The Effect of CDKN1A on the Expression of Genes Related to Milk Protein and Milk Fat Synthesis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Main Reagents
2.3. Experimental Methods
2.3.1. Construction of CDKN1A Over-Expression and Interference Vectors
2.3.2. Transfection
2.3.3. Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.3.4. Western Blot
2.4. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
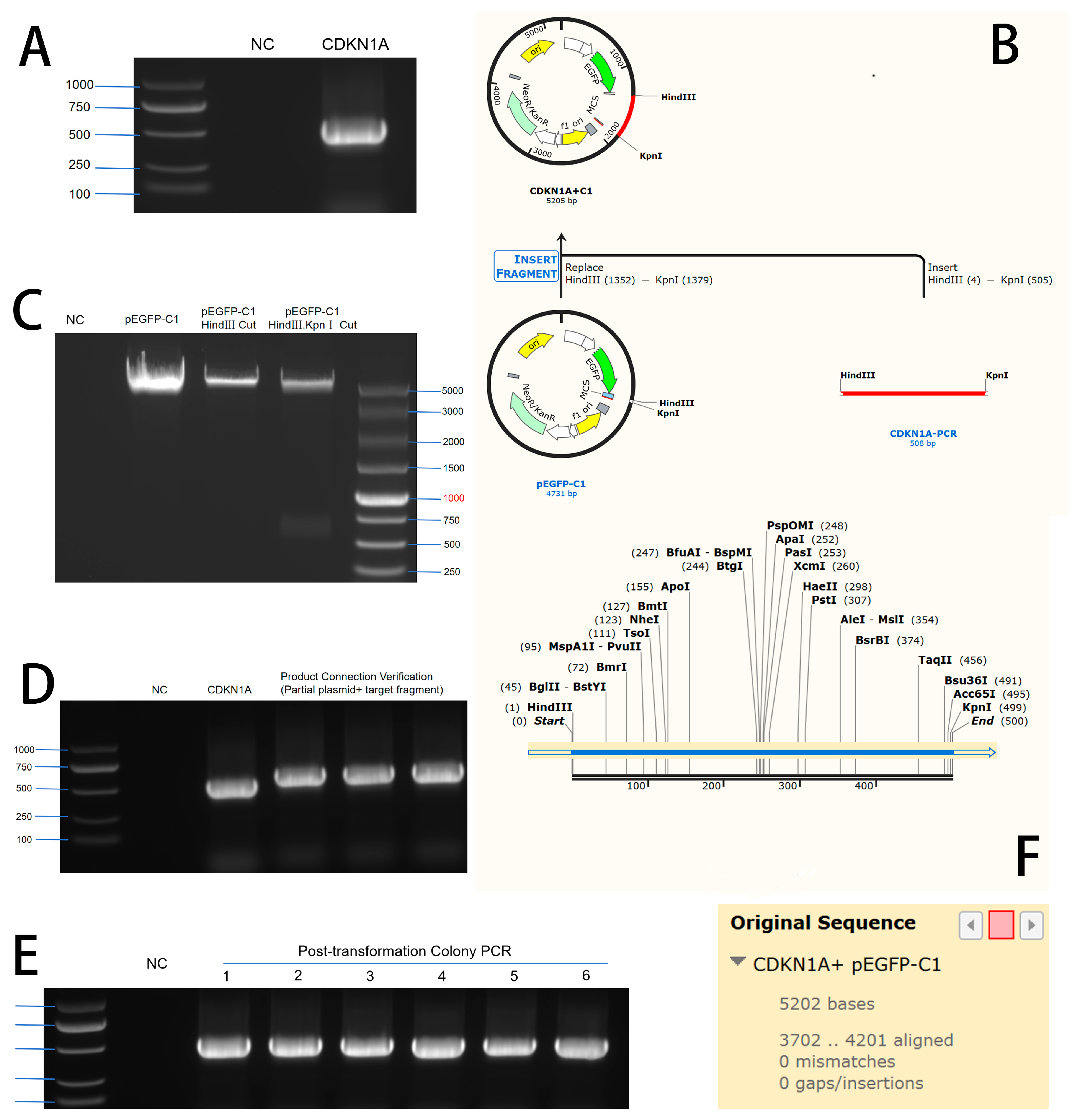
3.1. Construction of CDKN1A Overexpression and Interference Vectors
3.1.1. Construction of CDKN1A Overexpression Vector
3.1.2. Construction of CDKN1A Interference RNA
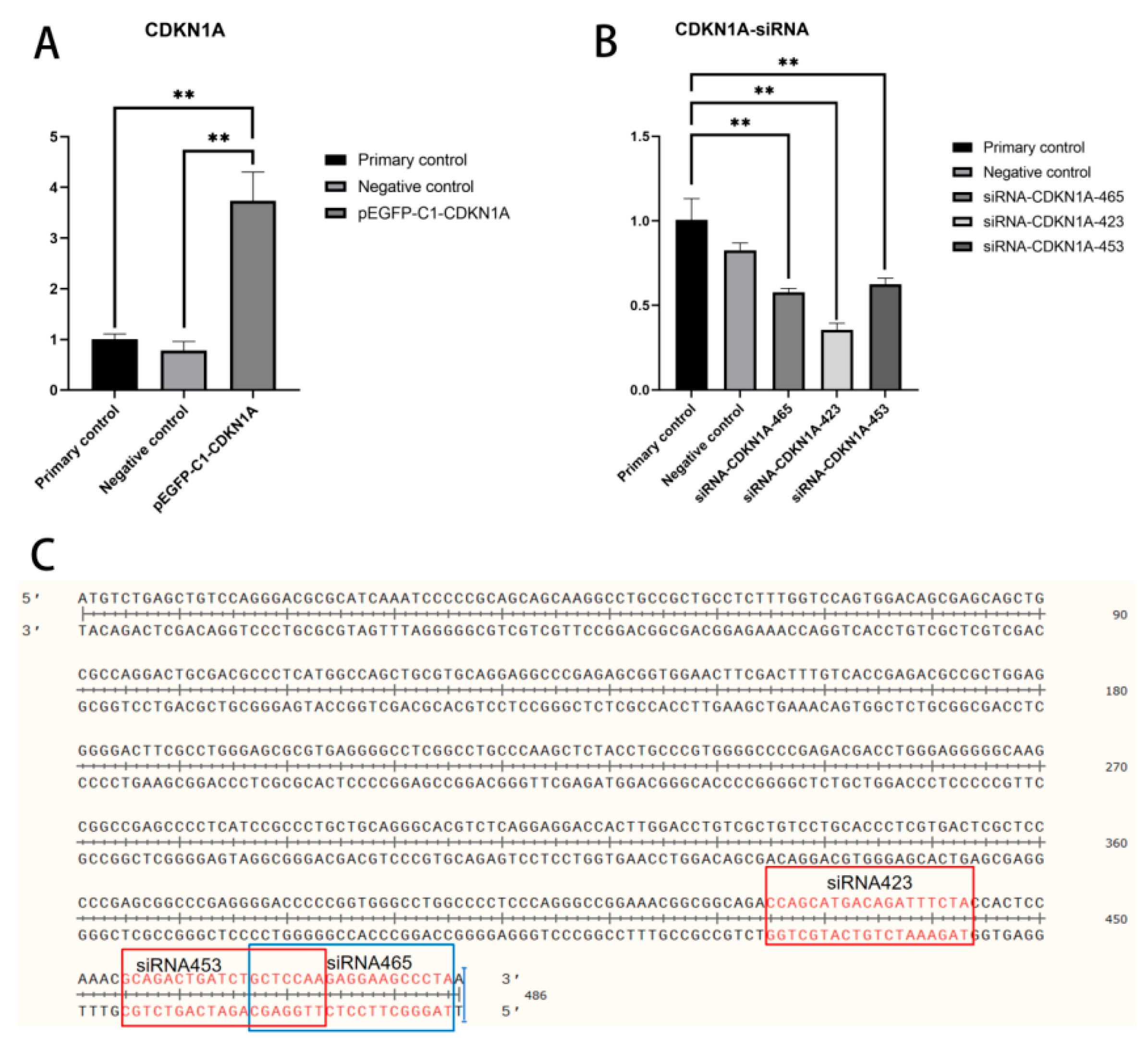
3.2. Transfection Effect Detection of Overexpression Vector and Interference RNA
3.3. Effect of CDKN1A on the Expression of Genes Related to Milk Protein and Milk Fat Synthesis
3.4. The Impact of CDKN1A on the Expression of Proteins Related to Milk Protein and Milk Fat Synthesis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDKN1A | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A gene |
| CSN2 | Casein beta gene |
| CSN3 | Casein kappa gene |
| OPN | Osteopontin |
| CD36 | Cluster of differentiation 36 |
| ACACA | Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Alpha |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
References
- von Keyserlingk, M.A.G.; Martin, N.P.; Kebreab, E.; Knowlton, K.F.; Grant, R.J.; Stephenson, M.; Sniffen, C.J.; Harner, J.P.; Wright, A.D.; Smith, S.I. Invited Review: Sustainability of the US Dairy Industry. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 5405–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Body and Milk Production Traits as Indicators of Energy Requirements and Efficiency of Purebred Holstein and 3-Breed Rotational Crossbred Cows from Viking Red, Montbéliarde, and Holstein Sires—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37164865/ (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Dong, W.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Ning, C.; Ding, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, L. Integrative Analysis of Genome-Wide DNA Methylation and Gene Expression Profiles Reveals Important Epigenetic Genes Related to Milk Production Traits in Dairy Cattle. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. Z. Tierz. Zucht. 2021, 138, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedholm, A.; Larsen, L.B.; Lindmark-Månsson, H.; Karlsson, A.H.; Andrén, A. Effect of Protein Composition on the Cheese-Making Properties of Milk from Individual Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 3296–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanigan, M.D.; Crompton, L.A.; Metcalf, J.A.; France, J. Modelling Mammary Metabolism in the Dairy Cow to Predict Milk