Utility of Urinary miRNA Biomarkers for Canine Urothelial Carcinoma Diagnostics
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dogs and Sampling
2.2. RNA Isolation
2.3. Quantification of miRNA by ddPCR
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparative Quantification of miRNA Isolated from Urine Sediment and Cell-Free Supernatant
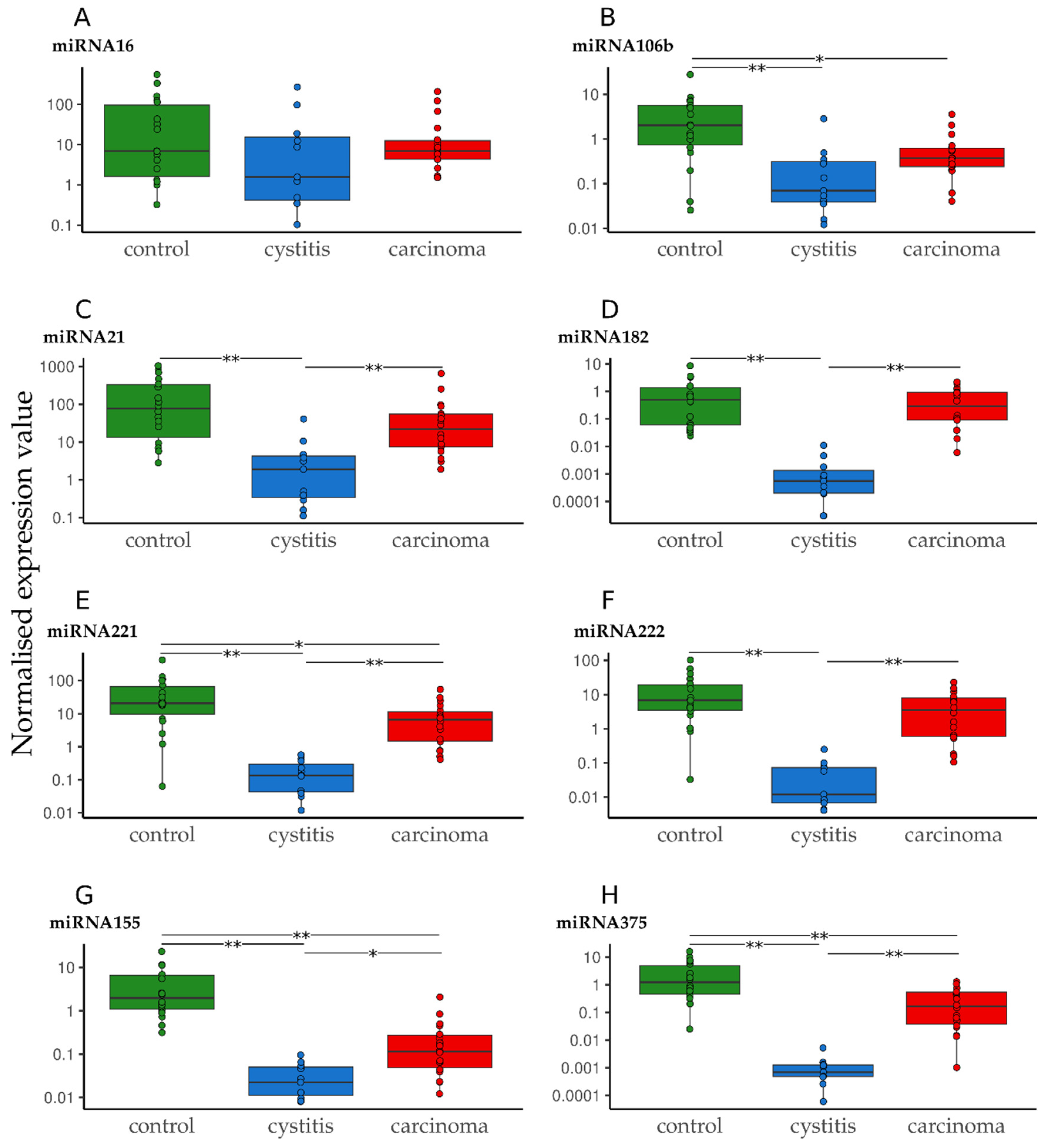
3.2. Quantification of miRNA in Urine Sediment in Cases of Cystitis and UC Compared to Healthy Controls
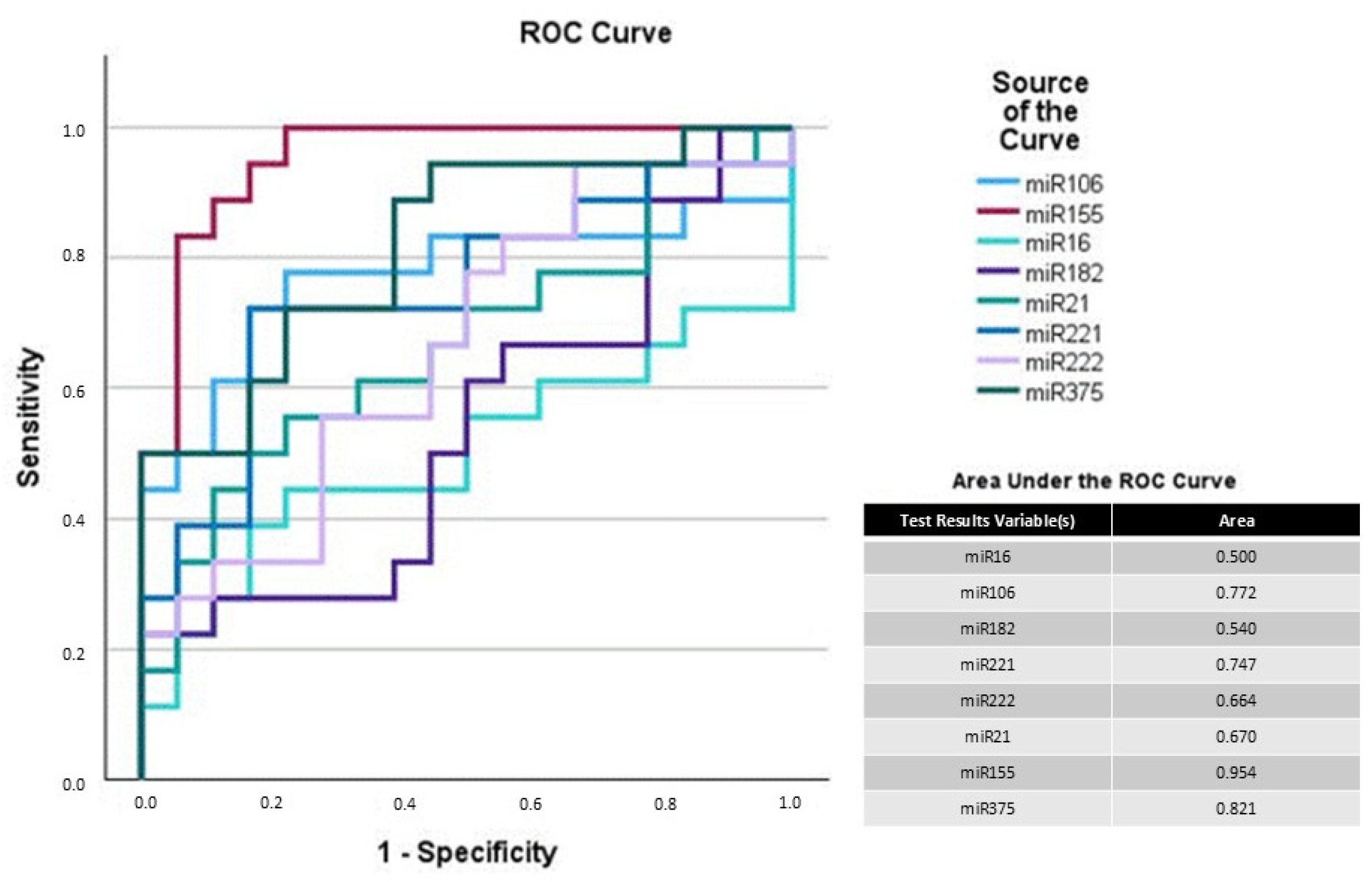
3.3. Potential of miRNAs as Biomarkers for UC in Dogs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knapp, D.W.; Glickman, N.W.; Denicola, D.B.; Bonney, P.L.; Lin, T.L.; Glickman, L.T. Naturally-occurring canine transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder A relevant model of human invasive bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2000, 5, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, B.W.; Ostrander, E.A. Domestic dogs and cancer research: A breed-based genomics approach. ILAR J. 2014, 55, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, A.M.; Laing, E.J.; Valli, V.E.; Withrow, S.J.; Macy, D.W.; Ogilvie, G.K.; Tomlinson, J.; McCaw, D.; Pidgeon, G.; Jacobs, R.M. Canine bladder and urethral tumors: A retrospective study of 115 cases (1980–1985). J. Vet. Int. Med. 1992, 6, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, H.; Shapiro, S.G.; Breen, M. Detection of BRAF Mutation in Urine DNA as a Molecular Diagnostic for Canine Urothelial and Prostatic Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, H.; Shapiro, S.G.; Breen, M. Detection of Copy Number Imbalance in Canine Urothelial Carcinoma with Droplet Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction. Vet. Pathol. 2016, 53, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aupperle-Lellbach, H.; Grassinger, J.; Hohloch, C.; Kehl, A.; Pantke, P. Diagnostische Aussagekraft der BRAF-Mutation V595E in Urinproben, Ausstrichen und Bioptaten beim kaninen Übergangszellkarzinom. Tierarztl. Prax. Ausg. K Kleintiere. Heimtiere. 2018, 46, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, X.; Cobb, G.P.; Anderson, T.A. microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev. Biol. 2007, 302, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.; Rana, S.; Espinosa-Diez, C.; Anand, S. MicroRNAs in Cancer: Challenges and opportunities in early detection, disease monitoring, and therapeutic agents. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2017, 5, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leva, G.; Garofalo, M.