Influence of Native S. cerevisiae Strains on the Final Characteristics of “Pago” Garnacha Wines from East Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Winery Characteristics
2.2. Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Garnacha Grape Musts
2.3. Counts and Isolation of Native Yeasts from Industrial Fermentations
2.4. Identification and Typing of Yeasts
2.5. S. cerevisiae Strain Characterisation
2.6. Small-Scale Red Wine Fermentation
2.7. Analytical Methods
2.8. Statistical Analysis
2.9. Sensory Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Counts, Isolation, Identification, and Typing of Yeast Counts from Industrial Garnacha Fermentations
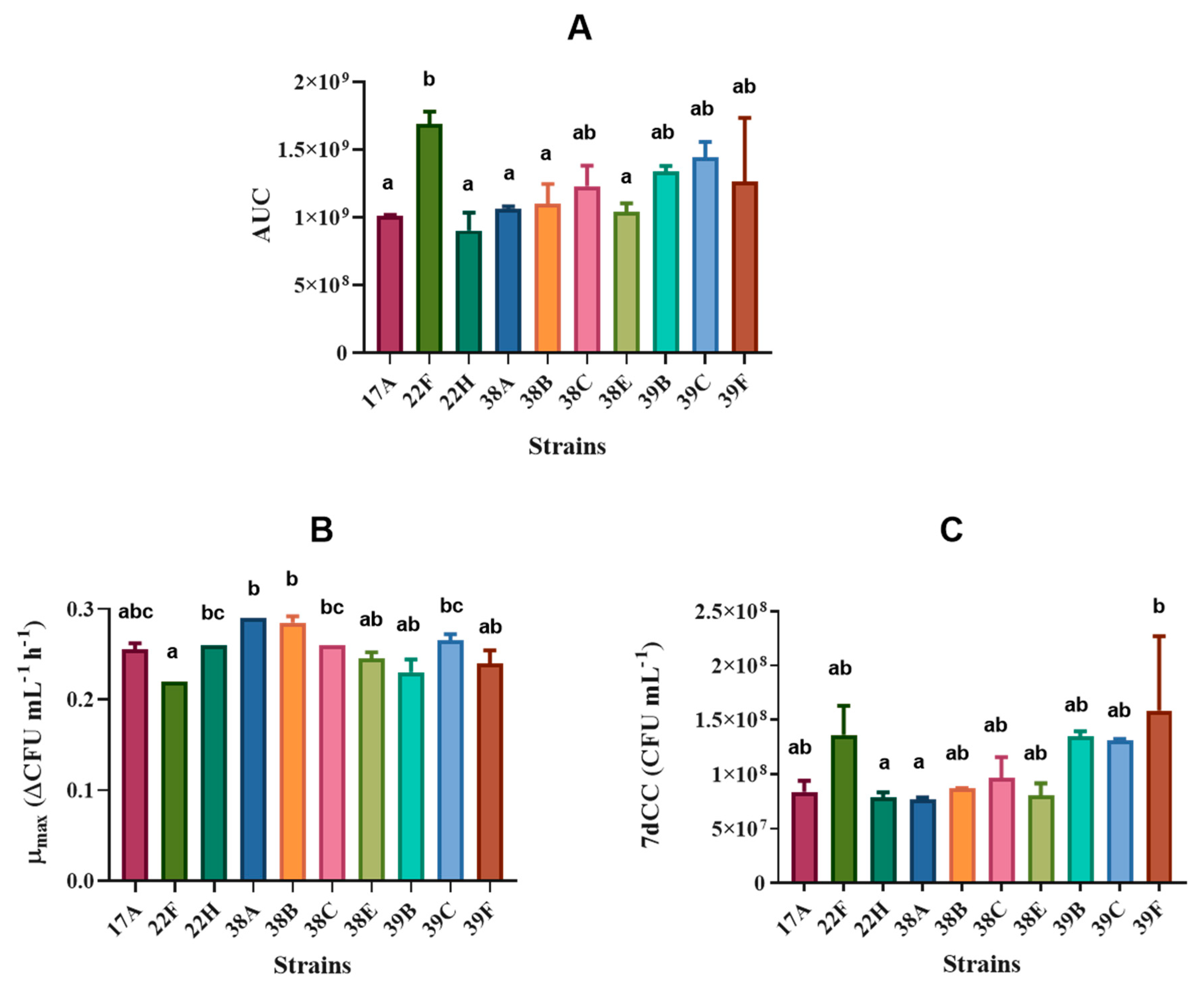
3.2. S. cerevisiae Yeast Characterisation
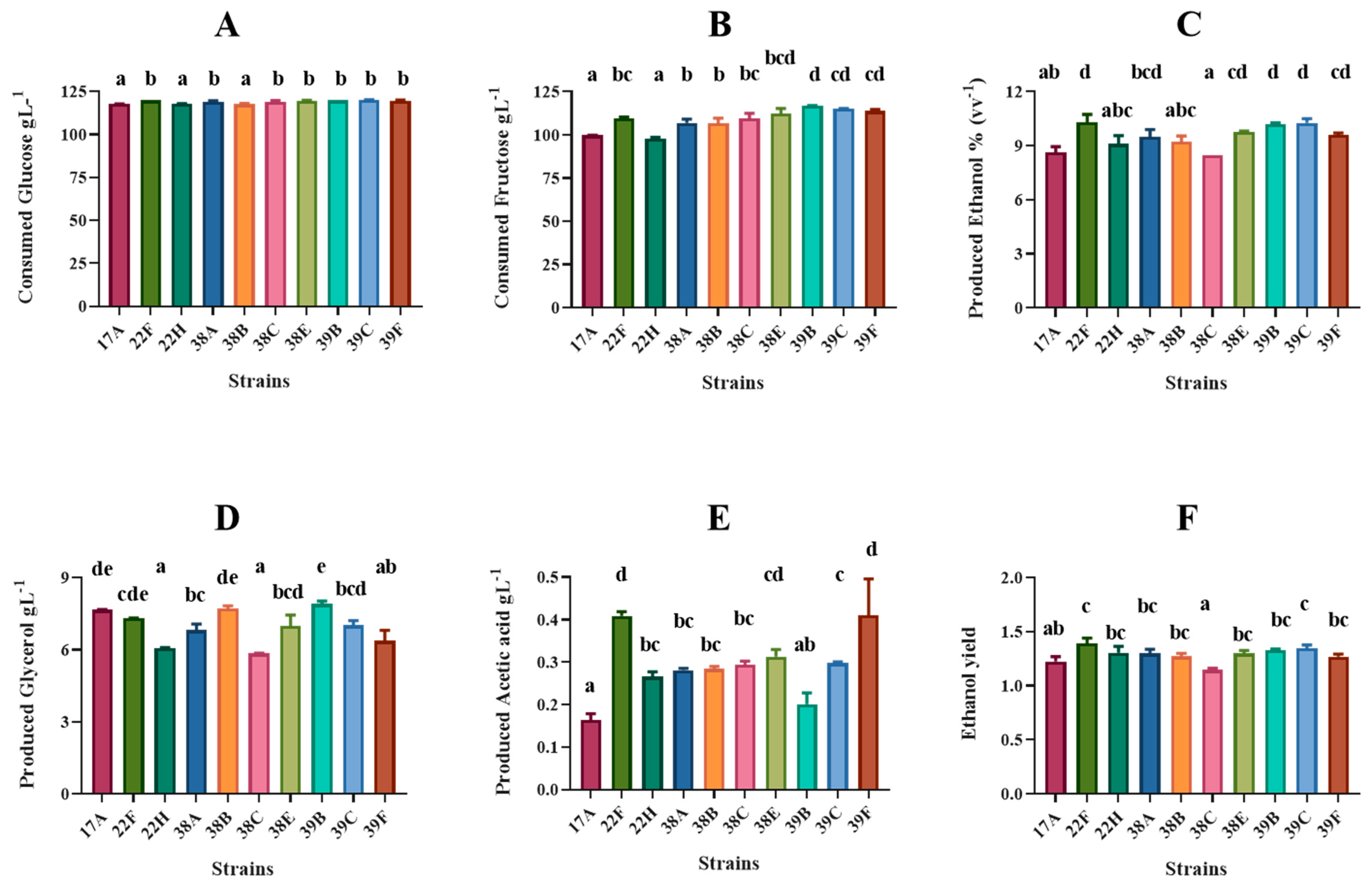
