Molecular Epidemiology of Brucella spp. in Aborted Livestock in the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
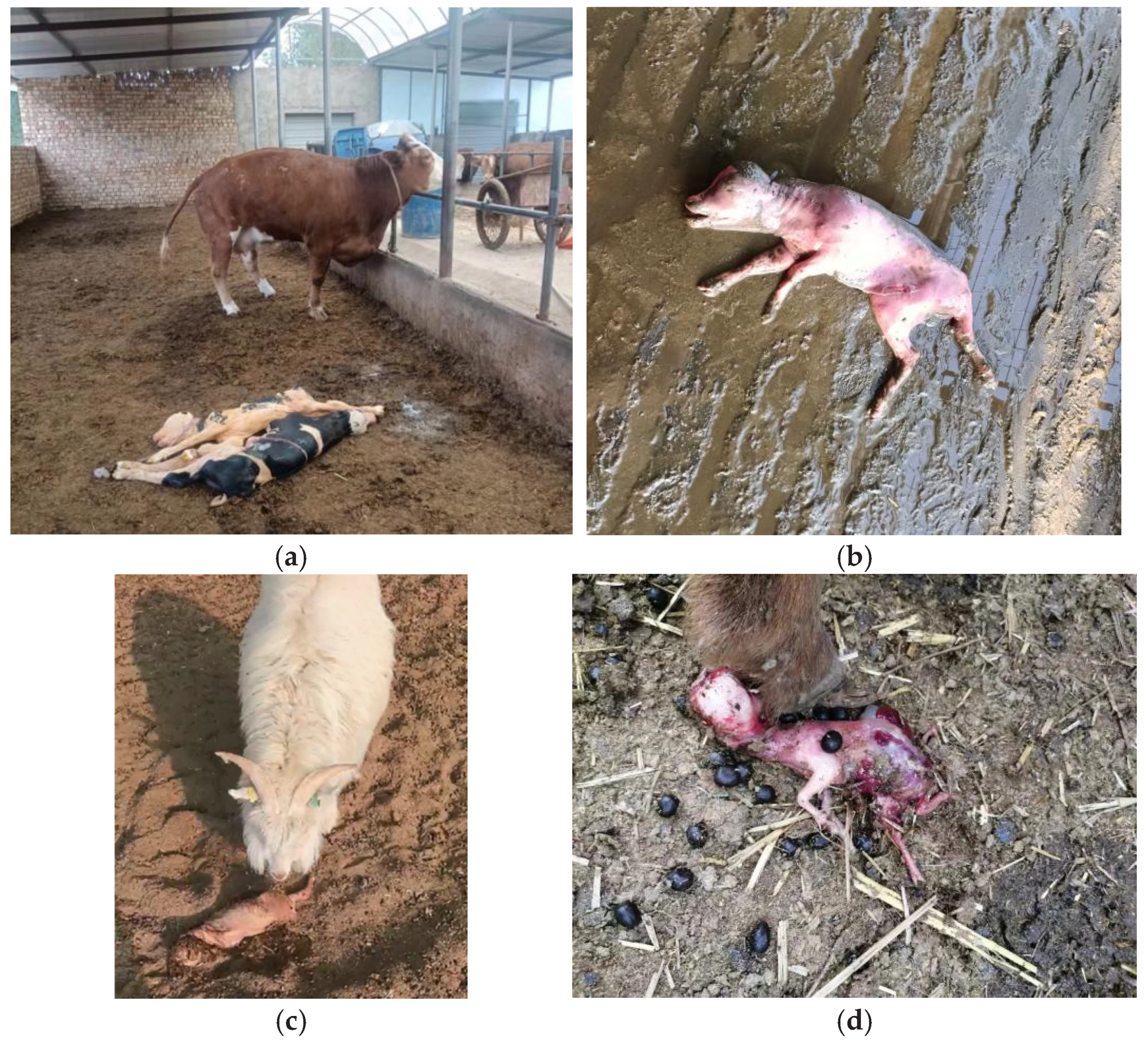
