An Observational Study of Skeletal Malformations in Four Semi-Intensively Reared Carp Species
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
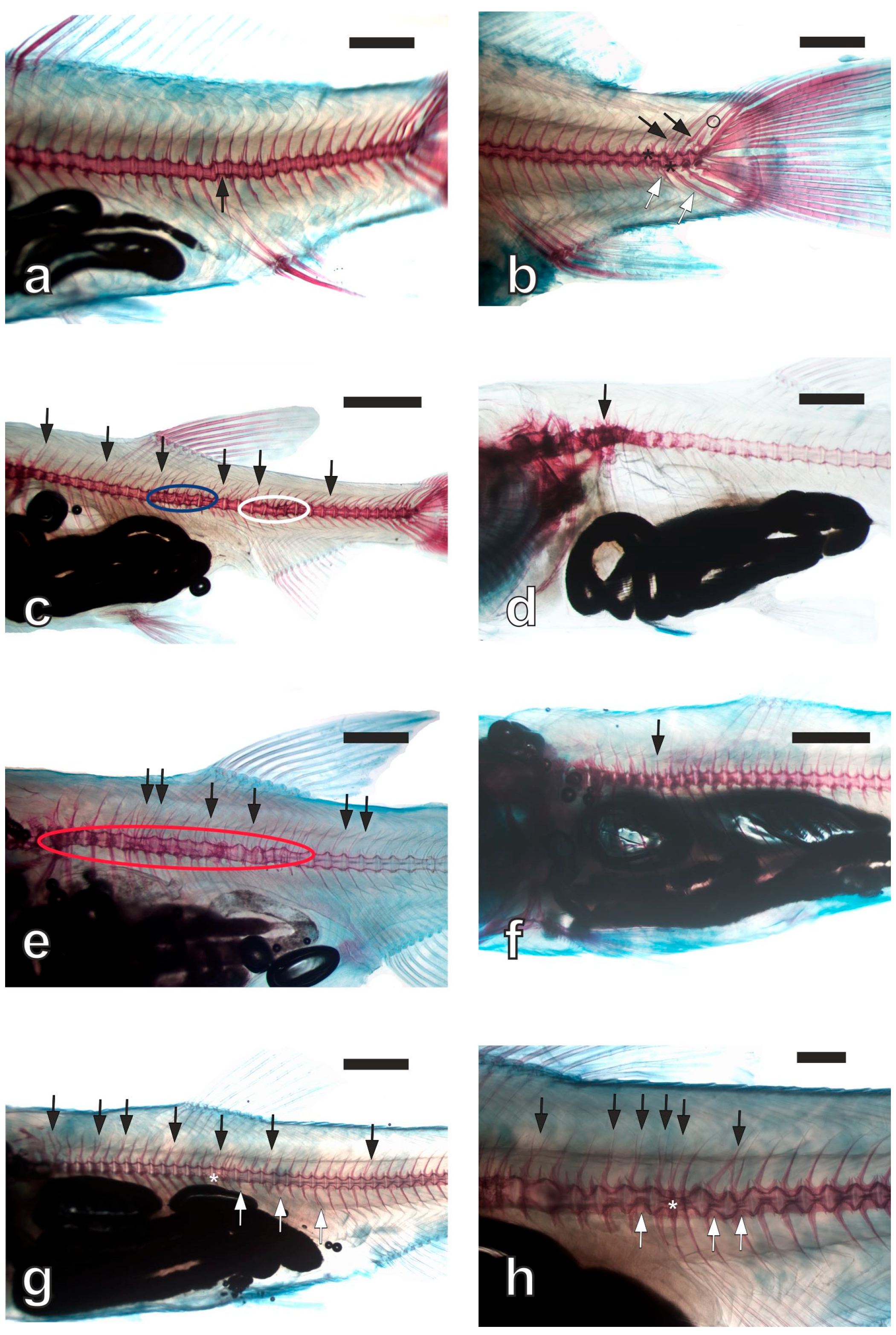
2.1. Sampling and Double in Toto Staining
2.2. Stereoscopic Analysis
2.3. Statistics
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boglione, C.; Gagliardi, F.; Scardi, M.; Cataudella, S. Skeletal descriptors and quality assessment in larvae and post-larvae of wild-caught and hatchery-reared gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L. 1758). Aquaculture 2001, 192, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahu, C.; Zambonino-Infante, J.; Takeuchi, T. Nutritional components affecting skeletal development in fish larvae. Aquaculture 2003, 227, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argüello-Guevara, W.; Bohórquez-Cruz, M.; Silva, A. Malformaciones craneales en larvas y juveniles de peces cultivados. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 42, 950–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas, T.M.; Lopes, I.G.; da Silva Lopes, T.; Buzollo, H.; Portella, M.C. Growth performance and incidence of skeletal anomalies in pacu larvae under different weaning protocols. Bol. Inst. Pesca 2019, 45, e433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boglione, C.; Cataudella, S. Monitoraggio larvale. In Lo Stato Della Pesca e Dell’Acquacoltura nei Mari Italiani; Ministero delle Politiche Agricole Alimentari e Forestali: Roma, Italy, 2012; pp. 797–800. [Google Scholar]
- Boglione, C.; Gisbert, E.; Gavaia, P.; Witten, P.E.; Moren, M.; Fontagné, S.; Koumoundouros, G. Skeletal anomalies in reared European fish larvae and juveniles. Part 2: Main typologies, occurrences and causative factors. Rev. Aquacult. 2013, 5, S121–S167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boglione, C.; Gavaia, P.; Koumoundouros, G.; Gisbert, E.; Moren, M.; Fontagne, S.; Witten, P.E. Skeletal anomalies in reared European fish larvae and juveniles. Part 1: Normal and anomalous skeletogenic processes. Rev. Aquacult. 2013, 5, S99–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pousis, C.; Di Comite, M.; Zupa, R.; Passantino, L.; Hala, E.; Corriero, A. Microradiography as a useful technique for the rapid detection of skeletal anomalies in early sea bream juveniles. J. Fish Dis. 2022, 45, 1237–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, S. Carps. In Aquaculture: Farming Aquatic Animals and Plants, 2nd ed.; Lucas, J.S., Southgate, P.C., Tucker, C.S., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 294–312. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture. Sustainability in Action. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Na-tions, Rome, 2020. Available online: https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/ca9229en (accessed on 11 November 2023).