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2014, 9, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Ochiya, T. Circulating microRNA in body fluid: A new potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 2087–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Sen, A.; Saini, S.; Dwivedi, S.; Agrawal, R.; Bansal, A.; Shekhar, S. MicroRNA Significance in Cancer: An Updated Review on Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Perspectives. EJIFCC 2024, 35, 265–284. [Google Scholar]
- Sohel, M.M.H. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers in cancer diagnosis. Life Sci. 2020, 248, 117473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xinyi, L.; Jinlong, L.; Bin, Z. Low-Invasive Biomarkers of Canine Mammary Tumours. Vet. Med. Sci. 2025, 11, e70280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, L.; Treleaven, H.; Moorehead, R.; Foster, R.A.; Wood, R.D.; Ali, R.A.; Wood, G.A. Classification and Prognostication of B-Cell and T-Cell Multicentric Lymphoma in Dogs Using Serum MicroRNAs. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2025, 23, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvil, M.S.; Bailey, T.; Dhawan, D.; Knapp, D.W.; Ramos-Vara, J.A.; Dos Santos, A.P. The miRNome of canine invasive urothelial carcinoma. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 945638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinall, R.L.; Kent, M.S.; deVere White, R.W. Expression of microRNAs in urinary bladder samples obtained from dogs with grossly normal bladders, inflammatory bladder disease, or transitional cell carcinoma. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 73, 1626–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, M.S.; Zwingenberger, A.; Westropp, J.L.; Barrett, L.E.; Durbin-Johnson, B.P.; Ghosh, P.; Vinall, R.L. MicroRNA profiling of dogs with transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder using blood and urine samples. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karttunen, J.; Kalmar, L.; Grant, A.; Ying, J.; Stewart, S.E.; Wang, X.; Frankl, F.K.; Williams, T. miR-182, miR-221 and miR-222 are potential urinary extracellular vesicle biomarkers for canine urothelial carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foj, L.; Ferrer, F.; Serra, M.; Arévalo, A.; Gavagnach, M.; Giménez, N.; Filella, X. Exosomal and Non-Exosomal Urinary miRNAs in Prostate Cancer Detection and Prognosis. Prostate 2017, 77, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamdouh, S.; Sherif, H.; Romeih, M.; Elesaily, K. Urine micro-RNA signature as a potential non-invasive diagnostic biomarker in bladder cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2023, 24, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbanmehr, N.; Gharbi, S.; Korsching, E.; Tavallaei, M.; Einollahi, B.; Mowla, S.J. miR-21-5p, miR-141-3p, and miR-205-5p levels in urine-promising biomarkers for the identification of prostate and bladder cancer. Prostate 2019, 79, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Kang, S.J.; Lee, J.; Park, K.H.; Rhee, W.J. Isolation and Characterization of Urinary Extracellular Vesicles from Healthy Donors and Patients with Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, K.; Fujita, K.; Jingushi, K.; Kawashima, A.; Ujike, T.; Nagahara, A.; Ueda, Y.; Tanigawa, G.; Yoshioka, I.; Ueda, K.; et al. MiR-21-5p in urinary extracellular vesicles is a novel biomarker of urothelial carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 24668–24678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu, Z.; Otta Oshiro, R.; Redruello, A.; López-Martín, S.; Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Morato, E.; Marina, A.I.; Olivier Gómez, C.; Yáñez-Mó, M. Extracellular vesicles as a source for non-invasive biomarkers in bladder cancer progression. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 98, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-T.; Tsai, K.-W. Circulating miRNAs Act as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Bladder Cancer in Urine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, H.; Yoshiike, M.; Nozawa, S.; Usuba, W.; Katsuoka, Y.; Aida, K.; Kitajima, K.; Kudo, H.; Hoshikawa, M.; Yoshioka, Y.; et al. Expression Level of Urinary MicroRNA-146a-5p Is Increased in Patients with Bladder Cancer and Decreased in Those After Transurethral Resection. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2016, 14, e493–e499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgart, S.; Meschkat, P.; Edelmann, P.; Heinzelmann, J.; Pryalukhin, A.; Bohle, R.; Heinzelbecker, J.; Stöckle, M.; Junker, K. MicroRNAs in tumor samples and urinary extracellular vesicles as a putative diagnostic tool for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 2725–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Liu, X.; Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Jia, J.; Li, Z. Smartphone-Based Fluorescent Profiling of Quaternary MicroRNAs in Urine for Rapid Diagnosis of Urological Cancers Using a Multiplexed Isothermal Exponential Amplification Reaction. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Fang, A.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Du, L.; Wang, C. Direct quantitative detection for cell-free miR-155 in urine: A potential role in diagnosis and prognosis for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3255–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvil, M.S.; Dos Santos, A.P. A review of the current standing of microRNA expression in canine urothelial carcinoma. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2024, 85, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benning, L.; Robinson, S.; Follo, M.; Heger, L.A.; Stallmann, D.; Duerschmied, D.; Bode, C.; Ahrens, I.; Hortmann, M. Digital PCR for Quantifying Circulating MicroRNAs in Acute Myocardial Infarction and Cardiovascular Disease. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 137, e57950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedon, J.; Kehl, A.; Aupperle-Lellbach, H.; von Bomhard, W.; Schmidt, J.M. BRAF mutation status and its prognostic significance in 79 canine urothelial carcinomas: A retrospective study (2006–2019). Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2022, 20, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aveta, A.; Cilio, S.; Contieri, R.; Spena, G.; Napolitano, L.; Manfredi, C.; Franco, A.; Crocerossa, F.; Cerrato, C.; Ferro, M.; et al. Urinary MicroRNAs as Biomarkers of Urological Cancers: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvil, M.S.; Clark, S.L.; Bailey, T.W.; Ramos-Vara, J.A.; Santos, A.P.D. Canine urothelial carcinoma: A pilot study of microRNA detection in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue samples and in normal urine. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2024, 36, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall, C.; Rocke, D.M.; Durbin-Johnson, B.; Weiss, R.H. Stability of miRNA in human urine supports its biomarker potential. Biomark. Med. 2013, 7, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.J.; Jeong, P.; Kim, W.-T.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Song, P.H.; Choi, Y.-H.; Kim, I.Y.; Moon, S.-K.; Kim, W.-J. Cell-free microRNAs in urine as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers of bladder cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roest, H.P.; IJzermans, J.N.M.; van der Laan, L.J.W. Evaluation of RNA isolation methods for microRNA quantification in a range of clinical biofluids. BMC Biotechnol. 