Determination of Sage Tea Polyphenols and Their Antioxidant Effects Using an Electrochemical DNA-Based Biosensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Solutions for Electrochemical DNA Biosensor
2.3. Preparation of Sage Tea
2.4. Instrumentation
2.5. Methodology
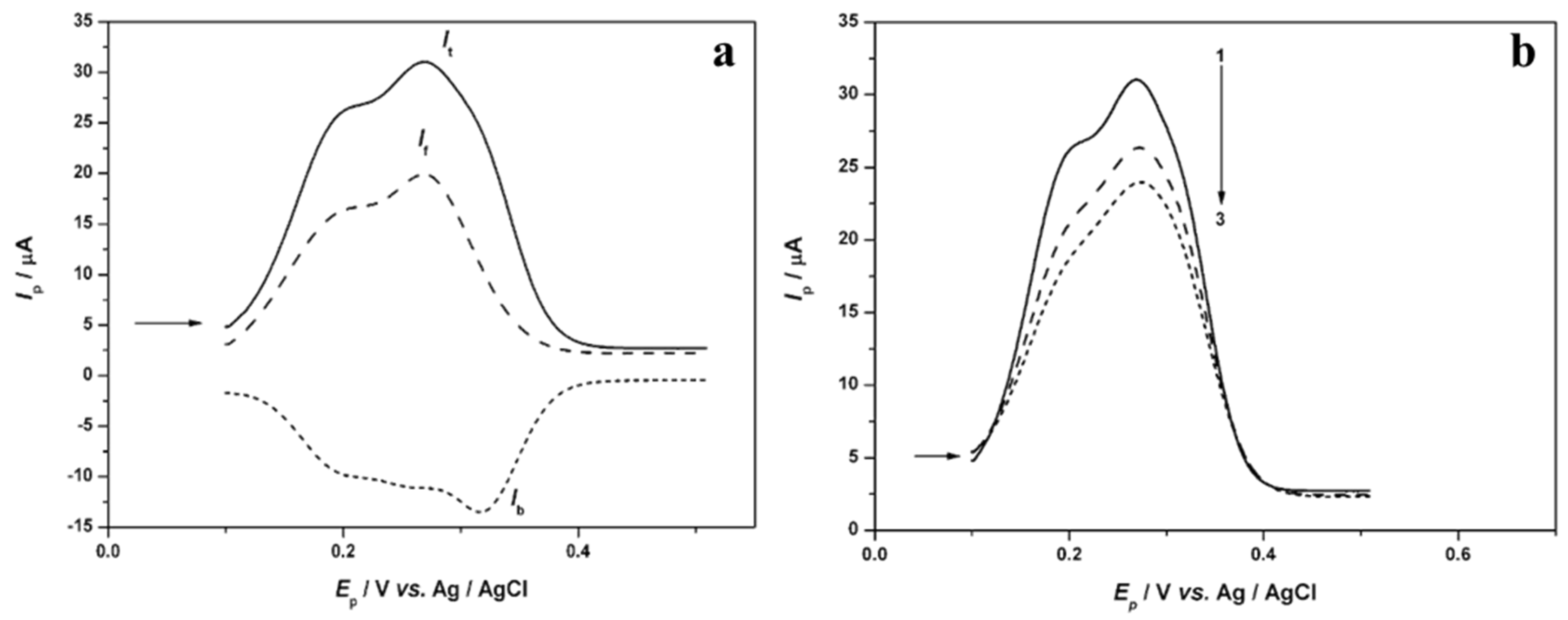
2.6. Determination of the Antioxidant Effect by Electrochemical DNA-Based Biosensor
2.7. Total Phenolic Content
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
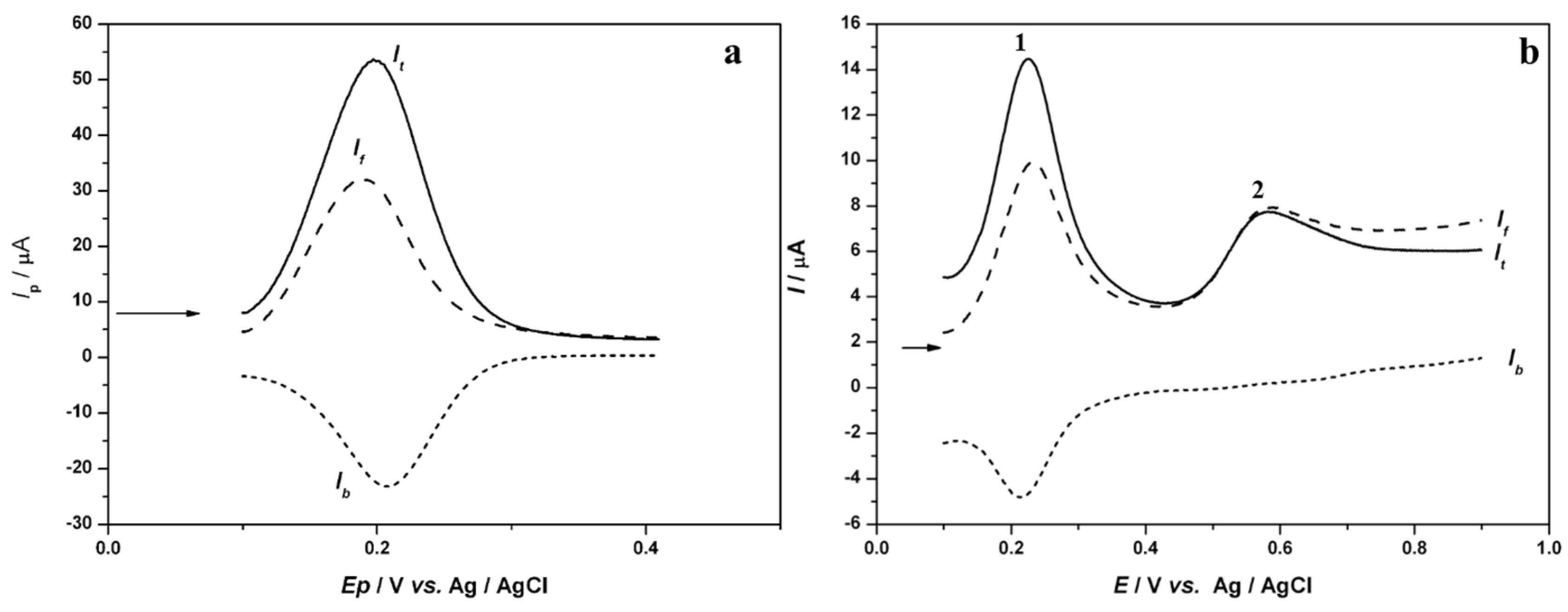
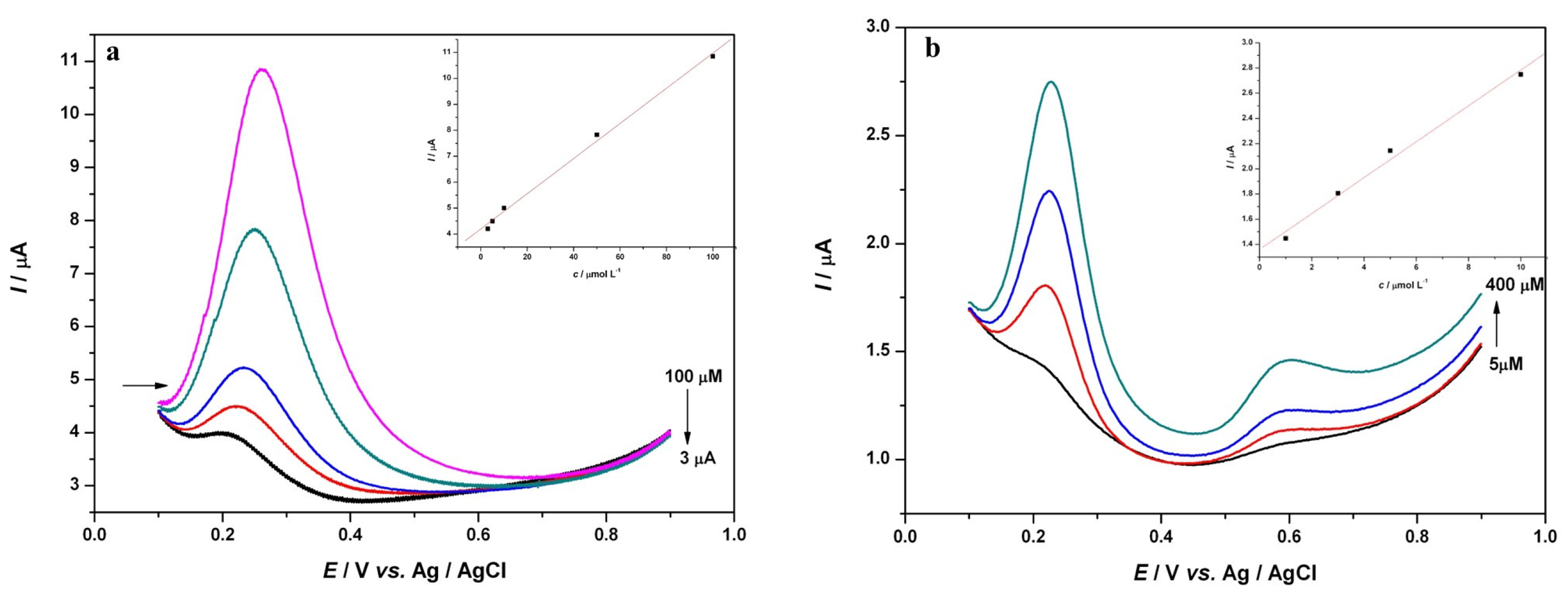
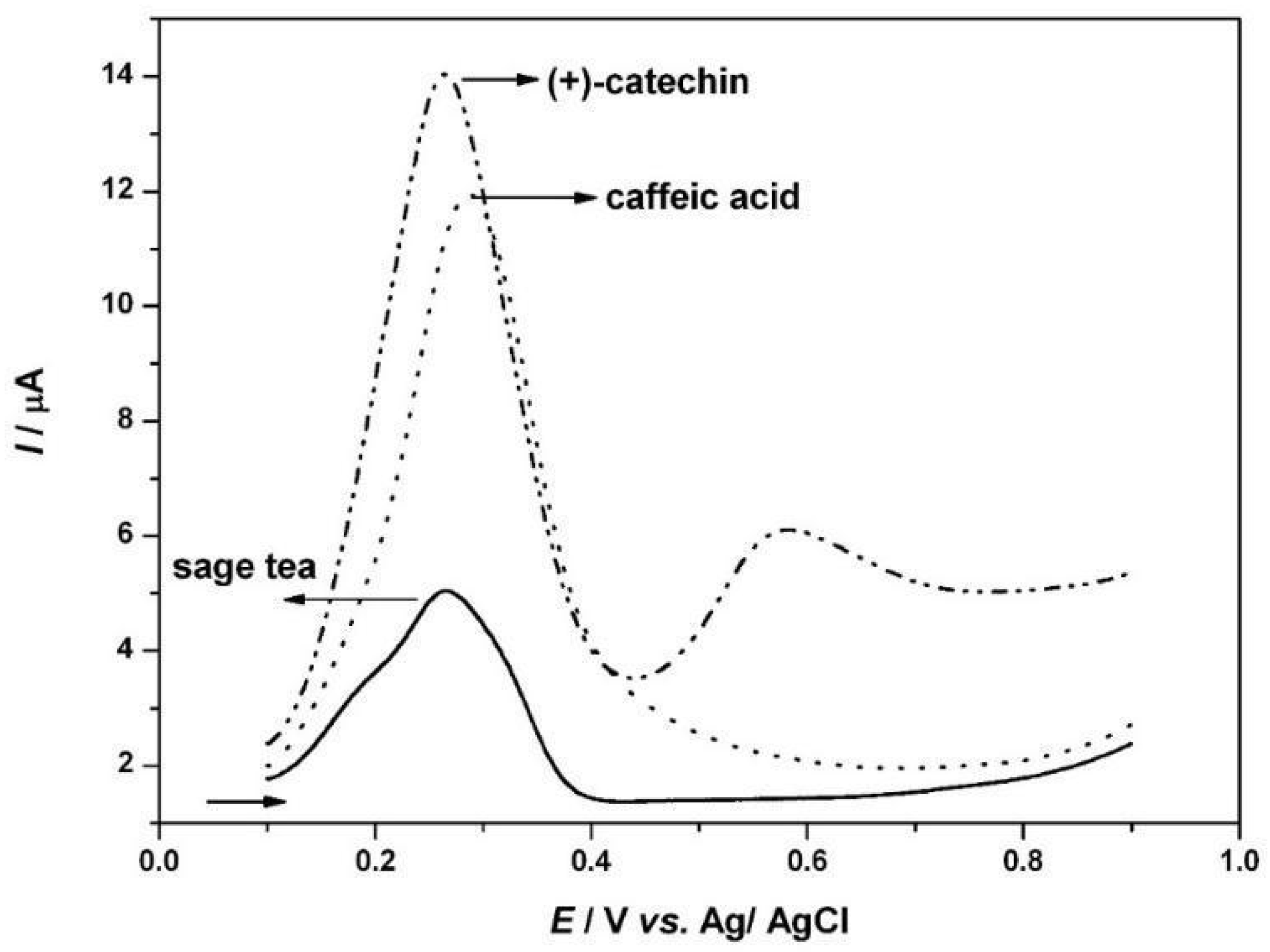
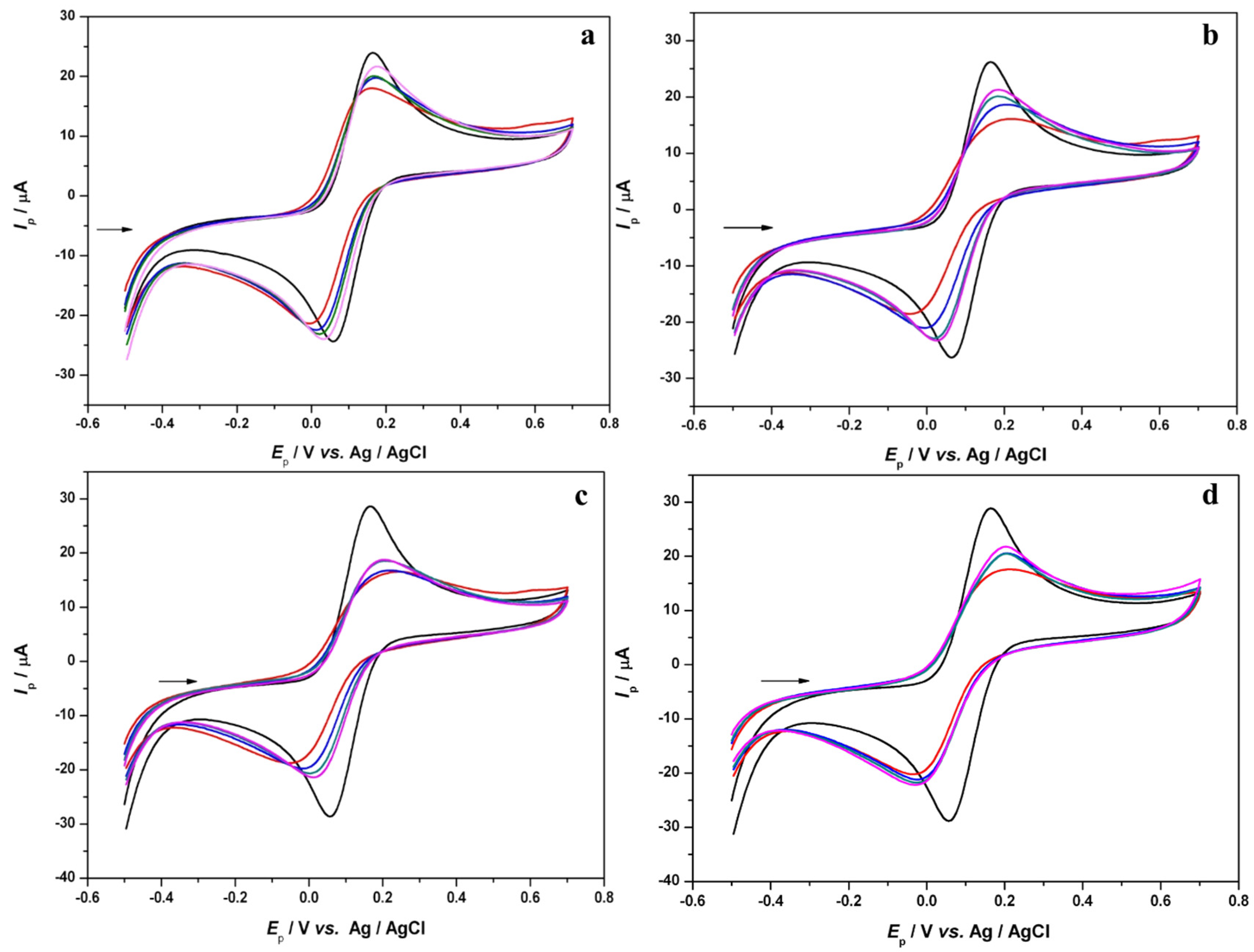
3.1. Voltammetric Study of Polyphenols in Sage Tea
3.2. Determination of the Antioxidant Effect of Sage Tea Using Electrochemical DNA-Based Biosensor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bors, W.; Michel, C.; Stettmaier, K.; Lu, Y.; Foo, L.Y. Antioxidant Mechanisms of Polyphenolic Caffeic Acid Oligomers, Constituents of Salvia officinalis. Biol. Res. 2004, 37, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walch, S.G.; Tinzoh, L.N.; Zimmermann, B.F.; Stühlinger, W.; Lachenmeie, D.W. Antioxidant capacity and polyphenolic composition as quality indicators for aqueous infusions of Salvia officinalis L. (sage tea). Front. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, B.F.; Walch, S.G.; Tinzoh, L.N.; Stühlinger, W.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Rapid UHPLC determination of polyphenols in aqueous infusions of Salvia officinalis L. (sage tea). J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 2459–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Foo, L.Y. Polyphenolics of Salvia—A review. Phytochemistry 2002, 59, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, I.G.; Bizgan, A.