Effects of Bacteroides fragilis and Enterococcus faecium Administration as Probiotic Candidates: Impact on Growth Performance, Organ Indices, and Gut Microbiota Balance in Mice
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
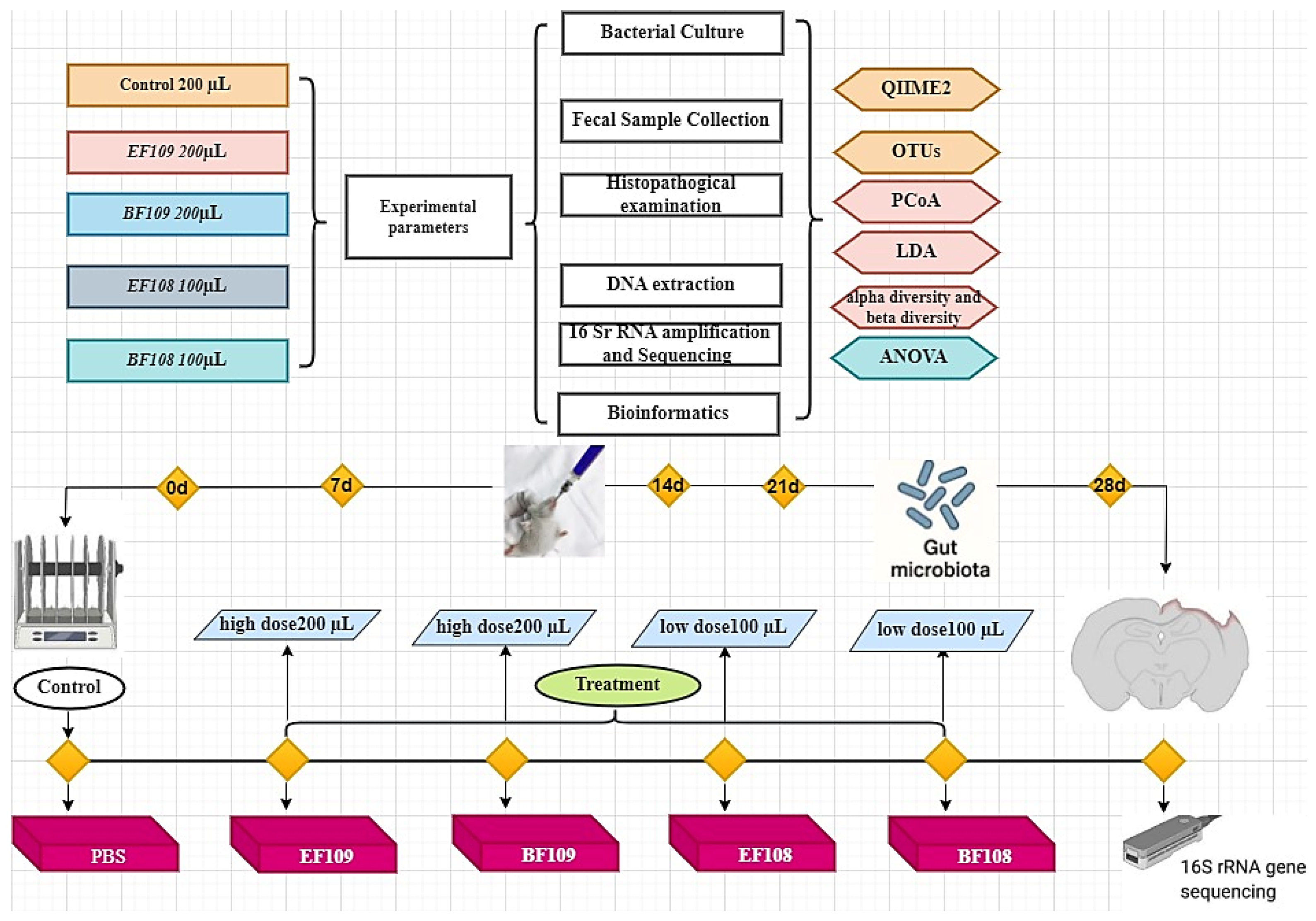
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Culture
2.2. Animal Grouping and Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Histopathological Examination
2.5. Fecal Sample Collection, DNA Extraction, 16 S rRNA Amplification and Sequencing
2.6. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Determination of Body Weight, Colon Length, and Organ Index of Mice
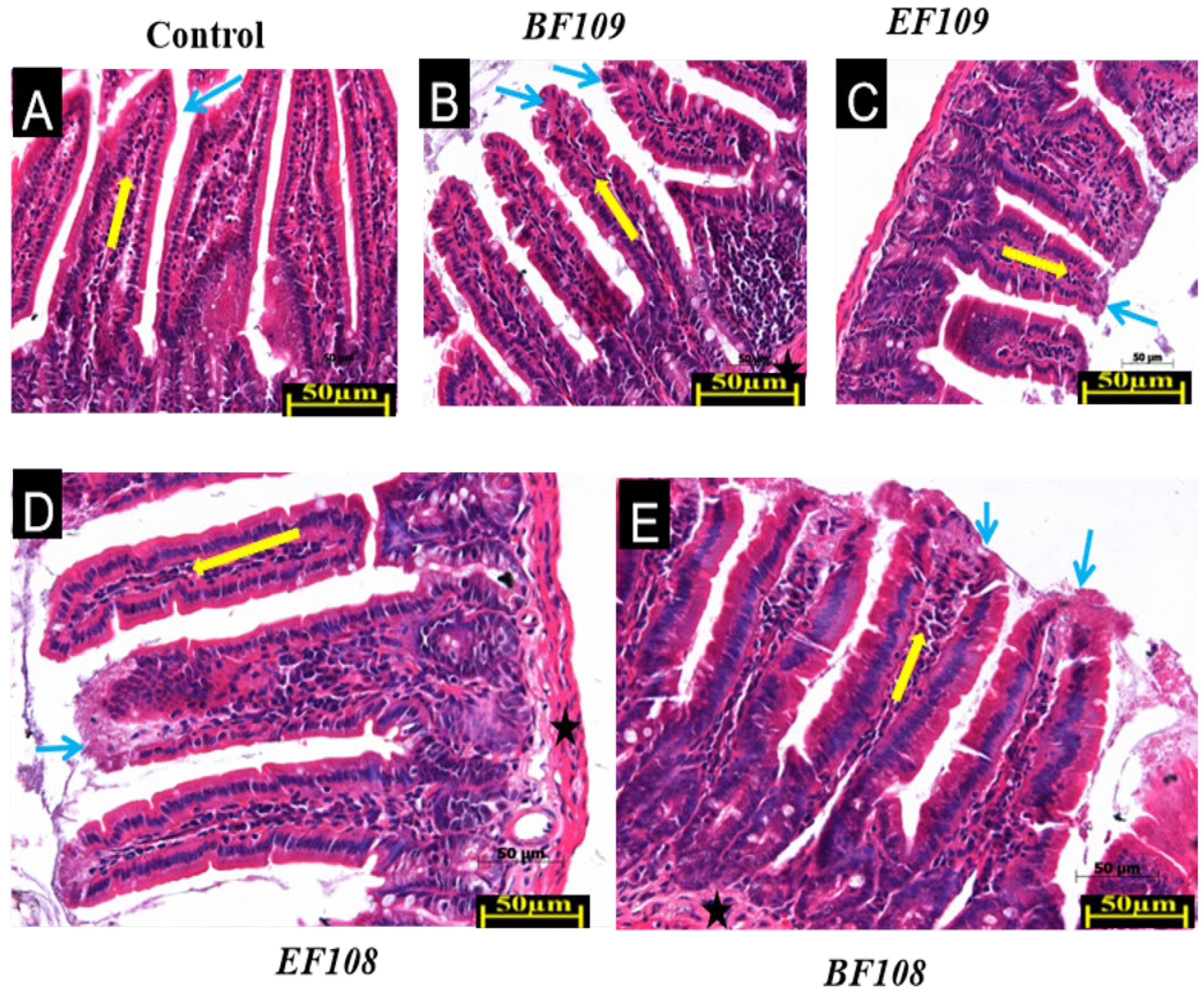
3.2. Effect of Bacterial Administration on Histopathological Changes
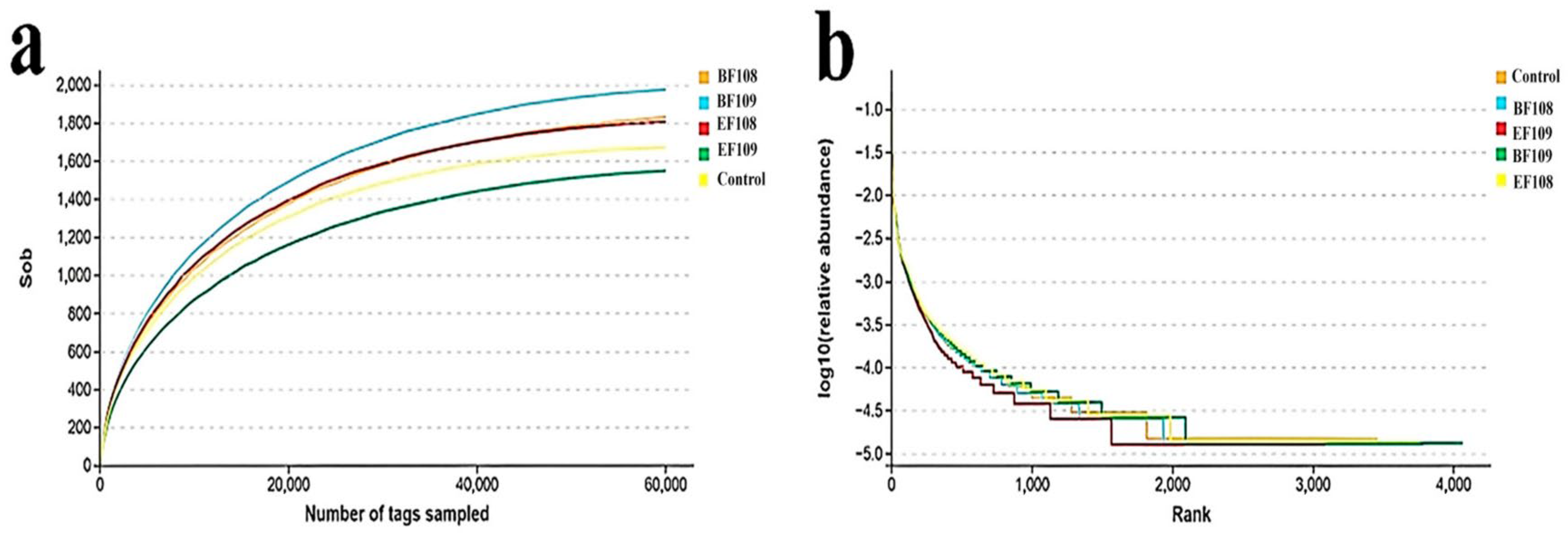
3.3. Analysis of DNA Sequences
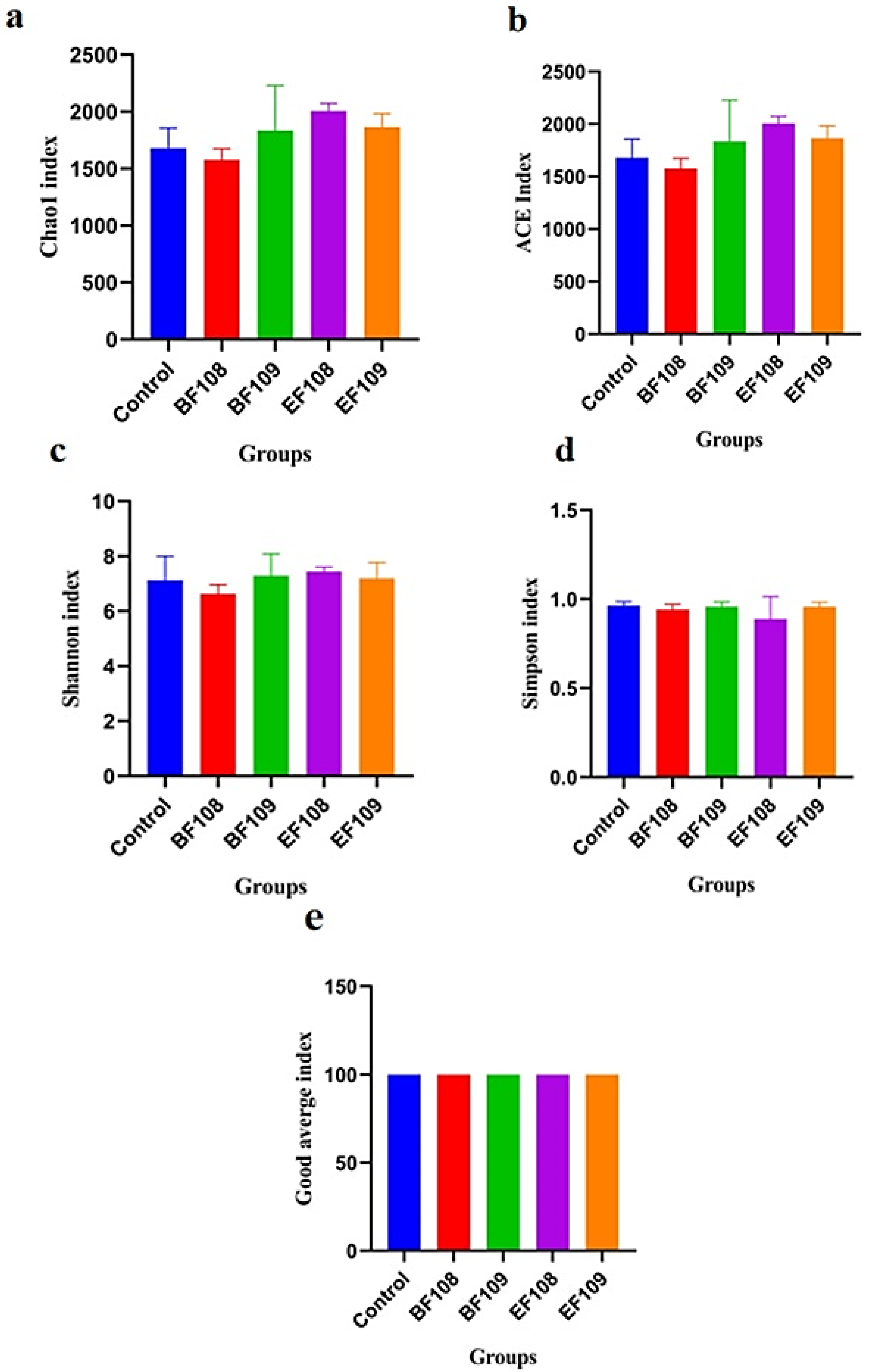
3.4. Microbial Diversity Index in Different Groups
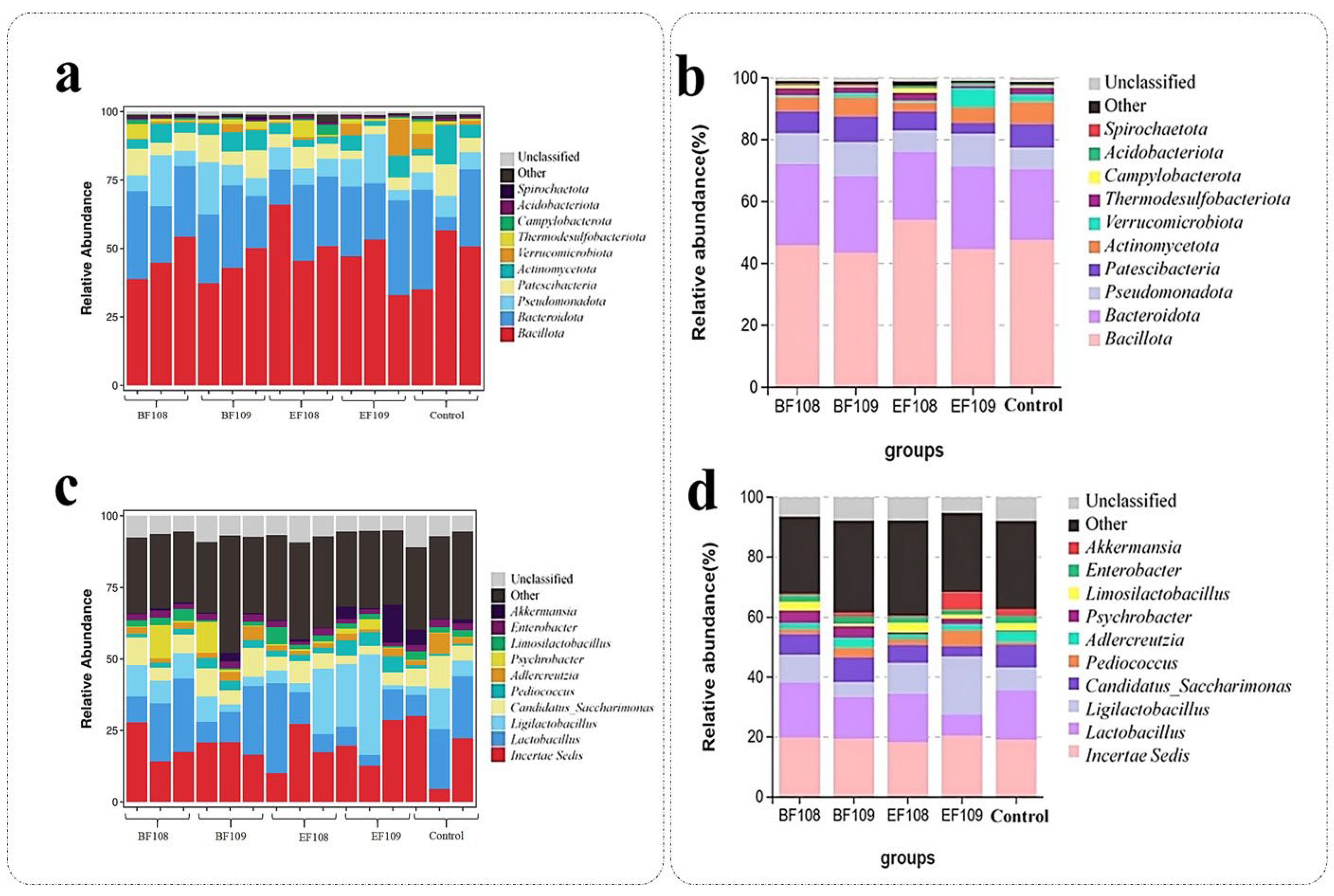
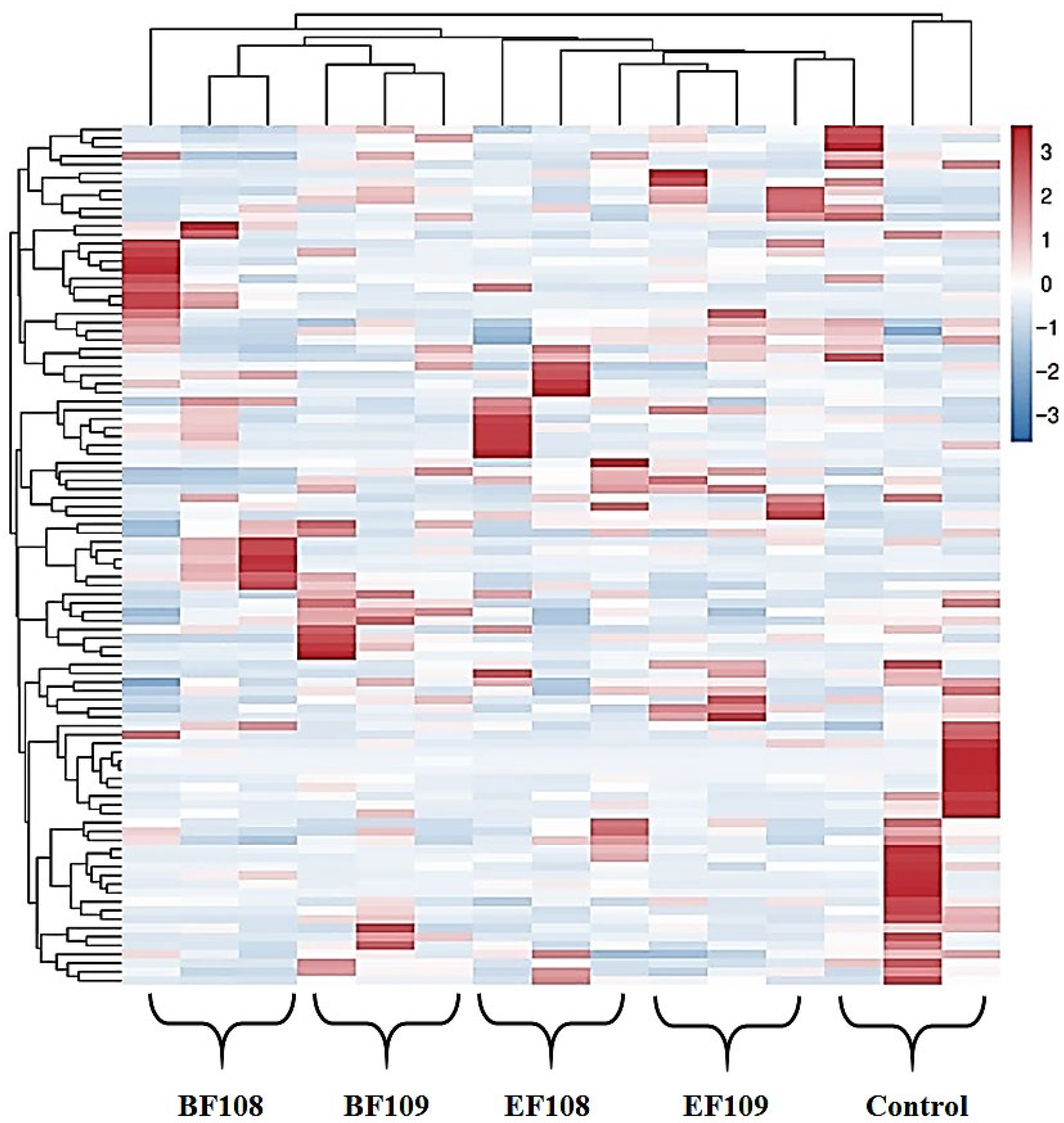
3.5. Alteration the Composition of Gut-Microbiota in Different Group
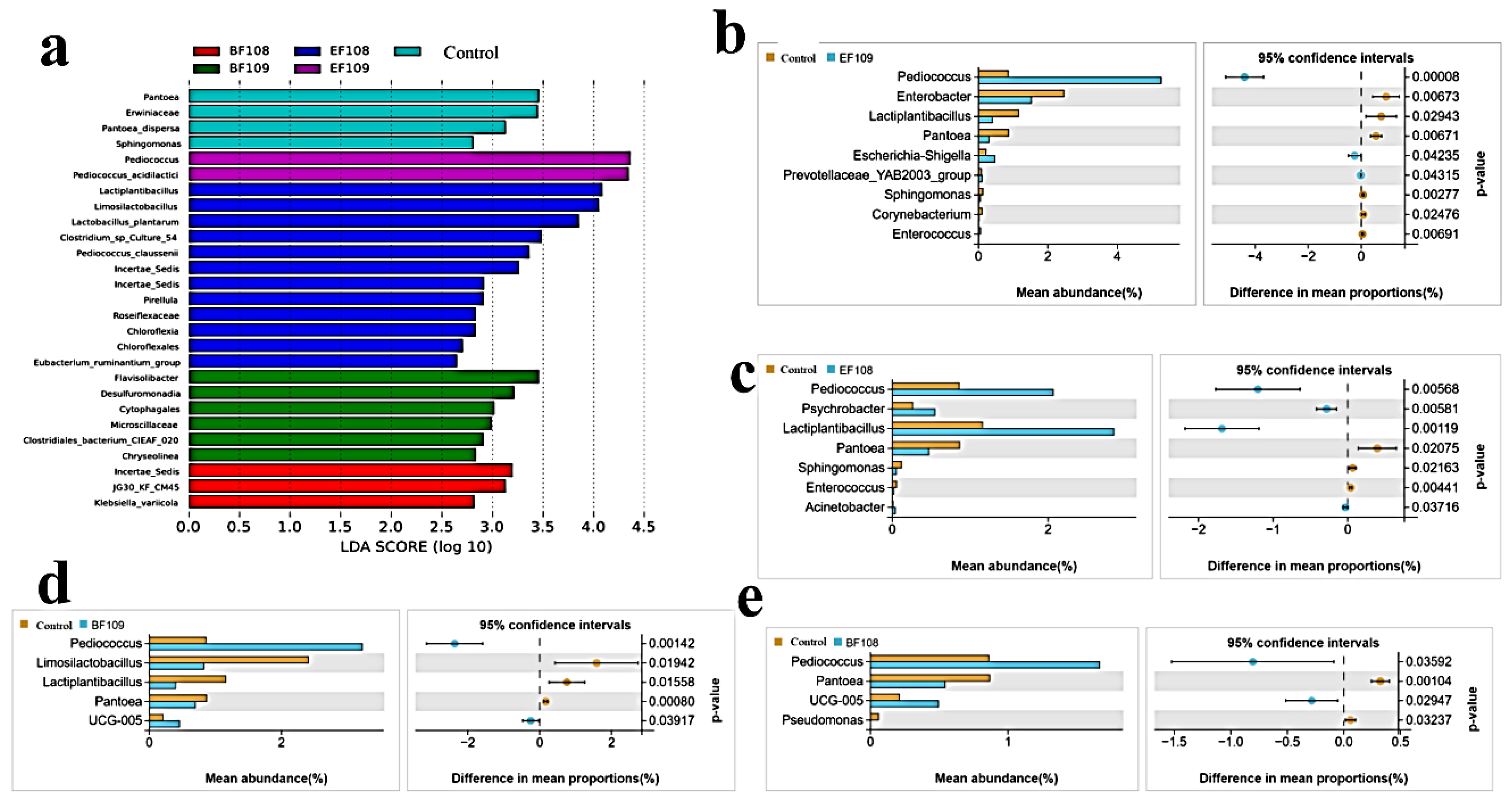
3.6. LEfse Analysis
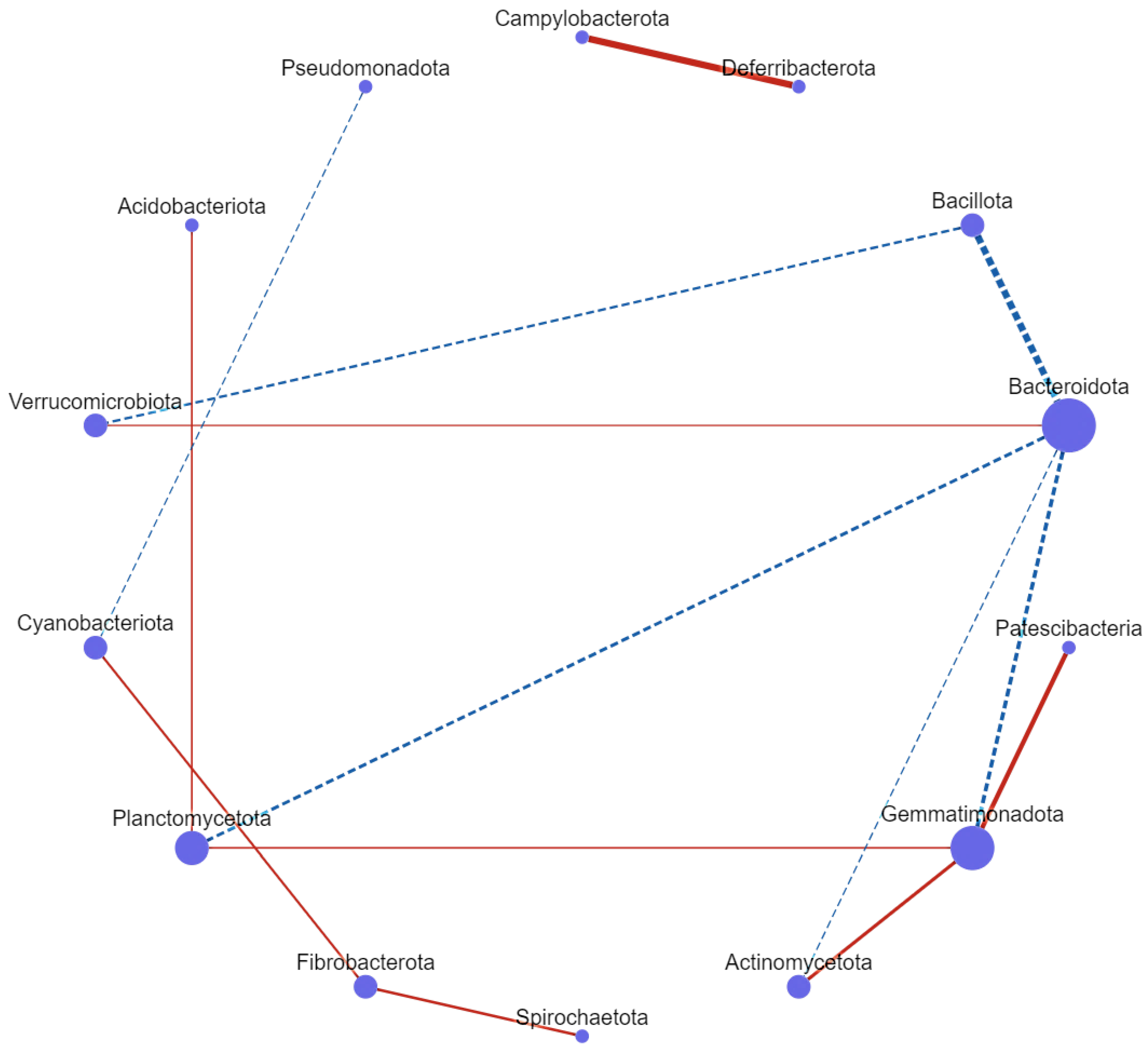
3.7. Correlation Network Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gholami, H.; Chmiel, J.A.; Burton, J.P.; Maleki Vareki, S. The Role of Microbiota-Derived Vitamins in Immune Homeostasis and Enhancing Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Shi, G.; Zheng, X.; Chang, J.; Lin, Q.; Tian, Z.; Yang, H. The Impact of Gut Microbial Signals on Hematopoietic Stem Cells and the Bone Marrow Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1338178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Wang, C.; Huang, L.; Qin, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhong, Y.; Ma, Q.; Yan, W.; Li, T.; Peng, Q.; et al. TET1s deficiency exacerbates oscillatory shear flow-induced atherosclerosis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 2163–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in Health and Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paray, B.A.; Albeshr, M.F.; Jan, A.T.; Rather, I.A. Leaky Gut and Autoimmunity: An Intricate Balance in Individuals Health and the Diseased State. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Imran, A.; Malik, A.; Chaudhary, A.A.; Rub, A.; Jan, A.T.; Syed, J.B.; Rolfo, C. Bacterial imbalance and gut pathologies: Association and contribution of E. coli in inflammatory bowel disease. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2019, 56, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.H.; Yeh, W.L.; Chou, C.H.; Wu, C.L.; Lai, C.H.; Yeh, Y.T.; Liao, C.A.; Wu, C.C. Suppressive Effects of Lactobacillus on Depression through Regulating the Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in C57BL/6J Mice Induced by Ampicillin. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Młynarska, E.; Wasiak, J.; Gajewska, A.; Steć, G.; Jasińska, J.; Rysz, J.; Franczyk, B. Exploring the Significance of Gut Microbiota in Diabetes Pathogenesis and Management-A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Lee, Y.K.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Roles of intestinal bacteroides in human health and diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 3518–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasemi, S.; Molicotti, P.; Fais, M.; Cossu, I.; Simula, E.R.; Sechi, L.A. Biological Mechanisms of Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis Toxin: Linking Inflammation, Colorectal Cancer, and Clinical Implications. Toxins 2025, 17, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cao, X.; Kato, N.; Wang, Y. Gut Bacteroides fragilis in health and diseases: An updated review. J. Future Foods 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Bai, Y.; Zhi, F. Isolation and identification of a non-enterotoxigenic strain of B. fragilis from a healthy term infant. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2014, 94, 2372–2374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, H.; Li, Z.; Tan, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, X.; Du, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, R.; Bai, Y.; et al. Safety Evaluation of a Novel Strain of B. fragilis. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Deng, H.; Zhou, Y.; Tan, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, R.; Bi, Y.; et al. Bioluminescence Imaging to Track B. fragilis Inhibition of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Infection in Mice. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, L.; Lin, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Liu, W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Kang, X.; Guo, K. Analysis of Characteristics of Bovine-Derived Non-Enterotoxigenic B. Fragilis and Validation of Potential Probiotic Effects. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztürk, H.; Geniş, B.; Özden Tuncer, B.; Tuncer, Y. Bacteriocin production and technological properties of Enterococcus mundtii and Enterococcus faecium strains isolated from sheep and goat colostrum. Vet. Res. Commun. 2023, 47, 1321–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, D.; Zhang, J.; Diao, Q.; Cui, K. Sheep-Derived Lactobacillus johnsonii M5 Enhances Immunity and Antioxidant Capacity, Alleviates Diarrhea, and Improves Intestinal Health in Early-Weaned Lambs. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, J.; Lei, M.; Gan, B.; Wan, Z.; Wu, L.; Luo, G.; Cao, S.; An, T.; et al. Targeted Screening of Fiber Degrading Bacteria with Probiotic Function in Herbivore Feces. Probiot. Antimicrob. Proteins 2025, 17, 1473–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Nie, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Wei, J.