Simple Summary
Hemangiosarcoma (HSA) is a highly aggressive vascular tumor. It is the most common splenic cancer and the cause of non-traumatic abdominal hemorrhage in dogs. The short overall survival and high dissemination potential of HSA demonstrate the necessity of new and more effective therapies, especially with specific tumoral targets. This study investigates recent advances in molecular aspects of canine hemangiosarcoma and presents promising therapeutic targets.
Abstract
Canine hemangiosarcoma (HSA) is a relatively common neoplasia, occurring mainly in the skin, spleen, liver and right atrium. Despite the numerous studies investigating the treatment of canine HSA, no significant improvement in survival has been achieved in the last 20 years. Advancements in genetic and molecular profiling presented molecular similarities between canine HSA and human angiosarcoma. It could therefore serve as a valuable model for investigating new and more effective treatments in people and dogs. The most common genetic abnormalities in canine HSA have been found in the phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA) and neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog (NRAS) pathways. Mutations are also found in tumor protein p53 (TP53), phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) and cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (CDKN2A). Known abnormal protein expression could be exploited to trial new target treatments that could be beneficial for both canine and human patients. Despite the high expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor (VEGFR), no correlation with overall survival time has ever been found. In this review, we explore the most recent developments in molecular profiling in canine HSA and discuss their possible applications in the prognosis and treatment of this fatal disease.
1. Introduction
Angiosarcoma is an aggressive cancer that carries a poor prognosis in people, with 5-year survival tallying at less than 30% [1]. In dogs, malignancies of lymphatic vessels are rarely described, while a tumor of the blood vessels—hemangiosarcoma (HSA)—is relatively common. HSA may arise in any region of the body, especially the skin, spleen, liver and atrium [2,3]. Skin lesions can be multiple, often small and related to ultraviolet radiation (UV) and actinic damage, especially in the lower abdomen of dogs with white or thin hair coats [4,5]. However, HSA may also occur in the subcutis, muscle and visceral organs. Non-cutaneous HSAs are highly aggressive tumors with a high metastatic rate [6,7,8,9]. The splenic form shows nonspecific clinical signs during its initial progression, yet is the most common cause of acute hemoperitoneum [10,11] with a high rate of metastases to the liver, mesentery, abdominal lymph nodes and lungs [7,8]. Cardiac HSA has a poor prognosis due to its fast local growth and progression, with frequent concurrent involvement of the lungs, spleen and liver [6]. HSA has a variable breed predisposition. Whereas dermal neoplasia seems to be directly caused by UV exposure in white dog breeds, especially in Pitbull Terrier and Boxer [4,5], the visceral forms are overrepresented in breeds such as Golden Retriever, Labrador Retriever, German Shepherd and Miniature Schnauzer [3,7,8,12,13,14].
The anatomical form of HSA is directly related to its cytogenetic origin. Older studies suggest the development of HSA from transformed mature endothelial cells based on the histological presentation and negative staining for leukocytes and histiocytes but positive for CD31, CD105, CD146, VEGFR, factor VIII and avb3-i-integrin (from activated endothelial cells) [15,16]. This theory may be true for cutaneous HSA, which justifies the biological behavior and rare identification of metastases. However, this classic model, in which a primary tumor arises in an organ and metastasizes from there, does not completely explain the behavior of canine HSA in its other forms [15,16,17].
A second theory has been gaining momentum over the last 15–20 years. Except for the actinic cutaneous form, canine HSA could arise from a precursor (pluripotent) endothelial cell. This theory has been confirmed in several molecular studies, based on the expression of CD34, CD45, CD133 and KITr, which are endothelial precursor cell proteins [15,16]. These cells can be identified in the circulation, with values higher than 0.5% in dogs with HSA and less than 0.3% in dogs without HSA or dogs with HSA already submitted to surgery. These pluripotent cells leave the bone marrow to disseminate to different parts of the body [15]. Their survival, growth and proliferation are dependent on the microenvironment. Possibly, the spleen is a more favorable environment, followed by the liver and right atrium. One study classified HSA according to distinct endothelial, myeloid and hematopoietic markers (CD14, CD34, D105, CD115, CD117, CD133 and CD146), suggesting that it could arise from different pluripotent progenitors [18], further classified as angiogenic, inflammatory and adipogenic [16]. Figure 1 illustrates an adaptation of the hematopoietic progenitor theory for HSA dissemination presented by Kim et al. (2015) and Lamerato-Kozicki et al. (2006) [15,16].
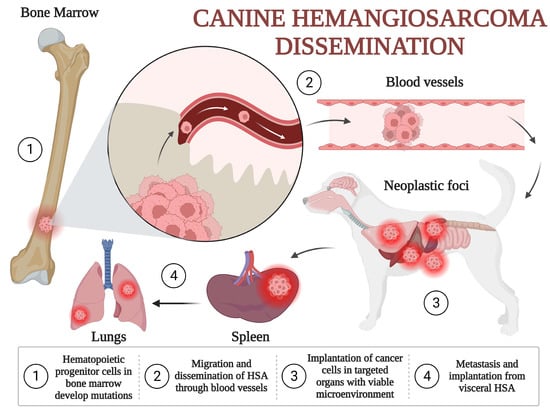
Figure 1.
Canine hemangiosarcoma dissemination: (1) Hematopoietic progenitor cells in bone marrow develop mutations and from non-neoplastic stem cells transform to HSA cells. (2) Initial migration and dissemination of the tumor occur from the bone marrow to systemic circulation, able to reach multiple organs. (3) Cancer cells reach and colonize targeted organs with viable microenvironments, such as the spleen, liver and right atrium. (4) Secondary dissemination may occur from the tumors to lungs or through cavitary implantation in cases of rupture, as in the peritoneum and omentum [15,16,19,20].
The diagnosis of canine HSA is commonly achieved by histopathology due to the inherent limitations of cytology [21,22]. Histopathology, however, is not always possible without performing invasive surgery. A novel minimally invasive diagnostic test (liquid biopsy of a blood sample) was recently validated. Although based on a small sample size (n = 12), this test was shown to achieve a specificity of 83.3% for the diagnosis of canine HSA [23]. A different liquid biopsy test, which measured plasma nucleosome concentrations for canine HSA, included a six times higher number of cases than the previous study (n = 77), demonstrated improved specificity (97%) and exhibited a sensitivity of 81.2% [24]. However, the sensitivity of liquid biopsy is likely to be affected by the stage of the disease, with lower stages less likely to be detected [23,24]. Even though more research is needed, liquid biopsy could become a non-invasive screening exam, especially for certain breeds of dogs with a high predisposition for HSA.
The prognosis for actinic cutaneous lesions is favorable and surgery is usually curative with long survival rates [25,26]. Nevertheless, aggressive systemic forms of disease are associated with poor prognosis with a median survival time (MST) of 23–292 days [4,25,26,27].
Despite the numerous studies investigating the treatment of canine HSA, no significant improvement in survival has been achieved in the past 20 years. Standard treatment consists of surgical resection followed by anthracycline-based chemotherapy at the highest tolerated dose. The most used tyrosine kinase inhibitors in dogs, toceranib and masitinib, were not effective in the treatment of canine HSA [28,29]. In a study of dogs with splenic hemangiosarcoma treated with standard splenectomy and subsequent adjuvant doxorubicin, the addition of toceranib phosphate did not result in an improvement in overall survival or disease-free interval [29]. Although masitinib has some anti-proliferative effects on canine HSA cells in vitro, the in vivo effect has not been reliably demonstrated in clinical trials [28]. The addition of maintenance metronomic chemotherapy was not effective in enhancing overall survival either [30]. However, treatment with metronomic chemotherapy with or without thalidomide could be as effective as the standard-of-care adjuvant doxorubicin [31,32,33,34]. The outcomes of studies exploring different treatments, including immunotherapy strategies, for HSA have been largely disappointing [35,36,37,38,39]. Advancements in the genetic and molecular profiling of specific cancers have opened new avenues for personalized and targeted treatment in both human and veterinary medicine. Few studies have investigated the molecular profiling of HSA in dogs [40,41,42]. Although the morphological and immunohistochemical studies of canine HSA have deciphered important aspects concerning its origin and behavior, research on the molecular basis of the disease may be more important for targeted therapy. Several molecular similarities between canine HSA and human angiosarcoma could be advantageous for the development of targeted therapies [43,44].
Histone acetylation is an epigenetic mechanism of cancer modulation, recently studied for potential targeted therapies [45,46]. One in vitro study has demonstrated its potential for canine HSA: histone acetylation levels were high in canine HSA cell lines and some in vivo cases, suppressed by a bromodomain and extraterminal domain inhibitor (BETi), JQ1 [46]. The potential for this therapy is still unclear, so new studies are required to characterize it properly.
