Effects of Guanidine Acetic Acid on the Growth and Slaughter Performance, Meat Quality, Antioxidant Capacity, and Cecal Microbiota of Broiler Chickens
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Animals and Diets
2.3. Growth Performance
2.4. Slaughter Performance
2.5. Meat Quality
2.6. Serum Biochemical Indicators
2.7. Cecal Microbiota
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance
3.2. Slaughter Performance
3.3. Meat Quality
3.4. Serum Biochemical Parameters
3.5. Antioxidant Capacity
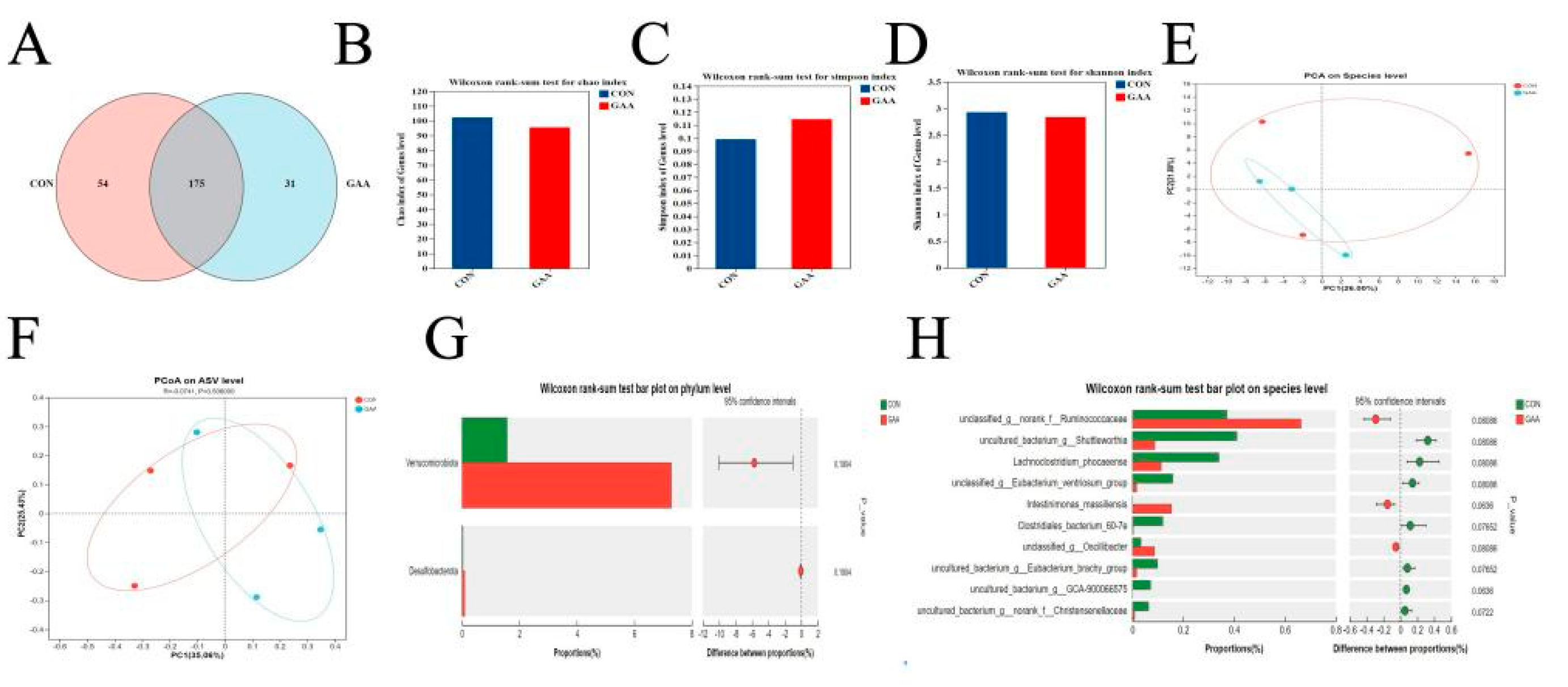
3.6. Cecal Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fonseca, A.; Kenney, S.; Van Syoc, E.; Bierly, S.; Dini-Andreote, F.; Silverman, J.; Boney, J.; Ganda, E. Investigating antibiotic free feed additives for growth promotion in poultry: Effects on performance and microbiota. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández Miyakawa, M.E.; Casanova, N.A.; Kogut, M.H. How did antibiotic growth promoters increase growth and feed efficiency in poultry? Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, A.; Liu, Z.; Lv, X.; Zhou, C.; Ran, T.; Tan, Z. Prospects and challenges of bacteriophage substitution for antibiotics in livestock and poultry production. Biology 2024, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Ghany, W.A. Potential effects of garlic (Allium sativum L.) on the performance, immunity, gut health, anti-oxidant status, blood parameters, and intestinal microbiota of poultry: An updated comprehensive review. Animals 2024, 14, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plata, G.; Baxter, N.T.; Susanti, D.; Volland-Munson, A.; Gangaiah, D.; Nagireddy, A.; Mane, S.P.; Balakuntla, J.; Hawkins, T.B.; Kumar Mahajan, A. Growth promotion and antibiotic induced metabolic shifts in the chicken gut microbiome. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, K.; Tofazzal Hossain, M.; Ahmed, R.; Hasan, M.M.; Islam, R.; Hossen, M.I.; Shaha, S.N.; Islam, M.R. Role of different growth enhancers as alternative to in-feed antibiotics in poultry industry. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 8, 794588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Wu, Q.C.; Cui, Z.Y.; Jiang, Y.W.; Aisikaer, A.; Zhang, F.; Chen, H.W.; Wang, W.K.; Wang, Y.L.; Lv, L.K.; et al. Guanidine acetic acid resulted in greater growth performance in younger (13–30 kg) than in older (30–50 kg) lambs under a high-concentrate feedlot pattern. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 954675. [Google Scholar]
- Tossenberger, J.; Rademacher, M.; Németh, K.; Halas, V.; Lemme, A. Digestibility and metabolism of dietary guanidino acetic acid fed to broilers. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 2058–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdeddin, M.; Braun, U.; Lemme, A.; Golian, A.; Kermanshahi, H.; De Smet, S.; Michiels, J. Guanidinoacetic acid supplementation improves feed conversion in broilers subjected to heat stress associated with muscle creatine loading and arginine sparing. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 4442–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portocarero, N.; Braun, U. The physiological role of guanidinoacetic acid and its relationship with arginine in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Tian, Z.; Yu, M.; Liu, Z.; Rong, T.; Ma, X. Effect of guanidine acetic acid on meat quality, muscle amino acids, and fatty acids in Tibetan pigs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 998956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cui, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Aisikaer, A.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Wang, W.; Bo, Y.; Yang, H. Dietary guanidine acetic acid improves ruminal antioxidant capacity and alters rumen fermentation and microflora in rapid-growing lambs. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Jiang, Y.W.; Cui, Z.Y.; Wu, Q.C.; Zhang, F.; Chen, H.W.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, W.K.; Lv, L.K.; Xiong, F.L.; et al. The addition of dietary guanidine acetic acid improved carcass quality, lowered back-fat thickness, and remarkably increased meat protein deposition in rapidly growing lambs fed different forage types. Foods 2023, 12, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zou, T.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, L.; Guo, X.; He, Q.; Chen, L.; You, J. Dietary guanidinoacetic acid improves the growth performance and skeletal muscle development of finishing pigs by changing myogenic gene expression and myofiber characteristics. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2020, 104, 1875–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, N.; Kang, K.; Zhang, R.; Hao, M.; Song, P.; Wang, Q.; Xie, Y.; Li, C. Dietary guanidineacetic acid supplementation ameliorated meat quality and regulated muscle metabolism of broilers subjected to pre-slaughter transport stress by metabolomic analysis. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; He, W.; Qi, G.; Wang, J.; Qiu, K.; Ayalew, H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, S. Inclusion of guanidinoacetic acid in a low metabolizable energy diet improves broilers growth performance by elevating energy utilization efficiency through modulation serum metabolite profile. J. Anim. Sci. 2024, 102, skae001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.Y.; Xing, T.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, F. Guanidinoacetic acid supplementation improves intestinal morphology, mucosal barrier function of broilers subjected to chronic heat stress. J. Anim. Sci. 2023, 101, skac355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bian, J.; Xing, T.; Zhao, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Gao, F. Effects of guanidinoacetic acid supplementation on growth performance, hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis, and immunity of broilers challenged with chronic heat stress. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 103114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zheng, A.; Chen, Z.; Pirzado, S.A.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Zou, Z.; Liu, G. Potassium diformate affects the growth and development of broilers by improving intestinal function and digestive enzyme activity. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Ku, K.L.; Chen, P.Y.; Chen, K.L. The fermented product of the high-yield surfactin strain Bacillus subtilis LYS1 improved the growth performance and intestinal villi morphology in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, S.T.; Kim, I.H. Effects of DHA supplementation on broilers’ growth performance, meat quality, and blood profile. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2023, 107, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Wang, A.; Yang, Z.; Li, J. Dietary supplementation with different alternative to in-feed antibiotic improves growth performance of broilers during specific phases. Poult. Sci. 2023, 02, 102919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janes, D., Jr.; Suehs, B.; Gatlin, D.M. Dietary creatine and guanidinoacetic acid supplementation had limited effects on the hybrid striped bass. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2023, 49, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Dong, B.; Lai, W.; Zhang, L. Effects of guanidinoacetic acid on growth performance, creatine metabolism, and plasma amino acid profile in broilers. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 103, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Xing, T.; Zhang, L.; Gao, F. Effects of guanidinoacetic acid and complex antioxidant supplementation on growth performance, meat quality, and antioxidant function in broiler chickens. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 3961–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostojic, S.M.; Jorga, J. Guanidinoacetic acid in human nutrition: Beyond creatine synthesis. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 1606–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostojic, S.M. Guanidinoacetic acid as a performance-enhancing agent. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 1867–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Yan, Z.; Liu, S.; Yin, Y.; Yang, T.; Chen, Q. Regulative mechanism of guanidinoacetic acid on skeletal muscle development and its application prospects in animal husbandry: A review. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 714567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Cheng, S.; Yin, J.; Zhang, R.; Su, Y.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Bao, J. Influence of pre-slaughter fasting time on weight loss, meat quality and carcass contamination in broilers. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 34, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yao, X.; Zhang, H.; Song, Z.; He, X.; Cao, R. Effects of feeding fermented mulberry leaf powder on growth performance, slaughter performance, and meat quality in chicken broilers. Animals 2021, 11, 3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Qiu, H.; Gao, S.; Hou, L.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; Chen, F. A combination of selenium and Bacillus subtilis improves the quality and flavor of meat and slaughter performance of broilers. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1259760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T. Effect of pre-slaughter fasting time on carcass yield, blood parameters, and meat quality in broilers. Anim. Biosci. 2024, 37, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Sun, M.; Li, P.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Gao, P.; Ma, J.; et al. Effects of dietary supplementation of fermented Artemisia argyi on growth performance, slaughter performance, and meat quality in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xie, J.; Peng, W.; Ji, F.; Qian, J.; Shen, Q.; Hou, G. Effects of guanidinoacetic acid supplementation on liver and breast muscle fat deposition, lipid levels, and lipid metabolism-related gene expression in ducks. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1364815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.K.; Cadogan, D.J.; Chrystal, P.V.; McGilchrist, P.; Wilkinson, S.J.; Inhuber, V.; Moss, A.F. Guanidinoacetic acid, as a partial replacement for arginine with or without betaine in broilers, was offered moderately low crude protein diets. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, E.; Hu, Q.; Ren, M.; Jin, G.; Liang, L.; Li, S. Effects of selenium yeast in combination with boron on muscle growth and muscle quality in broilers. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 190, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.Y.; An, Y.C.; Zhang, S.Y.; Huang, M.Y.; Ye, X.Q.; Zhao, Z.H.; Liu, W.C. Biogenic selenium nanoparticles synthesized using alginate oligosaccharides attenuate heat stress-induced impairment of breast meat quality by regulating oxidative stress, metabolome and ferroptosis in broilers. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Lu, L.; Li, S.F.; Zhang, L.Y.; Xi, L.; Zhang, K.Y.; Luo, X.G. Effects of supplemental Zn source and level on growth performance, carcass traits, and meat quality of broilers. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 1782–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J.L.; Wang, X.F.; Zhu, X.D.; Gao, F.; Zhou, G.H. Attenuating the effects of guanidinoacetic acid on preslaughter transport-induced muscle energy expenditure and rapid glycolysis in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 3223–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Qiu, W.; Zhang, J.; Feng, S.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Jin, L.; Long, K.; Liu, L.; et al. Guanidinoacetic acid regulates myogenic differentiation and muscle growth through miR-133a-3p and miR-1a-3p co-mediated Akt/mTOR/S6K signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Deng, P.; Jiang, G.; Dai, Q. Dietary rosemary extract modulated gut microbiota and influenced the growth, meat quality, serum biochemistry, antioxidant, and immune capacities of broilers. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1024682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhanja, S.K.; Goel, A.; Pandey, N.; Mehra, M.; Majumdar, S.; Mandal, A.B. In ovo carbohydrate supplementation modulates growth and immunity-related genes in broiler chickens. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 99, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, H.; Xin, H. Responses of thyroid hormones of market-size broilers to thermoneutral constant and warm cyclic temperatures. Poult. Sci. 2006, 85, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, J.; Li, Q.; Zhou, H.; Li, G.; Wu, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, G. Tryptophan alleviates chronic heat stress-induced impairment of antioxidant capacities, inflammatory response, and mitochondrial function in broilers. Trop Anim. Health Prod. 2023, 55, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y. Effects of dietary supplementation with different levels of palygorskite-based composite on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, and meat quality of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, C.; Miao, F. Immunomodulatory and antioxidant effects of hydroxytyrosol in cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed broilers. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, G.; Tang, Z.; Du, H.; Zheng, Y.; Chang, L.; Li, H.; Xu, F.; Fu, H.; Zhang, W.; Lin, J. Effects of dietary ferulic acid supplementation on hepatic injuries in Tianfu broilers challenged with lipopolysaccharide. Toxins 2022, 14, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.S.; Sui, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zou, Q.; Cui, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, Z.; Li, D. Regulating effects of chlorinated drinking water on cecal microbiota of broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 103140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.S.; Zou, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Li, D. Growth performance and cecal microbiota of broiler chicks as affected by drinking water disinfection and/or herbal extract blend supplementation. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Items | Contents | |
|---|---|---|
| Days 1 to 21 | Days 22 to 42 | |
| Corn | 54.34 | 59.00 |
| Corn gluten meal | 4.60 | 5.60 |
| Extruded full-fat soybean | 3.40 | 1.70 |
| 43% Soybean meal | 30.23 | 25.69 |
| Soybean oil | 2.80 | 4.00 |
| Limestone | 1.25 | 1.20 |
| CaHPO4 | 2.10 | 1.90 |
| NaCl | 0.22 | 0.30 |
| Premix (1) | 0.18 | 0.18 |
| L-Lysine | 0.37 | 0.18 |
| DL-Methionine | 0.19 | 0.05 |
| L-Threonine | 0.05 | 0.00 |
| L-Tryptophan | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| Valine | 0.06 | 0.00 |
| 50% Choline chloride | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Phaytase | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Compound enzyme | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| Antioxidant | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Nutrients (2) | ||
| Digestive energy, MJ/kg | 12.83 | 13.33 |
