Antitumor Effects of Esculetin, a Natural Coumarin Derivative, against Canine Mammary Gland Tumor Cells by Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell culture and Reagents
2.2. Crystal Violet Staining
2.3. 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) Assay
2.4. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Release Assay
2.5. In Vitro Scratch Migration Assay
2.6. Annexin-V/Propidium Iodide (PI) Staining
2.7. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase dUTP Nick end-Labeling (TUNEL) Assay
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
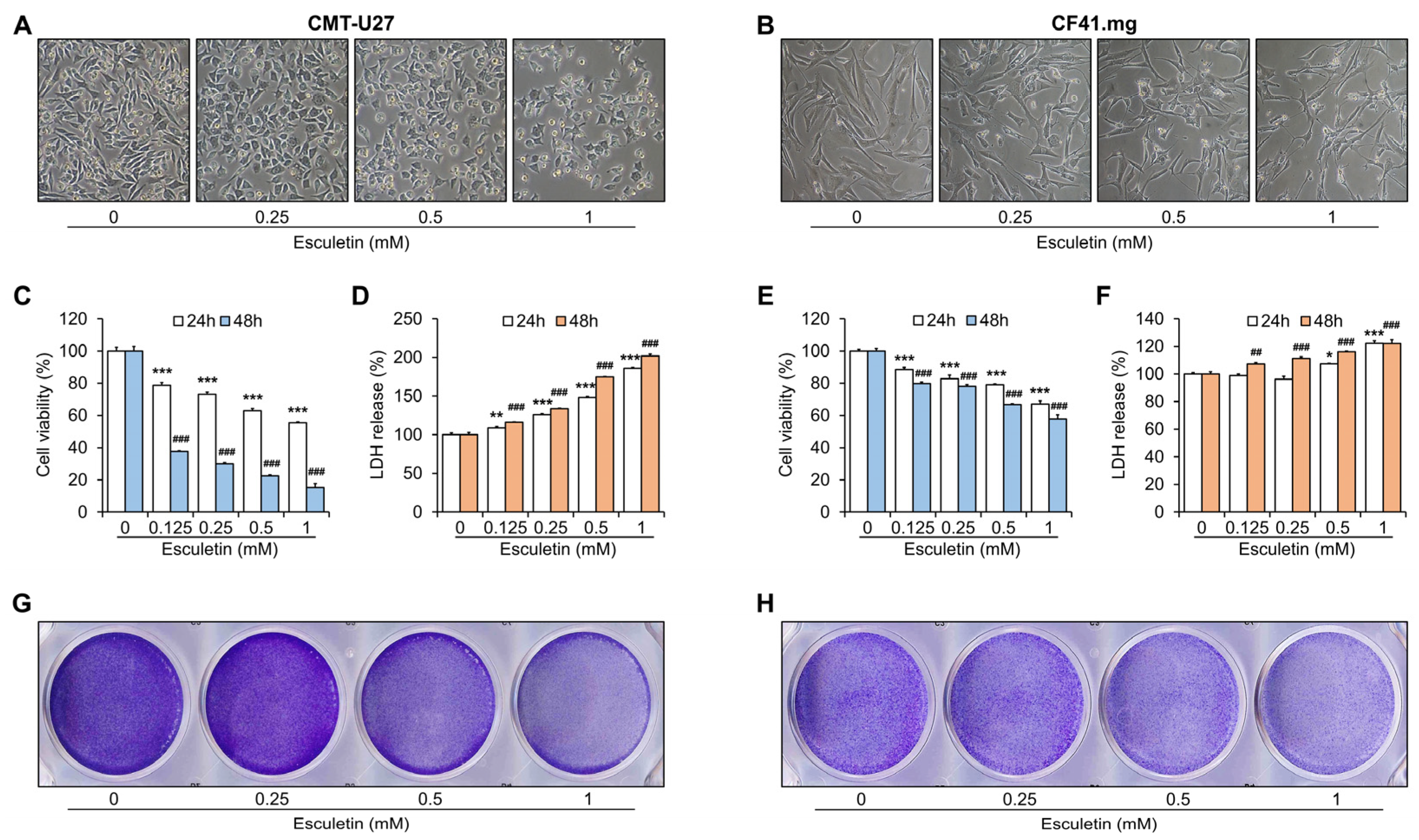
3.1. Esculetin Exerts Cytotoxic Effects on CMT Cells
3.2. Esculetin Suppresses Cell Migration in CMT Cells
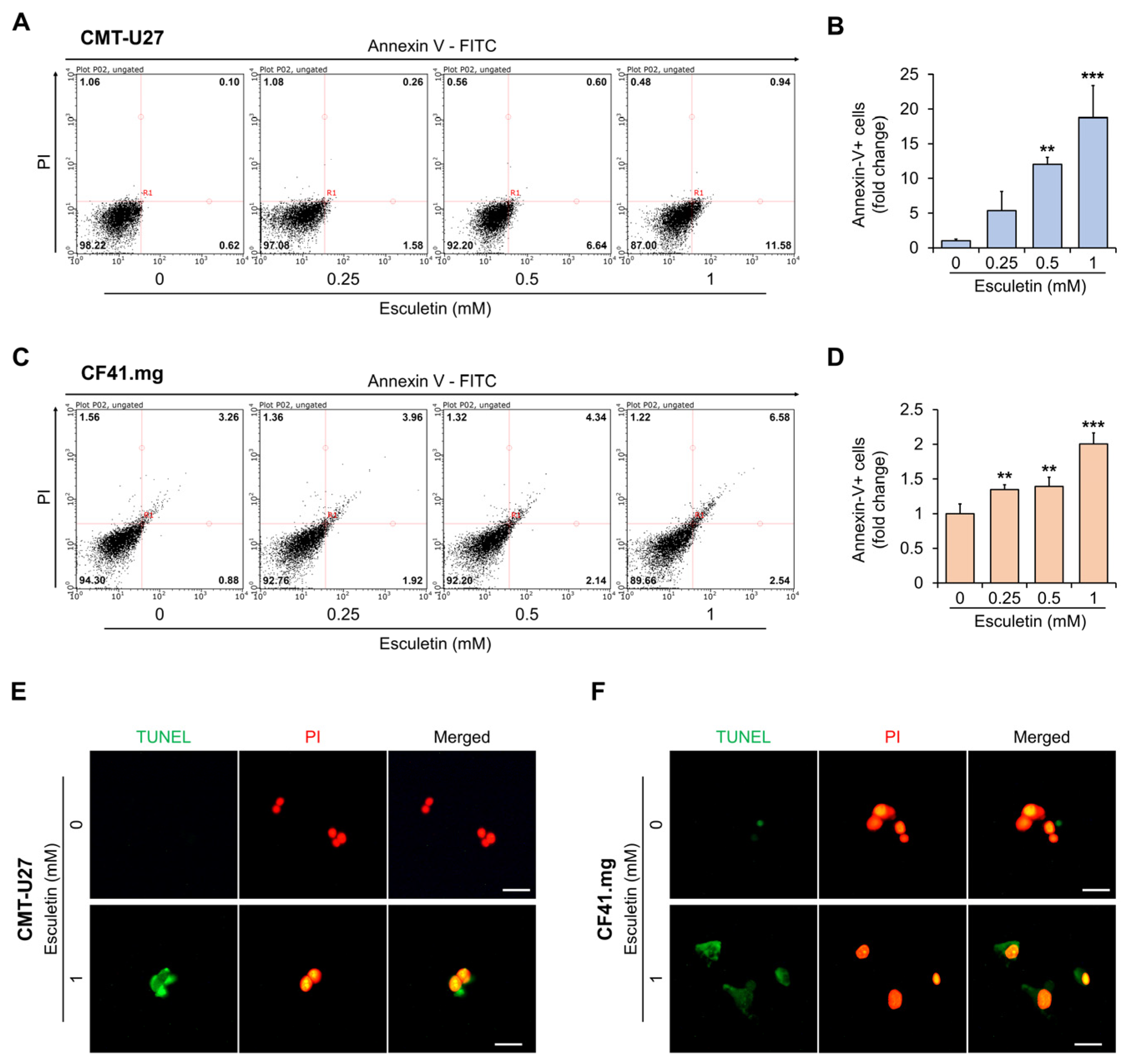
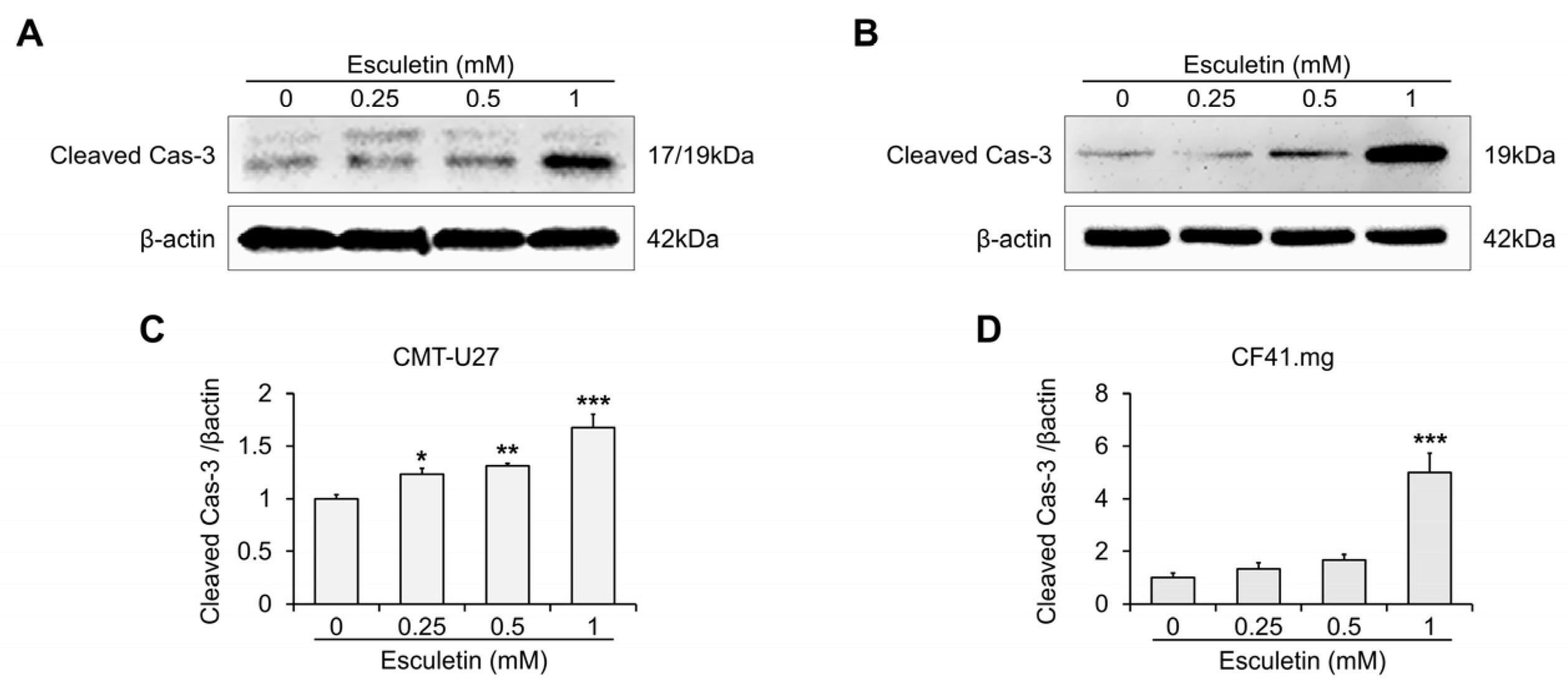
3.3. Esculetin Cause Apoptosis Via Caspase-3 Activation in CMT Cells
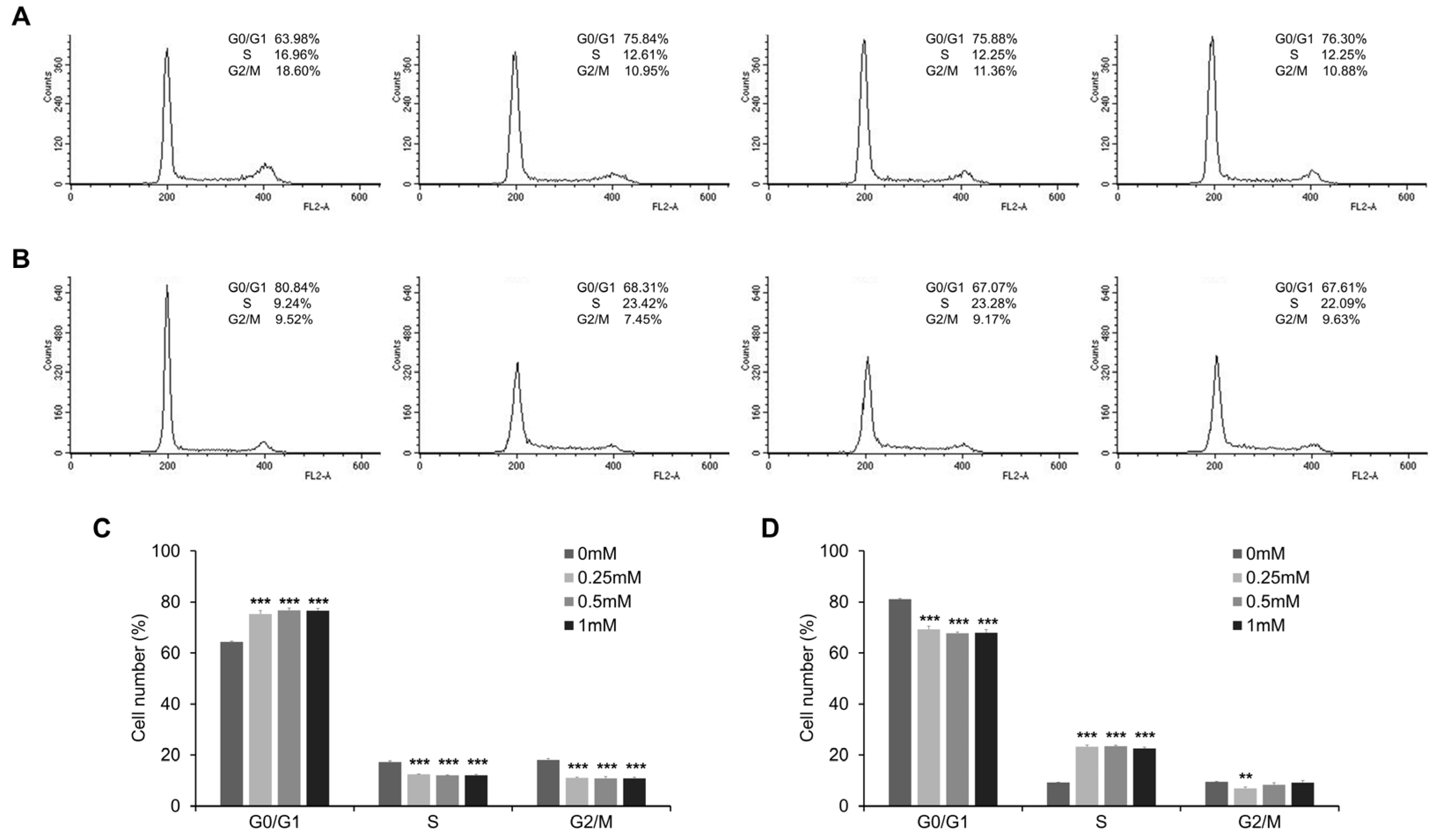
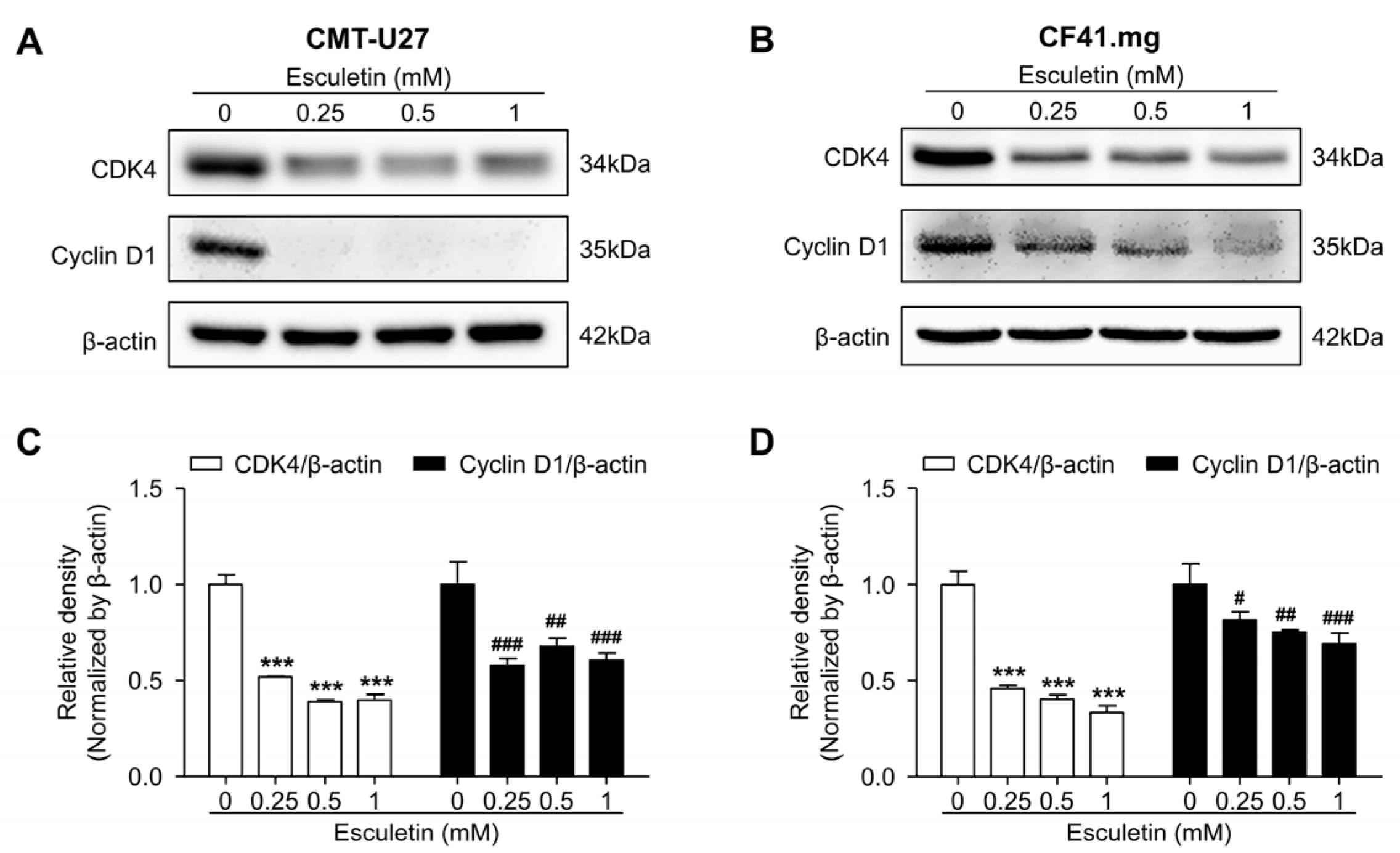
3.4. Esculetin Promotes Cell Cycle Arrest and Regulate Cell Cycle Related Proteins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burrai, G.P.; Gabrieli, A.; Moccia, V.; Zappulli, V.; Porcellato, I.; Brachelente, C.; Pirino, S.; Polinas, M.; Antuofermo, E. A Statistical Analysis of Risk Factors and Biological Behavior in Canine Mammary Tumors: A Multicenter Study. Animals 2020, 10, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.H.; Du, C.T.; Yu, C.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Huang, R.L.; Tang, X.Y.; Xie, G.H. Epidemiological Investigation of Canine Mammary Tumors in Mainland China Between 2017 and 2021. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 843390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratmann, N.; Failing, K.; Richter, A.; Wehrend, A. Mammary tumor recurrence in bitches after regional mastectomy. Vet. Surg. 2008, 37, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misdorp, M. Tumor of the