- STECF. Scientific, Technical and Economic Committee for Fisheries—Economic Report on the EU Aquaculture (STECF-22-17); Nielsen, R., Virtanen, J., Guillen Garcia, J., Eds.; EUR 28359 EN; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2023; ISBN 978-92-76-99317-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Fisheries and Aquaculture—FishStatJ—Software for Fishery and Aquaculture Statistical Time Series. In FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Division; FAO: Rome, Italy. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fishery/en/topic/166235?lang=en (accessed on 11 November 2023).
- FAO. Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics. Global Aquaculture Production 1950–2021 (FishStatJ). In FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Division; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Rome: Rome, Italy, 2023; Available online: www.fao.org/fishery/en/statistics/software/fishstatj (accessed on 11 November 2023).
- Viviani, P.; Hala, E. Sustainable Development of rural areas in Albania—Sector Analyses—2017.2192.7-001.00. Fishery Sector Study Report. Carrying out selected sectoral analysis as a solid ground for the preparation of IPARD III programme and of Strategy for Agriculture, Rural Development and Fishery 2021–2027. Available online: https://ipard.gov.al/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/03-Fishery-Sector-Study_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2023).
- Horváth, L.; Tamás, G.; Seagrave, C. Carp and Pond Fish Culture Including Chinese Herbivorous Species, Pike, Tench, Zander, Wels Catfish and Goldfish, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 1–192. [Google Scholar]
- Park, E.H.; Kim, D.S. A procedure for staining cartilage and bone of whole vertebrate larvae while rendering all other tissues transparent. Stain. Technol. 1984, 59, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataudella, S.; Boglione, C.; Prestinicola, L.; Russo, T. Manuale di Tecniche Semintensive per la Produzione di Giovanili di Specie Ittiche Marine in Acquacoltura Biologica. 2014. Available online: https://www.sinab.it/sites/default/files/Manuale%20PROSEGAB_0.pdf (accessed on 3 November 2023).
