Thirty Thousand 3D Models from Thingiverse
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Acquisition
- Download counter, indicating how often parts of the Thing have been downloaded;
- View counter, indicating how often the Thing has been watched in a browser by a third party;
- Like counter, similar to other online communities,
- Watch counter, indicating how often the Thing has been added to watch lists by other users. Watch lists are for users to keep track on changes of other users Things;
- Remix counter, indicating how often the respective Thing was remixed, i.e., re-used in other user’s designs,
- Collection counter, indicating how often the respective Thing is added to collections or groups of Things, most often on a specific topic or theme;
- Zero or more comments by members of the online community;
- Zero or more tags, that categorize the Thing according to the creator;
- A textual description;
- An associated license, detailing the conditions under which the Thing can be used
3. Results
- all-stl.zip, contains 31,121 files of a total (uncompressed) size of approximately 66.2 GiB.
- all-gif.zip, contains 31,120 files of a total (uncompressed) size of approximately 13.0 GiB.
- all-png.zip, contains 31,121 files of a total (uncompressed) size of approximately 2.4 GiB.
- all-amf.zip, contains 31,032 files of a total (uncompressed) size of approximately 30.0 GiB.
- [0–9]-gcode.zip, contains 30,515 files of a total (uncompressed) size of approximately 230.0 GiB. The archives are sorted by the first digit of the filename.
4. Dataset Description
- File #, internal file number
- Filename, the original name of the downloaded STL file.
- Filesize [Byte], the file size of the original STL file in bytes.
- Thing ID, the ID of the Thing for which the model was downloaded. This entry is enriched with a hypertext URL that points to the Thing on https://thingiverse.com.
- Download Date, datestamp when the file was downloaded from https://thingiverse.com.
- Download Time, timestamp when the file was downloaded from https://thingiverse.com.
- Processing Time [s], time that was required to analyse the model file geometrically. Processing time is measured in seconds.
- Thingname, the original title provided for the Thing of which the download is part of.
- License, the license information under which the original Thing is made available.
- User, the original creator of the model and the Thing. This entry is enriched with a hypertext URL that points to the user’s page on https://thingiverse.com.
- Creation Date, the data on which the original Thing was uploaded to https://thingiverse.com.
- Likes, the number of likes registered on https://thingiverse.com for the specific Thing as of the date on which the file was downloaded.
- Comments, the number of comments registered on https://thingiverse.com for the specific Thing as of the date on which the file was downloaded.
- Views, the number of views registered on https://thingiverse.com for the specific Thing as of the date on which the file was downloaded.
- Downloads, the number of downloads registered on https://thingiverse.com for the specific Thing as of the date on which the file was downloaded.
- # of Files, the number of files that are registered for the specific Thing on https://thingiverse.com.
- Tags, the tags that are registered for this specific Thing. These entries are enriched with hypertext URLs that link to the tag collection site on https://thingiverse.com. In the CSV file, the tags are separated by vertical bars, |.
- Genus, describes the number of holes that are in the model. Calculated as /.
- Vertices, the number of vertices in the model file as reported by the analysis script utilizing the freecad library.
- Edges, the number of edges in the model file as reported by the analysis script utilizing the freecad library.
- Facets, the number of facets in the model file as reported by the analysis script utilizing the freecad library.
- Max Distance, the maximum distance between any two vertices in from the random selection of 20% of all vertices in the model.
- Min Distance, the minimum distance between any two vertices in from the random selection of 20% of all vertices in the model.
- Metric Hash, the hash value of the derived metric describing the object. Described in detail in Section 5.4.
- Rendering (PNG), the name of the PNG rendering of the model.
- Rendering (GIF), the name of the GIF rendering of the model.
- # of Moves, the total number of moves that are present in the GCode file. This is derived from the G1 instructions in the file.