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, K.; Shao, D.; Liu, H.; Ma, Z.; et al. Two Enterococcus faecium Isolates Demonstrated Modulating Effects on the Dysbiosis of Mice Gut Microbiota Induced by Antibiotic Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, R.; Khanal, S.; Mathias, A.; Gupta, S.; Lallo, J.; Sahu, S.; Ohanyan, V.; Patel, A.; Storm, K.; Datta, S.; et al. TSP-1 (Thrombospondin-1) Deficiency Protects ApoE(-/-) Mice Against Leptin-Induced Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, e112–e127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Lan, B.; Zheng, T.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, L.; Tuerhongjiang, G.; Yuan, Z.; Wu, Y. GSDME-mediated pyroptosis promotes the progression and associated inflammation of atherosclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Wang, Y.C.; Hespen, C.W.; Espinosa, J.; Salje, J.; Rangan, K.J.; Oren, D.A.; Kang, J.Y.; Pedicord, V.A.; Hang, H.C. Enterococcus faecium secreted antigen A generates muropeptides to enhance host immunity and limit bacterial pathogenesis. eLife 2019, 8, e45343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, M.R.; Fang, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Ozkan, B.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Boyko, E.J.; Magliano, D.J.; Selvin, E. Global Prevalence of Prediabetes. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bytzer, P.; Talley, N.J.; Leemon, M.; Young, L.J.; Jones, M.P.; Horowitz, M. Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms associated with diabetes mellitus: A population-based survey of 15,000 adults. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 1989–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Du, J.; Tao, J.; Cheng, D. Growth Characteristics of Sheep-Derived B. Fragilisand and Preliminary Research on Effects in Mice and Lambs. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeder, A.M.; Spiller, F.; Carlstrom, M.; Izídio, G.S. Enterococcus faecalis: Implications for host health. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Zhong, Y.; Xie, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Pi, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Luo, J.; Xu, W. Bacteroides acidifaciens and its derived extracellular vesicles improve DSS-induced colitis. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1304232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delday, M.; Mulder, I.; Logan, E.T.; Grant, G. Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron Ameliorates Colon Inflammation in Preclinical Models of Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihekweazu, F.D.; Fofanova, T.Y.; Queliza, K.; Nagy-Szakal, D.; Stewart, C.J.; Engevik, M.A.; Hulten, K.G.; Tatevian, N.; Graham, D.Y.; Versalovic, J.; et al. Bacteroides ovatus ATCC 8483 monotherapy is superior to traditional fecal transplant and multi-strain bacteriotherapy in a murine colitis model. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 504–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mang, Q.; Gao, J.; Li, Q.; Sun, Y.; Xu, G.; Xu, P. Probiotics Enhance Coilia nasus Growth Performance and Nutritional Value by Regulating Glucolipid Metabolism via the Gut-Liver Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamphogoro, T.P.; Makete, G.; Modika, K.Y.; Kamutando, C.N. Probiotics as Feed Additives for Improved Animal Health and Nutrition: The Current Perspectives. In Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Postbiotics in Human Health and Sustainable Food Systems; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, B.; Tang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Gong, L.; Ni, J.; Li, W. Probiotic Bacillus Alleviates Oxidative Stress-Induced Liver Injury by Modulating Gut-Liver Axis in a Rat Model. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, S.; Kang, S.W.; Yang, J.-Y.; Baek, I.-J.; Sung, Y.H.; Park, Y.-Y. Microbiota-derived lactate accelerates intestinal stem-cell-mediated epithelial development. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 833–846.e836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Arioli, S.; Wang, A.; Villa, C.R.; Jahani, R.; Song, Y.S.; Mora, D.; Guglielmetti, S.; Comelli, E.M. Impact of Bifidobacterium bifidum MIMBb75 on mouse intestinal microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 85, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargari, G.; Taverniti, V.; Balzaretti, S.; Ferrario, C.; Gardana, C.; Simonetti, P.; Guglielmetti, S. Consumption of a Bifidobacterium bifidum Strain for 4 Weeks Modulates Dominant Intestinal Bacterial Taxa and Fecal Butyrate in Healthy Adults. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5850–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmetti, S.; Zanoni, I.; Balzaretti, S.; Miriani, M.; Taverniti, V.; De Noni, I.; Presti, I.; Stuknyte, M.; Scarafoni, A.; Arioli, S.; et al. Murein lytic enzyme TgaA of Bifidobacterium bifidum MIMBb75 modulates dendritic cell maturation through its cysteine- and histidine-dependent amidohydrolase/peptidase (CHAP) amidase domain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5170–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, T.; Makizaki, Y.; Oikawa, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Maeda, A.; Shimakawa, M.; Komoto, S.; Moriguchi, K.; Ohno, H.; Taniguchi, K. Oral administration of Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 alleviates rotavirus gastroenteritis through regulation of intestinal homeostasis by inducing mucosal protective factors. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taibi, A.; Singh, N.; Chen, J.; Arioli, S.; Guglielmetti, S.; Comelli, E.M. Time- and strain-specific downregulation of intestinal EPAS1 via miR-148a by Bifidobacterium bifidum. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Tsukahara, T.; Yanagi, T.; Nakahara, S.; Furukawa, O.; Tsutsui, H.; Koshida, S. Bifidobacterium bifidum OLB6378 Simultaneously Enhances Systemic and Mucosal Humoral Immunity in Low Birth Weight Infants: A Non-Randomized Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, A.; Yan, F.; Polk, D.B.; Rao, R.K. Probiotics ameliorate the hydrogen peroxide-induced epithelial barrier disruption by a PKC- and MAP kinase-dependent mechanism. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G1060–G1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczewski, J.; Troost, F.J.; Konings, I.; Dekker, J.; Kleerebezem, M.; Brummer, R.J.; Wells, J.M. Regulation of human epithelial tight junction proteins by Lactobacillus plantarum in vivo and protective effects on the epithelial barrier. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 298, G851–G859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Qu, C.; Wang, B.; Liang, S.; Zeng, B. Probiotics for Preventing and Treating Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Current Evidence. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 51, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; DeLuca, J.A.A.; Menon, R.; Garcia-Vilarato, E.; Callaway, E.; Landrock, K.K.; Lee, K.; Safe, S.H.; Chapkin, R.S.; Allred, C.D.; et al. Effect of diet and intestinal AhR expression on fecal microbiome and metabolomic profiles. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, L.; Xu, Y.; Liu, N.; Sun, X.; Hu, L.; Huang, H.; Wei, K.; Zhu, R. Dynamic Distribution of Gut Microbiota in Goats at Different Ages and Health States. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, A.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, H.; Mehmood, K.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, J.; Waqas, M.; Iqbal, M.; Li, J. Probiotic Potential of Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides and Lactobacillus Strains Isolated from Yaks. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Sato, A.; Kishimoto, Y.; Mabashi-Asazuma, H.; Kondo, K.; Iida, K. Gallic Acid Inhibits Lipid Accumulation via AMPK Pathway and Suppresses Apoptosis and Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation in Hepatocytes. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, S.; Jin, T.; Li, K.; Han, Z.; Li, Y. Microbiome analysis reveals the alterations in gut microbiota in different intestinal segments of Yimeng black goats. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 155, 104900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Hu, M.; Tao, J.; Yang, H.; Yan, P.; An, G.; Wang, H. The protective effects of Chinese yam polysaccharide against obesity-induced insulin resistance. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 55, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsonowati, W.; Marian, M.; Surono; Narisawa, K. The Effectiveness of a Dark Septate Endophytic Fungus, Cladophialophora chaetospira SK51, to Mitigate Strawberry Fusarium Wilt Disease and With Growth Promotion Activities. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.S.; Jo, H.E.; Lee, J.; Choi, K.S.; Yu, D.; Oh, Y.S.; Park, J.; Choi, H.J. Alteration of the gut microbiota in post-weaned calves following recovery from bovine coronavirus-mediated diarrhea. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ren, Y.; Wen, X.; Yue, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Peng, Q.; Hu, R.; Zou, H.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Comparison of coated and uncoated trace elements on growth performance, apparent digestibility, intestinal development and microbial diversity in growing sheep. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1080182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liang, Z.; Ding Kao, R.; Han, J.; Du, M.; Ahmad, A.A.; Wang, S.; Salekdeh, G.H.; Long, R.; Yan, P.; et al. Maternal Fecal Microbes Contribute to Shaping the Early Life Assembly of the Intestinal Microbiota of Co-inhabiting Yak and Cattle Calves. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 916735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shao, M.; Huang, H.; Wang, S.; Ma, L.; Wang, H.; Hu, L.; Wei, K.; Zhu, R. The Dynamic Distribution of Small-Tail Han Sheep Microbiota across Different Intestinal Segments. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahowald, M.A.; Rey, F.E.; Seedorf, H.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fulton, R.S.; Wollam, A.; Shah, N.; Wang, C.; Magrini, V.; Wilson, R.K.; et al. Characterizing a model human gut microbiota composed of members of its two dominant bacterial phyla. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5859–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, N.R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, A.; Zhang, L.; Waqas, M.; Mehmood, K.; Iqbal, M.; Muyou, C.; Li, Z.; Lian, Y.; Sizhu, S.; et al. Probiotic potential of Lactobacillus on the intestinal microflora against Escherichia coli induced mice model through high-throughput sequencing. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 137, 103760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Ijaz, M.; Mehmood, K.; Ali, M.; Tian, F.; Li, J.; Ahmed, S.; Shaukat, A.; Chang, Z.; Wu, Q. Protective effects of salidroside and dexamethasone against E. coli-induced inflammatory response on endometrial epithelium cells in yaks. Pak. Vet. J. 2019, 39, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.N.; Yang, J.; Yeom, S.J.; Kim, S.S.; Park, J.H.; Song, B.S.; Eun, J.B.; Park, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.B.; et al. Lactiplantibacillus argentoratensis AGMB00912 protects weaning mice from ETEC infection and enhances gut health. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1440134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.Y.; Qi, W.P.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.Y.; Mei, S.J.; Mao, S.Y. Changes in rumen fermentation and bacterial community in lactating dairy cows with subacute rumen acidosis following rumen content transplantation. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 10780–10795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, X.; Sun, J.; Liang, X.; Lv, Y.; Bai, L.; Zhang, J.; Gong, P.; Liu, T.; et al. Lactobacillus casei YRL577 ameliorates markers of non-alcoholic fatty liver and alters expression of genes within the intestinal bile acid pathway. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 125, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Wen, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, X. Lactobacillus delbrueckii Ameliorates Intestinal Integrity and Antioxidant Ability in Weaned Piglets after a Lipopolysaccharide Challenge. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 6028606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leys, N.M.; Ryngaert, A.; Bastiaens, L.; Verstraete, W.; Top, E.M.; Springael, D. Occurrence and phylogenetic diversity of Sphingomonas strains in soils contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1944–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippo, C.; Cavalieri, D.; Di Paola, M.; Ramazzotti, M.; Poullet, J.B.; Massart, S.; Collini, S.; Pieraccini, G.; Lionetti, P. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14691–14696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Wu, S.; Zeng, Z.; Fu, Z. Effects of environmental pollutants on gut microbiota. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 222, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboré, O.D.; Godreuil, S.; Drancourt, M. Planctomycetes as Host-Associated Bacteria: A Perspective That Holds Promise for Their Future Isolations, by Mimicking Their Native Environmental Niches in Clinical Microbiology Laboratories. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 519301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.E.; Merenstein, D.J.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Rastall, R.A. Probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health and disease: From biology to the clinic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhalhel, K.; Cavallaro, M.; Pansera, L.; Ledesma, L.H.; Levanti, M.; Germanà, A.; Sutera, A.M.; Tardiolo, G.; Zumbo, A.; Aragona, M.; et al. Histological Assessment of Intestinal Changes Induced by Liquid Whey-Enriched Diets in Pigs. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutera, A.M.; Arfuso, F.; Tardiolo, G.; Riggio, V.; Fazio, F.; Aiese Cigliano, R.; Paytuví, A.; Piccione, G.; Zumbo, A. Effect of a Co-Feed Liquid Whey-Integrated Diet on Crossbred Pigs’ Fecal Microbiota. Animals 2023, 13, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardiolo, G.; Romeo, O.; Zumbo, A.; Di Marsico, M.; Sutera, A.M.; Cigliano, R.A.; Paytuví, A.; D’Alessandro, E. Characterization of the Nero Siciliano Pig Fecal Microbiota after a Liquid Whey-Supplemented Diet. Animals 2023, 13, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Group | Treatment Strain | Dose Volume (µL) | Concentration (CFU/mL) | Total CFU Per Mouse Per Day | Average Mouse Weight (g) | Equivalent CFU/kg BW/day |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | PBS | 200 | -- | -- | 22 | -- |
