Alterations in the Microbiome of Horses Affected with Fecal Water Syndrome
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Horses
2.2. Fecal Sample Collection
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. 16S rRNA Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatics
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
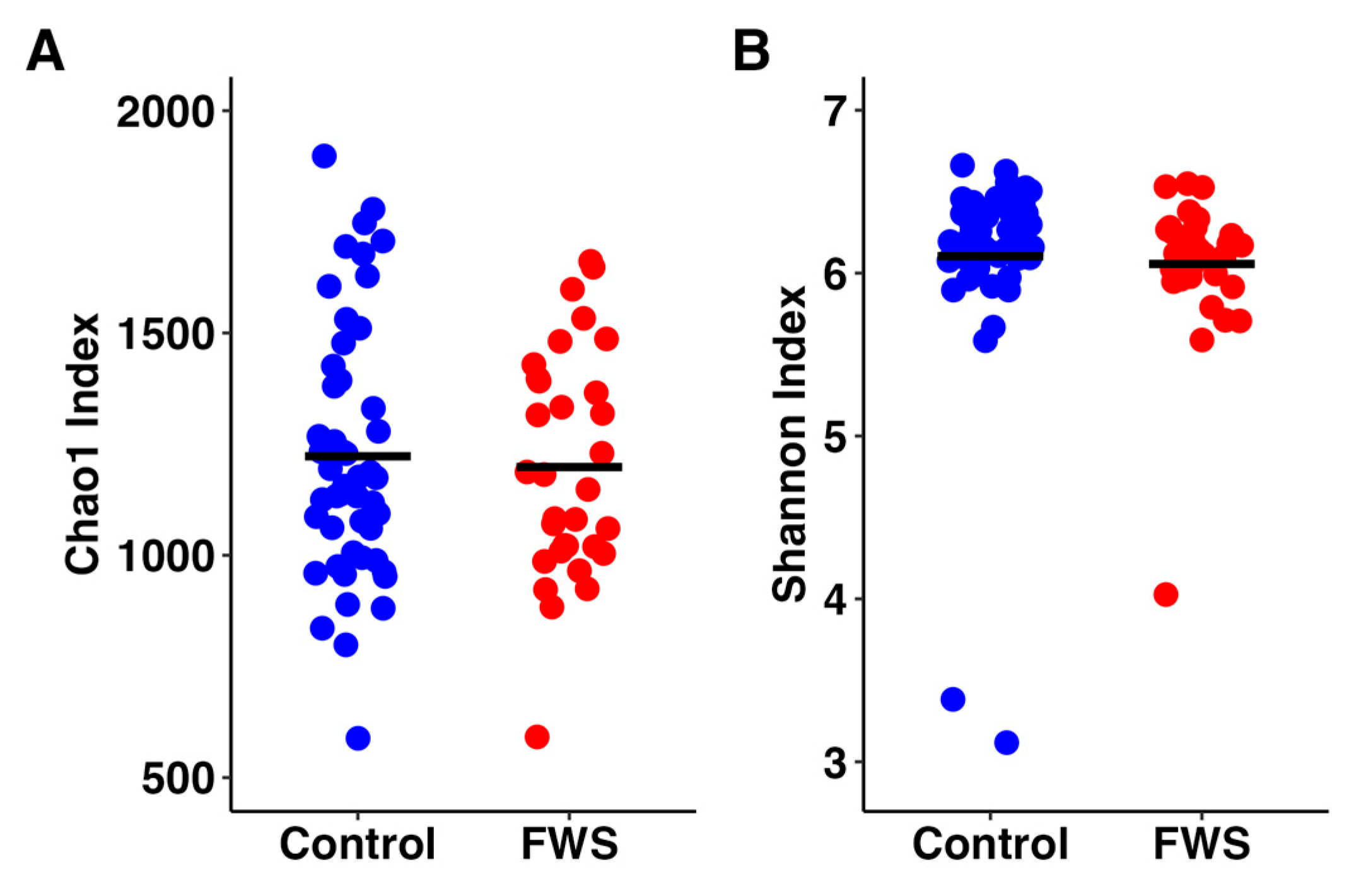
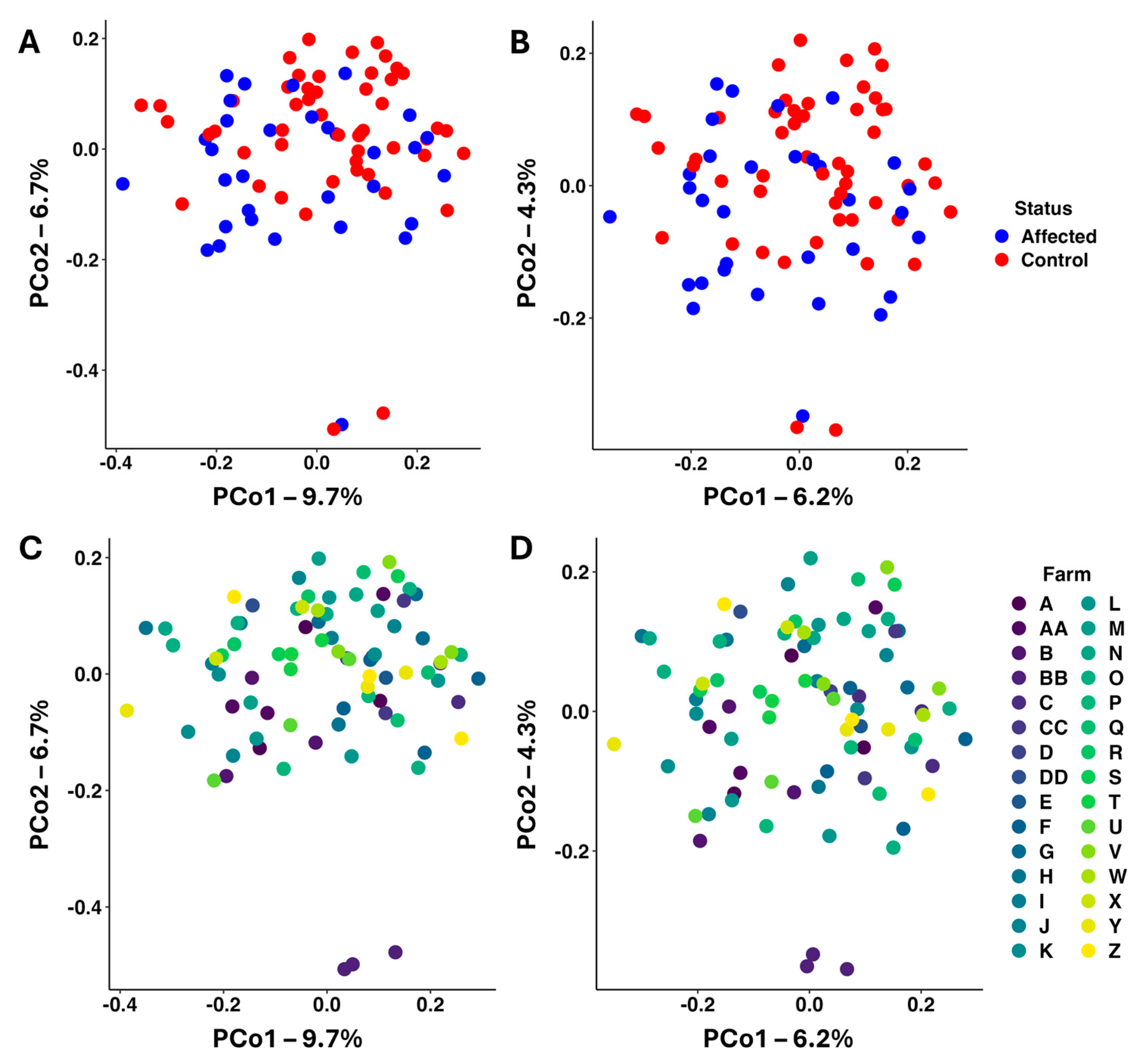
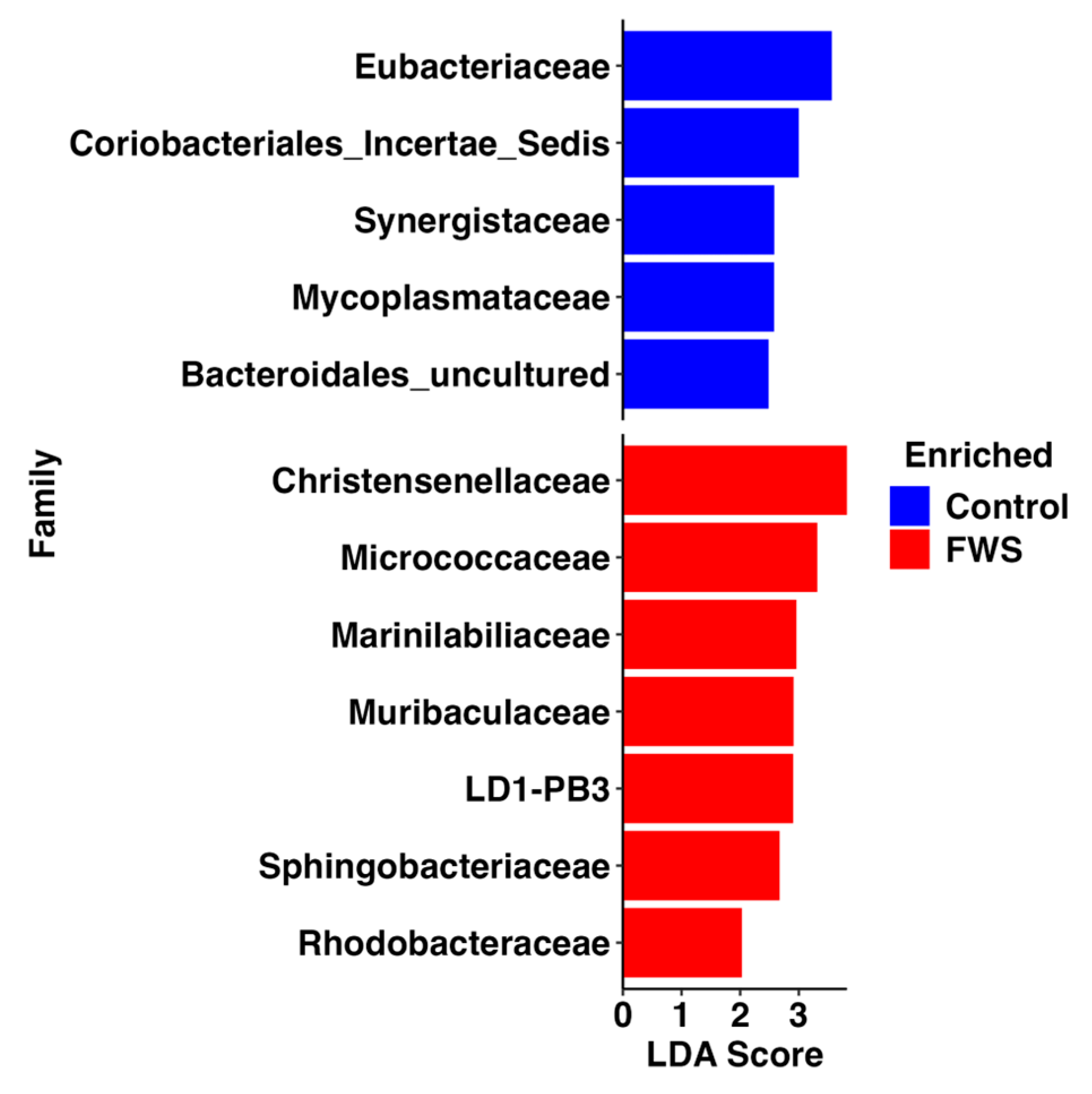
3.2. Bacterial Microbiome Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| ASV | Amplicon sequence variant |
| FWS | Fecal water syndrome |
| GIT | Gastrointestinal tract |
| LEfSe | Linear discriminant analysis effect size |
| PCoA | Principal coordinate analysis |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PERMANOVA | Permutational multivariate analysis of variance |
References
- Kienzle, E.; Zehnder, C.; Pfister, K.; Gerhards, H.; Sauter-Louis, C.; Harris, P. Field study on risk factors for free fecal water in pleasure horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2016, 44, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindroth, K.M.; Johansen, A.; Baverud, V.; Dicksved, J.; Lindberg, J.E.; Muller, C.E. Differential Defecation of Solid and Liquid Phases in Horses-A Descriptive Survey. Animals 2020, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altermatt, N.; Dolf, G.; Ramseyer, A.; Burger, D.; Gerber, V. Prevalence of health problems in midlife Swiss warm-blooded horses. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2021, 163, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindroth, K.M.; Lindberg, J.E.; Johansen, A.; Muller, C.E. Feeding and Management of Horses with and without Free Faecal Liquid: A Case-Control Study. Animals 2021, 11, 2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.C.; Arroyo, L.G.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Stampfli, H.R.; Kim, P.T.; Sturgeon, A.; Weese, J.S. Comparison of the fecal microbiota of healthy horses and horses with colitis by high throughput sequencing of the V3-V5 region of the 16S rRNA gene. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Tang, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, W. Role of gut microbiota-derived signals in the regulation of gastrointestinal motility. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 961703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waclawikova, B.; Codutti, A.; Alim, K.; El Aidy, S. Gut microbiota-motility interregulation: Insights from in vivo, ex vivo and in silico studies. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 1997296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoster, A.; Weese, J.S.; Gerber, V.; Nicole Graubner, C. Dysbiosis is not present in horses with fecal water syndrome when compared to controls in spring and autumn. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laustsen, L.; Edwards, J.E.; Hermes, G.D.A.; Luthersson, N.; van Doorn, D.A.; Okrathok, S.; Kujawa, T.J.; Smidt, H. Free Faecal Water: Analysis of Horse Faecal Microbiota and the Impact of Faecal Microbial Transplantation on Symptom Severity. Animals 2021, 11, 2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindroth, K.M.; Dicksved, J.; Pelve, E.; Baverud, V.; Muller, C.E. Faecal bacterial composition in horses with and without free faecal liquid: A case control study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wester, R.J.; Baillie, L.L.; McCarthy, G.C.; Keever, C.C.; Jeffery, L.E.; Adams, P.J. Dysbiosis not observed in Canadian horse with free fecal liquid (FFL) using 16S rRNA sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.J. Free Fecal Water Syndrome in Horses. Available online: https://www.merckvetmanual.com/digestive-system/miscellaneous-intestinal-diseases-in-horses/free-fecal-water-syndrome-in-horses (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108 (Suppl. S1), 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaehler, B.D.; Bokulich, N.A.; McDonald, D.; Knight, R.; Caporaso, J.G.; Huttley, G.A. Species abundance information improves sequence taxonomy classification accuracy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahti, L.; Shetty, S. Tools for Microbiome Analysis in R, version 2.1.26; Bioconductor: Groningen, The Netherlands, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Wagner, H. R Package, Version 2.2-0. Vegan: Community Ecoloy Package. CRAN: Vienna, Austria, 2014. Available online: http://CRAN.Rproject.org/package=vegan (accessed on 30 October 2024).
