Establishment of the Maximum Residual Limit in the Milk of Dairy Cows Injected Intramuscularly with Prednisolone
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Animals
2.3. PSL Administration and Sample Collection
2.4. Preparation of Standard Stock Solutions and Concentration Standards
2.5. Sample Pretreatment
2.6. LC-MS/MS Conditions
2.7. Validation
2.8. Establishment of a Residual Withdrawal Period for PSL in Milk
3. Results
3.1. Chromatogram of PSL
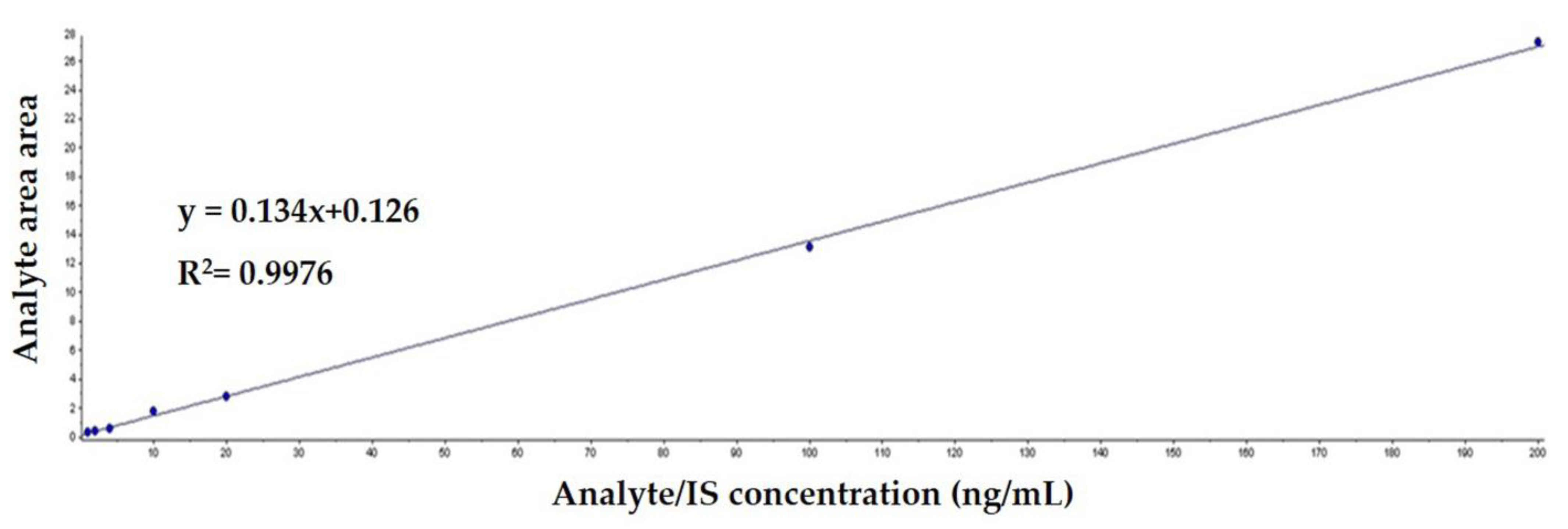
3.2. Calibration Curve and the Limits of Detection and Quantification
3.3. Recovery Rate and Precision
3.4. Analysis of PSL Residues in Milk
3.5. PSL Residual Withdrawal Period Set in Milk
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, G.I.; Han, H.S.; Son, E.Y. Analysis of Trends in Korean Food Consumption; Korea Rural Economic Institute: Naju, Republic of Korea, 2007; pp. 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Piras, C.; Roncada, P.; Rodrigues, P.M.; Bonizzi, L.; Soggiu, A. Proteomics in food: Quality, safety, microbes, and allergens. Proteomics 2016, 16, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, N.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Choi, S.J. Safety aspects of natural food additives frequently used at their maximum levels in South Korea. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2022, 18, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, T. Veterinary drug residues in food-animal products: Its risk factors and potential effects on public health. J. Vet. Sci. Technol. 2016, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Jimenez, L.E.; Aranda-Aguirre, E.; Castelan-Ortega, O.A.; Shettino-Bermudez, B.S.; Ortiz-Salinas, R.; Miranda, M.; Li, X.; Angeles-Hernandez, J.C.; Vargas-Bello-Pérez, E.; Gonzalez-Ronquillo, M. Worldwide traceability of antibiotic residues from livestock in wastewater and soil: A systematic review. Animals 2021, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La, T.M.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, T.S.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Shin, H.J.; Song, Y.J.; Ahn, G.H.; Hur, W.; Lee, J.B.; et al. The optimal standard protocols for whole-genome sequencing of antibiotic-resistant pathogenic bacteria using third-generation sequencing platforms. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2021, 17, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baynes, R.E.; Dedonder, K.; Kissell, L.; Mzyk, D.; Marmulak, T.; Smith, G.; Tell, L.; Gehring, R.; Davis, J.; Riviere, J.E. Health concerns and management of select veterinary drug residues. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 88, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.H.; Kang, D.; Lim, M.W.; Kang, C.S.; Sung, H.J. Risk assessment of growth hormones and antimicrobial residues in meat. Toxicol. Res. 2010, 26, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malekinejad, H.; Rezabakhsh, A. Hormones in dairy foods and their impact on public health—A narrative review article. Iran. J. Public. Health 2015, 44, 742–758. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nebbia, C.; Capra, P.; Leporati, M.; Girolami, F.; Barbarino, G.; Gatto, S.; Vincenti, M. Profile of the urinary excretion of prednisolone and its metabolites in finishing bulls and cows treated with a therapeutic schedule. BMC Vet. Res. 2014, 10, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Famele, M.; Ferranti, C.; Palleschi, L.; Abenavoli, C.; Fidente, R.M.; Pezzolato, M.; Botta, M.; Bozzetta, E.; Draisci, R. Quantifi-cation of natural and synthetic glucocorticoids in calf urine following different growth-promoting prednisolone treat-ments. Steroids 2015, 104, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, M.; Granelli, K.; Sjöberg, P. Rapid multiresidue method for the quantitative determination and confirmation of glucocorticosteroids in bovine milk using liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 588, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.H.; Kwon, C.H.; Jeon, J.S.; Choi, D. Management of veterinary drug residues in food. Korean J. Environ. Agric. 2009, 28, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS). Reinforcement of Veterinary Drug Residue Management for Livestock and Fishery Products. 2020. Available online: https://www.mfds.go.kr/brd/m_99/view.do?seq=44885&srchFr=&srchTo=&srchWord=&srchTp=&itm_seq_1=0&itm_seq_2=0&multi_itm_seq=0&company_cd=&company_nm=&page=1 (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency (APQA). Press Release–Preliminary Preparation for the Introduction of the Positive List System for Livestock Products. 2022. Available online: https://www.qia.go.kr/viewwebQiaCom.do?id=55368&type=6_18_1bdsm (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS). Food Code. Chapter 8. General test methods. In Residue Analytical Methods for Veterinary Drugs in Food; Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS): Cheongju, Republic of Korea, 2016; p. 8.3.33. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Park, J.S.; Kim, S.D.; Yang, H.R.; Kim, E.H.; Yi, Y.J.; Cho, S.J.; Jo, H.B.; Kim, J.H.; Chae, Y.Z. Simultaneous determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and corticosteroids added to foods as adulterants using LC-ESI-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Fd. Hyg. Safe 2013, 28, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS). Practical Handbook for Analysis of Residual Veterinary Drugs; Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS): Cheongju, Republic of Korea, 2014; pp. 48–59. [Google Scholar]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Guideline on Determination of Withdrawal Periods for Milk. Amsterdam, The Netherlands. 2022. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/adopted-guideline-determination-withdrawal-periods-milk-revision-1_en.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2022).