- # of Non-Extrusion Moves, the number of moves that are present in the GCode file which do not instruct to extrude material. This is derived from the G1 instructions in the file where the extrusion parameter, i.e., A, B, or E, is not larger than the same parameter in the previous extruding instruction.
- # of X-Only Direction Moves, the number of moves that are only in the X direction. Derived from the G1 command in the file where both Y and Z parameters are not set or are equal to the parameters in a previous movement instruction.
- # of Y-Only Direction Moves, the number of moves that are only in the Y direction. Derived from the G1 command in the file where both X and Z parameters are not set or are equal to the parameters in a previous movement instruction.
- # of Z-Only Direction Moves, the number of moves that are only in the Z direction. Derived from the G1 command in the file where both X and Y parameters are not set or are equal to the parameters in a previous movement instruction.
- # of X Dominant Moves, the number of moves where the amount of movement in the X direction is dominant over movement in any other direction. Derived from the G1 command in the file.
- # of Y Dominant Moves, the number of moves where the amount of movement in the Y direction is dominant over movement in any other direction. Derived from the G1 command in the file.
- # of Z Dominant Moves, the number of moves where the amount of movement in the Z direction is dominant over movement in any other direction. Derived from the G1 command in the file.
- # of X-Y Equal Moves, the number of moves where the distance traveled in the X and Y direction are equal, i.e., diagonal moves. Derived from the G1 command in the file.
- Distance Traveled X [mm], the total distance traveled in the X direction over the complete file. The individual distances for each movement are summarised and yield this result.
- Distance Traveled Y [mm], the total distance traveled in the Y direction over the complete file. The individual distances for each movement are summarised and yield this result.
- Distance Traveled Z [mm], the total distance traveled in the Z direction over the complete file. The individual distances for each movement are summarised and yield this result.
- Avg. Length Move X Direction [mm], the average length of a movement in the X direction over the complete file. This value is calculated by dividing the total length traveled in the X direction by the number of movements involving the X axis.
- Avg. Length Move Y Direction [mm], the average length of a movement in the Y direction over the complete file. This value is calculated by dividing the total length traveled in the X direction by the number of movements involving the Y axis.
- Avg. Length Move Z Direction [mm], the average length of a movement in the Z direction over the complete file. This value is calculated by dividing the total length traveled in the X direction by the number of movements involving the Z axis.
- # Instructions involving X-axis, the total number of instructions that involve the X axis. This value includes extrusion and non-extrusion instructions.
- # Instructions involving Y-axis, the total number of instructions that involve the Y axis. This value includes extrusion and non-extrusion instructions.
- # Instructions involving Z-axis, the total number of instructions that involve the Z axis. This value includes extrusion and non-extrusion instructions.
- # of Lines, the total number of lines present in the GCode file. This value includes blank lines and comments.
- # of Instructions, the number of instructions in the GCode file that are not comments or other non-instructing lines.
- Extrusion (A) Length [mm], the amount of material extruded in the 3D printing process by the first extruder. Most GCode dialects support two extruders (A and B) per 3D printer. When the currently active extruder is selected in the GCode, extrusion instructions via the E parameter are also possible.
- Extrusion (B) Length [mm], the amount of material extruded in the 3D printing process by the second extruder.
- Extrusion (E) Length [mm], the amount of material extruded in the 3D printing process by the all extruders.
- Filament Estimation (GPX) [m], the filament required for 3D printing the complete object as estimated by the GPX software.
- Print Time Estimation (GPX) [s], the processing time for 3D printing the complete object as estimated by the GPX software.
- Size X Dim [mm], the size of the bounding box enclosing the model in the X direction.
- Size Y Dim [mm], the size of the bounding box enclosing the model in the Y direction.
- Size Z Dim [mm], the size of the bounding box enclosing the model in the Z direction.
- # Facets, the number of facets of the model as reported by the admesh software.
- Shell, the number of shells of the model as reported by the admesh software.
- Model Volume [mm3], the volume of the model in mm as reported by the admesh software.
