Exploring Gastrointestinal Health in Diabetic Cats: Insights from Owner Surveys, Ultrasound, and Histopathological Analysis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
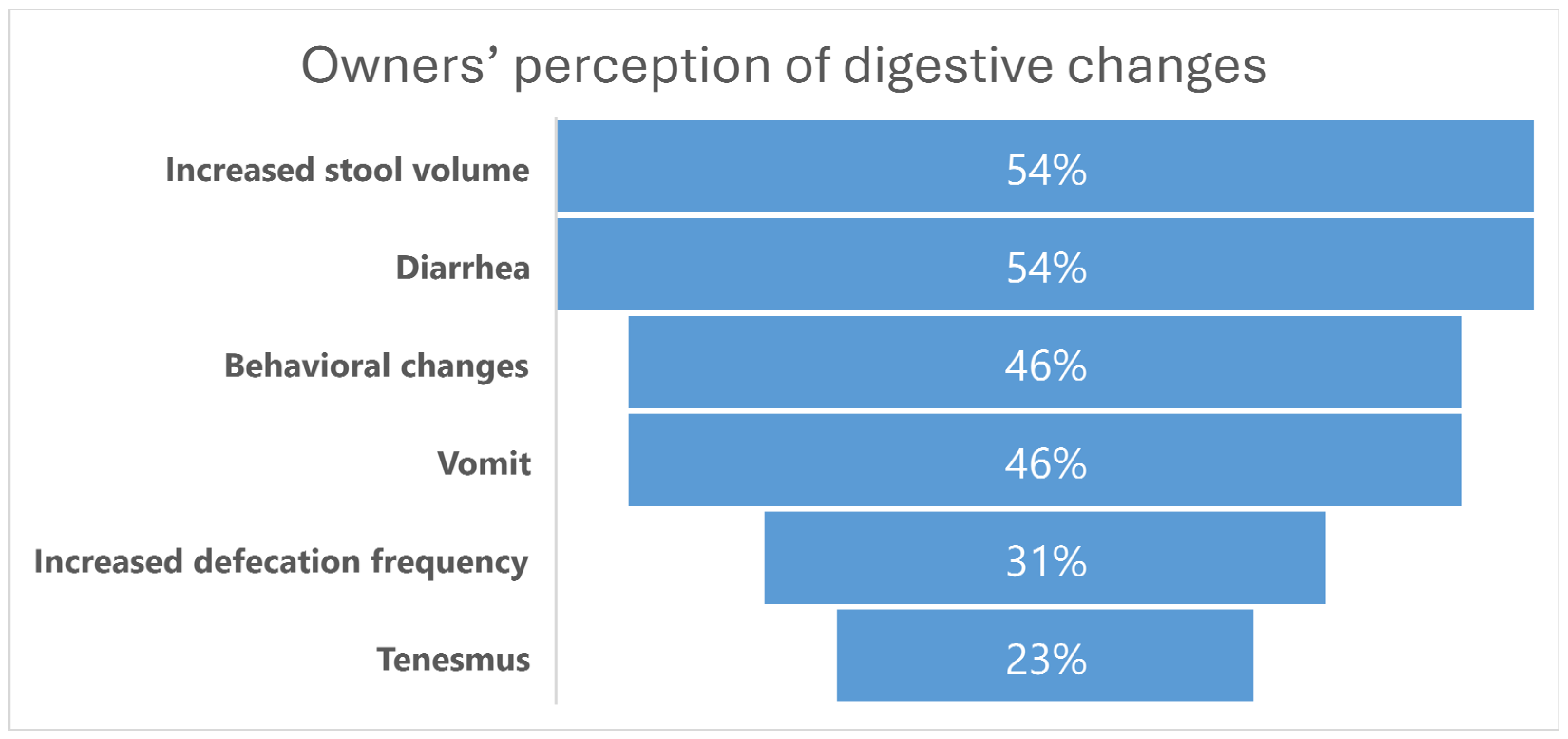
2.2. Owners’ Perception of Digestive Changes
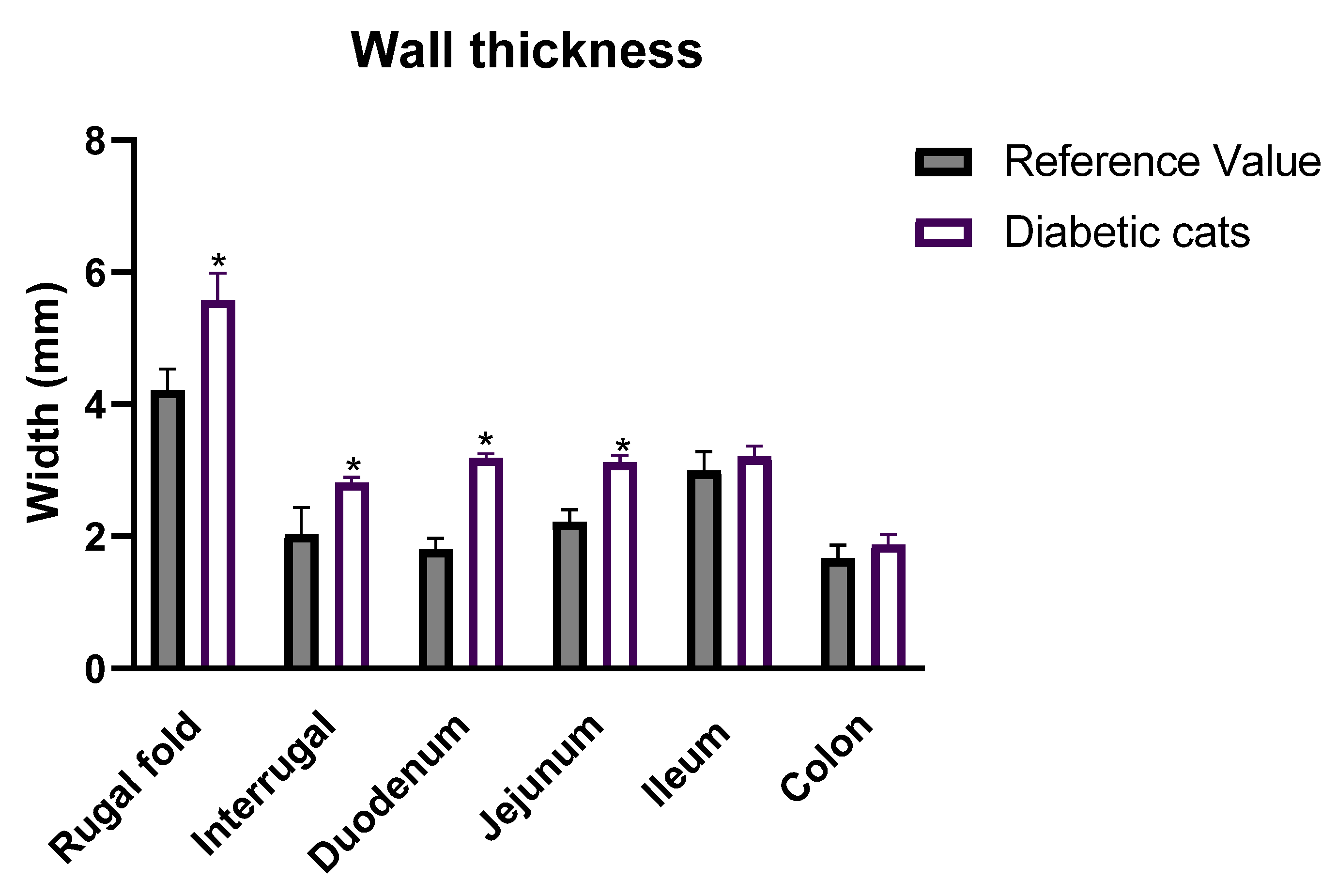
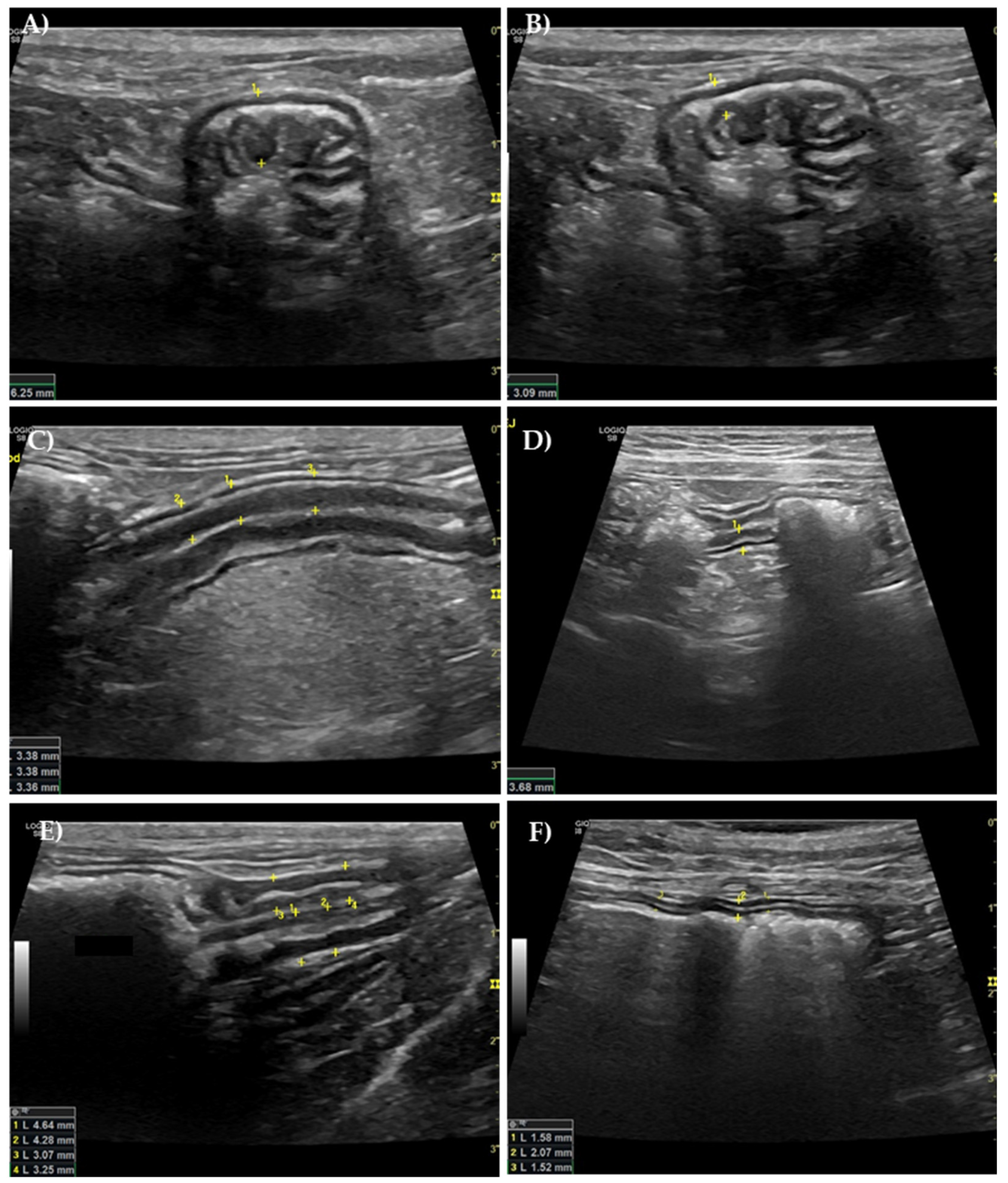
2.3. Ultrasound Evaluation of the GI Tract
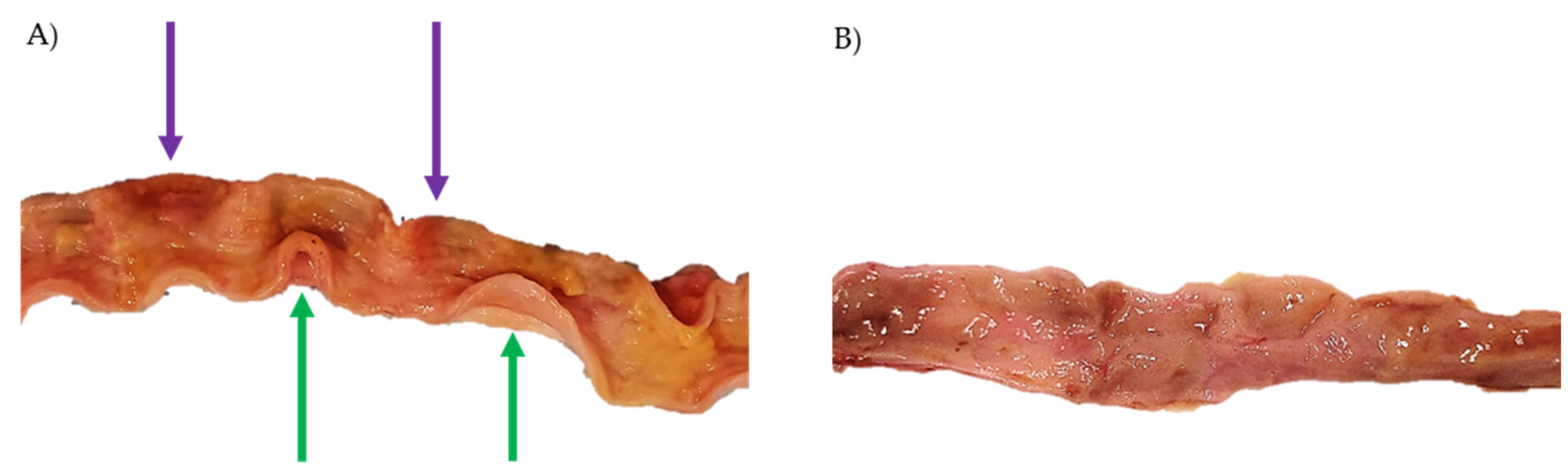
2.4. Necropsy and Histopathology
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Owners’ Perception of Digestive Changes
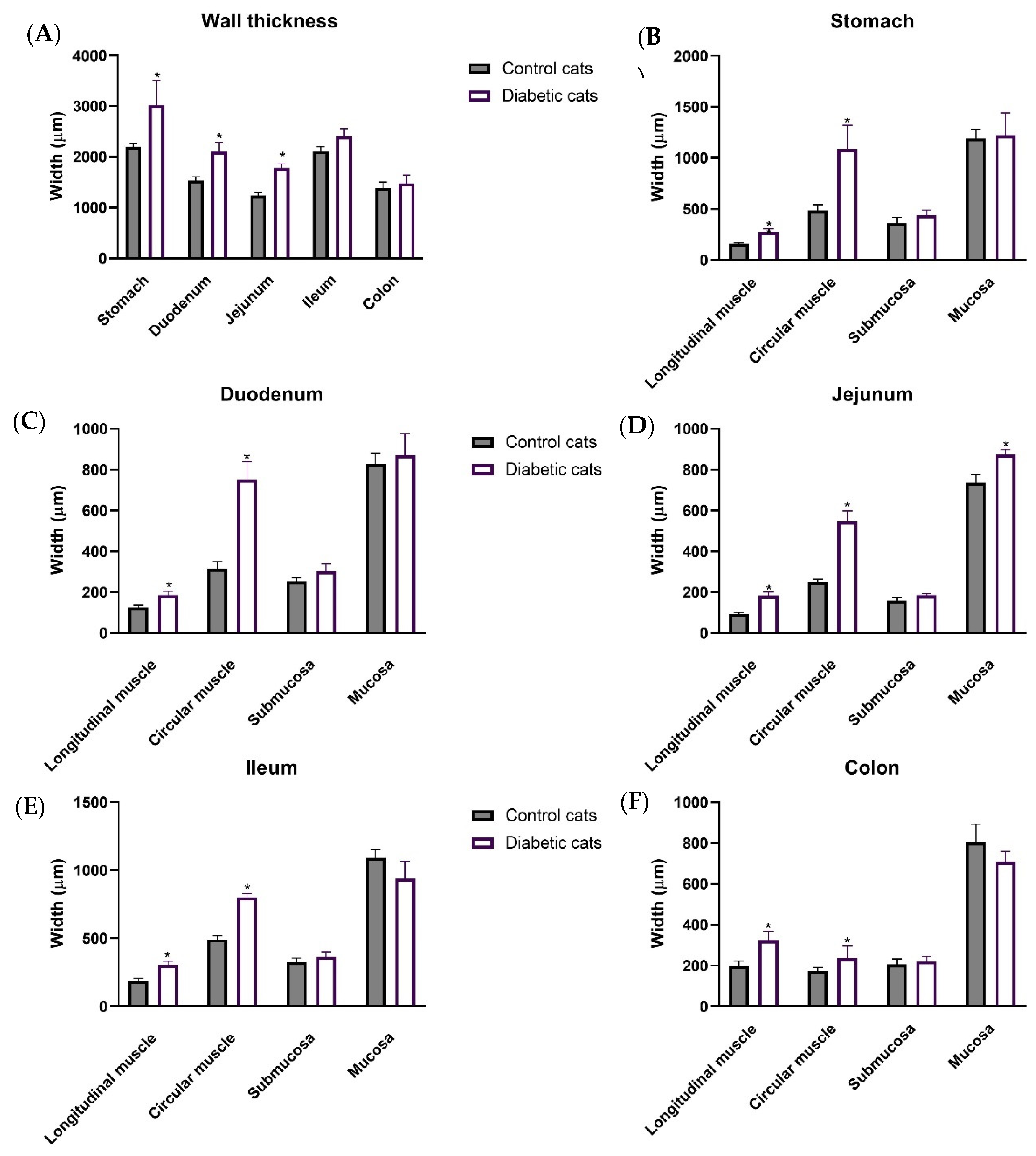
3.3. Ultrasound Evaluation of the GI Tract
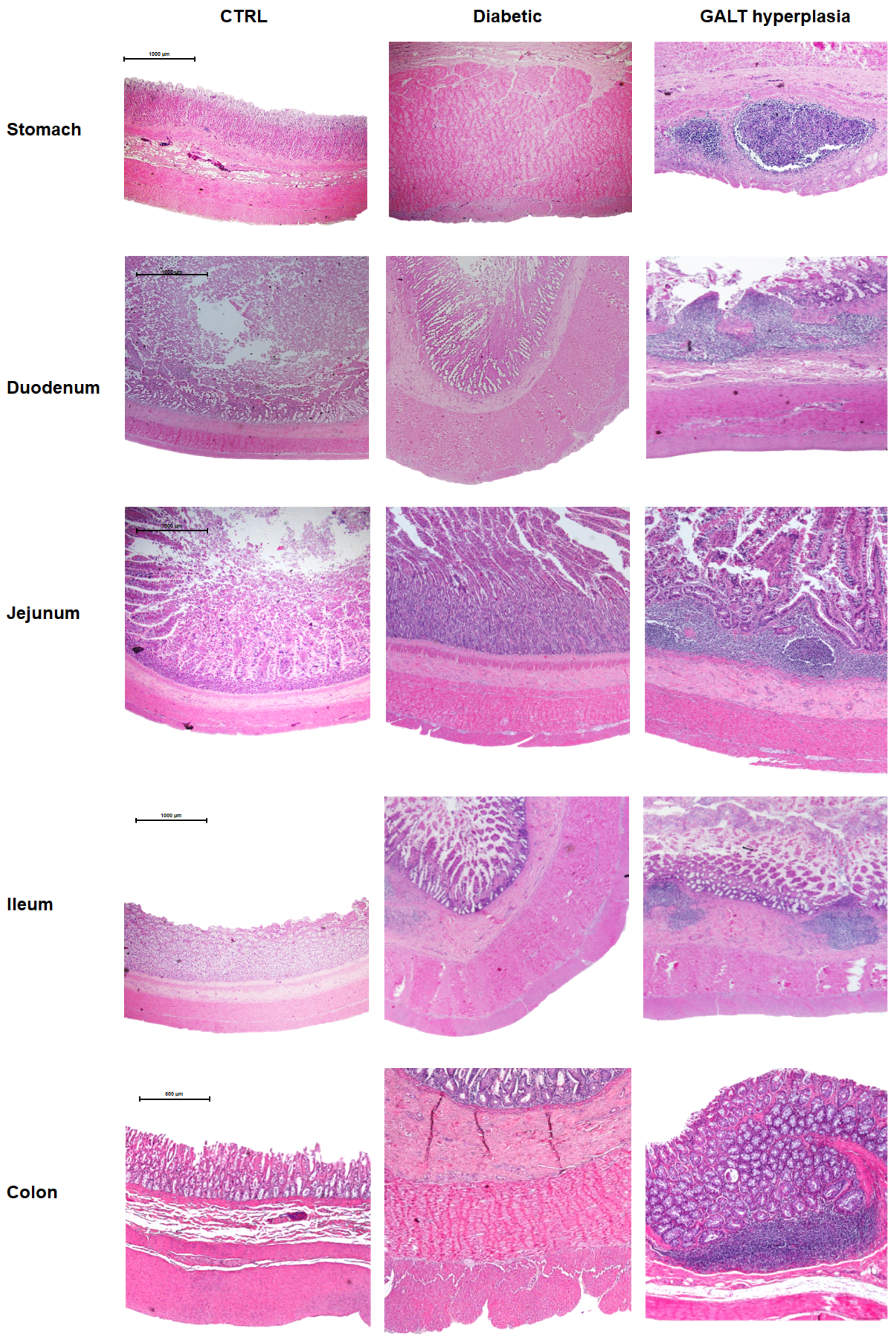
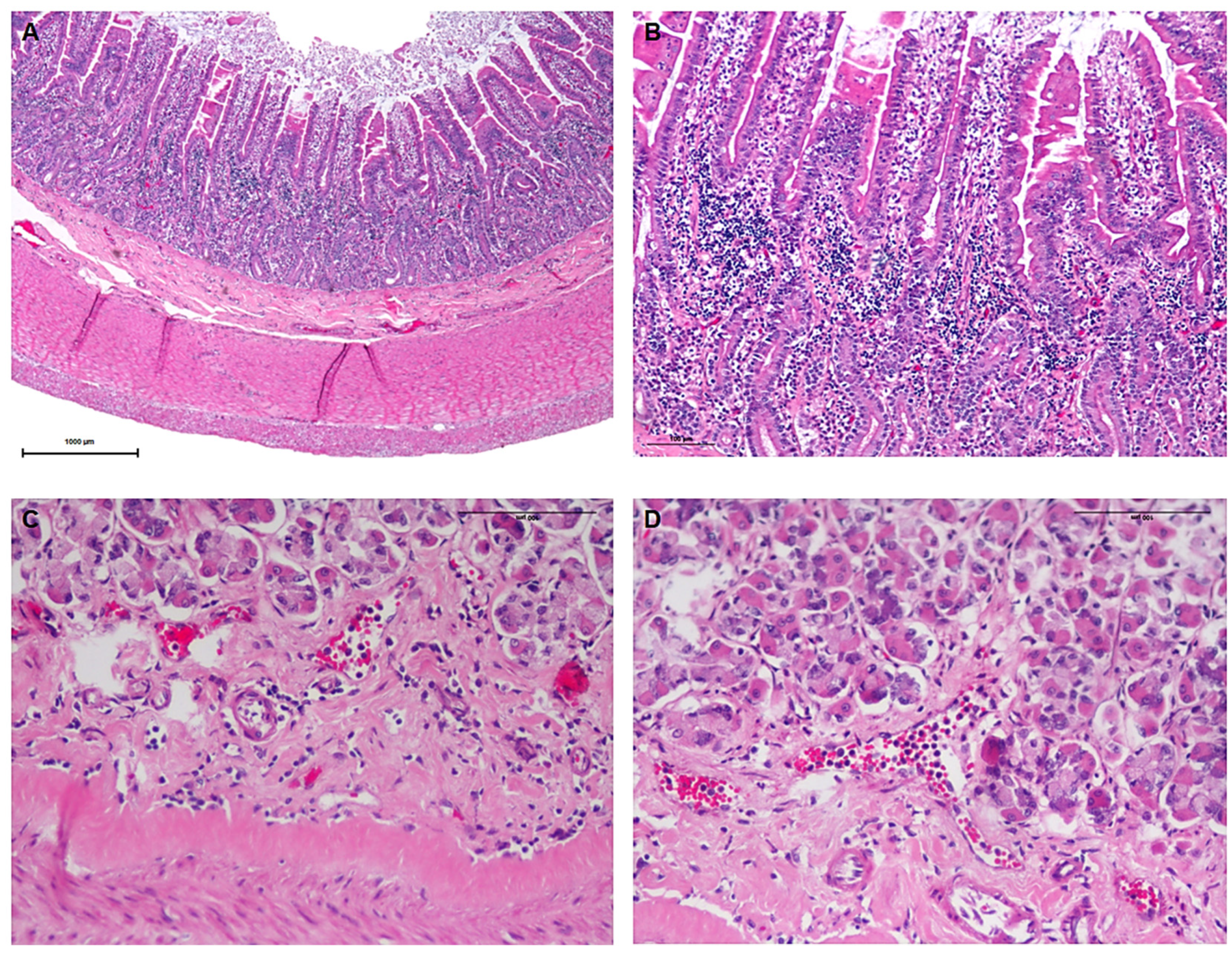
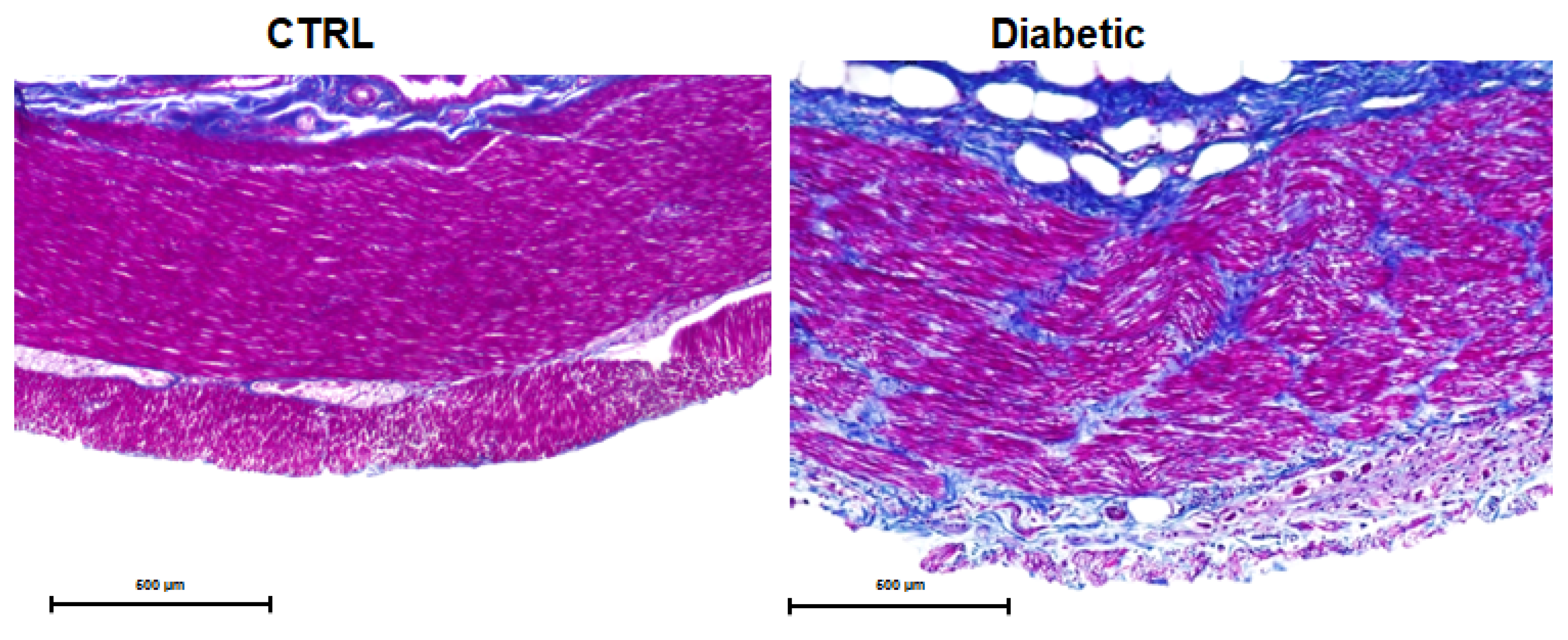
3.4. Necropsy and Histopathological Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
| TLA | Three-letter acronym |
| LD | Linear dichroism |
References
- World Health Organization. Global Report on Diabetes; WHO Library Cataloguing: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bommer, C.; Sagalova, V.; Heesemann, E.; Manne-Goehler, J.; Atun, R.; Bärnighausen, T.; Davies, J.; Vollmer, S. Global Economic Burden of Diabetes in Adults: Projections From 2015 to 2030. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gostelow, R.; Orme, C.; Church, D.B.; Verheyen, K.; Brodbelt, D.C. Epidemiology of Diabetes Mellitus among 193,435 Cats Attending Primary-Care Veterinary Practices in England. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2016, 30, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, J.S.; Marshall, R.D. Diabetes Mellitus in Cats. Vet. Clin. North. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2005, 35, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, J.S. Diabetes Mellitus in Dogs and Cats. In Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.W.; Reusch, C.E. Classification and Etiology of Diabetes in Dogs and Cats. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 222, T1–T9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothlin-Zachrisson, N.; Öhlund, M.; Röcklinsberg, H.; Ström, B. Survival, remission, and quality of life in diabetic cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2023, 37, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Bannuru, R.R.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Gaglia, J.L.; Hilliard, M.E.; Johnson, E.L.; Khunti, K.; et al. 