- Fischer-Tenhagen, C.; Bohm, D.; Finnah, A.; Arlt, S.; Schlesinger, S.; Borchardt, S.; Sutter, F.; Tippenhauer, C.M.; Heuwieser, W.; Venjakob, P.L. Residue Concentrations of Cloxacillin in Milk after Intramammary Dry Cow Treatment Considering Dry Period Length. Animals 2023, 13, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, L.J.; Gillingwater, S.; Keevil, B.G. Prednisolone measurement in human serum using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2005, 42, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finšgar, M.; Perva-Uzunalić, A.; Behr, H.; Ledinek, N.; Knez, Ž.; Novak, Z. An improved reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography method for the analysis of related substances of prednisolone in active ingredient. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 7987–8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United. Codex Alimentarius. Guidelines for the Design and Implementation of National Regulatory Food Safety Assurance Programme Associated with the Use of Veterinary Drugs in Food Producing Animals CAC/GL 71. Nations; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009; Available online: https://www.fao.org/input/download/standards/11252/CXG_071e_2014.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS). Food Code, Appendix 6. In Maximum Residue Limits of Veterinary Drugs in Food; Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS): Cheongju, Republic of Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann, A.; Butcher, P.; Maden, K.; Walker, S.; Widmer, M. Determination of corticosteroids, anabolic steroids, and basic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in milk and animal tissues. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Shao, B.; Zhao, R.; Yang, Y.; Hu, J.; Tu, X. Simultaneous determination of seventeen glucocorticoids residues in milk and eggs by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2006, 20, 2355–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medical Products (EMEA). Committee for Veterinary Medicinal Products, Prednisolone, Summary Report (EMEA/MRL/629/99 FINAL). 1999. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/mrl-report/prednisolone-free-alcohol-summary-report-committee-veterinary-medicinal-products_en.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Li, H.; Wu, G.Q.; Tang, S.S.; Xiao, X.L.; Li, J.C. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a novel amoxicillin/sulbactam/prednisolone intramammary infusion in lactating cows after repeated administrations. Vet. Med. 2014, 59, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, K.; Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, G.; Li, C.; Cao, J.; Ding, S. Simultaneous detection and comparative pharmacokinetics of amoxicillin, clavulanic acid and prednisolone in cows’ milk by UPLC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1008, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Veterinary Medicine. Prednisolone Injection-Prednisolone Acetate Injectable Suspension U.S.P. Injection (MSD Animal Health). 2022. Available online: https://theveterinarymedicine.com/product-detail/prednisolone-injection-for-dogs-cats-dosage/ (accessed on 23 December 2020).

| Concentration (ng/mL) | Recovery (%) | Recovery (%) | CV (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. 1 | No. 2 | No. 3 | |||
| 2.0 | 106.5 | 111.0 | 108.0 | 108.5 ± 2.3 | 2.12 |
| 20 | 101.0 | 113.0 | 109.5 | 110.0 ± 6.2 | 5.64 |
| 100 | 94.7 | 96.2 | 98.7 | 96.5 ± 2.0 | 2.07 |
| Group | No. | Concentration (µg/kg) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time after Treatment (h) | ||||||||||||
| 0 * | 12 | 24 | 36 | 48 | 60 | 72 | 84 | 96 | 108 | 120 | ||
| PSL-1 | 1 | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| 2 | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| 3 | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| 4 | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| 5 | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| 6 | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| 7 | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| 8 | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| M ± SD | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| PSL-2 | 1 | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| 2 | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| 3 | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| 4 | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| 5 | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| 6 | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| 7 | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| 8 | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
| M ± SD | ND | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rha, S.S.; Yang, Y.J.; Kim, W.H.; Jin, Y.B.; Park, K.I.; Lee, H.-J. Establishment of the Maximum Residual Limit in the Milk of Dairy Cows Injected Intramuscularly with Prednisolone. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10100614
Rha SS, Yang YJ, Kim WH, Jin YB, Park KI, Lee H-J. Establishment of the Maximum Residual Limit in the Milk of Dairy Cows Injected Intramuscularly with Prednisolone. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(10):614. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10100614
Chicago/Turabian StyleRha, Seung Shik, Ye Jin Yang, Woo Hyun Kim, Yeung Bae Jin, Kwang Il Park, and Hu-Jang Lee. 2023. "Establishment of the Maximum Residual Limit in the Milk of Dairy Cows Injected Intramuscularly with Prednisolone" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 10: 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10100614
APA StyleRha, S. S., Yang, Y. J., Kim, W. H., Jin, Y. B., Park, K. I., & Lee, H.-J. (2023). Establishment of the Maximum Residual Limit in the Milk of Dairy Cows Injected Intramuscularly with Prednisolone. Veterinary Sciences, 10(10), 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10100614






