick bites | Moderate | [27] | |
| Staphylococcus aureus [including MRSA) | Yes | Yes | Contact | Moderate to high | [27,28,37] | |
| ESC-resistant Escherichia coli | Common | Not reported | Fecal contamination | High (AMR) | [30,38] | |
| Pasteurella multocida | Yes | Yes | Bites, scratches | Moderate | [10] | |
| Corynebacterium ulcerans | Yes | Yes | Contact | Moderate | [10] | |
| Campylobacter spp. | Yes | Yes | Fecal–oral | Moderate | [10] | |
| Mycobacterium avium, M. bovis | Rare | Present | Aerosols; contact | Moderate | [10] | |
| Fungi | Trichophyton erinacei | Common | Present | Direct contact | High | [40,41,42,43,44] |
| Microsporum spp. | Occasional | Rare | Direct contact | Low to moderate | [42] | |
| Candida albicans | Occasional | Occasional | Opportunistic | Low | [42] | |
| Protozoa | Toxoplasma gondii | Yes | Yes (often higher) | Ingestion of oocysts | Moderate | [27] |
| Giardia spp. | Yes (including human-hedgehog case) | Yes | Fecal–oral | Moderate | [27] | |
| Cryptosporidium spp. | Yes | Yes | Fecal–oral | Moderate | [26] | |
| Nematodes | Crenosoma striatum | Yes | Very common | Snails and slugs (intermediate hosts) | Low (not zoonotic) | [2,21,29] |
| Eucoleus aerophilus | Yes | Yes | Ingestion of eggs | Moderate (rare in humans) | [27] | |
| Ectoparasites | Ticks (Ixodidae) feeding on E. europaeus | Common | Common | Tick bites | High (vector role) | [26,27,33] |
| Fleas from E. europaeus | Frequent | Present | Contact | Low | [27] | |
| Mites | Occasional | Occasional | Contact | Low | [27] | |
| Viruses | Erinaceus coronavirus (EriCoV) | Yes | Yes | Unknown | Unknown (emerging) | [25,27,30] |
| Belerina-related paramyxoviruses | Yes | Yes | Unknown | Unknown | [25,39] | |
| Tahyna virus | Yes | Rare | Mosquito bites | Moderate | [37] | |
| Tick-borne encephalitis virus | Yes | Yes | Tick bites | Moderate | [27] | |
| Rabies virus | Rare | Present | Bites | High (rare in hedgehogs) | [27,37] | |
| Herpesviruses | Occasional | Occasional | Contact | Low | [37] | |
| SFTSV antibodies detected in E. europaeus | Yes | — | Unknown | Unknown | [27] |
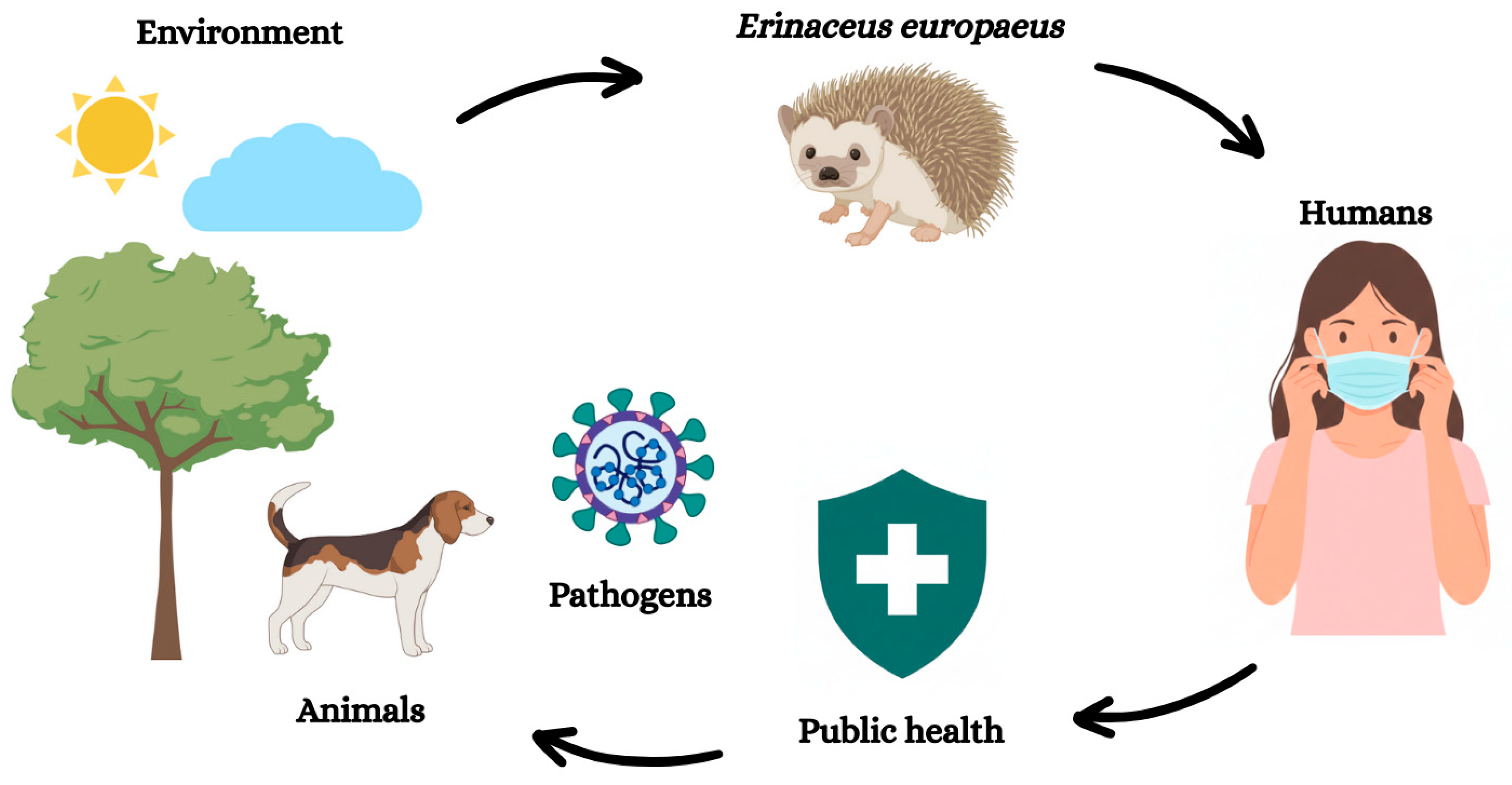
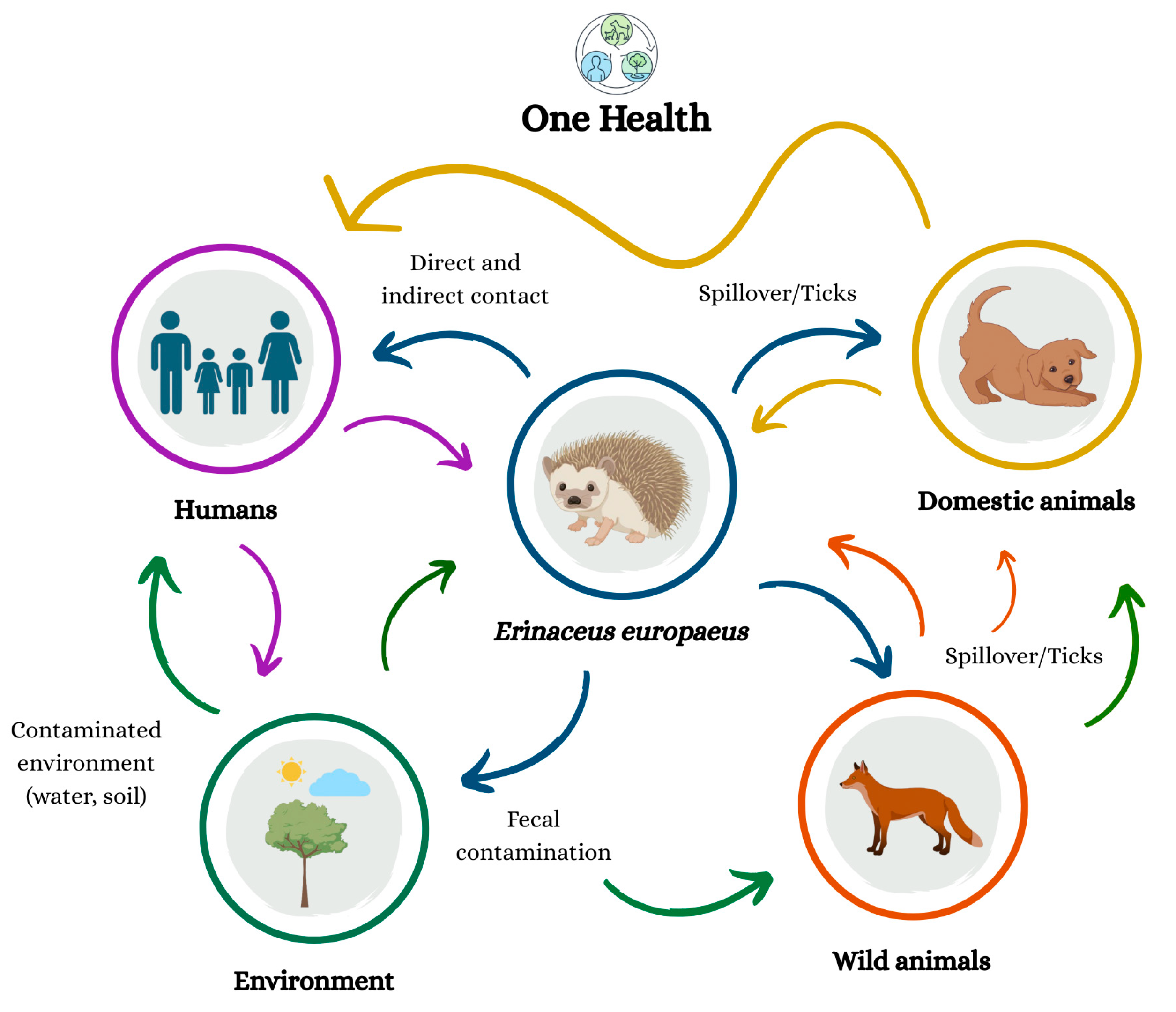
2. One Health Context: Western-European Hedgehogs as Sentinels of Zoonotic Diseases
3. Integrated Synthesis and One Health Implications
4. Knowledge Gaps and Future Research
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morris, P. Hedgehogs (The British Natural History Collection), 3rd ed.; Whittet Books Ltd.: Essex, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pfäffle, M. Influence of Parasites on Fitness Parameters of the European Hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus). Ph.D. Thesis, Karlsruhe Institute for Technology, Karlsruhe, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Seddon, J.M.; Santucci, F.; Reeve, N.J.; Hewitt, G.M. DNA footprints of European hedgehogs, Erinaceus europaeus and E. concolor: Pleistocene refugia, postglacial expansion and colonization routes. Mol. Ecol. 2001, 10, 2187–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.J. Husbandry and Nutrition of Hedgehogs. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 1999, 2, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, M.; Guerri, C.R.; Ruiz-Lopera, S. Mecanismo de Defensa del Erizo Europeo (Erinaceus europaeus). Rev. Complut. Cienc. Vet. 2007, 1, 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Bexton, S. Hedgehogs. In BSAVA Manual of Wildlife Casualties, 2nd ed.; Mullineaux, E., Keeble, E., Eds.; British Small Veterinary Association: Gloucestershire, UK, 2016; pp. 117–136. [Google Scholar]
