Soil Erosion as an Environmental Concern in Vineyards: The Case Study of Celler del Roure, Eastern Spain, by Means of Rainfall Simulation Experiments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
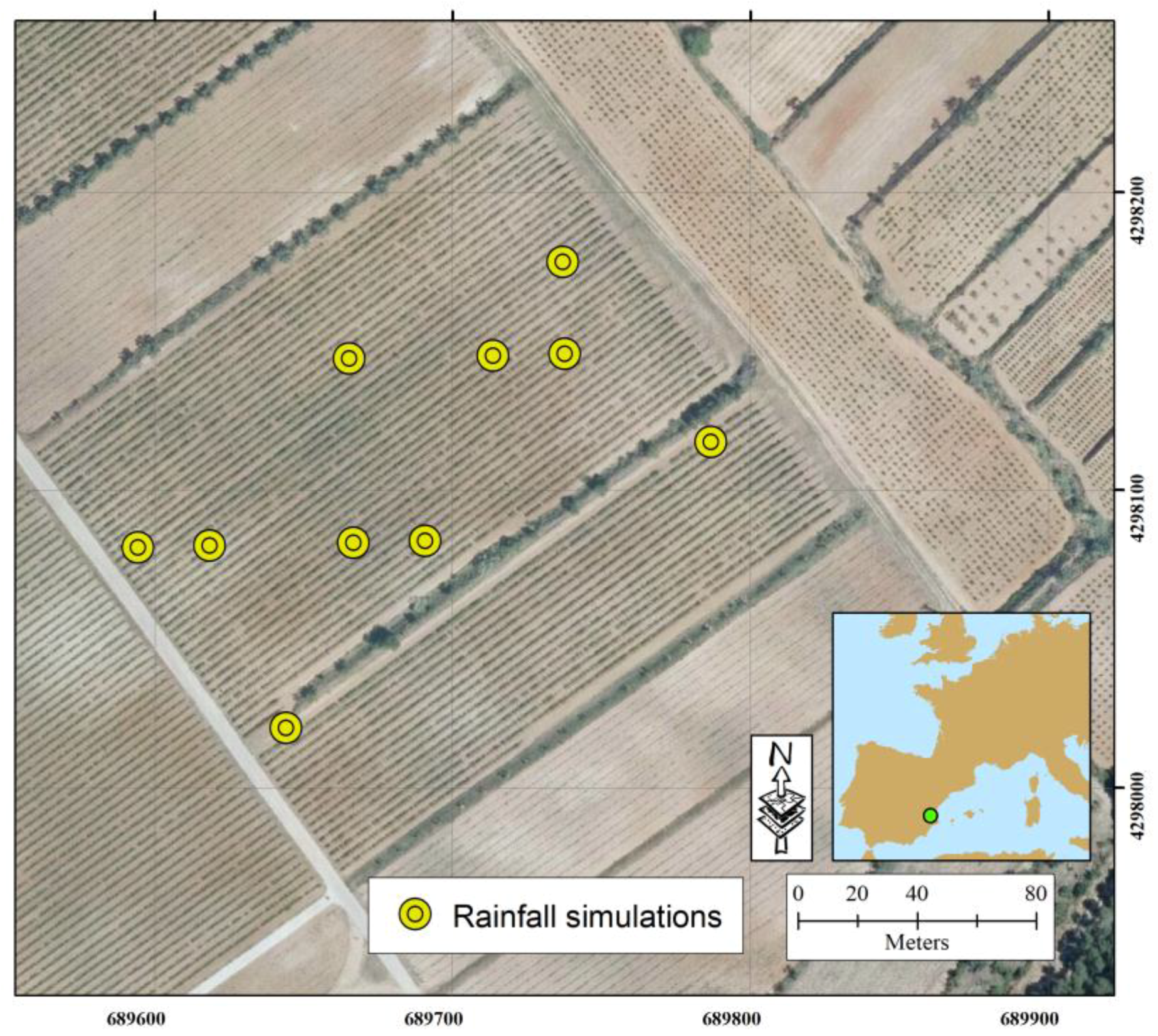
2.1. Study Area
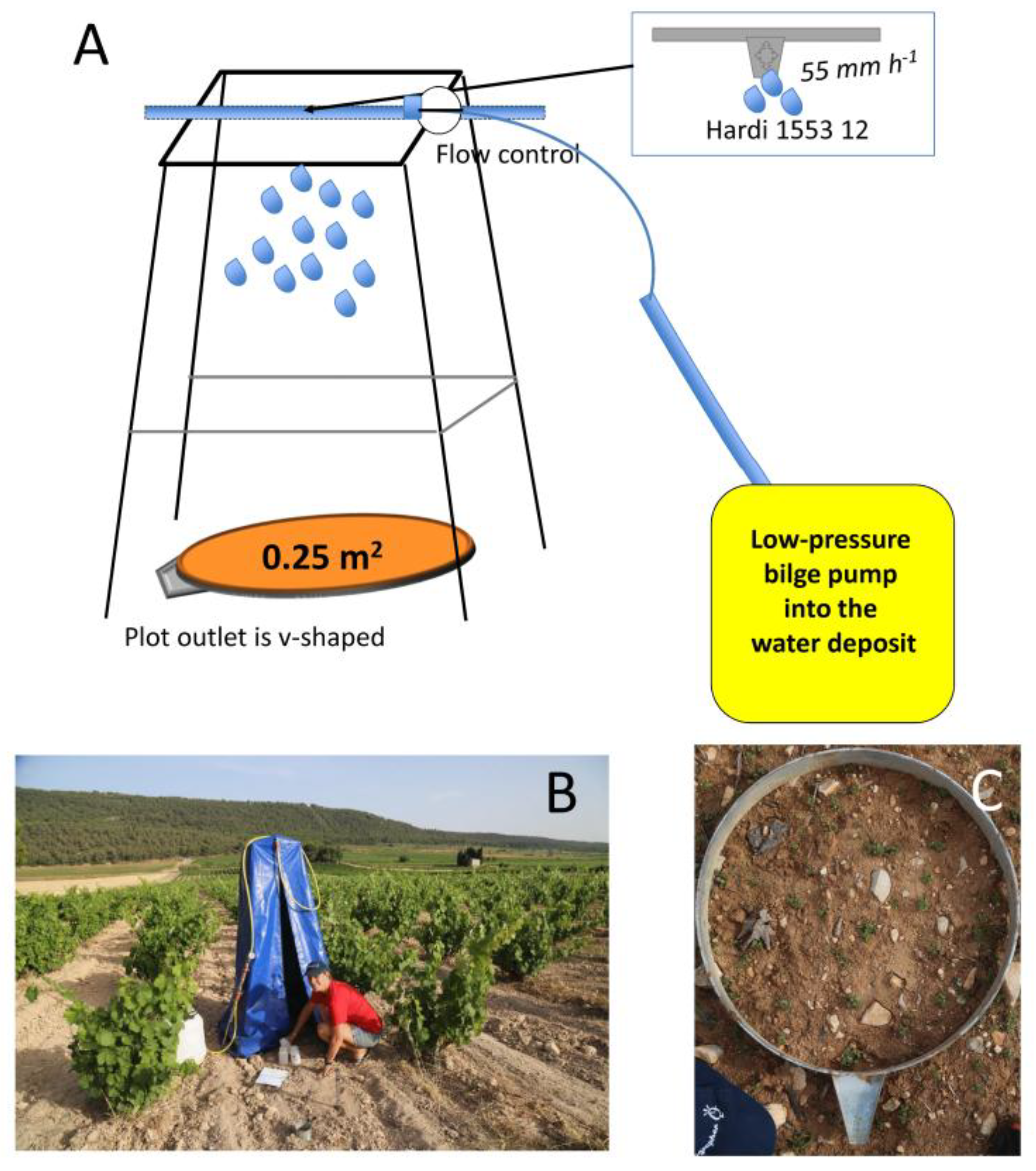
2.2. Rainfall Simulations
3. Results and Discussion
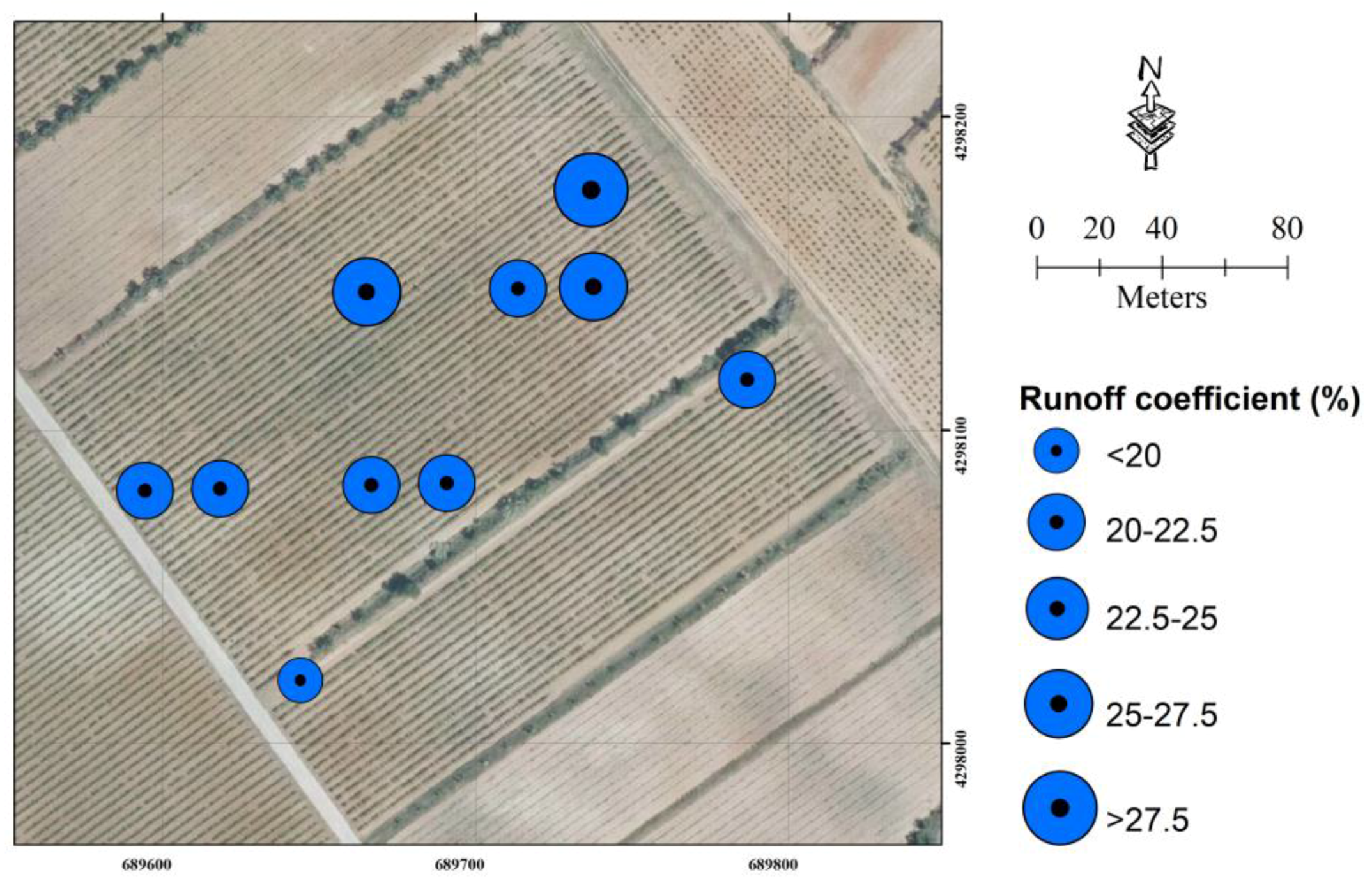
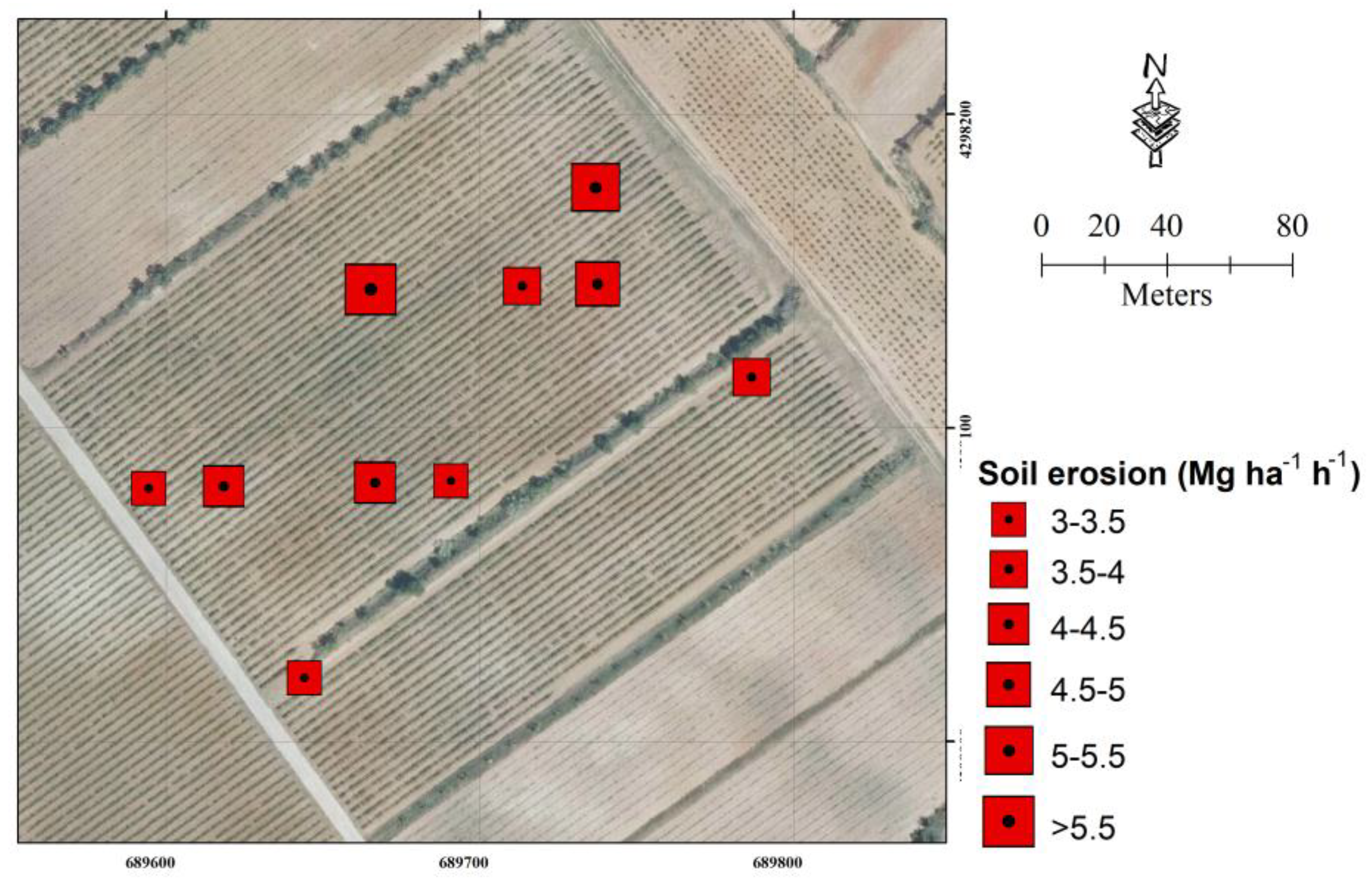
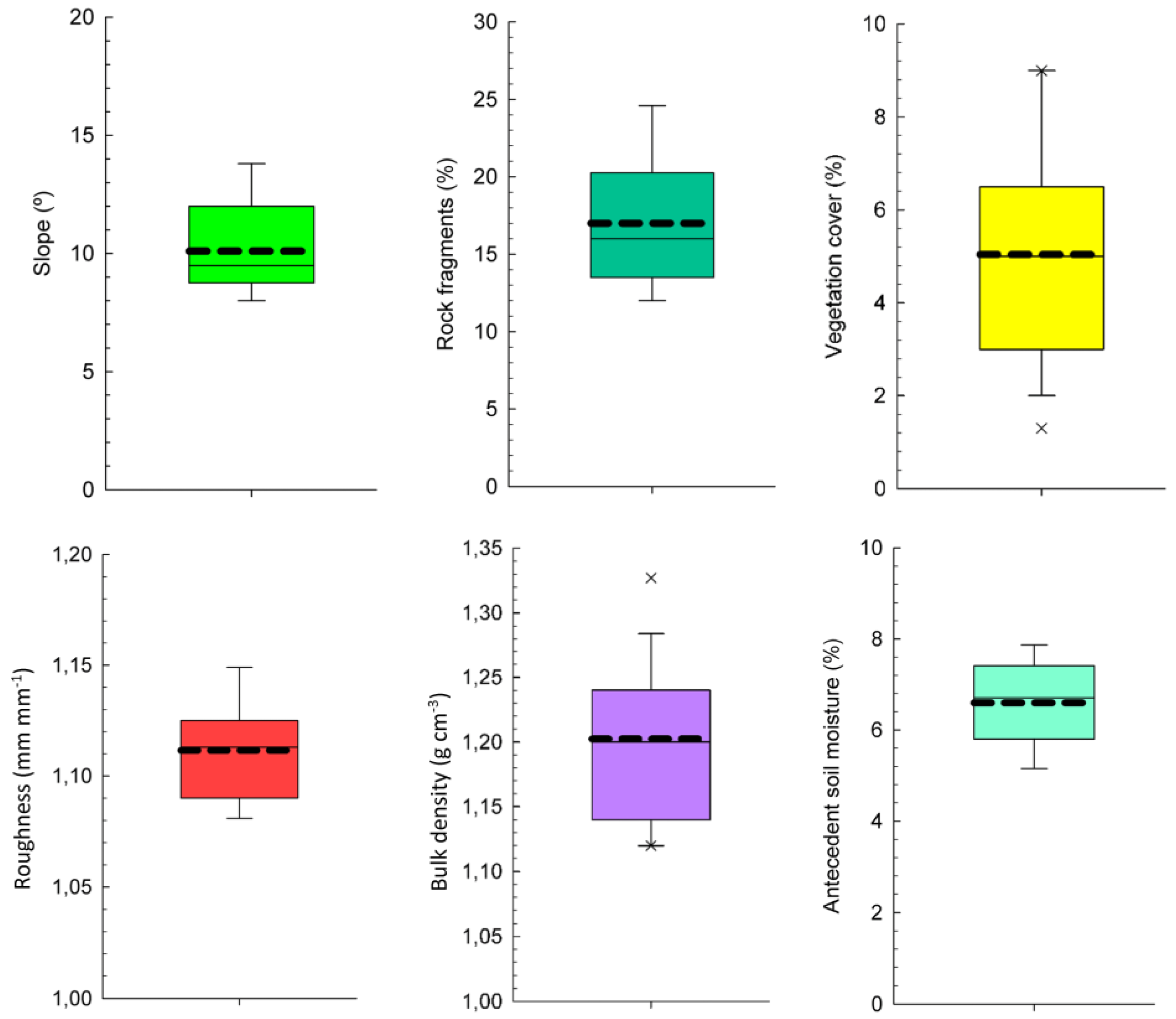
3.1. Plot Characteristics
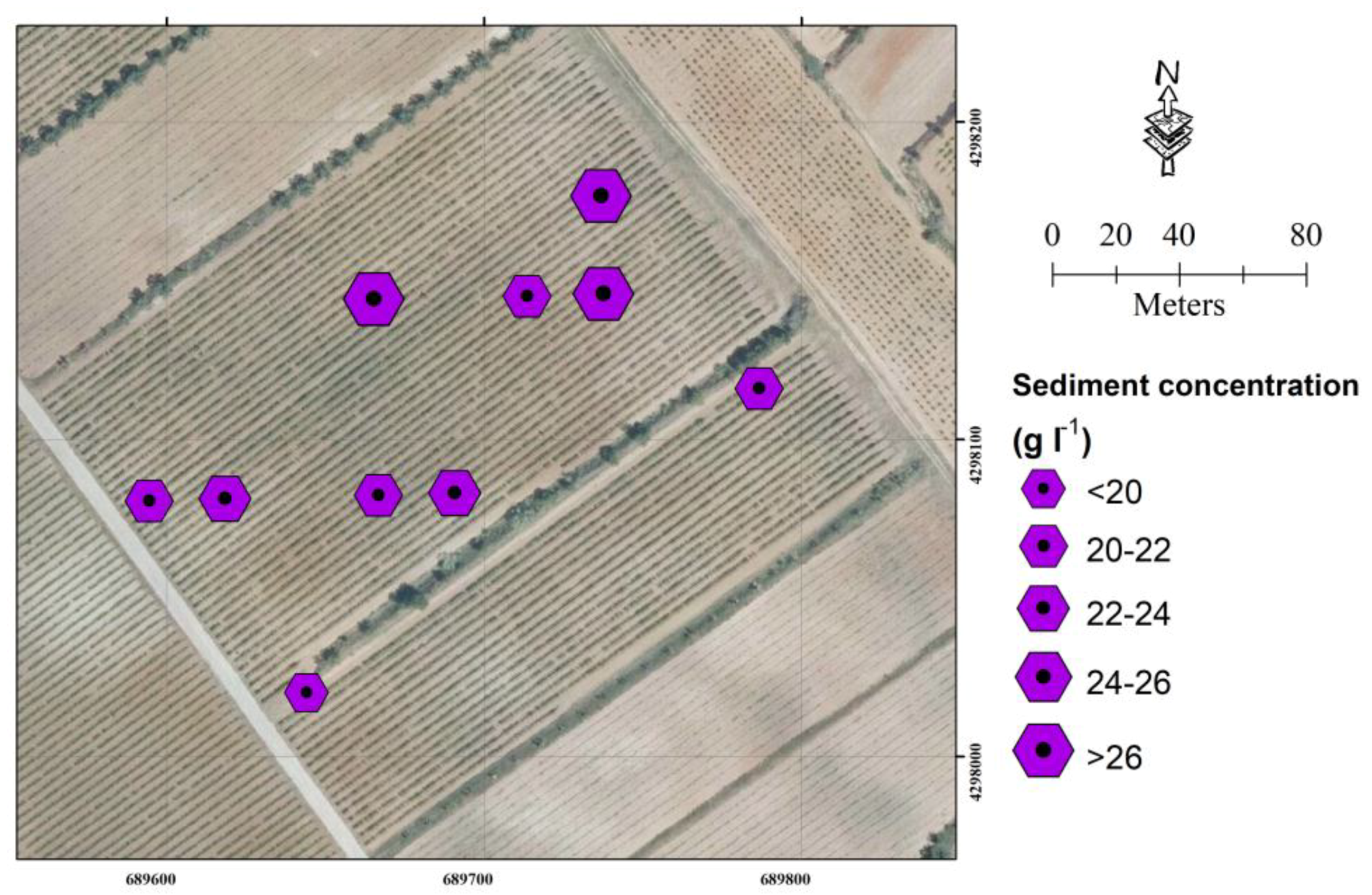
3.2. Hydrological Soil Response
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laudicina, V.A.; Palazzolo, E.; Catania, P.; Vallone, M.; García, A.D.; Badalucco, L. Soil quality indicators as affected by shallow tillage in a vineyard grown in a semiarid Mediterranean environment. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salome, C.; Coll, P.; Lardo, E.; Villenave, C.; Blanchart, E.; Hinsinger, P.; Marsden, C.; Le Cadre, E. Relevance of use-invariant soil properties to assess soil quality of vulnerable ecosystems: The case of Mediterranean vineyards. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 43, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calleja-Cervantes, M.E.; Fernández-González, A.J.; Irigoyen, I.; Fernández-López, M.; Aparicio-Tejo, P.M.; Menéndez, S. Thirteen years of continued application of composted organic wastes in a vineyard modify soil quality characteristics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 90, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaudour, E. The Quality of Grapes and Wine in Relation to Geography: Notions of Terroir at Various Scales. J. Wine Res. 2002, 13, 117–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaudour, E.; Costantini, E.; Jones, G.V.; Mocali, S. An overview of the recent approaches to terroir functional modelling, footprinting and zoning. SOIL 2015, 1, 287–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Díaz, A.; Marqués, M.J.; Sastre, B.; Bienes, R. Labile and stable soil organic carbon and physical improvements using groundcovers in vineyards from central Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 621, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novara, A.; Gristina, L.; Saladino, S.S.; Santoro, A.; Cerdà, A. Soil erosion assessment on tillage and alternative soil managements in a Sicilian vineyard. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 117, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddoccu, M.; Ferraris, S.; Opsi, F.; Cavallo, E. Long-term monitoring of soil management effects on runoff and soil erosion in sloping vineyards in Alto Monferrato (North-West Italy). Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J. Five decades of soil erosion research in “terroir”. The State-of-the-Art. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 179, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddoccu, M.; Ferraris, S.; Pitacco, A.; Cavallo, E. Temporal variability of soil management effects on soil hydrological properties, runoff and erosion at the field scale in a hillslope vineyard, North-West Italy. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 165, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.J.; Bienes, R.; Pérez-Rodríguez, R.; Jiménez, L. Soil degradation in central Spain due to sheet water erosion by low-intensity rainfall events. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2008, 33, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.C. Martinez-Casasnovas, J.A. Erosion rates and nutrient losses affected by composted cattle manure application in vineyard soils of NE. CATENA 2006, 68, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Casasnovas, J.A.; Ramos, M.C. The cost of soil erosion in vineyard fields in the Penedès–Anoia Region (NE Spain). CATENA 2006, 68, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Casasnovas, J.A.; Ramos, M.C.; Ribes-Dasi, M. On-site effects of concentrated flow erosion in vineyard fields: Some economic implications. CATENA 2005, 60, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galati, A.; Gristina, L.; Crescimanno, M.; Barone, E.; Novara, A. Towards more efficient incentives for agri-environment measures in degraded and eroded vineyards. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novara, A.; Pisciotta, A.; Minacapilli, M.; Maltese, A.; Capodici, F.; Cerdà, A.; Gristina, L. The impact of soil erosion on soil fertility and vine vigor. A multidisciplinary approach based on field, laboratory and remote sensing approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, C.S.S.; Keizer, J.J.; Santos, L.M.B.; Serpa, D.; Silva, V.; Cerqueira, M.; Ferreira, A.J.D.; Abrantes, N. Runoff, sediment and nutrient exports from a Mediterranean vineyard under integrated production: An experiment at plot scale. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 256, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey-Caramés, C.; Tardaguila, J.; Sanz-Garcia, A.; Chica-Olmo, M.; Diago, M.P. Quantifying spatio-temporal variation of leaf chlorophyll and nitrogen contents in vineyards. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 150, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendramini, C.; Beltran, G.; Nadai, C.; Giacomini, A.; Mas, A.; Corich, V. The role of nitrogen uptake on the competition ability of three vineyard Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 258, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Gamboa, G.; Garde-Cerdán, T.; Gonzalo-Diago, A.; Moreno-Simunovic, Y.; Martínez-Gil, A.M. Effect of different foliar nitrogen applications on the must amino acids and glutathione composition in Cabernet Sauvignon vineyard. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, N.; Antón, A.; Kamilaris, A.; Fantke, P. Modeling ecotoxicity impacts in vineyard production: Addressing spatial differentiation for copper fungicides. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozpinar, S.; Ozpinar, A.; Cay, A. Soil management effect on soil properties in traditional and mechanized vineyards under a semiarid Mediterranean environment. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 178, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofia, G.; Tarolli, P. Hydrological response to ~30 years of agricultural surface water management. Land 2017, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaudour, E.; Leclercq, L.; Gilliot, J.M.; Chaignon, B. Retrospective 70 y-spatial analysis of repeated vine mortality patterns