- Prestinicola, L.; Boglione, C.; Makridis, P.; Spanò, A.; Rimatori, V.; Palamara, E.; Scardi, M.; Cataudella, S. Environmental conditioning of skeletal anomalies typology and frequency in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L., 1758) juveniles. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, J.A. The Reaction of Small Fish to Perforated Plates. In Report of a Workshop on the Impact of Thermal Power Plant Cooling Systems on Aquatic Environments Held in Asilomar, Pacific Grove, California, September 28-October 2 1975; Electric Power Research Institute: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka, K. Mechanisms of frequency and pattern control in the neural rhythm generators. Biol. Cybern. 1987, 56, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultze, H.P.; Arratia, G. The composition of the caudal skeleton of teleosts (Actinopterygil: Osteichthyes). Zool. J. Linn. Soc-Lond. 1989, 97, 189–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumoundouros, G. Morpho-anatomical abnormalities in Mediterranean marine aquaculture. In Recent Advances in Aquaculture Research; Koumoundouros, G., Ed.; Transworld Research Network: Trivandrum, India, 2010; pp. 125–148. [Google Scholar]
- Divanach, P.; Boglione, C.; Menu, B.; Koumoundouros, G.; Kentouri, M.; Cataudella, S. Abnormalities in finfish mariculture: An overview of the problem, causes and solutions. In Handbook of Contributions and Short Communications, Proceedings of the International Workshop on ‘Seabass and Seabream Culture: Problems and Prospects’, Verona, Italy, 16–18 October 1996; European Aquaculture Society: Oostende, Belgium, 1996; pp. 45–66. [Google Scholar]
- Gavaia, P.J.; Domingues, S.; Engrola, S.; Drake, P.; Sarasquete, C.; Dinis, M.T.; Cancela, M.L. Comparing skeletal development of wild and hatchery-reared Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis, Kaup 1858): Evaluation in larval and postlarval stages. Aquac. Res. 2009, 40, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, G.; Boglione, C.; Bertolini, B.; Rossi, A.; Ferreri, F.; Cataudella, S. Observations on development and abnormalities in the appendicular skeleton of sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax L. 1758, larvae and juveniles. Aquac. Res. 1993, 24, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boglione, C.; Costa, C.; Di Dato, P.; Ferzini, G.; Scardi, M.; Cataudella, S. Skeletal quality assessment of reared and wild sharpsnout sea bream and pandora juveniles. Aquaculture 2003, 227, 373–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaloro, E.; Mazzola, A. Meristic variation and skeletal anomalies of wild and reared sharpsnout seabream juveniles (Diplodus puntazzo, Cetti 1777) coastal Sicily, Mediterranean Sea. Aquac. Res. 2003, 34, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komada, N. Incidence of gross malformations and vertebral anomalies of natural and hatchery Plecoglossus altivelis. Copeia 1980, 1980, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreri, F.; Nicolais, C.; Boglione, C.; Bmertoline, B. Skeletal characterization of wild and reared zebrafish: Anomalies and meristic characters. J. Fish Biol. 2000, 56, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis-McCrea, L.M.; Lall, S.P. Effects of moderately oxidized dietary lipid and the role of vitamin E on the development of skeletal abnormalities in juvenile Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus). Aquaculture 2007, 262, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfuj, M.S.; Hossain, M.A.; Sarower, M.G. Effect of different feeds on larval development and survival of ornamental koi carp, Cyprinus carpio (Linnaeus, 1758) larvae in laboratory condition. J. Bangladesh Agril. Univ. 2012, 10, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, F.