| BF109 | High dose (Bacteroides fragilis) | 200 | 1 × 109 | 2 × 108 CFU | 22 | 9.1 × 109 |
| EF109 | High dose (Enterococcus faecium) | 200 | 1 × 109 | 2 × 108 CFU | 22 | 9.1 × 109 |
| BF108 | Low dose (Bacteroides fragilis) | 100 | 1 × 108 | 1 × 107 CFU | 22 | 4.5 × 108 |
| EF108 | Low dose (Enterococcus faecium) | 100 | 1 × 108 | 1 × 107 CFU | 22 | 4.5 × 108 |
| Group | Villus Height (µm) | Crypt Depth (µm) | VH/CD Ratio | Inflammation Score (0–1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 437 ±17 b | 129± 3.0 c | 4.5 ±0.2 b | 0.5 ± 0.2 a |
| BF109 | 579 ± 20 a | 221± 2.1 a | 3.4 ±0.3 c | 0.3 ± 0.1 b |
| EF109 | 579 ± 20 a | 203 ±5.2 b | 4.7 ± 0.2 b | 0.4 ± 0.2 a |
| BF108 | 368 ± 19 c | 207 ±5.0 b | 5.5 ± 0.1 a | 0.2 ± 0.1 c |
| EF108 | 368 ± 17 c | 203 ± 5.1 b | 4.7 ± 0.3 b | 0.3 ± 0.2 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Essa, M.O.A.; Cheng, C.; Chen, L.; Chi, G.-Y.; Abdelhadi, L.A.M.; Hassan, H.A.; Yaqoob, S.; Adam, S.Y.; Husien, H.M.; Saleh, A.A.; et al. Effects of Bacteroides fragilis and Enterococcus faecium Administration as Probiotic Candidates: Impact on Growth Performance, Organ Indices, and Gut Microbiota Balance in Mice. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111093
Essa MOA, Cheng C, Chen L, Chi G-Y, Abdelhadi LAM, Hassan HA, Yaqoob S, Adam SY, Husien HM, Saleh AA, et al. Effects of Bacteroides fragilis and Enterococcus faecium Administration as Probiotic Candidates: Impact on Growth Performance, Organ Indices, and Gut Microbiota Balance in Mice. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(11):1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111093
Chicago/Turabian StyleEssa, Mohamed Osman Abdalrahem, Cheng Cheng, Liang Chen, Geng-Yu Chi, Layla Ahmed Mohammed Abdelhadi, Huda Ahmed Hassan, Saniya Yaqoob, Saber Y. Adam, Hosameldeen Mohamed Husien, Ahmed A. Saleh, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Bacteroides fragilis and Enterococcus faecium Administration as Probiotic Candidates: Impact on Growth Performance, Organ Indices, and Gut Microbiota Balance in Mice" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 11: 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111093
APA StyleEssa, M. O. A., Cheng, C., Chen, L., Chi, G.-Y., Abdelhadi, L. A. M., Hassan, H. A., Yaqoob, S., Adam, S. Y., Husien, H. M., Saleh, A. A., & Cheng, D. (2025). Effects of Bacteroides fragilis and Enterococcus faecium Administration as Probiotic Candidates: Impact on Growth Performance, Organ Indices, and Gut Microbiota Balance in Mice. Veterinary Sciences, 12(11), 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12111093