- GCode File, the pre-sliced GCode file generated by the Slic3r software for the given layer-height and infill. Further parameters are available in the Appendix A.
- Layer Height [mm], the layer height in mm with which the GCode file is created by the Slic3r software. A layer height of 0.3 mm is set as a default.
- Infill [%], the percentage of infill with which the GCode file is created by the Slic3r software. 20% infill is set as a default value that is reflected by the value 0.2 in the results.
- Filesize Gcode [Byte], the file size of the pre-sliced GCode file created by the Slic3r software in bytes.
- Filament Used (Slic3r) [mm], the amount of filament to be extruded in the 3D printing process as calculated by the Slic3r software for the given infill and layer height.
- AMF File, the AMF file that is converted from the STL file and represents the identical model. The conversion script from Slic3r is utilized for the conversion.
- File size AMF [Byte], the file size of the AMF file in bytes.
5. Software
5.1. GPX
5.2. Slic3r
5.3. Admesh
5.4. Metric Hash
6. Summary
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AM | Additive Manufacturing |
| AMF | Additive Manufacturing File Format |
| CSV | Comma-separated Values |
| GCode | Machine Code |
| GiB | gibibyte |
| GIF | Graphics Interchange Format |
| HTML | Hypertext Markup Language |
| STL | Stereolithography File Format |
| PNG | Portable Network Graphics |
| ZIP | Zip File Format |
Appendix A. Slic3r Parameters
| avoid_crossing_perimeters = 0 |
| bed_shape = 0x0,200x0,200x200,0x200 |
| bed_temperature = 125 |
| before_layer_gcode = |
| bridge_acceleration = 0 |
| bridge_fan_speed = 100 |
| brim_width = 0 |
| complete_objects = 0 |
| cooling = 1 |
| default_acceleration = 0 |
| disable_fan_first_layers = 3 |
| duplicate_distance = 6 |
| end_gcode = M104 S0; turn off emperature\nG28 X0; home X axis\nM84; |
| disable motors\n |
| extruder_clearance_height = 20 |
| extruder_clearance_radius = 20 |
| extruder_offset = 0x0 |
| extrusion_axis = E |
| extrusion_multiplier = 1 |
| fan_always_on = 0 |
| fan_below_layer_time = 60 |
| filament_colour = #FFFFFF |
| filament_diameter = 1.75 |
| first_layer_acceleration = 0 |
| first_layer_bed_temperature = 0 |
| first_layer_extrusion_width = 200% |