Constituent Yield, with Emphasis on Amino Acid Metabolism and Milk Protein Production: Model Construction. J. Theor. Biol. 2001, 213, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Proud, C.G. The mTOR Pathway in the Control of Protein Synthesis. Physiol. Bethesda Md. 2006, 21, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xu, L.; Zhao, F.; Liu, H. Regulation of Milk Protein Synthesis by Free and Peptide-Bound Amino Acids in Dairy Cows. Biology 2021, 10, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Introductory Chapter: Milk Protein Synthesis, Progress, and Projections. IntechOpen. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/80992 (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Kim, J.-E.; Lee, H.-G. Amino Acids Supplementation for the Milk and Milk Protein Production of Dairy Cows. Animals 2021, 11, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Niu, H.; Luo, J.; Yao, W.; Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Geng, Y.; Gao, W.; Lei, A.; Gao, Z.; et al. Knockout of Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1 Decreased Milk Fat and Unsaturated Fatty Acid Contents of the Goat Model Generated by CRISPR/Cas9. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 4030–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H. L-Leucine Promotes the Synthesis of Milk Protein and Milk Fat in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells through the AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway under Hypoxic Conditions. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2024, 134, 109732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Han, B.; Sun, D. Bta-miR-106b Regulates Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cell Proliferation, Cell Cycle, and Milk Protein Synthesis by Targeting the CDKN1A Gene. Genes 2022, 13, 2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Liang, W.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, D. Determination of Genetic Effects of ATF3 and CDKN1A Genes on Milk Yield and Compositions in Chinese Holstein Population. BMC Genet. 2017, 18, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaya Arbeláez, M.I.; de Paula e Silva, A.C.A.; Navegante, G.; Valente, V.; Barbugli, P.A.; Vergani, C.E. Proto-Oncogenes and Cell Cycle Gene Expression in Normal and Neoplastic Oral Epithelial Cells Stimulated With Soluble Factors From Single and Dual Biofilms of Candida Albicans and Staphylococcus Aureus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 627043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gene Networks Driving Bovine Milk Fat Synthesis during the Lactation Cycle. BMC Genomics. Full Text. Available online: https://bmcgenomics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1471-2164-9-366 (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Ha, S.; Ha, H. Thr55 Phosphorylation of P21 by MPK38/MELK Ameliorates Defects in Glucose, Lipid, and Energy Metabolism in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Lee, C.Y.; Depamphilis, M.L. Cip/Kip Cyclin-Dependent Protein Kinase Inhibitors and the Road to Polyploidy. Cell Div. 2009, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manousakis, E.; Miralles, C.M.; Esquerda, M.G.; Wright, R.H.G. CDKN1A/P21 in Breast Cancer: Part of the Problem, or Part of the Solution? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, K.; Ryu, T.Y.; Jung, C.-R.; Lee, M.-S.; Lim, J.H.; Park, K.; Kim, D.-S.; Son, M.-Y.; Hamamoto, R.; et al. EHMT1 Knockdown Induces Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in Lung Cancer Cells by Increasing CDKN1A Expression. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 2989–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreis, N.-N.; Friemel, A.; Zimmer, B.; Roth, S.; Rieger, M.A.; Rolle, U.; Louwen, F.; Yuan, J. Mitotic p21Cip1/CDKN1A Is Regulated by Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 1 Phosphorylation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 50215–50228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druesne-Pecollo, N.; Pagniez, A.; Thomas, M.; Cherbuy, C.; Duée, P.-H.; Martel, P.; Chaumontet, C. Diallyl Disulfide Increases CDKN1A Promoter-Associated Histone Acetylation in Human Colon Tumor Cell Lines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 7503–7507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinford-Jackson, S.E.; Fant, B.; Wimmer, M.E.; Chan, D.; Knouse, M.C.; Sarmiento, M.; Thomas, A.S.; Huffman, P.J.; Mankame, S.; Worobey, S.J.; et al. Cocaine-Induced Changes in Sperm Cdkn1a Methylation Are Associated with Cocaine Resistance in Male Offspring. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 2905–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Zhao, J.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Chu, W.; Wang, W.-S.; Chen, Z.-J.; Du, Y. Lnc-MAP3K13-7:1 Inhibits Ovarian GC Proliferation in PCOS via DNMT1 Downregulation-Mediated CDKN1A Promoter Hypomethylation. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2021, 29, 1279–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, J.; Sabarwal, A.; Shyanti, R.K.; Singh, R.P. Berberine Enhances Posttranslational Protein Stability of P21/Cip1 in Breast Cancer Cells via down-Regulation of Akt. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 458, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez Galan, B.S.; Giolo De Carvalho, F.; Carvalho, S.C.S.; Cunha Brandao, C.F.; Morhy Terrazas, S.I.; Abud, G.F.; Meirelles, M.S.S.; Sakagute, S.; Ueta Ortiz, G.; Marchini, J.S.; et al. Casein and Whey Protein in the Breast Milk Ratio: Could It Promote Protein Metabolism Enhancement in Physically Active Adults? Nutrients 2021, 13, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gai, N.; Uniacke-Lowe, T.; O’Regan, J.; Goulding, D.A.; Kelly, A.L. Influence of β-Casein Genotype on Physicochemical Properties and Functionality of Bovine Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 8357–8367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasimi, N.; Sohrabi, Z.; Nunes, E.A.; Sadeghi, E.; Jamshidi, S.; Gholami, Z.; Akbarzadeh, M.; Faghih, S.; Akhlaghi, M.; Phillips, S.M. Whey Protein Supplementation with or without Vitamin D on Sarcopenia-Related Measures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2023, 14, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.C. Milk Nutritional Composition and Its Role in Human Health. Nutrition 2014, 30, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comin, A.; Cassandro, M.; Chessa, S.; Ojala, M.; Dal Zotto, R.; De Marchi, M.; Carnier, P.; Gallo, L.; Pagnacco, G.; Bittante, G. Effects of Composite Beta- and Kappa-Casein Genotypes on Milk Coagulation, Quality, and Yield Traits in Italian Holstein Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 4022–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, M.; Motmain, Z.; Ekinci, K.; Saygılı, E. Associations Between BLG, CSN3, DGAT1, GH, PIT1, and PRL Gene Polymorphisms and Milk Production Traits in Holstein Dairy Cows: A Meta-Analysis. Biochem. Genet. 2025, 63, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruchinin, A.G.; Illarionova, E.E.; Galstyan, A.G.; Turovskaya, S.N.; Bigaeva, A.V.; Bolshakova, E.I.; Strizhko, M.N. Effect of CSN3 Gene Polymorphism on the Formation of Milk Gels Induced by Physical, Chemical, and Biotechnological Factors. Foods 2023, 12, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.K.; Willi, M.; Liu, C.; Hennighausen, L. Cell-Specific and Shared Regulatory Elements Control a Multigene Locus Active in Mammary and Salivary Glands. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Wan, Y.; Guo, R.; Deng, M.; Deng, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F. Generation of Beta-Lactoglobulin Knock-out Goats Using CRISPR/Cas9. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashdulam, D.; Kim, I.-D.; Lee, H.; Lee, H.-K.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, J.-K. Osteopontin Heptamer Peptide Containing the RGD Motif Enhances the Phagocytic Function of Microglia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 524, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Huang, J.; Zhou, S.; Hou, X.; Ye, H.; Liu, X.; Xiang, S.; Shen, W.; et al. β-Catenin-Controlled Tubular Cell-Derived Exosomes Play a Key Role in Fibroblast Activation via the OPN-CD44 Axis. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osteopontin Promotes Tumor Growth and Metastasis and GPX4-Mediated Anti-Lipid Peroxidation in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Activating the PI3k/Akt/mTOR Pathway—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38526702/ (accessed on 9 March 2025).
