Haematochemical Profile of Healthy Dogs Seropositive for Single or Multiple Vector-Borne Pathogens
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Laboratory Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
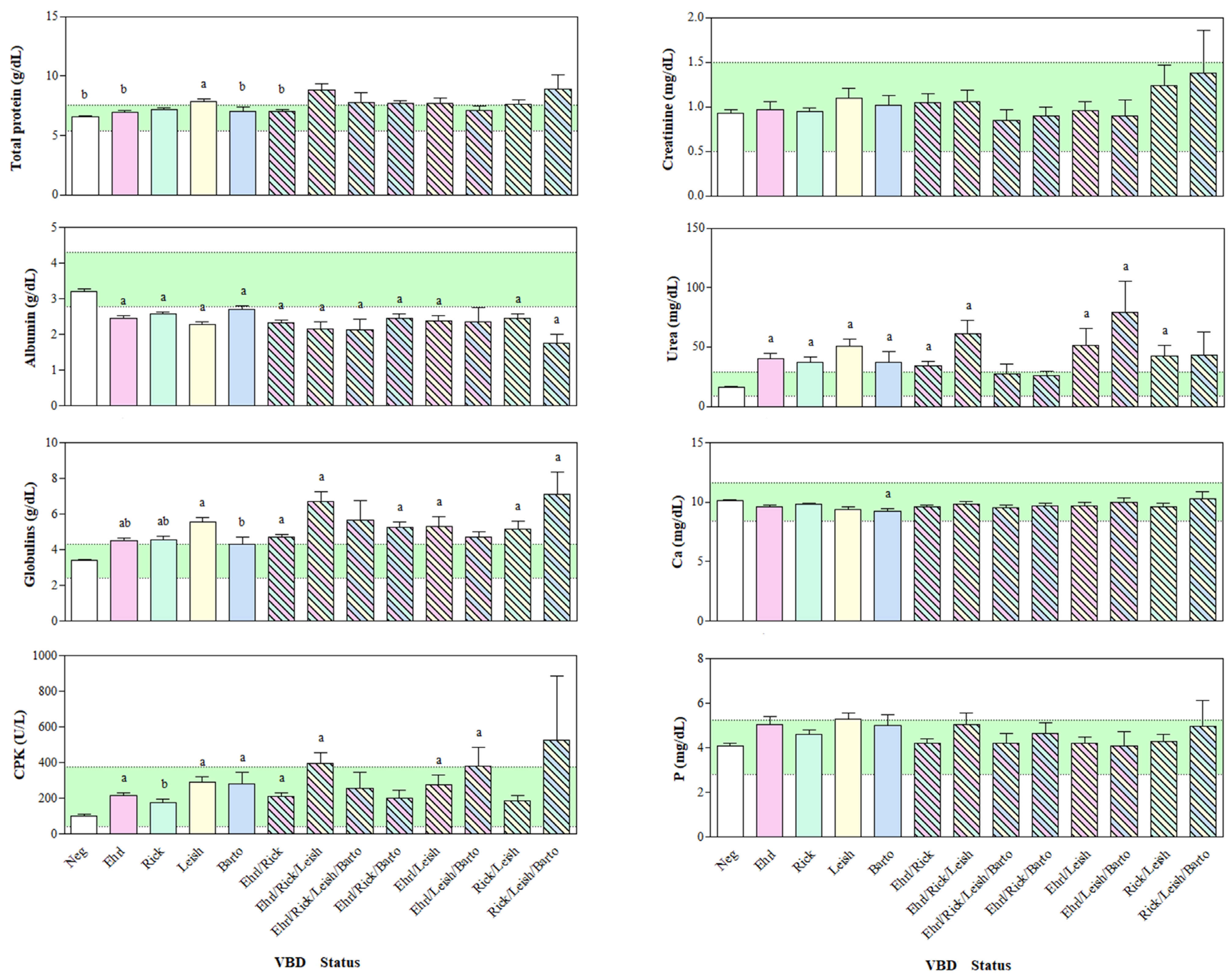
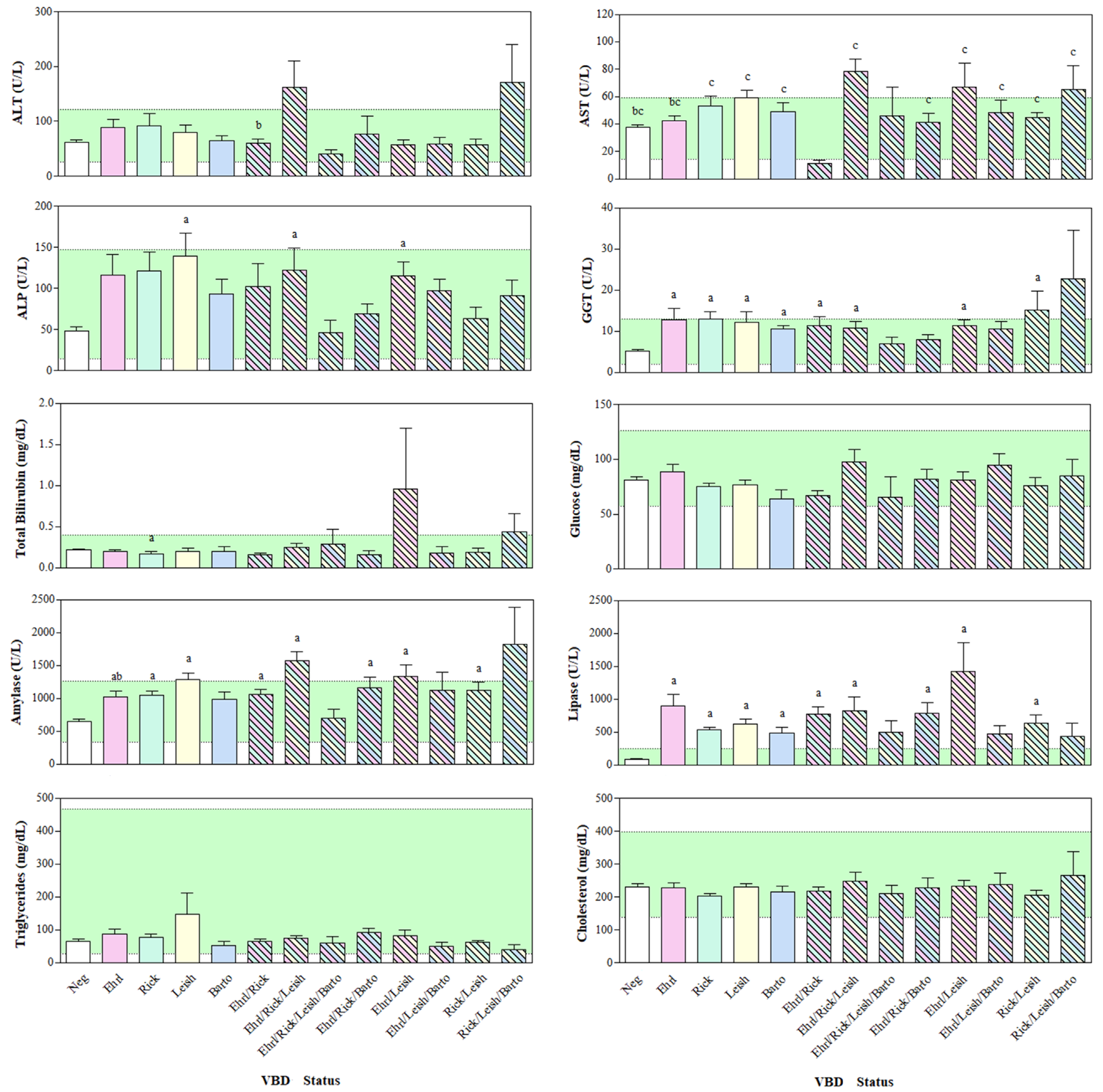
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Otranto, D. Arthropod-borne pathogens of dogs and cats: From pathways and times of transmission to disease control. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 251, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente, J.; Villar, M.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Ayllón, N.; Alberdi, P. Tick–Host–Pathogen Interactions: Conflict and Cooperation. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Control of Neglected Tropical Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/control-of-neglected-tropical-diseases (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Hotez, P.J. Neglected Parasitic Infections and Poverty in the United States. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baneth, G.; Bourdeau, P.; Bourdoiseau, G.; Bowman, D.; Breitschwerdt, E.; Capelli, G.; Cardoso, L.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Day, M.; Dedet, J.P.; et al. Vector-borne diseases—Constant challenge for practicing veterinarians: Recommendations from the CVBD World Forum. Parasit. Vectors 2012, 20, 5–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klink, J.C.; Rieger, A.; Wohlsein, P.; Siebert, U.; Obiegala, A. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Pathogens in Raccoon Dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides) and Raccoons (Procyon lotor) from Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. Pathogens 2024, 13, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giudice, E.; Di Pietro, S.; Alaimo, A.; Blanda, V.; Lelli, R.; Francaviglia, F.; Caracappa, S.; Torina, A. A molecular survey of Rickettsia felis in fleas from cats and dogs in Sicily (Southern Italy). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otranto, D.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Mihalca, A.D.; Traub, R.J.; Lappin, M.; Baneth, G. Zoonotic Parasites of Sheltered and Stray Dogs in the Era of the Global Economic and Political Crisis. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altizer, S.; Ostfeld, R.S.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Kutz, S.; Harvell, C.D. Climate change and infectious diseases: From evidence to a predictive framework. Science 2013, 341, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, S.J.; Leung, W.T.M.; Owen, C.J.; Puschendorf, R.; Sergeant, C.; Cunningham, A.A.; Balloux, F.; Garner, T.W.J.; Nichols, R.A. Effects of historic and projected climate change on the range and impacts of an emerging wildlife disease. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 2648–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, N. Impact of Anthropogenic Environmental Alterations on Vector-Borne Diseases. Medscape J. Med. 2008, 10, 238. [Google Scholar]
- Diakou, A.; Di Cesare, A.; Morelli, S.; Colombo, M.; Halos, L.; Simonato, G.; Tamvakis, A.; Beugnet, F.; Paoletti, B.; Traversa, D. Endoparasites and vector-borne pathogens in dogs from Greek islands: Pathogen distribution and zoonotic implications. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Regañón, D.; Roura, X.; Suárez, M.L.; León, M.; Sainz, Á. Serological evaluation of selected vector-borne pathogens in owned dogs from northern Spain based on a multicenter study using a commercial test. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruccelli, A.; Ferrara, G.; Iovane, G.; Schettini, R.; Ciarcia, R.; Caputo, V.; Pompameo, M.; Pagnini, U.; Montagnaro, S. Seroprevalence of Ehrlichia spp., Anaplasma spp., Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato, and Dirofilaria immitis in Stray Dogs, from 2016 to 2019, in Southern Italy. Animals 2020, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamponi, C.; Scarpa, F.; Carta, S.; Knoll, S.; Sanna, D.; Gai, C.; Pipia, A.P.; Dessì, G.; Casu, M.; Varcasia, A.; et al. Seroprevalence and risk factors associated with Leishmania infantum in dogs in Sardinia (Italy), an endemic island for leishmaniasis. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisu, V.; Dei Giudici, S.; Foxi, C.; Chessa, G.; Peralta, F.; Sini, V.; Masala, G. Anaplasma Species in Ticks Infesting Mammals of Sardinia, Italy. Animals 2023, 13, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, J.E.; Anderson, B.E.; Fishbein, D.B.; Sanchez, J.L.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Wilson, K.H.; Duntley, C.W. Isolation and characterization of an Ehrlichia sp. from a patient diagnosed with human ehrlichiosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 2741–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocco, R.; Sanna, G.; Cillara, M.G.; Tola, S.; Ximenes, L.; Pinnaparpaglia, M.L.; Masala, G. Ehrlichiosis and rickettsiosis in a canine population of Northern Sardinia. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 990, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Levy, M.G.; Davidson, M.G.; Walker, D.H.; Burgdorfer, W.; Curtis, B.C.; Baineau, C.A. Kinetics of IgM and IgG responses to experimental and naturally-occurring Rickettsia rickettsii infection in dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1990, 51, 1312–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comer, K.M. Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 1991, 21, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manual of diagnostic tests and vaccines for terrestrial animals. Off. Int. Epizooties 2018, 3, 11.