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2024, 47 (Suppl. S1), S20–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccardi, F.; Webb, D.R.; Yates, T.; Davies, M.J. Pathophysiology of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 90-Year Perspective. Postgrad. Med. J. 2016, 92, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMeglio, L.A.; Evans-Molina, C.; Oram, R.A. Type 1 Diabetes. Lancet 2018, 391, 2449–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moini, J. Pathophysiology of Diabetes. In Epidemiology of Diabetes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galicia-Garcia, U.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Jebari, S.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Siddiqi, H.; Uribe, K.B.; Ostolaza, H.; Martín, C. Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eizirik, D.L.; Pasquali, L.; Cnop, M. Pancreatic β-Cells in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Different Pathways to Failure. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J. Type 2 Diabetes. Lancet 2017, 389, 2239–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.T.; Rayner, C.K.; Jones, K.L.; Talley, N.J.; Horowitz, M. Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Diabetes: Prevalence, Assessment, Pathogenesis, and Management. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekharan, B.; Srinivasan, S. Diabetes and the Enteric Nervous System. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2007, 19, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talley, N.J.; Young, L.; Bytzer, P.; Hammer, J.; Leemon, M.; Jones, M.; Horowitz, M. Impact of Chronic Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Diabetes Mellitus on Health-Related Quality of Life. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bytzer, P.; Talley, N.J.; Hammer, J.; Young, L.J.; Jones, M.P.; Horowitz, M. GI Symptoms in Diabetes Mellitus Are Associated With Both Poor Glycemic Control and Diabetic Complications. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, B.; Babu, S.; Walker, J.; Walker, A.B.; Pappachan, J.M. Gastrointestinal Complications of Diabetes Mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2013, 4, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, B.S.; Edelman, S.V.; Wolosin, J.D. Gastrointestinal Complications of Diabetes. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 42, 809–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisey, A. A Practical Approach to Gastrointestinal Complications of Diabetes. Diabetes Ther. 2016, 7, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves-Monteiro, M.; Menezes-Pinto, D.; Ferreira-Duarte, M.; Dias-Pereira, P.; Morato, M.; Duarte-Araújo, M. Histomorphometry Changes and Decreased Reactivity to Angiotensin II in the Ileum and