Exploring MAPK and mTOR Pathways in Feline Thyroid Tumors
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Primer Design and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
2.4. Sanger Sequencing
2.5. Immunohistochemical Assays (IHC)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical-Pathological Data
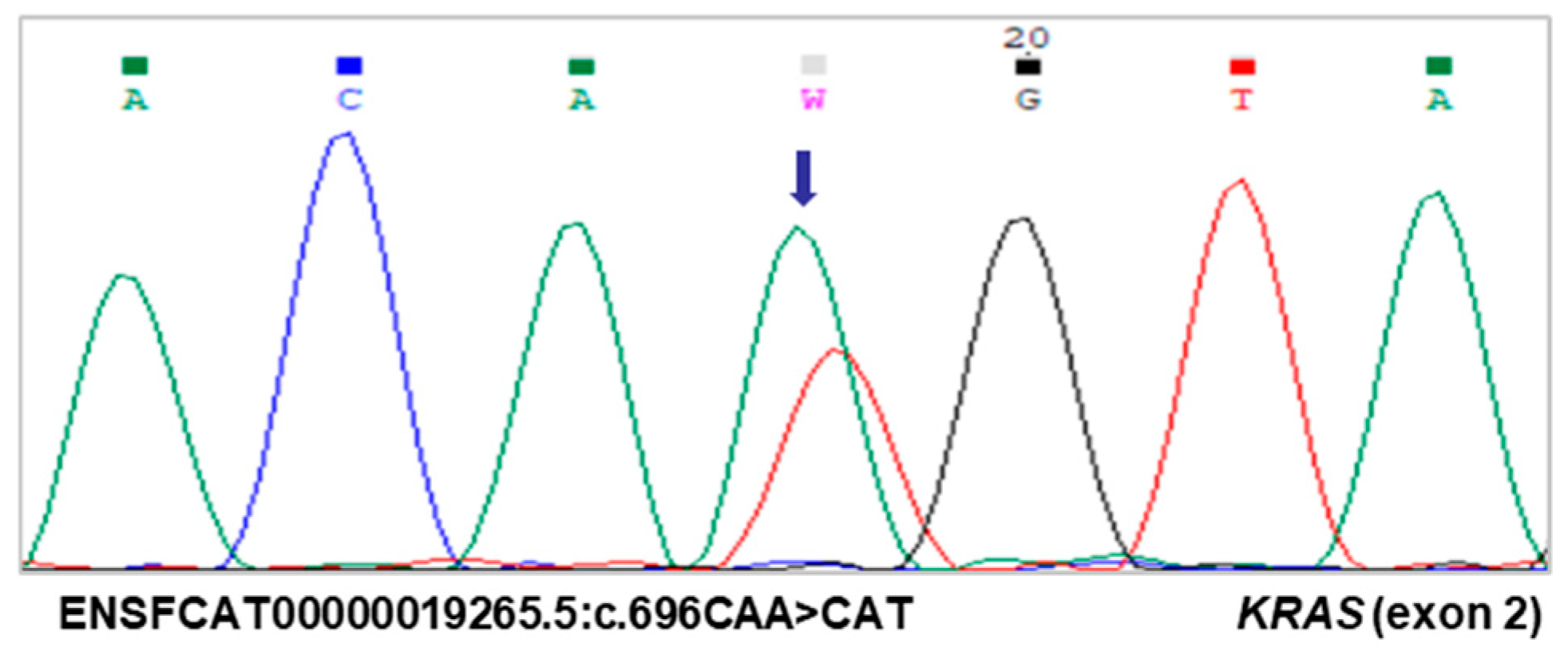
3.2. Identification of a Novel KRAS Mutation
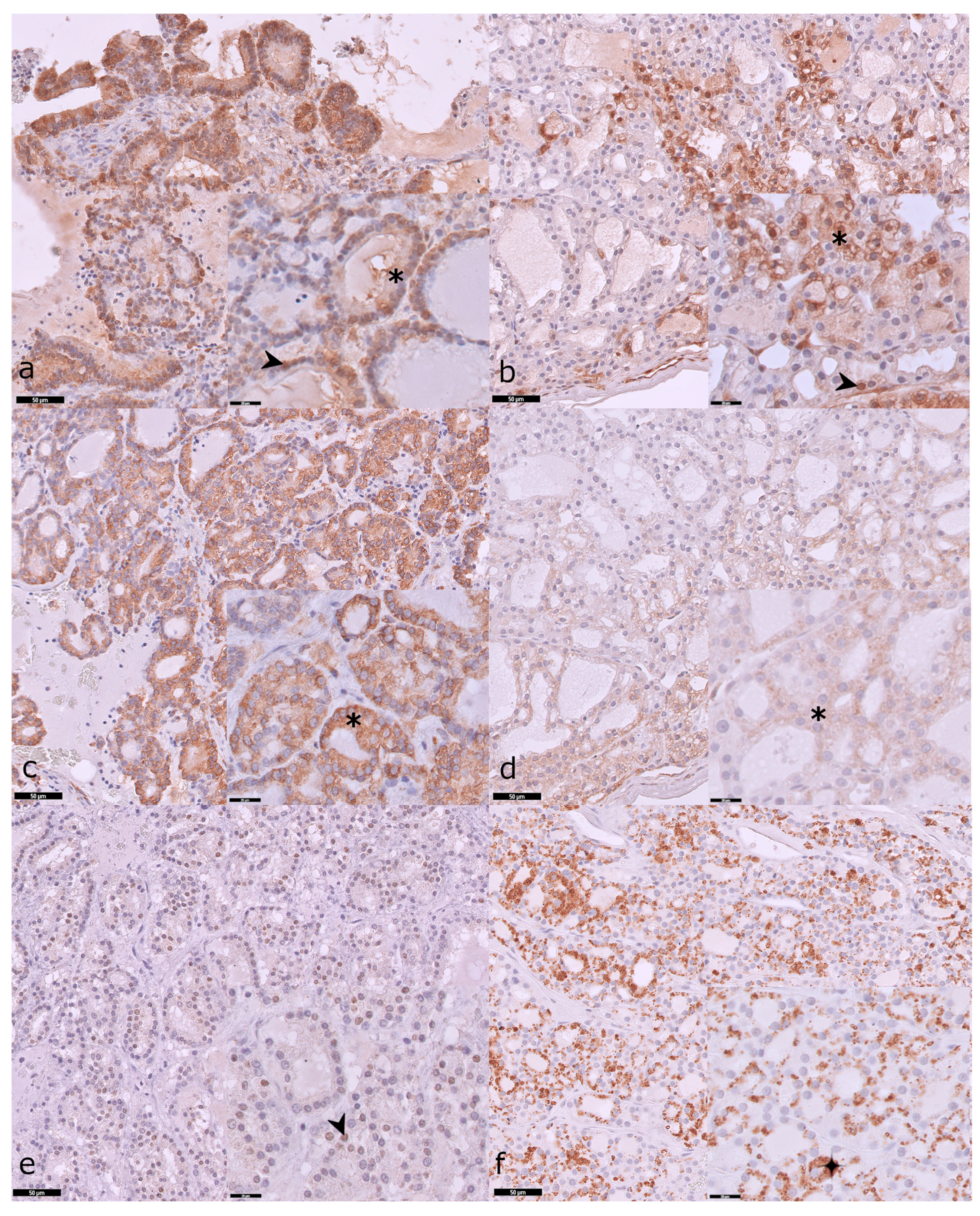
3.3. Expression Profiles of pERK, pS6, and pAKT
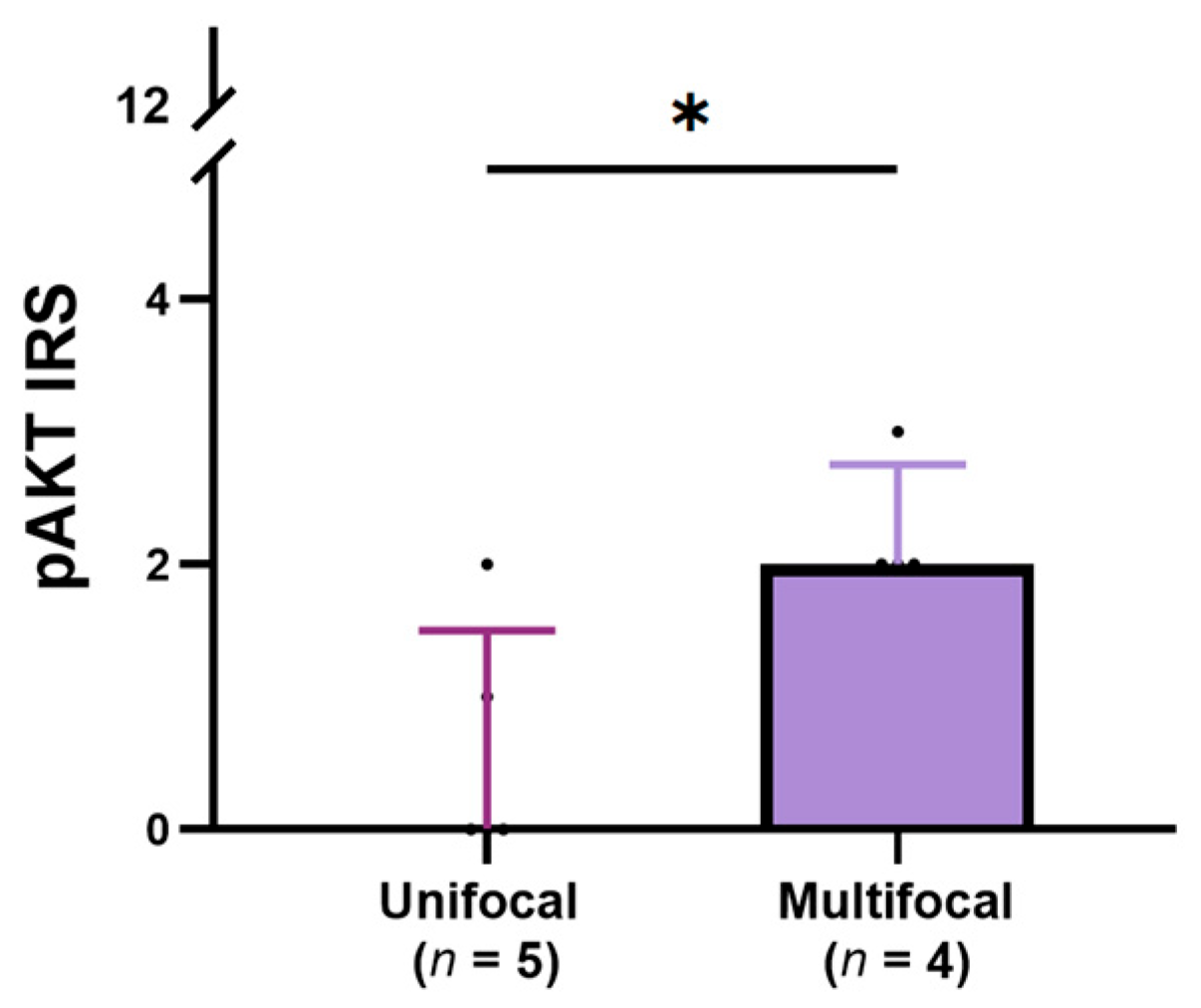
3.4. Relationship Between the Expression of pERK, pS6, and pAKT and Clinical-Pathological Features of Cats with TNA
3.5. The Correlation Between pERK, pS6, and pAKT in Tumors with No Atypia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TWA | Tumors with atypia |
| TNA | Tumors with no atypia |
| FA | Follicular (thyroid) adenoma |
| IRS | Immune reactive score |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| pAKT | Phosphorilated v-Akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog Ser473 |
| pERK | Phosphorilated extracellular signal-regulated kinase Thr202/Tyr204 |
| pS6 | Phosphorilated 40S ribosomal protein S6 Ser235/236 |
| RAS | Rat sarcoma virus protein family |
| TC | Thyroid carcinoma |
References
- Rosol, J.T.; Meuten, D.J. Tumors of the Endocrine Glands. In Tumors in Domestic Animals, 5th ed.; Meuten, D.J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2017; pp. 791–809. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, M. Hyperthyroidism in cats: What’s causing this epidemic of thyroid disease and can we prevent it? J. Feline Med. Surg. 2012, 14, 804–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, M.E.; Broome, M.R.; Rishniw, M. Prevalence and degree of thyroid pathology in hyperthyroid cats increases with disease duration: A cross-sectional analysis of 2096 cats referred for radioiodine therapy. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2016, 18, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugen, B.R.; Alexander, E.K.; Bible, K.C.; Doherty, G.M.; Mandel, S.J.; Nikiforov, Y.E.; Pacini, F.; Randolph, G.W.; Sawka, A.M.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, Q.T.; Lee, E.J.; Huang, M.G.; Park, Y.I.; Khullar, A.; Plodkowski, R.A. Diagnosis and treatment of patients with thyroid cancer. Am. Health Drug Benefits 2015, 8, 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Gharib, H.; Papini, E. Thyroid nodules: Clinical importance, assessment, and treatment. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 36, 707–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagag, P.; Strauss, S.; Weiss, M. Role of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy in evaluation of nonpalpable thyroid nodules. Thyroid 1998, 8, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M.E. Animal models of disease: Feline hyperthyroidism: An animal model for toxic nodular goiter. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 223, T97–T114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.G.; Radford, A.D.; Kipar, A.; Ibarrola, P.; Blackwood, L. Somatic mutations of the thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor gene in feline hyperthyroidism: Parallels with human hyperthyroidism. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 186, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, M.E.; Timmermans-Sprang, E.P.; Mol, J.A. Feline thyroid adenomas are in part associated with mutations in the G(s alpha) gene and not with polymorphisms found in the thyrotropin receptor. Thyroid 2002, 12, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, A. Companion Animal Model in Translational Oncology; Feline Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Canine Oral Melanoma. Biology 2021, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, C.M. Cats, Cancer and Comparative Oncology. Vet. Sci. 2015, 2, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaske, H.H.; Schermerhorn, T.; Armbrust, L.; Grauer, G.F. Diagnosis and management of feline hyperthyroidism: Current perspectives. Vet. Med. 2014, 5, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naan, E.C.; Kirpensteijn, J.; Kooistra, H.S.; Peeters, M.E. Results of thyroidectomy in 101 cats with hyperthyroidism. Vet. Surg. 2006, 35, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padgett, S. Feline thyroid surgery. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2002, 32, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pópulo, H.; Lopes, J.M.; Soares, P. The mTOR signalling pathway in human cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 1886–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, E.; Downward, J. RAS Interaction with PI3K: More Than Just Another Effector Pathway. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Medarde, A.; Santos, E. Ras in cancer and developmental diseases. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, C.; Melo, M.; Cameselle-Teijeiro, J.M.; Soares, P.; Sobrinho-Simoes, M. ENDOCRINE TUMOURS: Genetic predictors of thyroid cancer outcome. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 174, R117–R126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M. Molecular pathogenesis and mechanisms of thyroid cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merryman, J.I.; Buckles, E.L.; Bowers, G.; Neilsen, N.R. Overexpression of c-Ras in hyperplasia and adenomas of the feline thyroid gland: An immunohistochemical analysis of 34 cases. Vet. Pathol. 