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Xu, Q. Effects of a-ketoglutarate (AKG) supplementation in low phosphorous diets on the growth, phosphorus metabolism and skeletal development of juvenile mirror carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquaculture 2019, 507, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Tian, L.X.; Xie, S.W.; Guo, D.Q.; Yang, H.J.; Liang, G.Y.; Liu, Y.J. Interactions between dietary protein levels, growth performance, feed utilization, gene expression and metabolic products in juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquaculture 2015, 437, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.J.; Tian, L.X.; Wang, J.T.; Wang, Y.; Liang, G.Y. Effect of dietary lipid level on growth, feed utilization and body composition by juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquacult. Nutr. 2005, 11, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, M.H. Growth and survival of bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) fry fed at different intake levels and feeding frequencies. Aquaculture 1988, 68, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, K.; Miller, M.; Dabrowski, K. Comparison and optimization of a novel larval rearing method for bighead carp Hypophthalmichthys nobilis. Aquaculture 2021, 534, 736266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wargelius, A.; Fjelldal, P.G.; Hansen, T. Heat shock during early somitogenesis induces caudal vertebral column defects in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Dev. Genes Evol. 2005, 215, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfakianakis, D.G.; Koumoundouros, G.; Divanach, P.; Kentouri, M. Osteological development of the vertebral column and of the fins in Pagellus erythrinus (L. 1758). Temperature effect on the developmental plasticity and morpho-anatomical abnormalities. Aquaculture 2004, 232, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cort, J.L. Age and growth of the bluefin tuna, Thunnus thynnus (L.), of the northeast Atlantic. Col. Vol. Sci. Pap. ICCAT 1991, 35, 213–230. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, L.C.G.; Beamish, R.J.; Youson, J.H. Macroscopic structure of the fin-rays and their annuli in pectoral and pelvic fins of Chinook Salmon, Oncorhynchus tshawytscha. J. Morphol. 1999, 239, 297–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, N.; Bello, G.; Corriero, A.; Deflorio, M.; Vassallo-Agius, R.; Bök, T.; De Metrio, G. Age and growth of Atlantic bluefin tuna, Thunnus thynnus (Osteichthyes: Thunnidae), in the Mediterranean Sea. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2009, 25, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, N.; Bello, G.; Passantino, L.; Di Comite, M.; Zupa, R.; Pousis, C.; Corriero, A. Micro-anatomical structure of the first spine of the dorsal fin of Atlantic bluefin tuna, Thunnus thynnus (Osteichthyes: Scombridae). Ann. Anat. 2018, 219, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten, P.E.; Gil-Martens, L.; Hall, B.K.; Huysseune, A.; Obach, A. Compressed vertebrae in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): Evidence for metaplastic chondrogenesis as a skeletogenic response late in ontogeny. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2005, 64, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten, P.E.; Hall, B.K.; Huysseune, A. Are breeding teeth in Atlantic salmon a component of the drastic alterations of the oral facial skeleton? Arch. Oral Biol. 2005, 50, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten, P.E.; Obach, A.; Huysseune, A.; Baeverfjord, G. Vertebrae fusion in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar): Development, aggravation and pathways of containment. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antinero, A.; Printzi, A.; Kourkouta, C.; Fragkoulis, S.; Mazurais, D.; Zambonino-Infante, J.-L.; Koumoundouros, G. The role of starter diets in the development of skeletal abnormalities in zebrafish Danio rerio (Hamilton, 1822). J. Fish Dis. 2023, 46, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Printzi, A.; Koumoundouros, G.; Fournier, V.; Madec, L.; Zambonino-Infante, J.-L.; Mazurais, D. Effect of early peptide diets on zebrafish skeletal development. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, T.R.; Peterson, R.E.; Heideman, W. Early dioxin exposure causes toxic effects in adult zebrafish. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 135, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasco, M.; Cardeira, J.; Viegas, M.; Caria, J.; Martins, G.; Gavaia, P.; Cancela, M.; Laizé, V. Anti-osteogenic activity of cadmium in zebrafish. Fishes 2019, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harb, A.H. Skeletal deformities in cultured common carp Cyprinus carpio L. Asian Fish. Sci. 2001, 14, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzak, R.; Ostaszewska, T.; Wagner, B. The effect of feeding commercial diets on the development of juvenile crucian carp (Carassius carassius, L.). Part 1: Skeletal Deformations. Aquacult. Nutr. 2019, 25, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumoundouros, G.; Gagliardi, F.; Divanach, P.; Boglione, C.; Cataudella, S.; Kentouri, M. Normal and abnormal osteological development of caudal fin in Sparus aurata L. fry. Aquaculture 1997, 149, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurden, I.; Marion, D.; Charlon, N.; Coutteau, P.; Bergot, P. Comparison of different soybean phospholipidic fractions as dietary supplements for common carp, Cyprinus carpio, larvae. Aquaculture 1998, 161, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.Y.; Clouet, P.; Huang, L.M.; Degrace, P.; Zheng, W.H.; He, J.G.; Tian, L.X.; Liu, Y.J. Utilization of different dietary lipid sources at high level in herbivorous grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): Mechanism related to hepatic fatty acid oxidation. Aquacult. Nutr. 2008, 14, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Berthou, E. Size- and depth-dependent variation in habitat and diet of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquat. Sci. 2001, 63, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Zhu, S.; Li, J. Regionally divergent patterns of grass carp relative abundance, feeding habits and trophic niches in the subtropical Pearl River basin. Aquat. Ecol. 2022, 56, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, S.J.; Chick, J.H.; Pegg, M.A. Diet overlap among two Asian carp and three native fishes in backwater lakes on the Illinois and Mississippi rivers. Biol. Invasions 2009, 11, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumolo, B.B.; Flinn, M.B. Diet of invasive silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) in a mainstem reservoir ecosystem. J. Ky. Acad. Sci. 2019, 79, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rønnestad, I.; Tonheim, S.K.; Fyhn, H.J.; Rojas-García, C.R.; Kamisaka, Y.; Koven, W.; Finn, R.N.; Terjesen, B.F.; Barr, Y.; Conceição, L.E.C. The supply of amino acids during early feeding stages of marine fish larvae: A review of recent findings. Aquaculture 2003, 227, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamre, K.; Yúfera, M.; Rønnestad, I.; Boglione, C.; Conceição, L.E.C.; Izquierdo, M. Fish larval nutrition and feed formulation: Knowledge gaps and bottlenecks for advances in larval rearing. Rev. Aquacult. 2013, 5, S26–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, P.S.; Smith, T.K.; Cho, C.Y.; Ferguson, H.W. Dietary excesses of leucine influence growth and body composition of rainbow trout. J. Nutr. 1991, 121, 1932–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrazaga, I.; Micard, V.; Gueugneau, M.; Walrand, S. The role of the anabolic properties of plant-versus animal-based protein sources in supporting muscle mass maintenance: A critical review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarih, S.; Djellata, A.; La Barbera, A.; Fernández-Palacios Vallejo, H.; Roo, J.; Izquierdo, M.; Fernández-Palacios, H. High-quality spontaneous spawning in greater amberjack (Seriola dumerili, Risso 1810) and its comparison with GnRHa implants or injections. Aquac. Res. 2018, 49, 3442–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikos, N.; Phelps, R.P.; Williams, K.; Ferry, A.; Maus, D. Egg and larval quality of natural and induced spawns of red snapper, Lutjanus campechanus. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2003, 28, 487–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, M.D.; Hataley, J.M.; Kitchen, C.L.; Buchanan, L.G. Induction of developmental abnormalities in larval goldfish, Carassius auratus L., under cool incubation conditions. J. Fish Biol. 1989, 35, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vågsholm, I.; Djupvik, H.O. Risk factors for spinal deformities in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. J. Fish Dis. 1998, 21, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.H.; Tsai, C.L. Effects of temperature on the deformity and sex differentiation of tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. J. Exp. Zool. 2000, 286, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AccuWeather. Available online: https://www.accuweather.com/it/al/tirana/6522 (accessed on 16 October 2023).
