Oxidative Stress on Haemonchus contortus Larvae Exposed to Alternative Treatment with Artemisia cina n-Hexane Extract and Cinaguaiacin Metabolites
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. n-Hexane Extract and Lignans
2.3. Mass Spectrometry Lignans Evaluation
2.4. Haemonchus contortus Strain
2.5. Haemonchus contortus L3 Relative Expression Assay
2.6. Total RNA Extraction
2.7. Reverse Transcriptase
2.8. Real-Time PCR Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
Haemonchus contortus L3 Relative Expression Assay
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A. cina | Artemisia cina |
| H. contortus | Haemonchus contortus |
| GPx | Glutathione peroxidase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| SOD | Dismutase superoxide |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
References
- Zajac, A.M. Gastrointestinal Nematodes of Small Ruminants: Life Cycle, Anthelmintics, and Diagnosis. Vet. Clin. Food Anim. Pract. 2006, 22, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flay, K.J.; Hill, F.I.; Muguiro, D.H. A Review: Haemonchus contortus infection in pasture-based sheep production systems, with a focus on the pathogenesis of anaemia and changes in haematological parameters. Animals 2022, 12, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fissiha, W.; Kinde, M.Z. Anthelmintic resistance and its mechanism: A Review. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 5403–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuera-Piedrahita, R.I. Efecto de Artemisia cina 30CH y Artemisia cina En Extracto Etanólico Contra La Infección Natural e Inducida por Haemonchus contortus. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Cuautitlán, Mexico, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sakipova, Z.; Giorno, T.B.S.; Bekezhanova, T.; Siu Hai Wong, N.; Shukirbekova, A.; Fernandes, P.D.; Boylan, F. Pharmacological evaluation of Artemisia cina crude CO2 subcritical extract after the removal of santonin by means of high speed countercurrent chromatography. Molecules 2020, 25, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.H.; Ejo, M.; Feyera, T.; Regassa, D.; Mummed, B.; Huluka, S.A. In vitro anthelmintic activity of crude extracts of Artemisia Herba-Alba and Punica Granatum against Haemonchus contortus. J. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 2020, 4950196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prichard, R. Anthelmintic resistance. Vet Parasitol. 1994, 54, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuera-Piedrahita, R.I.; Dolores-Hernández, M.; Jiménez-Pérez, L.G.; Camacho-Enríquez, B.C.; Zamilpa, A.; López-Arellano, R.; Mendoza-de-Gives, P.; Cuéllar-Ordaz, J.A.; López-Arellano, M.E. In vitro nematocidal effect and anthelmintic activity of Artemisia cina against Haemonchus contortus in gerbils and relative expression of Hc29 Gene in Transitional Larvae (L3–L4). Acta Parasitol. 2021, 66, 938–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
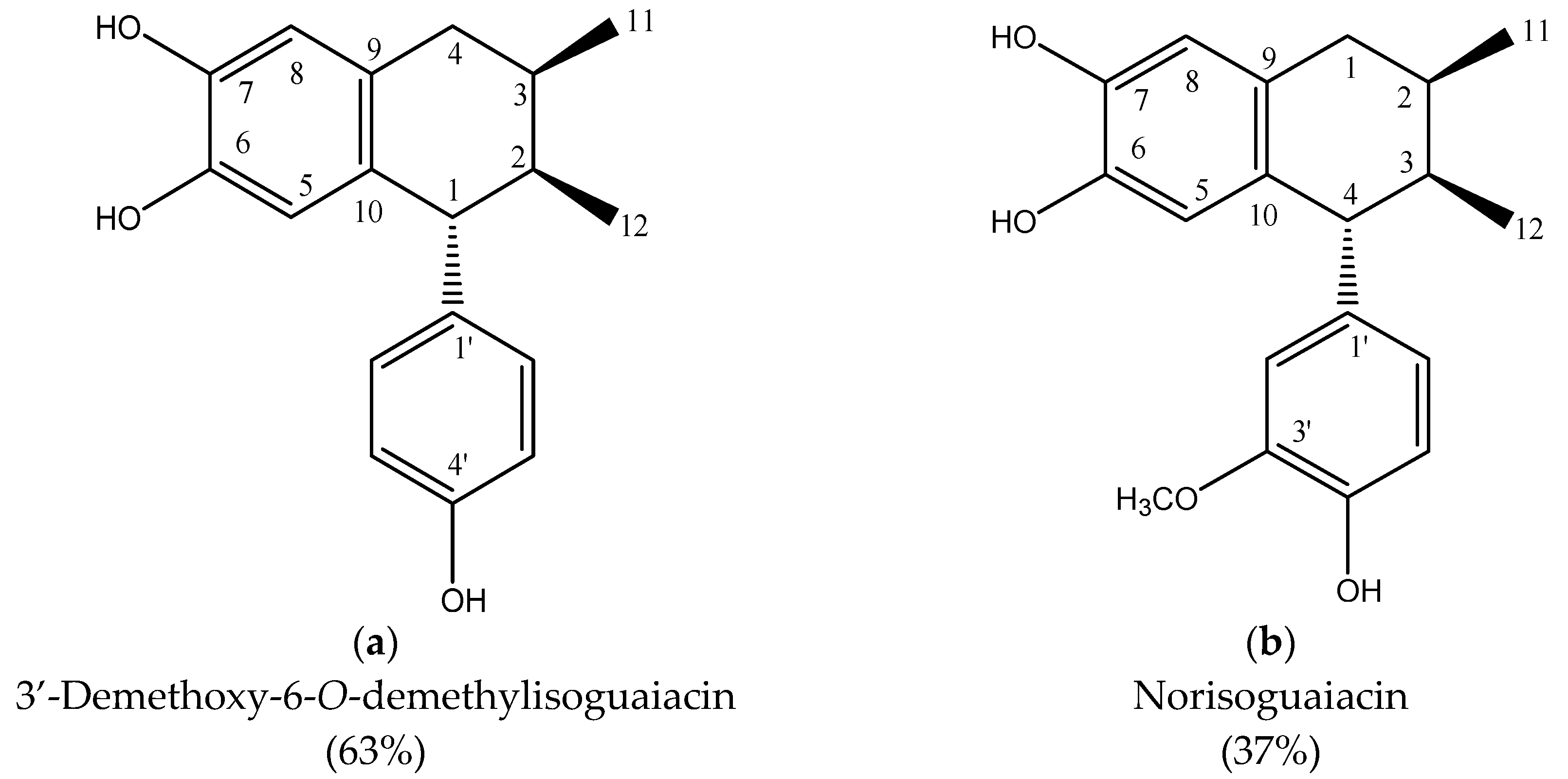
