Respiratory Animal Models in the Common Marmoset (Callithrix jacchus)
Abstract
:1. Introduction

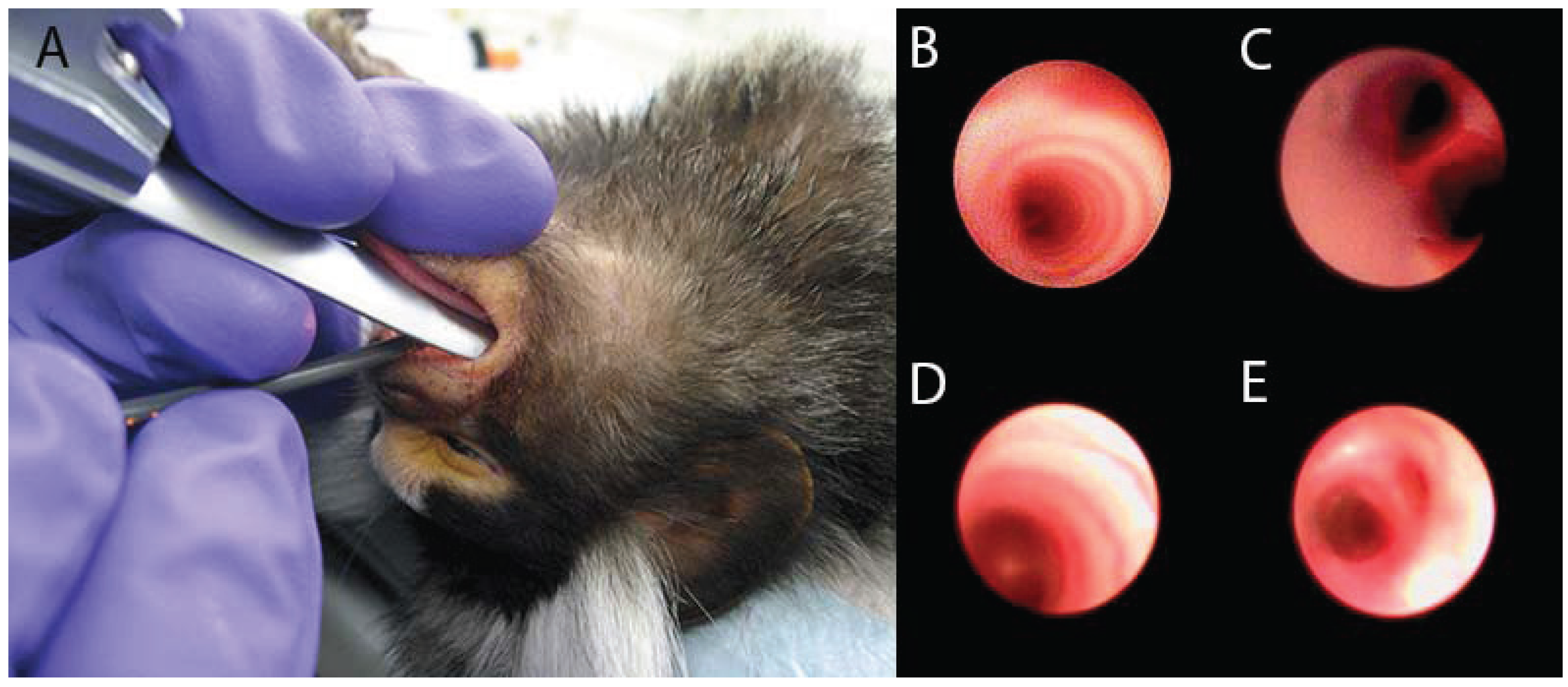
2. Models of Lung Inflammation
3. Models of Viral Infection
4. Models of Bacterial Infection
5. Further Models with Respiratory Implications
6. Conclusions
| Macaques | Common marmosets | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feature | |||
| Weight | 3.0–15.0 kg | 0.35–0.45 kg | [1] |
| Sexual maturity | 41–66 months | 18–24 months | [1] |
| Gestation length | 24 weeks | 21 weeks | [67] |
| Interbirth interval | 12 months | 6 months | [67] |
| Housing requirements (floor area × height) | 0.55 m2 × 1.5 m | 2 m2 × 1.8 m | European Directive 2010/63/EU |
| Purchase price 2014 | ~6,000–10,000 € | ~3,000–5,000 € | p.c. |
| Material costs (esp. drug compound) for pharmacology and toxicology studies | high | low | [3] |
| Hematopoietic chimerism of dizygotic twins | no | yes | [2] |
| Inter-individual variation of MHC class I and II loci | high | low | [1] |
| Identical aa residues in average for immunity-related genes compared to human | 95 ± 3.4 | 87 ± 5.4 | [7] |
| Susceptible for viral and bacterial infection with human-relevant pathogens | yes | yes | [23] |
| Alveolar size | equal | [9] | |
| Highly alveolarized respiratory bronchioles | yes | yes | [9] |
| Bronchial branching pattern | dichotomous | [10,11] | |
| Presence of Clara cells in the lung | not in trachea and major bronchi | in all airway segments | [13] |
| Respiratory rate (under anesthesia) | ~34 breaths/min | ~27 breaths/min | [19] |
| Latent Herpes Virus B infection | yes | no | [2] |
| Wasting syndrome in captive colonies | absent | evident | [6] |
| Methods | |||
| Handling | laborious | easy | [3] |
| Complete clinical examination | feasible | feasible | [3] |
| Blood sample volume (in vivo every two weeks) | 48 mL | 2.5 mL | Society for Laboratory
Animal Science |
| Bronchoscopy | yes | yes | [21,68,69] |
| BAL (uni- and bilateral) | yes | yes | [21,68,69] |
| BAL flush volume | 10–15 mL | 2 × 3 mL | [21,68,69] |
| Lung function assessment | yes | yes | [19,68,69] |
| Cross-reactivity of human-specific antibodies | frequent | limited | [70] |
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Abbott, D.H.; Barnett, D.K.; Colman, R.J.; Yamamoto, M.E.; Schultz-Darken, N.J. Aspects of common marmoset basic biology and life history important for biomedical research. Comp. Med. 2003, 53, 339–350. [Google Scholar]
- Mansfield, K. Marmoset models commonly used in biomedical research. Comp. Med. 2003, 53, 383–392. [Google Scholar]
- Orsi, A.; Rees, D.; Andreini, I.; Venturella, S.; Cinelli, S.; Oberto, G. Overview of the marmoset as a model in nonclinical development of pharmaceutical products. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 59, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, C.; Ward, J.; Vallender, E.J. Naturally occurring, physiologically normal, primate chimeras. Chimerism 2012, 3, 43–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, J.L.; Barry, P.A. B-virus (cercopithecine herpesvirus 1) infection in humans and macaques: Potential for zoonotic disease. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; Trennery, P.; Farningham, D.; Klapwijk, J. The selection of marmoset monkeys (callithrix jacchus) in pharmaceutical toxicology. Lab. Anim. 2001, 35, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohu, K.; Yamabe, E.; Matsuzawa, A.; Onda, D.; Suemizu, H.; Sasaki, E.; Tanioka, Y.; Yagita, H.; Suzuki, D.; Kametani, Y.; et al. Comparison of 30 immunity-related genes from the common marmoset with orthologues from human and mouse. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2008, 215, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ‘t Hart, B.A.; Abbott, D.H.; Nakamura, K.; Fuchs, E. The marmoset monkey: A multi-purpose preclinical and translational model of human biology and disease. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, A.; Bachofen, H. The lung of the marmoset (callithrix jacchus): Ultrastructure and morphometric data. Respir. Physiol. 2000, 120, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plopper, C.G.; Hyde, D.M. The non-human primate as a model for studying copd and asthma. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 21, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, V. Morphological investigations on the lung of common marmosets (Callithrix jacchus). Doctoral Thesis, School of Veterinary Medicine, Hannover, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wako, K.; Hiratsuka, H.; Katsuta, O.; Tsuchitani, M. Anatomical structure and surface epithelial distribution in the nasal cavity of the common cotton-eared marmoset (callithrix jacchus). Exp. Anim. 1999, 48, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, V.; Hoffmann, R.; Braun, A.; Seehase, S.; Knauf, S.; Kaup, F.-J.; Bleyer, M. Distribution and morphology of clara cells in common marmosets (callithrix jacchus). J. Med. Primatol. 2013, 42, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.; Braun, A.; Knauf, S.; Kaup, F.-J.; Bleyer, M. Distribution of ciliated epithelial cells in the trachea of common marmosets (callithrix jacchus). J. Med. Primatol. 2014, 43, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.M.; Kaup, F.-J.; Bleyer, M. Atypical cilia in the respiratory tract of common marmosets (callithrix jacchus) with and without concurrent lung disease. Exp. Lung Res. 2013, 39, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlepütz, M.; Rieg, A.D.; Seehase, S.; Spillner, J.; Perez-Bouza, A.; Braunschweig, T.; Schroeder, T.; Bernau, M.; Lambermont, V.; Schlumbohm, C.; et al. Neurally mediated airway constriction in human and other species: A comparative study using precision-cut lung slices (PCLS). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, D.; Matera, G.M.; Riccio, M.M.; Page, C.P. A comparison of sensory nerve function in human, guinea-pig, rabbit and marmoset airways. Life Sci. 1998, 63, 1629–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seehase, S.; Schlepütz, M.; Switalla, S.; Mätz-Rensing, K.; Kaup, F.-J.; Zöller, M.; Schlumbohm, C.; Fuchs, E.; Lauenstein, H.D.; Winkler, C.; et al. Bronchoconstriction in nonhuman primates: A species comparison. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curths, C.; Wichmann, J.; Dunker, S.; Windt, H.; Hoymann, H.G.; Lauenstein, H.D.; Hohlfeld, J.; Becker, T.; Kaup, F.-J.; Braun, A.; et al. Airway hyper-responsiveness in lipopolysaccharide-challenged common marmosets (callithrix jacchus). Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2014, 126, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.A.; Leach, M.C.; Flecknell, P.A. An alternative method of endotracheal intubation of common marmosets (callithrix jacchus). Lab. Anim. 2012, 46, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seehase, S.; Lauenstein, H.D.; Schlumbohm, C.; Switalla, S.; Neuhaus, V.; Forster, C.; Fieguth, H.G.; Pfennig, O.; Fuchs, E.; Kaup, F.