Determination of Caffeine and Elements in Hypertonic, Isotonic, and Hypotonic Beverages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. pH Value
2.3. Caffeine Content
2.4. Elements Content
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. pH
3.2. Caffeine
3.3. Elements
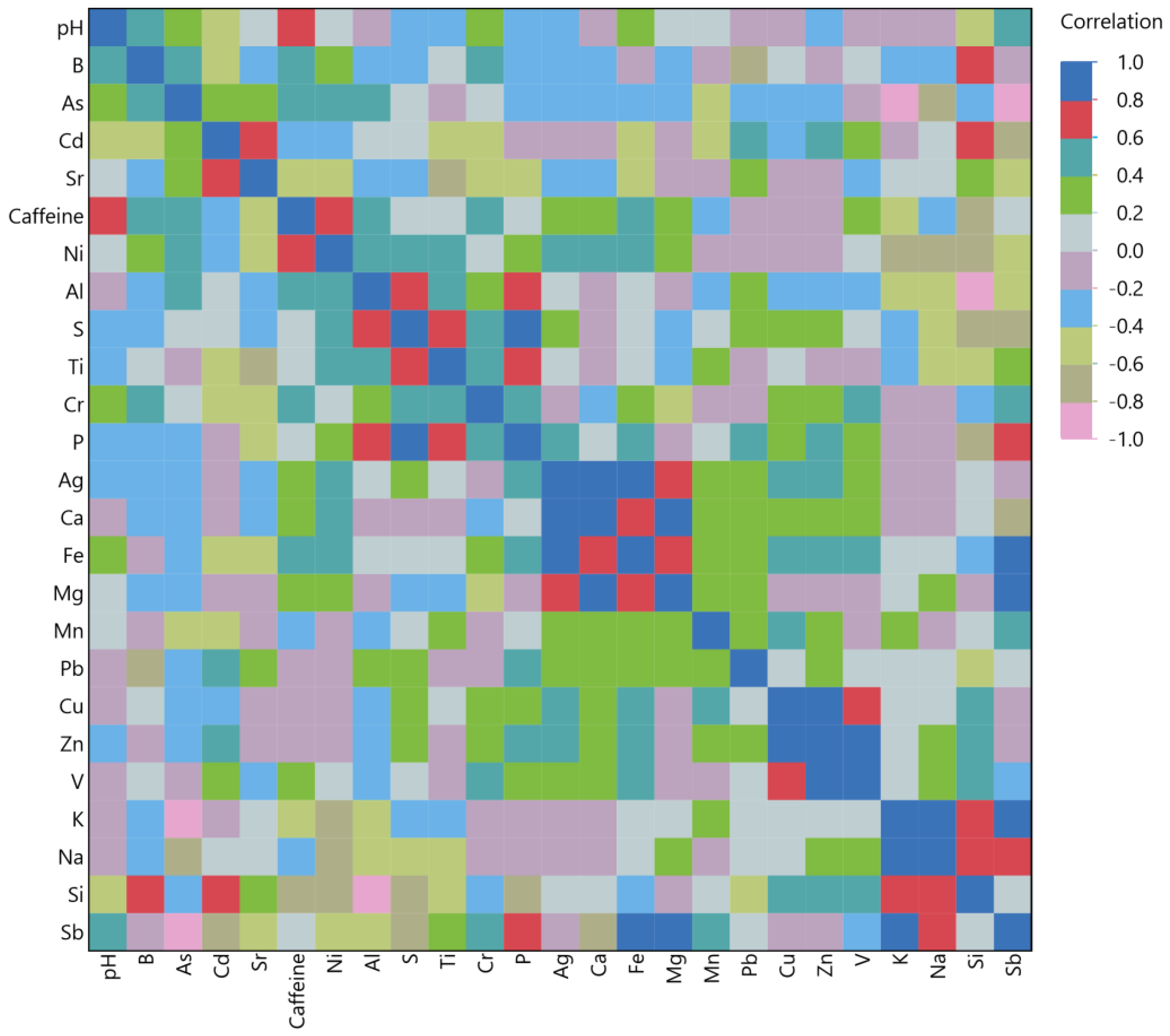
3.4. Multivariate Correlation Analysis
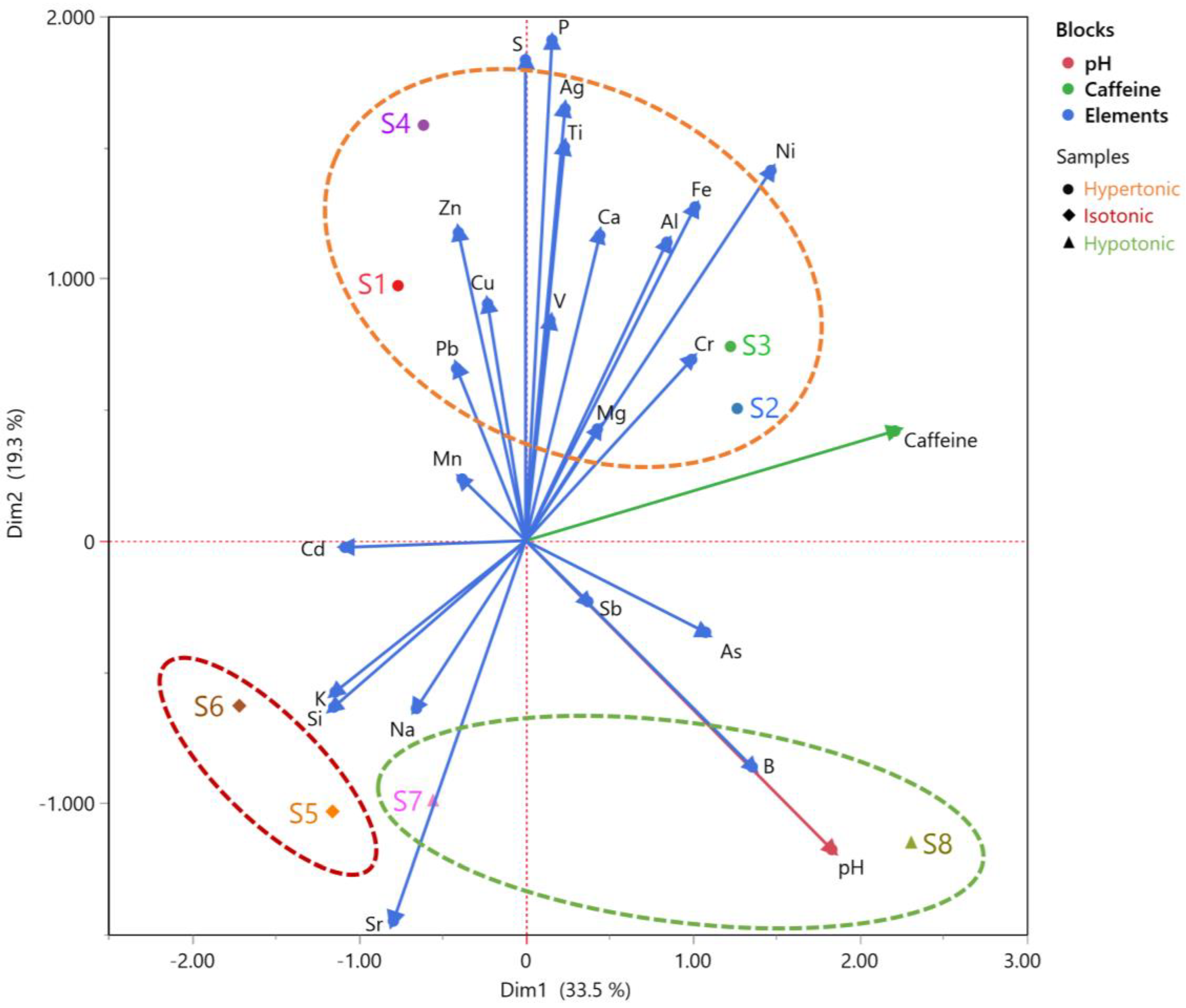
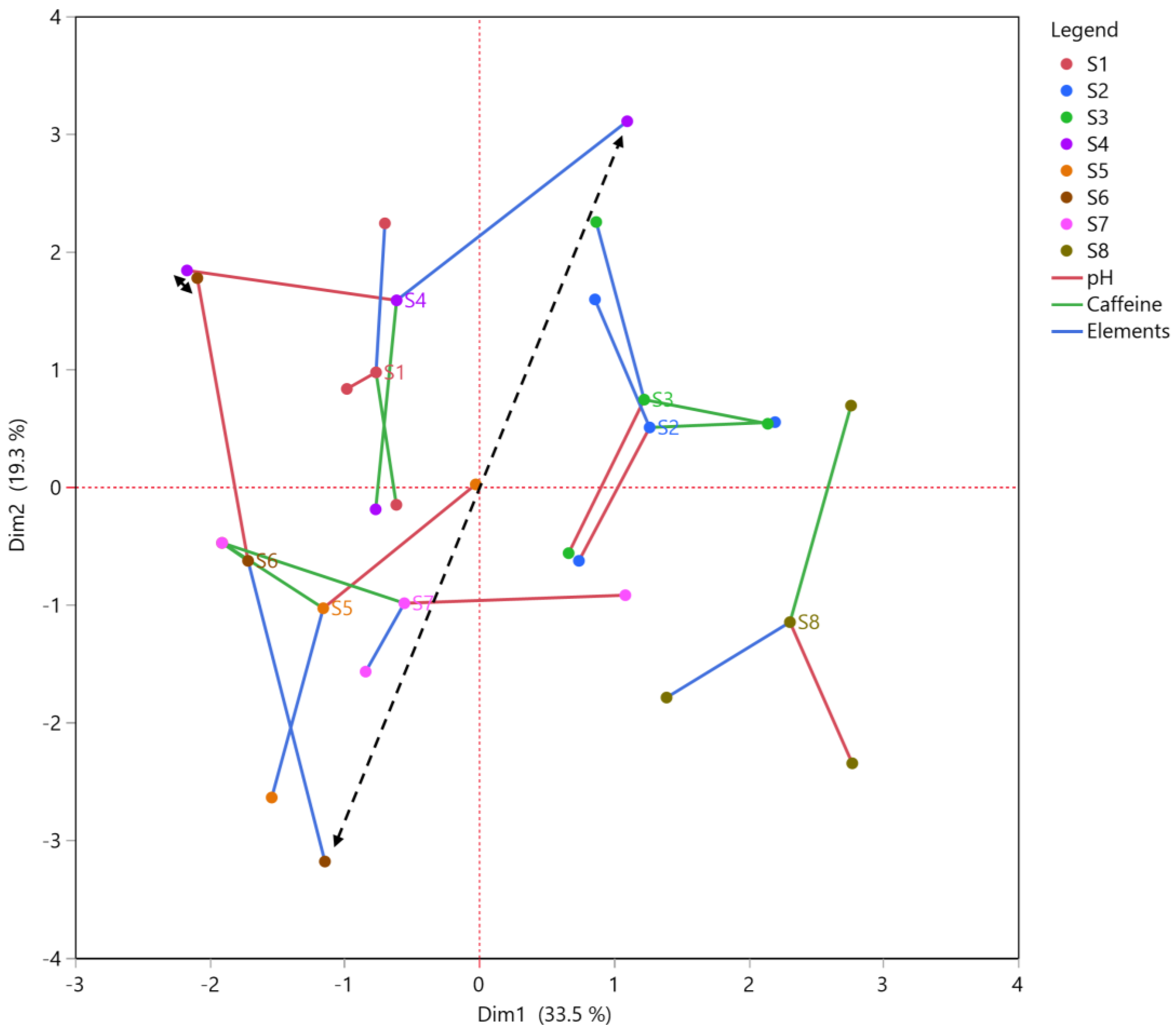
3.5. Multiple Factor Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission. Directorate-General for Research Functional Foods; Publications Office: Brussels, Belgium, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ozen, A.E.; Pons, A.; Tur, J.A. Worldwide Consumption of Functional Foods: A Systematic Review. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wootton-Beard, P.C.; Ryan, L. Improving Public Health?: The Role of Antioxidant-Rich Fruit and Vegetable Beverages. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 3135–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrù, S.; Imperlini, E.; Nigro, E.; Alfieri, A.; Cevenini, A.; Polito, R.; Daniele, A.; Buono, P.; Mancini, A. Role of Functional Beverages on Sport Performance and Recovery. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, S.K.; MacDonald, J.; Joseph, A.M.; Wold, L.E.; Collins, C.L.; Comstock, R.D. Consumption of Sports and Energy Drinks by High School Athletes in the United States: A Pilot Study. Beverages 2015, 1, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugajski, M.; Buszewska-Forajta, M.; Buszewski, B. Functional Beverages in the 21st Century. Beverages 2023, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simulescu, V.; Ilia, G.; Macarie, L.; Merghes, P. Sport and Energy Drinks Consumption before, during and after Training. Sci. Sports 2019, 34, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urdampilleta, A. Hydration and Chemical Ingredients in Sport Drinks: Food Safety in the European Context. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 31, 1889–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowlands, D.S.; Kopetschny, B.H.; Badenhorst, C.E. The Hydrating Effects of Hypertonic, Isotonic and Hypotonic Sports Drinks and Waters on Central Hydration During Continuous Exercise: A Systematic Meta-Analysis and Perspective. Sports Med. Auckl. NZ 2022, 52, 349–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombes, J.S.; Hamilton, K.L. The Effectiveness of Commercially Available Sports Drinks. Sports Med. 2000, 29, 181–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anissa, Z.; Sofiane, B.; Adda, A.; Marlie-Landy, J. Evaluation of Trace Metallic Element Levels in Coffee by Icp-Ms: A Comparative Study among Different Origins, Forms, and Packaging Types and Consumer Risk Assessment. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, N.; DeWolfe, J.; Story, M.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Adolescent Consumption of Sports and Energy Drinks: Linkages to Higher Physical Activity, Unhealthy Beverage Patterns, Cigarette Smoking, and Screen Media Use. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2014, 46, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ober, J.; Karwot, J. Tap Water Quality: Seasonal User Surveys in Poland. Energies 2021, 14, 3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, T.E. Caffeine and Exercise: Metabolism, Endurance and Performance. Sports Med. 2001, 31, 785–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbloom, C. Energy Drinks, Caffeine, and Athletes. Nutr. Today 2014, 49, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, D.B.; Del Coso, J.; Casonatto, J.; Polito, M.D. Acute Effects of Caffeine-Containing Energy Drinks on Physical Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, E.R.; Ziegenfuss, T.; Kalman, D.; Kreider, R.; Campbell, B.; Wilborn, C.; Taylor, L.; Willoughby, D.; Stout, J.; Graves, B.S.; et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: Caffeine and Performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2010, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reissig, C.J.; Strain, E.C.; Griffiths, R.R. Caffeinated Energy Drinks—A Growing Problem. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2009, 99, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attipoe, S.; Leggit, J.; Deuster, P.A. Caffeine Content in Popular Energy Drinks and Energy Shots. Mil. Med. 2016, 181, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudema, S.; Thomas, C.; Ngowi, H. The Caffeine Content of Energy Drinks in Accordance with the Information on the Package Label. Adv. Public Health 2023, 2023, e9938190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeranz, J.L.; Munsell, C.R.; Harris, J.L. Energy Drinks: An Emerging Public Health Hazard for Youth. J. Public Health Policy 2013, 34, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, B.B.A.; Brum, D.M.; Cassella, R.J. Determination of Metals in Soft Drinks Packed in Different Materials by ETAAS. Food Chem. 2015, 185, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilic, S.; Cengiz, M.F.; Kilic, M. Monitoring of Metallic Contaminants in Energy Drinks Using ICP-MS. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahaya, T.O.; Gulumbe, B.H.; Umar, A.K.; Yusuf, A.; Mohammed, A.Z.; Izuafa, A.; Abubakar, A. Heavy Metal Content and Associated Health Risks in Selected Energy Drinks Sold in Birnin Kebbi, Nigeria. Afr. J. Health Saf. Environ. 2022, 3, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalas, S.; Athanasiadis, V.; Dourtoglou, V.G. Humic and Fulvic Acids as Potentially Toxic Metal Reducing Agents in Water. CLEAN Soil Air Water 2018, 46, 1700608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palur, K.; Archakam, S.C.; Koganti, B. Chemometric Assisted UV Spectrophotometric and RP-HPLC Methods for Simultaneous Determination of Paracetamol, Diphenhydramine, Caffeine and Phenylephrine in Tablet Dosage Form. Spectrochim. Acta. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 243, 118801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.S.; Junior, J.B.P.; de Araújo Gomes, A.; Carvalho, F.I.M.; Filho, H.A.D.; das Graças Fernandes Dantas, K. Mineral Composition Evaluation in Energy Drinks Using ICP OES and Chemometric Tools. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 194, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, D.; Donangelo, C.M.; Farah, A. Fast Simultaneous Analysis of Caffeine, Trigonelline, Nicotinic Acid and Sucrose in Coffee by Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cindrić, I.J.; Zeiner, M.; Kröppl, M.; Stingeder, G. Comparison of Sample Preparation Methods for the ICP-AES Determination of Minor and Major Elements in Clarified Apple Juices. Microchem. J. 2011, 99, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leśniewicz, A.; Grzesiak, M.; Żyrnicki, W.; Borkowska-Burnecka, J. Mineral Composition and Nutritive Value of Isotonic and Energy Drinks. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 170, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onianwa, P.C.; Adetola, I.G.; Iwegbue, C.M.A.; Ojo, M.F.; Tella, O.O. Trace Heavy Metals Composition of Some Nigerian Beverages and Food Drinks. Food Chem. 1999, 66, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunden, S.; Wallace, T. Tin in Canned Food: A Review and Understanding of Occurrence and Effect. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 1651–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkar, J.; Rakesh, M. Leaching of Elements from Packaging Material into Canned Foods Marketed in India. Food Control 2014, 40, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kregiel, D. Health Safety of Soft Drinks: Contents, Containers, and Microorganisms. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 128697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, T.A.; Levy, S.M.; Broffitt, B.; Warren, J.J.; Eichenberger-Gilmore, J.M.; Burns, T.L.; Stumbo, P.J. Dental Caries and Beverage Consumption in Young Children. Pediatrics 2003, 112, e184–e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.M.; Vani, N.V.; Almutari, D.A.; Jafar, M.A.; Boreak, N. Analysis of Sugars and PH in Commercially Available Soft Drinks in Saudi Arabia with a Brief Review on Their Dental Implications. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2016, 6, S192–S196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the Safety of Caffeine. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P.A.; Attipoe, S.; Travis, J.; Stevens, M.; Deuster, P. Caffeine Content of Dietary Supplements Consumed on Military Bases. JAMA Intern. Med. 2013, 173, 592–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, T.M.; Lieberman, H.R. Do Energy Drinks Contain Active Components Other than Caffeine? Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 730–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bratty, M.; Alhazmi, H.A.; Rehman, Z.U.; Javed, S.A.; Ahsan, W.; Najmi, A.; Khuwaja, G.; Makeen, H.A.; Khalid, A. Determination of Caffeine Content in Commercial Energy Beverages Available in Saudi Arabian Market by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometric Analysis. J. Spectrosc. 2020, 2020, e3716343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament, Council of the European Union. Directive (EU) 2020/2184 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2020 on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption (Recast) (Text with EEA Relevance); European Union Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.P.; Tuttle, T.D.; Higgins, C.L. Energy Beverages: Content and Safety. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingöl, M.; Yentür, G.; Er, B.; Öktem, A.B. Determination of Some Heavy Metal Levels in Soft Drinks from Turkey Using ICP/OES Method. Czech J. Food Sci. 2010, 28, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, D.; Froberg, B.; Wolf, A.; Rusyniak, D.E. Heavy Metal Poisoning: Clinical Presentations and Pathophysiology. Clin. Lab. Med. 2006, 26, 67–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Al Rmalli, S.W.; Haris, P.I.; Harrington, C.F.; Ayub, M. A Survey of Arsenic in Foodstuffs on Sale in the United Kingdom and Imported from Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 337, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, B.K.; Suzuki, K.T. Arsenic Round the World: A Review. Talanta 2002, 58, 201–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filella, M. Antimony and PET Bottles: Checking Facts. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyataka, P.H.M.; Dantas, S.T.; Albino, A.C.; Pallone, J.A.L. Antimony Assessment in PET Bottles for Soft Drink. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhou, P.; Li, H.; Juhasz, A.; Cui, X. Leaching and In Vivo Bioavailability of Antimony in PET Bottled Beverages. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15227–15235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onianwa, P.C.; Adeyemo, A.O.; Idowu, O.E.; Ogabiela, E.E. Copper and Zinc Contents of Nigerian Foods and Estimates of the Adult Dietary Intakes. Food Chem. 2001, 72, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirwan, A.; Putra, M.D.; Lestari, R.A.; Haka, M.R.; Ulum, M.B. Effect of Acid Concentration on the Aluminum Leaching Process. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 524, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froes, R.E.S.; Borges Neto, W.; Naveira, R.L.P.; Silva, N.C.; Nascentes, C.C.; da Silva, J.B.B. Exploratory Analysis and Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP OES) Applied in the Determination of Metals in Soft Drinks. Microchem. J. 2009, 92, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolaylı, S.; Ocak, M.; Küçük, M.; Abbasoǧlu, R. Does Caffeine Bind to Metal Ions? Food Chem. 2004, 84, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khediri, S.; Fakhet, W.; Moulahi, T.; Khan, R.; Thaljaoui, A.; Kachouri, A. Improved Node Localization Using K-Means Clustering for Wireless Sensor Networks. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2020, 37, 100284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | pH | Container | Label |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 2.99 ± 0.2 b,c,d | PET bottle | carbon dioxide, citric acid, orange juice from concentrate (5%), caffeine, sodium gluconate, potassium sorbate, ascorbic acid |