- Higuera-Piedrahita, R.I.; Dolores-Hernández, M.; de la Cruz-Cruz, H.A.; López-Arellano, R.; Gives, P.M.; Olmedo-Juárez, A.; Cuéllar-Ordaz, J.A.; González-Cortazar, M.; Ble-González, E.A.; López-Arellano, M.E.; et al. 3′-Demethoxy-6-O-Demethylisoguaiacin and Norisoguaiacin Nematocidal Lignans from Artemisia cina against Haemonchus contortus infective Larvae. Plants 2023, 12, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuera-Piedrahita, R.I.; Dolores-Hernández, M.; de la-Cruz-Cruz, H.A.; Andrade-Montemayor, H.M.; Zamilpa, A.; López-Arellano, R.; González-Garduño, R.; Cuéllar-Ordaz, J.A.; Mendoza-de-Gives, P.; López-Arellano, M.E. An Artemisia cina n-hexane extract reduces the Haemonchus contortus and Teladorsagia circumcincta fecal egg count in naturally infected periparturient goats. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2022, 54, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sülsen, V.P.; Lizarraga, E.; Mamadalieva, N.Z.; Lago, J.H.G. Potential of terpenoids and flavonoids from Asteraceae as anti-Inflammatory, antitumor, and antiparasitic agents. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 6196198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolnik, A.; Olas, B. The plants of the Asteraceae family as agents in the protection of human health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaraj, C.; Ragavendran, C.; Kumar, R.C.S.; Ali, A.; Khan, S.U.; Mashwani, Z.-R.; Luna-Arias, J.P.; Pedroza, J.P.R. Antiparasitic potential of Asteraceae plants: A comprehensive review on therapeutic and mechanistic aspects for biocompatible drug discovery. Phytomedicine Plus 2022, 2, 100377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawłowska, M.; Mila-Kierzenkowska, C.; Szczegielniak, J.; Woźniak, A. Oxidative stress in parasitic diseases—Reactive oxygen species as mediators of interactions between the host and the parasites. Antioxidants 2023, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, I.; Kode, A.; Biswas, S.K. Assay for quantitative determination of glutathione and glutathione disulfide levels using enzymatic recycling method. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 3159–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, W.M.; Wilson-Delfosse, A.L.; Mieyal, J.J. Dysregulation of glutathione homeostasis in neurodegenerative diseases. Nutrients 2012, 4, 1399–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosskopf, H.M.; Grosskopf, R.K.; Biazus, A.H.; Leal, M.L.R.; Bottari, N.B.; Alves, M.S.; Schetinger, M.R.C.; Morsch, V.M.; Machado, G.; Baldissera, M.D.; et al. Supplementation with copper edetate in control of Haemonchus contortus of sheep, and its effect on cholinesterase’s and superoxide dismutase activities. Exp. Parasitol. 2017, 173, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, V.; Das Singla, L.; Choudhury, D. Cuminaldehyde induces oxidative stress-mediated physical damage and death of Haemonchus contortus. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maza-Lopez, J.; Jiménez-Jacinto, V.; Bermúdez-Morales, V.H.; Alonso-Morales, R.A.; Reyes-Guerrero, D.E.; Higuera-Piedrahita, R.I.; Camas-Pereyra, R.; López-Arellano, M.E. Molecular study of the transcription Factor SKN-1 and its putative relationship with genes that encode GST and antioxidant enzymes in Haemonchus contortus. Vet. Parasitol. 2024, 331, 110255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corticelli, B.; Lai, M. Ricerche sulla tecnica di coltura delle larve infestive degli strongili gastro-intestinali del bovino. Acta Med. Vet. 1963, 9, 347–357. [Google Scholar]
