Lactobacillus paracasei Expressing Porcine Trefoil Factor 3 and Epidermal Growth Factor: A Novel Approach for Superior Mucosal Repair
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Bacteria and Plasmid
2.2. Construction of Recombinant Lactobacillus
2.3. Protein Expression
2.4. Growth Characteristics and Expression Stability
2.5. Analysis of the Activity of pTFF3 and pEGF In Vitro
2.6. Animal Model
2.7. H&E Staining
2.8. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Activity Assay
2.9. Gene Expression Levels in Colon Tissue
2.10. Cytokine Detection
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
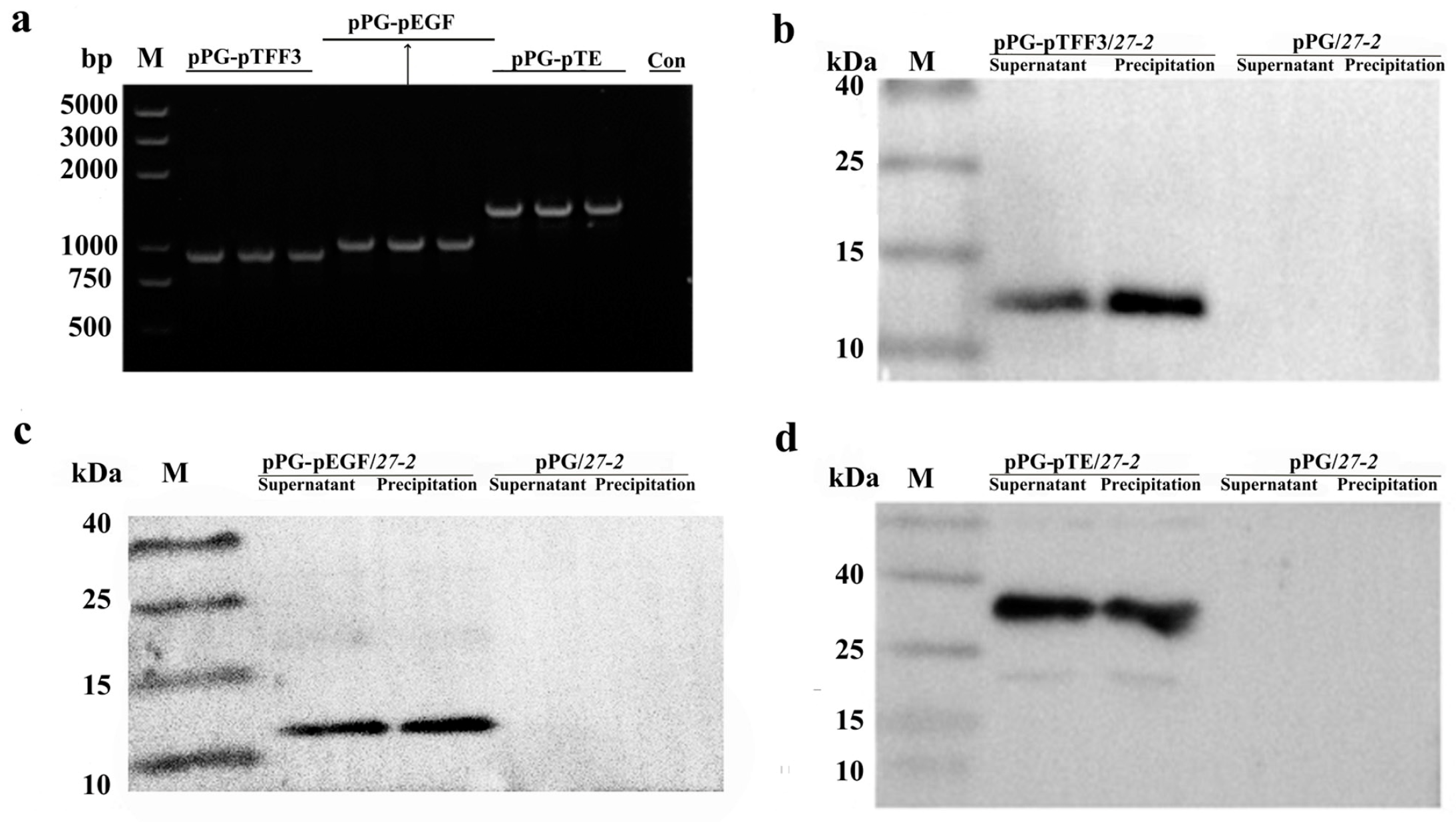
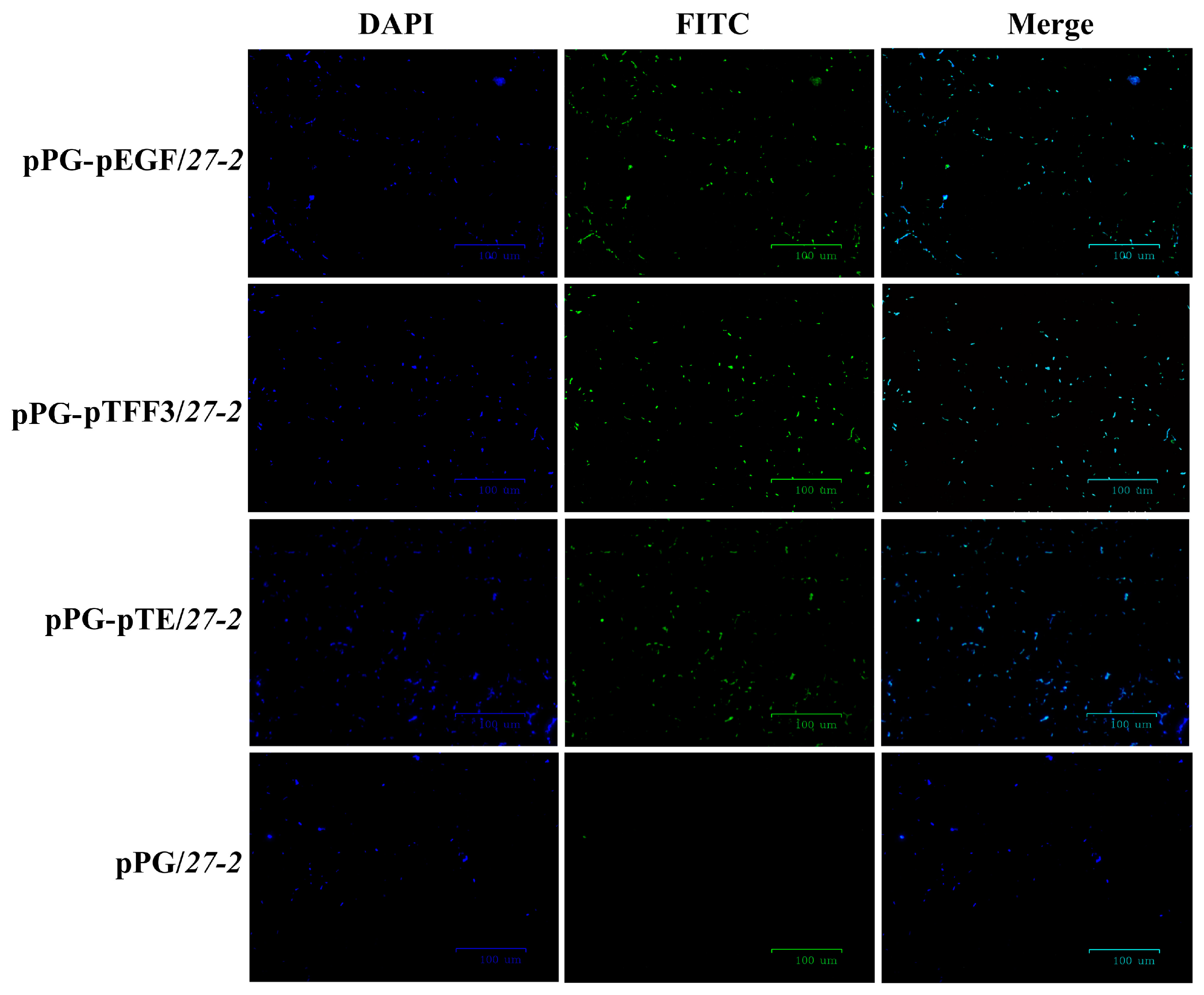
3.1. Construction and Characterization of Recombinant Lactobacillus Expressing pTFF3 and pEGF
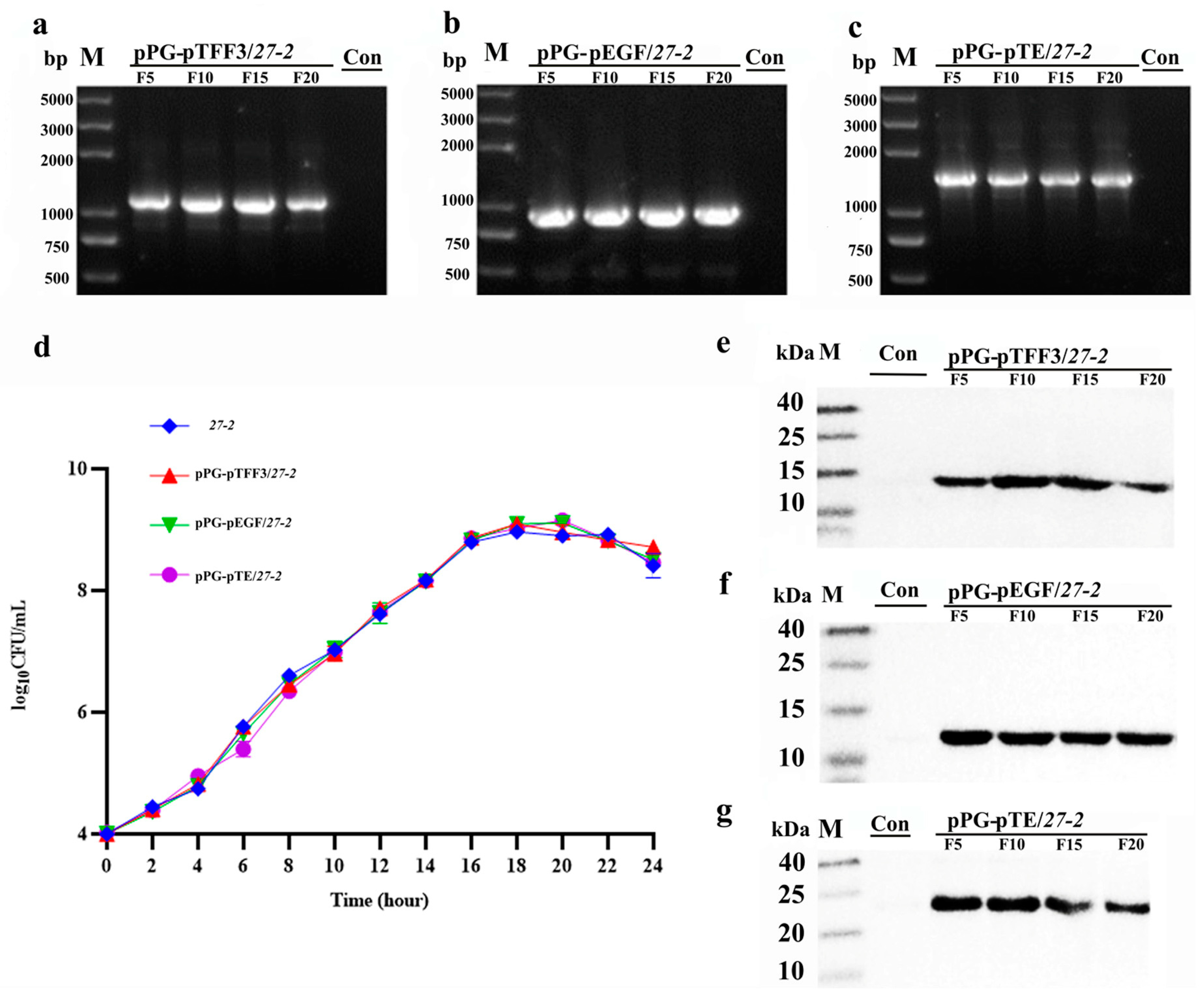
3.2. Growth Characteristics and Stability Analysis of Recombinant L. paracasei 27-2 Strains
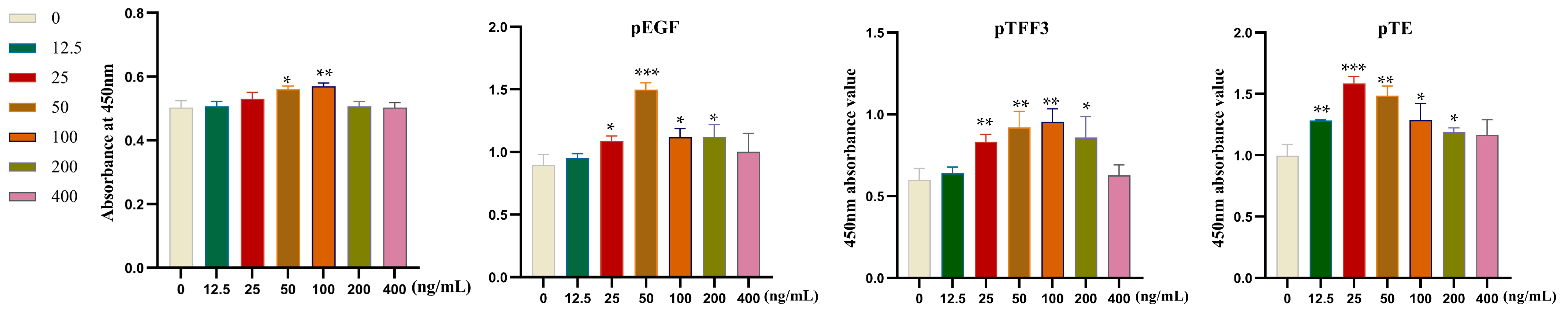
3.3. Examination of Cellular Proliferation in Relation to Specific Target Proteins
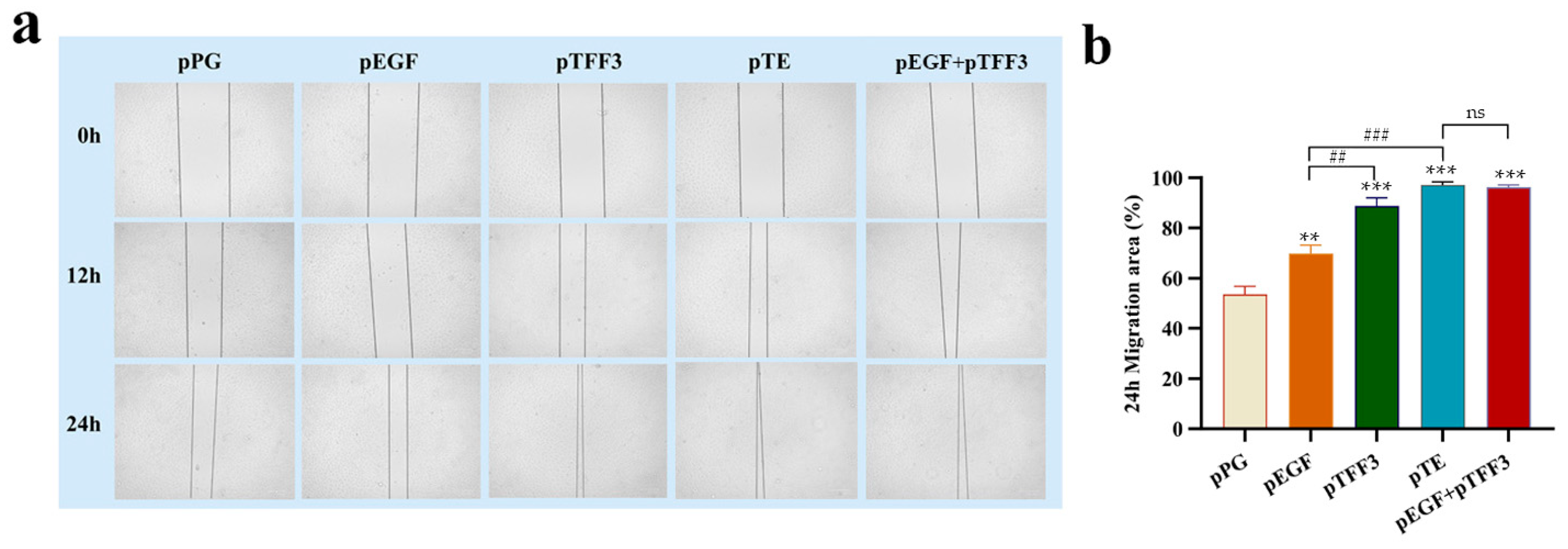
3.4. Analysis of the Effects of pTFF3, pEGF, and pTE on Cell Migration
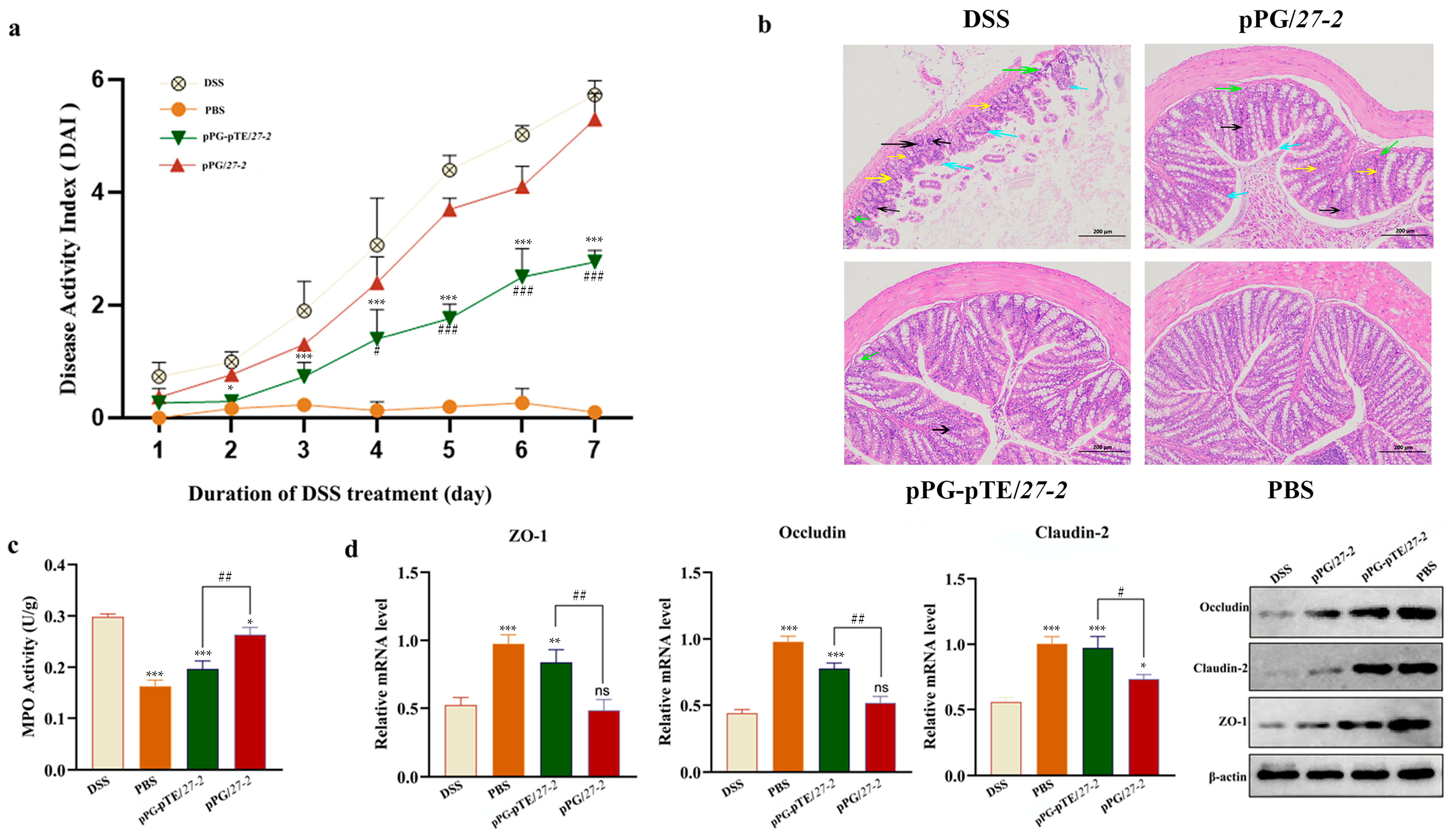
3.5. Study on the Repairing Effect of Oral Recombinant L. paracasei 27-2 Strains on Intestinal Injury in Colitis Model Mice
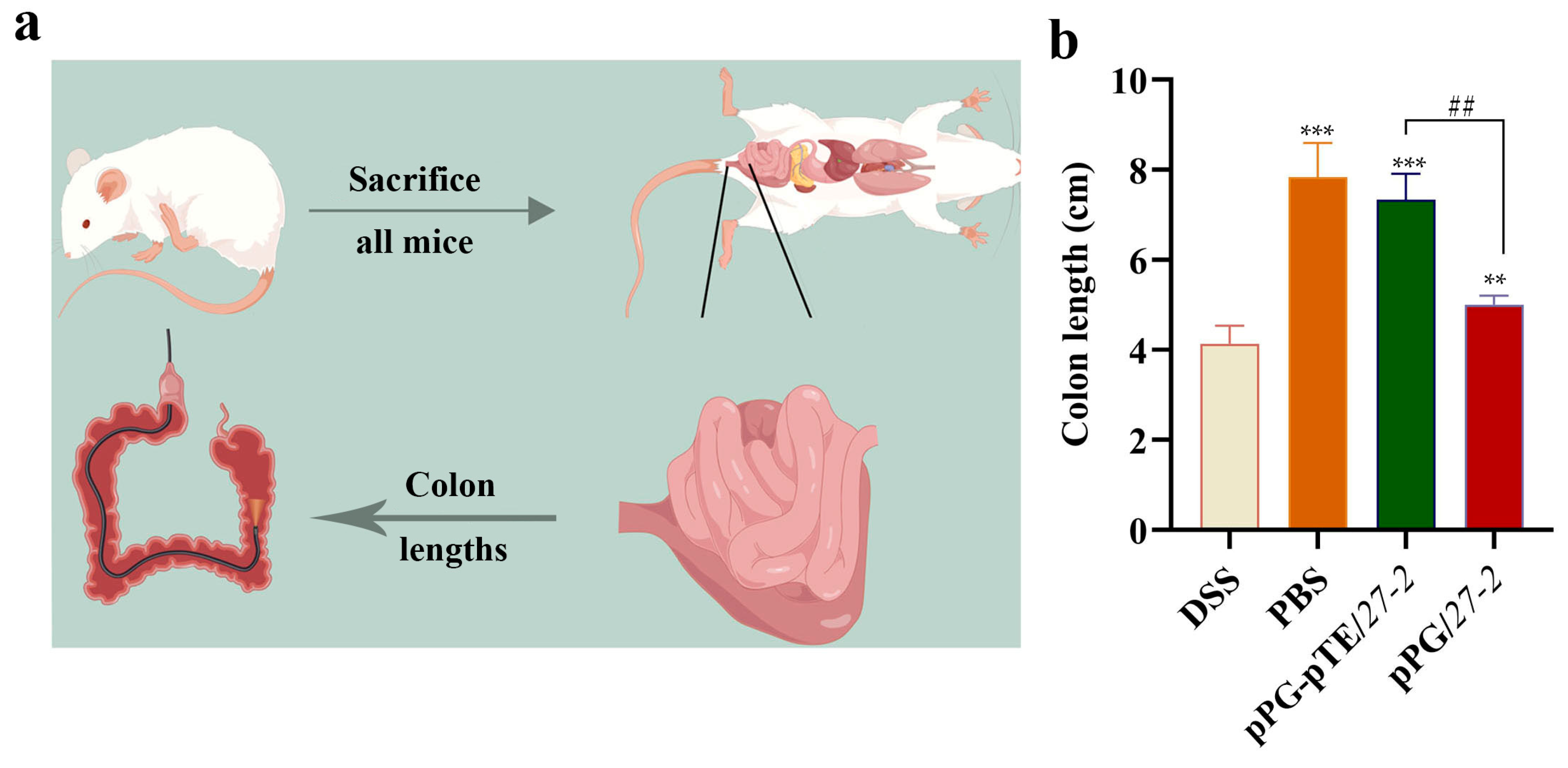
3.6. Changes in Colon Length
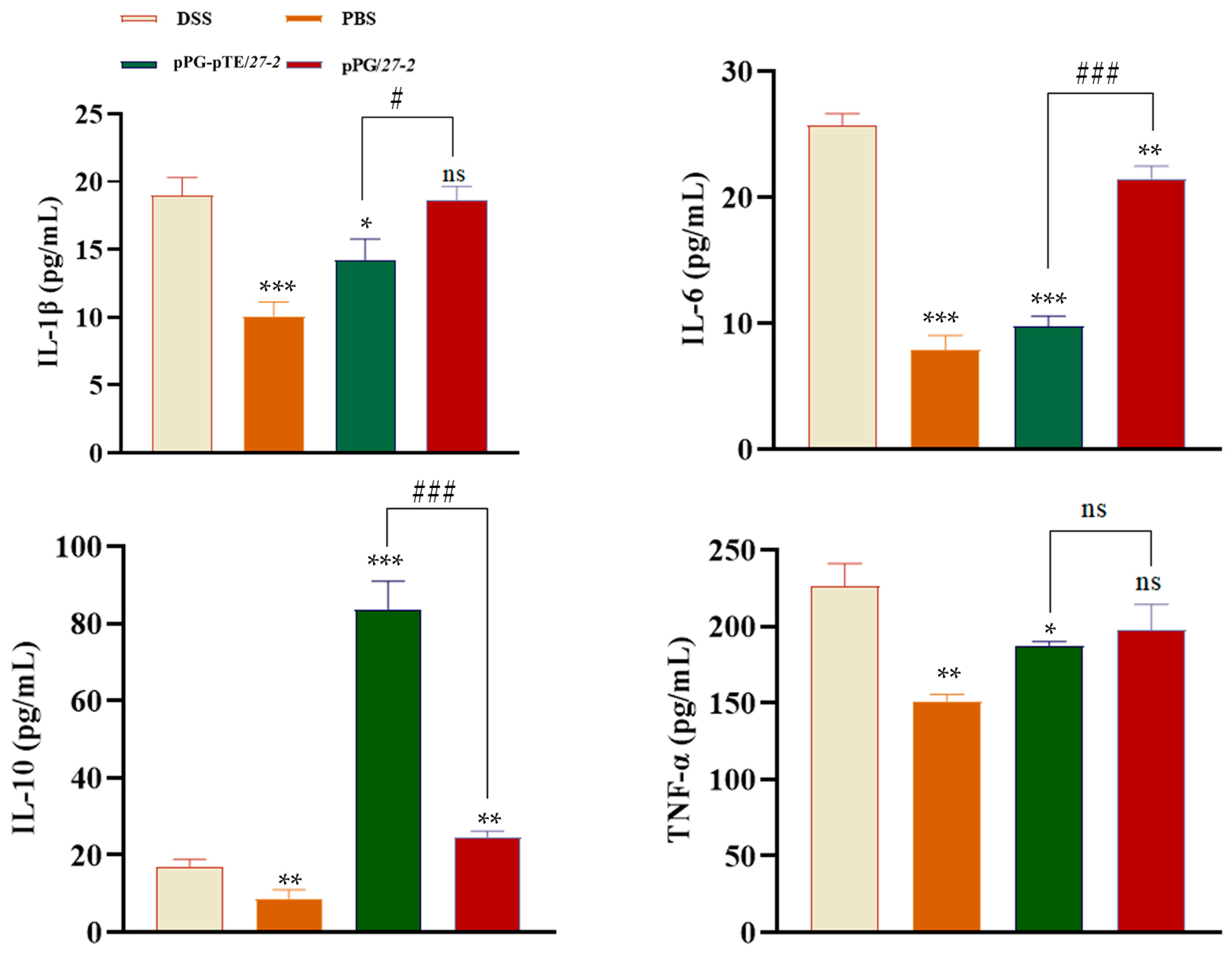
3.7. Cytokine Detection Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Research Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TFF | Trefoil factor |
| TFF1 | Trefoil factor 1 |
| TFF2 | Trefoil factor 2 |
| TFF3 | Trefoil factor 3 |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| pTFF3 | Porcine trefoil factor 3 |
| pEGF | Porcine epidermal growth factor |
| IPEC-J2 | Immortalized Porcine Enterocyte Cell line J2 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-α |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| DSS | Dextran sulfate sodium |
| TNBS | Trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid |
| MRS | Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe |
| TCA | Trichloroacetic acid |
| FITC | Fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| DAPI | 4′,6′-diamino-2-phenylindole |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| DAI | Disease activity index |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| MPO | Myeloperoxidase |
| qRT-PCR | Real-time quantitative PCR |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-β |
| TLR-2 | Toll-like receptor 2 |
| TLR-4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| LAB | Lactic acid bacteria |
| h | Hour |
| min | Minute |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor-kappa B |
References
- Bradford, E.M.; Ryu, S.H.; Singh, A.P.; Lee, G.; Goretsky, T.; Sinh, P.; Williams, D.B.; Cloud, A.L.; Gounaris, E.; Patel, V.; et al. Epithelial TNF Receptor Signaling Promotes Mucosal Repair in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 1886–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, K.; Arnone, B.; Buchman, A. Intestinal growth factors: Potential use in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease and their role in mucosal healing. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Lin, Q.; Bei, W.; Guo, J. Pathological and therapeutic roles of bioactive peptide trefoil factor 3 in diverse diseases: Recent progress and perspective. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, P.; Ling, H.; Lan, G.; Liu, J.; Hu, H.; Yang, R. Trefoil factors: Gastrointestinal-specific proteins associated with gastric cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 450, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grases-Pintó, B.; Torres-Castro, P.; Abril-Gil, M.; Castell, M.; Rodríguez-Lagunas, M.J.; Pérez-Cano, F.J.; Franch, À. TGF-β2, EGF and FGF21 influence the suckling rat intestinal maturation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2025, 135, 109778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Wang, W.; Li, L.; Meng, H.-Y.; Feng, C.-Z.; Dong, Y.-Y.; Fang, X.-C.; Dong, Q.-Q.; Jiang, W.; Xin, H.