| first_layer_speed = 30 |
| first_layer_temperature = 250 |
| gcode_arcs = 0 |
| gcode_comments = 0 |
| gcode_flavor = makerware |
| infill_acceleration = 0 |
| infill_first = 0 |
| layer_gcode = |
| max_fan_speed = 100 |
| max_print_speed = 80 |
| max_volumetric_speed = 0 |
| min_fan_speed = 35 |
| min_print_speed = 10 |
| min_skirt_length = 0 |
| notes = |
| nozzle_diameter = 0.4 |
| only_retract_when_crossing_perimeters = 1 |
| ooze_prevention = 0 |
| output_filename_format = [input_filename_base].gcode |
| perimeter_acceleration = 0 |
| post_process = |
| pressure_advance = 0 |
| resolution = 0 |
| retract_before_travel = 2 |
| retract_layer_change = 0 |
| retract_length = 2 |
| retract_length_toolchange = 10 |
| retract_lift = 0 |
| retract_restart_extra = 0 |
| retract_restart_extra_toolchange = 0 |
| retract_speed = 40 |
| skirt_distance = 6 |
| skirt_height = 1 |
| skirts = 1 |
| slowdown_below_layer_time = 5 |
| spiral_vase = 0 |
| standby_temperature_delta = -5 |
| start_gcode = G28; home all axes\nG1 Z5 F5000; lift nozzle\n |
| temperature = 240 |
| threads = 2 |
| toolchange_gcode = |
| travel_speed = 130 |
| use_firmware_retraction = 0 |
| use_relative_e_distances = 0 |
| use_volumetric_e = 0 |
| vibration_limit = 0 |
| wipe = 0 |
| z_offset = 0 |
| dont_support_bridges = 1 |
| extrusion_width = 0 |
| first_layer_height = 0.35 |
| infill_only_where_needed = 0 |
| interface_shells = 0 |
| layer_height = 0.2 |
| raft_layers = 0 |
| seam_position = aligned |
| support_material = 0 |
| support_material_angle = 0 |
| support_material_contact_distance = 0.2 |
| support_material_enforce_layers = 0 |
| support_material_extruder = 1 |
| support_material_extrusion_width = 0 |
| support_material_interface_extruder = 1 |
| support_material_interface_layers = 3 |
| support_material_interface_spacing = 0 |
| support_material_interface_speed = 100% |
| support_material_pattern = pillars |
| support_material_spacing = 2.5 |
| support_material_speed = 60 |
| support_material_threshold = 0 |
| xy_size_compensation = 0 |
| bottom_solid_layers = 3 |
| bridge_flow_ratio = 1 |
| bridge_speed = 60 |
| external_fill_pattern = rectilinear |
| external_perimeter_extrusion_width = 0 |
| external_perimeter_speed = 50% |
| external_perimeters_first = 0 |
| extra_perimeters = 1 |