- Lubisch, M.; Moyzio, S.; Kaiser, C.S.; Krafeld, I.; Leusder, D.; Scholz, M.; Hoepfner, L.; Hippler, M.; Liebau, E.; Kahl, J. Using Caenorhabditis elegans to produce functional secretory proteins of parasitic nematodes. Acta Trop. 2022, 225, 106176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, S.; Matthews, J.B.; Shaw, D.J.; Paterson, S.; McWilliam, H.E.G.; Inglis, N.F.; Nisbet, A.J. Ovine IgA-reactive proteins from Teladorsagia circumcincta infective larvae. Int. J. Parasitol. 2014, 44, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen WM, Mallinson CB. Parenteral methods of supplementation with copper and selenium. Vet. Rec. 1984, 114, 451–454. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeschke, E.; Ostermann, T.; Lüke, C.; Tabali, M.; Kröz, M.; Bockelbrink, A.; Witt, C.M.; Willich, S.N.; Matthes, H. Remedies containing Asteraceae extracts. Drug Saf. 2009, 32, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Liu, X.; Luo, X.; Lou, X.; Li, P.; Li, X.; Liu, X. Antiaging effects of dietary supplements and natural products. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1192714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-K.; Yeh, J.-Y.; Wei, J.-H. Protective effects of the crude extracts from Yam (Dioscorea alata) peel on Tert-Butylhydroperoxide-induced oxidative stress in mouse liver cells. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.R.; Trübenbach, K.; Teixeira, T.; Lopes, V.M.; Pires, V.; Baptista, M.; Repolho, T.; Calado, R.; Diniz, M.; Rosa, R. Oxidative stress in deep scattering layers: Heat shock response and antioxidant enzymes activities of myctophid fishes thriving in oxygen minimum zones. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2013, 82, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Leng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q. Effects of dietary Artemisia annua supplementation on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, immune function, and gut microbiota of geese. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Pan, L.; Xie, R.; Li, L.; Wen, J.; Zhou, X.; Dong, X.; Xie, S.; Tan, B.; Liu, H. Effects of dietary artemisinin on growth performance, digestive enzyme activity, intestinal microbiota, antioxidant capacity and immune biomarkers of coral trout (Plectropomus leopardus). Aquac. Rep. 2023, 29, 101525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, H.-Y.; Kuo, S.-C. Recent studies and progression of Yin Chen Hao (茵陳蒿 Yīn Chén Hāo), a long-term used traditional chinese medicine. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2013, 3, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reséndiz-González, G.; Olmedo-Juárez, A.; González-Garduño, R.; Cortes-Morales, J.A.; González-Cortazar, M.; Sánchez-Mendoza, A.E.; López-Arellano, M.E.; Mercado-Márquez, C.; Lara-Bueno, A.; Higuera-Piedrahita, R.I. Anthelmintic efficacy of an organic fraction from Guazuma ulmifolia leaves and evaluation of reactive oxidative stress on Haemonchus contortus. Exp. Parasitol. 2024, 261, 108768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhibi, S.; Bouzenna, H.; Samout, N.; Tlili, Z.; Elfeki, A.; Hfaiedh, N. Nephroprotective and antioxidant properties of Artemisia arborescens hydroalcoholic extract against oestroprogestative-induced kidney damages in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 82, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanshita, G.; Sunidhi, S.; Neloy Kumar, C.; Lachhman Das, S.; Diptiman, C. Targeting the nervous system of the parasitic worm, Haemonchus contortus with quercetin. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13699. [Google Scholar]