| Crude protein | 21.62 | 19.27 |
| Calcium, % | 1.06 | 0.98 |
| Nonphytate phosphorus | 0.46 | 0.42 |
| Lysine, % | 1.33 | 1.02 |
| Methionine, % | 0.54 | 0.40 |
| Threonine, % | 0.85 | 0.73 |
| Methionine + Cysteine, % | 0.95 | 0.86 |
| Items (1) | ADG, g | ADFI, g | F/G |
|---|---|---|---|
| Days 1 to 21 | |||
| CON | 29.98 | 40.26 | 1.34 |
| GAA | 29.42 | 39.36 | 1.34 |
| SEM | 0.145 | 0.337 | 0.015 |
| p-value | 0.447 | 0.167 | 0.989 |
| Days 22 to 42 | |||
| CON | 87.25 b | 139.89 b | 1.61 a |
| GAA | 93.21 a | 143.68 a | 1.57 b |
| SEM | 0.785 | 1.012 | 0.009 |
| p-value | 0.012 | 0.044 | 0.007 |
| Days 1 to 42 | |||
| CON | 60.20 b | 92.45 b | 1.54 a |
| GAA | 62.22 a | 94.07 a | 1.46 b |
| SEM | 0.471 | 0.559 | 0.012 |
| p-value | 0.029 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 |
| Items (1) | DP, % | SEWR, % | ECWR, % | PMR, % | LMR, % | AFR, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 93.49 | 89.36 | 77.61 | 24.22 | 25.54 | 0.58 a |
| GAA | 92.82 | 87.30 | 76.87 | 23.87 | 25.13 | 0.53 b |
| SEM | 0.158 | 0.281 | 0.224 | 0.612 | 0.227 | 0.041 |
| p-value | 0.413 | 0.079 | 0.217 | 0.117 | 0.671 | 0.032 |
| Items (1) | BRT, L | MMR, % | SF, N | DL, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 70.01 | 90.67 | 2.80 a | 4.48 a |
| GAA | 69.78 | 89.88 | 2.33 b | 4.34 b |
| SEM | 1.206 | 0.743 | 0.051 | 0.032 |
| p-value | 0.691 | 0.221 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Items (1) | TP, g/L | TG, mmol/L | HDL, mmol/L | LDL, mmol/L | INS, mU/L | CGH, ng/ml | T3, nmol/L | T4, nmol/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21 d | ||||||||
| CON | 18.02 | 0.54 a | 2.16 | 1.28 | 22.57 | 8.82 b | 2.09 b | 189.04 b |
| GAA | 18.29 | 0.46 b | 2.24 | 1.31 | 23.17 | 10.04 a | 2.16 a | 197.45 a |
| SEM | 0.044 | 0.008 | 0.015 | 0.016 | 0.519 | 0.098 | 0.011 | 0.845 |
| p-value | 0.573 | 0.022 | 0.134 | 0.559 | 0.312 | <0.001 | 0.024 | 0.005 |
| 42 d | ||||||||
| CON | 18.45 | 0.53 a | 2.16 b | 1.09 b | 29.42 | 9.40 b | 4.39 b | 112.27 b |
| GAA | 18.48 | 0.49 b | 2.33 a | 1.33 a | 30.15 | 10.57 a | 5.51 a | 120.52 a |
| SEM | 0.050 | 0.004 | 0.017 | 0.023 | 0.429 | 0.093 | 0.088 | 0.647 |
| p-value | 0.431 | 0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.557 | 0.013 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Items (1) | T-AOC, U/mL | SOD, U/mL | MDA, nmoL/mL | GSH-Px, U/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 0.14 b | 210.55 b | 10.21 a | 127.63 |
| GAA | 0.18 a | 261.91 a | 6.68 b | 129.66 |
| SEM | 0.002 | 12.187 | 0.339 | 7.163 |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.211 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, J. Effects of Guanidine Acetic Acid on the Growth and Slaughter Performance, Meat Quality, Antioxidant Capacity, and Cecal Microbiota of Broiler Chickens. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11110550
Li X, Chen Z, Li J. Effects of Guanidine Acetic Acid on the Growth and Slaughter Performance, Meat Quality, Antioxidant Capacity, and Cecal Microbiota of Broiler Chickens. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(11):550. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11110550
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xuedan, Zhimin Chen, and Jiantao Li. 2024. "Effects of Guanidine Acetic Acid on the Growth and Slaughter Performance, Meat Quality, Antioxidant Capacity, and Cecal Microbiota of Broiler Chickens" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 11: 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11110550
APA StyleLi, X., Chen, Z., & Li, J. (2024). Effects of Guanidine Acetic Acid on the Growth and Slaughter Performance, Meat Quality, Antioxidant Capacity, and Cecal Microbiota of Broiler Chickens. Veterinary Sciences, 11(11), 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11110550







