A Nutritional Supplement Containing Curcumin C3 Complex, Glucosamine, and Chondroitin Alleviates Osteoarthritis in Mice and Canines
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Products
2.2. Induction of Osteoarthritis in Mice and Treatment
2.3. Behavioral Tests Related to Osteoarthritis
2.4. Von Frey Test
2.5. Micro-CT
2.6. Histological Evaluation of Mouse Joint Tissues
2.7. Assessment of Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
2.8. Study of the Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Effects of C3GC on Dogs with Osteoarthritis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. C3GC Improves Motor Functions and Helps in Restoring Functions in OA Mice
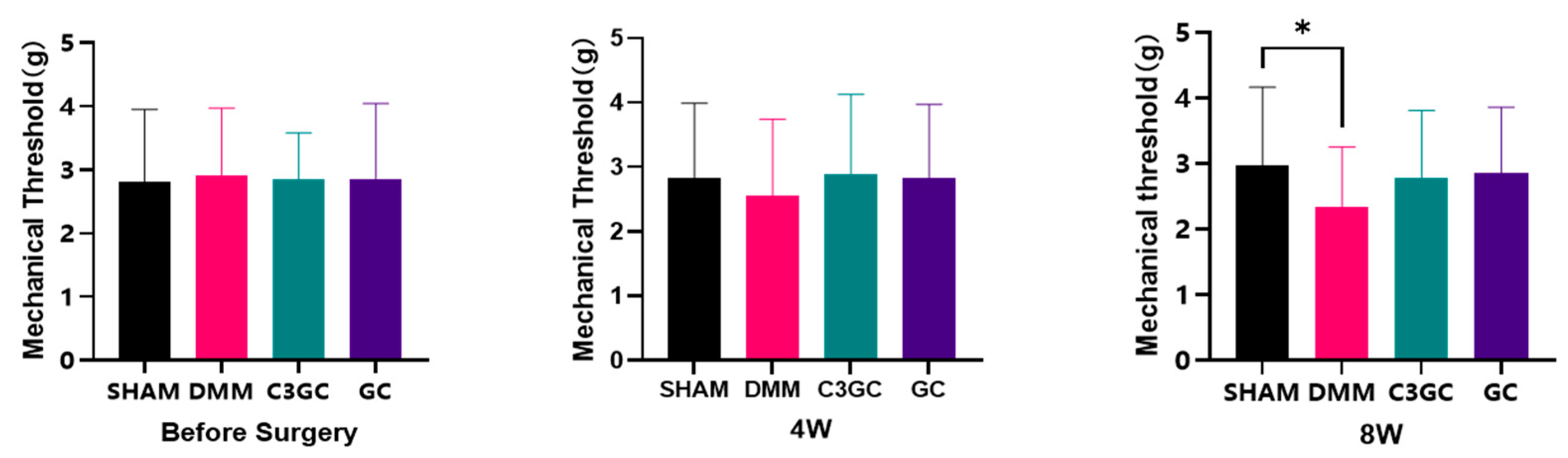
3.2. C3GC Alleviates Mechano-Hyperalgesia in Osteoarthritis
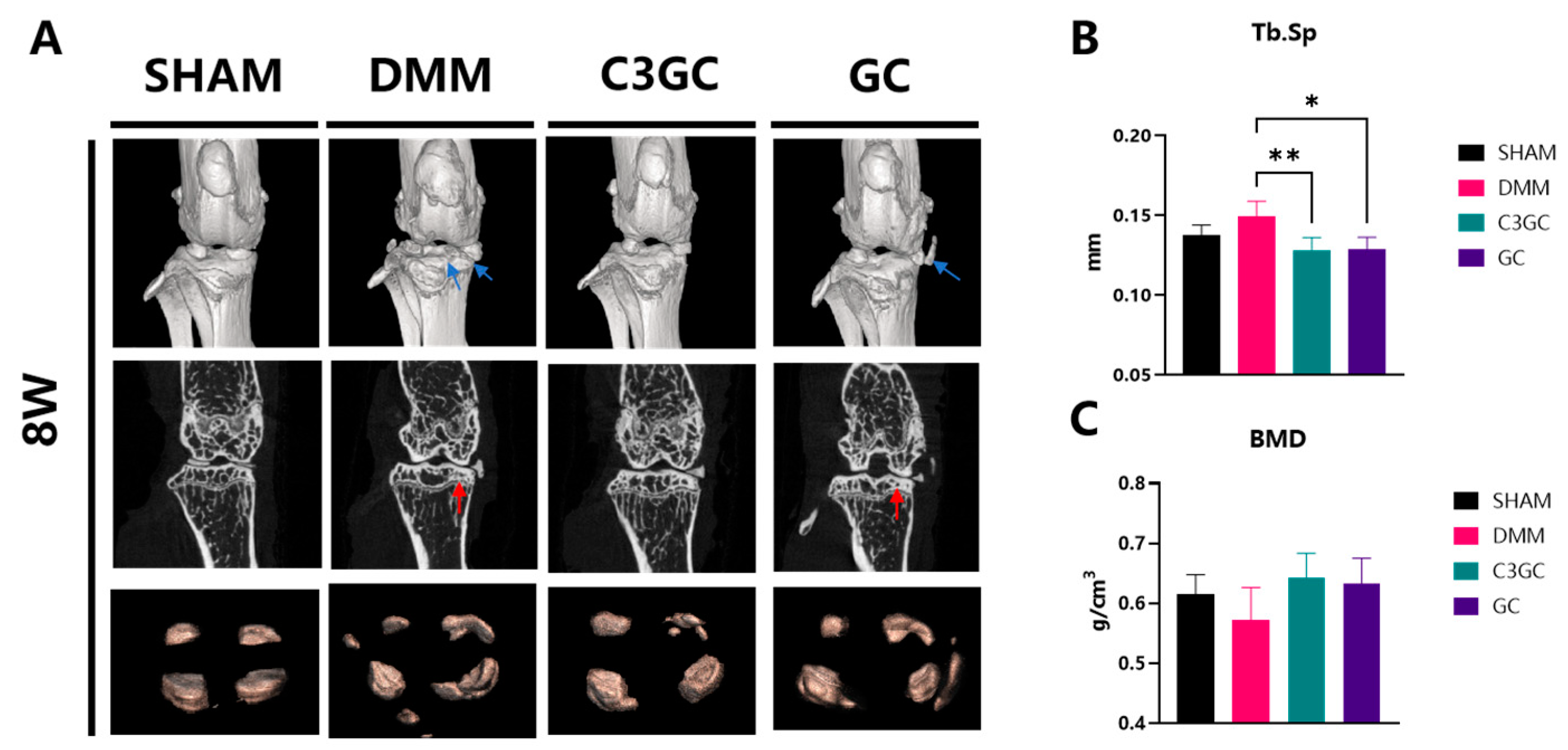
3.3. C3GC Protects Subchondral Bone Integrity and Prevents Degenerating Cartilage in Osteoarthritis
3.3.1. Subchondral Bone Remodeling and Degeneration Association
3.3.2. C3GC Preserves Cartilage and Reduces the Severity of Osteoarthritis
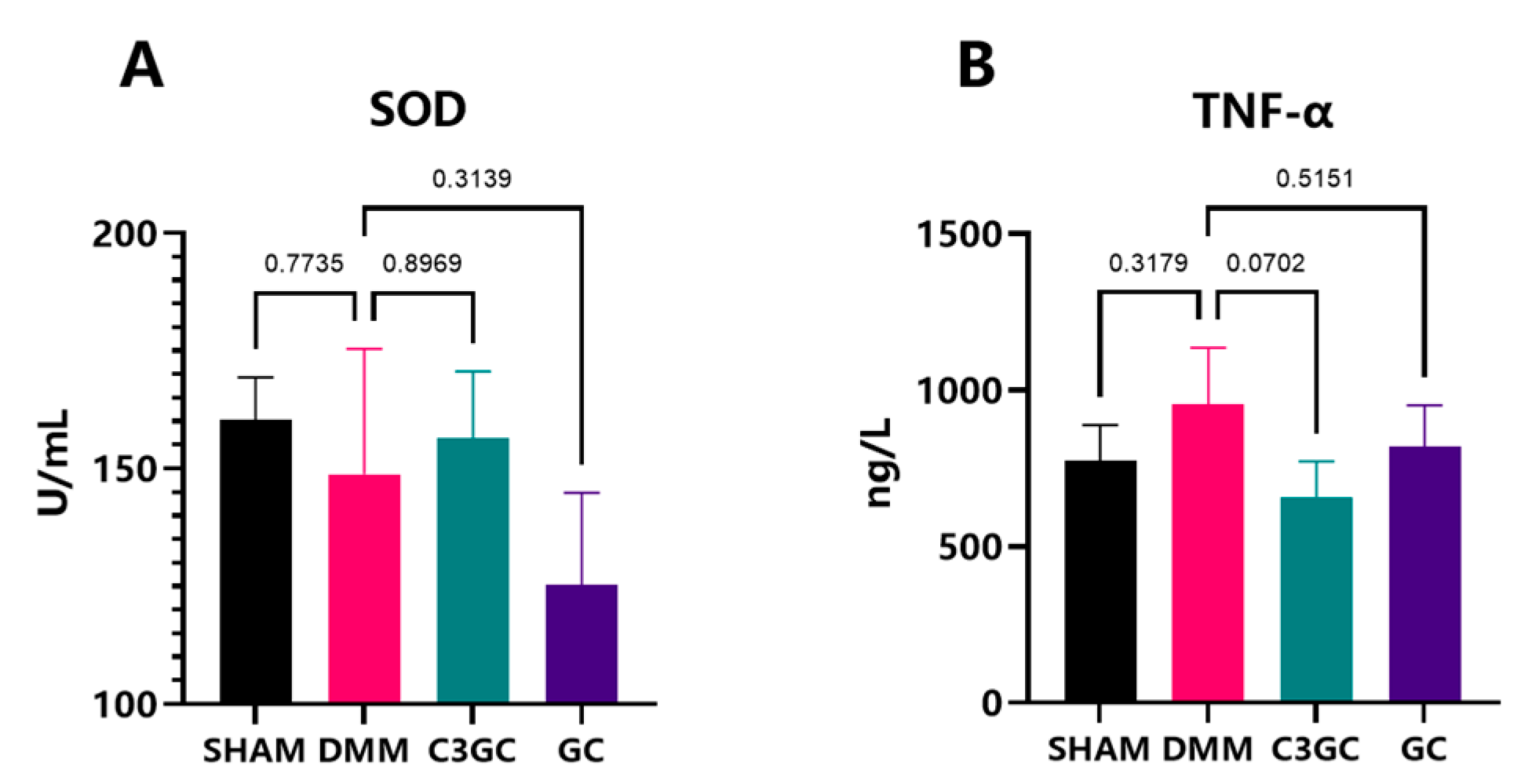
3.4. Curcumin Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects in OA Mice Models
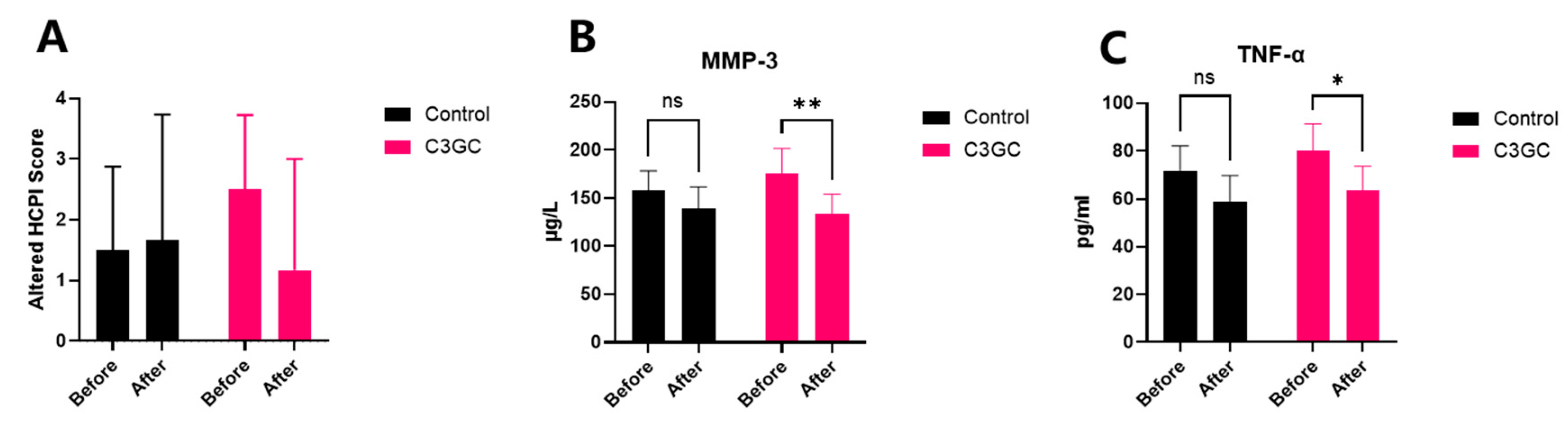
3.5. The Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of C3 Curcumin in Dogs with Osteoarthritis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ray, A.; Ray, B.K. An inflammation-responsive transcription factor in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Biorheology 2008, 45, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.L.; O’Neill, D.G.; Brodbelt, D.C.; Church, D.B.; Meeson, R.L.; Sargan, D.; Summers, J.F.; Zulch, H.; Collins, L.M. Prevalence, duration and risk factors for appendicular osteoarthritis in a UK dog population under primary veterinary care. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, V.L.; Robinson, D.A.; Evans, R.B.; Rothschild, M.F.; Conzenius, M.G. Estimate of the annual economic impact of treatment of cranial cruciate ligament injury in dogs in the United States. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2005, 227, 1604–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindu, S.; Mazumder, S.; Bandyopadhyay, U. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and organ damage: A current perspective. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 180, 114147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Leong, D.J.; Xu, L.; He, Z.; Wang, A.; Navati, M.; Kim, S.J.; Hirsh, D.M.; Hardin, J.A.; Cobelli, N.J.; et al. Curcumin slows osteoarthritis progression and relieves osteoarthritis-associated pain symptoms in a post-traumatic osteoarthritis mouse model. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Li, Z.; Tian, L.; Mu, P.; Hu, Y.; Xiong, F.; Ma, X. Efficacy and safety of curcuminoids alone in alleviating pain and dysfunction for knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Yu, G.; Hao, W.; Yang, K.; Chen, H. The efficacy and safety of Curcuma longa extract and curcumin supplements on osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20210817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, K.Y. The spice for joint inflammation: Anti-inflammatory role of curcumin in treating osteoarthritis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 3029–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalraj, A.; Pius, A.; Gopi, S.; Gopi, S. Biological activities of curcuminoids, other biomolecules from turmeric and their derivatives—A review. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2016, 7, 205–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepinska-Pacelik, J.; Biel, W. Turmeric and Curcumin-Health-Promoting Properties in Humans versus Dogs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.M.; Beier, F.; Pest, M.A. Recent developments in emerging therapeutic targets of osteoarthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2017, 29, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios, J.L.; Sapède, D.; Djouad, F.; Rapp, A.E.; Lang, A.; Larkin, J.; Ladel, C.; Mobasheri, A. Animal Models of Osteoarthritis Part 1-Preclinical Small Animal Models: Challenges and Opportunities for Drug Development. Curr. Protoc. 2022, 2, e596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Huang, L.; Welch, I.; Norley, C.; Holdsworth, D.W.; Beier, F.; Cai, D. Early Changes of Articular Cartilage and Subchondral Bone in The DMM Mouse Model of Osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ding, Z.; Liu, F.; Li, S.; Huang, W.; Zhou, S.; Han, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Yin, Z. Luteolin regulating synthesis and catabolism of osteoarthritis chondrocytes via activating autophagy. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Fang, Y.; Lou, C.; Yu, H.; Li, Y.; Lv, J.; Chen, H.; Cai, L.; Zheng, W. Vinpocetine protects against osteoarthritis by inhibiting ferroptosis and extracellular matrix degradation via activation of the Nrf2/GPX4 pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 135, 156115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, I.A.D.; Rieppo, L.; Pouran, B.; Afara, I.O.; Bragança, F.M.S.; van Rijen, M.H.P.; Kik, M.; Weinans, H.; Toyras, J.; van Weeren, P.R.; et al. Effects of body mass on microstructural features of the osteochondral unit: A comparative analysis of 37 mammalian species. Bone 2019, 127, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oláh, T.; Cai, X.; Michaelis, J.C.; Madry, H. Comparative anatomy and morphology of the knee in translational models for articular cartilage disorders. Part I Large Animals. Ann. Anat. 2021, 235, 151680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.I.; Park, I.Y.; Kim, H.A. Understanding the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Pathogenesis of Arthritis Pain Using Animal Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.M.C.; Pitsillides, A.A.; Meeson, R.L. Moving Beyond the Limits of Detection: The Past, the Present, and the Future of Diagnostic Imaging in Canine Osteoarthritis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 789898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhathal, A.; Spryszak, M.; Louizos, C.; Frankel, G. Glucosamine and chondroitin use in canines for osteoarthritis: A review. Open Vet. J. 2017, 7, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroljević, Z.D.; Jordan, K.; Ivković, J.; Bender, D.V.; Perić, P. Curcuma as an anti-inflammatory component in treating osteoarthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2023, 43, 589–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasson, S.S.; Chambers, M.G.; Van Den Berg, W.B.; Little, C.B. The OARSI histopathology initiative-recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the mouse. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, S17–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritzker, K.P.; Gay, S.; Jimenez, S.A.; Ostergaard, K.; Pelletier, J.P.; Revell, P.A.; Salter, D.; van den Berg, W.B. Osteoarthritis cartilage histopathology: Grading and staging. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2006, 14, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopresti, A.L.; Smith, S.J.; Jackson-Michel, S.; Fairchild, T. An Investigation into the Effects of a Curcumin Extract (Curcugen®) on Osteoarthritis Pain of the Knee: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutrients 2021, 14, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Wei, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.L.; Xie, D.X.; Yang, T.; Gao, S.G.; Li, Y.S.; Luo, W.; Lei, G.H. Effectiveness