The Role of clbF in the Pathogenicity of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Culture Conditions
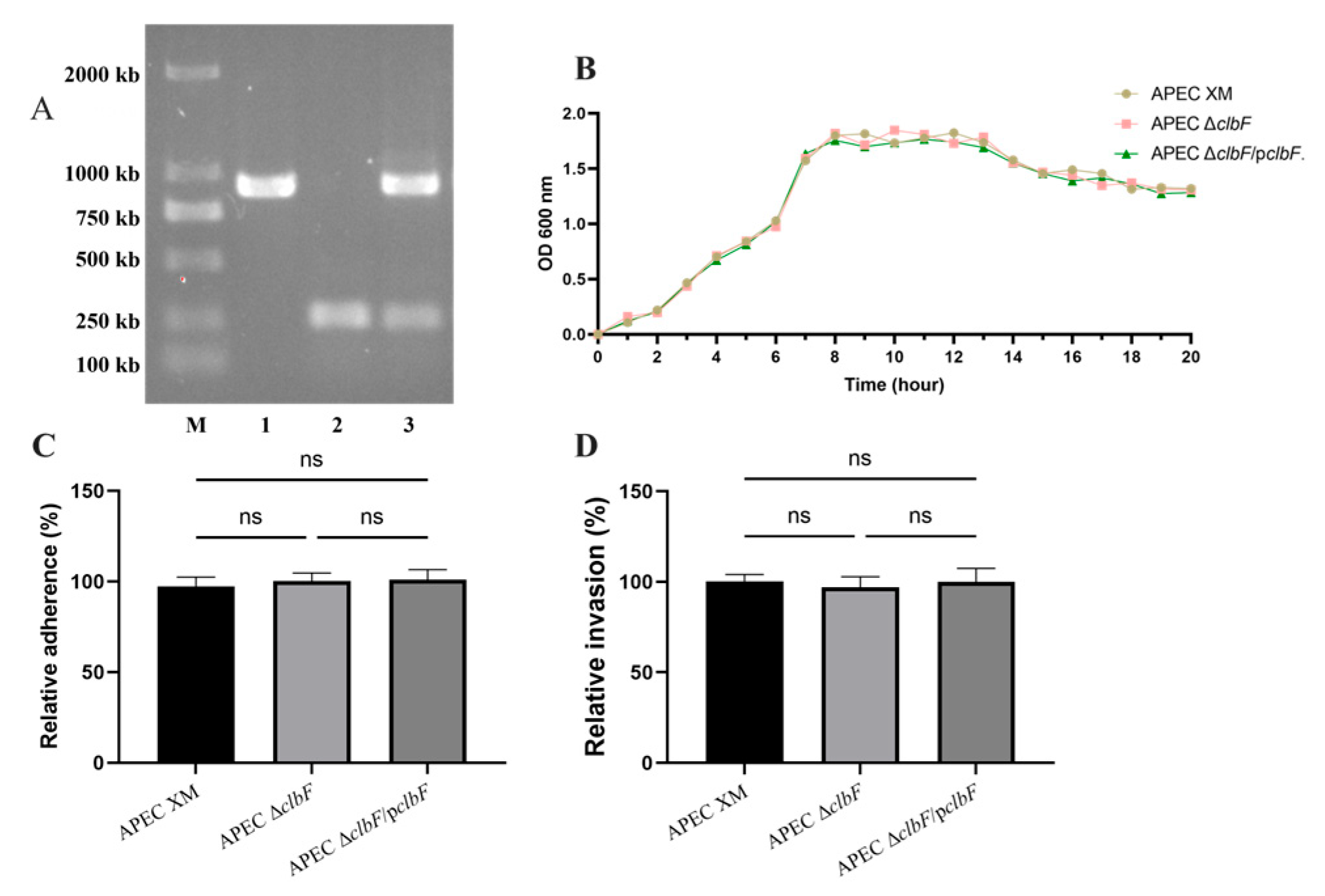
2.3. Construction of the clbF Deletion Mutant and the Complemented Mutant
2.4. Growth Test
2.5. Mouse Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells (bEnd.3) Adhesion and Invasion Assay
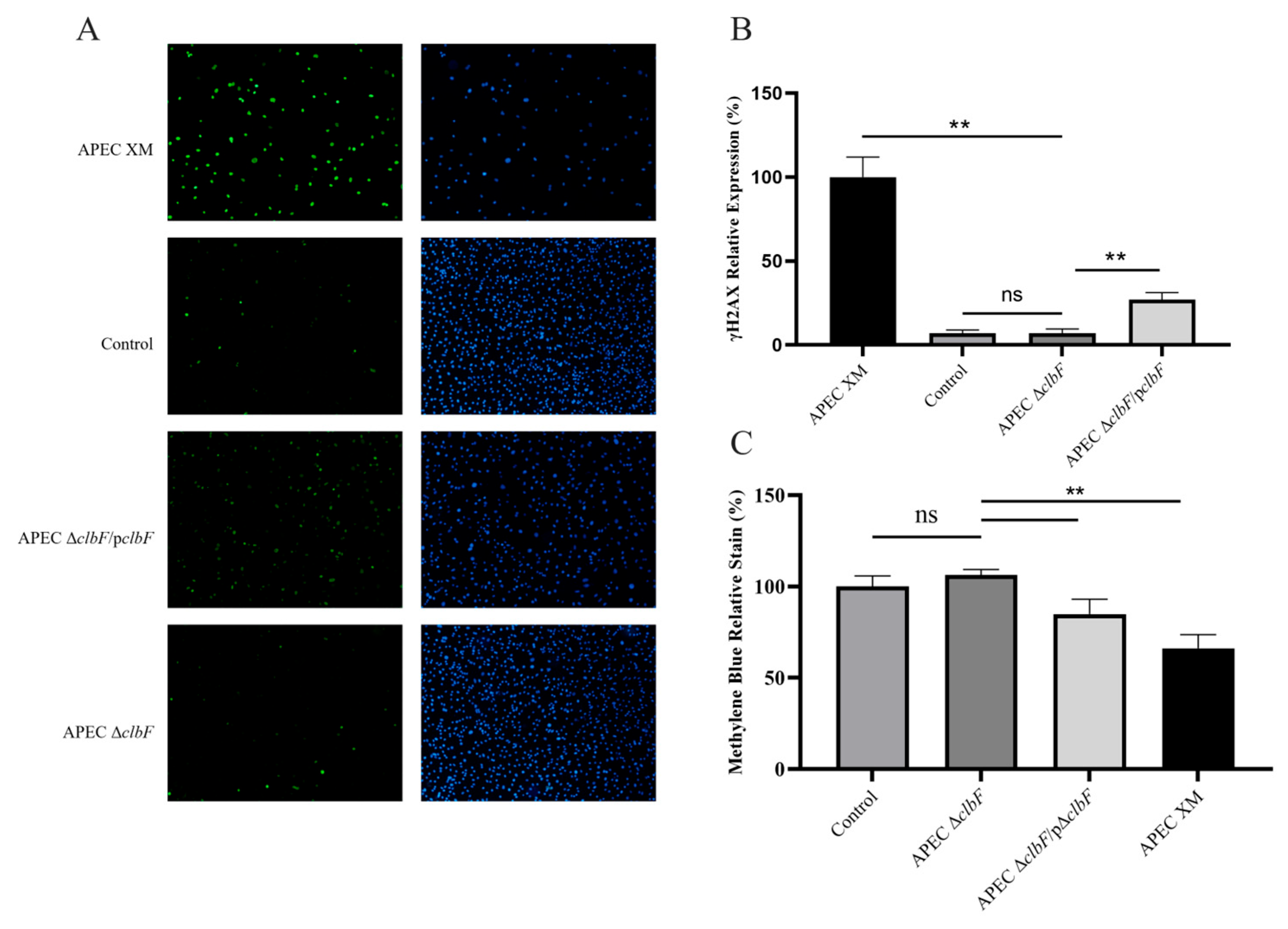
2.6. Colibactin Cytotoxicity Assays
2.7. Mouse Infection Model Experiment
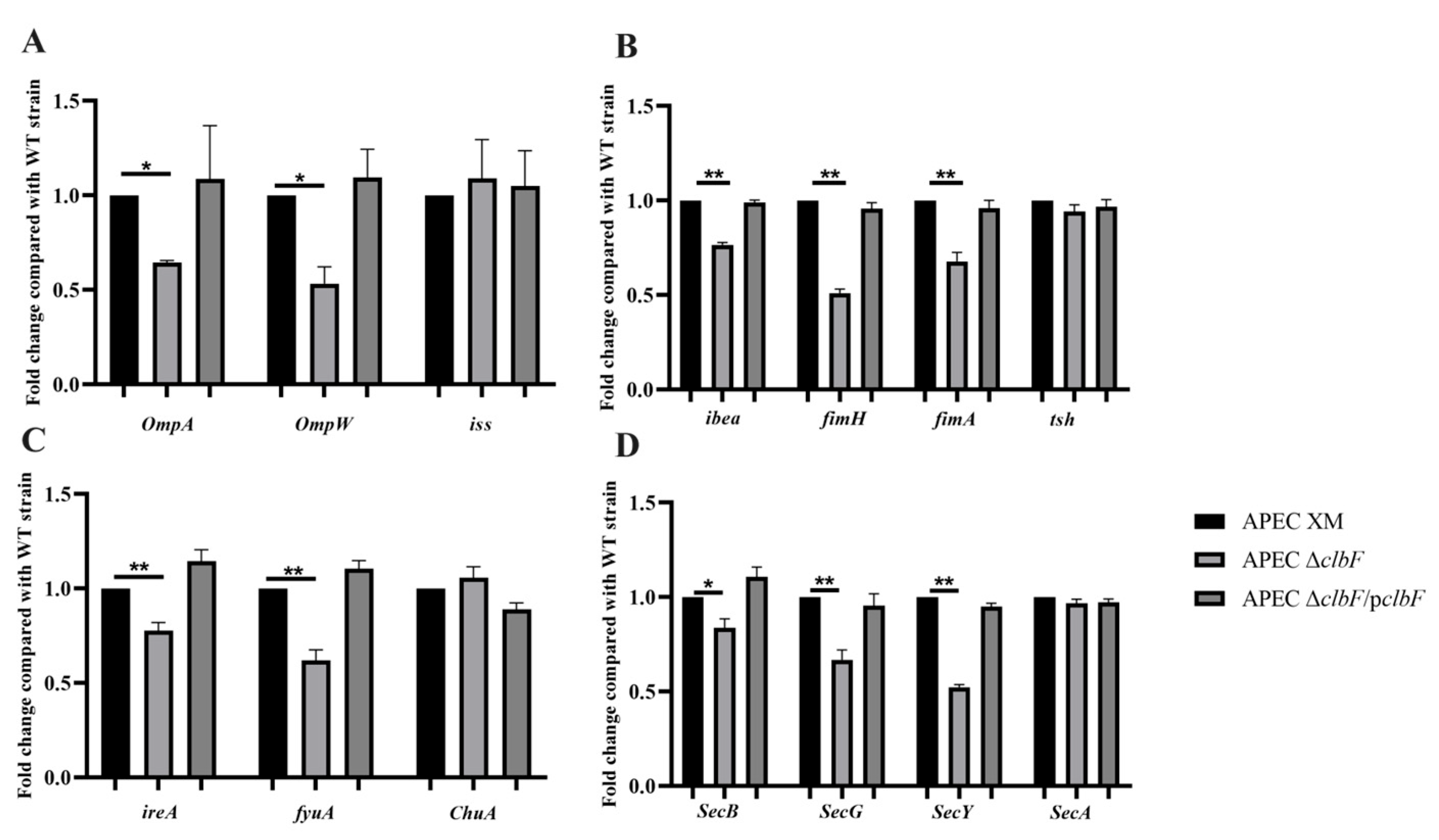
2.8. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Deletion of clbF Did Not Affect Growth Kinetics, Adhesion, or Invasion
3.2. clbF Affects the Colibactin Production
3.3. clbF-Attenuated Virulence in In Vivo Infection
3.4. Expression of Virulence Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mellata, M. Human and avian extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli: Infections, zoonotic risks, and antibiotic resistance trends. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 916–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tivendale, K.A.; Logue, C.M.; Kariyawasam, S.; Jordan, D.; Hussein, A.; Li, G.; Wannemuehler, Y.; Nolan, L.K. Avian-pathogenic Escherichia coli strains are similar to neonatal meningitis E. coli strains and are able to cause meningitis in the rat model of human disease. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 3412–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewers, C.; Li, G.; Wilking, H.; Kiessling, S.; Alt, K.; Antáo, E.M.; Laturnus, C.; Diehl, I.; Glodde, S.; Homeier, T.; et al. Avian pathogenic, uropathogenic, and newborn meningitis-causing Escherichia coli: How closely related are they? Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 297, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skyberg, J.A.; Johnson, T.J.; Johnson, J.R.; Clabots, C.; Logue, C.M.; Nolan, L.K. Acquisition of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli plasmids by a commensal E. coli isolate enhances its abilities to kill chicken embryos, grow in human urine, and colonize the murine kidney. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 6287–6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nougayrède, J.P.; Homburg, S.; Taieb, F.; Boury, M.; Brzuszkiewicz, E.; Gottschalk, G.; Buchrieser, C.; Hacker, J.; Dobrindt, U.; Oswald, E. Escherichia coli induces DNA double-strand breaks in eukaryotic cells. Science 2006, 313, 