- Marco-Tresserras, J.; López-Iborra, G.M. Nesting Ecology of European Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in Urban Areas in Southeast Spain: Nest Habitat Use and Characteristics. Animals 2023, 13, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paupério, J.; Vale-Gonçalves, H.M.; Cabral, J.A.; Mira, A.; Bencatel, J. Insetívoros. In Atlas de Mamíferos de Portugal; Bencatel, J., Álvares, F., Moura, A.E., Barbosa, A.M., Eds.; Universidade de Évora: Évora, Portugal, 2017; pp. 42–43. [Google Scholar]
- Hubert, P.; Julliard, R.; Biagianti, S.; Poulle, M.L. Ecological factors driving the higher hedgehog (Erinaceus europeaus) density in an urban area compared to the adjacent rural area. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2011, 103, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautio, A.; Isomursu, M.; Valtonen, A.; Hirvelä-Koski, V.; Kunnasranta, M. Mortality, diseases and diet of European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in an urban environment in Finland. Mammal Res. 2016, 61, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.P.; Davison, J.; Trewby, I.D.; Wilson, G.J.; Delahay, R.J.; Doncaster, C.P. Abundance of hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in relation to the density and distribution of badgers (Meles meles). J. Zool. 2006, 269, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullineaux, E. Veterinary treatment and rehabilitation of indigenous wildlife. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2014, 55, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temple, H.J.; Cuttelod, A. The Status and Distribution of Mediterranean Mammals; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland; Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zacharopoulou, M.; Guillaume, E.; Coupez, G.; Bleuart, C.; Le Loc’h, G.; Gaide, N. Causes of Mortality and Pathological Findings in European Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) Admitted to a Wildlife Care Centre in Southwestern France from 2019 to 2020. J. Comp. Pathol. 2022, 190, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcês, A.; Soeiro, V.; Lóio, S.; Sargo, R.; Sousa, L.; Silva, F.; Pires, I. Outcomes, Mortality Causes, and Pathological Findings in European Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus, Linnaeus 1758): A Seventeen Year Retrospective Analysis in the North of Portugal. Animals 2020, 10, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hérnandez, M.C. Erizo común—Erinaceus europaeus Linnaeus, 1758. In Enciclopedia Virtual de los Vertebrados Españoles; López, P., Martin, J., Barja, I., Eds.; Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales: Madrid, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Taucher, A.; Gloor, S.; Dietrich, A.; Geiger, M.; Hegglin, D.; Bontadina, F. Decline in Distribution and Abundance: Urban Hedgehogs under Pressure. Animals 2020, 10, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijser, M.P.; Bergers, P.J.M. The effect of roads and traffic on hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) populations. Biol. Conserv. 