3.3. Chemical Characteristics of Small-Scale Produced Wines
3.4. Colour and Tannins-Related Parameters
3.5. Volatile Aroma Analysis
3.6. Sensory Profile of Garnacha Wines
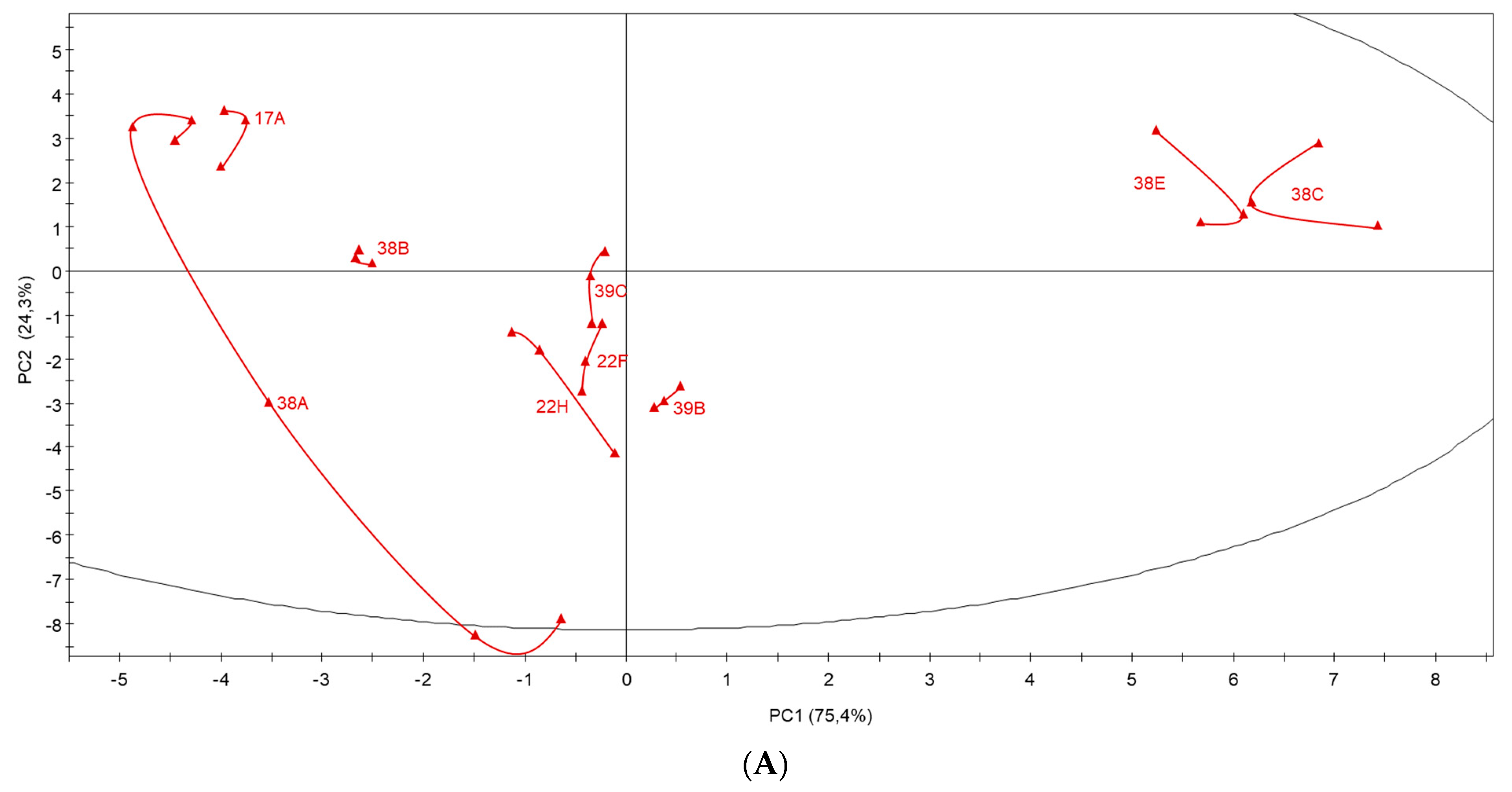
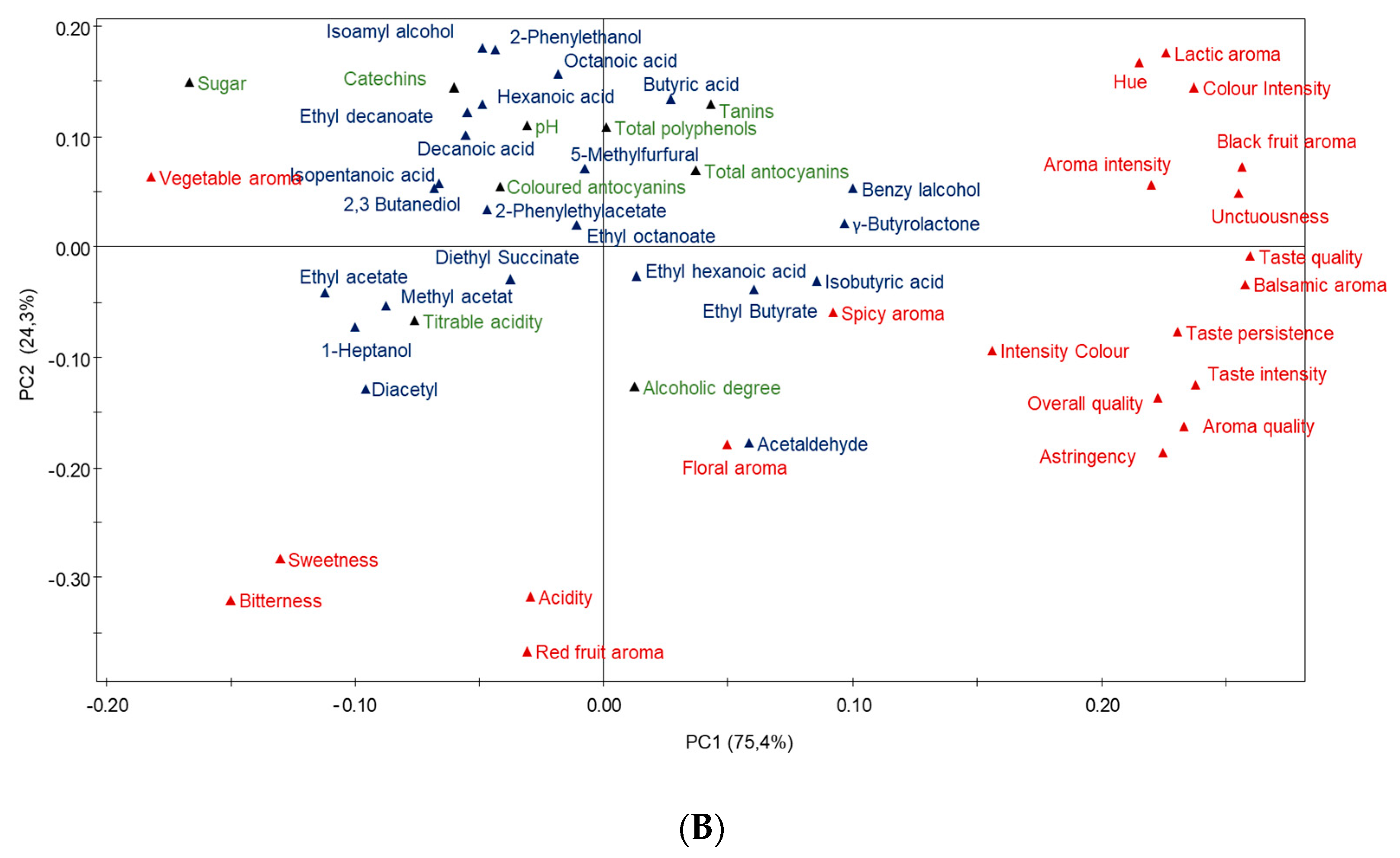
3.7. Multivariate Data Analysis of Garnacha Wines
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bokulich, N.A.; Collins, T.S.; Masarweh, C.; Allen, G.; Heymann, H.; Ebeler, S.E.; Mills, D.A. Associations among wine grape microbiome, metabolome, and fermentation behavior suggest microbial contribution to regional wine characteristics. mBio 2016, 7, e00631-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley 6/2015, de 12 de mayo, de Denominaciones de Origen e Indicaciones Geográficas Protegidas de ámbito territorial supraautonómico. Boletín Of. Del Estado 2015, 114, 41158–41188.
