Simple Summary
Micro- and Nanoplastics (MNPs), tiny particles found everywhere in the environment, pose an ever-growing threat as they reach the GITs of terrestrial and aquatic animals. These particles contaminate feed and water, enter the body, and spread to different organs, harming wildlife, livestock, and crops. This review aims to show how MNPs damage different organs of animals, reduce fertility, and also lead to feed shortages by stunting plant growth and reducing soil fertility. These small particles also carry notorious chemicals and lead to increased antimicrobial resistance by facilitating horizontal gene transfer (HGT) between bacteria, hence posing an increased risk of diseases to the livestock sector. This study underscores how these threats are linked to animals and environmental well-being. By demonstrating these risks, this review urges measures to curb plastic pollution and encourages further research to develop preventive and control strategies.
Abstract
Micro- and Nanoplastic (MNP) pollution is an emerging challenge globally, posing a significant threat to both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems worldwide. This review critically examines the sources, exposure routes, and impact of plastics, with particular focus on implications for the livestock sector. MNPs enter animals’ bodies primarily through ingestion of contaminated feed and water, inhalation, and dermal exposure, subsequently accumulating in various organs, disrupting physiological functions. Notably, MNPs facilitate the horizontal transfer of antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs), exacerbating the global challenge of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). In agricultural environments, sources such as organic fertilizers, wastewater irrigation systems, surface runoff, and littering contribute to soil contamination, adversely affecting plant growth and soil health, which in turn compromises feed quality and ultimately animals’ productivity. This review synthesizes current evidence demonstrating how MNP exposure impairs animal production, reproduction, and survival, and highlights the interconnected risks to food safety and ecosystem health. The findings call for the urgent need for comprehensive research under controlled conditions to underscore the fine details regarding mechanisms of MNP toxicity and to inform effective mitigation strategies. Addressing MNP pollution is crucial for safeguarding animal health, ensuring sustainable livestock production, and promoting environmental sustainability and integrity.
1. Introduction
Improper disposal, fragmentation, and/or degradation of plastics have increased the number MNPs in the environment, including both primary plastics intentionally produced at the micro- and nanoscale level and secondary plastics formed through the degradation of larger plastic items [1,2,3]. The emergence of these minute plastic particles has raised concerns due to their capacity to accumulate in water bodies and their potential adverse effects on aquatic organisms [4]. Therefore, their pollution has become an increasingly concerning global issue, along with its detrimental impacts on ecosystems [5]. While the effects of MNPs are well-documented, the presence and potential risks of MNPs in the environment have recently gained significant attention [6]. These small plastic particles, measuring less than 5 mm (MPs) and 100 nm (Nanoplastics) [7,8], have become pervasive contaminants in aquatic ecosystems, posing potential risks to aquatic organisms and overall ecosystem health.
Primary MPs are mass-produced for manufacturing and domestic applications, which include exfoliating facial scrubs, toothpaste, detergents, other personal care products, abrasive cleaning agents, plastic powder for molding, and synthetic clothing (nylon/polyester) [9,10], while paints, adhesives, electronics, etc., are responsible for NP release [11]. Secondary MNPs are formed by fragmentation of macroplastics (200–1000 µM) through shear forces [9,10], and account for 70–80% of all plastic released into the environment, while primary MPs contribute only 15–30% [12,13]. Additionally, synthetic microfibers are often the most commonly reported form of microplastics in environments, from soil to aquatic systems (e.g., oceans, rivers, shorelines, and lakes) [14,15]. Approximately 63% of textile fibers produced are synthetic (e.g., polyester, nylon), and over 42 million tons of synthetic fibers are produced each year by the clothing industry [16], with polyester dominating production (approximately 80%) [17]. As such, Boucher (2017) [18] estimated that of all primary microplastics in the world’s oceans, 35% arise from the laundering of synthetic textiles, an estimated 2–13 million tons per year globally. Without an instant mitigation strategy, plastic pollution in the oceans will be more than 6 million tons by 2040 [19]. Increased plastic accumulation in the environment is due to low degradation rates in addition to unsustainable use and improper disposal [20]. Although the impacts of these ever-present plastics are not fully understood, interest is shifting toward the plastics’ associated hazards in animals (especially food animals) and the environment.
MNPs enter the water bodies through domestic waste, sewage treatment plants (STPs), industrial effluents, stormwater, estuaries, riverine transport, surface runoff, wind currents, and disposal practices [21,22]. MNPs are present as fragments, pellets, fibers, films, granules, and Styrofoam that vary with surface–mass area ratios [23]. The chemical variations found in STPs include polyethylene (PE), polystyrene (PS), and polypropylene (PP), which tend to float, while polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are more likely to sink due to their density [24,25]. The presence of MNPs in the air, water, and food can cause ecotoxicological issues [26]. Research results indicated that MNPs fostered alterations in gene expressions, reduced fertilization efficiency [27], increased oxidative damage [28], and liver abnormalities in aquatic animals like zebrafish, rainbow trout, mollusks, mussels, oysters, etc. The hazardous effects of plastic particles have been proven in mice, sea birds, chickens, dogs, cats, and pigs [29,30]. In plants like wheat, corn, oats, tobacco, millet, etc., MNPs cause reduced biomass [31], decreased germination rate, and reduced growth [32]. MNPs also act as vectors to adsorb tenacious organic pollutants, trace metals, and harmful additives at rates that are multiple times higher than natural sediments [33]. The presence of MNPs in STPs impacts microbial communities, inhibits sludge hydrolysis, and accumulates acids [34].
MNPs indicate a higher risk because, due to their small size, these plastics are quickly able to penetrate cells and tissues. The complexity of MNP separation and identification, as well as their abundance in the environment, has been largely disregarded until now. As a result, the physical presence and health risks posed by MNPs may be underestimated. Although many studies have demonstrated the accumulation of MNPs in aquatic organisms, evidence for bioaccumulation and health implications in terrestrial livestock remains limited and mostly relies on extrapolation from laboratory models. Furthermore, most existing studies have rarely examined the complex interaction between MNPs and other environmental contaminants, nor do they address the long-term, low-dose exposures typical in agricultural settings.
This review aims to provide current perspectives on MNPs concerning (1) the occurrence of issues posed by MNP pollution, including their transmutation routes into animals via ingestion, inhalation, and hide/skin exposure, as well as indirect entry through feed; (2) the toxicokinetic and toxicodynamic of MNPs, highlighting their role as transporters for antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs), hazardous chemicals, and other pollutants; (3) the impact of MNPs on plant health, aquatic organisms, and livestock productivity, interconnecting human sources of plastic pollution, animals, and environmental health; (4) managemental strategies to mitigate MNPs through current understandings. By integrating recent advances on MNPS-mediated antimicrobial resistance and their effects on livestock health and productivity, this review provides novel perspectives that bridge environmental science and veterinary medicine.
2. Methodology
A rigorous search strategy was employed to retrieve articles from diverse databases. The literature search was conducted using the keywords “Micro-plastics” and “Nanoplastics”, “animals”, “human-based sources of plastics”, and “plastics in the environment” across multiple search engines, including Google Scholar, NCBI, Scopus, ScienceDirect, and PubMed. Sticking to the title, initially, 250 research and review articles were studied, and finally, 176 articles were included in this review. Use of the latest literature throughout the process remained our topmost priority. The synthesis of findings involved a thematic analysis, categorizing and summarizing key themes and trends identified across the selected studies, providing a coherent narrative of the current state of knowledge in the field after intense selection to divert the attention of readers toward this multidisciplinary issue.
3. Non-Polymeric Components in Plastics: Key Additives and Their Functions
Plastics are widely valued for their versatile mechanical and physicochemical properties, but many plastic products only achieve their specific functionalities through various additives. Flame retardants, stabilizers, and plasticizers are among the most commonly used, each serving a distinct purpose in enhancing the performance of plastics [35]. For instance, brominated flame retardants (BFRs), which are halogenated and can be either hydrophobic or reactive, are used to improve the fire resistance of plastic products. More than 75 different BFRs are currently in use, although some have been restricted due to their environmental and health impacts. As a result, newer types, such as brominated polymers and reactive BFRs, are gradually replacing older compounds like hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) [36]. Similarly, plasticizers play an essential role in improving the flexibility of plastics by increasing the distance between polymer chains. This loosens the dipolar forces, allowing the chains to slide against each other more easily. Phthalates are the most widely used plasticizers, making up about 90% of PVC plastic products [37]. Another critical category of additives is stabilizers, such as antioxidants, which prevent degradation by protecting polymer chains or eliminating hydroperoxides. Hydroperoxides can otherwise degrade into radicals that damage other polymer chains, compromising the integrity of the plastic [38,39]. While these additives are crucial for enhancing the properties of plastics, some of the substances used historically have been reevaluated due to their long-term impacts. Many of these are now classified as substances of very high concern (SVHCs) or persistent organic pollutants (POPs), earning them the designation of “legacy additives” due to their persistence in the environment and associated risks [35].
4. Accumulation of MPs in Terrestrial and Aquatic Environments and Associated Hazards in Animals
Concerns about the incorporation of MPs into feed have grown as the number of MPs in water bodies has increased. The effect of polymers or plastics starts from the lowest level of the food web itself in the aquatic environment. MPs are the same size as plankton and grains of other organic food materials, allowing them to be consumed by a variety of organisms with various feeding strategies [40]. Additionally, the differences in density and shape of these polymers affect their behavior [41] and distribution among different compartments (surface, water column, and sediment) of the aquatic environment, influencing their availability to organisms at various trophic levels [41]. The ingestion of MPs causes several physical and biological impacts on organisms. It disrupts feeding in algae and filter-feeding organisms [42], thereby reducing the weight of the organisms and thus leading to mortality and a decrease in fertility [43]. As discussed in the earlier section, apart from the physical impacts of ingested MPs alone on organisms, adverse health effects also occur from additives, absorbed contaminants, and so on, which are carcinogenic and even capable of endocrine disruption in organisms [44]. The ingestion could be due to a failure to distinguish MPs from prey, or it could be due to the intake of lifeforms from lower trophic levels that contain these particles [45]. MPs may also adhere directly to organisms [46]. In terms of food safety, MNPs are also an emerging threat, as these particles can eventually end up in the human food chain through fish and other kinds of aquatic and terrestrial food animals (Figure 1) [47].
