Cinnamaldehyde Alleviates Salmonellosis in Chicks by Regulating Gut Health
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Drug Reagent
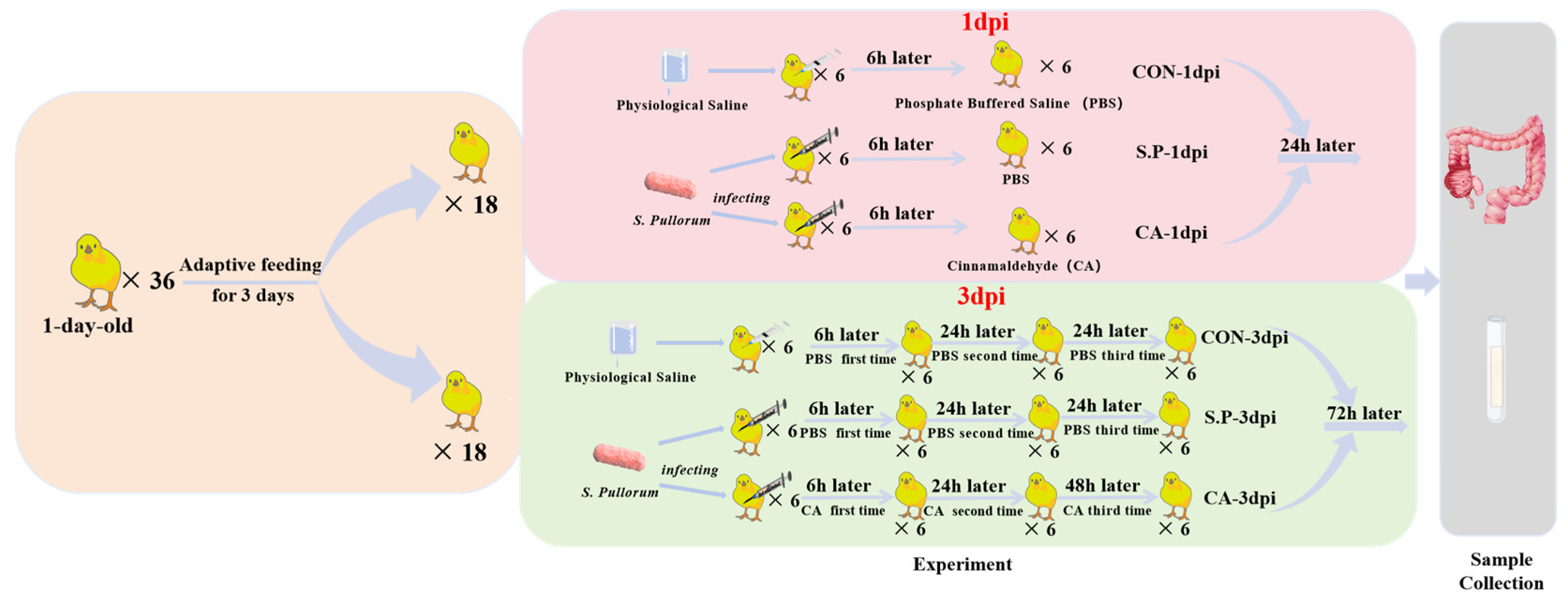
2.2. Experimental Modeling and Grouping
2.3. Sample Collection
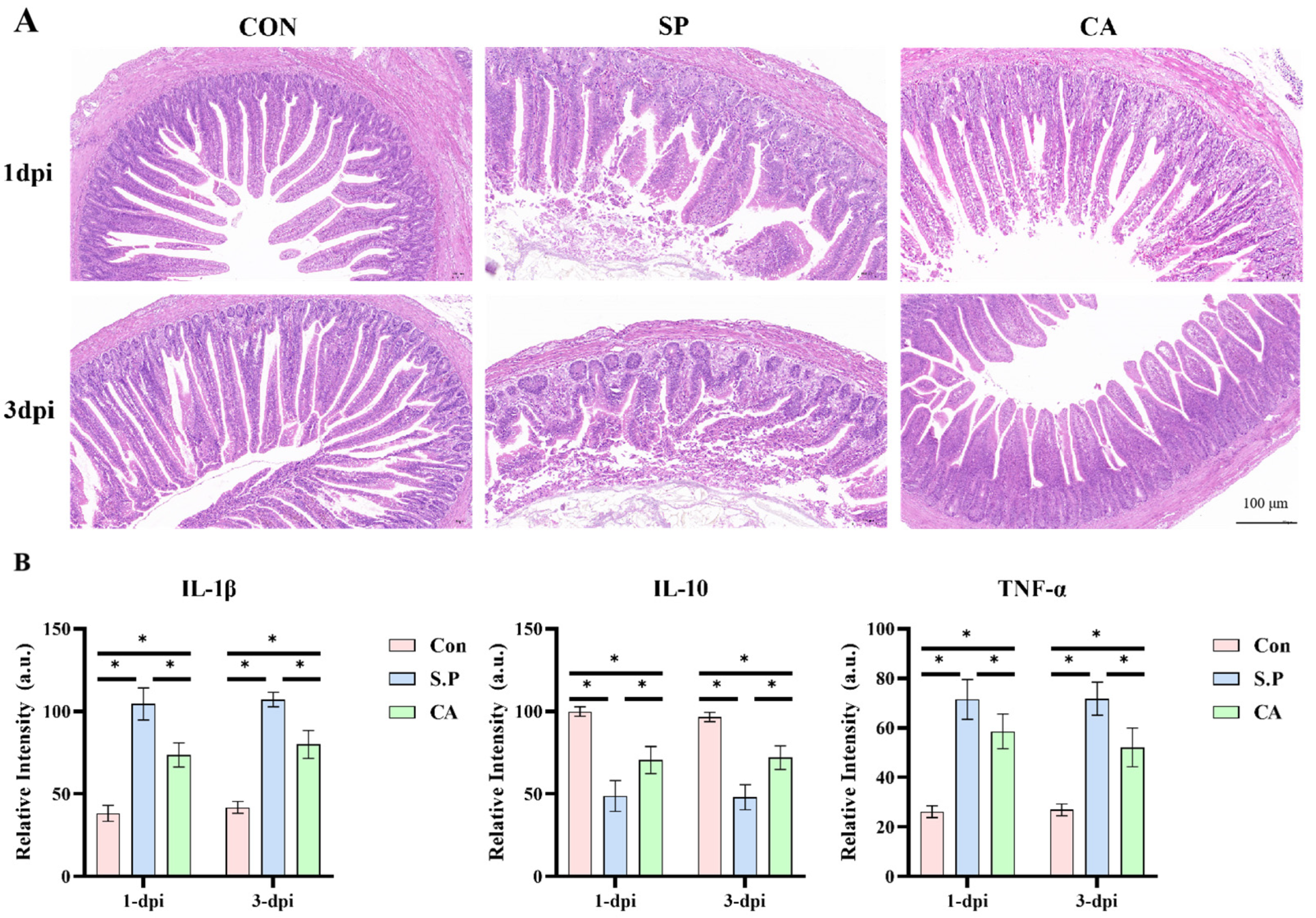
2.4. Histological Observations (H&E)
2.5. Biochemical Analyses
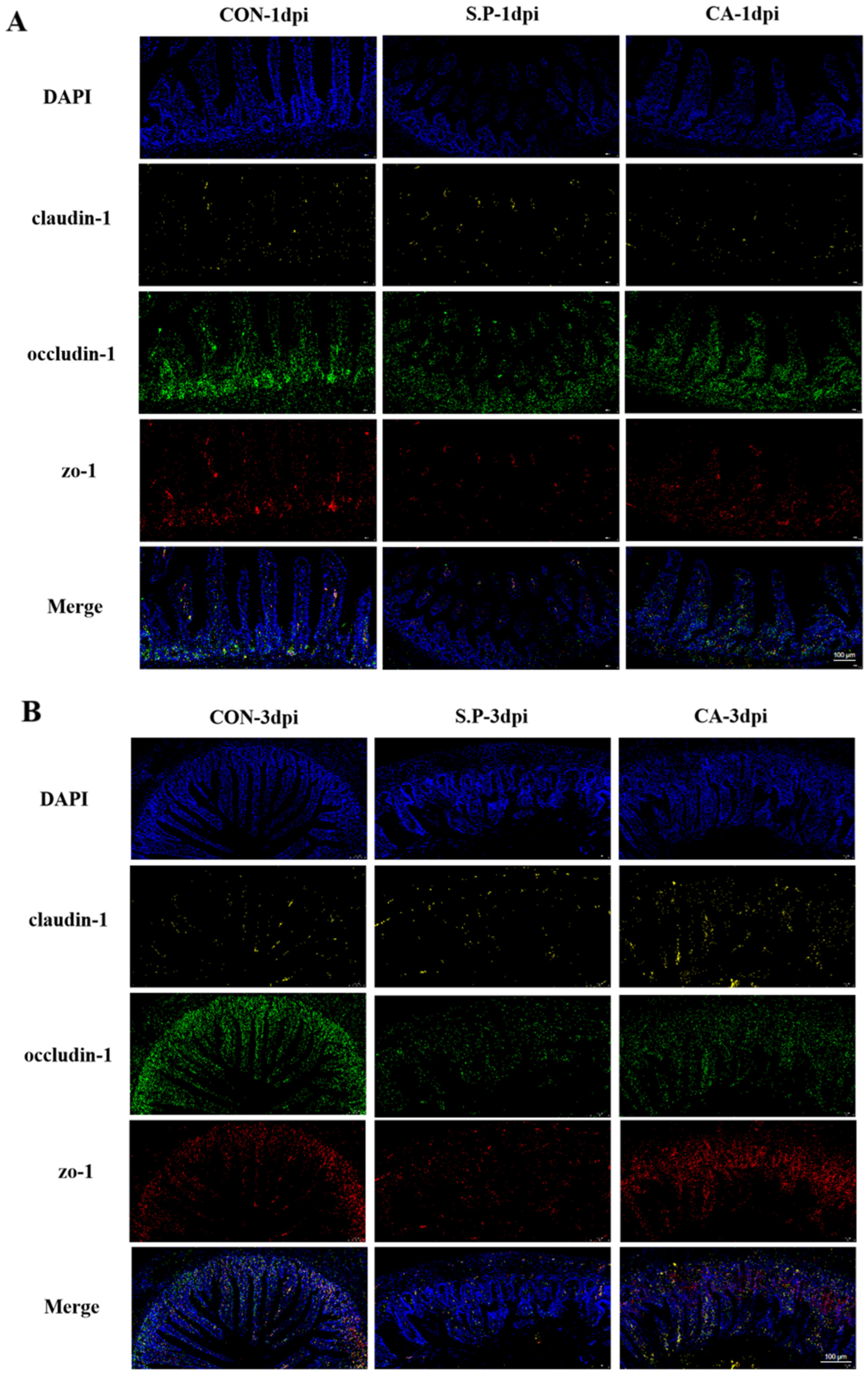
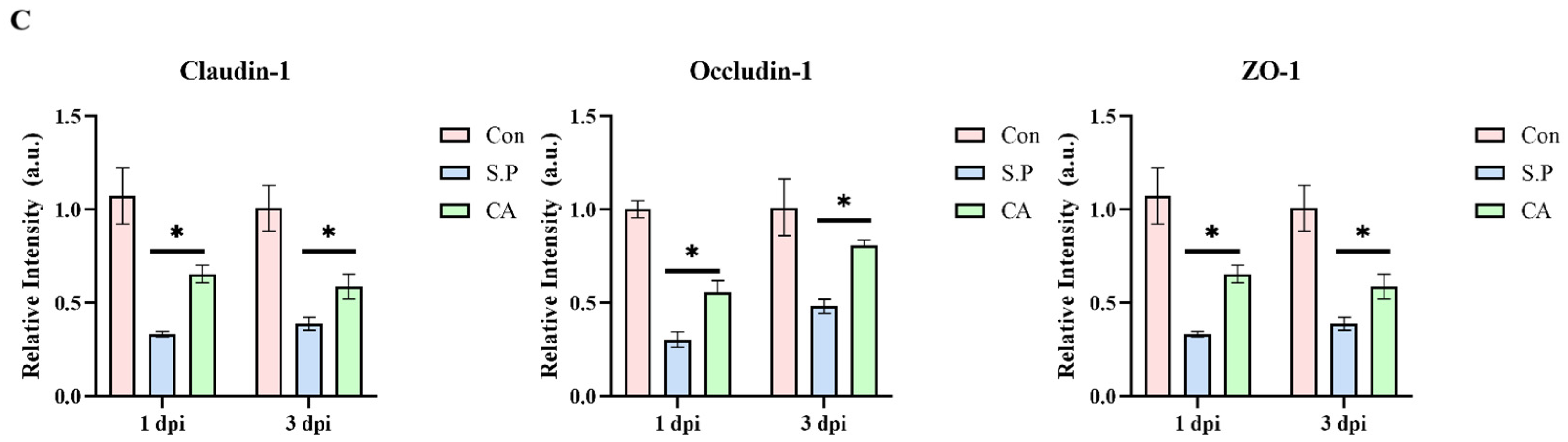
2.6. In Situ Hybridization
2.7. RT-qPCR
2.8. The 16S rRNA Sequencing and Microbial Composition Analysis
2.9. Untargeted Metabolomics
2.10. Correlation Analysis Between the Microbiome and Metabolome
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CA Protects Against Pullorum Disease by Restoring Intestinal Tight Junctions
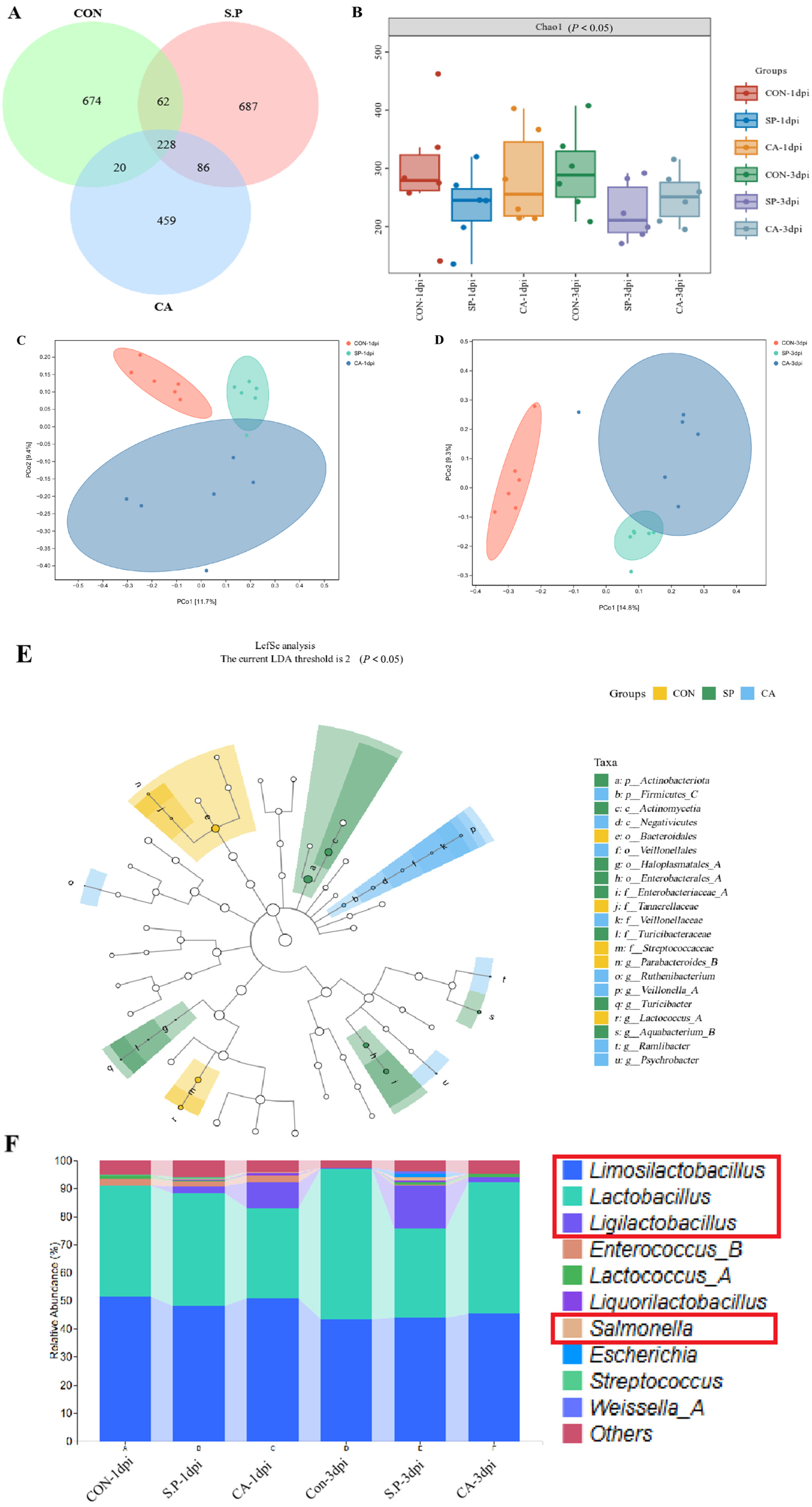
3.2. CA Affects the Structure of the Gut Microbial Composition
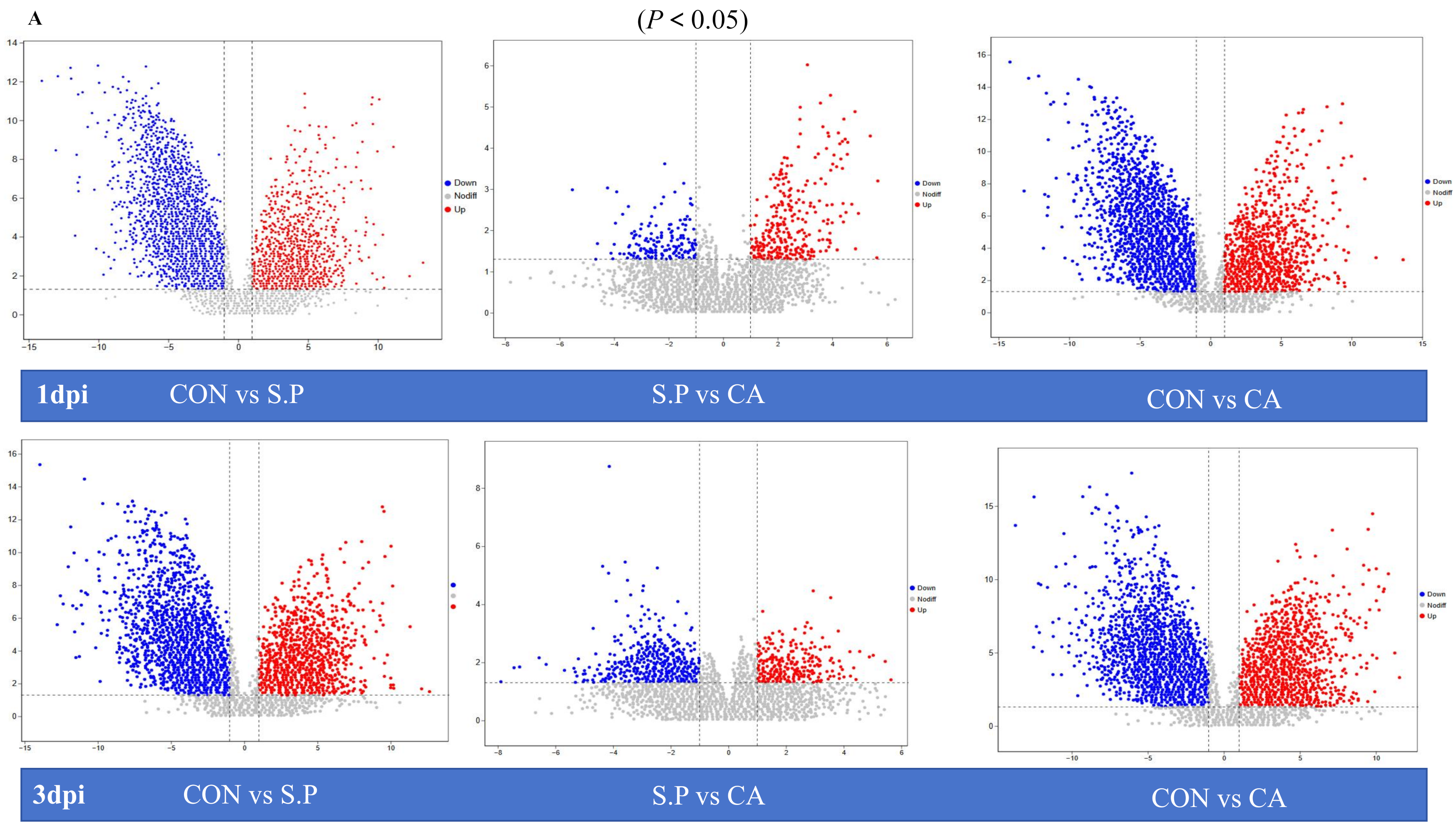
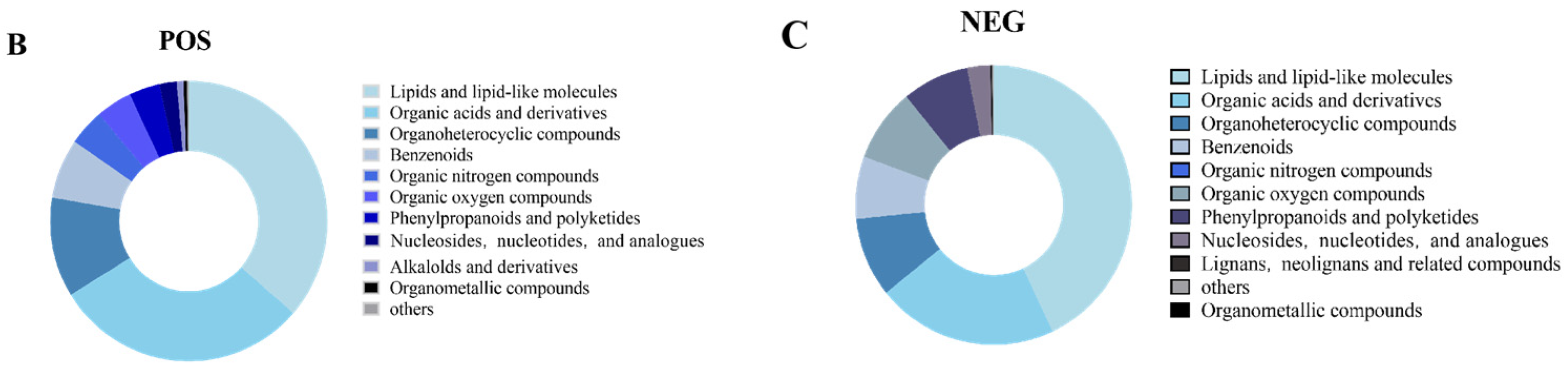
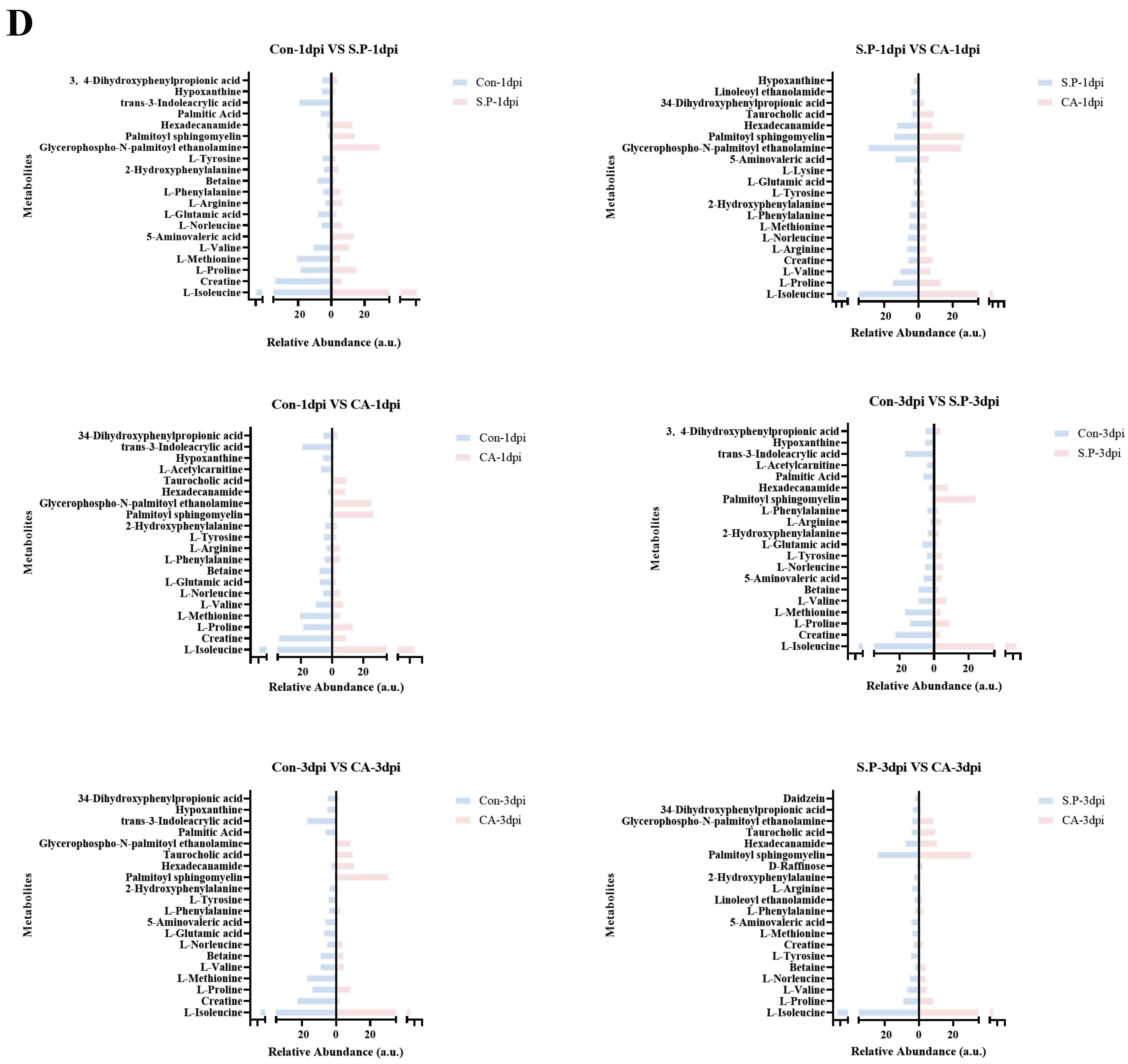
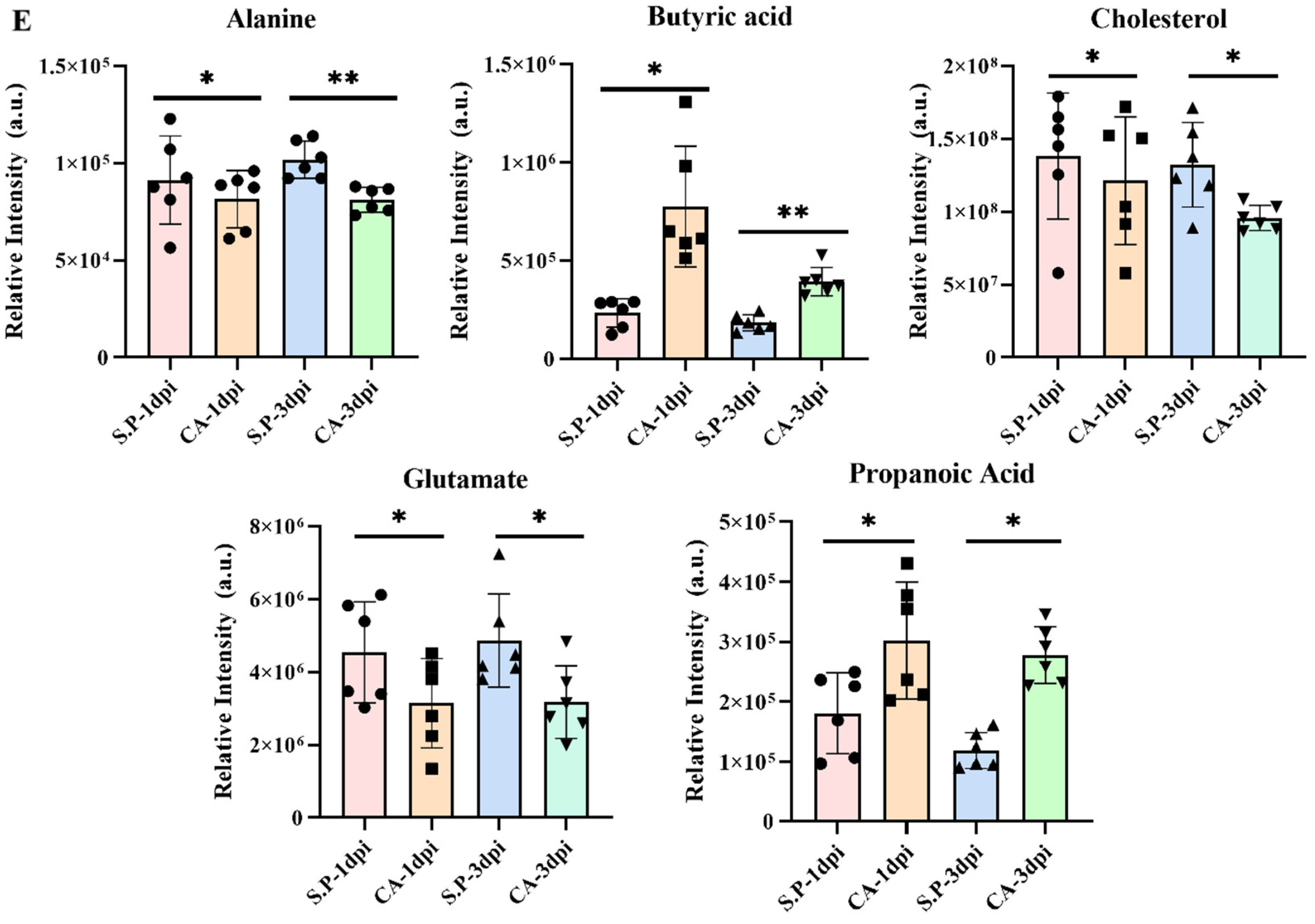
3.3. CA Improves S. pullorum-Induced Intestinal Metabolic Dysfunction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, X.; Jin, C.; Gu, P.; Wang, S.; Gao, Z.; Dai, C.; Zhou, X.; Siddique, A.; Zhou, H.; Huang, L. A dynamic platform for global pullorum disease and fowl typhoid. Anim. Dis. 2024, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Kang, X.; Wang, J.; Yue, M. Characterization of two-component system CitB family in Salmonella enterica serovar Gallinarum biovar Gallinarum. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 278, 109659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhat, M.; Khayi, S.; Berrada, J.; Mouahid, M.; Ameur, N.; El-Adawy, H.; Fellahi, S. Salmonella enterica Serovar Gallinarum Biovars Pullorum and Gallinarum in Poultry: Review of Pathogenesis, Antibiotic Resistance, Diagnosis and Control in the Genomic Era. Antibiotics 2023, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julianingsih, D. Causative Agents for Fowl Typhoid and Pullorum Disease in Poultry and Approach to Control. Master’s Thesis, University of Maryland, College Park, MD, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- de la Fuente-Nunez, C.; Cesaro, A.; Hancock, R.E. Antibiotic failure: Beyond antimicrobial resistance. Drug Resist. Updates 2023, 71, 101012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanda, G.; Acharya, Y.; Haldar, J. Antibiotic adjuvants: A versatile approach to combat antibiotic resistance. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 10757–10783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabetafika, H.; Razafindralambo, A.; Ebenso, B.; Razafindralambo, H. Probiotics as Antibiotic Alternatives for Human and Animal Applications. Encyclopedia 2023, 3, 561–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Deng, L.; Chen, M.; Che, Y.; Li, L.; Zhu, L.; Chen, G.; Feng, T. Phytogenic feed additives as natural antibiotic alternatives in animal health and production: A review of the literature of the last decade. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 17, 244–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayalew, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, S.; Qiu, K.; Qi, G.; Tekeste, A.; Wassie, T.; Chanie, D. Potential feed additives as antibiotic alternatives in broiler production. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 916473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Sun, J.; Yang, T.; Zhang, X.; Xu, C.; Wei, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Q. Therapeutic effects and mechanisms of berberine on enteritis caused by Salmonella in poultry. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1458579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.; Xu, D.; Yue, S.; Yan, C.; Liu, W.; Fu, R.; Ma, W.; Tang, Y. Recent advances in the pharmacological applications and liver toxicity of triptolide. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2023, 382, 110651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Ge, L.; Li, Z.; Chen, B.; Liao, S.; Lu, L.; Wu, Q.; Jiang, X.; An, Y.; Wang, Z. Antibacterial activity of cinnamon essential oil and its main component of cinnamaldehyde and the underlying mechanism. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1378434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yan, S.; Jiang, X.; Su, Z.; Zhang, F.; Xie, J.; Hao, E.; Yao, C. Advances in pharmacological effects and mechanism of action of cinnamaldehyde. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1365949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cai, Q.; Wu, X.; Tan, Z.; Chen, R.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L. A comparative study on chemical compositions and biological activities of four essential oils: Cymbopogon citratus (DC.) Stapf, Cinnamomum cassia (L.) Presl, Salvia japonica Thunb. and Rosa rugosa Thunb. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 280, 114472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, D.K.; Chaudhary, R.; Dey, A.; Nandy, S.; Banik, R.; Malik, T.; Dwivedi, P. Current knowledge of Cinnamomum species: A review on the bioactive components, pharmacological properties, analytical and biotechnological studies. Bioact. Nat. Prod. Drug Discov. 2020, 127–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, X.; Xue, R.; Wang, F.; Dong, J.; Tao, N.; Qin, Z. Cinnamaldehyde inhibits cytokine storms induced by the ORF3a protein of SARS-CoV-2 via ROS-elimination in activated T cells. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 6006–6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Christensen, L.; Bak, S.; Christensen, N.; Kragh, K. Immunomodulatory effects of thymol and cinnamaldehyde in chicken cell lines. J. Appl. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 8, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikrishnan, R.; Devi, G.; Balasundaram, C.; Van Doan, H.; Jaturasitha, S.; Saravanan, K.; Ringø, E. Impact of cinnamaldehyde on innate immunity and immune gene expression in Channa striatus against Aphanomyces invadans. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 117, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hamid, M.I.A.; El-Malt, R.M.; Al-Khalaifah, H.; Al-Nasser, A.; Elazab, S.T.; Basiony, A.; Ali, A.M.; Mohamed, D.I.; Nassan, M.A.; Ibrahim, D. Exploring the interactive impacts of citronellol, thymol, and trans-cinnamaldehyde in broilers: Moving toward an improved performance, immunity, gastrointestinal integrity, and Clostridium perfringens resistance. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 135, lxae206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Ning, N.; Shen, M.; Xu, H.-H.; Wang, L.; Ding, B.-Y.; Hou, Y.-Q.; Guo, S.-S. Effects of compound plant essential oil on growth performance and immune function of broilers challenged by Clostridium perfringens. Feed. Ind. 2023, 44, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar, R.J.; Dijkman, R.; Ter Veen, C.; Heuvelink, A.; van Kaam, F.; Augustijn, M.; Feberwee, A. A Salmonella Pullorum outbreak with neurological signs in adult layers and outbreak investigation using whole genome sequencing. Avian Pathol. 