- Fleet, G.H. Wine yeasts for the future. FEMS Yeast Res. 2008, 8, 979–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozzi, V.; Garofalo, C.; Chiriatti, M.A.; Grieco, F.; Spano, G. Microbial terroir and food innovation: The case of yeast biodiversity in wine. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 181, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fugelsang, K.C.; Edwards, C.G. Wine Microbiology: Practical Applications and Procedures, 2nd ed.; Springer Science + Business Media LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2007; p. 396. [Google Scholar]
- Ribéreau-Gayon, P.; Dubourdieu, D.; Donèche, B.; Lonvaud, A. Handbook of Enology. In The microbiology of Wine and Vinifications; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2000; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Granchi, L.; Ganucci, D.; Buscioni, G.; Mangani, S.; Guerrini, S. The biodiversity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in spontaneous wine fermentation: The occurrence and persistence of winery-strains. Fermentation 2019, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciani, M.; Comitini, F. Non-Saccharomyces wine yeasts have a promising role in biotechnological approaches to winemaking. Ann. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Pérez, J.M.; Campo, E.; San-Juan, F.; Coque, J.J.R.; Ferreira, V.; Hernández-Orte, P. Sensory and chemical characterisation of the aroma of Prieto Picudo rosé wines: The differential role of autochthonous yeast strains on aroma profiles. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loscos, N.; Hernandez-Orte, P.; Cacho, J.; Ferreira, V. Release and formation of varietal aroma compounds during alcoholic fermentation from nonfloral grape odorless flavor precursors fractions. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2007, 55, 6674–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiegers, J.H.; Pretorius, I.S. Modulation of volatile sulfur compounds by wine yeast. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 74, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugliano, M.; Bartowsky, E.J.; McCarthy, J.; Moio, L.; Henschke, P.A. Hydrolysis and transformation of grape glycosidically bound volatile compounds during fermentation with three Saccharomyces yeast strains. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2006, 54, 6322–6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regodón Mateos, J.A.; Pérez-Nevado, F.; Ramírez Fernández, M. Influence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast strain on the major volatile compounds of wine. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2006, 40, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez Viguera, A.R.; Santamaría Aquilué, M.P.; López Martín, R.; Sevilla, M.J. Selección de levaduras vínicas en la Denominación de Origen Calificada Rioja. Zubia 1995, 7, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Comitini, F.; Gobbi, M.; Domizio, P.; Romani, C.; Lencioni, L.; Mannazzu, I.; Ciani, M. Selected non-Saccharomyces wine yeasts in controlled multistarter fermentations with Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, H.; Cozzolino, D.; McCarthy, J.; Abrahamse, C.; Holt, S.; Solomon, M.; Smith, P.; Chambers, P.J.; Curtin, C. Influence of yeast strain on Shiraz wine quality indicators. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 165, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, A.; Guillamón, J.M.; Beltran, G. Editorial: Non-conventional yeast in the wine industry. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morata, A.; Benito, S.; Loira, I.; Palomero, F.; González, M.C.; Suárez-Lepe, J.A. Formation of pyranoanthocyanins by Schizosaccharomyces pombe during the fermentation of red must. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 159, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Ortín, A.B.; Romero-Cascales, I.; Fernández-Fernández, J.I.; López-Roca, J.M.; Gómez-Plaza, E. Influence of the yeast strain on Monastrell wine colour. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2007, 8, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caboulet, D.; Ducasse, M.A.; Roy, A.; Dagan, L.; Fauveau, C.; Pellerin, P.; Schneider, R. The influence of yeast strains on the phenolic and aromatic qualities of red wines. Wine Vitic. J. 2012, 27, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Orte, P.; Cersosimo, M.; Loscos, N.; Cacho, J.; Garcia-Moruno, E.; Ferreira, V. The development of varietal aroma from non-floral grapes by yeasts of different genera. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1064–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y. Genomic and transcriptomic analyses of the Chinese Maotai-flavored liquor yeast MT1 revealed its unique multi-carbon co-utilization. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monagas, M.; Gómez-Cordovés, C.; Bartolomé, B. Evolution of polyphenols in red wines from Vitis vinifera L. during aging in the bottle. I. Anthocyanins and pyranoanthocyanins. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2005, 220, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morata, A.; Gómez-Cordovés, M.C.; Colomo, B.; Suárez, J.A. Cell wall anthocyanin adsorption by different Saccharomyces strains during the fermentation of Vitis vinifera L. cv Graciano grapes. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2005, 220, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteve-Zarzoso, B.; Belloch, C.; Uruburu, F.; Querol, A. Identification of yeasts by RFLP analysis of the 5.8S rRNA gene and the two ribosomal internal transcribed spacers. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1999, 49, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querol, A.; Barrio, E.; Ramón, D. A comparative study of different methods of yeast strain characterization. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1992, 15, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucio, O. Acidificación Biológica de Vinos de pH Elevado Mediante la Utilización de Bacterias Lácticas. Ph. D. Thesis, Universidad de Valencia, Valencia, Spain, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Frayne, R.F. Direct analysis of the major organic components in grape must and wine using high performance liquid chromatography. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1986, 37, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission regulation (EEC) No 2676/90 of 17 September 1990 determining Community methods for the analysis of wines. Off. J. Eur. Communities 1990, 272, 1–192.
- Blouin, J. Techniques D’analyses des moûts et des Vins; Dujardin-Salleron: Noizay, France, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Glories, Y. La couleur des vins rouges. 2e partie: Mesure, origine et interprétation. OENO One 1984, 18, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peynaud, E.; Ribéreau-Gayon, J.; Ribéreau-Gayon, P.; Sudraud, P. Ciencias y Técnicas del Vino Tratado de Enología T.I. Análisis y Control de los Vinos; Hemisferio Sur: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- Boulton, R. The copigmentation of anthocyanins and its role in the color of red wine: A critical review. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2001, 52, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribéreau-Gayon, P.; Stonestreet, E. Le dosage des anthocyanes dans le vins rouge. Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. 1965, 9, 2649–2652. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Ricardo-Da-Silva, J.M.; Spranger, I. Critical factors of vanillin assay for catechins and proanthocyanidins. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 1998, 46, 4267–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivas, N.; Glories, Y.; Lagune, L.; Cédric, S.; Augustin, M. Estimation du degré de polymérisation des procyanidines du raisin et du vin par la méthode au ρ-dimethylaminocinnamaldéhyde. J. Int. Des Sci. Vigne Et Du Vin 1994, 28, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boido, E.; Alcalde-Eon, C.; Carrau, F.; Dellacassa, E.; Rivas-Gonzalo, J.C. Aging effect on the pigment composition and color of Vitis vinifera L. Cv. Tannat wines. Contribution of the main pigment families to wine color. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2006, 54, 6692–6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, C.; López, R.; Cacho, J.; Ferreira, V. Fast analysis of important wine volatile compounds development and validation of a new method based on gas chromatographic-flame ionisation detection analysis of dichloromethane microextracts. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 923, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norma UNE-EN ISO 8586:2014; Análisis Sensorial. Guía Para la Selección, Entrenamiento y Control de Catadores y Catadores Expertos. AENOR: Madrid, Spain, 2014.