- Foglia Manzillo, V.; Gizzarelli, M.; Vitale, F.; Montagnaro, S.; Torina, A.; Sotera, S.; Oliva, G. Serological and entomological survey of canine leishmaniasis in Lampedusa island, Italy. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Le Rhun, D.; Buffet, J.P.; Cotte, V.; Read, A.; Birtles, R.J.; Vayssier-Taussat, M. Strategies of exploitation of mammalian reservoirs by Bartonella species. Vet. Res. 2012, 43, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, K. Infective Endocarditis in Dogs: Diagnosis and Therapy. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2010, 40, 665–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escribano, D.; Cihan, H.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Levent, P.; Kocaturk, M.; Aytug, N.; Cerón, J.J.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Yilmaz, Z. Changes in serum proteins in dogs with Ehrlichia canis infection. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 113, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mylonakis, M.E.; Harrus, S.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. An update on the treatment of canine monocytic ehrlichiosis (Ehrlichia canis). Vet. J. 2019, 46, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, D.J.; Harvey, J.W. Veterinary Laboratory Medicine: Interpretation & Diagnosis: Interpretation and Diagnosis, 3rd ed.; W. B. Saunders Co: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ciaramella, P.; Corona, M. Leishmaniasis: Clinical and diagnostic aspects. Compendium 2003, 25, 358–368. [Google Scholar]
- Solano-Gallego, L.; Miró, G.; Koutinas, A.; Cardoso, L.; Pennisi, M.G.; Ferrer, L.; Bourdeau, P.; Oliva, G.; Baneth, G.; The LeishVet Group. LeishVet guidelines for the practical management of canine leishmaniosis. Parasit. Vectors 2011, 4, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrus, S.; Aroch, I.; Lavy, E.; Bark, H. Clinical manifestations of infectious canine cyclic thrombocytopenia. Vet. Rec. 1997, 141, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainz, Á.; Roura, X.; Miró, G.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Kohn, B.; Harrus, S.; Solano-Gallego, L. Guideline for veterinary practitioners on canine ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis in Europe. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravnik, U.; Tozon, N.; Smrdel, K.S.; Zupanc, T.A. Anaplasmosis in dogs: The relation of haematological, biochemical and clinical alterations to antibody titre and PCR confirmed infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 149, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|
| Owners informed consent for the scientific use of their animal’s data | Physical or historical signs of any kind |
| Dog clinically healthy on physical examination, free from external and internal parasites, and in good nutritional condition | Dog with history of vector-borne diseases |
| Biochemical profile checked at the time of hospital admission | Pharmacological treatment, including preventative flea/tick/mosquito treatments in the month prior to blood sampling |
| A serum aliquot stored at −20 °C | Dog vaccinated against the investigated diseases (i.e., leishmaniosis and borreliosis) |
| Breed | Number of Dogs (%) | Age | Gender | Number of Dogs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative status (8.75%) | 35 (8.75%) | |||
| Mixed | 11 | Median 6 years | Males | 22 |
| German shepered | 6 | Range 2–14 | Females | 13 |