-M.C.; Popa, D.E.; Buleandra, M.; Moldovan, Z.; Badea, I.A.; Tekiner, T.A.; Basaga, H.; Ciucu, A.A. Rapid determination of total polyphenolic content in tea samples based on caffeic acid voltammetric behaviour on a disposable graphite electrode. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyatdinova, G.K.; Guss, E.V.; Budnikov, H.C. Voltammetric Evaluation of Polyphenol–Protein Interactions and Their Influence on the Antioxidant Capacity of Tea. J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 75, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, I.; Šeruga, M.; Komorsky-Lovrić, Š. Characterisation of catechins in green and black teas using square-wave voltammetry and RP-HPLC-ECD. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veljković, J.N.; Stojković, M.; Brcanović, J.M. Evaluation of individual phenolic compounds and antioxidant properties of black, green, herbal and fruit tea infusions consumed in Serbia: Spectrophotometrical and electrochemical approaches. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2013, 52, 12–24. [Google Scholar]
- David, I.G.; Buleandră, M.; Popa, D.E.; Bizgan, A.-M.C.; Moldovan, Z.; Badea, I.-A.; Iorgulescu, E.E.; Tekiner, T.A.; Basaga, H. Voltammetric determination of polyphenolic content as rosmarinic acid equivalent in tea samples using pencil graphite electrodes. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 2589–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabela, M.I.; Gumede, N.J.; Singh, P.; Bisetty, K. Evaluation of antioxidants in herbal tea with a laccase biosensor. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 4918–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehru, R.; Hsu, Y.F.; Wang, S.F. Electrochemical determination of caffeic acid in antioxidant beverages samples via a facile synthesis of carbon/iron-based active electrocatalyst. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1122, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikrithika, S.; Kumar, A.S. Electrochemical Detections of Tea Polyphenols: A Review. Electroanalysis 2020, 32, 2343–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Wang, C.; Shen, Y.; Shi, J.; Ding, D. Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors for the Analysis of Tea Components: A Bibliometric Review. Front. Chem. 2022, 9, 818461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suroviec, A.H.; Jones, K.; Sarabia, G. Quantification of Catechins in Tea Using Cyclic Voltammetry. J. Chem. Educ. 2019, 96, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikova, T.N.; Porfireva, A.V.; Vorobev, V.V.; Saveliev, A.A.; Ziyatdinova, G.K.; Evtugyn, G.A. Discrimination of Tea by the Electrochemical Determination of its Antioxidant Properties by a Polyaniline–DNA–Polyphenazine Dye Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. Anal. Lett. 2019, 52, 2562–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Lin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, P.; Wang, C.; Fei, J.; Xie, Y. Detection of catechins in tea beverages using a novel electrochemical sensor based on cyclodextrin nanosponges composite. eFood 2023, 4, e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyatdinova, G.K.; Nizamova, A.M.; Aytuganova, I.I.; Budnikov, H.C. Voltammetric evaluation of the antioxidant capacity of tea on electrodes modified with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 68, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomac, I.; Šeruga, M.; Labuda, J. Evaluation of antioxidant activity of chlorogenic acids and coffee extracts by an electrochemical DNA-based biosensor. Food Chem. 2020, 325, 126787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferancová, A.; Heilerová, Ľ.; Korgová, E.; Šilhár, S.; Štěpánek, I.; Labuda, J. Anti/pro-oxidative properties of selected standard chemicals and tea extracts investigated by DNA-based electrochemical biosensor. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2004, 219, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.P.; dos Santos, W.T.P.; Nossol, E.; Richter, E.M.; Munoz, R.A.A. Critical evaluation of voltammetric techniques for antioxidant capacity and activity: Presence of alumina on glassy-carbon electrodes alters the results. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 358, 136925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilmartin, P.A.; Hsu, C.F. Characterisation of polyphenols in green, oolong, and black teas, and in coffee, using cyclic voltammetry. Food Chem. 2003, 82, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyatdinova, G.; Labuda, J. Complex electrochemical and impedimetric evaluation of DNA damage by using DNA biosensor based on a carbon screen-printed electrode. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 2777–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piljac-Žegarac, J.; Valek, L.; Stipčević, T.; Martinez, S. Electrochemical determination of antioxidant capacity of fruit tea infusions. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiya, Z.; Oualcadi, Y.; Gamar, A.; Berrekhis, F.; Zair, T.; El Hilali, F. Correlation of Total Polyphenolic Content with Antioxidant Activity of Hydromethanolic Extract and Their Fractions of the Salvia officinalis Leaves from Different Regions of Morocco. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 8585313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlavatá, L.; Vyskočil, V.; Beníková, K.; Borbélyová, M.; Labuda, J. DNA-based biosensors with external Nafion and chitosan membranes for the evaluation of the antioxidant activity of beer, coffee, and tea. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2014, 12, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of folin-ciocalteu reagent. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar]
- Dent, M.; Bursać Kovačević, D.; Bosiljkov, T.; Dragović-Uzelac, V. Polyphenolic Composition and Antioxidant Capacity of Indigenous Wild Dalmatian Sage (Salvia officinalis L.). Croat. Chem. Acta 2017, 90, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirceski, V.; Gulaboski, R.; Lovric, M.; Bogeski, I.; Kappl, R.; Hoth, M. Square-Wave Voltammetry: A Review on the Recent Progress. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 2411–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, K.S.; Belhadj Tahar, N.; Abdelhedi, R. Electrochemical behaviour of caffeic acid. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karikalan, N.; Karthik, R.; Chen, S.-M.; Chen, H.-A. A voltammetric determination of caffeic acid in red wines based on the nitrogen doped carbon modified glassy carbon electrode. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, H.R.; Golabi, S.M. Caffeic acid modified glassy carbon electrode for electrocatalytic oxidation of reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). J. Solid State Electrochem. 2000, 4, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Šeruga, M.; Tomac, I. Electrochemical Behaviour of Some Chlorogenic Acids and Their Characterization in Coffee by Square-Wave Voltammetry. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 6134–6154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, E.S.; Couto, R.O. Flavonoid electrochemistry: A review on the electrochemical applications. Braz. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 23, 542–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeiro, P.; Oliveira Brett, A.-M. Catechin electrochemical oxidation mechanisms. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 518, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiya, Z.; Hayani, M.; Hamar, A.; Kharchouf, S.; Amine, S.; Berrekhis, F.; Bouzoubae, A.; Zair, T.; El Hilali, F. Valorization of the Salvia officinalis L. of the Morocco bioactive extracts: Phytochemistry, antioxidant activity and corrosion inhibition. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2019, 31, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.S.; Costa, E.A.; Munoz, R.A.A.; Oliveira, A.; Sousa, R.M.F. Selective electrochemical detection of catechin compounds in herbal medicines. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 017516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labuda, J.; Brett, A.M.O.; Evtigyn, G.; Fojta, M.; Mascini, M.; Ozsoz, M.; Palchetti, I.; Palček, E.; Wang, J. Electrochemical nucleic acid-based biosensors: Concepts terms and methodology (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2010, 82, 1131–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisoschi, A.M.; Cimpeanu, C.; Predoi, G. Electrochemical Methods for Total Antioxidant Capacity and its Main Contributors