- Norma UNE-EN ISO 8589:2007; Análisis Sensorial. Guía General Para el Diseño de Una Sala de Cata. AENOR: Madrid, Spain, 2010.
- Norma UNE-EN ISO 4120:2004; Análisis Sensorial. Metodología. Prueba Triangular. AENOR: Madrid, Spain, 2008.
- NF ISO 11035; Analyse Sensorielle, Recherche et Sélection de Descripteurs Pour L’élaboration d’un Profil Sensoriel par Approche Multidimensionnelle. Partie 1: In Recueil de Normes Françaises, Contrôle de la Qualité des Produits Alimentaires-Analyse Sensorielle. AFNOR Association: Paris, France, 1995; pp. 75–102.
- Portillo, M.d.C.; Mas, A. Analysis of microbial diversity and dynamics during wine fermentation of Grenache grape variety by high-throughput barcoding sequencing. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 72, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, B.; García-Fernández, D.; González, B.; Izidoro, I.; Esteve-Zarzoso, B.; Beltran, G.; Mas, A. Yeast Biodiversity from DOQ Priorat Uninoculated Fermentations. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, C.; Molina, A.M.; Nähring, J.; Fischer, R. Characterization and dynamic behavior of wild yeast during spontaneous wine fermentation in steel tanks and amphorae. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 540465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Jimenez, J.M.A.; Mingorance-Cazorla, L.; Martínez-Rodríguez, S.; Heras-Vázquez, F.J.L.; Rodríguez-Vico, F. Molecular characterization and oenological properties of wine yeasts isolated during spontaneous fermentation of six varieties of grape must. Food Microbiol. 2004, 21, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocón, E.; Gutiérrez, A.R.; Garijo, P.; Tenorio, C.; López, I.; López, R.; Santamaría, P. Quantitative and qualitative analysis of non-Saccharomyces yeasts in spontaneous alcoholic fermentations. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 230, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maturano, Y.P.; Mestre, M.V.; Esteve-Zarzoso, B.; Nally, M.C.; Lerena, M.C.; Toro, M.E.; Vazquez, F.; Combina, M. Yeast population dynamics during prefermentative cold soak of Cabernet Sauvignon and Malbec wines. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 199, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, I.S. Tailoring wine yeast for the new millennium: Novel approches to the ancient art of winemaking. Yeast 2000, 16, 575–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, I.; García, M.J.; Zúñiga, M.; Uruburu, F. Dynamics of microbial populations during fermentation of wines from the Utiel-Requena region of Spain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Jeune, C.; Erny, C.; Demuyter, C.; Lollier, M. Evolution of the population of Saccharomyces cerevisiae from grape to wine in a spontaneous fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2006, 23, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albergaria, H.; Arneborg, N. Dominance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in alcoholic fermentation processes: Role of physiological fitness and microbial interactions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Torrado, R.; Rantsiou, K.; Perrone, B.; Navarro-Tapia, E.; Querol, A.; Cocolin, L. Ecological interactions among Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains: Insight into the dominance phenomenon. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthels, N.J.; Cordero Otero, R.R.; Bauer, F.F.; Thevelein, J.M.; Pretorius, I.S. Discrepancy in glucose and fructose utilisation during fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae wine yeast strains. FEMS Yeast Res. 2004, 4, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClellan, C.; Does, A.; Bisson, L. Characterization of hexose uptake in wine strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces bayanus. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1989, 40, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degre, R. Selection and commercial cultivation of wine yeast and bacteria. In Wine Microbiology and Biotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 421–447. [Google Scholar]
- Tronchoni, J.; Gamero, A.; Arroyo-López, F.N.; Barrio, E.; Querol, A. Differences in the glucose and fructose consumption profiles in diverse Saccharomyces wine species and their hybrids during grape juice fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 134, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodicio, R.; Heinisch, J.J. Sugar metabolism by Saccharomyces and non-Saccharomyces yeasts. In Biology of Microorganisms on Grapes, in Must and in Wine; König, H., Unden, G., Fröhlich, J., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 113–134. [Google Scholar]
- Zamora, F. Biochemistry of Alcoholic Fermentation. In Wine Chemistry and Biochemistry; Moreno-Arribas, M., Polo, M.C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Quirós, M.; Rojas, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Morales, P. Selection of non-Saccharomyces yeast strains for reducing alcohol levels in wine by sugar respiration. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 181, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo-González, M.; Cancho-Grande, B.; Simal-Gándara, J. Effects on colour and phenolic composition of sugar concentration processes in dried-on- or dried-off-vine grapes and their aged or not natural sweet wines. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigentini, I.; De Lorenzis, G.; Fabrizio, V.; Valdetara, F.; Faccincani, M.; Panont, C.A.; Picozzi, C.; Imazio, S.; Failla, O.; Foschino, R. The vintage effect overcomes the terroir effect: A three year survey on the wine yeast biodiversity in Franciacorta and Oltrepò Pavese, two northern Italian vine-growing areas. Microbiology 2015, 161, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forino, M.; Picariello, L.; Rinaldi, A.; Moio, L.; Gambuti, A. How must pH affects the level of red wine phenols. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 129, 109546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callejón, R.M.; Clavijo, A.; Ortigueira, P.; Troncoso, A.M.; Paneque, P.; Morales, M.L. Volatile and sensory profile of organic red wines produced by different selected autochthonous and commercial Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 660, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaou, E.; Soufleros, E.H.; Bouloumpasi, E.; Tzanetakis, N. Selection of indigenous Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains according to their oenological characteristics and vinification results. Food Microbiol. 2006, 23, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schvarczová, E.; Štefániková, J.; Jankura, E.; Kolek, E. Selection of autochthonous Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains for production of typical Pinot Gris wines. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 56, 389–397. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, K.; Boido, E.; Dellacassa, E.; Carrau, F. Yeast interactions with anthocyanins during red wine fermentation. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2005, 56, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morata, A.; Loira, I.; Heras, J.M.; Callejo, M.J.; Tesfaye, W.; González, C.; Suárez-Lepe, J.A. Yeast influence on the formation of stable pigments in red winemaking. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverrigaray, S.; Scariot, F.J.; Menegotto, M.; Delamare, A.P.L. Anthocyanin adsorption by Saccharomyces cerevisiae during wine fermentation is associated to the loss of yeast cell wall/membrane integrity. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 314, 108383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, A.; Blaiotta, G.; Aponte, M.; Moio, L. Effect of yeast strain and some nutritional factors on tannin composition and potential astringency of model wines. Food Microbiol. 2016, 53, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Gonzalo, J.C.; Bravo-Haro, S.; Santos-Buelga, C. Detection of compounds formed through the reaction of malvidin 3-monoglucoside and catechin in the presence of acetaldehyde. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 1995, 43, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, K.L.; Bisson, L.F.; Adams, D.O. A review of the effect of winemaking techniques on phenolic extraction in red wines. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2005, 56, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, S.; Francis, L.; Guyot, S.; Marnet, N.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Gawel, R.; Cheynier, V.; Waters, E.J. The mouth-feel properties of grape and apple proanthocyanidins in a wine-like medium. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2003, 83, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalde-Eon, C.; Escribano-Bailón, M.T.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Rivas-Gonzalo, J.C. Changes in the detailed pigment composition of red wine during maturity and ageing: A comprehensive study. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 563, 238–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurd, L. Anthocyanidins and related compounds—XI: Catechin-flavylium salt condensation reactions. Tetrahedron 1967, 23, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.M. Yeast Physiology and Biotechnology; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- del Barrio-Galán, R.; Medel-Marabolí, M.; Peña-Neira, Á. Effect of different aging techniques on the polysaccharide and phenolic composition and sensory characteristics of Syrah red wines fermented using different yeast strains. Food Chem. 2015, 179, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindon, K.A.; Kassara, S.; Solomon, M.; Bartel, C.; Smith, P.A.; Barker, A.; Curtin, C. Commercial Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast strains significantly impact shiraz tannin and polysaccharide composition with implications for wine colour and astringency. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caridi, A.; Cufari, A.; Lovino, R.; Palumbo, R.; Tedesco, I. Influence of yeast on polyphenol composition of wine. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 42, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Morata, A.; Gómez-Cordovés, M.C.; Suberviola, J.; Bartolomé, B.; Colomo, B.; Suárez, J.A. Adsorption of anthocyanins by yeast cell walls during the fermentation of red wines. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2003, 51, 4084–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Singh, P.N.; Sawant, S.D. Evaluation of fermentation efficiency of yeast strains and their effect on quality of young wines. Indian J. Microbiol. 2012, 52, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, A.; Castellari, L.; Zambonelli, C.; Carnacini, A. Yeast influence on volatile composition of wines. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 1999, 47, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.; Jarauta, I.; Ortega, L.; Cacho, J. Simple strategy for the optimization of solid-phase extraction procedures through the use of solid–liquid distribution coefficients: Application to the determination of aliphatic lactones in wine. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1025, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.-Q.; Luan, Y.; Duan, C.-Q.; Yan, G.-L. Use of Torulaspora delbrueckii co-fermentation with two Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains with different aromatic characteristic to improve the diversity of red wine aroma profile. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, Y.; Zhang, B.-Q.; Duan, C.-Q.; Yan, G.-L. Effects of different pre-fermentation cold maceration time on aroma compounds of Saccharomyces cerevisiae co-fermentation with Hanseniaspora opuntiae or Pichia kudriavzevii. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 92, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englezos, V.; Torchio, F.; Cravero, F.; Marengo, F.; Giacosa, S.; Gerbi, V.; Rantsiou, K.; Rolle, L.; Cocolin, L. Aroma profile and composition of Barbera wines obtained by mixed fermentations of Starmerella bacillaris (synonym Candida zemplinina) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V. Volatile aroma compounds and wine sensory attributes. In Managing Wine Quality; Reynolds, A.G., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2010; pp. 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Arribas, M.V.; Polo, M.C. Wine Chemistry and Biochemistry; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 735. [Google Scholar]
