Analytical Evaluation of Three Portable Blood Glucose Meters for Human Use in Dogs
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Blood Collection and Glycemia Determination
2.3. Technical Information of the Tested PBGMs
2.4. Statistical Analyses
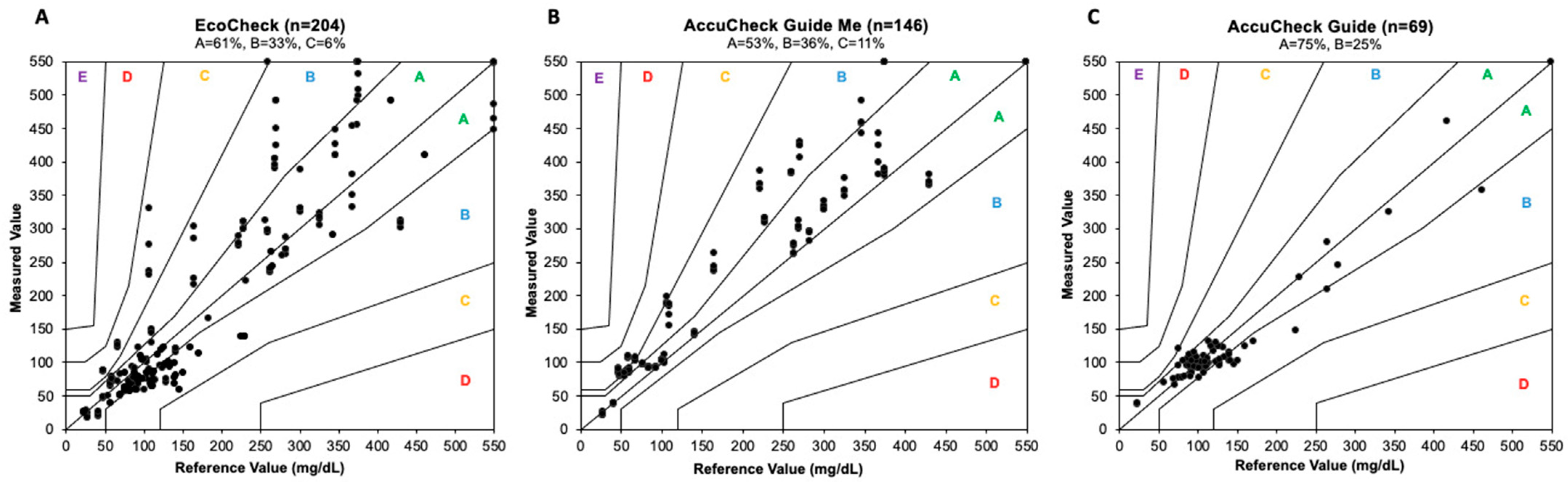
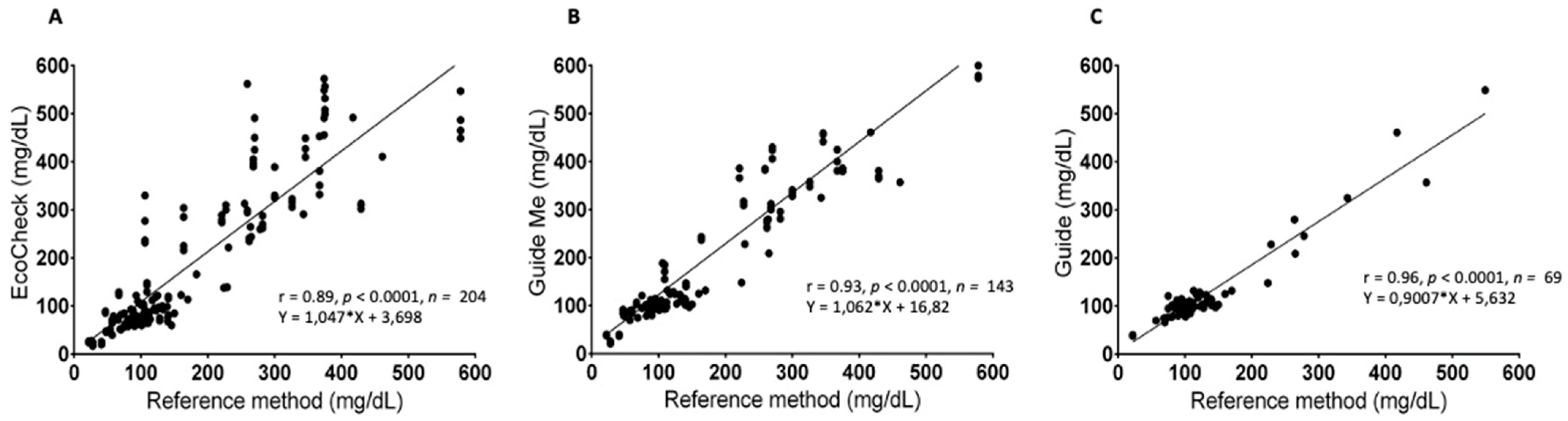
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PBGM | Portable blood glucose meters |
| ACGM | Accu-Chek Guide Me® |
| EC | EcoCheck® |
| ACG | Accu-Chek Guide® |
| GOM | Glucose oxidase method |
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization |
| RM | Reference method |
| CBC | Complete blood count |
| HT | Hematocrit |
| CV% | Coefficient of variation |
| OCP | One Call Plus II® |
| PO2 | Partial oxygen pressure |
References
- Cohn, L.A.; McCaw, D.L.; Tate, D.J.; Johnson, J.C. Assessment of five portable blood glucose meters, a point-of-care analyzer, and color test strips for measuring blood glucose concentration in dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2000, 216, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonagra, A.D.; Zubair, M.; Motiani, A. Hexoquinase Method. In Stat Pearls; 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK587446/ (accessed on 24 June 2024).
- Trinder, P. Determination of glucose in blood using glucose oxidase with an alternative oxygen acceptor. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 1969, 6, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaluddin, F.A.; Gunavathy, M.; Yean, C.Y.; Thevarajah, M. Variability of point-of-care testing blood glucometers versus the laboratory reference method in a tertiary teaching hospital. Asian Biomed. 2017, 6, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, M.; Hässig, M.; Reusch, C.E. Home-monitoring of blood glucose in cats with diabetes mellitus: Evaluation over a 4-month period. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2005, 7, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pöppl, A.G.; Lopes, J.L.X.; Nogueira, T.B.; da Silva, D.I.; Machado, B.D.S. Progesterone-Related Diabetes Mellitus in the Bitch: Current Knowledge, the Role of Pyometra, and Relevance in Practice. Animals 2024, 14, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrend, E.; Holford, A.; Lathan, P.; Rucinsky, R.; Schulman, R. AAHA Diabetes Management Guidelines for Dogs and Cats. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2018, 54, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleeman, L.M.; Rand, J.S. Evaluation of day-to-day variability of serial blood glucose concentration curves in diabetic dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2003, 222, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, K.L.; Freeman, K.P. ASVCP guidelines: Quality assurance for portable blood glucose meter (glucometer) use in veterinary medicine. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 45, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, B.; Savage, P.J.; Lomatach, D.; Gniadek, T.; Forbes, R.; Mitchell, R.; Hein, K.; Starr, R.; Nutter, M.; Scherdt, B. A comparison of accuracy and estimated cost of methods for home blood glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care 1981, 4, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 15197:2013; In Vitro Diagnostic Test Systems—Requirements for Blood-Glucose Monitoring Systems for Self-Testing in Managing Diabetes Mellitus. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland; European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 2013. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/54976.html (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Parkes, J.L.; Slatin, S.L.; Pardo, S.; Ginsberg, B.H. A New Consensus Error Grid to Evaluate the Clinical Significance of Inaccuracies in the Measurement of Blood Glucose. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, O.; Heading, K. Hypoglycemia in Dogs: Causes, Management, and Diagnosis. Can. Vet. J. 2018, 59, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suchowersky, N.D.; Carlson, E.A.; Lee, H.P.; Behrend, E.N. Comparison of Glucose Concentrations in Canine Whole Blood, Plasma, and Serum Measured with a Veterinary Point-of-Care Glucometer. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2021, 33, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistical Methods for Assessing Agreement Between Two Methods of Clinical Measurement. Lancet 1986, 327, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito-Casillas, Y.; Figueirinhas, P.; Wiebe, J.C.; López-Rios, L.; Pérez-Barreto, D.; Mélian, C.; Wägner, A.M. ISO-Based Assessment of Accuracy and Precision of Glucose Meters in Dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2014, 28, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, B.B.; Fry, M.M.; Flatland, B.; Kirk, C.A. Comparison of a Human Portable Blood Glucose Meter, Veterinary Portable Blood Glucose Meter, and Automated Chemistry Analyzer for Measurement of Blood Glucose Concentrations in Dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2009, 235, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobromylskyj, M.J.; Sparkes, A.H. Assessing Portable Blood Glucose Meters for Clinical Use in Cats in the United Kingdom. Vet. Rec. 2010, 167, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.H.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, I.S.; Choi, G.C.; Park, H.M. Evaluation of Four Portable Blood Glucose Meters in Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Dogs and Cats. Vet. Q. 2016, 36, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wess, G.; Reusch, C. Assessment of Five Portable Blood Glucose Meters for Use in Cats. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2000, 61, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail-Hamdi, S.; Romdane, M.N.; Romdhane, S.B. Comparison of a human portable blood glucose meter and automated chemistry analyzer for measurement of blood glucose concentrations in healthy dogs. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 2185–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, M.A.B.; Vargas, A.M.; Rosato, P.N.; Andrade, C.G.; Martins, C.M.; Petri, G. Evaluation of three human-use glucometers for blood glucose measurement in dogs. Vet. Med. Int. 2022, 2022, 9112961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, K.T.R.d.; Monteiro, L.F.; Knackfus, F.B.; Monteiro, L.M.V.W. Study of data obtained in the evaluation of two portable glucometers for human use in dogs. Multidiscip. Sci. J. 2021, 3, 2021019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, S.J.M.; Bjornvad, C.; Church, D.B.; Davison, L.; Esteban-Saltiveri, D.; Fleeman, L.M.; Forcada, Y.; Fracassi, F.; Gilor, C.; Hanson, J.; et al. Agreeing Language in Veterinary Endocrinology (ALIVE): Diabetes mellitus—A modified Delphi-method-based system to create consensus disease definitions. Vet. J. 2022, 289, 105910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, A.; Lee, P.; Yokoyama, T.; Oda, H.; Saeki, K.; Miki, Y.; Nozawa, S.; Azakami, D.; Momota, Y.; Makino, Y.; et al. Evaluation of artificial pancreas technology for continuous blood glucose monitoring in dogs. J. Artif. Organs. 2011, 14, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, J.H.; Howard, C.; Loman, K.; Miller, C.; Nyberg, D.; Chan, D.W. Laboratory and bedside evaluation of portable glucose meters. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1995, 103, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, S.J.; Powney, S.; Guitian, J.; Niessen, A.P.; Pion, P.D.; Shaw, J.A.; Church, D.B. Evaluation of a quality-of-life tool for dogs with diabetes mellitus. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2012, 26, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, S. Introdução à Bioestatística, 5th, ed.; Elsevier: Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, 2016; pp. 120–130. [Google Scholar]

| PBGM | Mean CV% | CV% CI 95% | CV% Minimum–Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|
| EC | 6.09 | 4.06−9.73 | 0.9−36 |
| ACG | 3.02 | 2.18−3.86 | 0.21−9.39 |
| ACGM | 2.4 | 1.61−4.28 | 0.8−5.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopes, J.L.X.; Nogueira, T.B.; Rodrigues, L.; Wodzik, V.S.; da Silva, D.I.; Machado, B.d.S.; Pöppl, Á.G. Analytical Evaluation of Three Portable Blood Glucose Meters for Human Use in Dogs. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050452
Lopes JLX, Nogueira TB, Rodrigues L, Wodzik VS, da Silva DI, Machado BdS, Pöppl ÁG. Analytical Evaluation of Three Portable Blood Glucose Meters for Human Use in Dogs. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(5):452. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050452
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopes, José Lucas Xavier, Taís Bock Nogueira, Luana Rodrigues, Vitória Strzeleski Wodzik, Denise Iparraguirre da Silva, Bruna dos Santos Machado, and Álan Gomes Pöppl. 2025. "Analytical Evaluation of Three Portable Blood Glucose Meters for Human Use in Dogs" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 5: 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050452
APA StyleLopes, J. L. X., Nogueira, T. B., Rodrigues, L., Wodzik, V. S., da Silva, D. I., Machado, B. d. S., & Pöppl, Á. G. (2025). Analytical Evaluation of Three Portable Blood Glucose Meters for Human Use in Dogs. Veterinary Sciences, 12(5), 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050452