2021, 21, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, C.; Moccia, V.; Molinari, A.; Torrigiani, F.; Ferro, L.; Ferraresso, S.; Bonsembiante, F.; Leo, C.; Zappulli, V. Free circulating versus extracellular vesicle-associated microRNA expression in canine T-cell lymphoma. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1461506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobrega, M.; Reis, M.B.D.; Souza, M.F.d.; Furini, H.H.; Costa Brandão Berti, F.; Souza, I.L.M.; Mingorance Carvalho, T.; Zanata, S.M.; Fuganti, P.E.; Malheiros, D.; et al. Comparative analysis of extracellular vesicles miRNAs (EV-miRNAs) and cell-free microRNAs (cf-miRNAs) reveals that EV-miRNAs are more promising as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for prostate cancer. Gene 2025, 939, 149186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosthuyzen, W.; Berg, P.W.L.t.; Francis, B.; Campbell, S.; Macklin, V.; Milne, E.; Gow, A.G.; Fisher, C.; Mellanby, R.J.; Dear, J.W. Sensitivity and specificity of microRNA-122 for liver disease in dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 1637–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
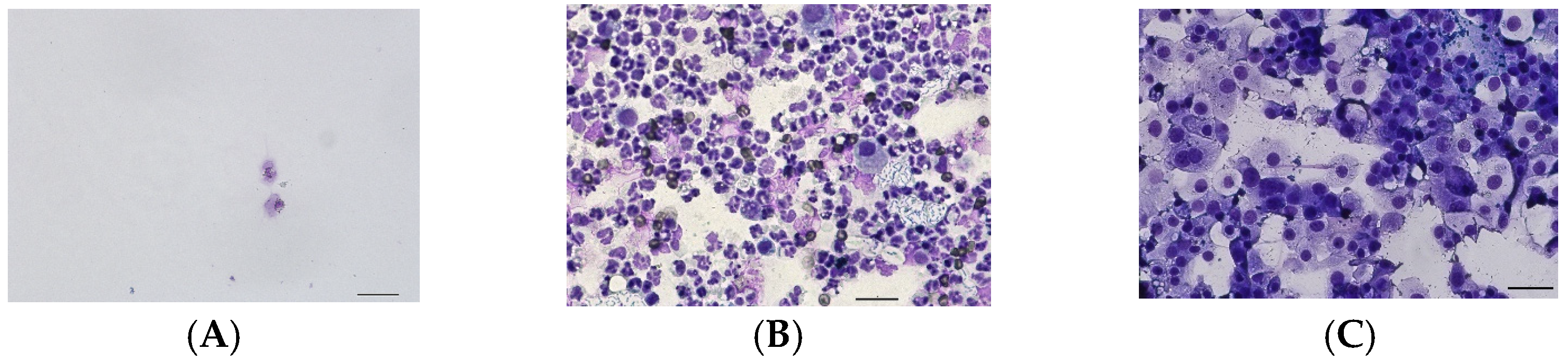

| Group | Breed | Age (Years) | Sex |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control n = 18 | 1 Beagle, 1 Chihuahua, 1 Dalmatian, 1 German Wirehaired Pointer, 2 Golden Retrievers, 1 Flat-Coated Retriever, 1 Husky, 1 Magyar Vizsla, 1 Malinois, 1 Pug, 1 Tibetan Terrier, 6 mixed breeds | 1–15 | 1f, 5fc, 6m, 5mc, 1u |
| Cystitis n = 11 | 1 Eurasier, 1 French Bulldog, 1 German Shepherd, 1 Golden Retriever, 1 Labrador Retriever, 1 Magyar Agar, 1 Olde English Bulldogge, 1 Rottweiler, 3 mixed breeds | 2–13 | 4f, 2fc, 1m, 4mc |
| Carcinoma n = 18 | 1 Border Collie, 1 Boxer, 1 Bullmastiff, 1 English Bulldog, 1 German Spitz, 2 Jack Russell Terriers, 1 Magyar Vizsla, 1 Pug, 1 Scottish Terrier, 1 Shih Tzu, 7 mixed breeds | 6–13 | 3f, 7fc, 4m, 4mc |
| miRNA | Controls (n = 7) | Carcinoma (n = 7) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | Range | Median | Range | |
| 16 | 0.9 | 0–16.3 | 0.49 | 0–12.8 |
| 21 | 11.8 | 0–48.6 | 11.2 | 1.15–185 |
| 103b | 0 | 0 | ||
| 106b | 0 | 0 | ||
| 146 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 155 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 182 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 221 | 0.9 | 0–16.7 | 5.5 | 0.19–29.5 |
| 222 | 1.01 | 0–2.8 | 1.19 | 0–1.7 |
| 375 | 0 | 0 | ||
| miRNA | Controls (n = 7) | Carcinoma (n = 7) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | Range | Median | Range | |