2024, 53, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saggar, S.; Mir, P.A.; Kumar, N.; Chawla, A.; Uppal, J.; Kaur, A. Traditional and herbal medicines: Opportunities and challenges. Pharmacogn. Res. 2022, 14, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momtaz, S.; Navabakhsh, M.; Bakouee, N.; Dehnamaki, M.; Rahimifard, M.; Baeeri, M.; Abdollahi, A.; Abdollahi, M.; Farzaei, M.H.; Abdolghaffari, A.H. Cinnamaldehyde targets TLR-4 and inflammatory mediators in acetic-acid induced ulcerative colitis model. Biologia 2021, 76, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Banerjee, S. Anticancer potential and molecular mechanisms of cinnamaldehyde and its congeners present in the cinnamon plant. Physiologia 2023, 3, 173–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, H.; Duan, M.; Liu, R.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, K.; Wang, L. Cinnamaldehyde improves metabolic functions in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice by regulating gut microbiota. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, ume 15, 2339–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Atawy, M.A.; Hanna, D.H.; Bashal, A.H.; Ahmed, H.A.; Alshammari, E.M.; Hamed, E.A.; Aljohani, A.R.; Omar, A.Z. Synthesis, Characterization, Antioxidant, and Anticancer Activity against Colon Cancer Cells of Some Cinnamaldehyde-Based Chalcone Derivatives. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Qazi, I.H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, G.; Han, H. Salmonella virulence and immune escape. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.-C. The interleukins orchestrate mucosal immune responses to salmonella infection in the intestine. Cells 2021, 10, 3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminsky, L.W.; Al-Sadi, R.; Ma, T.Y. IL-1β and the intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 767456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.T.; Odenwald, M.A.; Turner, J.R.; Zuo, L. Tight junction proteins occludin and ZO-1 as regulators of epithelial proliferation and survival. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2022, 1514, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutel, O.; Maraspini, R.; Pombo-Garcia, K.; Martin-Lemaitre, C.; Honigmann, A. Phase separation of zonula occludens proteins drives formation of tight junctions. Cell 2019, 179, 923–936.e911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.Y.; Nighot, P.; Al-Sadi, R. Tight junctions and the intestinal barrier. In Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 587–639. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, A.; Mikkelsen, H.; Jungersen, G. Intracellular pathogens: Host immunity and microbial persistence strategies. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 1356540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Liefferinge, E.; Forte, C.; Degroote, J.; Ovyn, A.; Van Noten, N.; Mangelinckx, S.; Michiels, J. In vitro and in vivo antimicrobial activity of cinnamaldehyde and derivatives towards the intestinal bacteria of the weaned piglet. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 21, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Huang, S.; Xu, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Ji, C.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y. Dietary selenium sources alleviate immune challenge induced by Salmonella Enteritidis potentially through improving the host immune response and gut microbiota in laying hens. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 928865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Round, J.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Jha, R. Strategies to modulate the intestinal microbiota and their effects on nutrient utilization, performance, and health of poultry. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducatelle, R.; Goossens, E.; Eeckhaut, V.; Van Immerseel, F. Poultry gut health and beyond. Anim. Nutr. 2023, 13, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagatake, T.; Kishino, S.; Urano, E.; Murakami, H.; Kitamura, N.; Konishi, K.; Ohno, H.; Tiwari, P.; Morimoto, S.; Node, E. Intestinal microbe-dependent ω3 lipid metabolite αKetoA prevents inflammatory diseases in mice and cynomolgus macaques. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Xie, L.; Yin, S.; Zhou, J.; Yi, L.; Ye, L. The Gut Microbial Lipid Metabolite 14 (15)-EpETE Inhibits Substance P Release by Targeting GCG/PKA Signaling to Relieve Cisplatin-Induced Nausea and Vomiting in Rats. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Duan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Yu, M.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. Lipidomics reveals serum lipid metabolism disorders in CTD-induced liver injury. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2024, 25, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Pan, C.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Shahzad, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, W. Multi-omics reveals the effects of dietary supplementation with Bupleuri radix branch powder on gut microbiota and lipid metabolism: Insights into gut microbial-muscle interactions. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0145724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Mahfuz, S.; Wang, J.; Piao, X. Effect of dietary supplementation with mixed organic acids on immune function, antioxidative characteristics, digestive enzymes activity, and intestinal health in broiler chickens. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 673316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, D.; Qiu, K.; Zhang, H.-J.; Wu, S.-G.; Han, Y.-M.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Qi, G.-H.; Wang, J. Organic acids as alternatives for antibiotic growth promoters alter the intestinal structure and microbiota and improve the growth performance in broilers. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 618144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Ghany, W.A. Applications of Organic Acids in Poultry Production: An Updated and Comprehensive Review. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entrenas-García, C.; Argüello, H.; Calderón-Santiago, M.; Priego-Capote, F.; Zaldívar-López, S.; Garrido, J.J. Salmonella typhimurium Alteration of Small Intestine Metabolism Early after Infection Is Linked to Microbiome Changes. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Gao, J.; Du, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M. Host metabolic shift during systemic Salmonella infection revealed by comparative proteomics. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 1849–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Yang, X.; Qin, M.; Pan, L.a.; Fang, H.; Chen, P.; Ni, Y. Dietary bile acids supplementation protects against Salmonella Typhimurium infection via improving intestinal mucosal barrier and gut microbiota composition in broilers. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 15, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Chen, X.; Xu, C.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, S.; Cai, D.; Fan, H. The Metabolic Pathway of Bile Secretion Is Vulnerable to Salmonella enterica Exposure in Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Animals 2024, 14, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, B.; Zhou, J. Mechanistic basis and preliminary practice of butyric acid and butyrate sodium to mitigate gut inflammatory diseases: A comprehensive review. Nutr. Res. 2021, 95, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deters, B.J.; Saleem, M. The role of glutamine in supporting gut health and neuropsychiatric factors. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2021, 10, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhong, Y.; Ouyang, X.; Wang, C.; Yin, L.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xie, J.; Huang, P. Effects of β-alanine on intestinal development and immune performance of weaned piglets. Anim. Nutr. 2023, 12, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Hu, M.; Li, M.; Hou, J.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Chachar, B.; Li, X. Dietary bioactive peptide alanyl-glutamine attenuates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis by modulating gut microbiota. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5543003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Jiang, F.; Cheng, R.; Luo, Y.; Wang, J.; Luo, Z.; Li, M.; Shen, X.; He, F. A high-fat diet and high-fat and high-cholesterol diet may affect glucose and lipid metabolism differentially through gut microbiota in mice. Exp. Anim. 2021, 70, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villette, R.; Kc, P.; Beliard, S.; Salas Tapia, M.F.; Rainteau, D.; Guerin, M.; Lesnik, P. Unraveling host-gut microbiota dialogue and its impact on cholesterol levels. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Fan, D.; Huang, J.-l.; Zuo, T. The gut microbiome: Linking dietary fiber to inflammatory diseases. Med. Microecol. 2022, 14, 100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, K.E.; Pfaffinger, J.M.; Ryznar, R. The interplay between gut microbiota, short-chain fatty acids, and implications for host health and disease. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2393270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Ling, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Peng, N.; Zhao, S. Functional comparison of Clostridium butyricum and sodium butyrate supplementation on growth, intestinal health, and the anti-inflammatory response of broilers. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 914212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Z.-N.; Jiang, Y.-F.; Ru, J.-N.; Lu, J.-H.; Ding, B.; Wu, J. Amino acid metabolism in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, W.; Wu, G. Amino acids in microbial metabolism and function. Recent Adv. Anim. Nutr. Metab. 2022, 1354, 127–143. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, C.T.; Perez Santiago, J.; Iablokov, S.N.; Chopra, D.; Rodionov, D.A.; Peterson, S.N. Short-chain fatty acids modulate healthy gut microbiota composition and functional potential. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krautkramer, K.A.; Fan, J.; Bäckhed, F. Gut microbial metabolites as multi-kingdom intermediates. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Wang, G.; Zheng, X.; Hao, H. Gut microbial metabolites of aromatic amino acids as signals in host–microbe interplay. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 818–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Do, J.-S.; Velankanni, P.; Lee, C.-G.; Kwon, H.-K. Gut microbial metabolites on host immune responses in health and disease. Immune Netw. 2023, 23, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene Name | Primer (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| β-actin F | CCAAAGCCAACAGAGAGAAG |
| β-actin R | ACACCATCACCAGAGTCCA |
| Claudin-1 F | GAAGCATTTGGAGAGGACAC |
| Claudin-1 R | GCTGGGAGAGAAAGGAGAA |
| Occludin-1 F | CTGCTCTGCCTCATCTGCTT |
| Occludin-1 R | GTTCTTCACCCACTCCTCCAC |
| zo-1 F | GTTTGTATGGCTTTTGTGCTT |
| zo-1 R | TTCCTCTGGTTCTCTTCTGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, L.; Li, L.; Lv, X.; Sun, F.; Dai, Y.; Guo, Y.; Peng, S.; Ye, C.; Liang, X.; He, C.; et al. Cinnamaldehyde Alleviates Salmonellosis in Chicks by Regulating Gut Health. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030237
Yin L, Li L, Lv X, Sun F, Dai Y, Guo Y, Peng S, Ye C, Liang X, He C, et al. Cinnamaldehyde Alleviates Salmonellosis in Chicks by Regulating Gut Health. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(3):237. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030237
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Lizi, Luxin Li, Xue Lv, Fengsheng Sun, Yuyun Dai, Yingzi Guo, Shihao Peng, Chenyu Ye, Xiaoxia Liang, Changliang He, and et al. 2025. "Cinnamaldehyde Alleviates Salmonellosis in Chicks by Regulating Gut Health" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 3: 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030237
APA StyleYin, L., Li, L., Lv, X., Sun, F., Dai, Y., Guo, Y., Peng, S., Ye, C., Liang, X., He, C., Shu, G., & Ouyang, P. (2025). Cinnamaldehyde Alleviates Salmonellosis in Chicks by Regulating Gut Health. Veterinary Sciences, 12(3), 237. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030237