using ancient aerial time series, Pléiades images and multi-source spatial and field data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 58, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Calviño, D.; Martín, A.; Arias-Estévez, M.; Bååth, E.; Díaz-Raviña, M. Microbial community structure of vineyard soils with different pH and copper content. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 46, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggisser, O.T.; Schmidt-Entling, M.H.; Bacher, S. Effects of vineyard management on biodiversity at three trophic levels. Biol. Conserv. 2010, 143, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre, B.; Barbero-Sierra, C.; Bienes, R.; Marques, M.J.; García-Díaz, A. Soil loss in an olive grove in Central Spain under cover crops and tillage treatments, and farmer perceptions. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.J.; Bienes, R.; Cuadrado, J.; Ruiz-Colmenero, M.; Barbero-Sierra, C.; Velasco, A. Analysing perceptions attitudes and responses of winegrowers about sustainable land management in Central Spain. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Casasnovas, J.A.; Ramos, M.C.; Cots-Folch, R. Influence of the EU CAP on terrain morphology and vineyard cultivation in the Priorat region of NE Spain. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A. Soil erosion after land abandonment in a semiarid environment of southeastern Spain. Arid Soil Res. Rehabil. 1997, 11, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A. Simuladores de lluvia y su aplicación a la Geomorfología: Estado de la cuestión. Cuad. Investig. Geogr. 1999, 25, 45–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.D.; Bouma, J.; Wallinga, J.; Tittonell, P.; Smith, P.; Cerdà, A.; Montanarella, L.; Quinton, J.N.; Pachepsky, Y.; van der Putten, W.H.; et al. The significance of soils and soil science towards realization of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. SOIL 2016, 2, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014; World Soil Resources Report; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, A. Soil roughness measurement: Chain method. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1993, 48, 527–529. [Google Scholar]