mammary gland. In Tumors in Domestic Animals 4th; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso-Miguel, D.; Valdivia, G.; Guerrera, D.; Perez-Alenza, M.D.; Pantelyushin, S.; Alonso-Diez, A.; Beiss, V.; Fiering, S.; Steinmetz, N.F.; Suarez-Redondo, M.; et al. Neoadjuvant in situ vaccination with cowpea mosaic virus as a novel therapy against canine inflammatory mammary cancer. J. ImmunoTherapy Cancer 2022, 10, e004044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Sabattini, S.; Vascellari, M.; Marconato, L. The impact of toceranib, piroxicam and thalidomide with or without hypofractionated radiation therapy on clinical outcome in dogs with inflammatory mammary carcinoma. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2018, 16, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Kim, Y.-S.; An, J.-H.; Kwon, J.-A.; Han, S.-H.; Song, W.-J.; Youn, H.-Y. Anti-tumor effects of rivoceranib against canine melanoma and mammary gland tumour in vitro and in vivo mouse xenograft models. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturriaga, M.P.; Paredes, R.; Arias, J.I.; Torres, C.G. Meloxicam decreases the migration and invasion of CF41. Mg canine mammary carcinoma cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 2198–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneau, A.L.; Rico, C.; Boerboom, D.; Paquet, M. Statins downregulate YAP and TAZ and exert anti-cancer effects in canine mammary tumour cells. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2021, 20, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azab, A.; Nassar, A.; Azab, A.N. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Natural Products. Molecules 2016, 21, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.P.; Li, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhou, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J.J.; Li, H.B. Natural Antioxidants in Foods and Medicinal Plants: Extraction, Assessment and Resources. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijo, P.; Pešić, M.; Fernandes, A.S.; Santos, C.N. Natural Products: Optimizing Cancer Treatment through Modulation of Redox Balance. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev 2020, 2020, 2407074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, R.; Dalvi, Y.B. Natural Products as Anticancer Agents. Curr. Drug Targets 2021, 22, 1272–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, E.S.A.; Prado, L.; Araújo, L.K.C.; Arnhold, E.; Matos, M.P.C.; de Paula, J.A.M.; Ramos, L.M.; Fonseca-Alves, C.E.; de Moura, V. Effects of the Latex of Synadenium grantii Hook F. (Euphorbiaceae) A Preclin. Model Canine Prostate Cancer. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 605286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefidabi, R.; Mortazavi, P.; Hosseini, S. Antiproliferative effect of berberine on canine mammary gland cancer cell culture. Biomed. Rep. 2017, 6, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Hsu, C.-H.; Kuo, T.-Y.; Liu, C.-C.; Liao, A.T.-C.; Lin, C.-S. Inhibiting autophagy potentiates the antitumor efficacy of Euphorbia royleana for canine mammary gland tumors. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Cruz-Martins, N.; López-Jornet, P.; Lopez, E.P.; Harun, N.; Yeskaliyeva, B.; Beyatli, A.; Sytar, O.; Shaheen, S.; Sharopov, F.; et al. Natural Coumarins: Exploring the Pharmacological Complexity and Underlying Molecular Mechanisms. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 6492346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khursheed, A.; Jain, V. Medicinal research progress of natural coumarin and its derivatives. Nat. Prod. J. 2021, 11, 648–662. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Xie, Q.; Li, X. Esculetin: A review of its pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; An, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, D.; He, W. Esculetin protects human corneal epithelial cells from oxidative stress through Nrf-2 signaling pathway. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 202, 108360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Wang, B.; Xu, M. Esculetin inhibits histamine-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines and mucin in nasal epithelial cells. Clin. Exp. Pharm. Physiol. 2019, 46, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.S.; Gupta, J.; Sharma, S.; Sahu, D. An insight into the therapeutic applications of coumarin compounds and their mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 152, 105424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edathara, P.M.; Chintalapally, S.; Makani, V.K.K.; Pant, C.; Yerramsetty, S.; Rao, M.D.; Bhadra, M.P. Inhibitory role of oleanolic acid and esculetin in HeLa cells involve multiple signaling pathways. Gene 2021, 771, 145370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-B.; Jung, W.K.; Kim, H.R.; Yu, H.-Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J. Esculetin has therapeutic potential via the proapoptotic signaling pathway in A253 human submandibular salivary gland tumor cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, S.-H.; Yeh, C.-C.; Chen, M.-L.; Kuo, M.Y.-P. Esculetin enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis through DR5 upregulation in human oral cancer SAS cells. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lu, M.; Dai, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Wei, N. Esculetin, a coumarin derivative, exerts in vitro and in vivo antiproliferative activity against hepatocellular carcinoma by initiating a mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis pathway. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2014, 48, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Lee, C.M.; Park, S.H.; Nam, M.J. Esculetin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human colon cancer LoVo cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2019, 34, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Shi, J.; Ma, X.; Xuan, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, H.; Fan, Y.; Gong, H.; Wang, L.; Pang, Y. Esculetin inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 110031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Ju, W.; Pei, S.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, Y. Pharmacological activities and synthesis of esculetin and its derivatives: A mini-review. Molecules 2017, 22, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Han, Z. Esculetin inhibits the proliferation of human lung cancer cells by targeting epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of the cells. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 65, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Gu, J.; Qian, H. Esculetin attenuates the growth of lung Cancer by downregulating Wnt targeted genes and suppressing NF-κB. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2018, 54, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Yu, H.-H.; Liu, Y.-S.; Wang, Y.-S.; Zhao, W.-H. Esculetin enhances the inhibitory effect of 5-Fluorouracil on the proliferation, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2019, 24, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.K.; Byun, W.S.; Chung, H.-J.; Oh, J.; Park, H.J.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, S.K. Esculetin suppresses tumor growth and metastasis by targeting Axin2/E-cadherin axis in colorectal cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 152, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Lu, M.; Yao, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, J. Esculetin exerts antitumor effect on human gastric cancer cells through IGF-1/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 814, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.Z.; Lee, I.S.; Pham, C.H.; Jeong, S.