848–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silpe, J.E.; Wong, J.W.H.; Owen, S.V.; Baym, M.; Balskus, E.P. The bacterial toxin colibactin triggers prophage induction. Nature 2022, 603, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.; Salesse, L.; Hoang, M.H.T.; Bonnet, M.; Sauvanet, P.; Larabi, A.; Godfraind, C.; Gagnière, J.; Pezet, D.; Rosenstiel, P.; et al. Autophagy of Intestinal Epithelial Cells Inhibits Colorectal Carcinogenesis Induced by Colibactin-Producing Escherichia coli in Apc(Min/+) Mice. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1373–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jans, M.; Kolata, M.; Blancke, G.; D’Hondt, A.; Gräf, C.; Ciers, M.; Sze, M.; Thiran, A.; Petta, I.; Andries, V.; et al. Colibactin-driven colon cancer requires adhesin-mediated epithelial binding. Nature 2024, 635, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcq, I.; Martin, P.; Payros, D.; Cuevas-Ramos, G.; Boury, M.; Watrin, C.; Nougayrède, J.P.; Olier, M.; Oswald, E. The genotoxin colibactin exacerbates lymphopenia and decreases survival rate in mice infected with septicemic Escherichia coli. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, A.J.; Martin, P.; Cloup, E.; Stabler, R.A.; Oswald, E.; Taylor, P.W. The Genotoxin Colibactin Is a Determinant of Virulence in Escherichia coli K1 Experimental Neonatal Systemic Infection. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 3704–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massip, C.; Branchu, P.; Bossuet-Greif, N.; Chagneau, C.V.; Gaillard, D.; Martin, P.; Boury, M.; Sécher, T.; Dubois, D.; Nougayrède, J.P.; et al. Deciphering the interplay between the genotoxic and probiotic activities of Escherichia coli Nissle 1917. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1008029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, L.; Wilson, M.R.; Brotherton, C.A.; Balskus, E. Characterization of Polyketide Synthase Machinery from the pks Island Facilitates Isolation of a Candidate Precolibactin. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachmann, A.O.; Garcie, C.; Wu, V.; Martin, P.; Ueoka, R.; Oswald, E.; Piel, J. Colibactin biosynthesis and biological activity depend on the rare aminomalonyl polyketide precursor. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 13138–13141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Wang, P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, G.; Cui, L.; Meng, X. ClpV1 in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli is a crucial virulence factor contributing to meningitis in a mouse model in vivo. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 263, 109273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Bin, P.; Zhu, G. The Amino Acid-mTORC1 Pathway Mediates APEC TW-XM-Induced Inflammation in bEnd.3 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hejair, H.M.A.; Ma, J.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, M.; Dong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yao, H. Role of outer membrane protein T in pathogenicity of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 115, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, H.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, G.; Xia, P.; Cui, L.; Li, J.; et al. ClbG in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Contributes to Meningitis Development in a Mouse Model. Toxins 2021, 13, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, P.; Xia, P.; Wang, J.; He, M.; Zhu, C.; Wang, H.; Zhu, G. Phosphopantetheinyl transferase ClbA contributes to the virulence of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli in meningitis infection of mice. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, H.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, G.; Xia, P.; Cui, L.; Li, J.; et al. Colibactin in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli contributes to the development of meningitis in a mouse model. Virulence 2021, 12, 2382–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datsenko, K.A.; Wanner, B.L. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6640–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Meng, X.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhong, H.; Xia, P.; Cui, L.; Zhu, G.; Wang, H. Transcriptome profiling of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli and the mouse microvascular endothelial cell line bEnd.3 during interaction. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuet-Greif, N.; Vignard, J.; Taieb, F.; Mirey, G.; Dubois, D.; Petit, C.; Oswald, E.; Nougayrède, J.P. The Colibactin Genotoxin Generates DNA Interstrand Cross-Links in Infected Cells. mBio 2018, 9, e02393-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auvray, F.; Perrat, A.; Arimizu, Y.; Chagneau, C.V.; Bossuet-Greif, N.; Massip, C.; Brugère, H.; Nougayrède, J.P.; Hayashi, T.; Branchu, P.; et al. Insights into the acquisition of the pks island and production of colibactin in the Escherichia coli population. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbar, R.; Nazari, S.; Farahani, O. Phylogenetic Analysis and Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles of Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from UTI-Suspected Patients. Iran. J. Public Health 2020, 49, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hejair, H.M.A.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yao, H. Functional role of ompF and ompC porins in pathogenesis of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 107, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, S.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, G. Melatonin Is Neuroprotective in Escherichia coli Meningitis Depending on Intestinal Microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruvada, R.; Kim, K.S. Extracellular loops of the Escherichia coli outer membrane protein A contribute to the pathogenesis of meningitis. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.; Prasadarao, N.V. Outer membrane protein A expression in Escherichia coli K1 is required to prevent the maturation of myeloid dendritic cells and the induction of IL-10 and TGF-beta. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 2672–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijetunge, D.S.; Gongati, S.; DebRoy, C.; Kim, K.S.; Couraud, P.O.; Romero, I.A.; Weksler, B.; Kariyawasam, S. Characterizing the pathotype of neonatal meningitis causing Escherichia coli (NMEC). BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediati, D.G.; Blair, T.A.; Costas, A.; Monahan, L.G.; Söderström, B.; Charles, I.G.; Duggin, I.G. Genetic requirements for uropathogenic E. coli proliferation in the bladder cell infection cycle. mSystems 2024, 9, e0038724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Niu, C.; Shi, Z.; Xia, Y.; Yaqoob, M.; Dai, J.; Lu, C. Effects of ibeA deletion on virulence and biofilm formation of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.H.; Chi, F.; Peng, L.; Bo, T.; Zhang, B.; Liu, L.Q.; Wu, X.; Mor-Vaknin, N.; Markovitz, D.M.; Cao, H.; et al. Vimentin, a Novel NF-κB Regulator, Is Required for Meningitic Escherichia coli K1-Induced Pathogen Invasion and PMN Transmigration across the Blood-Brain Barrier. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, S.M.; Bosch, J.; Jimenez de Anta, M.T.; Vila, J. Comparative study of virulence traits of Escherichia coli clinical isolates causing early and late neonatal sepsis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1123–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchesnokova, V.; Aprikian, P.; Kisiela, D.; Gowey, S.; Korotkova, N.; Thomas, W.; Sokurenko, E. Type 1 fimbrial adhesin FimH elicits an immune response that enhances cell adhesion of Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 3895–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puorger, C.; Vetsch, M.; Wider, G.; Glockshuber, R. Structure, folding stability of FimA, the main structural subunit of type 1 pili from uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 412, 520–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellata, M.; Dho-Moulin, M.; Dozois, C.M.; Curtiss, R., 3rd; Lehoux, B.; Fairbrother, J.M. Role of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli virulence factors in bacterial interaction with chicken heterophils and macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostakioti, M.; Stathopoulos, C. Functional analysis of the Tsh autotransporter from an avian pathogenic Escherichia coli strain. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 5548–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Carlino, U.B.; Johnson, J.R. Identification of a new iron-regulated virulence gene, ireA, in an extraintestinal pathogenic isolate of Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 6209–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Khan, A.; Singh, P.; Srivastava, A. Synthesis, nature and utility of universal iron chelator—Siderophore: A review. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 212–213, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunduki, G.K.; Heinz, E.; Phiri, V.S.; Noah, P.; Feasey, N.; Musaya, J. Virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance of uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) isolated from urinary tract infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Banda, D.A.; Carrillo-Casas, E.M.; Leyva-Leyva, M.; Orozco-Hoyuela, G.; Manjarrez-Hernández, Á.H.; Arroyo-Escalante, S.; Moncada-Barrón, D.; Villanueva-Recillas, S.; Xicohtencatl-Cortes, J.; Hernández-Castro, R. Identification of virulence factors genes in Escherichia coli isolates from women with urinary tract infection in Mexico. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 959206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Dai, J.; Zhuge, X.; Wang, H.; Hu, L.; Ren, J.; Chen, L.; Li, D.; Tang, F. Iron-regulated gene ireA in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli participates in adhesion and stress-resistance. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Torres, A.G.; Payne, S.M. Haem iron-transport system in enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 23, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nègre, V.L.; Bonacorsi, S.; Schubert, S.; Bidet, P.; Nassif, X.; Bingen, E. The siderophore receptor IroN, but not the high-pathogenicity island or the hemin receptor ChuA, contributes to the bacteremic step of Escherichia coli neonatal meningitis. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1216–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, J.J.; Yang, Y.; Tomkovich, S.; Shima, A.; Newsome, R.C.; Tripathi, P.; Oswald, E.; Bruner, S.D.; Jobin, C. MATE transport of the E. coli-derived genotoxin colibactin. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 15009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, J.M.; Randall, L.L. The Sec System: Protein Export in Escherichia coli. EcoSal Plus 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, E.R.; Mecsas, J. Bacterial Secretion Systems: An Overview. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 213–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Dose of Challenge (CFU) | No. of Dead Mice | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| APEC XM | APEC ΔclbF | APEC ΔclbF/pclbF | |
| 1 × 107 | 5/5 | 3/5 | 4/5 |
| 1 × 106 | 4/5 | 1/5 | 4/5 |
| 1 × 105 | 1/5 | 1/5 | 1/5 |
| 1 × 104 | 1/5 | 0/5 | 1/5 |
| LD50 | 1.79 × 105 | 5.66 × 106 | 3.16 × 105 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, M.; Wu, H.; Li, L.; Hao, P.; Wang, P. The Role of clbF in the Pathogenicity of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080727
Wu M, Wu H, Li L, Hao P, Wang P. The Role of clbF in the Pathogenicity of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(8):727. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080727
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Meng, Haitao Wu, Ling Li, Pan Hao, and Peili Wang. 2025. "The Role of clbF in the Pathogenicity of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 8: 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080727
APA StyleWu, M., Wu, H., Li, L., Hao, P., & Wang, P. (2025). The Role of clbF in the Pathogenicity of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Veterinary Sciences, 12(8), 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080727