-L.; et al. Recombinant human epidermal growth factor combined with vacuum sealing drainage for wound healing in Bama pigs. Mil. Med. Res. 2021, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, E.; Li, J. Generation of Lactococcus lactis capable of coexpressing epidermal growth factor and trefoil factor to enhance in vitro wound healing. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 4667–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinery, R.; Playford, R.J. Combined intestinal trefoil factor and epidermal growth factor is prophylactic against indomethacin-induced gastric damage in the rat. Clin. Sci. 1995, 88, 401–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshbin, K.; Camilleri, M. Effects of dietary components on intestinal permeability in health and disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 319, G589–G608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Wang, C.; Chen, A.; Bai, Z.; Tian, Y.; Lv, W. Lactobacillus paracasei influences the gut-microbiota-targeted metabolic modulation of the immune status of diarrheal mice. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 4368–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, F.; Pasolli, E.; Ercolini, D. The food-gut axis: Lactic acid bacteria and their link to food, the gut microbiome and human health. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 454–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Mei, Z.; Ju, N.; Sui, L.; Fan, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Cui, W.; Shan, Z.; et al. Evaluation of the immunogenicity of auxotrophic Lactobacillus with CRISPR-Cas9D10A system-mediated chromosomal editing to express porcine rotavirus capsid protein VP4. Virulence 2022, 13, 1315–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.-F.; Ju, L.-Z.; Li, Y.-J.; Tang, L.-J. Chromosomal insertions in the Lactobacillus casei upp gene that are useful for vaccine expression. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 3321–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingfield, P.T. Protein Precipitation Using Ammonium Sulfate. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2016, 84, A.3F.1–A.3F.