| fill_angle = 45 |
| fill_density = 30% |
| fill_pattern = honeycomb |
| gap_fill_speed = 20 |
| infill_every_layers = 1 |
| infill_extruder = 1 |
| infill_extrusion_width = 0 |
| infill_overlap = 15% |
| infill_speed = 80 |
| overhangs = 1 |
| perimeter_extruder = 1 |
| perimeter_extrusion_width = 0 |
| perimeter_speed = 60 |
| perimeters = 3 |
| small_perimeter_speed = 15 |
| solid_infill_below_area = 70 |
| solid_infill_every_layers = 0 |
| solid_infill_extruder = 1 |
| solid_infill_extrusion_width = 0 |
| solid_infill_speed = 20 |
| thin_walls = 1 |
| top_infill_extrusion_width = 0 |
| top_solid_infill_speed = 15 |
| top_solid_layers = 3 |
Appendix B. Metric Hash Calculation
| Listing 1: Metric Hash Conversion Script |
#!/bin/bash
STR=${1} CLEAN_STR=$( echo “${STR}” | tr −d “\[\],” ) for elem in ${CLEAN_STR}; do # multiplying by 4096 (16x16x16) because # we want to have 3 hex-digits for each value
HEX=$( bc <<< “obase=16;⎵${elem}⎵*⎵4096” )
if [ “${HEX}” == “0” ]; then
echo −n “000”
else
if [ “${HEX:2:1}” == “.” ]; then
echo −n “0${HEX:0:1}${HEX:1:1}”
elif [ “${HEX:1:1}” == “.” ]; then
echo −n “000”
elif [ “${HEX:0:1}” == “.” ]; then
echo −n “000”
else
echo −n “${HEX:0:1}${HEX:1:1}${HEX:2:1}”
fi
fi
done
|
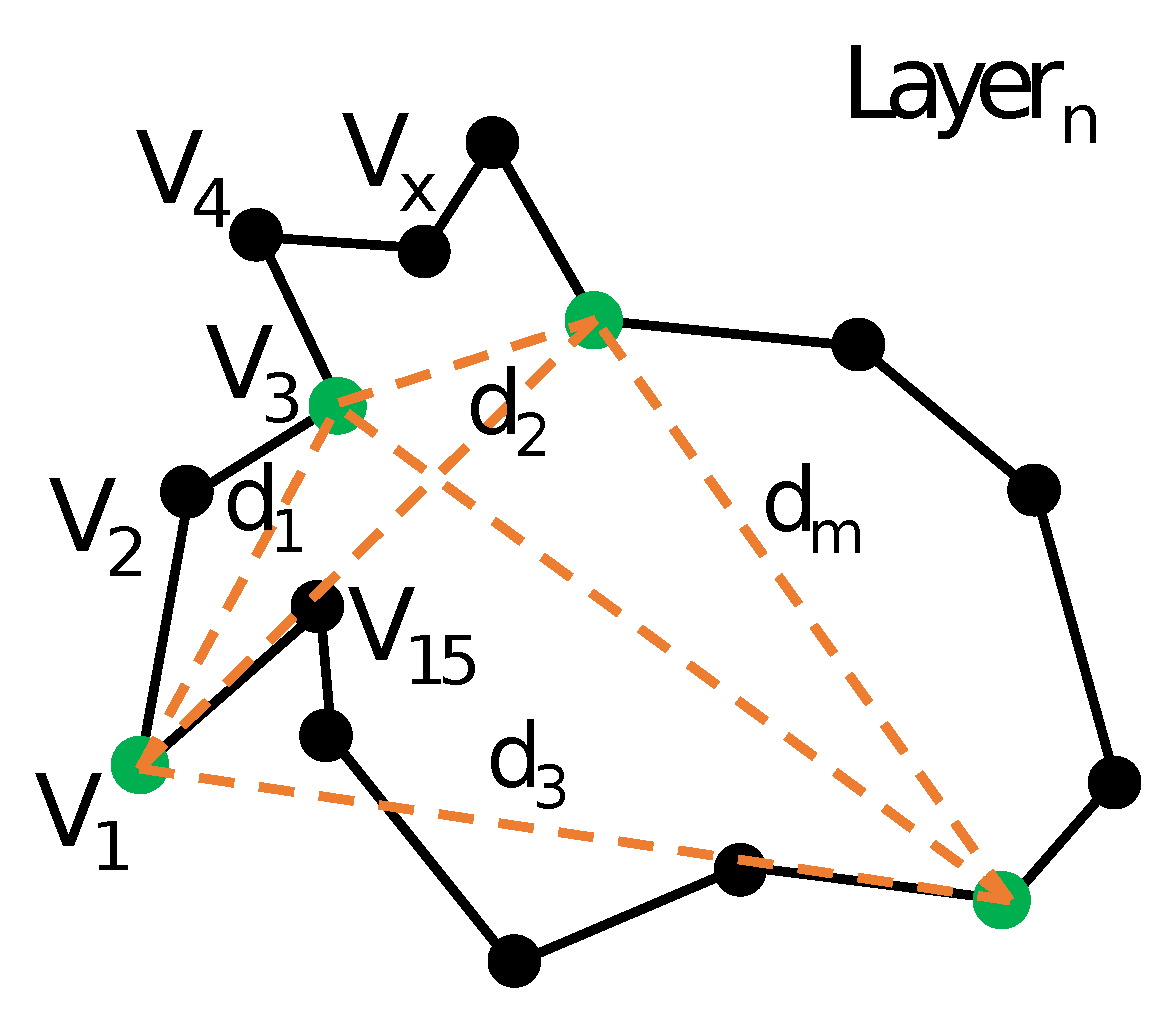
Appendix C. Geometrical Analysis
| Listing 2: Geometrical Analysis Script |
#!/usr/bin/python
import datetime as dt import numpy as np import sys import random t1 =dt.datetime.now() FREECADPATH = ‘/usr/lib/freecad/’ sys.path.append( FREECADPATH ) import FreeCAD import Mesh import Part import os import traceback filename = sys.argv[ 1 ] try: shapes = Mesh.Mesh( filename ) print( “Part:⎵%s” ) % filename BNAME = os.path.basename( filename ) print( “File:⎵%s” ) % BNAME shape = Part.Shape() shapes.removeDuplicatedPoints() shapes.removeDuplicatedFacets() shapes.fixDegenerations() shapes.fixSelfIntersections() shape.makeShapeFromMesh( shapes.Topology, 0.001 ) solid = Part.makeSolid( shape ) print “shells:⎵%d” % len( solid.Shells ) E = len( solid.Edges ) F = len( solid.Faces ) V = len( solid.Vertexes ) max_dist=0 min_dist=sys.maxint
for k in solid.Vertexes:
for l in solid.Vertexes:
# avoid to calculate distance of vertex with itself
if k.X != l.X and k.Y != l.Y and k.Z != l.Z:
cur_dist = np.sqrt( ( k.X − l.X )**2