| S2 | 3.44 ± 0.08 a,b | Aluminum can | carbon dioxide, citric acid, taurine, sodium citrate, L-carnitine, L-tartrate, caffeine, sorbic acid, benzoic acid, niacinamide (vit. B3), pyridoxine hydrochloride (vit. B6), riboflavin (vit. B2), cyanocobalamin (vit. B12) |
| S3 | 3.42 ± 0.17 a,b | Aluminum can | carbon dioxide, citric acid, taurine, sodium bicarbonate, magnesium carbonate, colors, caffeine, niacinamide (vit. B3), pyridoxine hydrochloride (vit. B6), calcium pantothenate, cyanocobalamin (vit. B12) |
| S4 | 2.68 ± 0.14 d | Aluminum can | carbon dioxide, phosphoric acid, natural flavors, caffeine |
| S5 | 3.24 ± 0.22 b,c | PET bottle | citric acid, sodium citrate, monopotassium phosphate, yellow 6 (sunset yellow FCF) |
| S6 | 2.7 ± 0.18 c,d | PET bottle | less than 0.5% of citric acid, monopotassium phosphate, magnesium chloride, calcium chloride, vitamins B3, B6, B12 (niacinamide, pyridoxine hydrochloride, cyanocobalamin), ascorbic acid, calcium disodium EDTA |
| S7 | 3.53 ± 0.25 a,b | PET bottle | citric acid, L-carnitine, acesulfame potassium, sucralose |
| S8 | 3.97 ± 0.27 a | PET bottle | citric acid monohydrate, L-carnitine, L-citrulline, beta-alanine, caffeine anhydrous, taurine, sucralose, acesulfame potassium, colors (sulfite ammonia caramel, ponceau 4R, carmoisine) |
| Code | Caffeine Content Listed on the Label (per 100 mL of Beverage) | Serving (mL) | Caffeine (mg/100 mL) Measured | mg Caf/Serving Measured | % Difference from Caffeine Label Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Caffeine listed as a flavoring ingredient but not quantified | 500 | 10.81 ± 0.74 c | 54.05 | n.a. |
| S2 | 32 mg | 500 | 34.23 ± 1.95 b | 171.15 | +6.97 |
| S3 | 32 mg | 250 | 33.78 ± 0.95 b | 84.45 | +5.56 |
| S4 | Caffeine listed as an ingredient | 330 | 9.53 ± 0.6 c | 31.45 | n.a. |
| S5 | n.a. | 500 | 0.04 ± 0 d | 0.20 | n.a. |
| S6 | n.a. | 500 | 0.02 ± 0 d | 0.10 | n.a. |
| S7 | n.a. | 500 | 0.03 ± 0 d | 0.15 | n.a. |
| S8 | 40 mg | 250 | 38.93 ± 0.9 a | 97.32 | –2.68 |
| Element | Parametric Value * (mg/L) | Coded HIH Beverage Samples | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | ||
| Ag | n.a. | 0.046 ± 0.001 a,b | 0.041 ± 0.001 b,c | 0.049 ± 0.003 a | 0.043 ± 0.001 b,c | 0.04 ± 0.002 c | 0.04 ± 0.001 c | 0.04 ± 0.003 c | 0.039 ± 0.002 c |