- Jarauta Gurría, I. Estudio Analítico de Fenómenos Concurrentes en la Generación del Aroma Durante la Crianza del Vino en Barricas de Roble con Diferentes Grados de Uso. In Nuevos Métodos de Análisis de Importantes Aromas y Caracterización de su Papel Sensorial; Universidad de Zaragoza: Zaragoza, Spain, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Aznar, M.; López, R.; Cacho, J.F.; Ferreira, V. Identification and quantification of impact odorants of aged red wines from Rioja. GC−olfactometry, quantitative GC-MS, and odor evaluation of HPLC fractions. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2001, 49, 2924–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komes, D.; Ulrich, D.; Ganic, K.K.; Lovric, T. Study of phenolic and volatile composition of white wine during fermentation and a short time of storage. Vitis 2007, 46, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Wine Tasting; China Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 29–106. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, E.; Çelik, Z.; Cabaroğlu, T. Effects of pure and mixed autochthonous Torulaspora delbrueckii and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on fermentation and volatile compounds of Narince wines. Foods 2018, 7, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.S. Wine Science: Principles and Applications, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Akıllıoglu, H.G.; Mogol, B.A.; Gökmen, V. Degradation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural during yeast fermentation. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2011, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Lepe, J.A.; Morata, A. New trends in yeast selection for winemaking. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 23, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Isolates | Isolated From | Profile Number | Representative Profile Isolate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17A | GM | I | 17A |
| 22I | HAF | ||
| 17B, 22A, 22B, 22C, 22D, 22E, 22H, 22J, 23A, 23B, 23C, 23E | HAF | II | 22H |
| 38D, 38F, 38H, 39A, 39D | FAF | ||
| 22F, 22G | HAF | III | 22F |
| 24B | HAF | IV | 39C |
| 39C | FAF | ||
| 38A, 38G, 38J, 38I | FAF | V | 38A |
| 38B | FAF | VI | 38B |
| 38C | FAF | VII | 38C |
| 38E | FAF | VIII | 38E |
| 39B | FAF | IX | 39B |
| 39F | FAF | X | 39F |
| Strain | Sugar Consumed | Consumed Sugar/Ethanol Production Ratio | Residual Sugar | Alcohol Concentration (%v/v) | Density (g/mL) | Volatile Acidity (g acetic acid/L) | pH | Titratable Acidity (g tartaric acid/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17A | 193.00 ± 0.13 a | 17.71 ± 0.33 b | 2.1 ± 0.12 a | 10.91 ± 0.60 a | 993 ± 2.00 | 0.17 ± 0.13 a | 3.61 ± 0.18 ab | 6.1 ± 0.31 fg |
| 22F | 204.33 ± 1.53 b | 17.42 ± 0.24 a | 2.4 ± 0.23 a | 11.73 ± 0.15 bcd | 991 ± 0.00 | 0.37 ± 0.04 gh | 3.63 ± 0.04 ab | 5.73 ± 0.09 cd |
| 22H | 210.67 ± 2.52 b | 17.61 ± 0.26 b | 1.9 ± 0.18 a | 11.97 ± 0.12 d | 991 ± 0.00 | 0.24 ± 0.08 bc | 3.57 ± 0.07 a | 6.15 ± 0.15 ef |
| 38A | 211.67 ± 1.53 b | 17.69 ± 0.23 b | 2.2 ± 0.22 a | 11.93 ± 0.18 d | 991 ± 1.00 | 0.36 ± 0.04 fg | 3.76 ± 0.14 ab | 5.69 ± 0.29 def |
| 38B | 207.00 ± 2.00 b | 17.86 ± 0.73 c | 1.9 ± 0.25 a | 11.61 ± 0.36 bcd | 992 ± 2.00 | 0.24 ± 0.02 cd | 3.78 ± 0.02 c | 5.28 ± 0.04 ab |
| 38C | 204.00 ± 1.00 b | 17.44 ± 0.09 a | 2.3 ± 0.15 a | 11.71 ± 0.0 bcd | 991 ± 0.00 | 0.37 ± 0.0 gh | 3.8 ± 0.02 c | 5.2 ± 0.16 a |
| 38E | 204.67 ± 2.08 b | 17.80 ± 0.37 c | 1.7 ± 0.33 a | 11.51 ± 0.26 bc | 991 ± 0.00 | 0.29 ± 0.01 ef | 3.59 ± 0.07 a | 5.75 ± 0.16 d |
| 39B | 207.00 ± 2.00 b | 17.80 ± 0.55 c | 1.9 ± 0.09 a | 11.63 ± 0.25 bcd | 991 ± 0.00 | 0.18 ± 0.02 ab | 3.67 ± 0.02 b | 5.8 ± 0.16 de |
| 39C | 202.00 ± 2.65 b | 17.89 ± 0.48 c | 2.2 ± 0.16 a | 11.31 ± 0.36 ab | 991 ± 0.00 | 0.27 ± 0.02 de | 3.79 ± 0.03 c | 6.25 ± 0.11 g |
| 39F | 206.67 ± 3.52 b | 17.37 ± 0.50 a | 2.2 ± 0.31 a | 11.88 ± 0.15 cd | 991 ± 0.00 | 0.37 ± 0.05 h | 3.78 ± 0.1 d | 5.71 ± 0.22 bc |
| F-Ratio | 0.69 | 15.6 | 0.66 | 54.97 | 1.95 | 34.92 | 18.24 | 18.2 |
| p-Value | 0.4831 | 0.021 | 0.07312 | 0.0014 | 0.055 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Strain | Colour Intensity (CI) | Hue | Coloured Anthocyanins (mg/L) | Total Anthocyanins (mg/L) | Catechins (g/L) | Condensed Tannins (g/L) | Total Phenolic Compounds (g/L) | Total Polyphenol Index | DMACH Index (%) | Ethanol Index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17A | 3.33 ± 0.23 a | 61.09 ± 0.59 c | 334.55 ± 27.28 ab | 457.5 ± 35.88 a | 0.11 ± 0.01 d | 0.762 ± 0.049 bc | 2.62 ± 0.11 ab | 29.75 ± 1.89 ab | 171.9 ± 20.24 cd | 52.21 ± 3.7 a |
| 22F | 4.88 ± 0.40 bcd | 55.25 ± 1.99 b | 342.41 ± 9.22 ab | 447 ± 7 a | 0.07 ± 0.01 a | 0.718 ± 0.099 a | 2.561 ± 0.07 ab | 29.42 ± 0.82 a | 191.05 ± 36.36 d | 55.4 ± 1.24 abcd |
| 22H | 5.75 ± 0.62 cd | 62.54 ± 4.45 c | 398.99 ± 18.07 d | 522.5 ± 50.61 c | 0.07 ± 0.01 abc | 0.869 ± 0.083 d | 2.77 ± 0.18 cd | 33.49 ± 2.19 ef | 136.16 ± 24.75 d | 59.78 ± 4.86 de |
| 38A | 5.23 ± 0.87 d | 52.7 ± 3.22 a | 364.4 ± 45.2 ab | 472 ± 57.34 a | 0.08 ± 0.0081 | 0.861 ± 0.159 abc | 2.74 ± 0.18 ab | 33.19 ± 3.08 abc | 146.66 ± 29.72 bcd | 58.04 ± 3.03 de |
| 38B | 4.07 ± 0.62 b | 55.43 ± 4.43 b | 361.54 ± 35.4 a | 416.5 ± 20.67 abc | 0.08 ± 0.00 bc | 0.71 ± 0.085 ab | 2.45 ± 0.08 a | 29.17 ± 1.3 a | 180.82 ± 24.32 cd | 53.09 ± 4.04 ab |
| 38C | 6.22 ± 0.7 d | 54.78 ± 0.84 b | 398.83 ± 58.03 ab | 449.8 ± 39.18 c | 0.09 ± 0.01 bc | 0.779 ± 0.034 bc | 2.67 ± 0.53 d | 31.32 ± 1.6 bcd | 188.43 ± 31.63 d | 53.92 ± 2.25 abc |