+ ( k.Y − l.Y )**2 + ( k.Z − l.Z )**2 )
if cur_dist > max_dist:
max_dist = cur_dist
if cur_dist < min_dist:
min_dist = cur_dist
# select 1000 random vertices # compare difference between them # scale to max_dist # and bin into 10 categories: max_dist/10 * x # count how many fit
spacing = range( 0, 10 )
spacing[ 0 ] = spacing[ 1 ]
= spacing[ 2 ] = spacing[ 3 ] = spacing[ 4 ]
= spacing[ 5 ] = spacing[ 6 ] = spacing[ 7 ]
= spacing[ 8 ] = spacing[ 9 ] = 0
for i in range( 1, int (V / 20) ):
r = random.randint( 0, V − 1 )
k = random.randint( 0, V − 1 )
dist = np.sqrt( ( solid.Vertexes[ r ].X
− solid.Vertexes[ k ].X )**2
+ ( solid.Vertexes[ r ].Y
− solid.Vertexes[ k ].Y )**2
+ ( solid.Vertexes[ r ].Z
− solid.Vertexes[ k ].Z )**2 )
norm_dist = dist / max_dist
if norm_dist >= 0 and norm_dist < 0.1:
spacing[ 0 ] = spacing[ 0 ] + 1
elif norm_dist >= 0.1 and norm_dist < 0.2:
spacing[ 1 ] = spacing[ 1 ] + 1
elif norm_dist >= 0.2 and norm_dist < 0.3:
spacing[ 2 ] = spacing[ 2 ] + 1
elif norm_dist >= 0.3 and norm_dist < 0.4:
spacing[ 3 ] = spacing[ 3 ] + 1
elif norm_dist >= 0.4 and norm_dist < 0.5:
spacing[ 4 ] = spacing[ 4 ] + 1
elif norm_dist >= 0.5 and norm_dist < 0.6:
spacing[ 5 ] = spacing[ 5 ] + 1
elif norm_dist >= 0.6 and norm_dist < 0.7:
spacing[ 6 ] = spacing[ 6 ] + 1
elif norm_dist >= 0.7 and norm_dist < 0.8:
spacing[ 7 ] = spacing[ 7 ] + 1
elif norm_dist >= 0.8 and norm_dist < 0.9:
spacing[ 8 ] = spacing[ 8 ] + 1
elif norm_dist >= 0.9 and norm_dist <= 1:
spacing[ 9 ] = spacing[ 9 ] + 1
print spacing newSpacing = [ float( float(x) / int( V / 20 ) ) for x in spacing ] print “max_dist:⎵%f” % max_dist print “min_dist:⎵%f" % min_dist
print “E:⎵%d\nF:⎵%d\nV:⎵%d” % ( E, F, V )
Chi = V − E + F
print “Chi:⎵%d” % Chi
G = ( Chi − 2 ) / −2
print “Genus:⎵%d” % G
print “CompTime:”,
dur = dt.datetime.now() − t1
print dur
print “RES|%s|%s|%d|%f|%d|%d|%d|%f|%f|%s” % (
filename, BNAME, G, dur.seconds + dur.microseconds / 1000000.0,
V, E, F, max_dist, min_dist, newSpacing )
except:
print “Exception”
print >> sys.stderr, “(E)⎵Unexpected⎵error−3:”, sys.exc_info()[0]
traceback.print_exc( file=sys.stdout )
|
References
- MakerBot Industries, LLC. Thingiverse—Digital Designs for Physical Objects. 2008. Available online: https://www.thingiverse.com (accessed on 3 December 2017).