| Al | 0.2 | 0.19 ± 0.014 d | 0.434 ± 0.013 a | 0.242 ± 0.029 c | 0.35 ± 0.019 b | 0.081 ± 0.003 e | 0.109 ± 0.005 e | 0.161 ± 0.008 d | 0.116 ± 0.007 e |
| As | 0.01 | 0.004 ± 0 d | 0.009 ± 0.001 a | 0.006 ± 0 c | 0.006 ± 0 c | 0.003 ± 0 e | 0.008 ± 0 a,b | 0.007 ± 0 b | 0.008 ± 0 a |
| B | 1.5 | 0.277 ± 0.007 b | 0.246 ± 0.018 b,c | 0.218 ± 0.012 c,d | 0.258 ± 0.012 b,c | 0.197 ± 0.007 d | 0.271 ± 0.017 b | 0.267 ± 0.014 b | 0.56 ± 0.034 a |
| Ba | n.a. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Be | n.a. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Ca | n.a. | 40.295 ± 0.967 b | 2.262 ± 0.131 d | 86.70 ± 4.075 a | 15.034 ± 0.947 c | 3.806 ± 0.247 d | 6.19 ± 0.229 d | 5.618 ± 0.14 d | 2.37 ± 0.123 d |
| Cd | 0.005 | n.d. | 0.002 ± 0 b | n.d. | 0.001 ± 0 c | 0.002 ± 0 c | 0.002 ± 0 a | 0.002 ± 0 b | 0.001 ± 0 d |
| Co | n.a. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Cr | 0.05 | 0.008 ± 0 c | 0.01 ± 0 a | 0.001 ± 0 f | 0.008 ± 0 c | 0.004 ± 0 d | 0.001 ± 0 f | 0.003 ± 0 e | 0.009 ± 0 b |
| Cu | 2.0 | 0.187 ± 0.01 a | 0.035 ± 0.002 d | 0.048 ± 0.003 c | 0.047 ± 0.001 c,d | 0.014 ± 0 e | 0.018 ± 0.001 e | 0.072 ± 0.005 b | 0.044 ± 0.003 c,d |
| Fe | 0.2 | 0.087 ± 0.003 a | 0.073 ± 0.003 b | 0.093 ± 0.007 a | 0.065 ± 0.002 b,c | 0.066 ± 0.003 b,c | 0.04 ± 0.001 d | 0.058 ± 0.002 c | 0.064 ± 0.005 b,c |
| K | n.a. | 109.422 ± 8.207 b | 10.578 ± 0.434 d,e | 6.368 ± 0.452 e | 28.218 ± 1.411 c | 210.25 ± 12.405 a | 30.707 ± 1.781 c | 31.123 ± 2.085 c | 21.834 ± 1.419 c,d |
| Li | n.a. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.015 ± 0.001 |
| Mg | n.a. | 13.959 ± 0.335 c | 0.369 ± 0.018 d | 98.489 ± 6.205 a | 1.685 ± 0.113 d | 37.608 ± 1.88 b | 2.194 ± 0.156 d | 0.868 ± 0.036 d | 0.63 ± 0.013 d |
| Mn | 0.05 | 0.02 ± 0.001 b | 0.008 ± 0 e | 0.018 ± 0.001 b,c | 0.019 ± 0.001 b,c | 0.017 ± 0.001 c,d | 0.01 ± 0.001 e | 0.022 ± 0.001 a | 0.015 ± 0.001 d |
| Mo | n.a. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.006 ± 0.001 |
| Na | n.a. | 40.58 ± 2.8 b | 24.25 ± 1.091 c | 21.35 ± 0.705 c,d | 4.479 ± 0.228 f | 60.52 ± 2.179 a | 25.25 ± 1.162 c | 9.996 ± 0.59 e | 20.009 ± 0.68 d |
| Ni | n.a. | 0.012 ± 0.001 c | 0.015 ± 0.001 b | 0.018 ± 0.001 a | 0.016 ± 0.001 b | 0.007 ± 0 d | 0.012 ± 0.001 c | 0.01 ± 0.001 c | 0.015 ± 0.001 b |
| P | n.a. | 1.629 ± 0.101 b | 1.896 ± 0.118 a | 1.166 ± 0.03 c | 2.042 ± 0.047 a | 0.993 ± 0.065 c,d | 0.293 ± 0.012 f | 0.932 ± 0.022 d | 0.543 ± 0.023 e |