| 38E | 5.18 ± 0.45 cd | 53.69 ± 2.31 ab | 353.13 ± 29.14 ab | 441.9 ± 47.73 ab | 0.08 ± 0.01 bc | 0.886 ± 0.058 d | 2.76 ± 0.12 bcd | 31.9 ± 0.54 cde | 134.47 ± 25.66 a | 56.26 ± 3.43 bcde |
| 39B | 4.33 ± 0.54 bc | 54.54 ± 0.88 b | 327.19 ± 26.41 ab | 428.9 ± 39.81 a | 0.08 ± 0.01 bc | 0.793 ± 0.07 s | 2.47 ± 0.18 a | 30.77 ± 1.65 abc | 142.62 ± 10.69 ab | 59.53 ± 1.4 d |
| 39C | 4.69 ± 0.36 cd | 55.24 ± 1.62 b | 346.01 ± 38.19 bc | 473.5 ± 41.93 a | 0.08 ± 0.01 c | 0.878 ± 0.103 d | 2.71 ± 0.15 bc | 33.84 ± 1.67 c | 155.06 ± 13.37 abc | 57.2 ± 2.39 cde |
| 39F | 5.34 ± 0.55 bc | 53.12 ± 2.44 ab | 368.47 ± 25.27 cd | 477.8 ± 45.85 bc | 0.08 ± 0.01 bc | 0.855 ± 0.132 d | 2.71 ± 0.12 cd | 32.98 ± 2.87 def | 155.56 ± 21.76 a | 58.74 ± 4.31 de |
| F-Ratio | 15.09 | 9.75 | 4.35 | 3.88 | 10.7 | 9.65 | 3.52 | 5.01 | 4.58 | 4.36 |
| p-Value | 0 | 0 | 0.0003 | 0.0009 | 0 | 0.0002 | 0.0026 | 0.0001 | 0.0003 | 0.0005 |
| Concentration (mg/L) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volatile Compounds | 17A | 22F | 22H | 38A | 38B | 38C | 38E | 39B | 39C | F-Ratio | p-Value |
| Isoamyl alcohol | 57.66 ± 7.60 e | 50.12 ± 18.59 de | 36.13 ± 18.17 bcd | 25.36 ± 15.66 ab | 30.98 ± 2.59 abc | 36.70 ± 19.99 bcd | 37.18 ± 12.78 bcd | 19.41 ± 3.73 a | 29.51 ± 6.91 abc | 13.87 | 0.0000 |
| 2.3 Butanediol | 0.02 ± 0.30 abc | 0.024 ± 0.01 abc | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 cd | 0.07 ± 0.02 e | 0.03 ± 0.00 bc | 0.02 ± 0.01 abc | 0.02 ± 0.00 ab | 0.03 ± 0.01 cd | 78.73 | 0.0000 |
| 1-Heptanol | 0.041 ± 0.01 a | 0.09 ± 0.02 c | 0.15 ± 0.01 d | 0.10 ± 0.03 c | 0.05 ± 0.05 ab | 0.04 ± 0.04 a | 0.08 ± 0.00 bc | 0.08 ± 0.00 bc | 0.08 ± 0.00 bc | 10.50 | 0.0000 |
| Benzyl alcohol | 0.03 ± 0.01 ab | 0.03 ± 0.02 ab | 0.04 ± 0.00 bc | 0.04 ± 0.01 ab | 0.04 ± 0.009 ab | 0.07 ± 0.02 d | 0.035 ± 0.015 ab | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.06 ± 0.01 cd | 20.55 | 0.0000 |
| 2-Phenylethanol | 16.99 ± 2.58 c | 14.10 ± 5.94 bc | 14.41 ± 5.25 bc | 7.39 ± 2.89 a | 12.24 ± 1.72 ab | 12.71 ± 8.30 b | 10.80 ± 2.95 ab | 7.43 ± 0.78 a | 12.08 ± 4.48 ab | 10.54 | 0.0000 |
| Total alcohols | 74.75 | 64.38 | 50.75 | 32.93 | 43.39 | 49.87 | 48.12 | 26.96 | 41.76 | ||
| Methyl acetate | 0.06 ± 0.02 ab | 0.08 ± 0.05 ab | 0.16 ± 0.13 cd | 0.08 ± 0.05 ab | 0.17 ± 0.03 d | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.08 ± 0.03 ab | 0.13 ± 0.02 bcd | 0.09 ± 0.07 abc | 40.56 | 0.0000 |
| Ethyl acetate | 0.07 ± 0.09 a | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 0.02 ± 0.01 a | 0.23 ± 0.08 b | 0.37 ± 0.08 c | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 0.02 ± 0.01 a | 0.19 ± 0.13 b | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 18.67 | 0.0000 |
| Isobutyl acetate | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | nd | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | 0.19 ± 0.28 b | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.03 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 4.57 | 0.0164 |
| Ethyl isobutyrate | 0.03 ± 0.01 abc | 0.06 ± 0.01 bc | 0.26 ± 0.09 d | 0.03 ± 0.01 abc | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.07 ± 0.02 c | 0.05 ± 0.03 abc | 0.05 ± 0.01 abc | 0.03 ± 0.00 ab | 17.87 | 0.0000 |
| Hexyl acetate | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 de | 0.02 ± 0.01 c | 0.03 ± 0.01 d | 0.03 ± 0.00 de | 0.01 ± 0.00 ab | 0.02 ± 0.00 bc | 0.04 ± 0.01 f | 0.03 ± 0.00 de | 26.87 | 0.0000 |
| Ethyl octanoate | 0.19 ± 0.06 a | 0.45 ± 0.12 cd | 0.33 ± 0.21 abc | 0.35 ± 0.15 abc | 0.36 ± 0.16 bcd | 0.40 ± 0.17 bcd | 0.26 ± 0.06 ab | 0.20 ± 0.05 a | 0.52 ± 0.13 d | 43.56 | 0.0000 |
| Ethyl decanoate | 0.24 ± 0.07 bcd | 0.20 ± 0.08 abc | 0.34 ± 0.09 e | 0.13 ± 0.08 a | 0.30 ± 0.05 de | 0.17 ± 0.04 ab | 0.26 ± 0.05 cd | 0.23 ± 0.02 bcd | 0.25 ± 0.02 cd | 78.98 | 0.0000 |
| Diethyl succynate | 0.15 ± 0.02 bc | 0.19 ± 0.02 c | 0.32 ± 0.04 d | 0.18 ± 0.05 c | 0.04 ± 0.02 a | 0.14 ± 0.02 bc | 0.11 ± 0.05 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.18 ± 0.08 c | 20.34 | 0.0000 |
| 2-Phenylethylacetate | 0.59 ± 0.28 ab | 0.55 ± 0.30 a | 0.88 ± 0.20 c | 0.60 ± 0.21 ab | 0.80 ± 0.17 bc | 0.55 ± 0.18 a | 0.63 ± 0.13 ab | 0.48 ± 0.09 a | 0.59 ± 0.14 ab | 16.78 | 0.0000 |
| Total esters | 1.38 | 1.6 | 2.39 | 1.68 | 2.3 | 1.44 | 1.46 | 1.18 | 1.72 | ||
| Butyric acid | 0.06 ± 0.04 ab | 0.11 ± 0.04 bc | 0.22 ± 0.08 e | 0.02 ± 0.01 a | 0.18 ± 0.03 e | 0.18 ± 0.04 de | 0.14 ± 0.03 cd | 0.11 ± 0.01 bc | 0.12 ± 0.01 c | 34.65 | 0.0000 |
| Isopentanoic acid | 0.55 ± 0.06 cd | 0.76 ± 0.13 e | 0.38 ± 0.18 b | 0.41 ± 0.17 bc | 0.39 ± 0.09 b | 0.35 ± 0.15 ab | 0.39 ± 0.12 b | 0.23 ± 0.03 a | 0.57 ± 0.10 d | 16.82 | 0.0000 |
| Hexanoic acid | 0.80 ± 0.14 bc | 0.53 ± 0.33 a | 1.09 ± 0.37 d | 0.63 ± 0.25 ab | 0.84 ± 0.23 cd | 0.91 ± 0.29 cd | 0.66 ± 0.12 abc | 0.47 ± 0.05 a | 1.08 ± 0.16 d | 21.45 | 0.0000 |
| 2-Ethyl Hexanoic acid | 0.01 ± 0.01 ab | 0.01 ± 0.01 ab | 0.05 ± 0.01 d | 0.02 ± 0.01 bc | 0.01 ± 0.00 ab | 0.02 ± 0.00 c | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 6.87 | 0.0000 |
| Octanoic acid | 0.97 ± 0.25 bcd | 0.64 ± 0.29 ab | 0.84 ± 0.12 abc | 0.77 ± 0.32 abc | 0.82 ± 0.35 abc | 0.84 ± 0.15 abc | 1.01 ± 0.34 cd | 0.55 ± 0.08 a | 1.30 ± 0.38 d | 32.56 | 0.0000 |
| Decanoic acid | 0.23 ± 0.09 abc | 0.44 ± 0.14 e | 0.44 ± 0.12 bcde | 0.20 ± 0.06 ab | 0.40 ± 0.19 de | 0.28 ± 0.08 abcd | 0.23 ± 0.06 abc | 0.15 ± 0.04 a | 0.37 ± 0.20 cde | 14.58 | 0.0000 |
| Isobutyric acid | 0.29 ± 0.03 cd | 0.38 ± 0.03 d | 0.30 ± 0.15 cd | 0.23 ± 0.02 c | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.37 ± 0.19 d | 0.18 ± 0.09 bc | 0.06 ± 0.03 a | 0.08 ± 0.12 ab | 13.78 | 0.0000 |
| Total acids | 2.92 | 2.86 | 3.34 | 2.3 | 2.67 | 2.94 | 2.64 | 1.58 | 3.55 | ||
| γ-butirolactona | 0.17 ± 0.07 a | 0.15 ± 0.03 a | 0.35 ± 0.15 cd | 0.16 ± 0.01 a | 0.34 ± 0.03 cd | 0.32 ± 0.14 bcd | 0.37 ± 0.20 d | 0.23 ± 0.19 abc | 0.18 ± 0.01 ab | 24.67 | 0.0000 |
| Total lactons | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.35 | 0.16 | 0.34 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 0.24 | 0.18 | ||