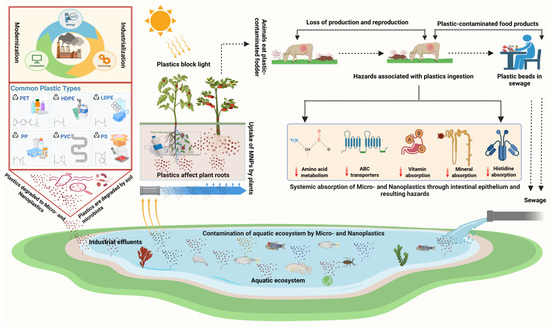
Figure 1.
The flow of MNPs through the terrestrial and aquatic environment. MNPs enter animal bodies by grazing, consuming feed containing plastics originating from human sources, e.g., plastic utensils, drinking water, personal care products, aquatic food items, and directly from plastic appliances. The entry of plastics into animal bodies leads to production- and reproduction-associated losses.
In livestock, mice, and poultry, MNPs can lead to enteritis, gut barrier dysfunction, gut microbiota dysbiosis, and reduced growth [48]. Similarly, hepatic inflammation, an altered cytokine profile (increased IL-6, TNF-α, and decreased IL-10), immune cell dysregulation, and metabolic disorders have been detected after the accumulation of MNPs, causing oxidative stress [48]. Reproductive toxicities and endocrine disruptions have been observed in rodents, aquatic species, and livestock, leading to reduced fertility, ovarian or testicular damage, and granulosa cell apoptosis [48,49]. Physiological damage and restricted growth have been detected in earthworms and chickens, with reduced gizzard volume and decreased foraging time due to physical obstruction and irritation by plastic particles [48]. Microbial contamination and the spread of antibiotic resistance have been reported in livestock and aquatic species, as MNPs act as vector for pathogens like bacteria, viruses, and fungi, which form biofilms on MNPs, facilitating microbial contamination and gene transfer [48,50]. Kidney, spleen, and tissue damage have been observed in many rodents and livestock species, leading to inflammation, fibrosis, loss of organ structure, and reduced tubular glands [49]. Neurological and behavioral effects have been observed in rodents and aquatic species, resulting in neuroinflammation, altered neurotransmitter levels, impaired behavioral cognition due to translocation of NPs across the blood–brain barrier, and oxidative stress [51]. Additionally, genotoxicity and epigenetic changes have been observed in rodents and aquatic species, characterized by DNA damage, altered gene expression, DNA hypomethylation, and oxidative damage [48,49]. Likewise, in different livestock, poultry, and aquatic species, accumulation of MNPS in muscle, liver, milk, eggs, and seafoods, can be a potential danger to humans through the food chain due to persistence of plastics and additives in tissues [52]. Metabolic disorders in rodents and livestock have been detected due to altered glucose and lipid metabolism, leading to increased blood glucose and cholesterol and resulting in the disruption of metabolic pathways via inflammation and oxidative stress [48].
5. Exposure Pathways and Associated Hazards of MNPs
5.1. Via Ingestion
Plastics are commonly found in atmospheric, terrestrial, and aquatic environments, and enter living organisms mostly via ingestion [53]. According to the study by Galloway (2015), ingestion is the major route for MPs entering into living organisms [54]. Particles may enter the digestive tract through contaminated feed and are absorbed by the gut lining, depending on their size and hydrophobicity. Smaller MNPs, particularly those in the nanoscale range, can pass through tight junctions among enteric epithelial cells [55]. Larger MNPs, however, are absorbed through endocytosis, a process in which cells swallow the particle. After ingestion, MNPs result in enteritis, increased gut permeability, increased oxidative damage, gut microbial dysbiosis, metabolic dysfunctions, genotoxicity, and immunotoxicity [56,57,58,59]. It has been reported that MPs, if ingested, may accumulate and cause localized toxicity by triggering and/or increasing immunological responses, thereby weakening the body’s defenses against infections and changing how energy reserves are used [60,61]. In aquatic organisms, particles are accumulated in the gill, liver, intestine, mantle, and stomach of bivalves through ingestion. The aggregation of MPs stimulates oxidative stress and imbalance of the antioxidation system [62]. The literature indicates that exposure to MPs could significantly induce inflammatory reactions by activating the NF-κB pathway in zebrafish larvae (Table 1) [63].

Table 1.
Differences in hazards between animals and humans concerning exposure routes.
5.2. Via Inhalation
In living organisms, inhalation of MNP-contaminated aerosols leads to their entry into the respiratory tract [69]. Animals inhale MPs from a variety of sources, including environmental dust (about 272 MPs because of polluted air), industrial emissions, and synthetic garment fibers [61]. The size and shape of airborne MPs determine where they are deposited in the respiratory system. For instance, larger particles are more likely to accumulate in the top airways, where mucociliary clearance mechanisms transport them to the GIT through swallowing [70]. On the other hand, smaller MNPs can penetrate alveolar surfaces, ultimately enter the circulation, and be transported to the whole body. Outdoor MNPs can originate from the disintegration of bigger plastic trash owing to UV radiation, weathering, and physical processes, and become airborne due to wind propagation [71]. Thus, previous investigations indicated that MNP inhalation can lead to severe respiratory disorders (Table 1).
5.3. Through Dermal Exposure
However, although inhalation is a well-documented exposure route, research studies have proved the possibility of dermal exposure through direct contact with sources such as agricultural waste, textiles, or contaminated water and personal care products [70,74]. Injured skin or extended exposure to specific environmental conditions increases the chances of MNPs permeating skin barriers [75]. Dermal absorption depends upon particle size, surface qualities, and shape, as well as the cutaneous barrier’s health and integrity. In general, larger MNPs (>100 nm) are less likely to penetrate the stratum corneum. Smaller MNPs, particularly of size (<100 nm), can penetrate hair follicles and pass through damaged skin to reach deeper layers [76]. According to a study by Raszewska-Famielec (2022), smaller MPs or NPs may concentrate within hair follicles, potentially resulting in prolonged skin exposure and deeper penetration into the dermal layer [77]. Smaller particles can pass through the intercellular lipid matrix or enter straight through epidermal keratinocytes, especially if they are injured [78]. Microplastics that pass through the skin can aggregate on the surface or migrate to lymph nodes; however, there is no compelling evidence that MNPs absorbed dermally enter systemic circulation in large proportions [74], and further research is needed to estimate their quantified absorption. MPs are not only responsible for physical damage (erosion, ulcers, fissures) but are also vectors for infectious pathogens. For example, Vibrio spp., Arcobacter spp., Clostridium perfringens, Enterobacter spp., Escherichia coli, and Helicobacter spp. have been identified on PE MPs in freshwater that come in contact with the dermal barrier (Table 2) [79].

Table 2.
Effects of MNPs exposure on aquatic organisms and associated details.
6. Influence of MNPs in Propagation of AMR
Recent studies have highlighted the role of MNPs in enhancing the mobility and transfer of ARGs and metal resistance genes (MRGs) in ecosystems, causing the enhanced spread of AMR. Any agent or situation promoting AMR is considered a threat to global public health. A growing body of scientific evidence correlates the elevation of AMR indicators (e.g., HGT, the abundance of ARGs, MGEs) with the presence of persistent MNPs in an ecosystem. However, elaborated information on underlying mechanisms and experimental evidence on the interaction of MNPs with microbes causing the propagation of AMR is still naïve [94,95,96]. The conjugative transfer or HGT of antibiotic resistance genes in E. coli is reported to be highly dependent on the size of MPs [97]. UV-aged PS-MPs were found to increase the HGT of ARGs in E. coli [98]. MNPs were reported to promote the propagation of ARGs in phosphorus-removing bacteria and induce microbial community shift [99]. MPs also demonstrated selective inhibition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and enrichment of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria, leading to partial nitrification [100]. The reports on the interaction of MNPs and microbial communities to date strongly show that MNPs could greatly influence the microbial resistome or changes in the resistomes of environmental niches. Several other reports provide evidence that changes in the resistome profile of different groups of microbes due to the presence of MNPs could further enhance the overall propagation of AMR genes in environmental compartments [101,102].
7. MNPs as “Shuttle Trojan Horses” and Their Associated Risks
Due to their surface characteristics, MPs act as “Shuttle Trojan horses” which carry toxic chemicals such as bisphenol A (BPA), different toxic monomers, additives used in plastic manufacturing, infectious agents, parasites, and absorbed/adsorbed contaminants [103]. Toxic chemicals associated with MPs may be heavy metals like arsenic (As), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), cadmium (Cd), lead (Pb), and chromium (Cr); organic pollutants, polychlorinated biphenyls, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), organic pesticides, antibiotics, and oligomers; and also microorganisms such as fungi, diatoms, algae, and pathogenic bacteria that are attached to MNPs [104].
MPs enter the ocean as virgin particles, and then microbial biofilms develop on them with time [105]. Aquatic biofilms (containing fish pathogens, Aeromonas spp., E. coli, etc.) on MPs serve as reservoirs of antibiotics and stimulate horizontal transfer of clinically important ARGs like sul1, tetA, tetC, tetX, ermE, macB, and blaTEM that are present on MPs [106]. Plastic-associated pollutants enter the tissues of different food animals and later become a threat to food safety [107]. Microplastics carry heavy metals and infectious agents (e.g., bacterial, viral, etc.) that cause GIT disturbances, pulmonary neoplasms, obesity, respiratory distress, birth anomalies, cardiovascular disorders, and asthma [108]. For example, Cd promotes cell apoptosis, damage to nucleic acid, skeletal and pulmonary damage, alterations in calcium metabolism, and the formation of renal stones. MPs and associated heavy metals (Cd) affect plant growth and root symbiosis, and also negatively affect soil biodiversity, an indicator of soil fertility [109]. Similarly, Pb can also damage muscles, the brain, and kidneys, and even prove fatal. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) adsorbed by MPs cause cancer, developmental anomalies, and genetic alterations [110].