1999, 36, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinello, K.; Pires, I.; Castro, A.F.; Carvalho, P.T.; Santos, A.; de Matos, A.; Queiroga, F.; Niza-Ribeiro, J. Vet-OncoNet: Developing a Network of Veterinary Oncology and Reporting a Pioneering Portuguese Experience. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiupel, M. Histological Classification of Tumors of the Endocrine System of Domestic Animals, 2nd ed.; Armed Forces Institute of Pathology in Cooperation with the CL Davis DVM Foundation and the World Health Organization Collaborating Center for Worldwide Reference on Comparative Oncology: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Povoa, A.A.; Teixeira, E.; Bella-Cueto, M.R.; Batista, R.; Pestana, A.; Melo, M.; Alves, T.; Pinto, M.; Sobrinho-Simoes, M.; Maciel, J.; et al. Genetic Determinants for Prediction of Outcome of Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, M.L.; Pinto, M.; Alves, M.; Canberk, S.; Goncalves, A.; Bugalho, M.J.; Papoila, A.L.; Soares, P. Comparative Cyto-Histological Genetic Profile in a Series of Differentiated Thyroid Carcinomas. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, F.J.; Amode, M.R.; Aneja, A.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov, A.G.; Barnes, I.; Becker, A.; Bennett, R.; Berry, A.; Bhai, J.; et al. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D933–D941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, F.; Allen, J.E.; Allen, J.; Alvarez-Jarreta, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov, A.G.; Barnes, I.; Bennett, R.; et al. Ensembl 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D988–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T.L. Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, W.J.; Sugnet, C.W.; Furey, T.S.; Roskin, K.M.; Pringle, T.H.; Zahler, A.M.; Haussler, D. The human genome browser at UCSC. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Dunnen, J.T.; Dalgleish, R.; Maglott, D.R.; Hart, R.K.; Greenblatt, M.S.; McGowan-Jordan, J.; Roux, A.F.; Smith, T.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Taschner, P.E. HGVS Recommendations for the Description of Sequence Variants: 2016 Update. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefter, M.; Vis, J.K.; Vermaat, M.; den Dunnen, J.T.; Taschner, P.E.M.; Laros, J.F.J. Mutalyzer 2: Next generation HGVS nomenclature checker. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 2811–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, C.; Eloy, C.; Melo, M.; Gaspar da Rocha, A.; Pestana, A.; Batista, R.; Bueno Ferreira, L.; Rios, E.; Sobrinho Simoes, M.; Soares, P. mTOR Pathway in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Different Contributions of mTORC1 and mTORC2 Complexes for Tumor Behavior and SLC5A5 mRNA Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, C.; Coelho, M.J.; Melo, M.; da Rocha, A.G.; Pestana, A.; Batista, R.; Salgado, C.; Eloy, C.; Ferreira, L.; Rios, E.; et al. pmTOR is a marker of aggressiveness in papillary thyroid carcinomas. Surgery 2016, 160, 1582–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, J.I.; Jang, H.W.; Choe, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Hur, K.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Chung, J.H. ERK phosphorylation is not increased in papillary thyroid carcinomas with BRAF(V600E) mutation compared to that of corresponding normal thyroid tissues. Endocr. Res. 2013, 38, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asproni, P.; Millanta, F.; Ressel, L.; Podesta, F.; Parisi, F.; Vannozzi, I.; Poli, A. An Immunohistochemical Study of the PTEN/AKT Pathway Involvement in Canine and Feline Mammary Tumors. Animals 2021, 11, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, Y.; Laser, M.; Shiraishi, H.; Willey, C.D.; Sundaravadivel, B.; Xu, L.; McDermott, P.J.; Kuppuswamy, D. c-Raf/MEK/ERK pathway controls protein kinase C-mediated p70S6K activation in adult cardiac muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 23065–23075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniscalco, L.; Iussich, S.; de Las Mulas, J.M.; Millan, Y.; Biolatti, B.; Sasaki, N.; Nakagawa, T.; De Maria, R. Activation of AKT in feline mammary carcinoma: A new prognostic factor for feline mammary tumours. Vet. J. 2012, 191, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott-Moncrieff, J.C. The Thyroid gland. In Canine and Feline Endocrinology, 4th ed.; Feldman, E.C., Nelson, R.W., Reusch, C.E., Scott-Moncrieff, J.C., Eds.; Elsevier Saunders: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2015; pp. 136–195. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, L.G. Thyroid tumors in dogs and cats. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2007, 37, 755–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinello, K.; Amorim, I.; Pires, I.; Canadas-Sousa, A.; Catarino, J.; Faisca, P.; Branco, S.; Peleteiro, M.C.; Silva, D.; Severo, M.; et al. Vet-OncoNet: Malignancy Analysis of Neoplasms in Dogs and Cats. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argenta, F.F.; de Mello, L.S.; Slaviero, M.; Cony, F.G.; Bandinelli, M.B.; Pavarini, S.P.; Driemeier, D.; Sonne, L. Pathological and Immunohistochemical Characterization of Thyroid Neoplasms in Cats. J. Comp. Pathol. 