A study analyzed DNA copy number variations and found distinct patterns of gain or loss of specific loci in dogs diagnosed with intrabdominal HSA [47]. Significative gains occurred in chromosome 13 in VEGFR2, PDGFRA and KIT genes. In chromosome 12, the dogs also presented VEGFA gene gain, a potential prognostic factor for HSA treatment, especially in Flat-Coated Retrievers, due to the higher rate of gene gain [47,48]. Most cases presented a loss of the CDKN2AIP gene (genomic location 16:49.9), an important tumoral suppressor gene, which encodes p14 and p16 [47]. Data regarding CDKN2AIP mutations in canine HSA are still scarce; however, a recent study revealed mutations in 11% of cases [40], a higher rate compared to mutations of PTEN, which is the most studied tumoral suppressor gene [49,50,51].
Canine HSA has been divided into specific subtypes according to the molecular patterns that might originate from different pathogenic pathways [18,43,44]. The differentiation of three distinct subtypes of HSA) in canines relies on the analysis of specific somatic mutations occurring most frequently in driver genes among affected canine patients: oncogene Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA), oncogene neuroblastoma rat sarcoma virus (NRAS) activation and tumoral suppressor gene tumor protein p53 (TP53). Changes in the NRAS and PIK3CA pathways may occur in up to 24% (15/50) and 46% (23/50) of canine HSA, respectively, and might be especially interesting for target therapies [18]. Figure 2 presents a summary of the recent literature regarding the main driver mutations associated with canine HSA. Golden retrievers’ HSAs express a different pattern of mutations compared to other pure breeds, present a higher frequency of mutations in AKT and PIK3CA genes and demonstrate the importance of heritable factors in analyzing mutations [41,52]. Thus, they may be beneficial for therapies targeting the products of such genes.
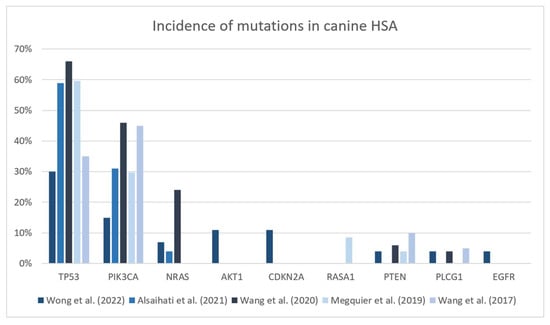
Figure 2.
Incidence of mutations in cancer-related genes in canine hemangiosarcoma cases [40,41,43,44,53].
To write this review, a PubMed search was conducted using the following key words: hemangiosarcoma, canine, dogs, angiosarcoma. The search strategy involved evaluating articles spanning 2015 to 2023. Additional studies were incorporated based on their relevance and references from the initially selected articles.
Inclusion criteria considered studies obtained through institutional access or an internet search, especially from peer-reviewed journals. We did not impose any restrictions regarding the characteristics of in vitro and in vivo studies for the selection process. Conventional and well-established treatments for canine HSA, such as surgery and chemotherapies such as doxorubicin and carboplatin, were not extensively evaluated and therefore served as exclusion criteria, considering that the focus of this study was to analyze molecular features. The process entailed several phases, including an initial search, the identification of relevant articles, screening for suitability, an assessment of the eligibility criteria and ultimately determining the final inclusion.
2. Hemangiosarcoma Carcinogenesis
Primary canine HSA can occur in distinct organs, at different frequencies. The most commonly diagnosed presentations are splenic, hepatic, cutaneous and cardiac [6,7,54,55]; however, this neoplasm can originate in the lungs, peritoneum, kidneys, skeletal muscles, pleura, oral cavity, pancreas, bones, intestines and virtually every malignant-transformed endothelial vascular tissue [8,9,52,53]. Thus, it should always be considered as a potential differential diagnosis.
The etiopathogenesis of this complex neoplasm relies on genetic predispositions, acquired mutations, hormonal aspects and exposure to environmental carcinogens, such as UV light [4,53,56,57]. These etiological factors can also influence individual clinical presentation, according to the dog’s breed, age, weight and skin characteristics [8,26,52,58]. The impact of gonadal steroids in HSA carcinogenesis is still discussed, with some studies demonstrating an increased risk for the development of HSA in neutered dogs [57,59,60]. Typical mutations in dogs with HSA occur in the TP53 genes, commonly called the “guardian of the genome”, and PIK3CA, active in the PI3K-AKT-mTOR cell proliferation signaling pathway [41,43,44].
Over the last decade, cell culture studies have significantly enhanced our understanding of ’as’s etiopathogenesis and its underlying mechanisms, including the characterization of mutations and cancer mechanisms through genome-wide and transcriptomic analyses [19,20,61,62]. In 2017, Im et al. presented a mechanism of cell migration and invasion through the CXCR4/CXCL12 axis, in which HSA may disseminate [19]. In 2022, Maeda et al. performed the first cloning of canine PIK3CA (GenBank accession no. LC625864), which is highly homologous to the respective human gene. The findings further highlight another potential similarity between human angiosarcoma and canine HSA [61].
A variety of oncogenes and tumoral suppressor genes are associated with the development and progression of HSA in dogs. Table 1 illustrates the genes and their role in canine HSA:

Table 1.
Genes associated with etiopathogenesis of canine HSA [40,41,42,43,44,47,53,56,63,64,65].
3. Mutations and Potential Therapeutic Targets
Table 2 presents the recently studied and potential therapeutic targets, as discussed in the following sections. This table provides details of specific targets and their potential target therapies. The specification of experimental conditions is relevant to determining whether the study was conducted in humans and/or dogs, rather than exclusively focusing on canine HSA.

Table 2.
Targets and potential targeted therapies for canine HSA [45,46,61,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78].
3.1. NRAS
RAS (rat sarcoma) includes a group of small proteins activated by GTP ligation to signal the transduction of diverse signaling pathways related to cell proliferation and survival. The dysregulation of RAS activity can lead to abnormal cell proliferation, with more than 30% of human cancers being driven by activating RAS mutations [79]. The RAS gene group includes HRAS, KRAS and NRAS, that when mutated lead to the carcinogenesis of different neoplasms in humans and domestic animals [80,81,82]. Mutations in NRAS are associated with canine leukemia and HSA [43,80], while changes in KRAS may induce pancreatic and pulmonary carcinomas in dogs [83,84]. HRAS still does not seem to be as important as the other genes in canine cancer pathogenic mechanisms [80]. In canine HSA, mutations in NRAS have been found in 24% (12/50) of HSA cases, independently of anatomical location [43].
The Ras p21 protein activator 1 gene (RASA1) is responsible for the RAS pathway regulation by controlling its ligation with GDP and GTP, and thus is considered a tumor-suppressor gene of the RAS/GAP group. The inhibition of RAS GAPs leads to the upregulation of the Ras pathway, possibly increasing cell proliferation and growth, and ultimately inducing tumorigenesis [85]. RASA1 is crucial for physiological mechanisms such as angiogenesis; however, its mutations are associated with common cancers in humans, including lung, breast, liver and colorectal neoplasms [86,87]. The downregulation of RASA1 may promote tumoral angiogenesis and metastasis [87]. These mutations were identified in 8.5% (4/47) of canine visceral HSA cases [44,64].
Cancers driven by such mutations are difficult to treat because there are no available drugs that can bind to RAS. Nevertheless, the RAF protein, later activated by RAS, can be inhibited by a group of tyrosine kinase inhibitors, including sorafenib, vemurafenib, dabrafenib and regorafenib [88,89].
In people, target treatment with the BRAF inhibitor sorafenib has shown some efficacy [48]. Despite that, there are no published results of clinical trials involving these drugs for canine HSA. Sorafenib has been generally considered quite safe in dogs [72,73,74]. In a small study, sorafenib proved to be safe and effective for dogs with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with a twice-daily dosage of 5 mg/kg. Dogs receiving target therapy had a median time to progression of 363 days, while dogs treated with metronomic chemotherapy had only 27 days (p = 0.079) [73]. Sorafenib could be a promising targeted therapy for canine HSA [72,73,90]; however, its cost may be a barrier for many pet owners.
The RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK pathway, also known as MAPK, consists of a signaling cascade for cell proliferation and differentiation [80,82,90]. RAS and RAF oncogenes have attracted the most attention within this group due to their well-described carcinogenic potential [79,81,82,83,85,86]. Nonetheless, there are many other genes and proteins of potential importance, including the mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MEK). Although not tested in canine HSA, MEK can be inhibited by trametinib or cobimetinib [90,91,92]. RAF functions by phosphorylating and activating MEK, which, subsequently, phosphorylates and activates ERK, ultimately resulting in gene transcription [85] (Figure 3).
