A Recombinant Lentiviral Vegfr2-Silencing Vector Attenuates Roxarsone-Promoted Growth of Rat Vascular Endothelial Cells and Angiogenesis in Matrigel Plug and B16F10 Xenograft Models
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Animals and Cells
2.3. Recombinant Lentivirus and Infection of Cells
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. BrdU Proliferation Test
2.6. Scratch Test
2.7. Matrigel Tubule Formation Test
2.8. Hemoglobin Amount Determination in Mouse Matrigel Plugs
2.9. Growth and Angiogenesis Evaluation of Mouse B16F10 Xenograft Tumor
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
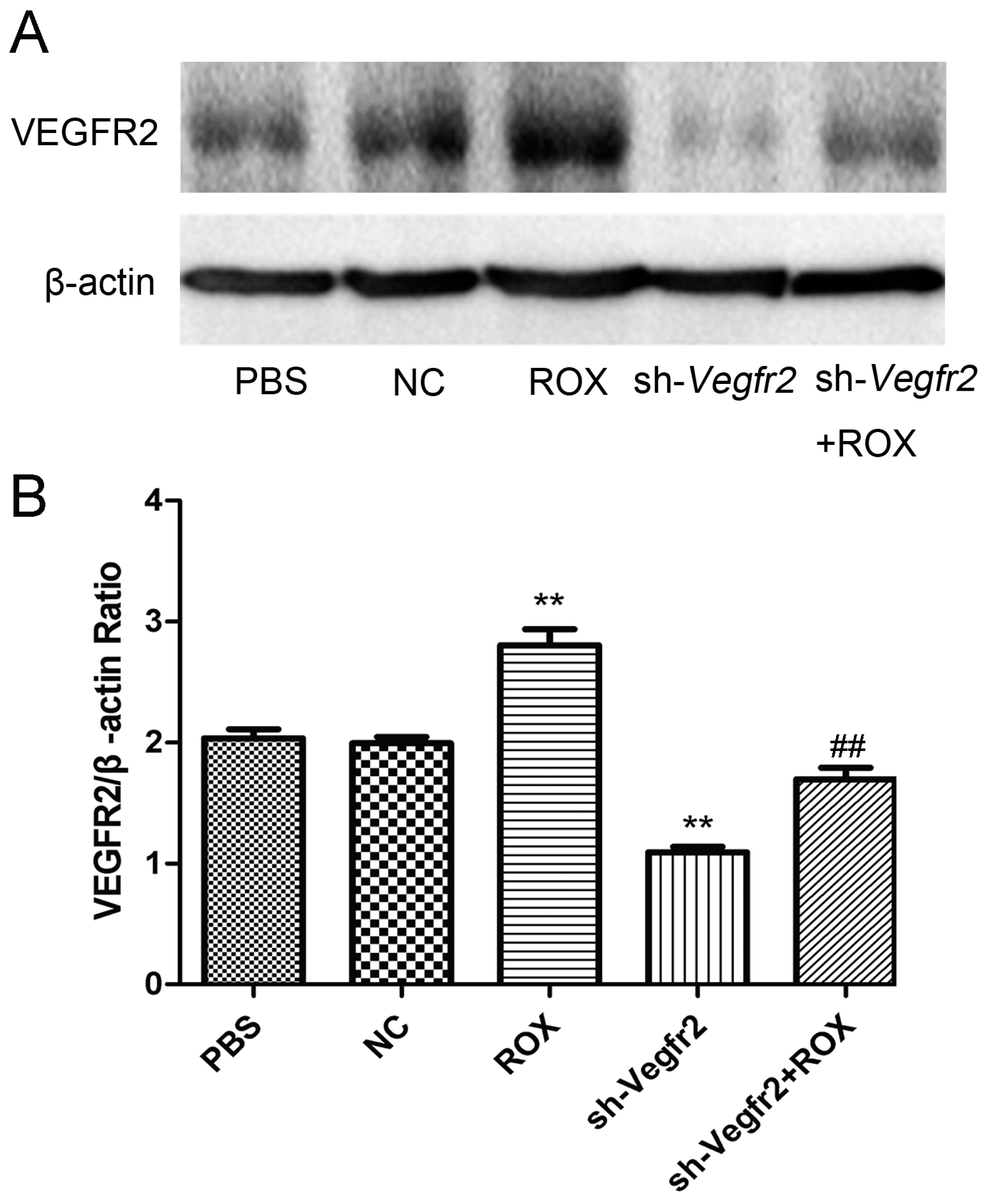
3.1. Effect of Recombinant Lentivirus Targeting Vegfr2 on the Expression of VEGFR2 Protein in Rat Vascular Endothelial Cells Exposed to ROX
3.2. Effects of Recombinant Lentivirus Targeting Vegfr2 on the Growth of Endothelial Cells Promoted by ROX
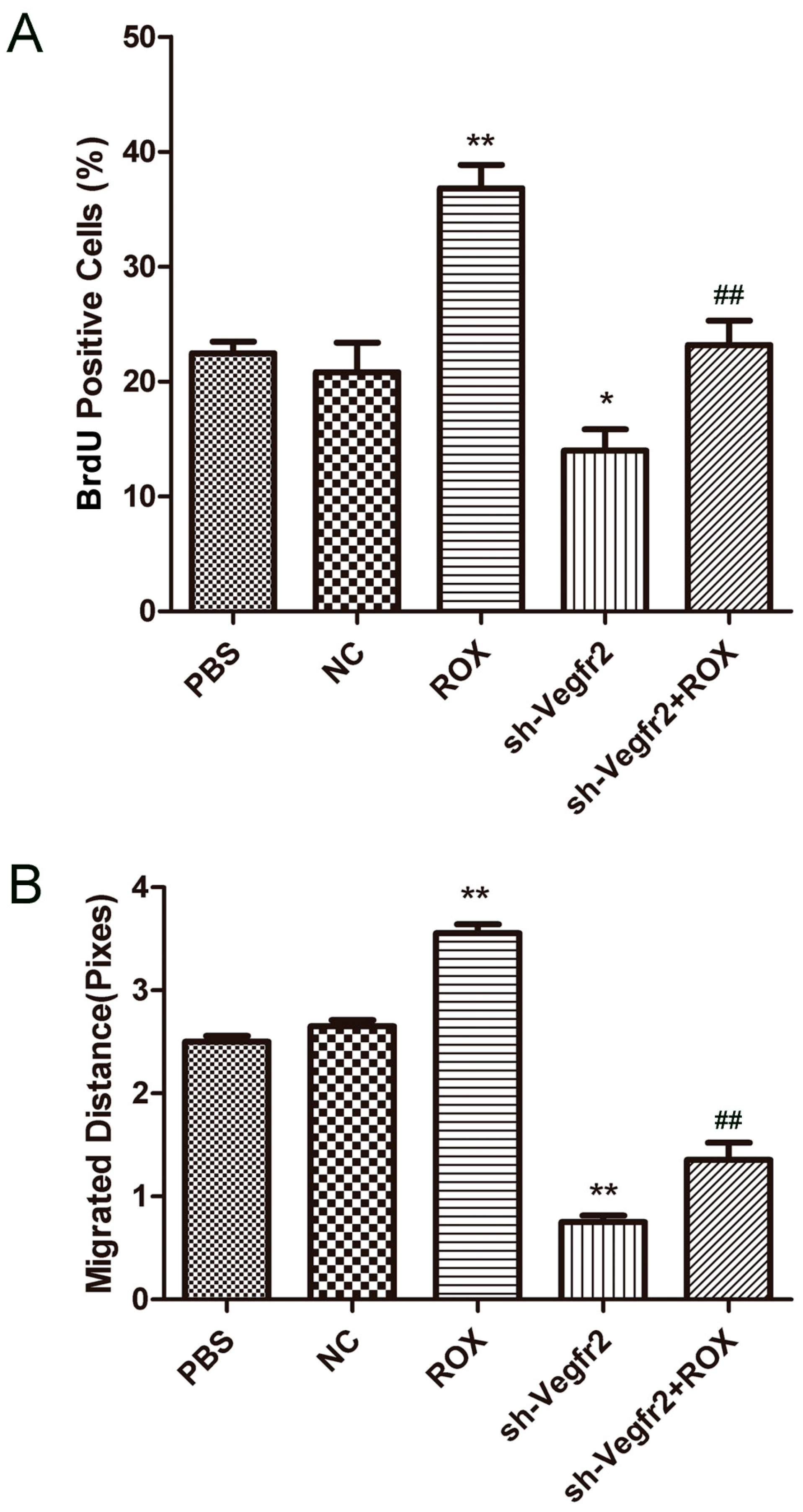
3.2.1. Effect on the Proliferation of Endothelial Cells
3.2.2. Effect on the Migration of Endothelial Cells
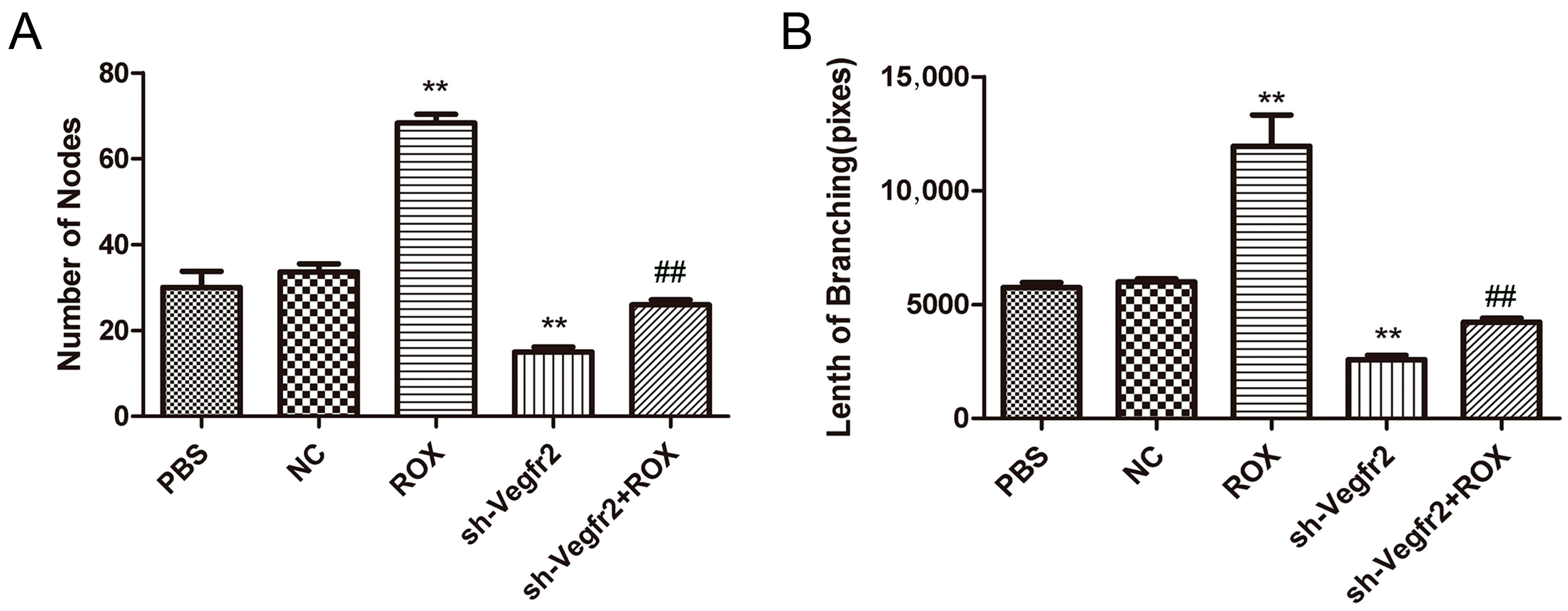
3.2.3. Effect on the Ability of Endothelial Cells to Form In Vitro Tubes
3.3. Effects of Recombinant Lentivirus on ROX-Promoted Growth of Mouse Matrigel Plugs
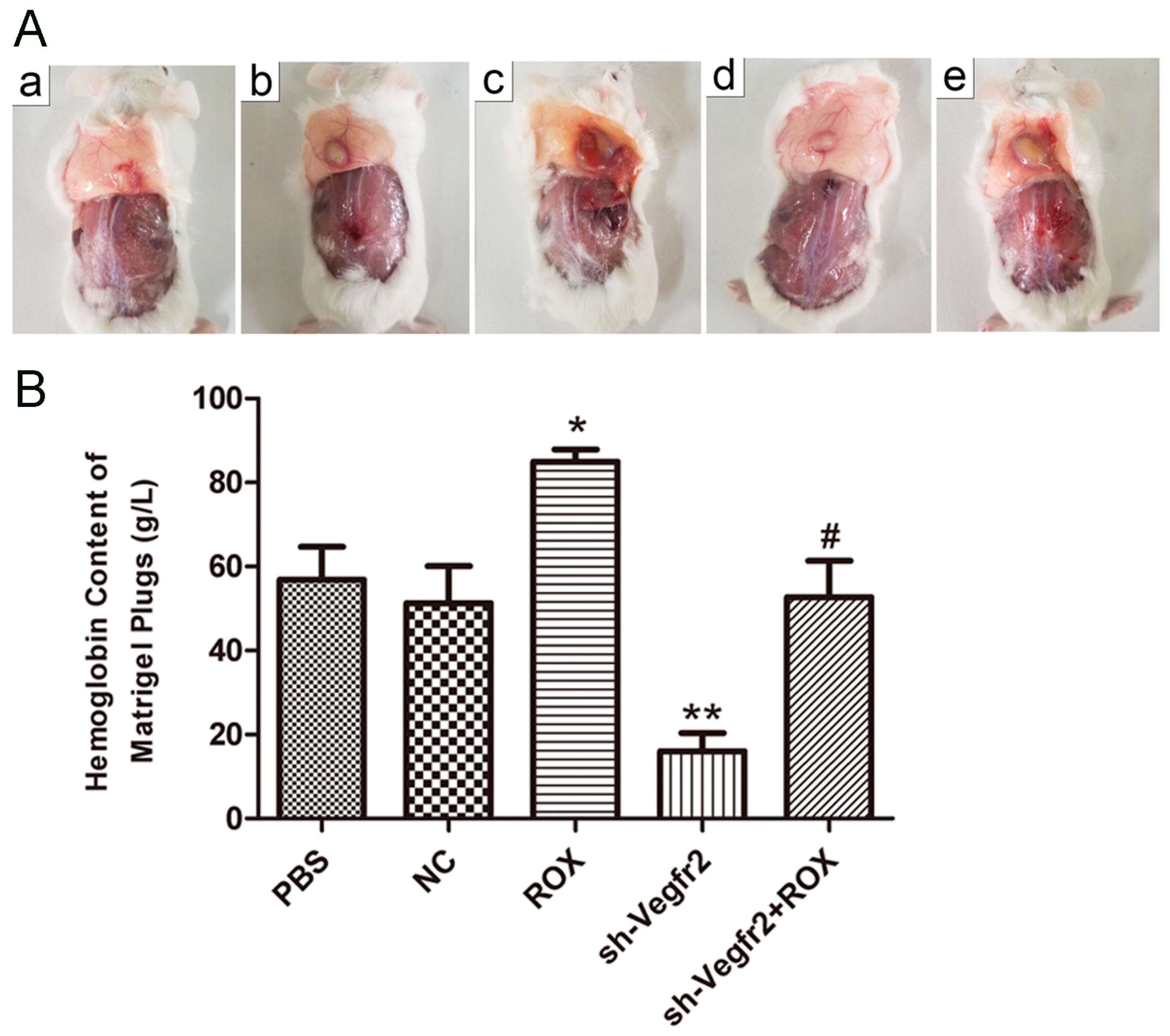
3.3.1. Establishment of Mouse Matrigel Plug Model
3.3.2. Influence on the Content of Hemoglobin in Matrigel Plugs
3.4. Effects of Recombinant Lentivirus on ROX-Promoted Growth of Mouse Melanoma Xenografts
3.4.1. Tumor Growth Evaluation
3.4.2. Immunohistochemistry of Tumor Tissue
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnston, N.L.; Quarles, C.L.; Fagerberg, D.J. Long-term broiler performance with bambermycins and bambermycins plus roxarsone. Poult. Sci. 1983, 62, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrick, C.; Klug, H.L.; Olson, O.E. Effect of 3-nitro-4-hydroxyphenylarsonic