- Facebook, Inc. Welcome to Facebook. 2004. Available online: https://www.facebook.com (accessed on 3 December 2017).
- Twitter, Inc. Twitter. It’s What’s Happening. 2006. Available online: http://twitter.com (accessed on 3 December 2017).
- Alcock, C.; Chilana, N.H.P.K. Barriers to Using, Customizing, and Printing 3D Designs on Thingiverse. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Supporting Group Work, Sanibel Island, FL, USA, 13–16 November 2016; pp. 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, B. 3D Models from the Cloud. In Practical 3D Printers; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 75–97. [Google Scholar]
- Mallon, M. Maker Mania. Public Serv. Q. 2014, 10, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hern, M.S.; Kahle, L.R. The Empowered Customer: User-Generated Content and the Future of Marketing. Glob. Econ. Manag. Rev. 2013, 18, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, A.; Pernot, J.P.; Giannini, F.; Falcidieno, B. Mapping Aesthetic Properties to 3D Free form Shapes through the Use of a Machine Learning Based Framework; IMATI REPORT Series 16-16; IMATI-CNR: Genova, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Killi, S.; Kempton, W.L.; Morrison, A. Design issues and orientations in additive manufacturing. Int. J. Rapid Manuf. 2015, 5, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.; Porter, S.; Bingham, G. Product personalisation using personally meaningful data and the creation of new product attributes. Int. J. Rapid Manuf. 2017, 6, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Vicente, M.; Canyada, M.; Conejero, A. Identifying limitations for design for manufacturing with desktop FFF 3D printers. Int. J. Rapid Manuf. 2015, 5, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, F.W.; Roller, D. Thingiverse: Review and Analysis of Available Files. Int. J. Rapid Manuf. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, H. Gcode to x3g Conversion Post Processor. 2013. Available online: https://github.com/whpthomas/GPX (accessed on 3 December 2017).
- MakerBot Industries, LLC. Connected 3D Printing Solutions. 2009. Available online: https://www.makerbot.com (accessed on 3 December 2017).
- Ranellucci, A.; Lenox, J.; Andersen, H.B.; Bubnik, V.; Dandrimont, N.; Hindness, M.; Ledvina, P.; Sapir, Y.; Sheldrake, M.; Yanev, K.; Hodgson, G. Slic3r—G-Code Generator for 3D Printers. 2011. Available online: http://slic3r.org (accessed on 3 December 2017).
- Hrončok, M.; Tomas Sykora, J. CLI and C Library for Processing Triangulated Solid Meshes. 1995. Available online: https://github.com/admesh/admesh (accessed on 3 December 2017).
- Free Software Foundation, Inc. Bash—GNU Project—Free Software Foundation. 2007. Available online: https://www.gnu.org/software/bash (accessed on 3 December 2017).
Sample Availability: The STL, AMF, GCode, PNG, and GIF files are deposited to https://zenodo.org. See https://dx.doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1098527 for the complete dataset. |

© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baumann, F.W. Thirty Thousand 3D Models from Thingiverse. Data 2018, 3, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/data3010005
Baumann FW. Thirty Thousand 3D Models from Thingiverse. Data. 2018; 3(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/data3010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaumann, Felix W. 2018. "Thirty Thousand 3D Models from Thingiverse" Data 3, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/data3010005
APA StyleBaumann, F. W. (2018). Thirty Thousand 3D Models from Thingiverse. Data, 3(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/data3010005