8. MPs Affect Plants, Leading to Shortage of Feed for Animals
Possible Sources of MPs in Agricultural Soil and Influences of MPs on Soil Structure, Function, Fertility, Soil Microbiota, and Ultimately Plants
Organic fertilizer is eco-friendly and a reservoir of soil nutrients [111]. Treated or composted animal dung contains MPs. For example, 150 MPs were detected in 1 kg of pig excrement (14,720 ± 2), 468 plastic particles were detected per kg of chicken manure compost, and 144 particles per kg of goat manure fertilizer were detected [112]. Pesticides used in plastic bottles, plastic processing and recycling plants [112,113], organisms such as earthworms (which play a role in the plastic breakdown) [113], atmospheric deposition of airborne MPs [114], irrigation by wastewater, littering and runoff from the plastic-contaminated surface [113], and the breakdown of the plastic mulch implemented over agricultural lands all add MPs into the soil, alongside other pollutants, e.g., heavy metals [115]. The migration of MPs downward into deeper soil enhances the likelihood of groundwater contamination with MPs and related compounds (Figure 2) [116].
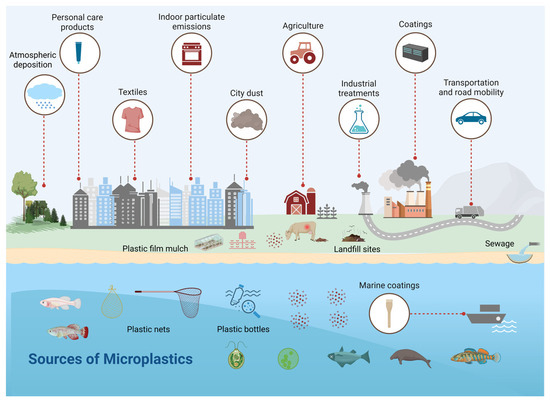
Figure 2.
This figure illustrates the flow of MNPs from terrestrial to aquatic ecosystems. Plastics ingested by grazing/indoor animals are hazardous, leading to decreased growth and production and reproductive disorders. Also, through animal food products, these plastic fragments are transferred to consumers through the food chain. Plastics from factories, landfills, human sewage, and agricultural and livestock production systems ultimately enter aquatic ecosystems and then again enter the terrestrial food chain, and this cycle continues.
The roots of plants can absorb MPs, particularly nanoparticles, transferred along the xylem route to edible parts. Polystyrene particles were found scattered throughout the leaf parenchyma [117]. About 80 g out of 400 g of fruit and vegetables that are consumed daily in the developed world contain MPs, which bio-persist and translocate in plants (Figure 3) [32]. In the European Union, 65.5% of people under the age of 15 consume vegetables and fruits every day, consuming high doses of MPs daily. This can be a cause for concern [118].
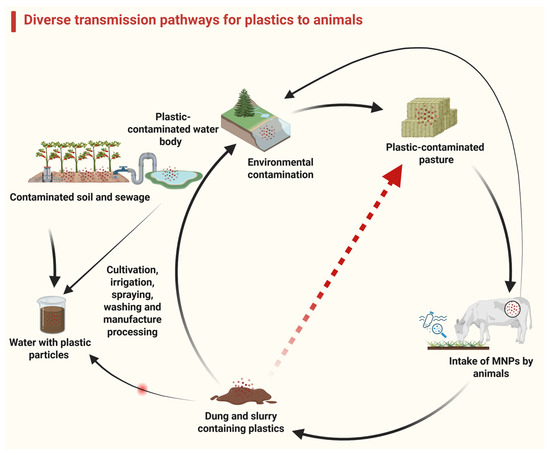
Figure 3.
This figure illustrates the various transmission routes of microplastics (indicated by arrows) between animals and the environment, highlighting the role of agricultural practices. Disrupting these transmission pathways can prevent plastic-associated damage in animals.
Microplastics in agricultural soil increase soil porosity [119], which accelerates the evaporation rate, inhibiting the growth of plants [120]. The high-density polyesters effectively decreased the soil’s pH [31]. Microplastics can disturb the diversity and function [121] of the microbial soil community and have a deleterious influence on other soil-based microorganisms [122]. Microplastics inhibit the activity of soil enzymes, for instance, urease, catalase, phenol oxidase, and fluorescein diacetate hydrolase [123]. Higher levels of MPs (28% w/w) and discharge of dissolved organic compounds such as carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus [123] lead to a decline in overall agricultural output.
Significant adverse effects of MPs in plants like wheat (Triticum aestivum), ryegrass (Lolium perenne), fava bean (Vicia faba) (reduction of growth, genotoxic and oxidative damage via PS particles of 100 nm) [124], cress (Lepidium sativum), and spring onion (Allium fistulosum) have been observed [125]. Microplastics and biodegradable MPs (BMPs) potentially prevent plant germination and root and aerial plant development [126].
Depending upon particle size, microplastics produce considerable changes in plant biomass, tissue constituents—such as moisture content, leaf nitrogen level, carbon–nitrogen ratio—root characteristics—like the length of root, mean root dimensions, root tissue stiffness—leaf diameter, and chlorophyll, thereby affecting photosynthetic performance and crop yield [127]. Microplastics as carriers of pathogens and toxic substances negatively impact the development of plant roots and rhizodeposition [128]. Microplastics promote the development of Hieracium and Calamagrostis, whereas Holcus and Festuca’s shoot masses have been reduced by microfibers by up to 78% and 51%, respectively (Table 3) [129]. Therefore, further investigation is still needed to determine the negative effects of microplastics on plants, and ultimately on animals.

Table 3.
Toxic effects of MNPs on terrestrial plants and associated details.
9. Emerging Challenges Associated with MNPs
MNPs are regarded as increasingly relevant particles in air pollution due to their inhalation and interaction with harmful micropollutants, including heavy metals, for instance, Pb, Hg, and Cd [147]. MNPs in the atmosphere may act as important carriers for microorganisms, making their relationship more complex [148]. The interaction of MNPs with pathogens (e.g., bacteria) might exacerbate their harmful effects on living organisms [149]. MNPs have high potential to serve as key carriers of harmful microorganisms, including bacterial pathogens such as antibiotic-resistant bacteria or viruses, which makes them carriers of such diseases [150]. Furthermore, MNPs may accumulate pollutants on their surface, such as hydrophobic organic pollutants, from their surroundings. Based on Lomonaco et al.’s (2020) research work [151], photochemical processes degrade plastic trash, releasing hazardous volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the atmosphere. This release constitutes a severe hazard linked to the deterioration of plastic waste in the environment.
Plastics’ influence is now recognized as a severe health concern, through two non-exclusive processes. Firstly, MNPs can cause direct neurotoxicity. MNPs can directly affect the central nervous system by percolating through the blood–brain barrier [152], which generates neuronal lesions, decreases synaptic esterases, and fosters proteinopathy and amyloidopathy [153]. Secondly, MNPs can cause indirect neurotoxicity by dysbiogenic impacts, which most likely disturb the microbiota–gut–brain axis (mGBA) [154]. However, the ecotoxicological impact of MNPs has never been investigated in any of these neuropathologies.
MNPs’ impacts on reproduction have also been extensively investigated across many life stages and sexes, with negative consequences such as decreased gametogenesis, reproductive organ damage, altered levels of hormones, and transgenerational impacts [155]. MNPs affect gametogenesis and the development of sperm and eggs. For instance, research investigations on marine invertebrates and small fish models such as zebrafish (Danio rerio) demonstrate that MNP exposure can cause structural defects in reproductive cells that result in impaired sperm motility and egg production [155]. Researchers attribute these problems mostly to oxidative damage caused by MPs, which destroy cell membranes and DNA in gametes, potentially leading to reduced fertility [156]. MNPs may affect hormonal balance by interfering with the endocrine system, particularly if they absorb endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) [157]. Studies have indicated that polystyrene MPs impair hormone production, resulting in altered amounts of estrogen, testosterone, and other reproductive hormones in animals [158]. Low levels of these hormones in mammals can affect spermatogenesis, folliculogenesis, and successful fertilization. Some EDCs have been associated with premature puberty, limited fertility, and unsuccessful pregnancies (Table 4) [159].

Table 4.
Adverse effects of MNPs on different terrestrial animals and associated case details.
10. Strategies for Reducing MNPs and Their Potential Hazards
Currently, there are critical initiatives for reducing the prevalence of MNPs and their associated hazards, including technological alternatives and preventative management. Advanced options for eliminating MNPs from the environment often incorporate physical, chemical, and biological technology.
10.1. Eco-Sustainability Management Approaches for Reducing Plastic Waste
To reduce ecological damage and health risks, the easiest and most efficient approach is to limit MNP sources. However, the disposal of plastic-based waste is becoming important due to insufficient legislation on long-term disposal methods. To reduce the consequences of MNPs, it is extremely important to effectively handle plastic waste in a cost-effective and environmentally responsible manner [178]. Waste handling can be facilitated by the 4Rs, “Reuse-Reduce-Recover-Recycle”, to reduce plastic pollution [179]. Using upcycling technology, it is feasible to remove MNPs from the waste stream while also creating new goods with greater value and usage [180]. Plastic bottles, for example, can be turned into bird feeders, planters, or structural construction elements. This sort of upcycling enables distinctive and environmentally beneficial artistic creations. Furthermore, Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based systems are now beneficial for handling and decreasing plastic waste and lessening carbon footprint [181].