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirica, K.A.; Lockett, M.R.; Snyder, P.W.; Shapiro, N.D.; Mack, E.T.; Nam, S.; Whitesides, G.M. Selective precipitation and purification of monovalent proteins using oligovalent ligands and ammonium sulfate. Bioconjug. Chem. 2012, 23, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Yu, Q.; Fang, R. Epidermal Growth Factor, through Alleviating Oxidative Stress, Protect IPEC-J2 Cells from Lipopolysaccharides-Induced Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, S.; Neufert, C.; Weigmann, B.; Neurath, M.F. Chemically induced mouse models of intestinal inflammation. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, S.N.S.; Cooper, H.S.; Shim, H.; Shah, R.S.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Sedergran, D.J. Treatment of dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine colitis by intracolonic cyclosporin. Dig. Dis. 1993, 38, 1722–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeepthi, K.; Rajani, K.; Rao, G.; Sravya, T.; Wahed, S.A.; Sailaja, J. Evaluation of biosafe alternative to eosin in hematoxylin and eosin staining procedure: A comparative study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2023, 27, 424–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Jänne, P.A.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Yanagitani, N.; Kim, S.-W.; Sugawara, S.; Yu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Geater, S.L.; et al. Osimertinib with or without Chemotherapy in EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1935–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Ning, T.; Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Yang, H.; Han, Y.; Deng, T.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.; et al. MiR-520b/e Regulates Proliferation and Migration by Simultaneously Targeting EGFR in Gastric Cancer. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 40, 1303–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.A.; Goto, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Felip, E.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Reck, M.; Yoh, K.; Lee, S.