Genomic Characterization of a Plasmid-Free and Highly Drug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Indiana Isolate in China
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain Collection and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.2. Whole Genome Sequencing, Assembly and Annotation
2.3. Sequence Analysis of the S. Indiana S1467 Genome
3. Results
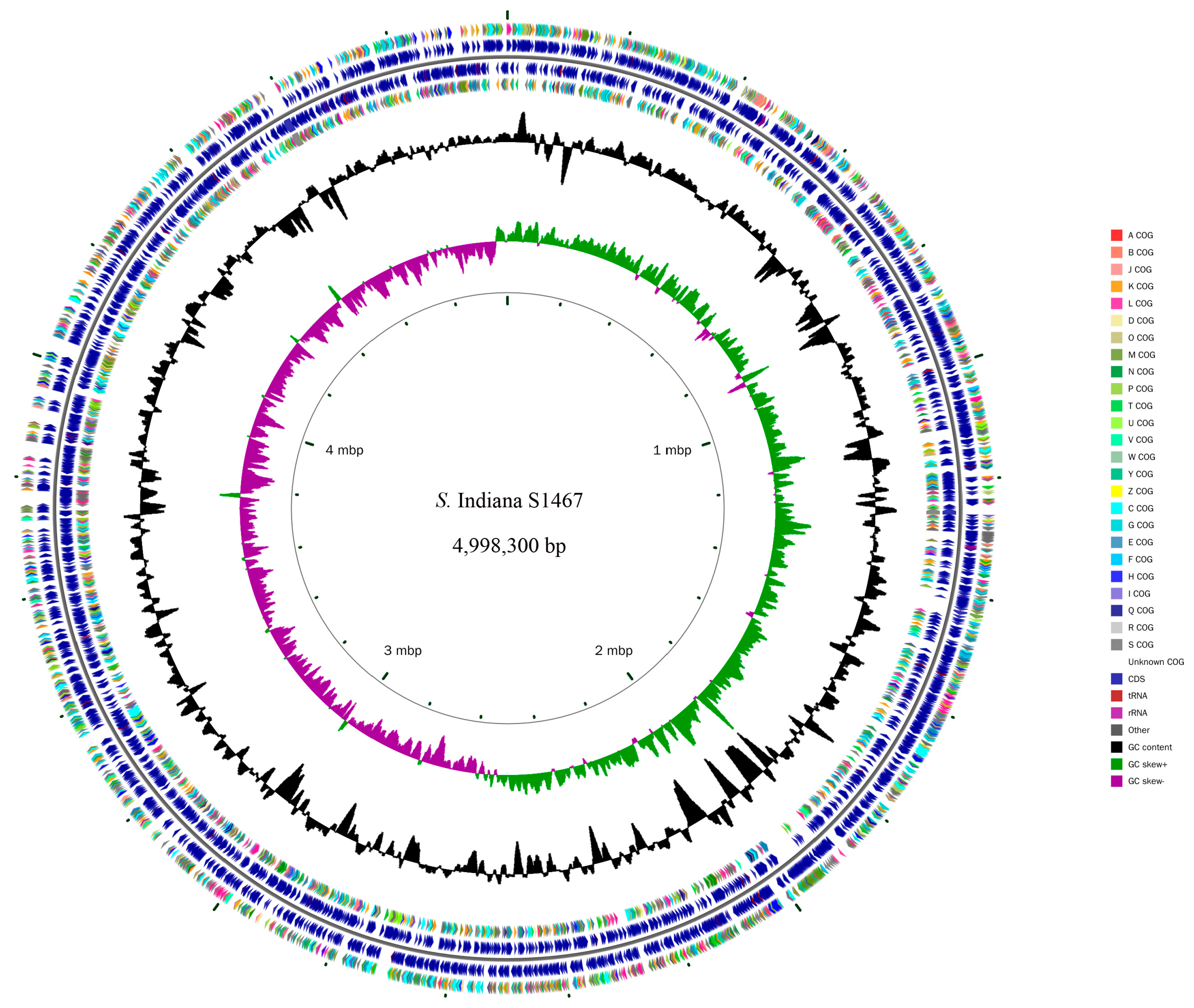
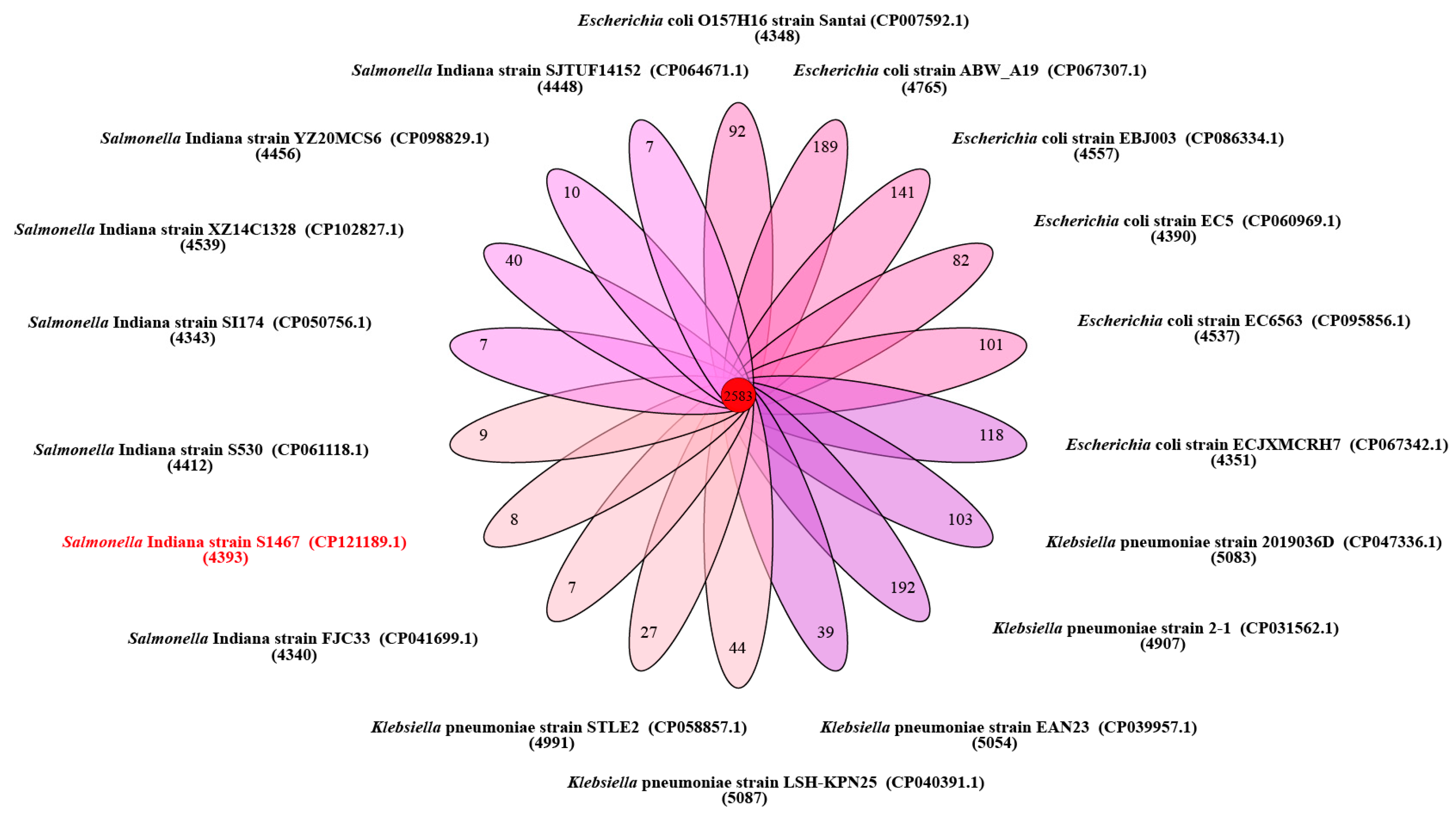
3.1. General Features of the S. Indiana S1467 Genome
3.2. Antimicrobial Resistance in S. Indiana S1467
3.3. Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Cassettes
3.4. Characteristics of a Drug-Resistance Genomic Island That Harbors YeeVU-TAS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Havelaar, A.H.; Kirk, M.D.; Torgerson, P.R.; Gibb, H.J.; Hald, T.; Lake, R.J.; Praet, N.; Bellinger, D.C.; de Silva, N.R.; Gargouri, N.; et al. World Health Organization Global Estimates and Regional Comparisons of the Burden of Foodborne Disease in 2010. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feasey, N.A.; Dougan, G.; Kingsley, R.A.; Heyderman, R.S.; Gordon, M.A. Invasive non-typhoidal salmonella disease: An emerging and neglected tropical disease in Africa. Lancet 2012, 379, 2489–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, J.; Guerra, B.; Rodicio, M.R. Resistance to Carbapenems in Non-Typhoidal Salmonella enterica Serovars from Humans, Animals and Food. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarestrup, F.M.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Lockett, J.; Gay, K.; Teates, K.; McDermott, P.F.; White, D.G.; Hasman, H.; Sørensen, G.; Bangtrakulnonth, A.; et al. International Spread of Multidrug-resistant Salmonella Schwarzengrund in Food Products. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriksen, R.S.; Vieira, A.R.; Karlsmose, S.; Lo Fo Wong, D.M.A.; Jensen, A.B.; Wegener, H.C.; Aarestrup, F.M. Global Monitoring of Salmonella Serovar Distribution from the World Health Organization Global Foodborne Infections Network Country Data Bank: Results of Quality Assured Laboratories from 2001 to 2007. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Kelly, P.; Wang, C. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella enterica Serovar Indiana in China (1984–2016). Zoonoses Public Health 2016, 64, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Lan, R.; Zhang, X.; Cui, S.; Xu, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, D. Prevalence of Salmonella Isolates from Chicken and Pig Slaughterhouses and Emergence of Ciprofloxacin and Cefotaxime Co-Resistant S. enterica Serovar Indiana in Henan, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Yang, Y.; Lei, C.; Jiang, W.; Liu, B.; Shi, H.; Kong, L.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, X.; et al. Emergence of Salmonella enterica serovar Indiana and California isolates with concurrent resistance to cefotaxime, amikacin and ciprofloxacin from chickens in China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 262, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, T.; Beier, R.C.; Hou, X. Characterization of quinolone resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar Indiana from chickens in China. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Wang, C.; Shi, S.; Bao, H.; Zhu, C.; Kelly, P.; Zhuang, L.; Lu, G.; Dou, X.; Wang, R.; et al. Highly Drug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Indiana Clinical Isolates Recovered from Broilers and Poultry Workers with Diarrhea in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 1943–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Zhao, J.; Gan, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Cui, S.; Xia, S.; Hu, Y.; Yan, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Emergence and Diversity of Salmonella enterica Serovar Indiana Isolates with Concurrent Resistance to Ciprofloxacin and Cefotaxime from Patients and Food-Producing Animals in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 3365–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Hurley, D.; Bai, X.; Yu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Wall, E.; Fanning, S.; Bai, L. Complete genetic analysis of a Salmonella enterica serovar Indiana isolate accompanying four plasmids carrying mcr-1, ESBL and other resistance genes in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 210, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.-X.; Deng, G.-H.; Jiang, Q.; Cen, D.-J.; Yang, R.-S.; Feng, Y.-Y.; Xia, J.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.-H.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Clonal expansion and horizontal transmission of epidemic F2:A1:B1 plasmids involved in co-spread of rmtB with qepA and blaCTX-M-27 in extensively drug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Indiana isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Baloch, Z.; Peng, Z.; Hu, Y.; Xu, J.; Fanning, S.; Li, F. Genomic characterization of a large plasmid containing a blaNDM-1 gene carried on Salmonella enterica serovar Indiana C629 isolate from China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Peng, Z.; Baloch, Z.; Hu, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W.; Fanning, S.; Li, F. Genomic characterization of an extensively-drug resistance Salmonella enterica serotype Indiana strain harboring blaNDM-1 gene isolated from a chicken carcass in China. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 204, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chang, J.; Xu, X.; Hu, M.; He, S.; Qin, X.; Zhou, M.; Shi, C.; Shi, X. Phylogenomic Analysis of Salmonella enterica Serovar Indiana ST17, an Emerging Multidrug-Resistant Clone in China. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0011522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, D.; Wang, C.; Lin, J. Characterization of the emerging multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Indiana strains in China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.-Y.; Guo, W.-Y.; Zhang, J.-X.; Wang, M.-G.; Wang, L.-L.; Lian, X.-L.; Ke, B.