Research Progress on the Gc Proteins of Akabane Virus
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
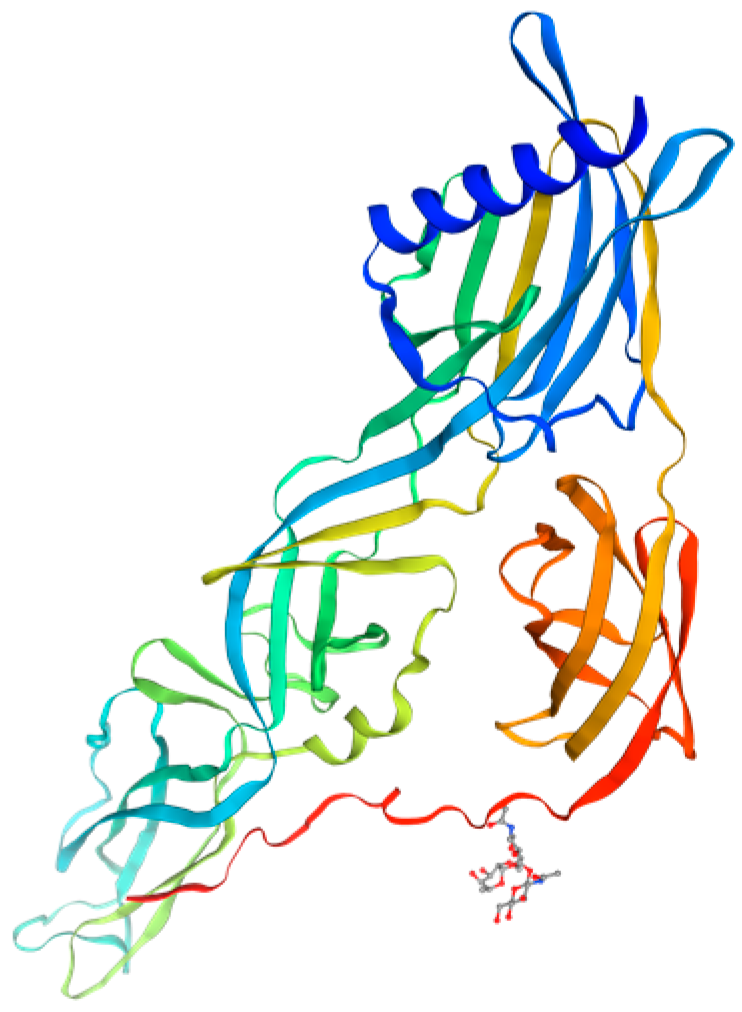
2. Analysis of the Structural Characteristics and Functional Domains of the Gc Protein
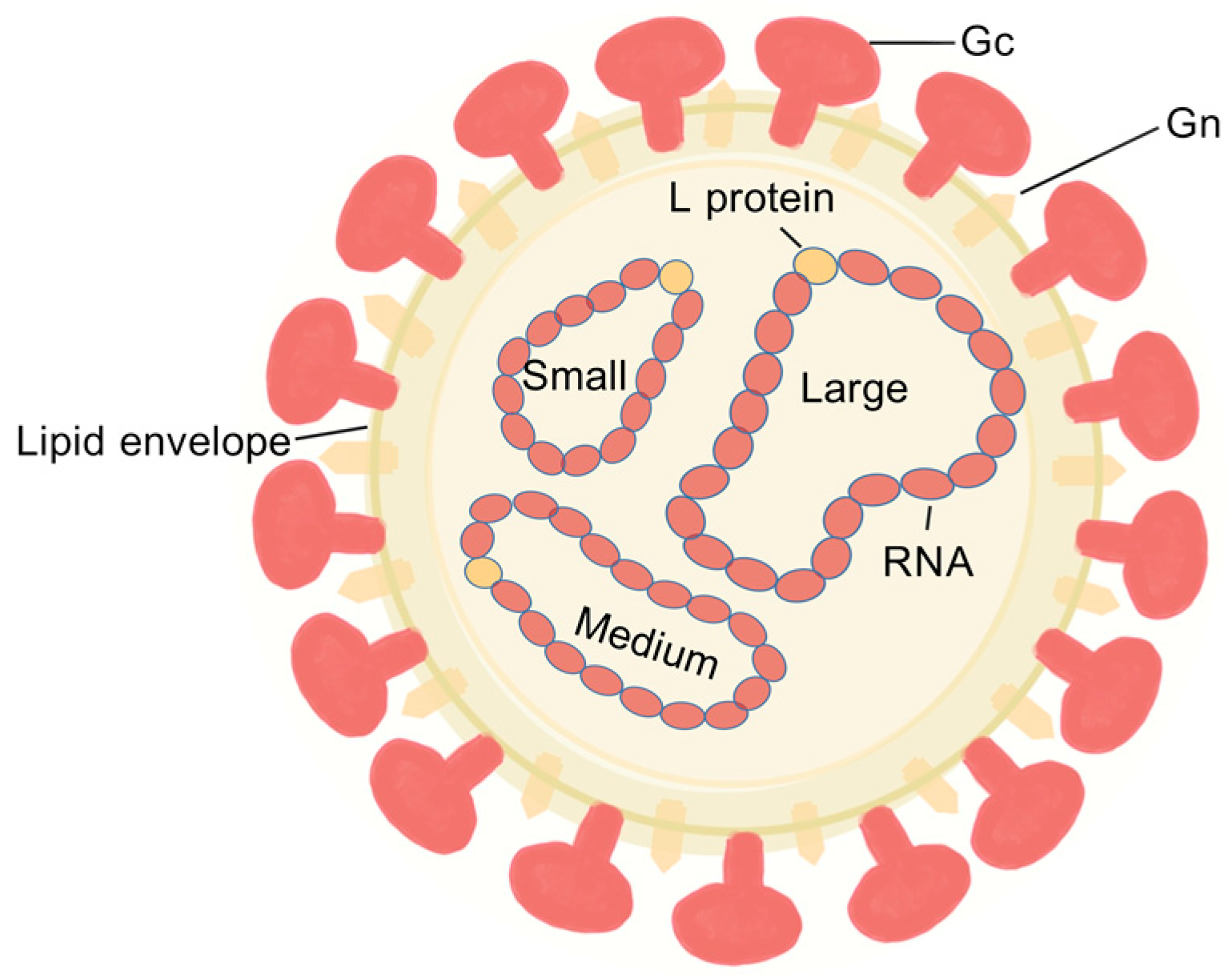
2.1. Akabane Virus Structural Domain Composition
2.2. Gc Protein Glycosylation Modification
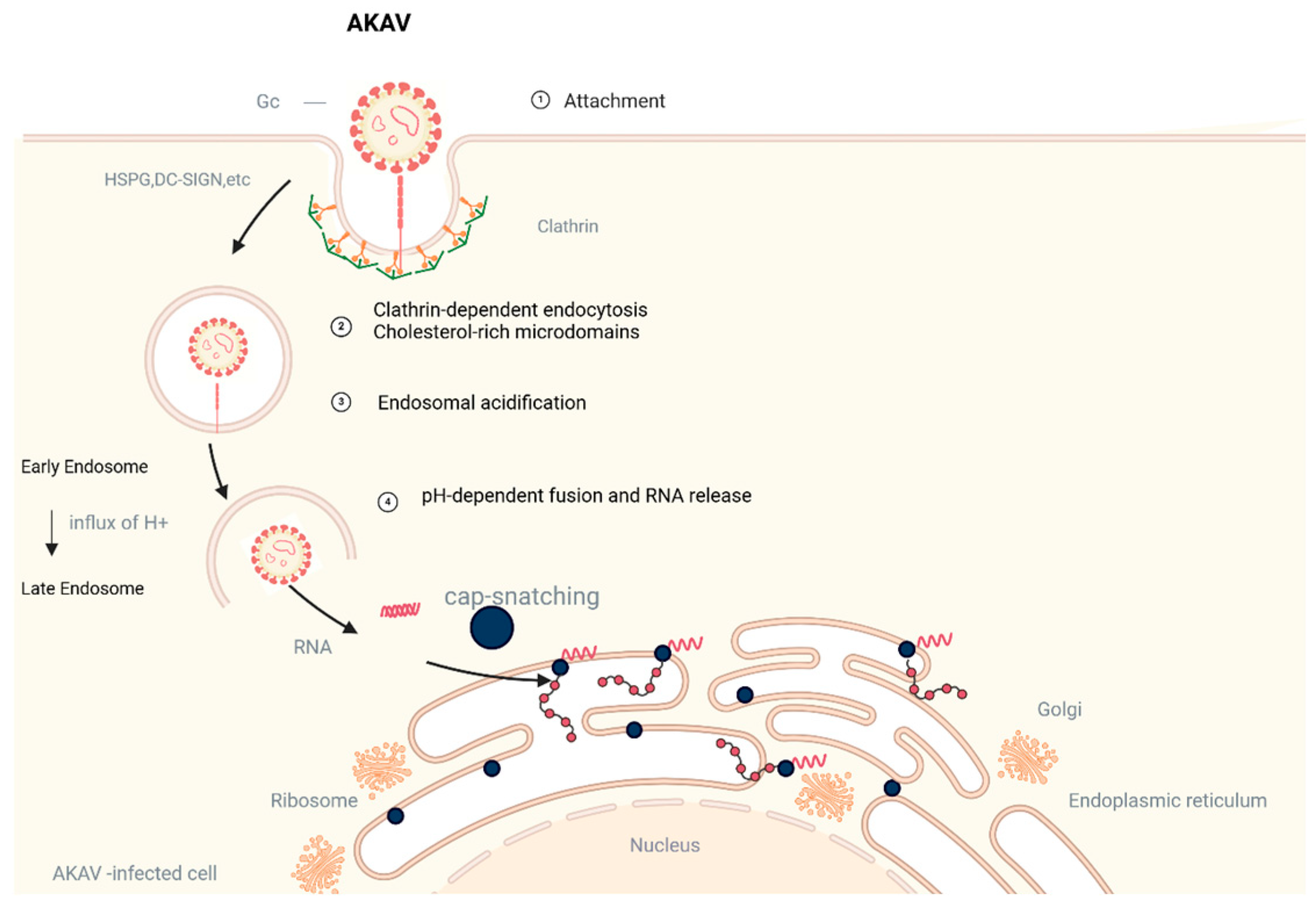
2.3. Gc Protein Fusion Mechanism and Receptor Binding
3. Immune Regulation and Pathogenic Mechanisms of the Gc Protein
3.1. Gc Protein Regulates Host Immune Response
3.2. Effect of Gc Protein on Virus Replication
3.3. Effect of Gc Protein on Virulence
4. Serological Diagnostic Techniques for AKAV Gc Protein
4.1. The Serum Neutralization Test
4.2. The Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.3. Colloidal Gold Immunochromatography
4.4. Indirect Fluorescent Antibody Technology
5. Challenges and Prospects of Utilizing the Gc Protein in Vaccine Research
6. Summary and Future Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.-Q.; Feng, Y.; Liu, X. Epidemiological characteristics and diagnostic methods of akaua spotting disease. Chin. J. Vet. Med. 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Kinney, R.M.; Calisher, C.H. Antigenic Relationships among Simbu Serogroup (Bunyaviridae) Viruses. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 30, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briese, T.; Calisher, C.H.; Higgs, S. Viruses of the family Bunyaviridae: Are all available isolates reassortants? Virology 2013, 446, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dağalp, S.B.; Dik, B.; Doğan, F. Akabane Virus Infection in Eastern Mediterranean Region in Turkey: Culicoides (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) as a Possible Vector. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Regge, N. Akabane, Aino and Schmallenberg Virus-Where Do We Stand and What Do We Know about the Role of Domestic Ruminant Hosts and Culicoides Vectors in Virus Transmission and Overwintering? Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 27, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Chen, C.; Ren, Y. Research Progress on Akabane Disease. J. Tarim Univ. 2008, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, Á.B.; Mee, J.F.; Kirkland, P.D. Pathogenicity and Teratogenicity of Schmallenberg Virus and Akabane Virus in Experimentally Infected Chicken Embryos. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 216, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Chen, D.; Wei, F. Establishment and Application of a Dual Fluorescent RT-PCR Detection Method for Akabane Virus and Schmallenberg Virus. Chin. J. Anim. Infect. Dis. 2023, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, S.; Takenaka-Uema, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Kato, K.; Shimojima, M.; Palmarini, M.; Horimoto, T. Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan Is an Important Attachment Factor for Cell Entry of Akabane and Schmallenberg Viruses. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00503-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Hoffmann, B.; Beer, M. Schmallenberg Virus. Dev. Biol. 2013, 135, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F.; Chen, D.; Wang, J. Overview of Diagnostic Techniques for Schmallenberg Disease. Chin. J. Anim. Quar. 2024, 41, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, Q.; Qingling, M.; Zaichao, Z. A Serological Survey of Akabane Virus Infection in Cattle and Sheep in North west China. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2012, 44, 1817–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, R.; Hirata, M.; Kaji, M.; Goto, Y. Bovine Epizootic Encephalomyelitis Caused by Akabane Virus in Southern Japan. BMC Vet. Res. 2008, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, J.; Yanase, T.; Kato, T. Serological Evidence Suggests That Several Simbu Serogroup Viruses Circulated in Israel. Vet. Ital. 2019, 55, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Coverdale, O.R.; Cybinski, D.H.; St George, T.D. Congenital Abnormalities in Calves Associated with Akabane Virus and Aino Virus. Aust. Vet. J. 1978, 54, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Shete, A.; Bondre, V. Isolation and Characterization of Oya Virus a Member of Simbu Serogroup, Family Bunyaviridae, Isolated from Karnataka, India. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2016, 44, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Tan, Q.; Zhang, H. Molecular Characterization of 10 Strains of Japanese Encephalitis Virus from Guangdong Province. Virol. J. 2018, 34, 474–481. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S. Investigation of Virus-Carrying Mosquitoes and Midges in Guizhou and Sichuan Provinces of China. Master’s Thesis, Qingdao University, Qingdao, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H. Detection and Molecular Characterization of Akabane Virus and OYAV in Guang dong Province. Virol. J. 2020, 36, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Lappin, D.F.; Nakitare, G.W.; Palfreyman, J.W. Localization of Bunyamwera Bunyavirus G1 Glycoprotein to the Golgi Requires Association with G2 but Not with NSm. J. Gen. Virol. 1994, 75 Pt 12, 3441–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanase, T.; Yoshida, K.; Ohashi, S. Sequence Analysis of the Medium RNA Segment of Three Simbu Serogroup Viruses, Akabane, Aino, and Peaton Viruses. Virus Res. 2003, 93, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Tong, T.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Q.; Wu, D. Eukaryotic Expression and Antigenicity Detection of the G1 Gene of Akabane Virus. Chin. J. Prev. Vet. Med. 2008, 6, 440–444. [Google Scholar]
- Reguera, J.; Malet, H.; Weber, F. Structural Basis for Encapsidation of Genomic RNA by La Crosse Orthobunya virus Nucleoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7246–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, P.; Malet, H.; Cusack, S. Structural Insights into Bunyavirus Replication and Its Regulation by the vRNA Promoter. Cell 2015, 161, 1267–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.M. Emerging Viruses: The Bunyaviridae. Mol. Med. 1997, 3, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Yanase, T.; Yamakawa, M. Genetic Diversity and Reassortments among Akabane Virus Field Isolates. Virus Res. 2007, 130, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.M. Orthobunyaviruses: Recent Genetic and Structural Insights. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Goli, J.; Clark, G.; Brauburger, K. Functional Analysis of the Bunyamwera Orthobunyavirus Gc Glycopro tein. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2483–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; van Mierlo, J.T.; French, A. Visualizing the Replication Cycle of Bunyamwera Orthobunyavirus Expressing Fluorescent Protein-Tagged Gc Glycoprotein. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 8460–8469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellert, J.; Aebischer, A.; Wernike, K. Orthobunyavirus Spike Architecture and Recognition by Neutralizing Antibodies. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Kohl, A.; Léonard, V.H.J. Requirement of the N-Terminal Region of Orthobunyavirus Nonstructural Protein NSm for Virus Assembly and Morphogenesis. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 8089–8099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endalew, A.D.; Morozov, I.; Davis, A.S. Virological and Serological Responses of Sheep and Cattle to Experimental Schmallenberg Virus Infection. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2018, 18, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhee, D.A.; Della-Porta, A.J. Biochemical and Serological Comparisons of Australian Bunyaviruses Belonging to the Simbu Serogroup. J. Gen. Virol. 1988, 69 Pt 5, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Botting, C.H.; Li, P. Bunyamwera Orthobunyavirus Glycoprotein Precursor Is Processed by Cellular Signal Peptidase and Signal Peptide Peptidase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 8825–8830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- .Roman-Sosa, G.; Brocchi, E.; Schirrmeier, H. Analysis of the Humoral Immune Response against the Envelope Glycoprotein Gc of Schmallenberg Virus Reveals a Domain Located at the Amino Terminus Targeted by mAbs with Neutralizing Activity. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman-Sosa, G.; Karger, A.; Kraatz, F. The Amino Terminal Subdomain of Glycoprotein Gc of Schmallenberg Virus: Disulfide Bonding and Structural Determinants of Neutralization. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 1259–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akashi, H.; Inaba, Y. Antigenic Diversity of Akabane Virus Detected by Monoclonal Antibodies. Virus Res. 1997, 47, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; Elankumaran, S.; Krishnamurthy, S. Loss of N-Linked Glycosylation from the Hemagglutinin-Neuraminidase Protein Alters Virulence of Newcastle Disease Virus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 4965–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braakman, I.; van Anken, E. Folding of Viral Envelope Glycoproteins in the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Traffic 2000, 1, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garry, C.E.; Garry, R.F. Proteomics Computational Analyses Suggest That the Carboxyl Terminal Glycoproteins of Bunyaviruses Are Class II Viral Fusion Protein (Beta-Penetrenes). Theor. Biol. Med. Model. 