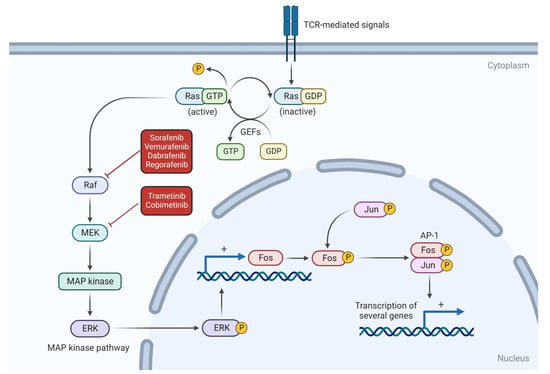
Figure 3.
RAS-RAF-MEK pathway and potential therapeutic targets. RAS protein leads to RAF activation, which can be inhibited by sorafenib, vemurafenib, dabrafenib and regorafenib. MEK protein, activated by RAF, can be inhibited by trametinib and cobimetinib.
The in vitro inhibition of MAPK has been demonstrated to downregulate tumoral growth in canine HSA cell cultures of primary splenic, cardiac and cutaneous presentations [90]. Three MEK inhibitors, CI-1040, Sorafenib and LY294002, were tested and provided evidence that, even in vivo, the inhibition of this pathway is able to suppress both human angiosarcoma and canine HSA proliferation [90].
3.2. PIK3CA
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) is an oncogene product, featured by a catalytic unit and considered a potential anticancer target. The phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA) plays a fundamental role, acting in the AKT-mTOR pathway, encoding the P110α oncoprotein and regulating this cellular metabolic pathway in several human cancers [51,93,94,95]. The PI3K-AKT-mTOR is considered one of the most important pathways in many cancers including vascular tumors. The independent phosphorylation of AKT (Ser473) was associated with cell cultures of canine HSA in the absence of PTEN deletion and unaltered by fetal bovine serum, suggesting a constitutive activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in these cell lines [95]. Dysregulation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway leads to increased proliferation signaling and dysregulation of cellular metabolism—a hallmark of cancer [94,96,97].
Mutations in PIK3CA are mostly identified in coding domains of P110α, a major hotspot, although different domains might be mutated according to the origin of the cancer [94]. The modification of amino acid 1047, responsible for P110α protein loop conformation, seems to be frequently mutated in canine HSA cases, representing 71% (10/14) of all mutations in PIK3CA and characterized as H1047R or H1047L [40,44,61].
In both human and veterinary medicine, the mutation of PI3K in general has a negative impact on survival time independently of the cancer type [42]. Targeting PIK3 appears to be an interesting anticancer treatment strategy, and in human medicine, Alpelisib and Copanlisib, two PIK3 inhibitors, have been approved for the treatment of various cancers [78]. A recent study assessed the impact of Alpelisib on PIK3CA-mutated canine HSA cell lines [61]. This PI3K inhibitor exhibits potential as a targeted therapy for dogs with PIK3CA mutations: in vitro effects demonstrated its capacity to inhibit cancer cell migration, suppress AKT phosphorylation, thereby inhibiting cell proliferation, and induce apoptosis through caspase-3/7 activation [61]. Clinical trials could provide further evidence regarding the effectiveness of Alpelisib for canine HSA and the potential of PIK3CA mutations as predictive markers for this therapy.
Gedatolisib is a drug under development used in cancer patients with mutations in PIK3CA. It inhibits the P110α catalytic subunit of the PI3K gene, inhibiting the PI3K/mTOR pathway [75,76,77,98]. Recent evidence shows that it declines the viability of canine tumor cells of specific cell lines, such as osteosarcoma and histiocytic sarcoma [75]. However, trials with PI3K in HSA and angiosarcoma in canine and human patients are lacking. Considering the high percentage of PI3K mutation in canine HSA and the preliminary in vitro results, the inhibition of PI3K could be a viable therapeutic strategy for this type of tumor [99].
The occurrence of a specific mutation in an oncogene does not exclude the possibility of mutations in other oncogenes; a synergism effect may occur in tumors with additional mutations, such as in different segments of the PIK3CA-AKT-mTOR pathway and PIK3CA mutations coexisting with different PI3K mutations in endometrial, breast and colorectal human cancer [100]. Coexisting mutations in PIK3CA and TP53 have been occasionally identified in splenic and cardiac canine HSA [44].
3.3. PTEN
The PTEN is a tumor-suppressor gene, located in chromosome 10, responsible for the regulation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway through the inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling [51,101,102,103,104]. Like TP53, PTEN is frequently mutated in animal neoplasms, and a loss of PTEN upregulates the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway, facilitating cell cycle progression and increasing proliferation and anabolic metabolism throughout enhancing protein synthesis in cancer cells [104]. PTEN mutations are frequently found in breast and prostate cancer in humans, where there is a positive correlation between the loss of PTEN and adverse outcomes and poor prognosis [51,103]. Mammary gland tumors might also be associated with dysregulations of PTEN expression [101,105]. In addition, there is evidence that PTEN may regulate more aspects of the cancer’s behavior independently of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway, affecting the tumoral microenvironment and immunomodulation that may affect the clinical response to immunotherapy [50,51,104].
Reported almost two decades ago [64], PTEN mutations in canine HSA can occur in 4% (2/47) to 10% (2/20) of cases [40,41,43,44] and appear to play an important role in regulating PIK3CA, a more frequently mutated gene in this tumor [41,44]. PTEN is also downregulated in human angiosarcomas of the scalp and face, documented by reduced expression in immunohistochemistry for malignant and higher-grade tumors [49]. Inactivation of PTEN leads to upregulation of the mTOR pathway and targeting the mTOR pathway could be an effective anticancer strategy [102].
Specific mTOR inhibitors, Temsirolimus and Everolimus, have been successfully used and approved for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma in people [106,107]. Despite the potential efficacy in vascular tumors, mTOR inhibitors have not been investigated in clinical trials in angiosarcoma in people. However, Everolimus showed some modest efficacy in people with bone and soft tissue sarcomas [108].
For canine mammary neoplasms, both Temsirolimus and Everolmius have exhibited evidence to inhibit the mTOR pathway in vitro, leading to suppressed growth of tumor-adherent cells and spheres [109]. Additionally, Everolimus presents an anti-growth potential in sphere-formation assays related to cancer stem cells with self-renewal ability. However, the precise antitumor effect of these inhibitors in this model remains uncertain, as no discernible differences were observed between the control group and the groups treated with mTOR inhibitors regarding mitotic figures count and angiogenesis [109]. Sirolimus (rapamycin), the first discovered mTOR inhibitor, has not been investigated in dogs with HSA. However, adding Sirolimus to the standard of treatment for canine appendicular osteosarcoma has not shown significant benefit in overall survival, compared to the standard of treatment alone [110]. The efficacy of Sirolimus in combination with the standard treatment of care for hemangiosarcoma is under investigation, but it is unlikely to be effective alone in a disease with a rapid course and aggressive behavior. A combination of various treatments, including standard chemotherapy, mTOR inhibitors and repurposed drugs such as β-blockers, could be more effective [111].
3.4. TP53
This tumor-suppressor gene is commonly affected in neoplasms from different origins in humans and domestic animals [41]. It is the gene most frequently mutated in canine HSA, thus playing a meaningful role in its growth mechanism, most importantly avoiding tumoral suppression when mutated [43,64,65]. TP53 is also able to promote the fusion of genes through genomic instability [44]. In immunohistochemistry, cutaneous HSA with actinic damage expressed a higher p53 index when compared to visceral manifestations and cutaneous forms without actinic changes [26]. In a recent study, mutations of TP53 were shown to be a negative prognostic factor, independently of cancer type. Furthermore, the most common cancer with this mutated tumor-suppressor gene was canine HSA [42]. Alsaihati et al. (2021) identified a similar pattern, in which HSA was the tumor with the highest frequency of TP53 mutations (59%) among the analyzed neoplasms, especially in Golden Retrievers, although a prognostic analysis was not elaborated [41].
Therapies targeting p53 could be very useful in preserving genomic stability and regulating the cell cycle in cancers [112,113,114]. Gene therapy works by targeting specific mutations and restoring the functionality of the affected gene [67,113]. Gene therapy restoring the functionality of p53 can be theoretically used in a wide variety of cancer types; however, the efficacy of this treatment is largely unknown for many tumors with a mutation of p53 [113]. The recombinant human p53 adenovirus (Gendicine) was the first gene therapy to be approved for the treatment of head and neck carcinomas with p53 loss in humans. Gendicine increases response rate and overall survival time when associated with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy in head and neck carcinoma [66,67]. Unfortunately, p53 genetic therapy is not yet available in small animal oncology and no studies have evaluated the efficacy of this treatment in dogs with cancer.
3.5. CDKN2A
The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (CDKN2A) is a tumor-suppressor gene that controls the cell cycle, mostly in the G1 to S phase, by encoding proteins p16 and p14 [115,116]. Aberrations in this gene lead to tumorigenesis and metastasis as a result of a lack of cell cycle regulation [116]. In humans, it has been associated with various tumors, including pancreatic cancer, melanoma and angiosarcoma [117,118,119]. An experimental study tested the inoculation of oncogenic HRAS with the knockdown of CDKN2A or TP53 in mice and detected that these associations were able to induce the development of angiosarcomas and other soft tissue sarcomas [119]. In canine HSA, few studies analyzed CDKN2A; nonetheless, recently it was detected that 11% of dogs with HSA expressed mutations in this gene [40].