- Carls, M.G.; Rice, S.D.; Hose, J. E Sensitivity of fish embryos to weathered crude oil. Part 1. Low level exposure during incubation causes malformations and genetic damage in larval Pacific herring (Clupea pallasi). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Common Carp | Silver Carp | Grass Carp | Bighead Carp | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of individuals | 53 | 86 | 44 | 40 |
| Total length (mm) | 28.9 ± 5.0 | 21.4 ± 2.1 | 32.8 ± 2.6 | 33.7 ± 5.7 |
| Number of anomalies recorded | 151 | 1119 | 1148 | 414 |
| Relative frequency (%) of individuals with at least one anomaly | 78.4 | 93.1 | 100.0 | 95.0 |
| Total anomalies load | 3.6 | 12.7 | 26.1 | 10.9 |
| Relative frequency of individuals with at least one severe anomaly (%) | 43.4 | 57.5 | 86.4 | 62.5 |
| Ratio (%) of observed severe anomalies on the total number of observed anomalies | 43.7 | 27.9 | 24.5 | 22.0 |
| Severe anomalies load | 23.0 | 5.7 | 7.4 | 3.6 |
| Region | Type of Anomaly | Common Carp | Silver Carp | Grass Carp | Bighead Carp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cephalic vertebrae | Kyphosis | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.0 |
| Lordosis | 2.0 | 0.6 | 0.3 ** | 0.0 ** | |
| Vertebral fusion | 0.7 | 3.6 | 2.1 | 0.2 | |
| Vertebral anomaly | 0.7 | 3.3 | 2.3 | 0.5 | |
| Anomalous neural arch and/or spine | 6.6 | 18.1 ** | 20.3 ** | 10.4 | |
| Anomalous haemal arch and/or spine | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.0 | |
| Pre-haemal vertebrae | Scoliosis | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Kyphosis | 1.3 | 0.3 | 0.0 ** | 0.0 * | |
| Lordosis | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Vertebral fusion | 0.0 | 3.4 * | 4.2 * | 4.8 ** | |
| Vertebral anomaly | 2.0 | 6.4 * | 5.6 | 5.3 | |
| Anomalous neural arch and/or spine | 2.0 | 28.2 ** | 26.5 ** | 22.9 ** | |
| Anomalous haemal arch and/or spine | 3.3 | 5.2 | 4.1 | 6.3 | |
| Haemal vertebrae | Kyphosis | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.0 |
| Lordosis | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Vertebral fusion | 3.3 | 0.8 ** | 2.7 | 0.5 ** | |
| Vertebral anomaly | 12.6 | 2.6 ** | 4.2 ** | 2.7 ** | |
| Anomalous neural arch and/or spine | 2.6 | 8.7 ** | 8.8 ** | 10.6 ** | |
| Anomalous haemal arch and/or spine | 7.9 | 4.9 | 9.7 | 10.4 | |
| Caudal vertebrae | Scoliosis | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Lordosis | 2.0 | 0.0 ** | 0.0 ** | 0.2 * | |
| Vertebral fusion | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.2 | |
| Vertebral anomaly | 17.9 | 2.8 ** | 2.2 ** | 7.5 ** | |
| Anomalous neural arch and/or spine | 17.2 | 7.4 ** | 4.4 ** | 11.8 | |
| Anomalous haemal arch and/or spine | 9.9 | 1.2 ** | 1.0 ** | 4.3 * | |
| Caudal fin | Anomalous hypural | 1.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 * | 0.2 |
| Anomalous epural | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | |
| Dorsal soft rays | Anomalous pterygiophores | 2.6 | 0.0 ** | 0.0 * | 0.2 ** |
| Anal fin | Anomalous pterygiophores | 1.3 | 0.1 ** | 0.2 ** | 0.5 |
| Supernumerary bone | 0.7 | 0.0 ** | 0.1 | 0.0 |
| Region | Type of Anomaly | Common Carp | Silver Carp | Grass Carp | Bighead Carp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cephalic vertebrae | Kyphosis | 0.0 | 3.4 | 6.8 | 0.0 |
| Lordosis | 5.7 | 6.9 | 6.8 | 0.0 | |
| Vertebral fusion | 1.9 | 31.0 ** | 36.4 ** | 2.5 | |
| Vertebral anomaly | 1.9 | 20.7 ** | 25.0 ** | 2.5 | |