| Yorkshire terrier | 5 | |||
| English setter | 3 | |||
| Boxer, Poodle, Rottweiler (two each) | 6 | |||
| Beagle, Labrador retriever, Pitbull, Italian rough-haired segugio (one each) | 4 | |||
| Erlichia-positive status | 57 (14.25%) | |||
| Mixed | 25 | Median 5 years | Males | 26 |
| Fonni’ Dog | 10 | Range 1–15 | Females | 31 |
| German shepered, Italian rough-haired segugio (four each) | 8 | |||
| Pitbull, Yorkshire terrier, Rottweiler, English setter (two each) | 8 | |||
| Boxer, Pointer, Labrador retriever, Chihuahua, Dobermann, Jack russel terrier (one each) | 6 | |||
| Rickettsia-positive status | 75 (18.75%) | |||
| Mixed | 25 | Median 5 years | Males | 47 |
| Fonni’ Dog | 23 | Range 1–15 | Females | 28 |
| German shepered, Italian rough-haired segugio, (four each) | 12 | |||
| Yorkshire terrier, Rottweiler (three each) | 6 | |||
| Poodle, Dobermann, English setter (two each) | 6 | |||
| Dachs hound, Cocker spaniel, Pitbull, (one each) | 3 | |||
| Leishmania-positive status | 51 (12.75%) | |||
| Mixed | 16 | Median 4 years | Males | 33 |
| Fonni’ Dog | 7 | Range 1–13 | Females | 18 |
| German shepered | 5 | |||
| Italian rough-haired segugio, English setter (four each) | 8 | |||
| Yorkshire terrier, Rottweiler, Boxer, Dobermann, Pitbull, Jack russel terrier, Labrador retriever, Pointer (two each) | 8 | |||
| Poodle, American Staffordshire terrier, Dachs hound, Chihuahua, Cocker spaniel, Dalmatian, Shar-pei (one each) | 7 | |||
| Anaplasma-positive status | 1 (0.25%) | |||
| Mixed | 1 | Median 5 years | Females | 1 |
| Bartonella-positive status | 16 (4.00%) | |||
| Fonni’ Dog | 5 | Median 4 years | Males | 10 |
| Mixed | 4 | Range 2–18 | Females | 6 |
| German shepered, Italian rough-haired segugio (two each) | 4 | |||
| Yorkshire terrier, Rottweiler, Dobermann (one each) | 3 | |||
| Multiple seropositivity status | 165 (41.25%) | |||
| Mixed | 65 | Median 5 years | Males | 86 |
| Fonni’ Dog | 32 | Range 1–18 | Females | 79 |
| German shepered | 15 | |||
| Italian rough-haired segugio | 15 | |||
| Yorkshire terrier | 6 | |||
| English setter | 5 | |||
| Boxer, Pitbull, Chihuahua, Labrador retriever, Pointer, Rottweiler (three each) | 18 | |||
| Poodle, Dobermann, Dalmatian (two each) | 6 | |||
| Dachs hound, Shih-tzu, Jack russel terrier (one each) | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cocco, R.; Sechi, S.; Rizzo, M.; Bonomo, A.; Arfuso, F.; Giudice, E. Haematochemical Profile of Healthy Dogs Seropositive for Single or Multiple Vector-Borne Pathogens. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11050205
Cocco R, Sechi S, Rizzo M, Bonomo A, Arfuso F, Giudice E. Haematochemical Profile of Healthy Dogs Seropositive for Single or Multiple Vector-Borne Pathogens. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(5):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11050205
Chicago/Turabian StyleCocco, Raffaella, Sara Sechi, Maria Rizzo, Andrea Bonomo, Francesca Arfuso, and Elisabetta Giudice. 2024. "Haematochemical Profile of Healthy Dogs Seropositive for Single or Multiple Vector-Borne Pathogens" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 5: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11050205
APA StyleCocco, R., Sechi, S., Rizzo, M., Bonomo, A., Arfuso, F., & Giudice, E. (2024). Haematochemical Profile of Healthy Dogs Seropositive for Single or Multiple Vector-Borne Pathogens. Veterinary Sciences, 11(5), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11050205