Numerous works highlight the circular economy as the most effective and viable approach to minimizing plastic pollution and reducing the possible impact of MNPs on living organisms [182]. The circular economy method can prove crucial in boosting an in-depth understanding of optimizing reduction tactics and reducing the harmful environmental impacts of MNPs [183]. Furthermore, life cycle assessment (LCA) concepts are a widely employed approach for identifying and evaluating ecological and biological effects [184]. They are tools that help in environmentally friendly decision-making and proposing alternative methods for protecting habitats, animals, and human well-being. Furthermore, the focus should be on promoting consumer environmental consciousness and education. A continuous approach that requires public understanding and instruction of the MNPs issue and possible responses is needed to accomplish the common aim of reducing plastic waste at its sources or preventing plastic pollution [185].
10.2. Technical Ways to Increase the Elimination Efficiency of MNP-Contaminated Waste Streams
MNP elimination techniques include biodegradation, composting, recycling, and thermal processing. Biodegradation uses enzymes and microorganisms to break down and mineralize MNPs [183]. After mineralization, the plastic derivatives are transported into the cytoplasm of microbes and further metabolized, yielding chemicals such as N2, CO2, and H2O. Additionally, numerous enzymes have been widely employed to degrade synthetic MP polymers [186]. Overall, biodegradation techniques are usually an effective way to reduce MNP levels while needing minimal energy input and showing potential performance [183]. Many studies have proven the degradability of MNPs by biological species such as fungi and bacteria [187], algae, earthworms [188], and snails [189]. The findings also demonstrate that hyper-thermophilic bacteria strains play an important role in MP biodegradation during hyper-thermophilic composting (hTC), indicating that hTC has the potential to be used to remove MPs [190]. This demonstrates that microorganisms, including fungi, bacteria, mealworms, algae, etc., can be used to biodegrade MPs and successfully reduce plastic contamination.
11. Suggestions for Setting an Animal Health Hazard Assessment Index for MNP Exposure
Developing a robust animal health hazard assessment index for MNP exposure necessitates an interdisciplinary approach, integrating exposure science, toxicokinetics, toxicodynamics, and environmental detection. Based on the current literature, the following suggestions are integral:
- Multi-Route Exposure Quantification
Exposure evaluation should distinctly consider the three key routes (inhalation, ingestion, and dermal contact), as each has distinct absorption and toxicological profiles (Table 1). Hence, exposure doses can be quantified by combining environmental monitoring data (quantities of MNPs in water, feed, soil, and air) with species-specific behavioral and ecological information [52].
- Species-Targeted Toxicokinetics and Toxicodynamics
The index should include species-specific variations in absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of MNPs. Physiological characteristics such as gut morphology, respiratory architecture, and dermal barrier integrity significantly affect MNP uptake and systemic effects (Table 1) [52].
- Effect-Based Biomarkers
These include bioindicators that reflect oxidative damage, inflammatory cascades, immune dysfunction, reproductive issues, and metabolic disruptions. Molecular markers, such as gene expression, that vary in stress response and detoxification pathways, can enhance sensitivity and specificity in hazard detection and quantification [49,191].
- Bioaccumulation and Trophic Transfer
This includes evaluating the accumulation of MNPs and linked chemicals in animal tissues, as well as potential biomagnification through food webs, which can worsen hazard severity [49,52,191].
- Chemical Additives and Adsorbed Pollutants
Researchers should integrate the potential hazards associated with plastic additives (e.g., bisphenols, phthalates) and adsorbed foreign contaminants (pathogens, heavy metals) carried by MNPs, as these can exaggerate toxicity [49].
- Composite Hazard Scoring System
Researchers should develop a weighted scoring system that integrates exposure dose, toxicological endpoints, and species sensitivity to generate an overall hazard index. This system should be adaptable to different environmental contexts and animal species [192].
- Probabilistic Risk Assessment
The index should apply probabilistic models to incorporate variability and uncertainty in exposure and response, enhancing the reliability and robustness of hazard assessments [193,194].
- Chronic and Cumulative Effects
Researchers should include long-term, low-dose exposures and cumulative impacts with other environmental stressors to better reflect real-world scenarios and chronic health risks [194].
12. Conclusions and Future Research Considerations
This review identifies MNPs as an important consideration and discusses their detrimental impact on plants, and aquatic and terrestrial animals. It also explains the mechanisms of potential MNP influences via ingestion, inhalation, and dermal routes, as well as future challenges and opportunities for MNP waste management. The study of MNP pollution has attracted global interest, and some progress has been made in certain areas. While there are still many difficulties with this growing pollution, this review’s findings provide current and thorough information regarding the properties of MNPs, which may be used to promote future research trends. Based on these findings, various strategies, such as filters, barriers, and clean-up efforts, have been developed to mitigate macro- and microplastic pollution. However, no established methods currently exist for addressing nanoplastic pollution. This represents a critical gap in the literature, emphasizing the need for further research and innovative solutions.
At present, MPs pose an imminent danger to the environment. Studies on exposure-related toxicity in conjunction with harmful chemicals are critical for comprehending MP characteristics and establishing a mitigation plan. Sensitivity and toxicological impacts on aquatic and freshwater creatures are characterized by exposure dosage as either extremely high (resulting in lower reproductive output, organ damage, and mortality) or low (resulting in behavioral changes over time). According to reports, toxicity research for people is still ongoing, but plants and animals have received less attention. It is suggested that if a study conducted an evaluation of co-exposure to MNPs and chemical pollutants, the experimental setup must enable some form of contrast between individual and combination hazards [185], because comparing these studies is still challenging.
It is critical to design easy, precise, effective, and inexpensive techniques. A more extensive study is required to control MNP pollution and assist local governments with making decisions and associated policies. For example, screening roadways and residential dust should be regarded as a low-cost strategy for MNP contamination in residential regions. As previously noted, additional efforts must be taken to establish international standards, attempt to record health impact assessments, and develop policy frameworks that may be assessed in the surrounding air.
Finally, regulations for plastic prevention, waste stream control, and alternative eco-friendly resources should be promoted. To effectively tackle the environmental implications of MNPs, it is critical to set legislation and standards governing plastic use and dumping. Studies can give scientific data that will encourage the formulation of these rules and ensure that they are centered on environmental sustainability and health concerns. MNPs are capable of being biodegraded and transformed into CO2 and H2O, hence protecting ecosystems. It is important to establish an important cycle that lowers MNPs release at sources. In terms of the circular economy, the establishment of integrated techniques to transform MPs into microbial polymers, which may be used and processed by microorganisms into innovative biopolymers, is worth investigating [183,195,196,197,198]. However, it should be noted that such technologies are still in the early developmental stages and far from being commercialized. Recent studies highlight the technical and economic hurdles that crucially must be overcome before these processes can be implemented at a commercial scae [187].
Recent studies suggest that MNPs can lead to alterations in the gut microbiota of animals [57,58], potentially affecting enteric absorption and immune response, an area that remains largely unexplored currently. In addition, the role of MNPs in facilitating the transfer of antimicrobial resistance genes within livestock is an emerging concern with significant implications in both animals and the public health sector, so it can be focused on in future research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A. and K.L.; methodology M.A. and K.L.; software, M.A. and K.L.; validation, M.A. and K.L.; formal analysis, M.A. and K.L.; investigation, M.A., K.L. and C.X.; resources, K.L.; data curation, K.L. and M.A.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A. and K.L.; writing—review and editing, M.A., C.X. and K.L.; visualization, K.L., M.A. and C.X.; project administration, K.L.; funding acquisition, K.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32102692).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study because this study was a comprehensive review.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Habumugisha, T.; Zhang, Z.; Ndayishimiye, J.C.; Nkinahamira, F.; Kayiranga, A.; Cyubahiro, E.; Rehman, A.; Yan, C.; Zhang, X. Evaluation and Optimization of the Influence of Silver Cluster Ions on the MALDI-TOF-MS Analysis of Polystyrene Nanoplastic Polymers. Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, A.-K.; Brehm, J.; Völkl, M.; Jérôme, V.; Laforsch, C.; Freitag, R.; Greiner, A. Disentangling Biological Effects of Primary Nanoplastics from Dispersion Paints’ Additional Compounds. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 242, 113877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Singh, E.; Singh, S.; Pandey, A.; Bhargava, P.C. Micro- and Nano-Plastics (MNPs) as Emerging Pollutant in Ground Water: Environmental Impact, Potential Risks, Limitations and Way Forward towards Sustainable Management. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 459, 141568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Huang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Habumugisha, T.; Yan, C.; Shaheen, U.; Zhang, X. Nanoplastic Contamination: Impact on Zebrafish Liver Metabolism and Implications for Aquatic Environmental Health. Environ. Int. 2024, 187, 108713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allouzi, M.M.A.; Tang, D.Y.Y.; Chew, K.W.; Rinklebe, J.; Bolan, N.; Allouzi, S.M.A.; Show, P.L. Micro (Nano) Plastic Pollution: The Ecological Influence on Soil-Plant System and Human Health. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashed, A.H.; Yesilay, G.; Hazeem, L.; Rashdan, S.; AlMealla, R.; Kilinc, Z.; Ali, F.; Abdulrasool, F.; Kamel, A.H. Micro-and Nano-Plastics Contaminants in the Environment: Sources, Fate, Toxicity, Detection, Remediation, and Sustainable Perspectives. Water 2023, 15, 3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habumugisha, T.