3.6. VEGF, Angiogenesis and Hypoxia
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a signal protein that induces the development of blood vessels, both in physiological and pathological conditions [120]. Its dysregulation enhances cancer growth by overstimulating angiogenesis, already supported by tumoral chemokines. As a result, the angiogenesis leads cancer cells to proliferate despite hypoxia [120,121]. Different types of VEGF play distinct functions in blood and lymphatic vasculature development, even in tumoral conditions, most notably VEGF-A and VEGF-D, usually overexpressed in breast cancer and angiosarcoma in humans [122,123,124]. Hypoxia is a dichotomous factor in some neoplasms [120,124,125]. Despite the need for nutrients and blood supply for a tumor cell to survive, some cancers, such as angiosarcoma, may have better development in a hypoxic microenvironment, evading immune antitumoral response and facilitating proliferation and migration [121,125,126,127]. The lack of tumoral oxygenation and the overexpression of VEGF may be poor prognostic factors that alter the cancer microenvironment in order to promote growth [123,125,128].
Vascular neoplasms commonly express VEGF and its receptors, and its overexpression appears to accelerate tumor proliferation [124,129,130]. The low expression of circulating VEGF-A in people with vascular sarcomas treated with sorafenib, including angiosarcoma, is correlated with a more favorable outcome [48]. A similar pattern occurs with low serum rates of VEGF-C, which are associated with poor prognosis and shorter disease-free time in humans with angiosarcoma treated with paclitaxel and bevacizumab [131]. No studies reported correlations between tyrosine kinase inhibitors or commercial monoclonal antibodies and VEGF expression or its blood rate in dogs with any type of cancer.
In canine cutaneous HSA, no correlation has been identified between VEGF expression and overall survival time [26]. Splenic HSA in dogs expressed a higher number of VEGF+ cells in comparison to splenic hemangiomas (p = 0.004) [132] and an average staining expression of VEGFR-2 that was four times higher than in normal spleens [130]. Evidence suggests that VEGF and VEGFR-2 may be useful diagnostic markers, although neither VEGF nor its receptors are well established as predictive or prognostic factors for canine HSA yet [26,130,132]. Antibodies that bind VEGF, VEGFR blockers and modified receptors are therapeutic options potentially able to reduce VEGF action in angiogenesis in canine cancer patients. Sorafenib is a tyrosine kinase that inhibits VEGFR-2 and PDGFR, suitable for human angiosarcoma treatment [48,133] and well tolerated by dogs [72,74]. Thus, it could be effective in disease control as a canine-HSA-targeted therapy, considering the high expression of VEGFR-2 in splenic HSA cells [130]. However, the use of toceranib, a TKI that blocks VEGFR, has not proven to be beneficial in splenic HSA after the standard treatment [29]. Immunotherapy is not frequently used for vascular tumors. Bevacizumab (Avastin®; Genentech, Inc., South San Francisco, CA, USA) is a monoclonal antibody anti-VEGF, potentially inhibiting tumoral angiogenesis, considered as a promising therapy, but in recent studies was found to not be beneficial for human angiosarcoma treatment [134].
3.7. PD-1/PD-L1 Complex
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) and vaccines are promising treatment modalities for several tumors in humans and domestic animals. Studies in the last decade have shown some evidence of efficacy for treating invasive urothelial carcinoma and melanoma in dogs, namely Oncotherad nano-immunotherapy and the Oncept vaccine [135,136,137,138,139]. Few studies have focused on evaluating the PD-1/PD-L1 complex as a potential target for canine HSA [70,140,141]. Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) is a lymphocyte surface protein that, when bound to its ligand, programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), can downregulate T cells. This interaction acts as a tumor immune system evasion mechanism [70]. The pathways of this mechanism include the inhibition and apoptosis of tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes, reduced secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and cell cycle arrest in the G0/G1 phase [70,141,142].
The ISOS-1 (RRID:CVCL_C517) angiosarcoma cell line shares molecular similarities with canine hemangiosarcoma (HSA) [140]. Notably, a study revealed that these tumor cells exert control over macrophages, polarizing them into the M2 phase, associated with pro-tumor effects, and upregulating the expression of PD-L1. This ligand expression is observed in most canine HSA cases [140], and also in tumor-infiltrating macrophages, indicating a pro-tumor role of the PD-1/PD-L1 complex in canine HSA [140].
The in vivo effectiveness of an anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor (ca-4F12-E6) was documented in two dogs diagnosed with melanoma [68]. These patients exhibited a complete response that lasted over a year, surpassing the expected outcomes of conventional therapy [68,71]. Additional studies are warranted to evaluate the therapy’s efficacy and safety, involving a larger cohort of dogs and comprehensive safety assessments. Currently, some effective antibodies targeting PD-1 and PD-L1, such as Pembrolizumab and Atezolizumab, have been approved for the treatment of human tumors [69,70]. However, in veterinary medicine, there are no commercially available immune checkpoint inhibitors yet.
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
The prognosis for visceral canine HSA remains poor. Recent studies have improved our knowledge of the most common molecular profile of HSA in dogs, clarifying different patterns according to each presentation of the neoplasm.
In our study, the most frequently analyzed mutated genes in canine HSA identified in recent articles are TP53, PIK3CA and NRAS. Nonetheless, few investigations in recent decades have searched for mutations in other genes, such as CDKN2A, PTEN and AKT1, which could provide more knowledge regarding this tumor’s resistance and etiopathogenesis. Targeting one, or more likely several dysregulated molecular pathways, such as RAS-RAF-MEK and AKT-mTOR, could be beneficial in treating this fatal disease. Thus, new studies should test different strategies focused on specific pathways.
As demonstrated previously, canine HSA’s molecular profile differs from other neoplasms. A different molecular background could even be present in different portions of the same neoplasm. In the near future, the treatment of HSA should focus on a more personalized treatment, based on the specific molecular profile of individual dogs with HSA.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.A.B.P. and R.D.S.H.; methodology, P.A.B.P., R.D.S.H. and A.G.; investigation, P.A.B.P., R.D.S.H. and A.G.; writing—original draft preparation, P.A.B.P., R.D.S.H. and A.G.; writing—review and editing, P.A.B.P., P.M.B., R.D.S.H. and A.G.; visualization, P.A.B.P., P.M.B., R.D.S.H. and A.G.; supervision, R.D.S.H. and A.G.; project administration, P.A.B.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data analyzed within this article are considered secondary due to the study type (narrative review). Any inquiries regarding our data should be directed to the designated corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the institutional Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) linked to the Ministry of Education of Brazil.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Naka, N.; Ohsawa, M.; Tomita, Y.; Kanno, H.; Uchida, A.; Myoui, A.; Aozasa, K. Prognostic Factors in Angiosarcoma: A Multivariate Analysis of 55 Cases. J. Surg. Oncol. 1996, 61, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.S.T.; Lucci, C.M.; dos Santos, J.A.M.; Longo, J.P.F.; Muehlmann, L.A.; Azevedo, R.B. Photodynamic Therapy for Cutaneous Hemangiosarcoma in Dogs. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2019, 27, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnio, A.; Eleni, C.; Cocumelli, C.; Bartolomé Del Pino, L.E.; Simeoni, S.; Spallucci, V.; Scaramozzino, P. Evaluation of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Risk Factors for Dog Visceral Hemangiosarcoma: A Retrospective Case-Control Study Register-Based in Lazio Region, Italy. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 181, 105074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baretta, L.T.; De Oliveira Dhein, J.; Lupion, C.G.; Figueiredo, C.D.; Gerardi, D.G. Occurrence of Cutaneous Neoplasia in Dogs with Actinic Dermatitis in a Veterinary Medical Teaching Hospital—UFRGS, Brazil. Acta Sci. Vet. 2021, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, H.; Fox, L.E.; Calderwood-Mays, M.B.; Hammer, A.S.; Couto, C.G. Cutaneous Hemangiosarcoma in 25 Dogs: A Retrospective Study. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1994, 8, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Hoshi, K.; Hirakawa, A.; Chimura, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Machida, N. Epidemiological, Clinical and Pathological Features of Primary Cardiac Hemangiosarcoma in Dogs: A Review of 51 Cases. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendelburg, K.M.; Price, L.L.; Burgess, K.E.; Lyons, J.A.; Lew, F.H.; Berg, J. Survival Time of Dogs with Splenic Hemangiosarcoma Treated by Splenectomy with or without Adjuvant Chemotherapy: 208 Cases (2001–2012). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2015, 247, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Story, A.L.; Wavreille, V.; Abrams, B.; Egan, A.; Cray, M.; Selmic, L.E. Outcomes of 43 Small Breed Dogs Treated for Splenic Hemangiosarcoma. Vet. Surg. 2020, 49, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carloni, A.; Terragni, R.; Morselli-Labate, A.M.; Paninarova, M.; Graham, J.; Valenti, P.; Alberti, M.; Albarello, G.; Millanta, F.; Vignoli, M. Prevalence, Distribution, and Clinical Characteristics of Hemangiosarcoma-Associated Skeletal Muscle Metastases in 61 Dogs: A Whole Body Computed Tomographic Study. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, J.; Giuffrida, M.A.; Runge, J.J.; Balsa, I.M.; Culp, W.T.N.; Mayhew, P.D.; Steffey, M.; Epstein, S.E. Anatomic Site and Etiology of Hemorrhage in Small versus Large Dogs with Spontaneous Hemoperitoneum. Vet. Surg. 2018, 47, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, L.V.; Renwick, M.; Soh, R.W.Y.; Fan, N.R.; Tebb, A.J.; Indrawirawan, Y.H. Outcomes and Blood Product Use in 89 Surgically Managed and 79 Medically Managed Cases of Acute Spontaneous Hemoperitoneum in the Dog. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 736329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.E.; Liptak, J.M.; Gall, T.T.; Monteith, G.J.; Woods, J.P. Paul Woods Epirubicin in the Adjuvant Treatment of Splenic Hemangiosarcoma in Dogs: 59 Cases (1997–2004). JAVMA 2007, 231, 1550–1557. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama, A.; Poirier, V.J.; Mantovani, F.; Foster, R.A.; Mutsaers, A.J. Adjuvant Doxorubicin with or without Metronomic Cyclophosphamide for Canine Splenic Hemangiosarcoma. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2017, 53, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masyr, A.R.; Rendahl, A.K.; Winter, A.L.; Borgatti, A.; Modiano, J.F. Retrospective Evaluation of Thrombocytopenia and Tumor Stage as Prognostic Indicators in Dogs with Splenic Hemangiosarcoma. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2021, 258, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamerato-Kozicki, A.R.; Helm, K.M.; Jubala, C.M.; Cutter, G.C.; Modiano, J.F. Canine Hemangiosarcoma Originates from Hematopoietic Precursors with Potential for Endothelial Differentiation. Exp. Hematol. 2006, 34, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Graef, A.J.; Dickerson, E.B.; Modiano, J.F. Pathobiology of Hemangiosarcoma in Dogs: Research Advances and Future Perspectives. Vet. Sci. 2015, 2, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, B.D.C.; Torres, B.B.J.; Rodriguez, A.A.M.; Gamba, C.O.; Cassali, G.D.; Lavalle, G.E.; Martins, G.D.C.; Melo, E.G. Clinical and Pathological Aspects of Multicentric Hemangiosarcoma in a Pinscher Dog. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec. 2013, 65, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorden, B.H.; Kim, J.H.; Sarver, A.L.; Frantz, A.M.; Breen, M.; Lindblad-Toh, K.; O’Brien, T.D.; Sharkey, L.C.; Modiano, J.F.; Dickerson, E.B. Identification of Three Molecular and Functional Subtypes in Canine Hemangiosarcoma through Gene Expression Profiling and Progenitor Cell Characterization. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, K.S.; Graef, A.J.; Breen, M.; Lindblad-Toh, K.; Modiano, J.F.; Kim, J.H. Interactions between CXCR4 and CXCL12 Promote Cell Migration and Invasion of Canine Hemangiosarcoma. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2017, 15, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Frantz, A.M.; Anderson, K.L.; Graef, A.J.; Scott, M.C.; Robinson, S.; Sharkey, L.C.; O’Brien, T.D.; Dickerson, E.B.; Modiano, J.F. Interleukin-8 Promotes Canine Hemangiosarcoma Growth by Regulating the Tumor Microenvironment. Exp. Cell. Res. 2014, 323, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, E.J.; Stern, A.W.; Fox, R.J.; Dark, M.J. Understanding the Efficiency of Splenic Hemangiosarcoma Diagnosis Using Monte Carlo Simulations. Vet. Pathol. 2019, 56, 856–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tecilla, M.; Gambini, M.; Forlani, A.; Caniatti, M.; Ghisleni, G.; Roccabianca, P. Evaluation of Cytological Diagnostic Accuracy for Canine Splenic Neoplasms: An Investigation in 78 Cases Using STARD Guidelines. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flory, A.; Kruglyak, K.M.; Tynan, J.A.; McLennan, L.M.; Rafalko, J.M.; Fiaux, P.C.; Hernandez, G.E.; Marass, F.; Nakashe, P.; Ruiz-Perez, C.A.; et al. Clinical Validation of a Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Multi-Cancer Early Detection “Liquid Biopsy” Blood Test in over 1000 Dogs Using an Independent Testing Set: The CANcer Detection in Dogs (CANDiD) Study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson-Robles, H.M.; Bygott, T.; Kelly, T.K.; Miller, T.M.; Miller, P.; Matsushita, M.; Terrell, J.; Bougoussa, M.; Butera, T. Evaluation of Plasma Nucleosome Concentrations in Dogs with a Variety of Common Cancers and in Healthy Dogs. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarff, D. Solar (Actinic) Dermatoses in the Dog and Cat. Companion Anim. 2017, 22, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nóbrega, D.F.; Sehaber, V.F.; Madureira, R.; Bracarense, A.P.F.R.L. Canine Cutaneous Haemangiosarcoma: Biomarkers and Survival. J. Comp. Pathol. 2019, 166, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.S.; Rassnick, K.M.; Frimberger, A.E. Evaluation of Clinical and Histologic Factors Associated with Survival Time in Dogs with Stage II Splenic Hemangiosarcoma Treated by Splenectomy. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2017, 251, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyles, S.E.; Milner, R.J.; Kow, K.; Salute, M.E. In Vitro Effects of the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Masitinib Mesylate, on Canine Hemangiosarcoma Cell Lines. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2012, 10, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, H.L.; London, C.A.; Portela, R.A.; Nguyen, S.; Rosenberg, M.P.; Klein, M.K.; Clifford, C.; Thamm, D.H.; Vail, D.M.; Bergman, P.; et al. Maintenance Therapy with Toceranib Following Doxorubicin-Based Chemotherapy for Canine Splenic Hemangiosarcoma. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.E.; Colyer, A.; Haydock, R.M.; Hayek, M.G.; Park, J. Understanding How Dogs Age: Longitudinal Analysis of Markers of Inflammation, Immune Function, and Oxidative Stress. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2018, 73, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Campos, C.B.; Lavalle, G.E.; Monteiro, L.N.; Arantes Pêgas, G.R.; Fialho, S.L.; Balabram, D.; Cassali, G.D. Adjuvant Thalidomide and Metronomic Chemotherapy for the Treatment of Canine Malignant Mammary Gland Neoplasms. In Vivo (Brooklyn) 2018, 32, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treggiari, E.; Borrego, J.F.; Gramer, I.; Valenti, P.; Harper, A.; Finotello, R.; Toni, C.; Laomedonte, P.; Romanelli, G. Retrospective Comparison of First-Line Adjuvant Anthracycline vs Metronomic-Based Chemotherapy Protocols in the Treatment of Stage I and II Canine Splenic Haemangiosarcoma. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2020, 18, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finotello, R.; Stefanello, D.; Zini, E.; Marconato, L. Comparison of Doxorubicin–Cyclophosphamide with Doxorubicin–Dacarbazine for the Adjuvant Treatment of Canine Hemangiosarcoma. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2017, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, J.P.; Munday, J.S. Thalidomide Reduces Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Immunostaining in Canine Splenic Hemangiosarcoma. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musser, M.L.; Coto, G.M.; Lingnan, Y.; Mochel, P.; Johannes, C.M. Pilot Safety Evaluation of Doxorubicin Chemotherapy Combined with Non-Specific Immunotherapy (Immunocidin®) for Canine Splenic Hemangiosarcoma. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0279594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucroy, M.D.; Clauson, R.M.; Suckow, M.A.; El-Tayyeb, F.; Kalinauskas, A. Evaluation of an Autologous Cancer Vaccine for the Treatment of Metastatic Canine Hemangiosarcoma: A Preliminary Study. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konduri, V.; Halpert, M.M.; Baig, Y.C.; Coronado, R.; Rodgers, J.R.; Levitt, J.M.; Cerroni, B.; Piscoya, S.; Wilson, N.; DiBernardi, L.; et al. Dendritic Cell Vaccination plus Low-Dose Doxorubicin for the Treatment of Spontaneous Canine Hemangiosarcoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2019, 26, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulhaber, E.A.; Janik, E.; Thamm, D.H. Adjuvant Carboplatin for Treatment of Splenic Hemangiosarcoma in Dogs: Retrospective Evaluation of 18 Cases (2011-2016) and Comparison with Doxorubicin-Based Chemotherapy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 1929–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedney, A.; Salah, P.; Mahoney, J.A.; Krick, E.; Martins, R.; Scavello, H.; Lenz, J.A.; Atherton, M.J. Evaluation of the Anti-Tumour Activity of Coriolus Versicolor Polysaccharopeptide (I’m-Yunity) Alone or in Combination with Doxorubicin for Canine Splenic Hemangiosarcoma. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2022, 20, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.; Ehrhart, E.J.; Stewart, S.; Zismann, V.; Cawley, J.; Halperin, R.; Briones, N.; Richter, K.; Sivaprakasam, K.; Perdigones, N.; et al. Genomic Landscapes of Canine Splenic Angiosarcoma (Hemangiosarcoma) Contain Extensive Heterogeneity within and between Patients. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaihati, B.A.; Ho, K.L.; Watson, J.; Feng, Y.; Wang, T.; Dobbin, K.K.; Zhao, S. Canine Tumor Mutational Burden Is Correlated with TP53 Mutation across Tumor Types and Breeds. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Rodrigues, L.; Post, G.; Harvey, G.; White, M.; Miller, A.; Lambert, L.; Lewis, B.; Lopes, C.; Zou, J. Analyses of Canine Cancer Mutations and Treatment Outcomes Using Real-World Clinico-Genomics Data of 2119 Dogs. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2023, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wu, M.; Durham, A.C.; Radaelli, E.; Mason, N.J.; Xu, X.W.; Roth, D.B. Molecular Subtypes in Canine Hemangiosarcoma Reveal Similarities with Human Angiosarcoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Megquier, K.; Thomas, R.; Sarver, A.L.; Song, J.M.; Kim, Y.T.; Cheng, N.; Schulte, A.J.; Linden, M.A.; Murugan, P.; et al. Genomically Complex Human Angiosarcoma and Canine Hemangiosarcoma Establish Convergent Angiogenic Transcriptional Programs Driven by Novel Gene Fusions. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 847–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neganova, M.E.; Klochkov, S.G.; Aleksandrova, Y.R.; Aliev, G. Histone Modifications in Epigenetic Regulation of Cancer: Perspectives and Achieved Progress. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 83, 452–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Aoshima, K.; Yamazaki, J.; Kobayashi, A.; Kimura, T. Manipulating Histone Acetylation Leads to Antitumor Effects in Hemangiosarcoma Cells. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2022, 20, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, R.; Borst, L.; Rotroff, D.; Motsinger-Reif, A.; Lindblad-Toh, K.; Modiano, J.F.; Breen, M. Genomic Profiling Reveals Extensive Heterogeneity in Somatic DNA Copy Number Aberrations of Canine Hemangiosarcoma. Chromosom. Res. 2014, 22, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penel, N.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Bal-Mahieu, C.; Chevreau, C.; Le Cesne, A.; Italiano, A.; Bompas, E.; Clisant, S.; Baldeyrou, B.; Lansiaux, A.; et al. Low Level of Baseline Circulating VEGF-A Is Associated with Better Outcome in Patients with Vascular Sarcomas Receiving Sorafenib: An Ancillary Study from a Phase II Trial. Target Oncol. 2014, 9, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Zhang, D.; Hu, W.; Xie, Z.; Du, Q.; Xia, Q.; Wen, T.; Jia, H. Aberrant PTEN, PIK3CA, PMAPK, and TP53 Expression in Human Scalp and Face Angiosarcoma. Medicine 2021, 100, e26779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conciatori, F.; Bazzichetto, C.; Falcone, I.; Ciuffreda, L.; Ferretti, G.; Vari, S.; Ferraresi, V.; Cognetti, F.; Milella, M. Pten Function at the Interface between Cancer and Tumor Microenvironment: Implications for Response to Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, A.; Pandolfi, P.P. The PTEN–PI3K Axis in Cancer. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamburini, B.A.; Trapp, S.; Phang, T.L.; Schappa, J.T.; Hunter, L.E.; Modiano, J.F. Gene Expression Profiles of Sporadic Canine Hemangiosarcoma Are Uniquely Associated with Breed. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wu, M.; Maloneyhuss, M.A.; Wojcik, J.; Durham, A.C.; Mason, N.J.; Roth, D.B. Actionable Mutations in Canine Hemangiosarcoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clendaniel, D.C.; Sivacolundhu, R.K.; Sorenmo, K.U.; Donovan, T.A.; Turner, A.; Arteaga, T.; Bergman, P.J. Association between Macroscopic Appearance of Liver Lesions and Liver Histology in Dogs with Splenic Hemangiosarcoma: 79 Cases (2004–2009). J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2014, 50, e6–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batschinski, K.; Nobre, A.; Vargas-Mendez, E.; Tedardi, M.V.; Cirillo, J.; Cestari, G.; Ubukata, R.; Dagli, M.L.Z. Canine Visceral Hemangiosarcoma Treated with Surgery Alone or Surgery and Doxorubicin: 37 Cases (2005–2014). Can. Vet. J. 2018, 59, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- García-Iglesias, M.J.; Cuevas-Higuera, J.L.; Bastida-Sáenz, A.; De Garnica-García, M.G.; Polledo, L.; Perero, P.; González-Fernández, J.; Fernández-Martínez, B.; Pérez-Martínez, C. Immunohistochemical Detection of P53 and Pp53 Ser392in Canine Hemangiomas and Hemangiosarcomas Located in the Skin. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, K.L.; Bryan, M.E.; Atkinson, E.S.; Keeler, M.R.; Hahn, A.W.; Bryan, J.N. Neutering Is Associated with Developing Hemangiosarcoma in Dogs in the Veterinary Medical Database: An Age and Time-Period Matched Case-Control Study (1964–2003). Can. Vet. J. 2020, 61, 499–504. [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood, J.M.; Haynes, A.M.; Klocke, E.; Higginbotham, M.L.; Thomson, E.M.; Weng, H.Y.; Millard, H.A.T. Occurrence and Clinicopathologic Features of Splenic Neoplasia Based on Body Weight: 325 Dogs (2003–2013). J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2016, 52, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres de la Riva, G.; Hart, B.L.; Farver, T.B.; Oberbauer, A.M.; Messam, L.L.M.V.; Willits, N.; Hart, L.A. Neutering Dogs: Effects on Joint Disorders and Cancers in Golden Retrievers. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 55937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, B.L.; Hart, L.A.; Thigpen, A.P.; Willits, N.H. Neutering of German Shepherd Dogs: Associated Joint Disorders, Cancers and Urinary Incontinence. Vet. Med. Sci. 2016, 2, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, M.; Ochiai, K.; Michishita, M.; Morimatsu, M.; Sakai, H.; Kinoshita, N.; Sakaue, M.; Onozawa, E.; Azakami, D.; Yamamoto, M.; et al. In Vitro Anticancer Effects of Alpelisib against PIK3CA-mutated Canine Hemangiosarcoma Cell Lines. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 47, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igase, M.; Fujiki, N.; Shibutani, S.; Sakai, H.; Noguchi, S.; Nemoto, Y.; Mizuno, T. Tenovin-6 Induces the SIRT-Independent Cell Growth Suppression and Blocks Autophagy Flux in Canine Hemangiosarcoma Cell Lines. Exp. Cell. Res. 2020, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megquier, K.; Turner-Maier, J.; Swofford, R.; Kim, J.H.; Sarver, A.L.; Wang, C.; Sakthikumar, S.; Johnson, J.; Koltookian, M.; Lewellen, M.; et al. Comparative Genomics Reveals Shared Mutational Landscape in Canine Hemangiosarcoma and Human Angiosarcoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 2410–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, E.B.; Thomas, R.; Fosmire, S.P.; Lamerato-Kozicki, A.R.; Bianco, S.R.; Wojcieszyn, J.W.; Breen, M.; Helfand, S.C.; Modiano, J.F. Mutations of Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog Deleted from Chromosome 10 in Canine Hemangiosarcoma. Vet. Pathol. 2005, 42, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.; Ludwig, L.; Krijgsman, O.; Adams, D.J.; Wood, G.A.; Van Der Weyden, L. Comparison of the Oncogenomic Landscape of Canine and Feline Hemangiosarcoma Shows Novel Parallels with Human Angiosarcoma. DMM Dis. Models Mechan. 2021, 14, dmm049044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasbullah, H.H.; Musa, M. Gene Therapy Targeting P53 and Kras for Colorectal Cancer Treatment: A Myth or the Way Forward? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.W.; Li, L.; Li, D.