2004, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helenius, A.; Aebi, M. Intracellular Functions of N-Linked Glycans. Science 2001, 291, 2364–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Lappin, D.F.; Elliott, R.M. Mapping the Golgi Targeting and Retention Signal of Bunyamwera Virus Glycoproteins. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 10793–10802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Brauburger, K.; Elliott, R.M. Role of N-Linked Glycans on Bunyamwera Virus Glycoproteins in Intracellular Trafficking, Protein Folding, and Virus Infectivity. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 13725–13734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apellániz, B.; Huarte, N.; Largo, E. The Three Lives of Viral Fusion Peptides. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2014, 181, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plassmeyer, M.L.; Soldan, S.S.; Stachelek, K.M. Mutagenesis of the La Crosse Virus Glycoprotein Supports a Role for Gc (1066–1087) as the Fusion Peptide. Virology 2007, 358, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windhaber, S.; Xin, Q.; Lozach, P.-Y. Orthobunyaviruses: From Virus Binding to Penetration into Mammalian Host Cells. Viruses 2021, 13, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldan, S.S.; Hollidge, B.S.; Wagner, V. La Crosse Virus (LACV) Gc Fusion Peptide Mutants Have Impaired Growth and Fusion Phenotypes, but Remain Neurotoxic. Virology 2010, 404, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollidge, B.S.; Salzano, M.-V.; Ibrahim, J.M. Targeted Mutations in the Fusion Peptide Region of La Crosse Virus Attenuate Neuroinvasion and Confer Protection against Encephalitis. Viruses 2022, 14, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Kohl, A.; Li, P. Role of the Cytoplasmic Tail Domains of Bunyamwera Orthobunyavirus Glycoproteins Gn and Gc in Virus Assembly and Morphogenesis. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 10151–10160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plassmeyer, M.L.; Soldan, S.S.; Stachelek, K.M. California Serogroup Gc (G1) Glycoprotein Is the Principal Determinant of pH-Dependent Cell Fusion and Entry. Virology 2005, 338, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, N.S.; Mendonça, L.R.; Dias, M.V.S. ESCRT Machinery Components Are Required for Orthobunyavirus Particle Production in Golgi Compartments. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoa, R.R.; Calderita, G.; Arranz, R. Virus Factories: Associations of Cell Organelles for Viral Replication and Morphogenesis. Biol. Cell 2005, 97, 147–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salanueva, I.J.; Novoa, R.R.; Cabezas, P. Polymorphism and Structural Maturation of Bunyamwera Virus in Golgi and Post-Golgi Compartments. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 1368–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerrard, S.R.; Nichol, S.T. Characterization of the Golgi Retention Motif of Rift Valley Fever Virus G(N) Glycoprotein. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 12200–12210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Elliott, R.M. Golgi Localization of Hantaan Virus Glycoproteins Requires Coexpression of G1 and G2. Virology 2002, 300, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiropoulou, C.F.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Shoemaker, T.R. Sin Nombre Virus Glycoprotein Trafficking. Virology 2003, 308, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikkert, M.; Verschoor, A.; Kormelink, R. Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus Glycoproteins Exhibit Trafficking and Localization Signals That Are Functional in Mammalian Cells. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hover, S.; Charlton, F.W.; Hellert, J. Organisation of the Orthobunyavirus Tripodal Spike and the Structural Changes Induced by Low pH and K+ during Entry. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellert, J.; Aebischer, A.; Haouz, A. Structure, Function, and Evolution of the Orthobunyavirus Membrane Fusion Glycoprotein. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halldorsson, S.; Li, S.; Li, M. Shielding and Activation of a Viral Membrane Fusion Protein. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halldorsson, S.; Behrens, A.-J.; Harlos, K. Structure of a Phleboviral Envelope Glycoprotein Reveals a Consolidated Model of Membrane Fusion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7154–7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, G.V.; Israel, B.A.; Christensen, B.M. Role of La Crosse Virus Glycoproteins in Attachment of Virus to Host Cells. Virology 1991, 181, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Tsuda, T. Rapid Detection of Antigenic Diversity of Akabane Virus Isolates by Dot Immunobinding Assay Using Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1998, 5, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Kato, K.; Tohya, Y. Characterization of Temperature-Sensitive Akabane Virus Mutants and Their Roles in Attenuation. Arch. Virol. 2007, 152, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Beer, M. Schmallenberg Virus: To Vaccinate, or Not to Vaccinate? Vaccines 2020, 8, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollitt, E.; Zhao, J.; Muscat, P. Characterization of Maguari Orthobunyavirus Mutants Suggests the Nonstructural Protein NSm Is Not Essential for Growth in Tissue Culture. Virology 2006, 348, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, J.N. Bunyavirus mRNA Synthesis Is Coupled to Translation to Prevent Premature Transcription Termination. RNA 2007, 13, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, J.N.; Elliott, R.M.; Dunn, E.F. Segment-Specific Terminal Sequences of Bunyamwera Bunyavirus Regulate Genome Replication. Virology 2003, 311, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D. Advances in Molecular Pathogenesis and Pathogenic Mechanisms of Akabane Virus. Chin. J. Vet. Med. 2023, 43, 2389–2395. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, G.F.; Tien, P.; Liu, W. Bunyavirales Ribonucleoproteins: The Viral Replication and Transcription Machinery. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 522–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamamongood, T.; Aebischer, A.; Wagner, V. A Genome-Wide CRISPR-Cas9 Screen Reveals the Requirement of Host Cell Sulfation for Schmallenberg Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00752-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motlou, T.P.; Venter, M. Shuni Virus in Cases of Neurologic Disease in Humans, South Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangphoomi, N.; Takenaka-Uema, A.; Sugi, T. Akabane Virus Utilizes Alternative Endocytic Pathways to Entry into Mammalian Cell Lines. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2014, 76, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.I.M.; Rodrigues, A.H.; Silva, M.L. Oropouche Virus Entry into HeLa Cells Involves Clathrin and Requires Endosomal Acidification. Virus. Res. 2008, 138, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollidge, B.S.; Nedelsky, N.B.; Salzano, M.-V. Orthobunyavirus Entry into Neurons and Other Mammalian Cells Occurs via Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis and Requires Trafficking into Early Endosomes. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 7988–8001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardado-Calvo, P.; Bignon, E.A.; Stettner, E. Mechanistic Insight into Bunyavirus-Induced Membrane Fusion from Structure-Function Analyses of the Hantavirus Envelope Glycoprotein Gc. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Z.; Li, S.Q.; Wu, D.L. Study on diagnostic method of micro virus neutralization test for Akabane disease. Chin. J. Prev. Vet. Med. 2001, 1, 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, Y.; Eguchi, M.; Shimoji, Y. Two Akabane Virus Glycoprotein Gc Domains Induce Neutralizing Antibodies in Mice. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 84, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.W. Establishment of a Novel Double-Antigen Sandwich CLEIA and ELISA for Akabane Virus Antibody Detection and Preliminary Investigation of Infection Spectrum. Master’s Thesis, Guangxi University, Nanning, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, H.; Li, L.; Liao, D. Establishment and comparative evaluation of a competitive ELISA for Akabane virus antibody detection. Chin. J. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 41, 371–375. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, D.; Chen, B. Establishment of an indirect ELISA method for antibodies against Akabane disease virus based on recombinant truncated Gcaa407-614 protein. China Anim. Quar. 2019, 36, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.H.; Ye, L.L.; Xiao, Y. Preparation of monoclonal antibody to Akabane disease virus and establishment of c-ELISA antibody detection method. North China J. Agric. 2023, 38, 452–456. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, D.; Wei, F. Identification of a Broadly Neutralizing Epitope within Gc Protein of Akabane Virus Using Newly Prepared Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 295, 110123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Chen, D.; Deng, J. Baculovirus Expression and Monoclonal Antibody Development of Akabane Virus Gc aa465–704. Chin. Vet. J. 2023, 59, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, D. Efficient Soluble Expression and Antigenicity Identification of the Akabane Virus Gc 405aa–480aa Peptide Segment. Chin. J. Anim. Quar. 2019, 36, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, L.B.; Wang, J.L.; Li, J. Application of colloidal gold immunochromatography to the diagnosis of animal diseases. Adv. Anim. Med. 2010, 31, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wen, W.; Tang, T. A study on the detection of antibodies to red plume disease by spot immunogold osmosis. J. Econ. Zool. 2010, 14, 139–142, 153. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Chen, B.; Sha, C. Development of colloidal gold immunochromatographic test strips for red feather disease. China Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2009, 36, 42–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, H. Development of colloidal gold antibody test strips for bovine red plume disease. Feed. Res. 2023, 46, 123–125. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Ran, D.; Yin, X. A preliminary study on the rapid detection of indirect fluorescent antibody to Akabane disease virus. Adv. Anim. Med. 2005, 11, 82–84. [Google Scholar]
- Boshra, H.Y.; Charro, D.; Lorenzo, G. DNA vaccination regimes against Schmallenberg virus infection in IFNAR−/− mice suggest two targets for immunization. Antivir. Res. 2017, 141, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Mundt, A.; Link, E.K.; Aebischer, A.; Schlotthauer, F.; Sutter, G.; Fux, R.; Beer, M. N-Terminal Domain of Schmallenberg Virus Envelope Protein Gc Delivered by Recombinant Equine Herpesvirus Type 1 and Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara: Immunogenicity and Protective Efficacy in Cattle. Vaccine 2018, 36, 5116–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Aebischer, A.; Roman-Sosa, G. The N-Terminal Domain of Schmallenberg Virus Envelope Protein Gc Is Highly Immunogenic and Can Provide Protection from Infection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhao, D.; Li, C. The Role of Orthobunyavirus Glycoprotein Gc in the Viral Life Cycle: From Viral Entry to Egress. Molecules 2025, 30, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lan, X.; Liang, F.; Li, G.; Kong, W.; Wang, R.; Wang, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, K. Research Progress on the Gc Proteins of Akabane Virus. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080701
Lan X, Liang F, Li G, Kong W, Wang R, Wang L, Zhao M, Zhang K. Research Progress on the Gc Proteins of Akabane Virus. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(8):701. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080701
Chicago/Turabian StyleLan, Xiaolin, Fang Liang, Gan Li, Weili Kong, Ruining Wang, Lin Wang, Mengmeng Zhao, and Keshan Zhang. 2025. "Research Progress on the Gc Proteins of Akabane Virus" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 8: 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080701
APA StyleLan, X., Liang, F., Li, G., Kong, W., Wang, R., Wang, L., Zhao, M., & Zhang, K. (2025). Research Progress on the Gc Proteins of Akabane Virus. Veterinary Sciences, 12(8), 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080701