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, C.; Yan, C.; Zhang, X. Uptake, Bioaccumulation, Biodistribution and Depuration of Polystyrene Nanoplastics in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habumugisha, T.; Zhang, Z.; Ndayishimiye, J.C.; Nkinahamira, F.; Uwizewe, C.; Cyubahiro, E.; Rehman, A.; Yan, C.; Zhang, X. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Accumulation and Biodistribution of Polystyrene Nanoplastics in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) via Artificial Freshwater. Environ. Sci. Nano 2023, 10, 2141–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, B.R.; Kopperi, H.; Venkata Mohan, S. Micro/Nano-Plastics Occurrence, Identification, Risk Analysis and Mitigation: Challenges and Perspectives. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2022, 21, 169–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Ren, S.-Y.; Ni, H.-G. Incidence of Microplastics in Personal Care Products: An Appreciable Part of Plastic Pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, Y.; Mir, A.R.; Zieliński, P.; Hayat, S.; Bajguz, A. Microplastics and Nanoplastics: Source, Behavior, Remediation, and Multi-Level Environmental Impact. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 356, 120618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, C.M.; Browne, M.A.; Halpern, B.S.; Hentschel, B.T.; Hoh, E.; Karapanagioti, H.K.; Rios-Mendoza, L.M.; Takada, H.; Teh, S.; Thompson, R.C. Classify Plastic Waste as Hazardous. Nature 2013, 494, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannabiran, K. A Critical Review on Effect of Macro, Micro and Nanoplastics Pollution on Human Health and Their Control Measures. Mater. Int. 2024, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.; Fauziah, S. Distribution and Importance of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Review of the Sources, Fate, Effects, and Potential Solutions. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napper, I.E.; Baroth, A.; Barrett, A.C.; Bhola, S.; Chowdhury, G.W.; Davies, B.F.R.; Duncan, E.M.; Kumar, S.; Nelms, S.E.; Niloy, M.N.H. The Abundance and Characteristics of Microplastics in Surface Water in the Transboundary Ganges River. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 116348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, S.A.; Liu, J.; Tesoro, A.G. Transport and Fate of Microplastic Particles in Wastewater Treatment Plants. Water Res. 2016, 91, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krifa, M.; Stevens, S.S. Cotton Utilization in Conventional and Non-Conventional Textiles—A Statistical Review. Agric. Sci. 2016, 7, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Friot, D. Primary Microplastics in the Oceans: A Global Evaluation of Sources; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson, M. Whither Plastics?—Petrochemicals, Plastics and Sustainability in a Garbage-Riddled World. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2019, 56, 101229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Moore, C.J.; vom Saal, F.S.; Swan, S.H. Plastics, the Environment and Human Health: Current Consensus and Future Trends. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2153–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, R.; Mason, S.A.; Stanek, S.K.; Willis-Norton, E.; Wren, I.F.; Box, C. Microplastic Contamination in the San Francisco Bay, California, USA. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Li, L.; Zhao, X.; Song, K. An Evaluation of the Effects of Nanoplastics on the Removal of Activated-Sludge Nutrients and Production of Short Chain Fatty Acid. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 148, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Nor, N.H.M.; Hermsen, E.; Kooi, M.; Mintenig, S.M.; De France, J. Microplastics in Freshwaters and Drinking Water: Critical Review and Assessment of Data Quality. Water Res. 2019, 155, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.-M.; Yang, J.; Criddle, C.S. Microplastics Pollution and Reduction Strategies. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G.; Cardelli, L.R.; Gorbi, S.; Pellegrini, D.; Regoli, F. Microplastics Pollution after the Removal of the Costa Concordia Wreck: First Evidences from a Biomonitoring Case Study. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y. Effects of Microplastics on Wastewater and Sewage Sludge Treatment and Their Removal: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallec, K.; Huvet, A.; Di Poi, C.; González-Fernández, C.; Lambert, C.; Petton, B.; Le Goïc, N.; Berchel, M.; Soudant, P.; Paul-Pont, I. Nanoplastics Impaired Oyster Free Living Stages, Gametes and Embryos. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Diab, H.; Thompson, J. Microplastic Pollution: Chemical Characterization and Impact on Wildlife. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Wang, Y.; Kulyar, M.F.-A.; Iqbal, M.; Lai, R.; Zhu, H.; Li, K. Environmental Microplastics Exposure Decreases Antioxidant Ability, Perturbs Gut Microbial Homeostasis and Metabolism in Chicken. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.D.; Van Valkenburgh, B. The Dog–Human Connection. Anat. Rec. 2021, 304, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Luo, Y.; Li, R.; Zhou, Q.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Yin, N.; Yang, J.; Tu, C.; Zhang, Y. Effective Uptake of Submicrometre Plastics by Crop Plants via a Crack-Entry Mode. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Yang, X.; Pelaez, A.M.; Huerta Lwanga, E.; Beriot, N.; Gertsen, H.; Garbeva, P.; Geissen, V. Macro- and Micro- Plastics in Soil-Plant System: Effects of Plastic Mulch Film Residues on Wheat (Triticum aestivum) Growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Qiao, Y.; Klobučar, G.; Li, M. Toxicological Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics on Earthworm (Eisenia fetida). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, J. The Removal of Microplastics in the Wastewater Treatment Process and Their Potential Impact on Anaerobic Digestion Due to Pollutants Association. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, S.; Schlummer, M. Legacy Additives in a Circular Economy of Plastics: Current Dilemma, Policy Analysis, and Emerging Countermeasures. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 158, 104800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, L.S.; Staskal, D.F. Brominated Flame Retardants: Cause for Concern? Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erythropel, H.C.; Maric, M.; Nicell, J.A.; Leask, R.L.; Yargeau, V. Leaching of the Plasticizer Di (2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP) from Plastic Containers and the Question of Human Exposure. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 9967–9981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilitewski, B.; Darbra, R.M.; Barceló, D. Global Risk-Based Management of Chemical Additives I: Production, Usage and Environmental Occurrence; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 18, ISBN 3642248764. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, J. The Additives for Plastics Handbook: Antioxidants, Antistatics, Compatibilisers, Conductive Fillers, Flame-Retardants, Pigments, Plasticisers, Reinforcements: Classification, Data, Tables, Descriptions, Market Trends, Suppliers/Brand Names; Elsevier Advanced Technology: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Carbery, M.; O’Connor, W.; Palanisami, T. Trophic Transfer of Microplastics and Mixed Contaminants in the Marine Food Web and Implications for Human Health. Environ. Int. 2018, 115, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastics as Contaminants in the Marine Environment: A Review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sussarellu, R.; Suquet, M.; Thomas, Y.; Lambert, C.; Fabioux, C.; Pernet, M.E.J.; Le Goïc, N.; Quillien, V.; Mingant, C.; Epelboin, Y. Oyster Reproduction Is Affected by Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2430–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canniff, P.M.; Hoang, T.C. Microplastic Ingestion by Daphnia Magna and Its Enhancement on Algal Growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talsness, C.E.; Andrade, A.J.M.; Kuriyama, S.N.; Taylor, J.A.; Vom Saal, F.S. Components of Plastic: Experimental Studies in Animals and Relevance for Human Health. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2079–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- do Sul, J.A.I.; Costa, M.F. The Present and Future of Microplastic Pollution in the Marine Environment. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Fileman, E.; Halsband, C.; Goodhead, R.; Moger, J.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastic Ingestion by Zooplankton. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6646–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, M.; Loeschner, K. Detection of Nanoplastics in Food by Asymmetric Flow Field-Flow Fractionation Coupled to Multi-Angle Light Scattering: Possibilities, Challenges and Analytical Limitations. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5603–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urli, S.; Corte Pause, F.; Crociati, M.; Baufeld, A.; Monaci, M.; Stradaioli, G. Impact of Microplastics and Nanoplastics on Livestock Health: An Emerging Risk for Reproductive Efficiency. Animals 2023, 13, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, E.; Lee, J.-Y.; Redwan, M. Animal Exposure to Microplastics and Health Effects: A Review. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.P.; Reddy, C.M. We Need Better Data about the Environmental Persistence of Plastic Goods. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 14618–14621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahiduzzaman, F.; Rahman, M.Z.; Akhi, M.A.J.; Manik, M.; Khatun, M.M.; Islam, M.A.; Matin, M.N.; Haque, M.A. Potential Biological Impacts of Microplastics and Nanoplastics on Farm Animals: Global Perspectives with Insights from Bangladesh. Animals 2025, 15, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Liu, X.; Hou, Q.; Wang, Z. From Natural Environment to Animal Tissues: A Review of Microplastics(Nanoplastics) Translocation and Hazards Studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.; Love, D.C.; Rochman, C.M.; Neff, R.A. Microplastics in Seafood and the Implications for Human Health. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, T.S. Micro- and Nano-Plastics and Human Health. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 343–366. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzfischer, M.; Rogler, G. The Intestinal Barrier—Shielding the Body from Nano-and Microparticles in Our Diet. Metabolites 2022, 12, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revel, M.; Châtel, A.; Mouneyrac, C. Micro (Nano) Plastics: A Threat to Human Health? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-H.; Chen, Y.-Z.; Chiang, Y.-T.; Chang, Y.-T.; Wang, Y.-W.; Hsu, K.-T.; Hsu, Y.-Y.; Wu, P.-T.; Lee, B.-H. Polystyrene Nanoplastics Disrupt the Intestinal Microenvironment by Altering Bacteria-Host Interactions through Extracellular Vesicle-Delivered MicroRNAs. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, M.; Wang, L.; Gu, W.; Li, X.; Han, Z.; Fu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Su, Z. Continuous Oral Exposure to Micro- and Nanoplastics Induced Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis, Intestinal Barrier and Immune Dysfunction in Adult Mice. Environ. Int. 2023, 182, 108353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Ran, L.; He, Y.; Huang, Y. Mechanisms of Microplastics on Gastrointestinal Injury and Liver Metabolism Disorder (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2025, 31, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enyoh, C.E.; Shafea, L.; Verla, A.W.; Verla, E.N.; Qingyue, W.; Chowdhury, T.; Paredes, M. Microplastics Exposure Routes and Toxicity Studies to Ecosystems: An Overview. Environ. Anal. Health Toxicol. 