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, M.J.; Chandler, L.A.; Lin, H.; et al. The First Approved Gene Therapy Product for Cancer Ad-P53 (Gendicine): 12 Years in the Clinic. Hum. Gene Ther. 2018, 29, 160–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igase, M.; Inanaga, S.; Tani, K.; Nakaichi, M.; Sakai, Y.; Sakurai, M.; Kato, M.; Tsukui, T.; Mizuno, T. Long-term Survival of Dogs with Stage 4 Oral Malignant Melanoma Treated with Anti-canine Therapeutic Antibody: A Follow-up Case Report. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2022, 20, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelyushin, S.; Ranninger, E.; Guerrera, D.; Hutter, G.; Maake, C.; Markkanen, E.; Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R.; Bley, C.R.; Läubli, H.; Vom Berg, J. Cross-Reactivity and Functionality of Approved Human Immune Checkpoint Blockers in Dogs. Cancers 2021, 13, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, M.; Nie, H.; Yuan, Y. PD-1 and PD-L1 in Cancer Immunotherapy: Clinical Implications and Future Considerations. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2019, 15, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boston, S.E.; Lu, X.; Culp, W.T.N.; Montinaro, V.; Romanelli, G.; Dudley, R.M.; Liptak, J.M.; Mestrinho, L.A.; Buracco, P. Efficacy of Systemic Adjuvant Therapies Administered to Dogs after Excision of Oral Malignant Melanomas: 151 Cases (2001–2012). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2014, 245, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cawley, J.R.; Stewart, S.D.; Mochel, J.P.; Veluvolu, S.; Khanna, C.; Fenger, J.M. Pharmacokinetic Exposures Associated With Oral Administration of Sorafenib in Dogs With Spontaneous Tumors. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 888483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marconato, L.; Sabattini, S.; Marisi, G.; Rossi, F.; Leone, V.F.; Casadei-Gardini, A. Sorafenib for the Treatment of Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Preliminary Toxicity and Activity Data in Dogs. Cancers 2020, 12, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foskett, A.; Manley, C.; Naramore, R.; Gordon, I.; Stewart, B.; Khanna, C. Tolerability of Oral Sorafenib in Pet Dogs with a Diagnosis of Cancer. Vet. Med. Res. Rep. 2017, 8, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murase, Y.; Hosoya, K.; Sato, T.; Kim, S.; Okumura, M. Antitumor Activity of the Dual PI3K/MTOR Inhibitor Gedatolisib and the Involvement of ABCB1 in Gedatolisib Resistance in Canine Tumor Cells. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 47, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.D.; Wilson, T.G.; Hanna, A.; Dabjan, M.; Buelow, K.; Torma, J.; Marples, B.; Galoforo, S. Dacomitinib and Gedatolisib in Combination with Fractionated Radiation in Head and Neck Cancer. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 26, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xing, W.; Yu, H.; Zhang, W.; Si, T. ABCB1 and ABCG2 Restricts the Efficacy of Gedatolisib (PF-05212384), a PI3K Inhibitor in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, A. Alpelisib: First Global Approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, I.A.; Hood, F.E.; Hartley, J.L. The Frequency of Ras Mutations in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 2669–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usher, S.G.; Radford, A.D.; Villiers, E.J.; Blackwood, L. RAS, FLT3, and C-KIT Mutations in Immunophenotyped Canine Leukemias. Exp. Hematol. 2009, 37, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Liu, W.W.; Nie, W.J.; Li, D.F.; Xie, Z.J.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.H.; Mei, P.; Li, Z.J. MiR-21/RASA1 Axis Affects Malignancy of Colon Cancer Cells via RAS Pathways. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 1488–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, H.; Breen, M. Sequence Analysis of RAS and RAF Mutation Hot Spots in Canine Carcinoma. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2017, 15, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr, B.; Schaffner, G.; Reifinger, M. K-Ras Mutations in Canine Pancreatic Cancers. Vet. Rec. 2003, 153, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffey, S.M.; Kraegel, S.A.; Madewell, B.R. Rapid Detection of K-Ras Gene Mutations in Canine Lung Cancer Using Single-Strand Conformational Polymorphism Analysis. Carcinogenesis 1998, 19, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degirmenci, U.; Wang, M.; Hu, J. Targeting Aberrant RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK Signaling for Cancer Therapy. Cells 2020, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Su, B.; Xu, H.; Sun, Y.; Sun, P.; Li, R.; Peng, X.; Cai, J. Role of RASA1 in Cancer: A Review and Update (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 2386–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Zheng, S.; Zou, Y.; Yang, A.; Xie, X.; Tang, H.; Xie, X. CircAHNAK1 Inhibits Proliferation and Metastasis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer by Modulating MiR-421 and RASA1. Aging 2019, 11, 12043–12056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottier, C.; Fresnais, M.; Gilon, M.; Jérusalem, G.; Longuespée, R.; Sounni, N.E. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Cancer: Breakthrough and Challenges of Targeted Therapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, J.; Ma, L.; Shan, J.; Shen, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Yao, C.; Qian, C. MicroRNA-122 Confers Sorafenib Resistance to Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Targeting IGF-1R to Regulate RAS/RAF/ERK Signaling Pathways. Cancer Lett. 2016, 371, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, N.J.; Nickoloff, B.J.; Dykema, K.J.; Boguslawski, E.A.; Krivochenitser, R.I.; Froman, R.E.; Dawes, M.J.; Baker, L.H.; Thomas, D.G.; Kamstock, D.A.; et al. Pharmacologic Inhibition of MEK Signaling Prevents Growth of Canine Hemangiosarcoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1701–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signorelli, J.; Shah Gandhi, A. Cobimetinib: A Novel MEK Inhibitor for Metastatic Melanoma. Ann. Pharmacother. 2017, 51, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.L.; Arenas, A.; Ortiz-Ruiz, A.; Leivas, A.; Rapado, I.; Rodríguez-García, A.; Castro, N.; Zagorac, I.; Quintela-Fandino, M.; Gómez-López, G.; et al. MEK Inhibition Enhances the Response to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cathomas, G. PIK3CA in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arafeh, R.; Samuels, Y. PIK3CA in Cancer: The Past 30 Years. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, A.; Asa, S.A.; Kodama, A.; Hirata, A.; Yanai, T.; Sakai, H. Constitutive Phosphorylation of the MTORC2/Akt/4E-BP1 Pathway in Newly Derived Canine Hemangiosarcoma Cell Lines. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langdon, S.P.; Kay, C.; Um, I.H.; Dodds, M.; Muir, M.; Sellar, G.; Kan, J.; Gourley, C.; Harrison, D.J. Evaluation of the Dual MTOR/PI3K Inhibitors Gedatolisib (PF-05212384) and PF-04691502 against Ovarian Cancer Xenograft Models. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyuen, A.A.; Meuten, T.; Rose, B.J.; Thamm, D.H. In Vitro Effects of PI3K/MTOR Inhibition in Canine Hemangiosarcoma. PLoS ONE 2022, 13, e0200634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, K.; Okada, J.; Timmerman, L.; Rodriguez-Viciana, P.; Stokoe, D.; Shoji, K.; Taketani, Y.; Kuramoto, H.; Knight, Z.A.; Shokat, K.M.; et al. PIK3CA Cooperates with Other Phosphatidylinositol 3′-Kinase Pathway Mutations to Effect Oncogenic Transformation. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8127–8136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Seung, B.J.; Cho, S.H.; Lim, H.Y.; Bae, M.K.; Sur, J.H. Dysregulation of Pi3k/Akt/Pten Pathway in Canine Mammary Tumor. Animals 2021, 11, 2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wei, J.; Liu, P. Attacking the PI3K/Akt/MTOR Signaling Pathway for Targeted Therapeutic Treatment in Human Cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 85, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaspishvili, T.; Berman, D.M.; Ross, A.E.; Scher, H.I.; De Marzo, A.M.; Squire, J.A.; Lotan, T.L. Clinical Implications of PTEN Loss in Prostate Cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2018, 15, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Garcia, V.; Tawil, Y.; Wise, H.M.; Leslie, N.R. Mechanisms of PTEN Loss in Cancer: It’s All about Diversity. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, C.; Lin, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. Expression and Significance of PTEN in Canine Mammary Gland Tumours. Res. Vet. Sci. 2008, 85, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyeth Pharmaceuticals. TORISELTMKit (Temsirolimus). U.S Patent No. 5,362,718, 2 January 2007.