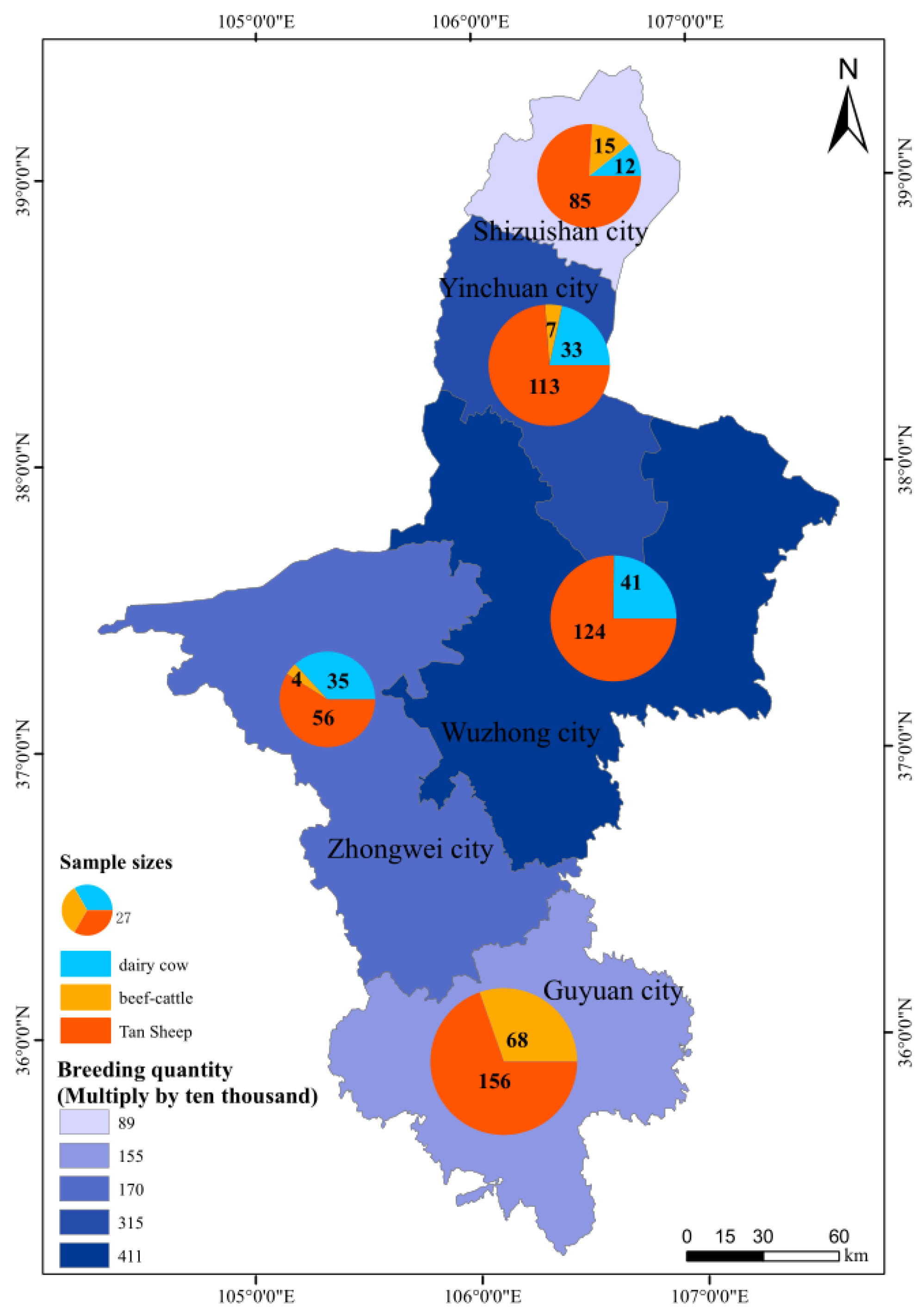
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Isolation and Culture of Brucella spp. from Aborted Samples