2000, 95, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowding, C.V.; Shore, R.F.; Worgan, A.; Baker, P.J.; Harris, S. Accumulation of anticoagulant rodenticides in a non-target insectivore, the European hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus). Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.L.; Berg, T.B.; Martens, H.J.; Jones, O.R. Anyone Can Get Old—All You Have to Do Is Live Long Enough: Understanding Mortality and Life Expectancy in European Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus). Animals 2023, 13, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, S.L.; Berg, T.B.; Dabelsteen, T.; Jones, O.R. The ecology of suburban juvenile European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in Denmark. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 13174–13187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jota Baptista, C.; Seixas, F.; Gonzalo-Orden, J.M.; Patinha, C.; Pato, P.; Ferreira Da Silva, E.; Oliveira, P.A. The first full study of heavy metal(loid)s in western-European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) from Portugal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 11983–11994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jota Baptista, C.; Seixas, F.; Gonzalo-Orden, J.M.; Oliveira, P.A. Biomonitoring of heavy metals and metalloids with wild mammals in the Iberian Peninsula: A systematic review. Environ. Rev. 2023, 31, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jota Baptista, C.; Seixas, F.; Gonzalo-Orden, J.M.; Patinha, C.; Pato, P.; Ferreira Da Silva, E.; Oliveira, P.A. High Levels of Heavy Metal(loid)s Related to Biliary Hyperplasia in Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus). Animals 2023, 13, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delogu, M.; Cotti, C.; Lelli, D.; Sozzi, E.; Trogu, T.; Lavazza, A.; Sola, T. Eco-Virological Preliminary Study of Potentially Emerging Pathogens in Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) Recovered at a Wildlife Treatment and Rehabilitation Center in Northern Italy. Animals 2020, 10, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, S.; Silvestre-Ferreira, A.C.; Queiroga, F.L. A Review on Blood Reference Values as a Valuable Marker of Wildlife Welfare in Erinaceus europaeus. Animals 2024, 14, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Đuričić, D.; Lukač, M. Hedgehogs in Contact with Humans: Zoonotic and Reverse Zoonotic Transmission of Pathogens. J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2025, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jota Baptista, C.V.; Seixas, F.; Gonzalo-Orden, J.M.; Oliveira, P.A. Can the European Hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) Be a Sentinel for One Health Concerns? Biologics 2021, 1, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariacher, A.; Santini, A.; Del Lesto, I.; Tonon, S.; Cardini, E.; Barone, A.; Trotta, S.; Morini, M. Endoparasite Infections of the European Hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) in Central Italy. Animals 2021, 11, 3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jota Baptista, C.; Oliveira, P.A.; Gonzalo-Orden, J.M.; Seixas, F. Do Urban Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) Represent a Relevant Source of Zoonotic Diseases? Pathogens 2023, 12, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skuballa, J.; Petney, T.; Pfäffle, M.; Oehme, R.; Hartelt, K.; Fingerle, V.; Kahl, O. Occurrence of different Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato genospecies including B. afzelii, B. bavariensis, and B. spielmanii in hedgehogs (Erinaceus spp.) in Europe. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesiczka, P.M.; Hrazdilová, K.; Majerová, K.; Fonville, M.; Sprong, H.; Hönig, V.; Svitálková, K. The Role of Peridomestic Animals in the Eco-Epidemiology of Anaplasma phagocytophilum. Microb. Ecol. 2021, 82, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thamm, S.; Kalko, E.K.V.; Wells, K. Ectoparasite Infestations of Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) are Associated with Small-Scale Landscape Structures in an Urban–Suburban Environment. EcoHealth 2009, 6, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schütte, K.; Springer, A.; Brandes, F.; Reuschel, M.; Fehr, M.; Strube, C. Ectoparasites of European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in Germany and their health impact. Parasit. Vectors 2024, 17, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keymer, I.F.; Gibson, E.A.; Reynolds, D.J. Zoonoses and other findings in hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus): A survey of mortality and review of the literature. Vet. Rec. 1991, 128, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, B.; Franklinos, L.H.V.; Rodriguez-Ramos Fernandez, J.; Wend-Hansen, C.; Nair, S.; Macgregor, S.K.; Brown, C.D.; Macpherson, C.; Phipps, L.P.; O’Connell, S.; et al. Salmonella Enteritidis ST183: Emerging and endemic biotypes affecting western European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) and people in Great Britain. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, P.Y.; Chomel, B.B. Hedgehog Zoonoses. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, A.I.; Van Leeuwen, A.D.; Jacobs-Reitsma, W.; Wijnands, L.M.; Bouw, E.; Jahfari, S.; Sprong, H.; Van der Giessen, J.W.B. Presence of zoonotic agents in engorged ticks and hedgehog faeces from Erinaceus europaeus in (sub) urban areas. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanmechelen, B.; Vergote, V.; Merino, M.; Verbeken, E.; Maes, P. Common occurrence of Belerina virus, a novel paramyxovirus found in Belgian hedgehogs. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnat, S.; Łagowski, D.; Dyląg, M.; Nowakiewicz, A. European Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus L.) as a Reservoir of Dermatophytes in Poland. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 84, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpot, C.M.; Bowen, R.G. Hazards from hedgehogs: Two case reports with a survey of the epidemiology of hedgehog ringworm. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 1992, 17, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, P.; English, M.P. Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. erinacei in British hedgehogs. Med. Mycol. 1969, 7, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Barzic, C.; Cmokova, A.; Denaes, C.; Arné, P.; Hubka, V.; Guillot, J.; Nabet, C. Detection and Control of Dermatophytosis in Wild European Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) Admitted to a French Wildlife Rehabilitation Centre. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidwell, R.U.; Chan, I.; Francis, N.; Bunker, C.B. Trichophyton erinacei kerion barbae from a hedgehog with direct osculatory transfer to another person. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2014, 39, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, S.J.; Gunn, A. The One Health Concept. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2024, 81, 12366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Animals as Sentinels of Environmental Health Hazards; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Silaghi, C.; Skuballa, J.; Thiel, C.; Pfister, K.; Petney, T.; Pfäffle, M.; Kahl, O. The European hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus)—A suitable reservoir for variants of Anaplasma phagocytophilum? Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valverde, I.; Defosseux, I.; Le Bot, T.; Jouvion, G.; Le Barzic, C.; Arné, P.; Hubka, V.; Guillot, J.; Nabet, C. Effect of urbanization on the trace element concentrations in the kidney, liver and spines of the European hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, G.; Mangiagalli, G.; Paracchini, G.; Paltrinieri, S. Hematologic and biochemical variables of hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) after overwintering in rehabilitation centers. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 43, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, S.L.; Kalliokoski, O.; Dabelsteen, T.; Abelson, K. An exploratory investigation of glucocorticoids, personality and survival rates in wild and rehabilitated hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in Denmark. BMC Ecol. Evol. 2021, 21, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.L.; Roslev, P.; Nielsen, J.L.; Pertoldi, C.; Vorkamp, K. Pesticides in the population of European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in Denmark. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1436965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, S.; Silvestre-Ferreira, A.C.; Sargo, R.; Silva, F.; Queiroga, F.L. Hematology, Biochemistry, and Protein Electrophoresis Reference Intervals of Western European Hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) from a Rehabilitation Center in Northern Portugal. Animals 2023, 13, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Rosa, S.; Silvestre-Ferreira, A.C.; Queiroga, F.P. A Review of the Sentinel Role of Erinaceus europaeus in Zoonotic Diseases Across Urban and Rural Environments: A One Health Perspective. Vet. Sci. 2026, 13, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci13010029
Rosa S, Silvestre-Ferreira AC, Queiroga FP. A Review of the Sentinel Role of Erinaceus europaeus in Zoonotic Diseases Across Urban and Rural Environments: A One Health Perspective. Veterinary Sciences. 2026; 13(1):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci13010029
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosa, Sofia, Ana C. Silvestre-Ferreira, and Felisbina Pereira Queiroga. 2026. "A Review of the Sentinel Role of Erinaceus europaeus in Zoonotic Diseases Across Urban and Rural Environments: A One Health Perspective" Veterinary Sciences 13, no. 1: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci13010029
APA StyleRosa, S., Silvestre-Ferreira, A. C., & Queiroga, F. P. (2026). A Review of the Sentinel Role of Erinaceus europaeus in Zoonotic Diseases Across Urban and Rural Environments: A One Health Perspective. Veterinary Sciences, 13(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci13010029