| 16 | 124.1 | 24–548 | 10.5 | 1.6–121 |
| 21 | 343.1 | 45–1047 | 51.1 | 3–253 |
| 103b | 0 | 0 | ||
| 106b | 6.9 | 0.5–28 | 0.6 | 0.1–4 |
| 146 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 155 | 5.5 | 0.7–23 | 0.2 | 0.1–0.8 |
| 182 | 3.3 | 0.1–8 | 0.5 | 0.1–1.3 |
| 221 | 72.2 | 18–418 | 5.8 | 0.8–54 |
| 222 | 28.5 | 7–102 | 2.9 | 0.1–23 |
| 375 | 3.8 | 0.6–10 | 0.5 | 0.1–1.3 |
| Tukey | ANOVA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control vs. Cystitis | Control vs. Carcinoma | Cystitis vs. Carcinoma | Control/Cystitis vs. Carcinoma | Control vs. Cystitis/Carcinoma | Control/Carcinoma vs. Cystitis | |
| miR-16 | 0.210 | 0.896 | 0.380 | 0.763 | 0.274 | 0.095 |
| miR-21 | <0.001 | 0.167 | <0.001 | 0.655 | 0.002 | <0.001 |
| miR-106b | <0.001 | 0.030 | 0.067 | 0.506 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| miR-155 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.005 | 0.042 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| miR-182 | <0.001 | 0.727 | <0.001 | 0.044 | 0.004 | <0.001 |
| miR-221 | <0.001 | 0.049 | <0.001 | 0.525 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| miR-222 | <0.001 | 0.172 | <0.001 | 0.256 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| miR-375 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.691 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kehl, A.; Aupperle-Lellbach, H.; Brockmann, M.; Weyer, A.-L.v.d.; Appenzeller, M.; Steiger, K. Utility of Urinary miRNA Biomarkers for Canine Urothelial Carcinoma Diagnostics. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070621
Kehl A, Aupperle-Lellbach H, Brockmann M, Weyer A-Lvd, Appenzeller M, Steiger K. Utility of Urinary miRNA Biomarkers for Canine Urothelial Carcinoma Diagnostics. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(7):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070621
Chicago/Turabian StyleKehl, Alexandra, Heike Aupperle-Lellbach, Maria Brockmann, Anna-Lena van de Weyer, Marielle Appenzeller, and Katja Steiger. 2025. "Utility of Urinary miRNA Biomarkers for Canine Urothelial Carcinoma Diagnostics" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 7: 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070621
APA StyleKehl, A., Aupperle-Lellbach, H., Brockmann, M., Weyer, A.-L. v. d., Appenzeller, M., & Steiger, K. (2025). Utility of Urinary miRNA Biomarkers for Canine Urothelial Carcinoma Diagnostics. Veterinary Sciences, 12(7), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070621