2.3. Molecular Analysis
2.3.1. DNA Extraction
2.3.2. Detection of Brucella spp. via qPCR
2.3.3. Identification of Brucella spp.
2.3.4. MLST Genotyping
2.3.5. MLVA Genotyping
2.4. Analysis of the Data
3. Results
3.1. Detecting Brucella spp. in Cattle and Sheep Abortion Tissues
3.2. Identification of Brucella spp.
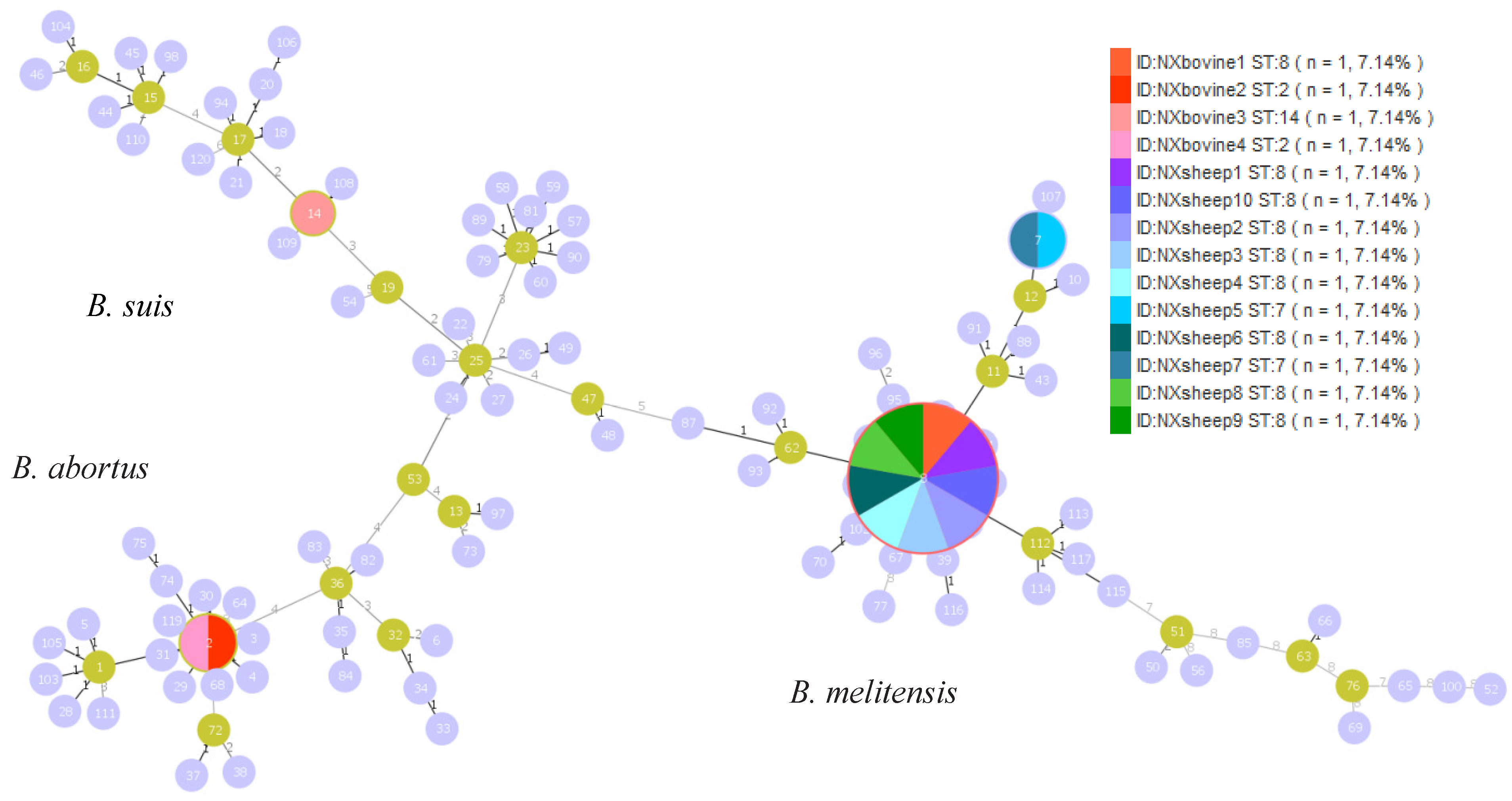
3.3. MLST Genotyping
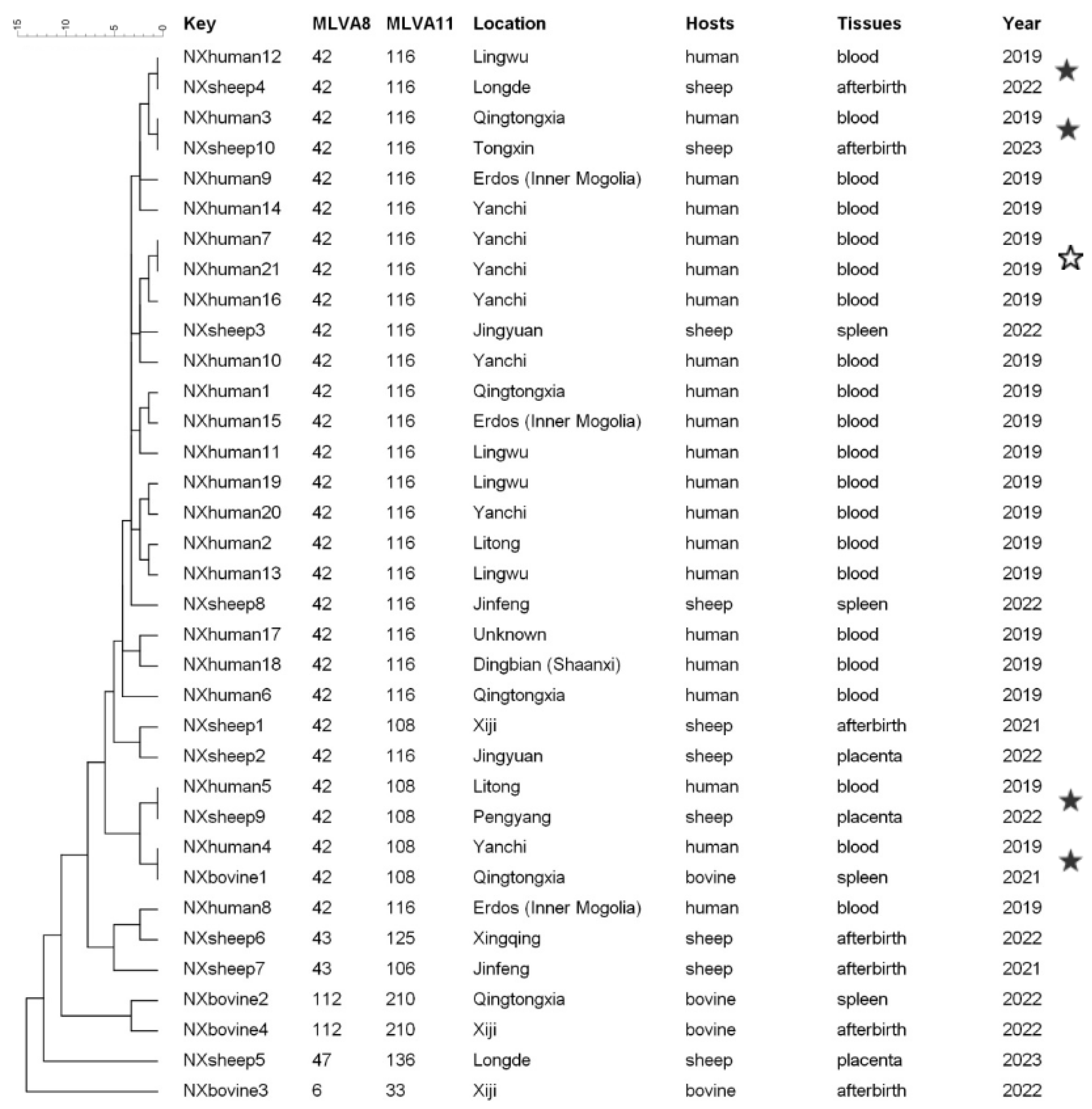
3.4. MLVA Genotyping
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ntivuguruzwa, J.B.; Kolo, F.B.; Mwikarago, E.I.; van Heerden, H. Characterization of Brucella spp. and other abortigenic pathogens from aborted tissues of cattle and goats in Rwanda. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clune, T.; Beetson, S.; Besier, S.; Knowles, G.; Paskin, R.; Rawlin, G.; Suter, R.; Jacobson, C. Ovine abortion and stillbirth investigations in Australia. Aust. Vet. J. 2020, 99, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfroid, J.; Cloeckaert, A.; Liautard, J.-P.; Kohler, S.; Fretin, D.; Walravens, K.; Garin-Bastuji, B.; Letesson, J.-J. From the discovery of the Malta fevers agent to the discovery of a marine mammal reservoir, brucellosis has continuously been a re-emerging zoonosis. Vet. Res. 2005, 36, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Gizaw, F.; Fekadu, G.; Alemayehu, G.; Kandi, V. Public Health and Economic Importance of Bovine Brucellosis: An Overview. Am. J. Epidemiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 5, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, S.; Qureshi, A.S.; Deeba, F.; Rashid, I.; Usman, M. Brucellosis in Cattle and Buffaloes. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2023, 2, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Spickler, A.R. Brucellosis. 2018. Available online: http://www.cfsph.iastate.edu/DiseaseInfo/factsheets.php (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Fereig, R.M.; Wareth, G.; Abdelbaky, H.H.; Mazeed, A.M.; El-Diasty, M.; Abdelkhalek, A.; Mahmoud, H.Y.A.H.; Ali, A.O.; El-tayeb, A.; Alsayeqh, A.F.; et al. Seroprevalence of Specific Antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum, and Brucella spp. in Sheep and Goats in Egypt. Animals 2022, 12, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.-R.; Xu, H.-J.; Wang, X.; Bu, Z.-Y.; Yao, T.; Zheng, Z.-R.; Sun, Y.; Ji, X.; Liu, J. Molecular characterization and antimicrobial susceptibility of human Brucella in Northeast China. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1137932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugaliyeva, A.; Daugaliyeva, S.; Kydyr, N.; Peletto, S. Molecular typing methods to characterize Brucella spp. from animals: A review. Vet. World 2024, 17, 1778–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, E. Retrospective and prospective perspectives on zoonotic brucellosis. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesner, O.; Riesenberg, K.; Biliar, N.; Borstein, E.; Bouhnik, L.; Peled, N.; Yagupsky, P. The Many Faces of Human-to-Human Transmission of Brucellosis: Congenital Infection and Outbreak of Nosocomial Disease Related to an Unrecognized Clinical Case. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, e135–e140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagupsky, P.; Morata, P.; Colmenero, J.D. Laboratory Diagnosis of Human Brucellosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 33, e00073-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tao, Z.; Yu, C.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X.; Ying, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, S. Molecular epidemiological characteristics of Brucella in Guizhou Province, China, from 2009 to 2021. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1188469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, D.-R.; Liu, X.; Di, D.-D.; Xiao, P.; Zhao, Z.-Z.; Xu, L.-Q.; Tian, G.-Z.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Fan, W.-X.; Cui, B.-Y.; et al. Genetic polymorphisms identify in species/biovars of Brucella isolated in China between 1953 and 2013 by MLST. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Ma, X.; Zhang, R.; Lü, J.; Zhou, P.; Liu, B.; Liu, T.; Ren, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. Epidemiological changes and molecular characteristics of Brucella strains in Ningxia, China. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1320845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Ali, Q.; Melzer, F.; Khan, I.; Akhter, S.; Neubauer, H.; Jamal, S.M. Isolation and identification of bovine Brucella isolates from Pakistan by biochemical tests and PCR. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2013, 46, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Gao, J.; Xian, R.; Liu, X.; Kuai, W.; Yin, C.; Fan, H.; Tian, J.; Ma, X.; Ma, J. Molecular epidemiology of Brucella abortus isolated from the environment in Ningxia Hui autonomous region, China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2024, 123, 105635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricker, B.J.; Halling, S.M. Differentiation of Brucella abortus bv. 1, 2, and 4, Brucella melitensis, Brucella-ovis, and Brucella suis bv. 1 by PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 2660–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whatmore, A.M.; Koylass, M.S.; Muchowski, J.; Edwards-Smallbone, J.; Gopaul, K.K.; Perrett, L.L. Extended Multilocus Sequence Analysis to Describe the Global Population Structure of the Genus Brucella: Phylogeography and Relationship to Biovars. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, M.; Sousa, A.; Ramirez, M.; Francisco, A.P.; Carriço, J.A.; Vaz, C.; Kelso, J. PHYLOViZ 2.0: Providing scalable data integration and visualization for multiple phylogenetic inference methods. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Dahouk, S.; Flèche, P.L.; Nöckler, K.; Jacques, I.; Grayon, M.; Scholz, H.C.; Tomaso, H.; Vergnaud, G.; Neubauer, H. Evaluation of Brucella MLVA typing for human brucellosis. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2007, 69, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, L.; Hu, G.; Ma, J.; Xiao, P.; Fan, W.; Di, D.; Tian, G.; Fan, M.; et al. MLVA Genotyping of Brucella melitensis and Brucella abortus Isolates from Different Animal Species and Humans and Identification of Brucella suis Vaccine Strain S2 from Cattle in China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loo, H.; Bogado Pascottini, O.; Ribbens, S.; Hooyberghs, J.; Opsomer, G.; Pardon, B. Enhancing bovine abortion surveillance: A learning experience. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 1766–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, S.; Zhang, H.; Deng, X.; Cui, B.; Shao, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Q.; Song, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; et al. Abortion and various associated risk factors in dairy cow and sheep in Ili, China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232568. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.B.; Dhand, N.K.; Gill, J.P.S. Economic losses occurring due to brucellosis in Indian livestock populations. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 119, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadar, M.; Tiwari, R.; Sharun, K.; Dhama, K. Importance of brucellosis control programs of livestock on the improvement of one health. Vet. Q. 2021, 41, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Sun, P.; Zhai, C.; Yuan, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, Y. Accessibility of the three-year comprehensive prevention and control of brucellosis in Ningxia: A mathematical modeling study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidary, M.; Dashtbin, S.; Ghanavati, R.; Mahdizade Ari, M.; Bostanghadiri, N.; Darbandi, A.; Navidifar, T.; Talebi, M. Evaluation of Brucellosis Vaccines: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 925773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kydyshov, K.; Usenbaev, N.; Berdiev, S.; Dzhaparova, A.; Abidova, A.; Kebekbaeva, N.; Abdyraev, M.; Wareth, G.; Brangsch, H.; Melzer, F.; et al. First record of the human infection of Brucella melitensis in Kyrgyzstan: Evidence from whole-genome sequencing-based analysis. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2022, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, M.; Ta, N.; Fang, M.; Mi, J.; Yu, R.; Luo, Y.; Cao, X.; Li, Z. Seroprevalence of human brucellosis and molecular characteristics of Brucella strains in Inner Mongolia Autonomous region of China, from 2012 to 2016. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.-Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.-F.; Xu, L.-Q.; Hu, G.-Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Piao, D.-R.; Qin, Y.-M.; et al. MLVA and MLST typing of Brucella from Qinghai, China. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2016, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-g.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H.-y.; Piao, D.-r.; Jiang, H.; Li, Z.-j. Investigation of the molecular characteristics of Brucella isolates from Guangxi Province, China. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronner, A.; Hénaux, V.; Fortané, N.; Hendrikx, P.; Calavas, D. Why do farmers and veterinarians not report all bovine abortions, as requested by the clinical brucellosis surveillance system in France. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbers, A.R.W.; Gorgievski-Duijvesteijn, M.J.; Zarafshani, K.; Koch, G. To report or not to report: A psychosocial investigation aimed at improving early detection of avian influenza outbreaks. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2010, 29, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, A.; Thompson, P.N.; Michel, A.L. Approaches to increase recovery of bacterial and fungal abortion agents in domestic ruminants. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2023, 90, e1–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, C.; Yang, C.; Wu, Y.; Di, J.; Bai, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, L.; Zhou, S.; Ma, L.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of Brucella spp. in Aborted Livestock in the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080702
Yin C, Yang C, Wu Y, Di J, Bai T, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Luo L, Zhou S, Ma L, et al. Molecular Epidemiology of Brucella spp. in Aborted Livestock in the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(8):702. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080702
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Cai, Cong Yang, Yawen Wu, Jing Di, Taotao Bai, Yumei Wang, Yuling Zhang, Longlong Luo, Shuang Zhou, Long Ma, and et al. 2025. "Molecular Epidemiology of Brucella spp. in Aborted Livestock in the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 8: 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080702
APA StyleYin, C., Yang, C., Wu, Y., Di, J., Bai, T., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Luo, L., Zhou, S., Ma, L., Wang, X., Zeng, Q., & Li, Z. (2025). Molecular Epidemiology of Brucella spp. in Aborted Livestock in the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. Veterinary Sciences, 12(8), 702. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080702