- Singh, A.; Malla, W.A.; Kumar, A.; Jain, A.; Thakur, M.S.; Khare, V.; Tiwari, S.P. Review: Genetic Background of Milk Fatty Acid Synthesis in Bovines. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2023, 55, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Yue, Z.; Tian, M.; Luo, X.; Wang, W.; Shi, H.; Luo, J.; Deng, L.; Li, C. Leucine-Mediated SLC7A5 Promotes Milk Protein and Milk Fat Synthesis through mTOR Signaling Pathway in Goat Mammary Epithelial Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 13728–13739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Li, M.; Peng, R.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Sun, N. ACACA Reduces Lipid Accumulation through Dual Regulation of Lipid Metabolism and Mitochondrial Function via AMPK- PPARα- CPT1A Axis. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, L.; Petersen, T.E.; Rasmussen, J.T. Structural Characterization of Bovine CD36 from the Milk Fat Globule Membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1309, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre, D.; Pulvirenti, N.; Covino, D.A.; Varano, B.; Purificato, C.; Rainaldi, G.; Gauzzi, M.C.; Fantuzzi, L.; Conti, L.; Donninelli, G.; et al. Bovine Lactoferrin-Induced CCL1 Expression Involves Distinct Receptors in Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells and Their Monocyte Precursors. Toxins 2015, 7, 5472–5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eda, S.; Eda, K.; Prudhomme, J.G.; Sherman, I.W. Inhibitory Activity of Human Lactoferrin and Its Peptide on Chondroitin Sulfate A-, CD36-, and Thrombospondin-Mediated Cytoadherence of Plasmodium Falciparum-Infected Erythrocytes. Blood 1999, 94, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.R.; Ramadei, A.; Doymaz, A.; Varriano, S.; Natelson, D.M.; Yu, A.; Aktas, S.; Mazzeo, M.; Mazzeo, M.; Zakusilo, G.; et al. Long Non-Coding RNA Generated from CDKN1A Gene by Alternative Polyadenylation Regulates P21 Expression during DNA Damage Response. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 11911–11926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Dual Role of RBM42 in Modulating Splicing and Translation of CDKN1A/P21 during DNA Damage Response. Nature Communications. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-43495-6 (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Zyla, J.; Kabacik, S.; O’Brien, G.; Wakil, S.; Al-Harbi, N.; Kaprio, J.; Badie, C.; Polanska, J.; Alsbeih, G. Combining CDKN1A Gene Expression and Genome-Wide SNPs in a Twin Cohort to Gain Insight into the Heritability of Individual Radiosensitivity. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2019, 19, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaens, I.; Bonekamp, G.; Ten Napel, J.; Kamphuis, C.; De Haas, Y. Differences across Herds with Different Dairy Breeds in Daily Milk Yield Based Proxies for Resilience. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1120073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, R.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Xu, X. CDKN1A as a Target of Senescence in Heart Failure: Insights from a Multiomics Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1446300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | GenBank ID |
|---|---|---|
| CDKN1A | F: CCACCTGGACCTGAGCCTGAG R: CGCCGCTTGCTGTGGTAGAAG | NM_001098958.2 |
| CSN2 | F: CACAGTCTCTAGTCTATCCCTTCCC R: GGCGGCACCACCACAGG | NC_037333.1 |
| CSN3 | F: CGTCACCCACACCCACATTTATC R: TGTACTTGTAGGCTCGCCACTAG | NM_174294.2 |
| OPN | F: TTCAGAGTCCAGATGCCACAGAG R: CTCGTCTTCTTAGGTGCGTCATG | NM_174187.2 |
| ACACA | F: GCAGGCATCAGAAGATTATTGAAGAAG R: CGCACTCACATAACCAACCATCC | NM_174224.2 |
| CD36 | F: GAAGGCGGAAATGTTCAGAAATCAAG R: CCACACCAACACTGAGCAAGAC | NM_001278621.1 |
| β-ACTIN | F: CCATCGGCAATGAGCGGTTC R: GGAATTGAAGGTAGTTTCGTGAATGC | NM_173979 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhang, K.; Su, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, F.; Sun, Z.; Wu, Z.; Cao, G.; et al. The Effect of CDKN1A on the Expression of Genes Related to Milk Protein and Milk Fat Synthesis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060534
Zhang Y, Liang J, Zhang K, Su H, Wang D, Zhang M, Zhao F, Sun Z, Wu Z, Cao G, et al. The Effect of CDKN1A on the Expression of Genes Related to Milk Protein and Milk Fat Synthesis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(6):534. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060534
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuanyuan, Junxi Liang, Kai Zhang, Hong Su, Daqing Wang, Min Zhang, Feifei Zhao, Zhiwei Sun, Zhimin Wu, Guifang Cao, and et al. 2025. "The Effect of CDKN1A on the Expression of Genes Related to Milk Protein and Milk Fat Synthesis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 6: 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060534
APA StyleZhang, Y., Liang, J., Zhang, K., Su, H., Wang, D., Zhang, M., Zhao, F., Sun, Z., Wu, Z., Cao, G., & Zhang, Y. (2025). The Effect of CDKN1A on the Expression of Genes Related to Milk Protein and Milk Fat Synthesis in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Veterinary Sciences, 12(6), 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060534