Colon of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Liao, D.; Zhao, J. Diabetes-Induced Mechanophysiological Changes in the Small Intestine and Colon. World J. Diabetes 2017, 8, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partha, P.; Subhodip, P.; Sayantan, R. Disorders of Gastrointestinal Motility in Diabetes Mellitus—An Unattended Borderline Between Diabetologists and Gastroenterologists. Diabetes 2021, 9, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, J.; Gregersen, H. Biomechanical and Morphometric Intestinal Remodelling during Experimental Diabetes in Rats. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 1688–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, J. Long-term complications of diabetes mellitus, part ii: Gastrointestinal and infectious. Vet. Clin. North. Am.: Small Anim. Pract. 1995, 25, 731–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, K.; Cortes, Y.; Eirmann, L. Gastrointestinal Dysmotility Disorders in Critically Ill Dogs and Cats. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2016, 26, 234–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenig, M. The Cat as a Model for Human Obesity and Diabetes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2012, 6, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladwin, N.E.; Penninck, D.G.; Webster, C.R.L. Ultrasonographic Evaluation of the Thickness of the Wall Layers in the Intestinal Tract of Dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2014, 75, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, M.; Pallares, F.J.; Soler, M.; Agut, A. Relationship between Ultrasonographic and Histopathological Measurements of Small Intestinal Wall Layers in Fresh Cat Cadavers. Vet. J. 2018, 237, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Donato, P.; Penninck, D.; Pietra, M.; Cipone, M.; Diana, A. Ultrasonographic Measurement of the Relative Thickness of Intestinal Wall Layers in Clinically Healthy Cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2014, 16, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeoni, F.; Terragni, R.; Rubini, G.; Tamburro, R.; Del Signore, F.; Falerno, I.; Aste, G.; Russo, M.; Mastromatteo, G.; Vignoli, M. B-Mode and Contrast Enhanced Ultrasonography Features of Gastric Inflammatory and Neoplastic Diseases in Cats. Animals 2020, 10, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, S.M.; Graham, J.P.; Roberts, G.D.; Ginn, P.E.; Harrison, J.M. Sonography of the Normal Feline Gastrointestinal Tract. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 1999, 40, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, L.; Becvarova, I.; Cave, N.; MacKay, C.; Nguyen, P.; Rama, B.; Takashima, G.; Tiffin, R.; van Beukelen, P.; Yathiraj, S. WSAVA Nutritional Assessment Guidelines. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2011, 13, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penninck, D.G.; Nyland, T.G.; Fisher, P.E.; Kerr, L.Y. Ultrasonography of the normal canine gastrointestinal tract. Vet. Radiol. 1989, 30, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharun, K.; Banu, S.A.; Mamachan, M.; Subash, A.; Mathesh, K.; Kumar, R.; Vinodhkumar, O.R.; Dhama, K.; Abualigah, L.; Pawde, A.M.; et al. Comparative Evaluation of Masson’s Trichrome and Picrosirius Red Staining for Digital Collagen Quantification Using ImageJ in Rabbit Wound Healing Research. J. Exp. Biol. Agric. Sci. 2023, 11, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhlund, M.; Egenvall, A.; Fall, T.; Hansson-Hamlin, H.; Röcklinsberg, H.; Holst, B.S. Environmental Risk Factors for Diabetes Mellitus in Cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleton, D.; Rand, J.; Sunvold, G. Insulin Sensitivity Decreases with Obesity, and Lean Cats with Low Insulin Sensitivity Are at Greatest Risk of Glucose Intolerance with Weight Gain. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2001, 3, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.; Hoenig, M. Feline Comorbidities: Pathophysiology and Management of the Obese Diabetic Cat. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2021, 23, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeley, A.M.; O’Neill, D.G.; Davison, L.J.; Church, D.B.; Corless, E.K.; Brodbelt, D.C. Diabetes Mellitus in Dogs Attending UK Primary-Care Practices: Frequency, Risk Factors and Survival. Canine Med. Genet. 2020, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.B.; Davis, P.J. Water Metabolism in Diabetes Mellitus. Am. J. Med. 1991, 70, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyton, E.; Hall, J. Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology, 12th ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie, R.A.; Guthrie, D.W. Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus. Crit. Care Nurs. Q. 2004, 27, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, S.; Hazuchova, K.; Powney, S.; Guitian, J.; Niessen, A.; Pion, P.; Shaw, J.; Church, D. The Big Pet Diabetes Survey: Perceived Frequency and Triggers for Euthanasia. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, M.; Calvert, C.; Jacobs, G.; Brown, J. Feline Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Mortality Study of 55 Cats (1982–1994). J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 1997, 33, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, M.M.C.; Nelson, R.W.; Feldman, E.C.; Griffey, S.M. Response to Insulin Treatment and Survival in 104 Cats with Diabetes Mellitus (1985–1995). J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1998, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callegari, C.; Mercuriali, E.; Hafner, M.; Coppola, L.M.; Guazzetti, S.; Lutz, T.A.; Reusch, C.E.; Zini, E. Survival Time and Prognostic Factors in Cats with Newly Diagnosed Diabetes Mellitus: 114 Cases (2000–2009). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2013, 243, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegeberg, A.-M.; Brock, C. Diabetes and the Gastrointestinal Tract. Medicine 2024, 52, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fregonesi, C.; Miranda-neto, M.; Molinari, S.L.; Zanoni, J.N. Quantitative Study If the Myenteric Plexus of the Stomach of Rats with Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2001, 59, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, M.; Chu, N.V.; Edelman, S.V. Gastrointestinal Disturbances in Diabetes. Curr. Diab Rep. 2003, 3, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarandi, S.S.; Srinivasan, S. Diabetic Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders and the Role of Enteric Nervous System: Current Status and Future Directions. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagyánszki, M. Diabetes-Related Alterations in the Enteric Nervous System and Its Microenvironment. World J. Diabetes 2012, 3, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giancola, F.; Fracassi, F.; Gallucci, A.; Sadeghinezhad, J.; Polidoro, G.; Zini, E.; Asti, M.; Chiocchetti, R. Quantification of Nitrergic Neurons in the Myenteric Plexus of Gastric Antrum and Ileum of Healthy and Diabetic Dogs. Auton. Neurosci. 2016, 197, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, C.S.; Rayner, C.K.; Wu, T.; Jones, K.L.; Horowitz, M. Gastrointestinal Disorders in Diabetes; Endotext: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Forgacs, I.; Patel, V. Diabetes and the Gastrointestinal Tract. Medicine 2011, 39, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mare, R.; Sporea, I. Gastrointestinal and Liver Complications in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus—A Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, M.S.; Saad, R.J. Diabetes Mellitus and the Colon. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2017, 15, 460–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, F. Urinary and Fecal Incontinence. In Treatment and Care of the Geriatric Veterinary Patient; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, C. Toileting Troubles Part 1: Factors Influencing House Soiling in Cats and Dogs. Companion Anim. 2016, 21, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, H.C.; Sadek, T.P.; Curtis, T.M.; Halls, V.; Heath, S.; Hutchison, P.; Mundschenk, K.; Westropp, J.L. AAFP and ISFM Guidelines for Diagnosing and Solving House-Soiling Behavior in Cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2014, 16, 579–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaschen, L. Ultrasonography of Small Intestinal Inflammatory and Neoplastic Diseases in Dogs and Cats. Vet. Clin. North. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2011, 41, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penninck, D.; Smyers, B.; Webster, C.R.L.; Rand, W.; Moore, A.S. Diagnostic Value of Ultrasonography in Differentiating Enteritis from Intestinal Neoplasia in Dogs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2003, 44, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsikas, M.N.; Jakovljevic, S.; Moustardas, N.; Papazoglou, L.G.; Kazakos, G.M.; Dessiris, A.K. Ultrasonographic Signs of Intestinal Intussusception Associated with Acute Enteritis or Gastroenteritis in 19 Young Dogs. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2003, 39, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejskjaer, N.T.; Bradley, J.L.; Buxton-Thomas, M.S.; Edmonds, M.E.; Howard, E.R.; Purewal, T.; Thomas, P.K.; Watkins, P.J. Novel Surgical Treatment and Gastric Pathology in Diabetic Gastroparesis. Diabet. Med. 1999, 16, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Asanuma, A.; Tanaka, M.; Akiba, T.; Koga, T. Morphological Study on the Gastric Mucosa in Diabetes Mellitus Rats Induced by Streptozotocin. Exp. Anim. 1994, 43, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.-B. Upper Gastrointestinal Sensory-Motor Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatopoulou, A.; Papanas, N.; Maltezos, E. Diabetic Gastrointestinal Autonomic Neuropathy: Current Status and New Achievements for Everyday Clinical Practice. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 23, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, P.; Gregersen, H. Morpho-Mechanical Intestinal Remodeling in Type 2 Diabetic GK Rats—Is It Related to Advanced Glycation End Product Formation? J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, H.; Tong, X.; Zhao, J. Abnormal Expressions of AGEs, TGF-β1, BDNF and Their Receptors in Diabetic Rat Colon—Associations with Colonic Morphometric and Biomechanical Remodeling. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteves-Monteiro, M.; Ferreira-Duarte, M.; Vitorino-Oliveira, C.; Costa-Pires, J.; Oliveira, S.; Matafome, P.; Morato, M.; Dias-Pereira, P.; Costa, V.M.; Duarte-Araújo, M. Oxidative Stress and Histomorphometric Remodeling: Two Key Intestinal Features of Type 2 Diabetes in Goto–Kakizaki Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, B.; Thulesen, J.; Juul, K.; Kissow, H. Immunoneutralization of Endogenous Glucagon-like Peptide-2 Reduces Adaptive Intestinal Growth in Diabetic Rats. Regul. Pept. 2002, 105, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, T.; Iwakiri, R.; Fujimoto, K.; Yoshida, T.; Utsumi, H.; Sakata, H.; Hisatomi, A.; Aw, T.Y. Suppression of Apoptosis Is Responsible for Increased Thickness of Intestinal Mucosa in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Metabolism 2001, 50, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegman, M.J.; Eto, M.; Butler, T.M. Remodeling of the Rat Distal Colon in Diabetes: Function and Ultrastructure. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2016, 19107, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinge, M.W.; Haase, A.; Mark, E.B.; Sutter, N.; Fynne, L.V.; Drewes, A.M.; Schlageter, V.; Lund, S.; Borghammer, P.; Krogh, K. Colonic Motility in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes and Gastrointestinal Symptoms. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e13948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harberson, J.; Thomas, R.M.; Harbison, S.P.; Parkman, H.P. Gastric Neuromuscular Pathology in Gastroparesis: Analysis of Full-Thickness Antral Biopsies. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meldgaard, T.; Brock, C. Diabetes and the Gastrointestinal Tract. Medicine 2019, 47, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portincasa, P.; Bonfrate, L.; Wang, D.Q.-H.; Frühbeck, G.; Garruti, G.; Di Ciaula, A. Novel Insights into the Pathogenic Impact of Diabetes on the Gastrointestinal Tract. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2022, 52, e13846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lempesis, I.G.; Georgakopoulou, V.E. Physiopathological Mechanisms Related to Inflammation in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. World J. Exp. Med. 2023, 13, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, W.; Su, Y. Role of Gut Microbiota in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Diabetes Mullites: Advanced Research-Based Review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1029890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Vincenzo, F.; Del Gaudio, A.; Petito, V.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F. Gut Microbiota, Intestinal Permeability, and Systemic Inflammation: A Narrative Review. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 19, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Animal Data | |