| Acetaldehyde | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.15 ± 0.02 bcd | 0.13 ± 0.07 bc | 0.21 ± 0.12 de | 0.13 ± 0.02 bc | 0.17 ± 0.07 cd | 0.099 ± 0.06 abc | 0.17 ± 0.03 cd | 0.28 ± 0.06 e | 25.44 | 0.0000 |
| Diacetyl | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.01 a | 0.04 ± 0.01 b | 0.04 ± 0.02 b | 0.03 ± 0.00 ab | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.02 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a | 0.04 ± 0.02 b | 45.78 | 0.0000 |
| 5-Methylfurfural | 0.51 ± 0.08 c | 0.52 ± 0.12 c | 0.32 ± 0.15 ab | 0.32 ± 0.01 ab | 0.39 ± 0.05 abc | 0.45 ± 0.16 bc | 0.31 ± 0.11 ab | 0.26 ± 0.03 a | 0.52 ± 0.25 c | 21.65 | 0.0000 |
| Total aldehydes | 0.55 | 0.69 | 0.49 | 0.58 | 0.55 | 0.63 | 0.42 | 0.45 | 0.85 | ||
| Scale of 1–10 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensory Attributes | 17A | 22F | 22H | 38A | 38B | 38C | 38E | 39B | 39C | F-Ratio | p-Value |
| Colour | |||||||||||
| Colour quality | 6.89 ± 1.2 a | 7.11 ± 1.5 a | 8.89 ± 1.6 a | 6.24 ± 1.9 a | 8.6 ± 1.9 a | 7.63 ± 1.1 a | 6.46 ± 1.58 a | 8.33 ± 1.5 a | 7.11 ± 1.8 a | 0.59 | 0.740 |
| Colour intensity | 6.22 ± 1.04 a | 6.78 ± 1.48 a | 7.17 ± 1.29 a | 6.34 ± 1.8 a | 7.00 ± 1.85 a | 7.00 ± 1.1 a | 6.59 ± 1.59 a | 7 ± 1.78 a | 6.44 ± 1.02 a | 0.30 | 0.940 |
| Aroma | |||||||||||
| Aroma intensity | 6.78 ± 0.4 a | 7.67 ± 1.1 a | 7.9 ± 1.4 b | 5.98 ± 0.97 a | 7.22 ± 0.97 b | 7.38 ± 0.83 b | 6.07 ± 1.10 a | 7.11 ± 1.2 b | 6.89 ± 1.9 a | 4.30 | 0.009 |
| Aroma quality | 5.89 ± 1.05 ab | 7.22 ± 1.09 bc | 7.89 ± 0.92 c | 5.29 ± 1.1 a | 7.33 ± 0.87 c | 4.75 ± 0.89 a | 5.22 ± 1.58 a | 7.72 ± 1.53 bc | 5.56 ± 2.55 a | 5.52 | 0.005 |
| Red fruits | 3.56 ± 1.1 a | 6.00 ± 1.1 b | 5.89 ± 1.2 b | 4.57 ± 0.88 a | 4.22 ± 0.5 a | 2.75 ± 0.90 a | 3.44 ± 0.6 a | 5.67 ± 1.01 b | 3.75 ± 0.55 a | 3.75 | 0.013 |
| Black fruits | 3.00 ± 0.5 a | 3.67 ± 1.1 a | 4.89 ± 1.3 a | 3.12 ± 0.76 a | 4.22 ± 1.2 a | 2.38 ± 0.67 a | 3.08 ± 0.8 a | 4.56 ± 1.00 a | 3.13 ± 0.8 a | 0.50 | 0.810 |
| Floral | 1.44 ± 0.33 a | 1.56 ± 0.7 a | 2.44 ± 0.6 a | 2.12 ± 0.55 a | 1.67 ± 0.6 a | 1.38 ± 0.55 | 1.66 ± 0.50 a | 1.78 ± 0.9 a | 1.75 ± 0.7 a | 0.30 | 0.960 |
| Balsamic | 1.11 ± 0.3 a | 2.89 ± 0.6 a | 2.78 ± 0.7 a | 2.31 ± 0.61 a | 2.89 ± 0.7 a | 1.66 ± 0.43 | 1.32 ± 0.6 a | 2.56 ± 0.3 a | 1.5 ± 0.55 a | 1.02 | 0.420 |
| Spicy | 2.22 ± 0.1 a | 2.33 ± 0.3 a | 2.11 ± 0.33 | 2.44 ± 0.55 | 2.00 ± 1.9 a | 1.66 ± 0.76 a | 2.79 ± 0.2 a | 2.67 ± 0.43 a | 1.13 ± 0.3 a | 0.72 | 0.600 |
| Lactic | 1.00 ± 0.00 a | 1.00 ± 0.00 a | 1.00 ± 0.00 a | 1.06 ± 0.11 a | 1.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.88 ± 0.11 a | 1.74 ± 0.00 a | 1.00 ± 0.00 a | 1.13 ± 0.00 a | 1.10 | 0.370 |
| Vegetable | 2.44 ± 0.4 a | 1.56 ± 0.10 a | 1.56 ± 0.52 a | 2.57 ± 0.77 | 2.33 ± 3.11 a | 2.38 ± 0.97 | 2.62 ± 2.10 a | 2.22 ± 0.40 a | 2.50 ± 0.5 a | 0.44 | 0.840 |
| Aromatics herbs | 1.11 ± 0.33 a | 1.78 ± 1.33 a | 1.67 ± 1.33 a | 1.68 ± 0.43 a | 1.22 ± 1.3 a | 1.00 ± 0.33 | 1.3 ± 0.4 a | 1.67 ± 0.4 a | 1.38 ± 0.7 a | 0.52 | 0.590 |
| Chocolate | 1.11 ± 0.33 a | 1.33 ± 0.001 a | 1.89 ± 0.2 a | 1.42 ± 0.43 a | 1.00 ± 0.0 a | 1.38 ± 0.26 a | 1.21 ± 0.0 a | 1.33 ± 1.4 a | 1.00 ± 0.0 a | 0.97 | 0.450 |
| Taste | |||||||||||
| Taste intensity | 6.11 ± 1.5 a | 7.33 ± 1.1 a | 7.67 ± 1.2 | 6.11 ± 1.1 a | 7.67 ± 1.5 a | 6.75 ± 1.1 a | 6.32 ± 1.2 a | 8.11 ± 0.78 a | 6.43 ± 1.5 a | 1.52 | 0.190 |
| Taste quality | 5.89 ± 1.2 a | 7.22 ± 1.4 a | 8.19 ± 2.3 a | 5.67 ± 1.4 a | 7.11 ± 1.9 a | 6.25 ± 1.5 a | 5.72 ± 1.3 a | 7.67 ± 1.2 a | 6.07 ± 1.9 a | 0.59 | 0.730 |
| Acidity | 5.00 ± 1.3 a | 7.67 ± 2.3 a | 7.56 ± 1.4 a | 5.36 ± 1.5 a | 7.78 ± 1.3 a | 5.88 ± 1.5 a | 5.16 ± 1.09 a | 6.89 ± 1.05 a | 6.29 ± 1.03 a | 2.74 | 0.061 |
| Sweetness | 2.33 ± 0.21 a | 2.33 ± 0.43 a | 2.44 ± 0.21 a | 2.78 ± 0.42 a | 2.22 ± 0.27 a | 2.5 ± 0.42 a | 2.88 ± 0.34 a | 2.22 ± 0.32 a | 2.86 ± 0.72 a | 0.22 | 0.970 |
| Unctuousness | 2.44 ± 0.55 a | 2.89 ± 0.43 a | 3.89 ± 0.53 a | 2.9 ± 1.03 a | 3.00 ± 0.76 a | 3.63 ± 0.53 a | 2.64 ± 0.43 a | 3.33 ± 0.43 a | 2.14 ± 0.32 a | 0.44 | 0.840 |
| Structure | 3.33 ± 0.33 a | 4.00 ± 0.55 a | 3.67 ± 0.44 a | 3.67 ± 0.44 a | 3.33 ± 0.35 a | 3.25 ± 0.37 a | 3.87 ± 0.67 a | 3.33 ± 0.43 a | 2.29 ± 0.55 a | 0.16 | 0.980 |
| Astringency | 2.56 ± 0.56 a | 3.67 ± 0.65 a | 3.67 ± 0.59 a | 2.9 ± 0.65 a | 3.44 ± 0.72 a | 0.76 ± 0.54 a | 2.98 ± 0.65 a | 3.56 ± 0.65 a | 2.43 ± 0.54 a | 0.36 | 0.900 |
| Bitterness | 2.89 ± 0.77 a | 4.00 ± 0.64 a | 4.11 ± 0.63 a | 2.68 ± 0.56 a | 3.44 ± 0.55 a | 3.63 ± 0.85 a | 2.77 ± 0.63 a | 4.00 ± 0.54 a | 3.00 ± 0.53 a | 0.17 | 0.980 |
| Taste persistence | 3.44 ± 0.43 a | 4.78 ± 0.53 a | 5.56 ± 0.44 a | 3.98 ± 0.43 a | 5.22 ± 1.02 a | 4.25 ± 0.98 a | 3.62 ± 0.65 a | 5.67 ± 0.78 a | 3.57 ± 0.54 a | 0.81 | 0.560 |
| Overall quality | 5.89 ± 0.56 a | 7.94 ± 0.76 ab | 8.7 ± 0.87 b | 6.12 ± 0.88 a | 8.39 ± 0.99 b | 6.44 ± 0.65 a | 6.26 ± 0.55 a | 8.67 ± 0.74 b | 6.71 ± 0.77 a | 10.55 | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berbegal, C.; Polo, L.; Lizama, V.; Álvarez, I.; Ferrer, S.; Pardo, I.; García-Esparza, M.J. Influence of Native S. cerevisiae Strains on the Final Characteristics of “Pago” Garnacha Wines from East Spain. Beverages 2023, 9, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9010017
Berbegal C, Polo L, Lizama V, Álvarez I, Ferrer S, Pardo I, García-Esparza MJ. Influence of Native S. cerevisiae Strains on the Final Characteristics of “Pago” Garnacha Wines from East Spain. Beverages. 2023; 9(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerbegal, Carmen, Lucía Polo, Victoria Lizama, Inmaculada Álvarez, Sergi Ferrer, Isabel Pardo, and Mª José García-Esparza. 2023. "Influence of Native S. cerevisiae Strains on the Final Characteristics of “Pago” Garnacha Wines from East Spain" Beverages 9, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9010017
APA StyleBerbegal, C., Polo, L., Lizama, V., Álvarez, I., Ferrer, S., Pardo, I., & García-Esparza, M. J. (2023). Influence of Native S. cerevisiae Strains on the Final Characteristics of “Pago” Garnacha Wines from East Spain. Beverages, 9(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9010017