2020, 35, e2020004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.L.; Kelly, F.J. Plastic and Human Health: A Micro Issue? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6634–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Feng, C.; Wu, Y.; Guo, X. Impacts of Nanoplastics on Bivalve: Fluorescence Tracing of Organ Accumulation, Oxidative Stress and Damage. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Lai, H.; Huang, J.; Sun, L.; Mennigen, J.A.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Tu, W. Polystyrene Microplastics Decrease F–53B Bioaccumulation but Induce Inflammatory Stress in Larval Zebrafish. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 127040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, Q.; Deng, J.; Ma, X.; Liao, X.; Zou, J.; Liao, J.; Huang, H.; Dai, H. Response Mechanism of Soil Leachate and Disinfection By-Product Formation to Extreme Precipitation Events under Continuous Drought Scenario. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 916, 170123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, K.D.; Hawkes, J.A.; Berg, M.; Clarijs, B.; Gill, C.G.; Bergquist, J.; Lanekoff, I.; Krogh, E.T. Membrane Sampling Separates Naphthenic Acids from Biogenic Dissolved Organic Matter for Direct Analysis by Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 3096–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilge, S.; Sınağ, A. Current Trends and Strategies in the Development of Green MXene-Based Photoelectrochemical Sensing Application. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 163, 117059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hong, X.; Yan, S.; Zha, J. Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Fenvalerate Induces Immunotoxicity and Reduces Pathogen Resistance in Chinese Rare Minnow (Gobiocypris rarus). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhan, X.; Hong, S.; Lin, L.; Tan, P.; Xiong, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, Z.; Bi, R.; et al. Legacy and Novel Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Raw and Cooked Squids: Perspective from Health Risks and Nutrient Benefits. Environ. Int. 2023, 177, 108024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.L.; Ng, C.T.; Zou, L.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J.; Bay, B.H.; Shen, H.-M.; Ong, C.N. Targeted Metabolomics Reveals Differential Biological Effects of Nanoplastics and NanoZnO in Human Lung Cells. Nanotoxicology 2019, 13, 1117–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prata, J.C. Airborne Microplastics: Consequences to Human Health? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, S.; Allen, D.; Phoenix, V.R.; Le Roux, G.; Durántez Jiménez, P.; Simonneau, A.; Binet, S.; Galop, D. Atmospheric Transport and Deposition of Microplastics in a Remote Mountain Catchment. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dinkler, K.; Zhao, N.; Ran, X.; Sobhi, M.; Dong, R.; Müller, J.; Xiong, W.; Huang, G.; Guo, J.; et al. Response of Phosphorus Speciation to Organic Loading Rates and Temperatures during Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Animal Manures and Wheat Straw. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Deng, F.; Tang, X.; Chen, W.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, T.; Mao, X.; Shu, F. Long-Term Effect of PBDE-99 Prenatal Exposure on Spermatogenic Injuries via the Dysregulation of Autophagy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwabl, P.; Köppel, S.; Königshofer, P.; Bucsics, T.; Trauner, M.; Reiberger, T.; Liebmann, B. Detection of Various Microplastics in Human Stool: A Prospective Case Series. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.A.; Dissanayake, A.; Galloway, T.S.; Lowe, D.M.; Thompson, R.C. Ingested Microscopic Plastic Translocates to the Circulatory System of the Mussel, Mytilus edulis (L.). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5026–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lademann, J.; Richter, H.; Schaefer, U.F.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Teichmann, A.; Otberg, N.; Sterry, W. Hair Follicles–a Long-Term Reservoir for Drug Delivery. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 19, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raszewska-Famielec, M.; Flieger, J. Nanoparticles for Topical Application in the Treatment of Skin Dysfunctions—An Overview of Dermo-Cosmetic and Dermatological Products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M.; Stracke, F.; Hansen, S.; Schaefer, U.F. Nanoparticles and Their Interactions with the Dermal Barrier. Derm.-Endocrinol. 2009, 1, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, L.; Germaine, K.; Dowling, D.N.; Kakouli-Duarte, T.; Cleary, J. Association of Potential Human Pathogens with Microplastics in Freshwater Systems. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Microplastic Pollution in the Mediterranean Sea; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 112–120. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Du, Q.; Zhong, Z.; Xu, Y.; Peng, J. Protein-Coated Microplastics Corona Complex: An Underestimated Risk of Microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 157948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandts, I.; Teles, M.; Gonçalves, A.P.; Barreto, A.; Franco-Martinez, L.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Martins, M.A.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Tort, L.; Oliveira, M. Effects of Nanoplastics on Mytilus galloprovincialis after Individual and Combined Exposure with Carbamazepine. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Han, Y.; Sun, S.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Du, X.; Liu, G. Immunotoxicities of Microplastics and Sertraline, Alone and in Combination, to a Bivalve Species: Size-Dependent Interaction and Potential Toxication Mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 396, 122603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, C.; García Beltrán, J.M.; Esteban, M.A.; Cuesta, A. In Vitro Effects of Virgin Microplastics on Fish Head-Kidney Leucocyte Activities. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, L.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Lu, S.; Hu, J.; Cao, C.; Xie, B.; Shi, H.; He, D. Polystyrene (Nano)Microplastics Cause Size-Dependent Neurotoxicity, Oxidative Damage and Other Adverse Effects in Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 2009–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Qiao, R.; An, H.; Zhang, Y. Influence of Microplastics on the Accumulation and Chronic Toxic Effects of Cadmium in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2018, 202, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrendt, C.; Perez-Venegas, D.J.; Urbina, M.; Gonzalez, C.; Echeveste, P.; Aldana, M.; Pulgar, J.; Galbán-Malagón, C. Microplastic Ingestion Cause Intestinal Lesions in the Intertidal Fish Girella laevifrons. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.A.; Choi, C.Y.; Park, H.-S. Exposure of Bay Scallop Argopecten irradians to Micro-Polystyrene: Bioaccumulation and Toxicity. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 236, 108801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, R.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wolosker, M.B.; Zhu, Q.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y. Accumulation of Different Shapes of Microplastics Initiates Intestinal Injury and Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis in the Gut of Zebrafish. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.-M.; Byeon, E.; Jeong, H.; Kim, M.-S.; Chen, Q.; Lee, J.-S. Different Effects of Nano- and Microplastics on Oxidative Status and Gut Microbiota in the Marine Medaka Oryzias melastigma. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.-N.; Wen, B.; Zhu, J.-G.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Gao, J.-Z.; Chen, Z.-Z. Exposure to Microplastics Impairs Digestive Performance, Stimulates Immune Response and Induces Microbiota Dysbiosis in the Gut of Juvenile Guppy (Poecilia reticulata). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 138929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hämer, J.; Gutow, L.; Köhler, A.; Saborowski, R. Fate of Microplastics in the Marine Isopod Idotea emarginata. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13451–13458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergami, E.; Bocci, E.; Vannuccini, M.L.; Monopoli, M.; Salvati, A.; Dawson, K.A.; Corsi, I. Nano-Sized Polystyrene Affects Feeding, Behavior and Physiology of Brine Shrimp Artemia franciscana Larvae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 123, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosetto, L.; Brown, C.; Williamson, J.E. Microplastics on Beaches: Ingestion and Behavioural Consequences for Beachhoppers. Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Meng, X.; Dieketseng, M.Y.; Wang, X.; Yan, S.; Wang, B.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, G. A Neglected Risk of Nanoplastics as Revealed by the Promoted Transformation of Plasmid-borne Ampicillin Resistance Gene by Escherichia Coli. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 4946–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Ma, J.; Li, G.; Rillig, M.C.; Zhu, Y.-G. Soil Plastispheres as Hotspots of Antibiotic Resistance Genes and Potential Pathogens. ISME J. 2022, 16, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhang, N.; Pan, Z.; Xing, C.; Chen, X. Current Research Trends on Microplastics Pollution and Impacts on Agro-Ecosystems: A Short Review. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Ruan, Y.; Sun, L.; Zuo, F.; Li, L.; Hou, S. Size-Dependent Enhancement on Conjugative Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance Genes by Micro/Nanoplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Sun, R.; Yu, P.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, W.; Bao, J.; Alvarez, P.J.J. UV-Aging of Microplastics Increases Proximal ARG Donor-Recipient Adsorption and Leaching of Chemicals That Synergistically Enhance Antibiotic Resistance Propagation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 427, 127895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, J.; Liu, B.; Ma, W.; Yang, S.; Cao, G. (Micro) Nanoplastics Promote the Risk of Antibiotic Resistance Gene Propagation in Biological Phosphorus Removal System. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, J.; Dai, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, D.; Duan, W.; Guo, Y. Microplastics Affect the Ammonia Oxidation Performance of Aerobic Granular Sludge and Enrich the Intracellular and Extracellular Antibiotic Resistance Genes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhu, L.; Yang, K.; Li, H.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Cui, L. Impact of Urbanization on Antibiotic Resistome in Different Microplastics: Evidence from a Large-Scale Whole River Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 8760–8770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Luo, Y. Potential Risks of Microplastics Combined with Superbugs: Enrichment of Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria on the Surface of Microplastics in Mariculture System. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 187, 109852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thushari, G.G.N.; Senevirathna, J.D.M. Plastic Pollution in the Marine Environment. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, H.; Lovell, C.R. Microbial Surface Colonization and Biofilm Development in Marine Environments. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 91–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowley, J.; Baker-Austin, C.; Porter, A.; Hartnell, R.; Lewis, C. Oceanic Hitchhikers–Assessing Pathogen Risks from Marine Microplastic. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.M.; Maldonado, G.C.; Castro, R.O.; de Sá Felizardo, J.; Cardoso, R.P.; Dos Anjos, R.M.; de Araújo, F.V. Dispersal of Potentially Pathogenic Bacteria by Plastic Debris in Guanabara Bay, RJ, Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 141, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.-J.; Huang, X.-P.; Xiang, L.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Li, Y.-W.; Li, H.; Cai, Q.-Y.; Mo, C.-H.; Wong, M.-H. Source, Migration and Toxicology of Microplastics in Soil. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, T.K.; Uddin, M.E.; Jamal, M. Detection and Removal of Microplastics in Wastewater: Evolution and Impact. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 16925–16947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engwa, G.A.; Ferdinand, P.U.; Nwalo, F.N.; Unachukwu, M.N. Mechanism and Health Effects of Heavy Metal Toxicity in Humans. In Poisoning in the Modern World—New Tricks for an Old Dog; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; Volume 10, pp. 70–90. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, R.L.; Xiao, B.C.; Yu, N.; Chen, L.Q. Research Advance in Toxic Effects of PAHs on Aquatic Animals. Mar. Fish. 2014, 36, 372–384. [Google Scholar]