2021, 184, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun, L.; Salmon, I. Pathology and new insights in thyroid neoplasms in the 2022 WHO classification. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2024, 36, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, L.M.C.; Pereira, A.H.B.; de Campos, C.G.; Rocha, L.S.; Dos Santos, T.A.; Souza, M.A.; Jark, P.C.; Pescador, C.A. Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Characteristics of Thyroid Carcinoma in the Dog. J. Comp. Pathol. 2020, 177, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, R.V.; Osamura, R.Y.; Klöppel, G.; Rosai, J. WHO Classification of Tumours of Endocrine Organs, 4th ed.; World Health Organization (IARC): Lyon, France, 2017; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Derwich, A.; Sykutera, M.; Brominska, B.; Andrusiewicz, M.; Ruchala, M.; Sawicka-Gutaj, N. Clinical Implications of mTOR Expression in Papillary Thyroid Cancer-A Systematic Review. Cancers 2023, 15, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M. BRAF mutation in thyroid cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2005, 12, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbert, A.; Gruffydd-Jones, T.; Barrett, E.L.; Day, M.J.; Harvey, A.M. Feline thyroid carcinoma: Diagnosis and response to high-dose radioactive iodine treatment. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2009, 11, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M.E. Treatment of severe, unresponsive, or recurrent hyperthyroidism in cats. In Proceedings of the 2011 ACVIM Forum, Denver, CO, USA, 15–19 June 2011; pp. 104–106. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, B.; Schaffner, G.; Reifinger, M.; Loupal, G. K-ras protooncogene mutations in feline pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Vet. Rec. 2003, 153, 468–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uneyama, M.; Chambers, J.K.; Nakashima, K.; Uchida, K.; Nakayama, H. Histological Classification and Immunohistochemical Study of Feline Colorectal Epithelial Tumors. Vet. Pathol. 2021, 58, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasko, V.; Saji, M.; Hardy, E.; Kruhlak, M.; Larin, A.; Savchenko, V.; Miyakawa, M.; Isozaki, O.; Murakami, H.; Tsushima, T.; et al. Akt activation and localisation correlate with tumour invasion and oncogene expression in thyroid cancer. J. Med. Genet. 2004, 41, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, D.R.; Hardin, H.; Buehler, D.; Lloyd, R.V. AKT activity is elevated in aggressive thyroid neoplasms where it promotes proliferation and invasion. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2017, 103, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosevic, Z.; Pesic, M.; Stankovic, T.; Dinic, J.; Milovanovic, Z.; Stojsic, J.; Dzodic, R.; Tanic, N.; Bankovic, J. Targeting RAS-MAPK-ERK and PI3K-AKT-mTOR signal transduction pathways to chemosensitize anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. Transl. Res. 2014, 164, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz Ressel, B.L.; Massone, A.R.; Barbeito, C.G. Persistent activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin signalling pathway in cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas in cats. Vet. Dermatol. 2021, 32, 675-e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, M.; De Santis, M.C.; Braccini, L.; Gulluni, F.; Hirsch, E. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: An updated review. Ann. Med. 2014, 46, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza, M.C.; Er, E.E.; Blenis, J. The Ras-ERK and PI3K-mTOR pathways: Cross-talk and compensation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Hou, P.; Ji, M.; Guan, H.; Studeman, K.; Jensen, K.; Vasko, V.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Xing, M. Highly prevalent genetic alterations in receptor tyrosine kinases and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in anaplastic and follicular thyroid cancers. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 3106–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, M.C.; Barden, C.B.; Fahey, T.J., 3rd. p44/p42-MAP kinase expression in papillary thyroid carcinomas. Surgery 2001, 130, 936–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, C.; Yeager, N.; Di Cristofano, A. Thyroid-stimulating hormone initiated proliferative signals converge in vivo on the mTOR kinase without activating AKT. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8002–8006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene_Primer Direction | EN | Sequence (5′–3′) | GL | FS (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRAF_Fw | 16 | CACCTCAGATATTTTTCTTCACGA | ChrA2:155209670-155209647 | 151 |
| BRAF_Rv | TGGAGAAACAGCCTCAGTTCT | ChrA2:155209520-155209540 | ||
| NRAS_Fw | 2 | CCCAGGATTCTTACCGAAAA | ChrC1:97956864-97956845 | 188 |
| NRAS_Rv | GTACCTGTAAAGGTTAATATCTGCAA | ChrC1:97956677-97956702 | ||
| HRAS_Fw | 3 | TTATTGATGGCGAGACGTGC | ChrD1:115031688-115031707 | 147 |
| HRAS_Rv | GGATGTCCTCAAAGGACTTGGT | ChrD1:115031834-115031813 | ||
| KRAS_Fw | 2 | GGATTCCTACAGGAAACAAGTAGT | ChrB4:58575912-58575889 | 188 |
| KRAS_Rv | AAACCCACCTATAGTGGTGAATATC | ChrB4:58575725-58575749 |
| Ab | Reference (Company) | BS | CT | Ab Dilution | Ab Incubation | Epitope Revelation (DAB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pERK (Thr202/Tyr204) | 4370 (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, USA) | Rabbit (Monoclonal) | Feline and canine mammary carcinoma | 1:300 | Overnight (17 h), 4 °C | TA-125-QHDX, Epedria®, Kalamazoo, MI, USA |