acid and arsanilic acid on selenium poisoning in the rat. J. Nutr. 1953, 51, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, A.L.A.; Figueiredo, I.M.; Botero, W.G.; Santos, J.C.C. Interaction between roxarsone, an organic arsenic compound, with humic substances in the soil simulating environmental conditions. Chemosphere 2023, 339, 139688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangalgiri, K.P.; Adak, A.; Blaney, L. Organoarsenicals in poultry litter: Detection, fate, and toxicity. Environ. Int. 2015, 75, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, B.; Wang, C.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y. Roxarsone Promotes Glycolysis and Angiogenesis by Inducing Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1alpha In Vitro and In Vivo. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 9559–9566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Q.; Xin, W.; Cui, W.; Zhu, J. Organoarsenic Roxarsone Promotes Angiogenesis In Vivo. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 118, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Cui, W.; Liu, X.; Ying, J.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Y. In vitro and ex vivo angiogenic effects of roxarsone on rat endothelial cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 223, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Cao, S.; Li, Y.; Dong, H. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of arsenic transformed from feed additive organoarsenicals around chicken farms on the North China Plain. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, P.; Das, A.; Giri, A.K. Epigenetic regulations in alternative telomere lengthening: Understanding the mechanistic insight in arsenic-induced skin cancer patients. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul, K.S.; Jayasinghe, S.S.; Chandana, E.P.; Jayasumana, C.; De Silva, P.M. Arsenic and human health effects: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 828–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.F.; Beck, B.D.; Chen, Y.; Lewis, A.S.; Thomas, D.J. Arsenic exposure and toxicology: A historical perspective. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2011, 123, 305–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneda, H.; Arao, T.; Matsumoto, K.; De Velasco, M.A.; Tamura, D.; Aomatsu, K.; Kudo, K.; Sakai, K.; Nagai, T.; Fujita, Y.; et al. Activin A inhibits vascular endothelial cell growth and suppresses tumour angiogenesis in gastric cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1210–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N.; Adamis, A.P. Ten years of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 385–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor: Basic science and clinical progress. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 581–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibuya, M. Differential roles of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 and receptor-2 in angiogenesis. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 39, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.Y.; DeRuiter, S.L.; Turner, D.L. RNA interference by expression of short-interfering RNAs and hairpin RNAs in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6047–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, G.; Soohoo, C.; Affarel, B.; Gay, F.; Shi, Y.; Forrester, W.C. A DNA vector-based RNAi technology to suppress gene expression in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 5515–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishitsuji, H.; Kohara, M.; Kannagi, M.; Masuda, T. Effective suppression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through a combination of short- or long-hairpin RNAs targeting essential sequences for retroviral integration. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 7658–7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, D.; Kay, M.A. RNAi and gene therapy: A mutual attraction. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2007, 2007, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson-Welsh, L.; Welsh, M. VEGFA and tumour angiogenesis. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 273, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Song, X.; Guo, Y.; Song, P.; Duan, D.; Chen, Z.S. Natural Products: A Promising Therapeutics for Targeting Tumor Angiogenesis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 772915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, E.A.; Ahmed, T.; Flores, P.C.; Ortiz, H.R.; Langlais, P.R.; Mythreye, K.; Lee, N.Y. Beta IV spectrin inhibits the metastatic growth of melanoma by suppressing VEGFR2-driven tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 18981–18987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Lai, X.; Zhu, M.H.; Shi, J.; Pan, H.; Huang, Y.; Guo, R.J.; Lu, Q.; Fang, C.; Zhao, M. Jujuboside B suppresses angiogenesis and tumor growth via blocking VEGFR2 signaling pathway. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Kamal, M.A.; Akhtar, S. Tumor Angiogenesis and VEGFR-2: Mechanism, Pathways and Current Biological Therapeutic Interventions. Curr. Drug Metab. 2021, 22, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wang, R.; Li, H.; Lv, Q.; Meng, W.; Yang, X. Lentivirus mediated RNA interference of EMMPRIN (CD147) gene inhibits the proliferation, matrigel invasion and tumor formation of breast cancer cells. Cancer Biomark. Sect. A Dis. Markers 2016, 17, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Chenlin, Z.; Lei, W.; Zhang, Y. Tumor-promoting and pro-angiogenic effects of roxarsone via VEGFR2/PLCgamma/PKC signaling. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 292, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, D.; Xu, C.; Wang, K.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Y. Roxarsone induces angiogenesis via PI3K/Akt signaling. Cell Biosci. 2016, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Sun, S.; Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; Jiang, T.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Ren, Z. MCPIP1 promotes cell proliferation, migration and angiogenesis of glioma via VEGFA-mediated ERK pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 418, 113267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Dua, C.; Bajaj, A. Advances in Engineered Biomaterials Targeting Angiogenesis and Cell Proliferation for Cancer Therapy. Chem. Rec. 2022, 22, e202200152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamalice, L.; Le Boeuf, F.; Huot, J. Endothelial cell migration during angiogenesis. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 782–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cominetti, M.R.; Terruggi, C.H.; Ramos, O.H.; Fox, J.W.; Mariano-Oliveira, A.; De Freitas, M.S.; Figueiredo, C.C.; Morandi, V.; Selistre-de-Araujo, H.S. Alternagin-C, a disintegrin-like protein, induces vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF) expression and endothelial cell proliferation in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 18247–18255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashio, A.; Fujita, N.; Tsuruo, T. Topotecan inhibits VEGF- and bFGF-induced vascular endothelial cell migration via downregulation of the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 98, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benelli, R.; Albini, A. In vitro models of angiogenesis: The use of Matrigel. Int. J. Biol. Markers 1999, 14, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norrby, K. In vivo models of