| Pb | 0.01 | 0.008 ± 0 c,d | 0.009 ± 0.001 a,b | 0.008 ± 0 b,c | 0.007 ± 0 d | 0.008 ± 0 c,d | 0.005 ± 0 e | 0.01 ± 0.001 a | 0.003 ± 0 f |
| S | n.a. | 40.306 ± 2.701 c | 55.57 ± 2.89 b | 20.414 ± 0.817 e | 69.107 ± 3.317 a | 5.222 ± 0.261 g | 16.687 ± 0.567 e,f | 29.437 ± 0.706 d | 12.334 ± 0.863 f |
| Sb | n.a. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 0.003 ± 0 a | 0.002 ± 0 d | 0.002 ± 0 c | 0.002 ± 0 b |
| Se | 0.02 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Si | n.a. | 8.607 ± 0.577 a | 0.624 ± 0.028 c | 3.073 ± 0.187 b | 1.249 ± 0.086 c | n.d. | 8.097 ± 0.405 a | n.d. | n.d. |
| Sr | n.a. | 0.014 ± 0 e | 0.024 ± 0.001 c | 0.016 ± 0.001 d | 0.001 ± 0 g | 0.025 ± 0.001 c | 0.033 ± 0.001 b | 0.043 ± 0.001 a | 0.011 ± 0.001 f |
| Ti | n.a. | 0.019 ± 0.001 c | 0.022 ± 0.001 c | 0.018 ± 0.001 c | 0.084 ± 0.004 a | 0.007 ± 0 d,e | 0.003 ± 0 e | 0.011 ± 0.001 d | 0.027 ± 0.001 b |
| Th | n.a. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| V | n.a. | 0.008 ± 0 a | 0.005 ± 0 b | 0.003 ± 0 d | 0.001 ± 0 e,f | 0.002 ± 0 e | 0.003 ± 0 c,d | 0.001 ± 0 f | 0.003 ± 0 c |
| Zn | n.a. | 0.2 ± 0.014 a | 0.1 ± 0.002 b | 0.091 ± 0.005 b | 0.085 ± 0.002 b,c | 0.072 ± 0.004 c,d | 0.072 ± 0.005 c,d | 0.089 ± 0.006 b,c | 0.064 ± 0.002 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Athanasiadis, V.; Chatzimitakos, T.; Kalompatsios, D.; Mantiniotou, M.; Bozinou, E.; Lalas, S.I. Determination of Caffeine and Elements in Hypertonic, Isotonic, and Hypotonic Beverages. Beverages 2023, 9, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9030056
Athanasiadis V, Chatzimitakos T, Kalompatsios D, Mantiniotou M, Bozinou E, Lalas SI. Determination of Caffeine and Elements in Hypertonic, Isotonic, and Hypotonic Beverages. Beverages. 2023; 9(3):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9030056
Chicago/Turabian StyleAthanasiadis, Vassilis, Theodoros Chatzimitakos, Dimitrios Kalompatsios, Martha Mantiniotou, Eleni Bozinou, and Stavros I. Lalas. 2023. "Determination of Caffeine and Elements in Hypertonic, Isotonic, and Hypotonic Beverages" Beverages 9, no. 3: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9030056
APA StyleAthanasiadis, V., Chatzimitakos, T., Kalompatsios, D., Mantiniotou, M., Bozinou, E., & Lalas, S. I. (2023). Determination of Caffeine and Elements in Hypertonic, Isotonic, and Hypotonic Beverages. Beverages, 9(3), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9030056