| Anomalous neural arch and/or spine | 11.3 | 54.0 ** | 93.2 ** | 55.0 ** | |
| Anomalous haemal arch and/or spine | 1.9 | 1.1 | 2.3 | 0.0 | |
| Pre-haemal vertebrae | Scoliosis | 0.0 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Kyphosis | 3.8 | 3.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Lordosis | 0.0 | 2.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Vertebral fusion | 0.0 | 23.0 ** | 50.0 ** | 15.0 ** | |
| Vertebral anomaly | 3.8 | 27.6 ** | 45.5 ** | 12.5 | |
| Anomalous neural arch and/or spine | 5.7 | 64.4 ** | 95.5 ** | 60.0 ** | |
| Anomalous haemal arch and/or spine | 7.5 | 16.1 | 27.3 ** | 25.0 * | |
| Haemal vertebrae | Kyphosis | 1.9 | 2.3 | 11.4 | 0.0 |
| Lordosis | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Vertebral fusion | 9.4 | 5.7 | 27.3 * | 5.0 | |
| Vertebral anomaly | 22.6 | 9.2 ** | 36.4 | 12.5 | |
| Anomalous neural arch and/or spine | 7.5 | 27.6 ** | 43.2 ** | 27.5 ** | |
| Anomalous haemal arch and/or spine | 13.2 | 14.9 | 59.1 ** | 30.0 * | |
| Caudal vertebrae | Scoliosis | 0.0 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Lordosis | 5.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.5 | |
| Vertebral fusion | 0.0 | 4.6 | 6.8 | 2.5 | |
| Vertebral anomaly | 35.8 | 20.7 * | 38.6 | 52.5 | |
| Anomalous neural arch and/or spine | 43.4 | 70.1 ** | 72.7 ** | 80.0 ** | |
| Anomalous haemal arch and/or spine | 26.4 | 11.5 * | 15.9 | 35.0 | |
| Caudal fin | Anomalous hypural | 3.8 | 4.6 | 4.5 | 2.5 |
| Anomalous epural | 1.9 | 1.1 | 6.8 | 2.5 | |
| Dorsal soft rays | Anomalous pterygiophores | 7.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.5 |
| Anal fin | Anomalous pterygiophores | 3.8 | 1.1 | 4.5 | 5.0 |
| Supernumerary bone | 1.9 | 0.0 | 2.3 | 0.0 |
| Region | Common Carp | Silver Carp | Grass Carp | Bighead Carp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cephalic vertebrae region | 11.5 | 26.4 * | 25.3 * | 11.1 |
| Pre-haemal vertebrae region | 9.4 | 43.8 * | 40.4 * | 39.4 * |
| Haemal vertebrae region | 24.5 | 17.2 * | 25.8 | 24.2 |
| Caudal vertebrae region | 48.2 | 12.0 * | 7.8 * | 24.2 * |
| Caudal fin | 2.2 | 0.5 * | 0.4 * | 0.5 |
| Other fins | 4.3 | 0.1 * | 0.3 * | 0.7 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varvara, C.; Hala, E.; Di Comite, M.; Zupa, R.; Passantino, L.; Ventriglia, G.; Quaranta, A.; Corriero, A.; Pousis, C. An Observational Study of Skeletal Malformations in Four Semi-Intensively Reared Carp Species. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11010030
Varvara C, Hala E, Di Comite M, Zupa R, Passantino L, Ventriglia G, Quaranta A, Corriero A, Pousis C. An Observational Study of Skeletal Malformations in Four Semi-Intensively Reared Carp Species. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarvara, Caterina, Edmond Hala, Mariasevera Di Comite, Rosa Zupa, Letizia Passantino, Gianluca Ventriglia, Angelo Quaranta, Aldo Corriero, and Chrysovalentinos Pousis. 2024. "An Observational Study of Skeletal Malformations in Four Semi-Intensively Reared Carp Species" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11010030
APA StyleVarvara, C., Hala, E., Di Comite, M., Zupa, R., Passantino, L., Ventriglia, G., Quaranta, A., Corriero, A., & Pousis, C. (2024). An Observational Study of Skeletal Malformations in Four Semi-Intensively Reared Carp Species. Veterinary Sciences, 11(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11010030