angiogenesis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2006, 10, 588–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troiani, T.; Schettino, C.; Martinelli, E.; Morgillo, F.; Tortora, G.; Ciardiello, F. The use of xenograft models for the selection of cancer treatments with the EGFR as an example. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2008, 65, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, B.; Wei, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y. A Recombinant Lentiviral Vegfr2-Silencing Vector Attenuates Roxarsone-Promoted Growth of Rat Vascular Endothelial Cells and Angiogenesis in Matrigel Plug and B16F10 Xenograft Models. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11100451
Chen X, Chen L, Chen B, Wei Q, Wu Y, Zhang Y. A Recombinant Lentiviral Vegfr2-Silencing Vector Attenuates Roxarsone-Promoted Growth of Rat Vascular Endothelial Cells and Angiogenesis in Matrigel Plug and B16F10 Xenograft Models. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(10):451. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11100451
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xin, Lin Chen, Binlin Chen, Qianhan Wei, Yinchao Wu, and Yumei Zhang. 2024. "A Recombinant Lentiviral Vegfr2-Silencing Vector Attenuates Roxarsone-Promoted Growth of Rat Vascular Endothelial Cells and Angiogenesis in Matrigel Plug and B16F10 Xenograft Models" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 10: 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11100451
APA StyleChen, X., Chen, L., Chen, B., Wei, Q., Wu, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2024). A Recombinant Lentiviral Vegfr2-Silencing Vector Attenuates Roxarsone-Promoted Growth of Rat Vascular Endothelial Cells and Angiogenesis in Matrigel Plug and B16F10 Xenograft Models. Veterinary Sciences, 11(10), 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11100451