- Prosdocimi, M.; Jordán, A.; Tarolli, P.; Keesstra, S.; Novara, A.; Cerdà, A. The immediate effectiveness of barley straw mulch in reducing soil erodibility and surface runoff generation in Mediterranean vineyards. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keesstra, S.; Pereira, P.; Novara, A.; Brevik, E.C.; Azorin-Molina, C.; Parras-Alcántara, L.; Jordán, A.; Cerdà, A. Effects of soil management techniques on soil water erosion in apricot orchards. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551–552, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandolini, P.; Cevasco, A.; Capolongo, D.; Pepe, G.; Lovergine, F.; Del Monte, M. Response of terraced slopes to a very intense rainfall event and relationships with land abandonment: A case study from Cinque Terre (Italy). Land Degrad. Dev. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomaa, S.; Barry, D.A.; Brovelli, A.; Heng, B.C.P.; Sander, G.C.; Parlange, J.-Y.; Rose, C.W. Rain splash soil erosion estimation in the presence of rock fragments. CATENA 2012, 92, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo Comino, J.; Lassu, T.; González, J.M.S.; Sinoga, J.D.R.; Seeger, K.M.; Ries, J.B. Estudio de procesos geomorfodinámicos en campos cultivados de viñedos sobre laderas en pendientes en el valle del Ruwer (Alemania). Cuad. Geogr. 2015, 54, 6–26. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Wirtz, S.; Brevik, E.C.; Ruiz-Sinoga, J.D.; Ries, J.B. Assessment of agri-spillways as a soil erosion protection measure in Mediterranean sloping vineyards. J. Mt. Sci. 2017, 14, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blavet, D.; De Noni, G.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Leonard, M.; Maillo, L.; Laurent, J.Y.; Asseline, J.; Leprun, J.C.; Arshad, M.A.; Roose, E. Effect of land use and management on the early stages of soil water erosion in French Mediterranean vineyards. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 106, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vicente, M.; Álvarez, S. Influence of DEM resolution on modelling hydrological connectivity in a complex agricultural catchment with woody crops. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.C. Soil water content and yield variability in vineyards of Mediterranean northeastern Spain affected by mechanization and climate variability. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 2271–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; González-Pelayo, Ó.; Giménez-Morera, A.; Jordán, A.; Pereira, P.; Novara, A.; Brevik, E.C.; Prosdocimi, M.; Mahmoodabadi, M.; Keesstra, S.; et al. Use of barley straw residues to avoid high erosion and runoff rates on persimmon plantations in Eastern Spain under low frequency–high magnitude simulated rainfall events. Soil Res. 2016, 54, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, S.; Seeger, M.; Ries, J. B. Field experiments for understanding and quantification of rill erosion processes. CATENA 2012, 91, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguas, E.V.; Ayuso, J.L.; Pérez, R.; Giráldez, J.V.; Gómez, J.A. Intra and inter-annual variability of runoff and sediment yield of an olive micro-catchment with soil protection by natural ground cover in Southern Spain. Geoderma 2013, 206, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, F.G.A.; Jones, R.J.A.; Rickson, R.J.; Smith, C.J. Tolerable versus actual soil erosion rates in Europe. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2009, 94, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguas, E.V.; Guzmán, E.; Guzmán, G.; Vanwalleghem, T.; Gómez, J.A. Characteristics and importance of rill and gully erosion: A case study in a small catchment of a marginal olive grove. Cuad. Investig. Geogr. 2015, 41, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Giménez-Morera, A.; Novara, A.; Pulido, M.; Kapovic Solomun, M.; Keesstra, S. Policies can help to apply successful strategies to control soil and water losses. The case of chipped pruned branches (CPB) in Mediterranean citrus plantations. Land Use Policy 2018, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Cerdà, A.; Keesstra, S.D.