-J.; et al. Lps-induced lung inflammation in marmoset monkeys—An acute model for anti-inflammatory drug testing. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idell, S.; Thrall, R.S.; Maunder, R.; Martin, T.R.; McLarty, J.; Scott, M.; Starcher, B.C. Bronchoalveolar lavage desmosine in bleomycin-induced lung injury in marmosets and patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Exp. Lung Res. 1989, 15, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrion, R., Jr.; Patterson, J.L. An animal model that reflects human disease: The common marmoset (callithrix jacchus). Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, M.D.; Poutanen, S.M.; Loutfy, M.R.; Muller, M.P.; Low, D.E. Severe acute respiratory syndrome. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 1420–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenough, T.C.; Carville, A.; Coderre, J.; Somasundaran, M.; Sullivan, J.L.; Luzuriaga, K.; Mansfield, K. Pneumonitis and multi-organ system disease in common marmosets (callithrix jacchus) infected with the severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncla, L.H.; Ross, T.M.; Dinis, J.M.; Weinfurter, J.T.; Mortimer, T.D.; Schultz-Darken, N.; Brunner, K.; Capuano, S.V., 3rd; Boettcher, C.; Post, J.; et al. A novel nonhuman primate model for influenza transmission. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78750. [Google Scholar]
- Tsou, T.P.; Tan, B.F.; Chang, H.Y.; Chen, W.C.; Huang, Y.P.; Lai, C.Y.; Chao, Y.N.; Wei, S.H.; Hung, M.N.; Hsu, L.C.; et al. Community outbreak of adenovirus, Taiwan, 2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wevers, D.; Metzger, S.; Babweteera, F.; Bieberbach, M.; Boesch, C.; Cameron, K.; Couacy-Hymann, E.; Cranfield, M.; Gray, M.; Harris, L.A.; et al. Novel adenoviruses in wild primates: A high level of genetic diversity and evidence of zoonotic transmissions. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 10774–10784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersching, J.; Hernandez, M.I.; Cezarotto, F.S.; Ferreira, J.D.; Martins, A.B.; Switzer, W.M.; Xiang, Z.; Ertl, H.C.; Zanetti, C.R.; Pinto, A.R. Neutralizing antibodies to human and simian adenoviruses in humans and new-world monkeys. Virology 2010, 407, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Yagi, S.; Carrion, R., Jr.; Chen, E.C.; Liu, M.; Brasky, K.M.; Lanford, R.E.; Kelly, K.R.; Bales, K.L.; Schnurr, D.P.; et al. Experimental cross-species infection of common marmosets by titi monkey adenovirus. PLoS One 2013, 8, e68558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.C.; Yagi, S.; Kelly, K.R.; Mendoza, S.P.; Tarara, R.P.; Canfield, D.R.; Maninger, N.; Rosenthal, A.; Spinner, A.; Bales, K.L.; et al. Cross-species transmission of a novel adenovirus associated with a fulminant pneumonia outbreak in a new world monkey colony. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002155. [Google Scholar]