| Gender | 9 males (69.23%) 4 females (30.77%) |
| Age | 12.5 ± 1.17 [7–19 years] |
| Weight | 5.61 ± 0.65 [2.75–9 kg] |
| Body condition | Underweight (7.69%, n = 1) Normal (30.77%, n = 4) Overweight (23.07%, n = 3) Obese (38.46%, n = 5) |
| Time since diabetes diagnosis | 2 months [7 days to 60 months] |
| Glycemia | 371.56 ± 45.99 mg/dL [170–600 mg/dL] |
| Diabetes treatment | Caninsulin® (38.46%, n = 5) Lantus® (38.46%, n = 5) Prozinc® (7.69%, n = 1) Degludec® (7.69%, n = 1) Metformin® (7.69%, n = 1) |
| Comorbidities | FIV (7.69%, n = 1) Chronic pancreatitis (7.69%, n = 1) Blindness (7.69%, n = 1) Kidney and liver degenerative disease (7.69%, n = 1) |
| Typical diabetes signs | Polydipsia (92.31%, n = 12) Polyuria (92.31%, n = 12) Polyphagia (61.54%, n = 8) Weight loss (76.92%, n = 10) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Esteves-Monteiro, M.; Baptista, C.S.; Cardoso-Coutinho, D.; Landolt, C.; Dias-Pereira, P.; Duarte-Araújo, M. Exploring Gastrointestinal Health in Diabetic Cats: Insights from Owner Surveys, Ultrasound, and Histopathological Analysis. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060529
Esteves-Monteiro M, Baptista CS, Cardoso-Coutinho D, Landolt C, Dias-Pereira P, Duarte-Araújo M. Exploring Gastrointestinal Health in Diabetic Cats: Insights from Owner Surveys, Ultrasound, and Histopathological Analysis. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(6):529. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060529
Chicago/Turabian StyleEsteves-Monteiro, Marisa, Cláudia S. Baptista, Diogo Cardoso-Coutinho, Clara Landolt, Patrícia Dias-Pereira, and Margarida Duarte-Araújo. 2025. "Exploring Gastrointestinal Health in Diabetic Cats: Insights from Owner Surveys, Ultrasound, and Histopathological Analysis" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 6: 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060529
APA StyleEsteves-Monteiro, M., Baptista, C. S., Cardoso-Coutinho, D., Landolt, C., Dias-Pereira, P., & Duarte-Araújo, M. (2025). Exploring Gastrointestinal Health in Diabetic Cats: Insights from Owner Surveys, Ultrasound, and Histopathological Analysis. Veterinary Sciences, 12(6), 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060529