- Paradis, E.; Schliep, K. ape 5.0: An environment for modern phylogenetics and evolutionary analyses in R. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnicar, F.; Weingart, G.; Tickle, T.L.; Huttenhower, C.; Segata, N. Compact graphical representation of phylogenetic data and metadata with GraPhlAn. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Peddada, S.D. Analysis of compositions of microbiomes with bias correction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, A.D.; Reid, J.N.; Macklaim, J.M.; McMurrough, T.A.; Edgell, D.R.; Gloor, G.B. Unifying the analysis of high-throughput sequencing datasets: Characterizing RNA-seq, 16S rRNA gene sequencing and selective growth experiments by compositional data analysis. Microbiome 2014, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, P.K.; Newbold, C.J.; Jones, E.; Worgan, H.J.; Grove-White, D.H.; Dugdale, A.H.; Barfoot, C.; Harris, P.A.; Argo, C.M. The Equine Gastrointestinal Microbiome: Impacts of Age and Obesity. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, T.; McAdams, Z.L.; Townsend, K.S.; Martin, L.M.; Johnson, P.J.; Ericsson, A.C. Effect of Sugar Beet Pulp on the Composition and Predicted Function of Equine Fecal Microbiota. Biology 2023, 12, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, L.; Vinderola, G.; Endo, A.; Kantanen, J.; Jingfeng, C.; Binetti, A.; Burns, P.; Qingmiao, S.; Suying, D.; Zujiang, Y.; et al. Gut Microbiome Characteristics in feral and domesticated horses from different geographic locations. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Herd, R.P. Epidemiology of equine Cryptosporidium and Giardia infections. Equine Vet. J. 1994, 26, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, F.; Passamonti, F.; Caccio, S.; Diaferia, M.; Piergili Fioretti, D. Epidemiological survey on equine cryptosporidium and giardia infections in Italy and molecular characterization of isolates. Zoonoses Public Health 2010, 57, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, W.; Wang, R.; Zhang, L. The first report of Cryptosporidium andersoni in horses with diarrhea and multilocus subtype analysis. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Bauer, C. A review of Eimeria infections in horses and other equids. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 256, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzal, F.A.; Diab, S.S. Gastritis, Enteritis, and Colitis in Horses. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2015, 31, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Porter, M.M.; Davis, D.J.; McAdams, Z.L.; Townsend, K.S.; Martin, L.M.; Wilhite, C.; Johnson, P.J.; Ericsson, A.C. Alterations in the Microbiome of Horses Affected with Fecal Water Syndrome. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080724
Porter MM, Davis DJ, McAdams ZL, Townsend KS, Martin LM, Wilhite C, Johnson PJ, Ericsson AC. Alterations in the Microbiome of Horses Affected with Fecal Water Syndrome. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(8):724. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080724
Chicago/Turabian StylePorter, Madison M., Daniel J. Davis, Zachary L. McAdams, Kile S. Townsend, Lynn M. Martin, Christopher Wilhite, Philip J. Johnson, and Aaron C. Ericsson. 2025. "Alterations in the Microbiome of Horses Affected with Fecal Water Syndrome" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 8: 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080724
APA StylePorter, M. M., Davis, D. J., McAdams, Z. L., Townsend, K. S., Martin, L. M., Wilhite, C., Johnson, P. J., & Ericsson, A. C. (2025). Alterations in the Microbiome of Horses Affected with Fecal Water Syndrome. Veterinary Sciences, 12(8), 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080724