- García-Coraidas, L.; Angulo-Cubillán, F.; Méndez, S.; Larraga, V.; De la Fuente, C.; Cuquerella, M.; Alunda, J.M. Isolation and immunolocalization of a putative protective antigen (P26/23) from adult Haemonchus contortus. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 104, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, D.; de Araújo, M.; Carollo, C.; Lifschitz, A.; Conde, M.; de Freitas, M.; dos Santos Freire, Z.; Tutija, J.; Nakatani, M.; Borges, A. Combination of quercetin and ivermectin: In vitro and in vivo effects against Haemonchus contortus. Acta Trop. 2020, 201, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Genebank Access Number | Tm | Sequence | Amplicon Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glutathione peroxidase | AY603337 | 58 °C | Fw: 5′-TGACGTCAACGGAGAGAACC-3’ | 189 |
| Rv: 5′-GTTGGATGGAAACGGAAGCG-3’ | ||||
| Catalase | AY603335.1 | 60 °C | Fw: 5′-CACCGTGTTTCGTTCGCTTT-3’ | 184 |
| Rv: 5′-TGGGTGTGGATGAAGTTCGG-3’ | ||||
| Superoxide Dismutase | MT015608.1 | 57 °C | Fw: 5′-GCAGCGTATCCGGTCTACAA-3’ | 121 |
| Rv: 5′-CCCGCTCCAAGACAACCATT-3 | ||||
| β-tubulin | FJ981644.1 | 59 °C | Fw: 5′-GGGCAAAAGGTCACTACACA-3’ | 229 |
| Rv: 5′-TCGGAAACCTTTGGTGAAGG-3’ |
| Hydrogen Peroxide | Β-Tubuline | n-Hexane Extract | Cinaguaiacin | Tween 20 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | Fold Change | p Value | Fold Change | p Value | Fold Change | p Value | Fold Change | p Value | Fold Change | p Value |
| Glutathione peroxidase (GPx) | 0.00 * | 0.0208 | 1 | 0 | 113.64 * | <0.0001 | 0.05 * | 0.0277 | 2.38 | 0.08 |
| Catalase (CAT) | 1.05 | 0.4688 | 1 | 0 | 9.6 | 0.1433 | 0.27 | 0.0799 | 0 | 0 |
| Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) | 0.05 | 0.0553 | 1 | 0 | 0.27 | 0.0534 | 0.33 | 0.0972 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez-Mendoza, A.E.; Reséndiz-González, G.; Rico-Mejía, E.; de la Cruz-Cruz, H.A.; Ramírez-Rico, G.; Cuéllar-Ordaz, J.A.; Montiel-Sosa, J.F.; López-Arellano, M.E.; Reyes-Guerrero, D.E.; Domínguez-Delgado, C.L.; et al. Oxidative Stress on Haemonchus contortus Larvae Exposed to Alternative Treatment with Artemisia cina n-Hexane Extract and Cinaguaiacin Metabolites. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050467
Sánchez-Mendoza AE, Reséndiz-González G, Rico-Mejía E, de la Cruz-Cruz HA, Ramírez-Rico G, Cuéllar-Ordaz JA, Montiel-Sosa JF, López-Arellano ME, Reyes-Guerrero DE, Domínguez-Delgado CL, et al. Oxidative Stress on Haemonchus contortus Larvae Exposed to Alternative Treatment with Artemisia cina n-Hexane Extract and Cinaguaiacin Metabolites. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(5):467. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050467
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez-Mendoza, Ana Elvia, Guillermo Reséndiz-González, Eduardo Rico-Mejía, Héctor Alejandro de la Cruz-Cruz, Gerardo Ramírez-Rico, Jorge Alfredo Cuéllar-Ordaz, José Francisco Montiel-Sosa, María Eugenia López-Arellano, David Emmanuel Reyes-Guerrero, Clara Luisa Domínguez-Delgado, and et al. 2025. "Oxidative Stress on Haemonchus contortus Larvae Exposed to Alternative Treatment with Artemisia cina n-Hexane Extract and Cinaguaiacin Metabolites" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 5: 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050467
APA StyleSánchez-Mendoza, A. E., Reséndiz-González, G., Rico-Mejía, E., de la Cruz-Cruz, H. A., Ramírez-Rico, G., Cuéllar-Ordaz, J. A., Montiel-Sosa, J. F., López-Arellano, M. E., Reyes-Guerrero, D. E., Domínguez-Delgado, C. L., Medellín, M. O. P., Hernández-Patlán, D., & Higuera-Piedrahita, R. I. (2025). Oxidative Stress on Haemonchus contortus Larvae Exposed to Alternative Treatment with Artemisia cina n-Hexane Extract and Cinaguaiacin Metabolites. Veterinary Sciences, 12(5), 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050467