-K.; Lee, S.; Hong, K.; Yoo, H.M. Apoptosis in leukemic cells induced by anti-proliferative coumarin isolated from the stem bark of Fraxinus rhynchophylla. J. Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 1214–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S. In vitro anticancer effects of esculetin against human leukemia cell lines involves apoptotic cell death, autophagy, G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and modulation of Raf/MEK/ERK signalling pathway. J. BUON 2019, 24, 1686–1691. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio, V.; García-Pérez, A.I.; Herráez, A.; Diez, J.C. Different roles of Nrf2 and NFKB in the antioxidant imbalance produced by esculetin or quercetin on NB4 leukemia cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 294, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, V.; García-Pérez, A.I.; Herráez, A.; Tejedor, M.C.; Diez, J.C. Esculetin modulates cytotoxicity induced by oxidants in NB4 human leukemia cells. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2017, 69, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.T.; Chou, C.T.; Lin, Y.S.; Shieh, P.; Kuo, D.H.; Jan, C.R.; Liang, W.Z. Esculetin, a natural coumarin compound, evokes Ca(2+) movement and activation of Ca(2+)-associated mitochondrial apoptotic pathways that involved cell cycle arrest in ZR-75-1 human breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 4665–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Orozco, A.F., Sr.; Roman-Rosales, A.A.; Garcia-Mondragon, M.J.; Maldonado-Espinoza, A.; Mendoza-Patiño, N., Sr.; Martinez-Flores, F., Sr.; Mandoki, J.J., Sr. Evaluation of estrogenic activity of esculetin and daphnetin and their effects in cyclin D1 expression in the human breast adenocarcinoma cell line MCF-7. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, A134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, H.F. Esculetin Inhibits Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration of Laryngeal Cancer In Vitro and In Vivo by Inhibiting Janus Kinas (JAK)-Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription-3 (STAT3) Activation. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 7853–7863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.; Sasaki, A.; Saito, N.; Nakazato, Y. Immunohistochemical analysis of cleaved caspase-3 detects high level of apoptosis frequently in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of the central nervous system. Pathol. Int. 2005, 55, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponder, K.G.; Boise, L.H. The prodomain of caspase-3 regulates its own removal and caspase activation. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, J.; Yoo, M.-J.; Park, S.-Y.; Seol, J.-W. Antitumor Effects of Esculetin, a Natural Coumarin Derivative, against Canine Mammary Gland Tumor Cells by Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10020084
Choi J, Yoo M-J, Park S-Y, Seol J-W. Antitumor Effects of Esculetin, a Natural Coumarin Derivative, against Canine Mammary Gland Tumor Cells by Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(2):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10020084
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Jawun, Min-Jae Yoo, Sang-Youel Park, and Jae-Won Seol. 2023. "Antitumor Effects of Esculetin, a Natural Coumarin Derivative, against Canine Mammary Gland Tumor Cells by Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 2: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10020084
APA StyleChoi, J., Yoo, M.-J., Park, S.-Y., & Seol, J.-W. (2023). Antitumor Effects of Esculetin, a Natural Coumarin Derivative, against Canine Mammary Gland Tumor Cells by Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis. Veterinary Sciences, 10(2), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10020084