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Novara, A.; Pereira, P.; Brevik, E.; Giménez-Morera, A.; Fernández-Raga, M.; Pulido, M.; di Prima, S.; Jordán, A. Runoff initiation, soil detachment and connectivity are enhanced as a consequence of vineyards plantations. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 202, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiquerez, A.; Chevigny, E.; Allemand, P.; Curmi, P.; Petit, C.; Grandjean, P. Assessing the impact of soil surface characteristics on vineyard erosion from very high spatial resolution aerial images (Côte de Beaune, Burgundy, France). CATENA 2014, 116, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevigny, E.; Quiquerez, A.; Petit, C.; Curmi, P. Lithology, landscape structure and management practice changes: Key factors patterning vineyard soil erosion at metre-scale spatial resolution. CATENA 2014, 121, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Colmenero, M.; Bienes, R.; Marques, M.J. Soil and water conservation dilemmas associated with the use of green cover in steep vineyards. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 117, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacisalihoglu, S. Determination of soil erosion in a steep hill slope with different land-use types: A case study in Mertesdorf (Ruwertal/Germany). J. Environ. Biol. Acad. Environ. Biol. India 2007, 28, 433–438. [Google Scholar]
- Lieskovský, J.; Kenderessy, P. Modelling the effect of vegetation cover and different tillage practices on soil erosion in vineyards: A case study in Vráble (Slovakia) using WATEM/SEDEM. Land Degrad. Dev. 2014, 25, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaez, J.; Lasanta, T.; Ruiz-Flaño, P.; Ortigosa, L. Factors affecting runoff and erosion under simulated rainfall in Mediterranean vineyards. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 93, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, A.; Usowicz, B.; Lipiec, J. Effects of tractor traffic on spatial variability of soil strength and water content in grass covered and cultivated sloping vineyard. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 84, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vicente, M.; Quijano, L.; Palazón, L.; Gaspar, L.; Navas, A. Assessment of soil redistribution at catchment scale by coupling a soil erosion model and a sediment connectivity index (central spanish pre-pyrenees). Cuad. Investig. Geogr. 