- Perelman, P.; Johnson, W.E.; Roos, C.; Seuanez, H.N.; Horvath, J.E.; Moreira, M.A.; Kessing, B.; Pontius, J.; Roelke, M.; Rumpler, Y.; et al. A molecular phylogeny of living primates. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, B.S.; Benson, R.F.; Besser, R.E. Legionella and legionnaires’ disease: 25 years of investigation. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 506–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Luo, Z.Q. Cell biology of infection by legionella pneumophila. Microbes Infect. 2013, 15, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskerville, A.; Fitzgeorge, R.B.; Broster, M.; Hambleton, P. Histopathology of experimental legionnaires’ disease in guinea pigs, rhesus monkeys and marmosets. J. Pathol. 1983, 139, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskerville, A.; Dowsett, A.B.; Fitzgeorge, R.B.; Hambleton, P.; Broster, M. Ultrastructure of pulmonary alveoli and macrophages in experimental Legionnaires’ disease. J. Pathol. 1983, 140, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.C.; Currie, B.J. Melioidosis: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 383–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, B.J.; Dance, D.A.; Cheng, A.C. The global distribution of burkholderia pseudomallei and melioidosis: An update. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 102 (Suppl 1), S1–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choh, L.C.; Ong, G.H.; Vellasamy, K.M.; Kalaiselvam, K.; Kang, W.T.; Al-Maleki, A.R.; Mariappan, V.; Vadivelu, J. Burkholderia vaccines: Are we moving forward? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, M.; Dean, R.E.; Salguero, F.J.; Taylor, C.; Pearce, P.C.; Simpson, A.J.; Lever, M.S. Development of an acute model of inhalational melioidosis in the common marmoset (callithrix jacchus). Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2011, 92, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, N.J. Melioidosis. Lancet 2003, 361, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, C.A.; Laws, T.R.; Oyston, P.C. An assessment of common marmoset (callithrix jacchus) gamma9(+) t cells and their response to phosphoantigen in vitro. Cell. Immunol. 2012, 280, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws, T.R.; Nelson, M.; Bonnafous, C.; Sicard, H.; Taylor, C.; Salguero, F.J.; Atkins, T.P.; Oyston, P.C.; Rowland, C.A. In vivo manipulation of gamma9(+) t cells in the common marmoset (callithrix jacchus) with phosphoantigen and effect on the progression of respiratory melioidosis. PLoS One 2013, 8, e74789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lever, M.S.; Stagg, A.J.; Nelson, M.; Pearce, P.; Stevens, D.J.; Scott, E.A.; Simpson, A.J.; Fulop, M.J. Experimental respiratory anthrax infection in the common marmoset (callithrix jacchus). Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2008, 89, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food Drug Administration, H.H.S. New drug and biological drug products; evidence needed to demonstrate effectiveness of new drugs when human efficacy studies are not ethical or feasible. Final rule. Fed. Regist. 2002, 67, 37988–37998. [Google Scholar]
- Fellows, P.F.; Linscott, M.K.; Ivins, B.E.; Pitt, M.L.; Rossi, C.A.; Gibbs, P.H.; Friedlander, A.M. Efficacy of a human anthrax vaccine in guinea pigs, rabbits, and rhesus macaques against challenge by bacillus anthracis isolates of diverse geographical origin. Vaccine 2001, 19, 3241–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, D.M.; Kozarsky, P.E.; Stephens, D.S. Clinical issues in the prophylaxis, diagnosis, and treatment of anthrax. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 222–225. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, M.; Stagg, A.J.; Stevens, D.J.; Brown, M.A.; Pearce, P.C.; Simpson, A.J.; Lever, M.S. Post-exposure therapy of inhalational anthrax in the common marmoset. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 38, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchison, D.A.; Chang, K.C. Experimental models of tuberculosis: Can we trust the mouse? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 201–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Via, L.E.; Weiner, D.M.; Schimel, D.; Lin, P.L.; Dayao, E.; Tankersley, S.L.; Cai, Y.; Coleman, M.T.; Tomko, J.; Paripati, P.; et al. Differential virulence and disease progression following mycobacterium tuberculosis complex infection of the common marmoset (callithrix jacchus). Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 2909–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, C.D.; Stout, J.E.; Goodman, P.C.; Mosher, A.; Menzies, R.; Schluger, N.W.; Khan, A.; Johnson, J.L.; Vernon, A.N.; Tuberculosis Trials, C. The value of end-of-treatment chest radiograph in predicting pulmonary tuberculosis relapse. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2008, 12, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Helmerhorst, H.J.; van Tol, E.N.; Tuinman, P.R.; de Vries, P.J.; Hartskeerl, R.A.; Grobusch, M.P.; Hovius, J.W. Severe pulmonary manifestation of leptospirosis. Neth. J. Med. 2012, 70, 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, J.J.; Dalston, M.O.; Carvalho, J.E.; Setubal, S.; Oliveira, J.M.; Pereira, M.M. Clinicopathological and immunohistochemical features of the severe pulmonary form of leptospirosis. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2002, 35, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, E.L.; Metcalfe, J.; de Carvalho, A.L.; Aires, T.S.; Villasboas-Bisneto, J.C.; Queirroz, A.; Santos, A.C.; Salgado, K.; Reis, M.G.; Ko, A.I. Leptospirosis-associated severe pulmonary hemorrhagic syndrome, salvador, brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.M.; Da Silva, J.J.; Pinto, M.A.; Da Silva, M.F.; Machado, M.P.; Lenzi, H.L.; Marchevsky, R.S. Experimental leptospirosis in marmoset monkeys (callithrix jacchus): A new model for studies of severe pulmonary leptospirosis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 72, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, A.; Cohen, G.; Gilat, E.; Kapon, J.; Dachir, S.; Abraham, S.; Herskovitz, M.; Teitelbaum, Z.; Raveh, L. Extrapolating from animal studies to the efficacy in humans of a pretreatment combination against organophosphate poisoning. Arch. Toxicol. 2007, 81, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonijevic, B.; Stojiljkovic, M.P. Unequal efficacy of pyridinium oximes in acute organophosphate poisoning. Clin. Med. Res. 2007, 5, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Helden, H.P.; Trap, H.C.; Oostdijk, J.P.; Kuijpers, W.C.; Langenberg, J.P.; Benschop, H.P. Long-term, low-level exposure of guinea pigs and marmosets to sarin vapor in air: Lowest observable effect level. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2003, 189, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, H.; Hori, S.; Shinozawa, Y.; Fujishima, S.; Takuma, K.; Sagoh, M.; Kimura, H.; Ohki, T.; Suzuki, M.; Aikawa, N. Secondary exposure of medical staff to sarin vapor in the emergency room. Intensive Care Med. 1995, 21, 1032–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, Y.; Wakai, T.; Kubota, M.; Osawa, M.; Sanpei, A.; Fujimaki, S. Mycotoxins are conventional and novel risk biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 2587–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vleet, T.R.; Watterson, T.L.; Klein, P.J.; Coulombe, R.A., Jr. Aflatoxin b1 alters the expression of p53 in cytochrome p450-expressing human lung cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 89, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.W.; Ball, R.W.; Coulombe, R.A., Jr. Comparative action of aflatoxin b1 in mammalian airway epithelium. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 2493–2498. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, P.; Tjalve, H. Distribution and metabolism of aflatoxin b1 in the marmoset monkey (callithrix jacchus). Carcinogenesis 1993, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibino, H.; Tani, K.; Ikebuchi, K.; Wu, M.S.; Sugiyama, H.; Nakazaki, Y.; Tanabe, T.; Takahashi, S.; Tojo, A.; Suzuki, S.; et al. The common marmoset as a target preclinical primate model for cytokine and gene therapy studies. Blood 1999, 93, 2839–2848. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, E.; Hwang, G.S.; Pan, Z.H.; Troilo, D. Evaluation of aav-mediated expression of chop2-gfp in the marmoset retina. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 5288–5296. [Google Scholar]
- Farrow, N.; Miller, D.; Cmielewski, P.; Donnelley, M.; Bright, R.; Parsons, D.W. Airway gene transfer in a non-human primate: Lentiviral gene expression in marmoset lungs. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1287. [Google Scholar]
- Abee, C.R.; Mansfield, K. Nonhuman Primates in Biomedical Research, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2012; p. 201. [Google Scholar]
- Iwashita, K.; Kawasaki, H.; Sawada, M.; In, M.; Mataki, Y.; Kuwabara, T. Shortening of the induction period of allergic asthma in cynomolgus monkeys by ascaris suum and house dust mite. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 106, 92–99. [Google Scholar]
- Schelegle, E.S.; Gershwin, L.J.; Miller, L.A.; Fanucchi, M.V.; van Winkle, L.S.; Gerriets, J.P.; Walby, W.F.; Omlor, A.M.; Buckpitt, A.R.; Tarkington, B.K.; et al. Allergic asthma induced in rhesus monkeys by house dust mite (dermatophagoides farinae). Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagessar, S.A.; Vierboom, M.; Blezer, E.L.; Bauer, J.; Hart, B.A.; Kap, Y.S. Overview of models, methods, and reagents developed for translational autoimmunity research in the common marmoset (callithrix jacchus). Exp. Anim. 2013, 62, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Curths, C.; Knauf, S.; Kaup, F.-J. Respiratory Animal Models in the Common Marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). Vet. Sci. 2014, 1, 63-76. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci1010063
Curths C, Knauf S, Kaup F-J. Respiratory Animal Models in the Common Marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). Veterinary Sciences. 2014; 1(1):63-76. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci1010063
Chicago/Turabian StyleCurths, Christoph, Sascha Knauf, and Franz-Josef Kaup. 2014. "Respiratory Animal Models in the Common Marmoset (Callithrix jacchus)" Veterinary Sciences 1, no. 1: 63-76. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci1010063
APA StyleCurths, C., Knauf, S., & Kaup, F.-J. (2014). Respiratory Animal Models in the Common Marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). Veterinary Sciences, 1(1), 63-76. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci1010063