- Luca, M.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; Sriwichaiin, S.; Luca, A. Cognitive-Behavioural Correlates of Dysbiosis: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Jiang, X.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Yin, X.; Zhang, X. Occurrence and Distribution of Microplastics in Organic Fertilizers in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Zhu, C.; Wang, C.; Gu, C. Occurrence and Ecological Impacts of Microplastics in Soil Systems: A Review. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 102, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enyoh, C.E.; Verla, A.W. We Are Breathing Plastic; Don’t Just Look down, Look Up. In Proceedings of the 3rd IMSU World Environment Day International Conference, Owerri, Nigeria, 5 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Sun, Y.; Rathour, R.; Pandey, A.; Thakur, I.S.; Tsang, D.C.W. Algae as Potential Feedstock for the Production of Biofuels and Value-Added Products: Opportunities and Challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 137116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rillig, M.C.; Ingraffia, R.; de Souza Machado, A.A. Microplastic Incorporation into Soil in Agroecosystems. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhou, Q.; Yin, N.; Tu, C.; Luo, Y. Uptake and Accumulation of Microplastics in an Edible Plant. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebere, E.C.; Wirnkor, V.A.; Ngozi, V.E. Uptake of Microplastics by Plant: A Reason to Worry or to Be Happy? World Sci. News 2019, 131, 256–267. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Lehmann, A.; Yang, G.; Leifheit, E.F.; Rillig, M.C. Effects of Microplastic Fibers on Soil Aggregation and Enzyme Activities Are Organic Matter Dependent. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 650155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Powell, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Zhang, P. Microplastics as Contaminants in the Soil Environment: A Mini-Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Reverón, R.; Álvarez-Méndez, S.J.; Kropp, R.M.; Perdomo-González, A.; Hernández-Borges, J.; Díaz-Peña, F.J. Microplastics in Agricultural Systems: Analytical Methodologies and Effects on Soil Quality and Crop Yield. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Jinjin, C.; Ji, R.; Ma, Y.; Yu, X. Microplastics in Agricultural Soils: Sources, Effects, and Their Fate. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2022, 25, 100311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, G.; Liang, C.; Xue, S.; Chen, H.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Response of Soil Dissolved Organic Matter to Microplastic Addition in Chinese Loess Soil. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Chen, H.; Liao, Y.; Ye, Z.; Li, M.; Klobučar, G. Ecotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Polystyrene Microplastics on Higher Plant Vicia Faba. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza Machado, A.A.; Lau, C.W.; Kloas, W.; Bergmann, J.; Bachelier, J.B.; Faltin, E.; Becker, R.; Görlich, A.S.; Rillig, M.C. Microplastics Can Change Soil Properties and Affect Plant Performance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6044–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xia, M.; Su, X.; Yuan, P.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Wan, Z.; Zou, W. Photolytic Degradation Elevated the Toxicity of Polylactic Acid Microplastics to Developing Zebrafish by Triggering Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Apoptosis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colzi, I.; Renna, L.; Bianchi, E.; Castellani, M.B.; Coppi, A.; Pignattelli, S.; Loppi, S.; Gonnelli, C. Impact of Microplastics on Growth, Photosynthesis and Essential Elements in Cucurbita pepo L. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Ossowicki, A.; Yang, X.; Lwanga, E.H.; Dini-Andreote, F.; Geissen, V.; Garbeva, P. Effects of Plastic Mulch Film Residues on Wheat Rhizosphere and Soil Properties. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, Y.M.; Rillig, M.C. Effects of Microplastic Fibers and Drought on Plant Communities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6166–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fajardo, C.; Martín, C.; Costa, G.; Sánchez-Fortún, S.; Rodríguez, C.; de Lucas Burneo, J.J.; Nande, M.; Mengs, G.; Martín, M. Assessing the Role of Polyethylene Microplastics as a Vector for Organic Pollutants in Soil: Ecotoxicological and Molecular Approaches. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeb, A.; Liu, W.; Meng, L.; Lian, J.; Wang, Q.; Lian, Y.; Chen, C.; Wu, J. Effects of Polyester Microfibers (PMFs) and Cadmium on Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) and the Rhizospheric Microbial Communities: A Study Involving Physio-Biochemical Properties and Metabolomic Profiles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Hou, H.; Liu, Y.; Yin, S.; Bian, S.; Liang, S.; Wan, C.; Yuan, S.; Xiao, K.; Liu, B.; et al. Microplastics Affect Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Quality by Interfering Metabolite Accumulation and Energy Expenditure Pathways: A Field Study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, M.D.; Toro, M.T.; Riveros, G.; Illanes, M.; Noriega, F.; Schoebitz, M.; García-Viguera, C.; Moreno, D.A. Brassica Sprouts Exposed to Microplastics: Effects on Phytochemical Constituents. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Wu, D.; Yu, Y.; Han, S.; Sun, L.; Li, M. Impact of Microplastics on Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in Rape (Brassica napus L.). Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Zhao, F.; Tian, L.; Ni, K.; Lu, Y.; Borah, P. Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics on the Seed Germination of Herbaceous Ornamental Plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Dong, Y.; Song, Z. Effect of Polystyrene on Di-Butyl Phthalate (DBP) Bioavailability and DBP-Induced Phytotoxicity in Lettuce. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, T.; Guo, J.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gong, L.; Li, X. Polystyrene Microplastics Disturb the Redox Homeostasis, Carbohydrate Metabolism and Phytohormone Regulatory Network in Barley. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, Y.M.; Lehnert, T.; Linck, L.T.; Lehmann, A.; Rillig, M.C. Microplastic Shape, Polymer Type, and Concentration Affect Soil Properties and Plant Biomass. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 616645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, R.; Li, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wang, G. Physiological Response of Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) Leaves to Polystyrene Nanoplastics Pollution. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 127041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, X.; Hu, J.; Peng, J.; Qu, J. Ecotoxicity of Polystyrene Microplastics to Submerged Carnivorous Utricularia Vulgaris Plants in Freshwater Ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Guchhait, R.; De, S.; Pramanick, K. Cytogenotoxic Potential of a Hazardous Material, Polystyrene Microparticles on Allium Cepa L. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbina, M.A.; Correa, F.; Aburto, F.; Ferrio, J.P. Adsorption of Polyethylene Microbeads and Physiological Effects on Hydroponic Maize. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Gao, M.; Song, Z.; Qiu, W. Microplastic Particles Increase Arsenic Toxicity to Rice Seedlings. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.-C.; Nazygul, J.; Li, M.; Wang, X.-L.; Jiang, L.-J. Effects of Microplastics on the Growth, Physiology, and Biochemical Characteristics of Wheat (Triticum aestivum). Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2019, 40, 4661–4667. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boots, B.; Russell, C.W.; Green, D.S. Effects of Microplastics in Soil Ecosystems: Above and Below Ground. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11496–11506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalčíková, G.; Gotvajn, A.Ž.; Kladnik, A.; Jemec, A. Impact of Polyethylene Microbeads on the Floating Freshwater Plant Duckweed Lemna Minor. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puckowski, A.; Cwięk, W.; Mioduszewska, K.; Stepnowski, P.; Białk-Bielińska, A. Sorption of Pharmaceuticals on the Surface of Microplastics. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Zhuang, W.; Cui, H.; Liu, M.; Gao, T.; Li, A.; Gao, Z. Interactions of Microplastics with Organic, Inorganic and Bio-Pollutants and the Ecotoxicological Effects on Terrestrial and Aquatic Organisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mammo, F.K.; Amoah, I.D.; Gani, K.M.; Pillay, L.; Ratha, S.K.; Bux, F.; Kumari, S. Microplastics in the Environment: Interactions with Microbes and Chemical Contaminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, K.; Reddy, S.; Barathe, P.; Oak, U.; Shriram, V.; Kharat, S.S.; Govarthanan, M.; Kumar, V. Microplastic-Associated Pathogens and Antimicrobial Resistance in Environment. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 133005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonaco, T.; Manco, E.; Corti, A.; La Nasa, J.; Ghimenti, S.; Biagini, D.; Di Francesco, F.; Modugno, F.; Ceccarini, A.; Fuoco, R. Release of Harmful Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) from Photo-Degraded Plastic Debris: A Neglected Source of Environmental Pollution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prüst, M.; Meijer, J.; Westerink, R.H.S. The Plastic Brain: Neurotoxicity of Micro-and Nanoplastics. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windheim, J.; Colombo, L.; Battajni, N.C.; Russo, L.; Cagnotto, A.; Diomede, L.; Bigini, P.; Vismara, E.; Fiumara, F.; Gabbrielli, S. Micro-and Nanoplastics’ Effects on Protein Folding and Amyloidosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Yu, H.; Yi, J.; Lei, P.; He, J.; Ruan, J.; Xu, P.; Tao, R.; Jin, L.; Wu, W. Behavioral Studies of Zebrafish Reveal a New Perspective on the Reproductive Toxicity of Micro- and Nanoplastics. Toxics 2024, 12, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amereh, F.; Babaei, M.; Eslami, A.; Fazelipour, S.; Rafiee, M. The Emerging Risk of Exposure to Nano (Micro) Plastics on Endocrine Disturbance and Reproductive Toxicity: From a Hypothetical Scenario to a Global Public Health Challenge. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismanto, A.; Hadibarata, T.; Kristanti, R.A.; Maslukah, L.; Safinatunnajah, N.; Kusumastuti, W. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs) in Environmental Matrices: Occurrence, Fate, Health Impact, Physio-Chemical and Bioremediation Technology. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 302, 119061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, A.; Akhtar, M.F.; Saleem, A.; Akhtar, B.; Sharif, A. Reproductive and Metabolic Toxic Effects of Polystyrene Microplastics in Adult Female Wistar Rats: A Mechanistic Study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 63185–63199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maradonna, F.; Meccariello, R. EDCs: Focus on Reproductive Alterations in Mammalian and Nonmammalian Models. In Environmental Contaminants and Endocrine Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 89–108. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Wan, Z.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Polystyrene Microplastics Induce Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis and Hepatic Lipid Metabolism Disorder in Mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beriot, N.; Peek, J.; Zornoza, R.; Geissen, V.; Lwanga, E.H. Low Density-Microplastics Detected in Sheep Faeces and Soil: A Case Study from the Intensive Vegetable Farming in Southeast Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.-J.; Han, J.-S.; Park, E.-J.; Seong, E.; Lee, G.-H.; Kim, D.-W.; Son, H.-Y.; Han, H.-Y.; Lee, B.-S. Repeated-Oral Dose Toxicity of Polyethylene Microplastics and the Possible Implications on Reproduction and Development of the next Generation. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 324, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; Li, Y.; Han, Y.; Fang, Y.; Xiang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, B.; Zhong, R. Polystyrene Exposure Induces Lamb Gastrointestinal Injury, Digestive Disorders and Inflammation, Decreasing Daily Gain, and Meat Quality. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 277, 116389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, J.; Wei, X.; Chang, L.; Liu, S. Proinflammatory Properties and Lipid Disturbance of Polystyrene Microplastics in the Livers of Mice with Acute Colitis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 143085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Cheng, Z.; Xu, G.; Li, F.; Bu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Song, Y.; An, X. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Exacerbates Microplastics-Induced Toxicity in Animal Cells. Food Res. Int. 2024, 175, 113818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Žalmanová, T.; Hošková, K.; Nevoral, J.; Adámková, K.; Kott, T.; Šulc, M.; Kotíková, Z.; Prokešová, Š.; Jílek, F.; Králíčková, M.; et al. Bisphenol S Negatively Affects the Meotic Maturation of Pig Oocytes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Deng, T.; Duan, J.; Xie, J.; Yuan, J.; Chen, M. Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics Causes Reproductive Toxicity through Oxidative Stress and Activation of the P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, D.; Jeong, J.; Song, K.S.; Sung, J.H.; Oh, S.M.; Choi, J. Inhalation Toxicity of Polystyrene Micro(Nano)Plastics Using Modified OECD TG 412. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J.; Chen, R.; Wang, M.; Bai, R.; Cui, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, C.; Chen, C. Perturbation of Gut Microbiota Plays an Important Role in Micro/Nanoplastics-Induced Gut Barrier Dysfunction. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 8806–8816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, R.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Xu, F.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L. Polystyrene Microplastics Cause Granulosa Cells Apoptosis and Fibrosis in Ovary through Oxidative Stress in Rats. Toxicology 2021, 449, 152665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandinee, D.; Mishra, G.; Shukla, A.; Soni, N.L.; Sharma, P. Bisphenol A and Cattle Fertility. Pharma Innov. 2021, 10, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Lei, Z.; Cui, L.; Hou, Y.; Yang, L.; An, R.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L. Polystyrene Microplastics Lead to Pyroptosis and Apoptosis of Ovarian Granulosa Cells via NLRP3/Caspase-1 Signaling Pathway in Rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 212, 112012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shengchen, W.; Jing, L.; Yujie, Y.; Yue, W.; Shiwen, X. Polystyrene Microplastics-Induced ROS Overproduction Disrupts the Skeletal Muscle Regeneration by Converting Myoblasts into Adipocytes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 125962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrela, F.N.; Guimarães, A.T.B.; da Costa Araújo, A.P.; Silva, F.G.; Da Luz, T.M.; Silva, A.M.; Pereira, P.S.; Malafaia, G. Toxicity of Polystyrene Nanoplastics and Zinc Oxide to Mice. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Yan, Z.; Shen, R.; Huang, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced Reproductive Toxicities Induced by Phthalates Contaminated Microplastics in Male Mice (Mus musculus). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, S.B.; D’Errico, J.N.; Adler, D.S.; Kollontzi, S.; Goedken, M.J.; Fabris, L.; Yurkow, E.J.; Stapleton, P.A. Nanopolystyrene Translocation and Fetal Deposition after Acute Lung Exposure during Late-Stage Pregnancy. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Ding, Y.; Cheng, X.; Sheng, D.; Xu, Z.; Rong, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Y. Polyethylene Microplastics Affect the Distribution of Gut Microbiota and Inflammation Development in Mice. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, P.K.; Jain, M.; Kataria, N.; Sahoo, P.K.; Garg, V.K.; Yadav, A. Microplastics in Multimedia Environment: A Systematic Review on Its Fate, Transport, Quantification, Health Risk, and Remedial Measures. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 20, 100889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis, M.; Silveira, S. Technologies for Chemical Recycling of Household Plastics—A Technical Review and TRL Assessment. Waste Manag. 2020, 105, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Bolan, S.; Padhye, L.P.; Konarova, M.; Foong, S.Y.; Lam, S.S.; Wagland, S.; Cao, R.; Li, Y.; Batalha, N. Retrieving Back Plastic Wastes for Conversion to Value Added Petrochemicals: Opportunities, Challenges and Outlooks. Appl. Energy 2023, 345, 121307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Hu, X. Machine Learning May Accelerate the Recognition and Control of Microplastic Pollution: Future Prospects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syberg, K.; Nielsen, M.B.; Oturai, N.B.; Clausen, L.P.W.; Ramos, T.M.; Hansen, S.F. Circular Economy and Reduction of Micro (Nano) Plastics Contamination. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 5, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholewinski, A.; Dadzie, E.; Sherlock, C.; Anderson, W.A.; Charles, T.C.; Habib, K.; Young, S.B.; Zhao, B. A Critical Review of Microplastic Degradation and Material Flow Analysis towards a Circular Economy. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 315, 120334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, J.S.; Veltman, K.; Huijbregts, M.A.J.; Verones, F.; Hertwich, E.G. Towards a Meaningful Assessment of Marine Ecological Impacts in Life Cycle Assessment (LCA). Environ. Int. 2016, 89, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liang, C.; Song, J.; Yu, S.; Liao, G.; Zou, P.; Tang, K.H.D.; Wu, C. Airborne Microplastics: Occurrence, Sources, Fate, Risks and Mitigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, S.; Hiraga, K.; Taniguchi, I.; Oda, K. Ideonella Sakaiensis, PETase, and MHETase: From Identification of Microbial PET Degradation to Enzyme Characterization. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 648, pp. 187–205. ISBN 0076-6879. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Kumar, M.; Sarsaiya, S.; Sirohi, R.; Awasthi, S.K.; Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Pandey, A.; Bolan, N.S.; Zhang, Z. Challenges and Opportunities in Bioremediation of Micro-Nano Plastics: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaldoon, S.; Lalung, J.; Maheer, U.; Kamaruddin, M.A.; Yhaya, M.F.; Alsolami, E.S.; Alorfi, H.S.; Hussein, M.A.; Rafatullah, M. A Review on the Role of Earthworms in Plastics Degradation: Issues and Challenges. Polymers 2022, 14, 4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmberger, M.S.; Miesel, J.R.; Tiemann, L.K.; Grieshop, M.J. Soil Invertebrates Generate Microplastics from Polystyrene Foam Debris. J. Insect Sci. 2022, 22, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.K.; Hadi, M.; Lin, C.; Nguyen, H.-L.; Thai, V.-B.; Hoang, H.-G.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Tran, H.-T. Microplastics in Sewage Sludge: Distribution, Toxicity, Identification Methods, and Engineered Technologies. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, S.; Chatha, A.M.M.; Khan, N.A.; Ullah, Q.; Zaman, F.; Qadeer, A.; Khan, I.M.; Danabas, D.; Kiran, A.; Skalickova, S.; et al. Unraveling the Ecotoxicological Effects of Micro and Nano-Plastics on Aquatic Organisms and Human Health. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1390510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, E.E.; Wang, Q.; Andrew, W.V.; Tanzin, C. Index Models for Ecological and Health Risks Assessment of Environmental Micro-and Nano-Sized Plastics. AIMS Environ. Sci. 2022, 9, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthipan, P.; Sathish, V.; Rajasekar, A.; Vickram, A.S.; Thanigaivel, S.; Subbaiya, R.; Karmegam, N.; Kim, W.; Govarthanan, M.; Seralathan, K. Impact Assessment and Evaluation of Micro(Nano)Plastics Exposure in the Human Health System: A Review. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2025, e00143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; da Costa, J.P.; Lopes, I.; Andrady, A.L.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. A One Health Perspective of the Impacts of Microplastics on Animal, Human and Environmental Health. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, M.; Roy, A.; Popek, R.; Sarkar, A. Micro- and Nano- Plastic Degradation by Bacterial Enzymes: A Solution to “White Pollution”. Microbe 2024, 3, 100072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Li, M.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, T.; Gong, H.; Yan, M. Biological Degradation of Plastics and Microplastics: A Recent Perspective on Associated Mechanisms and Influencing Factors. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeenat; Elahi, A.; Bukhari, D.A.; Shamim, S.; Rehman, A. Plastics Degradation by Microbes: A Sustainable Approach. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2021, 33, 101538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariam, I.; Rova, U.; Christakopoulos, P.; Matsakas, L. Data-Driven Synthetic Microbes for Sustainable Future. NPJ Syst. Biol. Appl. 2025, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).