| pS6 (Ser235/236) | 4858 (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, USA) | Rabbit (Monoclonal) | 1:600 | Overnight (17 h), 4 °C | K3468, Dako, Santa Clara, CA, USA | |
| pAKT (Ser473) | 66444-Ig (Proteintech, Rosemont, IL, USA) | Mouse (Monoclonal) | 1:250 | Overnight (17 h), 4 °C |
| Clinical-Pathological Features | TNA (n = 11/15, 73%) | TWA (n = 4/15, 27%) |
|---|---|---|
| Age groups | (n = 10) | (n = 2) |
| Median ± IQR | 11.0 ± 6.3 | 10 ± 0.0 |
| Sex | (n = 11) | (n = 2) |
| Female | 6 (45.5%) | 1 (50.0%) |
| Male | 5 (54.5%) | 1 (50.0%) |
| Tumor size (cm) | (n = 9) | (n = 1) |
| Median ± IQR | 3.5 ± 2.2 | 2.1 ± 0.0 |
| Vascular invasion | (n = 9) | (n = 4) |
| No | 9 (100.0%) | 2 (50.0%) |
| Yes | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (50.0%) |
| Extrathyroidal extension | (n = 2) | (n = 2) |
| No | 2 (100.0%) | 1 (50.0%) |
| Yes | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (50.0%) |
| Focality | (n = 9) | (n = 4) |
| Unifocal | 5 (55.6%) | 2 (50.0%) |
| Multifocal | 4 (44.4%) | 2 (50.0%) |
| Mitosis count per 2.60 mm2 | (n = 11) | (n = 4) |
| Median ± IQR | 1.0 ± 3.0 | 2.5 ± 7.0 |
| KRAS | pS6 IRS * | pS6 Intensity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MR | RS | p (U) | MR | RS | p (U) | |
| WT (n = 9) | 5.89 | 53.0 | 0.214 | 5.065 | 45.5 | 0.046 |
| Mut (n = 1) | 2.00 | 2.0 | (1.0) | 10.50 | 10.5 | (0.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monteiro, A.; Gaspar, T.B.; Borges, I.; Canberk, S.; Pinto, M.; Pires, I.; Soares, P.; Tavares, C. Exploring MAPK and mTOR Pathways in Feline Thyroid Tumors. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070617
Monteiro A, Gaspar TB, Borges I, Canberk S, Pinto M, Pires I, Soares P, Tavares C. Exploring MAPK and mTOR Pathways in Feline Thyroid Tumors. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(7):617. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070617
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonteiro, Alexandra, Tiago Bordeira Gaspar, Inês Borges, Sule Canberk, Mafalda Pinto, Isabel Pires, Paula Soares, and Catarina Tavares. 2025. "Exploring MAPK and mTOR Pathways in Feline Thyroid Tumors" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 7: 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070617
APA StyleMonteiro, A., Gaspar, T. B., Borges, I., Canberk, S., Pinto, M., Pires, I., Soares, P., & Tavares, C. (2025). Exploring MAPK and mTOR Pathways in Feline Thyroid Tumors. Veterinary Sciences, 12(7), 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070617