-H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Besse, B.; et al. HERTHENA-Lung01, a Phase II Trial of Patritumab Deruxtecan (HER3-DXd) in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer After Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy and Platinum-Based Chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 5363–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Dai, W.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, L.; Ye, Q.; Lei, P.; Shen, G. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) induces apoptosis in a transfected cell line expressing EGF receptor on its membrane. Cell Biol. Int. 2013, 30, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, H. The expression and role of trefoil factors in human tumors. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagmeister, T.; Gubensäk, N.; Buhlheller, C.; Grininger, C.; Eder, M.; Ðordić, A.; Millán, C.; Medina, A.; Murcia, P.A.S.; Berni, F.; et al. The molecular architecture of Lactobacillus S-layer: Assembly and attachment to teichoic acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2401686121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenbroucke, K.; Hans, W.; Van Huysse, J.; Neirynck, S.; Demetter, P.; Remaut, E.; Rottiers, P.; Steidler, L. Active delivery of trefoil factors by genetically modified Lactococcus lactis prevents and heals acute colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Lv, S.; Tang, J.; Xing, Z.; Shi, M.; Lei, A.; Xiao, G.; He, Y. TFF3 mediates the NF-kB/COX2 pathway to regulate PMN-MDSCs activation and protect against necrotizing enterocolitis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 1110–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caluwaerts, S.; Vandenbroucke, K.; Steidler, L.; Neirynck, S.; Vanhoenacker, P.; Corveleyn, S.; Watkins, B.; Sonis, S.; Coulie, B.; Rottiers, P. AG013, a mouth rinse formulation of Lactococcus lactis secreting human Trefoil Factor 1, provides a safe and efficacious therapeutic tool for treating oral mucositis. Oral Oncol. 2010, 46, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedford, A.; Chen, T.; Huynh, E.; Zhu, C.; Medeiros, S.; Wey, D.; de Lange, C.; Li, J. Epidermal growth factor containing culture supernatant enhances intestine development of early-weaned pigs in vivo: Potential mechanisms involved. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 196–197, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichele, D.D.; Kharbanda, K.K. Dextran sodium sulfate colitis murine model: An indispensable tool for advancing our understanding of inflammatory bowel diseases pathogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6016–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murano, M.; Maemura, K.; Hirata, I.; Toshina, K.; Nishikawa, T.; Hamamoto, N.; Sasaki, S.; Saitoh, O.; Katsu, K. Therapeutic effect of intracolonically administered nuclear factor kappa B (p65) antisense oligonucleotide on mouse dextran sulphate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2000, 120, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casagrande, R.; Georgetti, S.R.; Verri, W.A.; Dorta, D.J.; dos Santos, A.C.; Fonseca, M.J. Protective effect of topical formulations containing quercetin against UVB-induced oxidative stress in hairless mice. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2006, 84, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, J.; Mizukure, T.; Park, S.-B.; Kishino, S.; Kimura, I.; Hirano, K.; Bergamo, P.; Rossi, M.; Suzuki, T.; Arita, M.; et al. A gut microbial metabolite of linoleic acid, 10-hydroxy-cis-12-octadecenoic acid, ameliorates intestinal epithelial barrier impairment partially via GPR40-MEK-ERK pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 2902–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasquinha, M.T.; Sur, M.; Lasrado, N.; Reddy, J. IL-10 as a Th2 Cytokine: Differences Between Mice and Humans. J. Immunol. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Immunol. 2021, 207, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.R.; Bartlett, N.W.; Clarke, D.; Birrell, M.; Belvisi, M.; Johnston, S.L. Targeting the NF-κB pathway in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 121, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.T.; Tergaonkar, V. Roles of NF-κB in health and disease: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Clin. Sci. 2009, 116, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couper, K.N.; Blount, D.G.; Riley, E.M. IL-10: The master regulator of immunity to infection. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 5771–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, T.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H. Vaccination with recombinant Lactococcus lactis expressing HA1-IgY Fc fusion protein provides protective mucosal immunity against H9N2 avian influenza virus in chickens. Virol. J. 2023, 20, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, T.; Kaur, H.; Kapila, S.; Kapila, R. Lactobacillus fermentum (MTCC-5898) alleviates Escherichia coli-induced inflammatory responses in intestinal epithelial cells by modulating immune genes and NF-kB signalling. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 3008–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
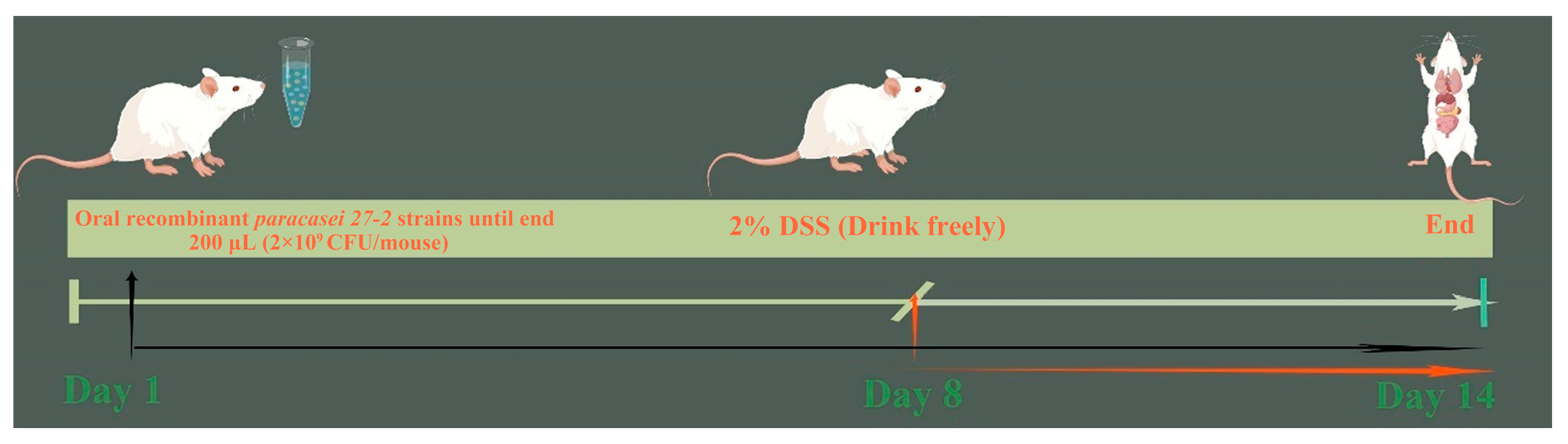
| Group | Oral Dosage, Per Mouse Per Day | Number |
|---|---|---|
| PBS | 200 μL (Days 1 to 14) | 8 |
| pPG-pTE/27-2 | 200 μL (2 × 109 CFU, days 1 to 14, 2%DSS (free access to water, days 8 to 14)) | 8 |
| pPG/27-2 | 200 μL (2 × 109 CFU, days 1 to 14, 2%DSS (free access to water, days 8 to 14)) | 8 |
| DSS | 2%DSS (free access to water, days 8 to 14) | 8 |
| Weight Loss (%) | Occult Blood/Bloody | Fecal Property | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Occult blood negative | Normal | 0 |
| 1–5 | Occult blood negative | Loose | 1 |
| 6–10 | Positive for occult blood | Loose | 2 |
| 11–15 | Positive for occult blood | Loose stools | 3 |
| >15 | Naked-eye bloody stool | Loose stools | 4 |
| Incubation Time | Expression in Supernatants of Recombinant L. paracasei 27-2 Strains pTFF3, pEGF, and pTE (μg/mg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| pTFF3 | pEGF | pTE | |
| 6 h | 0.15 ± 0.02 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.07 ± 0.03 |
| 10 h | 0.35 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.02 | 0.19 ± 0.04 |
| 14 h | 0.45 ± 0.04 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | 0.30 ± 0.05 |