-X.; Sun, J.; Ke, C.-W.; Liu, Y.-H.; et al. Phylogenomic analysis of Salmonella Indiana ST17, an emerging MDR clonal group in China. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 2937–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.H.-Y.; Chan, E.W.-C.; Xie, L.; Li, R.; Chen, S. IncHI2 Plasmids Are the Key Vectors Responsible for oqxAB Transmission among Salmonella Species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6911–6915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Emergence of IncHI2 plasmid-harboring blaNDM-5 from porcine Escherichia coli isolates in Guangdong, China. Pathogens 2021, 10, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoni, S.; Mingoia, M.; Brenciani, A.; Carelli, M.; Lleò, M.M.; Malerba, G.; Vignaroli, C. First IncHI2 plasmid carrying mcr-9.1, blaVIM-1, and double copies of blaKPC-3 in a multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli human isolate. mSphere 2021, 6, e0030221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Xia, J.; Fang, L.; Sun, J.; Liao, X.; Liu, Y. oqxAB-Positive IncHI2 plasmid pHXY0908 increase Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium strains tolerance to ciprofloxacin. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 28th ed.; M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Malvern, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bidinost, C.; Wilderman, P.J.; Dorsey, C.W.; Actis, L.A. Analysis of the Replication Elements of the pMJ101 Plasmid from the Fish Pathogen Vibrio ordalii. Plasmid 1999, 42, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Duan, X.; Li, X.; Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, S.J. Emerging of a highly pathogenic and multi-drug resistant strain of Escherichia coli causing an outbreak of colibacillosis in chickens. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 65, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Wang, G.; Sebra, R.; Zhuge, J.; Yin, C.; Aguero-Rosenfeld, M.E.; Schuetz, A.N.; Dimitrova, N.; Fallon, J.T. Emergence and evolution of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae with both blaKPC and blaCTX-M integrated in the chromosome. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00076-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.M.; Shaw, K.J. A Novel Family of Escherichia coli Toxin-Antitoxin Gene Pairs. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 6600–6608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.; Wang, P.; Sun, C.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X. Interaction of Type IV Toxin/Antitoxin Systems in Cryptic Prophages of Escherichia coli K-12. Toxins 2017, 9, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Patil, R.D.; Sahin, O.; Wu, Z.; Pu, X.; Dai, L.; Plummer, P.J.; Yaeger, M.J.; Zhang, Q. Identification and functional analysis of two toxin–antitoxin systems in Campylobacter jejuni. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 101, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, M.A.; Balani, P.; Min, J.; Chinnam, N.B.; Hansen, S.; Vulić, M.; Lewis, K.; Brennan, R.G. HipBA–promoter structures reveal the basis of heritable multidrug tolerance. Nature 2015, 524, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheverton, A.M.; Gollan, B.; Przydacz, M.; Wong, C.T.; Mylona, A.; Hare, S.A.; Helaine, S. A Salmonella Toxin Promotes Persister Formation through Acetylation of tRNA. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, A.; Maisonneuve, E.; Gerdes, K. Mechanisms of bacterial persistence during stress and antibiotic exposure. Science 2016, 354, aaf4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Classes | Resistance Phenotypes | Resistance Genes |
|---|---|---|
| β-lactams | ampicillin, cefazolin, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, ceftazidime | blaOXA-1, blaCTX-M-55, ftsI |
| monobactams | aztreonam | golS, mdsA |
| aminoglicosides | gentamicin, amikacin, kanamycin, streptomycin | armA, aph(3″)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, aadA5, aph(4)-Ia, aac(3)-Iva, aac(6′)-Iy, baeR, kdpE |
| tetracyclines | tetracycline | tetA, tetR, mdfA |
| quinolones | nalidixic acid, ciprofloxacin | rsmA, oqxB, oqxA, mdtK, sdiA, marA, acrA, acrB, adeF, soxR, soxS, acrAB-tolC, aac(6′)-Ib-cr6 |
| folate pathway inhibitors | sulfonamides, trimethoprim | sul1, sul2 a, dfrA17 |
| phenicols | chloramphenicol | catB3, floR a |
| nitroimidazoles | nitrofurantoin | msbA |
| rifamycin | ND b | arr3 |
| elfamycin | ND | EF-Tu a |
| glycopeptides | ND | vanG |
| macrolides | ND | CRP, mphE, msrE, emrB, emrR, H-NS, kpnF, kpnE |
| nucleoside | ND | leuO |
| peptides | ND | bacA, arnT, pmrF |
| phosphonic acid | ND | fosA3, glpT |
| disinfecting agents and antiseptics | ND | qacE |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, J.; Zeng, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, D.; Dou, X.; Lin, J.; Wang, C. Genomic Characterization of a Plasmid-Free and Highly Drug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Indiana Isolate in China. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11010046
Gong J, Zeng X, Xu J, Zhang D, Dou X, Lin J, Wang C. Genomic Characterization of a Plasmid-Free and Highly Drug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Indiana Isolate in China. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(1):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11010046
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Jiansen, Ximin Zeng, Jingxiao Xu, Di Zhang, Xinhong Dou, Jun Lin, and Chengming Wang. 2024. "Genomic Characterization of a Plasmid-Free and Highly Drug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Indiana Isolate in China" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 1: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11010046
APA StyleGong, J., Zeng, X., Xu, J., Zhang, D., Dou, X., Lin, J., & Wang, C. (2024). Genomic Characterization of a Plasmid-Free and Highly Drug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Indiana Isolate in China. Veterinary Sciences, 11(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11010046