and safety of Glucosamine, chondroitin, the two in combination, or celecoxib in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Sang, L.; Wu, D.; Rong, J.; Jiang, L. Effectiveness and safety of glucosamine and chondroitin for the treatment of osteoarthritis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2018, 13, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle, S.; Koppo, K. Is inflammatory signaling involved in disease-related muscle wasting? Evidence from osteoarthritis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and type II diabetes. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 137, 110964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencoglu, H.; Orhan, C.; Sahin, E.; Sahin, K. Undenatured Type II Collagen (UC-II) in Joint Health and Disease: A Review on the Current Knowledge of Companion Animals. Animals 2020, 10, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drevet, S.; Favier, B.; Brun, E.; Gavazzi, G.; Lardy, B. Mouse Models of Osteoarthritis: A Summary of Models and Outcomes Assessment. Comp. Med. 2022, 72, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.; Pabst, R.; von Hörsten, S. Behavioral phenotyping of mice in pharmacological and toxicological research. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2003, 55, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, T.N.; Greene, J.G.; Miller, G.W. Behavioral phenotyping of mouse models of Parkinson’s disease. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 211, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piel, M.J.; Kroin, J.S.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Kc, R.; Im, H.J. Pain assessment in animal models of osteoarthritis. Gene 2014, 537, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, X.; Zhang, H.; Hu, M.; Liu, X.; Han, M.; Xie, J.; Li, Z.; Zhao, F.; Liu, W.; Wei, S. A novel curcumin oil solution can better alleviate the motor activity defects and neuropathological damage of a Parkinson’s disease mouse model. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 984895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suokas, A.K.; Walsh, D.A.; McWilliams, D.F.; Condon, L.; Moreton, B.; Wylde, V.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Zhang, W. Quantitative sensory testing in painful osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2012, 20, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.E.; Malfait, A.M. Osteoarthritis pain: What are we learning from animal models? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 31, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Tripathi, A. Evaluation of analgesic and prophylactic activity of curcumin against chikungunya-infected acute/chronic arthralgic mice. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.; Kuhad, A.; Kaur, I.P.; Chopra, K. Curcumin loaded solid lipid nanoparticles ameliorate adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Eur. J. Pain 2015, 19, 940–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Y.; Yin, J.M.; Gao, J.J.; Cheng, T.S.; Pavlos, N.J.; Zhang, C.Q.; Zheng, M.H. Subchondral bone in osteoarthritis: Insight into risk factors and microstructural changes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Liu, G.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, F.; Wang, L. Curcumin alleviates osteoarthritis in mice by suppressing osteoclastogenesis in subchondral bone via inhibiting NF-kB/JNK signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0309807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, X.; Liu, C.; Wen, X.; Tian, F.; Li, Y. Curcumin Alleviates Osteoarthritis Through the p38MAPK Pathway: Network Pharmacological Prediction and Experimental Confirmation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 5039–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xiao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Jian, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, B.; Ye, Z.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; et al. Curcumenol regulates Histone H3K27me3 demethylases KDM6B affecting Succinic acid metabolism to alleviate cartilage degeneration in knee osteoarthritis. Phytomedicine 2024, 133, 155922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Martin, S.; Gonzalez-Cantalapiedra, A.; Muñoz, F.; Garcia-Gonzalez, M.; Permuy, M.; Lopez-Pena, M. Glucosamine and Chondroitin Sulfate: Is There Any Scientific Evidence for Their Effectiveness as Disease-Modifying Drugs in Knee Osteoarthritis Preclinical Studies?—A Systematic Review from 2000 to 2021. Animals 2021, 11, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunus, M.H.M.; Nordin, A.; Kamal, H. Pathophysiological Perspective of Osteoarthritis. Medicina 2020, 56, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.Y.; Ahmad, N.; Haqqi, T.M. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabas, M.; Orhan, C.; Er, B.; Tuzcu, M.; Durmus, A.S.; Ozercan, I.H.; Sahin, N.; Bhanuse, P.; Morde, A.A.; Padigaru, M.; et al. A Next Generation Formulation of Curcumin Ameliorates Experimentally Induced Osteoarthritis in Rats via Regulation of Inflammatory Mediators. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 609629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.; Ding, L.G.; Lu, B.Y.; Guo, J.Y.; Wu, M.Y.; Tan, Z.Q.; Hou, S.Z. Combined Administration of Curcumin and Chondroitin Sulfate Alleviates Cartilage Injury and Inflammation via NF-kB Pathway in Knee Osteoarthritis Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 882304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Qiu, X.; Ouyang, J.; Dai, J.; Min, S. Matrix Metalloproteinase 3: A Promoting and Destabilizing Factor in the Pathogenesis of Disease and Cell Differentiation. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 663978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; D’Amico, R.; Paola, R.D.; Schievano, C.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Dietary Supplementation with Palmitoyl-Glucosamine Co-Micronized with Curcumin Relieves Osteoarthritis Pain and Benefits Joint Mobility. Animals 2020, 10, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, E.; Cen, T.; Ma, Y.; Weng, Z.; Jiang, C.; Hou, L.; Leng, J.; Hu, C. A Nutritional Supplement Containing Curcumin C3 Complex, Glucosamine, and Chondroitin Alleviates Osteoarthritis in Mice and Canines. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050462
Zheng E, Cen T, Ma Y, Weng Z, Jiang C, Hou L, Leng J, Hu C. A Nutritional Supplement Containing Curcumin C3 Complex, Glucosamine, and Chondroitin Alleviates Osteoarthritis in Mice and Canines. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(5):462. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050462
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Enpei, Ting Cen, Ye Ma, Ziyuan Weng, Chuanheng Jiang, Luxi Hou, Jun Leng, and Changmin Hu. 2025. "A Nutritional Supplement Containing Curcumin C3 Complex, Glucosamine, and Chondroitin Alleviates Osteoarthritis in Mice and Canines" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 5: 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050462
APA StyleZheng, E., Cen, T., Ma, Y., Weng, Z., Jiang, C., Hou, L., Leng, J., & Hu, C. (2025). A Nutritional Supplement Containing Curcumin C3 Complex, Glucosamine, and Chondroitin Alleviates Osteoarthritis in Mice and Canines. Veterinary Sciences, 12(5), 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050462