| 18 h | 0.48 ± 0.02 a | 0.50 ± 0.01 a | 0.37 ± 0.05 b |
| 22 h | 0.30 ± 0.02 | 0.35 ± 0.02 | 0.31 ± 0.03 |
| 24 h | 0.20 ± 0.03 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 0.25 ± 0.05 |
| Incubation Time | Expression in Supernatants of Recombinant L. paracasei 27-2 Strains pTFF3, pEGF, and pTE (μg/mg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| pTFF3 | pEGF | pTE | |
| 6 h | 0.18 ± 0.02 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 0.12 ± 0.01 |
| 10 h | 0.35 ± 0.01 | 0.28 ± 0.02 | 0.27 ± 0.03 |
| 14 h | 0.45 ± 0.01 | 0.74 ± 0.06 | 0.45 ± 0.01 |
| 18 h | 0.95 ± 0.01 a | 0.91 ± 0.07 a | 0.90 ± 0.07 a |
| 22 h | 0.80 ± 0.01 | 0.41 ± 0.03 | 0.51 ± 0.06 |
| 24 h | 0.57 ± 0.01 | 0.36 ± 0.01 | 0.39 ± 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Meng, W.; Zhao, J.; Tang, L.; Li, Y.; et al. Lactobacillus paracasei Expressing Porcine Trefoil Factor 3 and Epidermal Growth Factor: A Novel Approach for Superior Mucosal Repair. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040365
Yin F, Chen Y, Zhang H, Zhao H, Li X, Wang Z, Meng W, Zhao J, Tang L, Li Y, et al. Lactobacillus paracasei Expressing Porcine Trefoil Factor 3 and Epidermal Growth Factor: A Novel Approach for Superior Mucosal Repair. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(4):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040365
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Fangjie, Ying Chen, Huijun Zhang, Hongzhe Zhao, Xuenan Li, Zi Wang, Weijing Meng, Jie Zhao, Lijie Tang, Yijing Li, and et al. 2025. "Lactobacillus paracasei Expressing Porcine Trefoil Factor 3 and Epidermal Growth Factor: A Novel Approach for Superior Mucosal Repair" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 4: 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040365
APA StyleYin, F., Chen, Y., Zhang, H., Zhao, H., Li, X., Wang, Z., Meng, W., Zhao, J., Tang, L., Li, Y., Li, J., & Wang, X. (2025). Lactobacillus paracasei Expressing Porcine Trefoil Factor 3 and Epidermal Growth Factor: A Novel Approach for Superior Mucosal Repair. Veterinary Sciences, 12(4), 365. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040365