Determination: A review. Open Chem. 2015, 13, 824–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| The Relative Portion of Surviving DNA/% | Total Polyphenols | Oxidative Potential | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antioxidant | ΔIa, rel | ΔIc, rel | Δ(ΔEp, rel) | mgE/g Sage Tea | Ep/V vs. Ag/AgCl |
| Absence of polyphenols | 39.05 | 39.21 | 26.09 | ||
| (+)-catechin | 64.91 | 64.82 | 57.50 | 0.232 | |
| Caffeic acid | 81.68 | 80.69 | 76.85 | 0.197 | |
| Sample | |||||
| Sage tea | 62.97 | 67.84 | 66.16 | 180 mgCE/g | |
| 102 mgCAE/g | |||||
| 107 mgGAE/g | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomac, I.; Budić, L.; Bobovec, J.; Jakobek, L.; Matić, P. Determination of Sage Tea Polyphenols and Their Antioxidant Effects Using an Electrochemical DNA-Based Biosensor. Beverages 2023, 9, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9030076
Tomac I, Budić L, Bobovec J, Jakobek L, Matić P. Determination of Sage Tea Polyphenols and Their Antioxidant Effects Using an Electrochemical DNA-Based Biosensor. Beverages. 2023; 9(3):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9030076
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomac, Ivana, Lea Budić, Josipa Bobovec, Lidija Jakobek, and Petra Matić. 2023. "Determination of Sage Tea Polyphenols and Their Antioxidant Effects Using an Electrochemical DNA-Based Biosensor" Beverages 9, no. 3: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9030076
APA StyleTomac, I., Budić, L., Bobovec, J., Jakobek, L., & Matić, P. (2023). Determination of Sage Tea Polyphenols and Their Antioxidant Effects Using an Electrochemical DNA-Based Biosensor. Beverages, 9(3), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9030076