- Motzer, R.J.; Escudier, B.; Oudard, S.; Hutson, T.E.; Porta, C.; Bracarda, S.; Grünwald, V.; Thompson, J.A.; Figlin, R.A.; Hollaender, N.; et al. Efficacy of Everolimus in Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Phase III Trial. Lancet 2008, 372, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, C.; Lee, J.; Rha, S.Y.; Park, K.H.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, K.H.; Ahn, J.H. Multicenter Phase II Study of Everolimus in Patients with Metastatic or Recurrent Bone and Soft-Tissue Sarcomas after Failure of Anthracycline and Ifosfamide. Invest. New Drugs 2013, 31, 1602–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michishita, M.; Ochiai, K.; Nakahira, R.; Azakami, D.; Machida, Y.; Nagashima, T.; Nakagawa, T.; Ishiwata, T. MTOR Pathway as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Cancer Stem Cells in Canine Mammary Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1100602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, A.K.; Mazcko, C.N.; Cherukuri, A.; Berger, E.P.; Kisseberth, W.C.; Brown, M.E.; Lana, S.E.; Weishaar, K.; Flesner, B.K.; Bryan, J.N.; et al. Adjuvant Sirolimus Does Not Improve Outcome in Pet Dogs Receiving Standard-of-Care Therapy for Appendicular Osteosarcoma: A Prospective, Randomized Trial of 324 Dogs. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 3005–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, A.; Horta, R.S.; Vieira, R.A.M.; Hume, K.R.; Dobson, J. Repurposing Drugs in Small Animal Oncology Repurposing Drugs in Small Animal Oncology. Animals 2023, 13, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marei, H.E.; Althani, A.; Afifi, N.; Hasan, A.; Caceci, T.; Pozzoli, G.; Morrione, A.; Giordano, A.; Cenciarelli, C. p53 Signaling in Cancer Progression and Therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunbar, C.E.; High, K.A.; Joung, J.K.; Kohn, D.B.; Ozawa, K.; Sadelain, M. Gene Therapy Comes of Age. Science 2018, 359, eaan4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Simon, M.; Seluanov, A.; Gorbunova, V. DNA Damage and Repair in Age-Related Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargen, M.R.; Merrill, S.L.; Chu, E.Y.; Nathanson, K.L. CDKN2A Mutations with P14 Loss Predisposing to Multiple Nerve Sheath Tumours, Melanoma, Dysplastic Naevi and Internal Malignancies: A Case Series and Review of the Literature. British J. Dermatol. 2016, 175, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Choi, B.Y.; Lee, M.H.; Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z. Implications of Genetic and Epigenetic Alterations of CDKN2A (P16INK4a) in Cancer. EBioMedicine 2016, 8, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicenas, J.; Kvederaviciute, K.; Meskinyte, I.; Meskinyte-Kausiliene, E.; Skeberdyte, A. KRAS, TP53, CDKN2A, SMAD4, BRCA1, and BRCA2 Mutations in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.I.; Zoumberos, N.A.; Johnson, B.; Rhodes, D.R.; Tomlins, S.A.; Chan, M.P.; Andea, A.A.; Lucas, D.R.; McHugh, J.B.; Smith, N.; et al. A Genomic Survey of Sarcomas on Sun-Exposed Skin Reveals Distinctive Candidate Drivers and Potentially Targetable Mutations. Hum. Pathol. 2020, 102, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, L.P.; Albers, J.; Hejhal, T.; Pfundstein, S.; Gonçalves, A.F.; Catalano, A.; Wild, P.J.; Frew, I.J. Mouse Genetic Background Influences Whether Hras G12V Expression plus Cdkn2a Knockdown Causes Angiosarcoma or Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 19753–19766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melincovici, C.S.; Boşca, A.B.; Şuşman, S.; Mărginean, M.; Mihu, C.; Istrate, M.; Moldovan, I.-M.; Roman, A.L.; Mihu, C.M. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)-Key Factor in Normal and Pathological Angiogenesis. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2018, 59, 455–467. [Google Scholar]
- Nejad, A.E.; Najafgholian, S.; Rostami, A.; Sistani, A.; Shojaeifar, S.; Esparvarinha, M.; Nedaeinia, R.; Haghjooy Javanmard, S.; Taherian, M.; Ahmadlou, M.; et al. The Role of Hypoxia in the Tumor Microenvironment and Development of Cancer Stem Cell: A Novel Approach to Developing Treatment. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.; Han, J.; Li, W.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, S.; Zeng, C.; et al. FOXP3 Inhibits Angiogenesis by Downregulating VEGF in Breast Cancer. Cell. Death Dis. 2018, 9, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R.J.; Woll, P.J. Anti-Angiogenic Therapies for the Treatment of Angiosarcoma: A Clinical Update. Mag. Eur. Med. Oncol. 2017, 10, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, P.S.; Wallin, J.J.; Mancao, C. Predictive Markers of Anti-VEGF and Emerging Role of Angiogenesis Inhibitors as Immunotherapeutics. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 52, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda-Otsuka, S.; Kajihara, I.; Tasaki, Y.; Yamada-Kanazawa, S.; Sakamoto, R.; Sawamura, S.; Masuzawa, M.; Masuzawa, M.; Amoh, Y.; Hoshina, D.; et al. Hypoxia Accelerates the Progression of Angiosarcoma through the Regulation of Angiosarcoma Cells and Tumor Microenvironment. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2019, 93, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschetta, M.G.; Maschio, L.B.; Jardim-Perassi, B.V.; Gelaleti, G.B.; Lopes, J.R.; Leonel, C.; Do Nascimento Goncalves, N.; Ferreira, L.C.; Martins, G.R.; Borin, T.F.; et al. Prognostic Value of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α in Canine Malignant Mammary Tumors. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2345–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, X.; Peng, M.; Liu, Y.; Mo, Y.; Ren, D.; Hua, Y.; Yu, B.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Mechanisms of Vasculogenic Mimicry in Hypoxic Tumor Microenvironments. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.C.; Lebedev, A.; Aten, E.; Madsen, K.; Marciano, L.; Kolb, H.C. The Clinical Importance of Assessing Tumor Hypoxia: Relationship of Tumor Hypoxia to Prognosis and Therapeutic Opportunities. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 1516–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahremani, M.F.; Radaelli, E.; Haigh, K.; Bartunkova, S.; Haenebalcke, L.; Marine, J.C.; Goossens, S.; Haigh, J.J. Loss of Autocrine Endothelial-Derived VEGF Significantly Reduces Hemangiosarcoma Development in Conditional P53-Deficient Mice. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 1502–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, M.; Hoshino, Y.; Izumi, Y.; Takagi, S. Immunohistochemical Detection of a Potential Molecular Therapeutic Target for Canine Hemangiosarcoma. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2016, 78, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebellec, L.; Bertucci, F.; Tresch-Bruneel, E.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Le Cesne, A.; Bompas, E.; Blay, J.Y.; Italiano, A.; Mir, O.; Ryckewaert, T.; et al. Prognostic and Predictive Factors for Angiosarcoma Patients Receiving Paclitaxel Once Weekly plus or Minus Bevacizumab: An Ancillary Study Derived from a Randomized Clinical Trial. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, G.A. Juliana Alvares Duarte Bonini Campos; Daniel Soares Sanches; Maria Lúcia Zaidan Dagli; Julia Maria Matera Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) in Splenic Hemangiomas and Hemangiosarcomas in Dogs. Open J. Vet. Med. 2012, 2, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, J.; He, C.; Fang, M. Angiosarcoma: A Review of Diagnosis and Current Treatment. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 2303–2313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sturm, E.C.; Marasco, I.S.; Katz, S.C. Multidisciplinary Management of Angiosarcoma—A Review. J. Surg. Res. 2021, 257, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verganti, S.; Berlato, D.; Blackwood, L.; Amores-Fuster, I.; Polton, G.A.; Elders, R.; Doyle, R.; Taylor, A.; Murphy, S. Use of Oncept Melanoma Vaccine in 69 Canine Oral Malignant Melanomas in the UK. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2017, 58, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, J.C.C.; MacIel, M.C.; Ferrari, H.A.; Gonçalves, J.M.; Sasaki, B.R.S.; Cintra, A.A.; Durán, N.; Billis, A.; Fávaro, W.J. Safety and Efficacy of OncoTherad Nano-Immunotherapy in Patients with Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1953, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böckelmann, P.K.; Tizziani, S.H.S.; Durán, N.; Fávaro, W.J. New Therapeutic Perspective for Bladder Cancer in Dogs: Toxicological and Clinical Effects of OncoTherad Nanostructured Immunotherapy. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1323, 012022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, N.; Dias, Q.C.; Fávaro, W.J. OncoTherad: A New Nanobiological Response Modifier, Its Toxicological and Anticancer Activities. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1323, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhea, L.P.; Mendez-Marti, S.; Kim, D.; Aragon-Ching, J.B. Role of Immunotherapy in Bladder Cancer. Cancer Treat Res. Commun. 2021, 26, 100296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulay, K.C.M.; Aoshima, K.; Maekawa, N.; Suzuki, T.; Konnai, S.; Kobayashi, A.; Kimura, T. Hemangiosarcoma Cells Induce M2 Polarization and PD-L1 Expression in Macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, N.; Konnai, S.; Okagawa, T.; Nishimori, A.; Ikebuchi, R.; Izumi, Y.; Takagi, S.; Kagawa, Y.; Nakajima, C.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. Immunohistochemical Analysis of PD-L1 Expression in Canine Malignant Cancers and PD-1 Expression on Lymphocytes in Canine Oral Melanoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, I.B.; Tibo, L.H.S.; de Souza, B.R.; Durán, N.; Fávaro, W.J. OncoTherad® Is an Immunomodulator of Biological Response That Downregulate RANK/RANKL Signaling Pathway and PD-1/PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint in Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).