2015, 41, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiquerez, A.; Brenot, J.; Garcia, J.-P.; Petit, C. Soil degradation caused by a high-intensity rainfall event: Implications for medium-term soil sustainability in Burgundian vineyards. CATENA 2008, 73, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paroissien, J.-B.; Lagacherie, P.; Le Bissonnais, Y. A regional-scale study of multi-decennial erosion of vineyard fields using vine-stock unearthing–burying measurements. CATENA 2010, 82, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morvan, X.; Naisse, C.; Malam Issa, O.; Desprats, J.F.; Combaud, A.; Cerdan, O. Effect of ground-cover type on surface runoff and subsequent soil erosion in Champagne vineyards in France. Soil Use Manag. 2014, 30, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Sinoga, J.D.; Garcia-Marin, R.; Gabarron-Galeote, M.A.; Martinez-Murillo, J.F. Analysis of dry periods along a pluviometric gradient in Mediterranean southern Spain. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 1558–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Results | Tp (s) | Tr (s) | Tro (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average | 251.5 | 434.2 | 774.3 |
| Standard deviation | 28.0 | 27.1 | 32.1 |
| Maximum | 298 | 467 | 824 |
| Results | R | RC | SC | Sy | Se1 | Se2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Units | L | % | g L−1 | g | g m−2 h−1 | Mg ha−1 h−1 |
| Average | 4.45 | 32.4 | 22.9 | 102.4 | 409.4 | 4.1 |
| Standard deviation | 0.4 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 19.9 | 79.8 | 0.8 |
| Maximum | 5.2 | 38.1 | 28.1 | 138.2 | 552.7 | 5.5 |
| Minimum | 3.9 | 28.5 | 19.5 | 78.6 | 314.5 | 3.1 |
| Results | RC | Se |
|---|---|---|
| Land use | % | Mg ha−1 h−1 |
| Persimmons (herbicides) [36] | 40.4 | 0.91 |
| Citrus [49] | 60.1 | 3.8 |
| Vineyards with straw mulch [35] | 39.3 | 0.63 |
| Young vineyards [50] | 72 | 12.6 |
| This research | 32.4 | 4.1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Keesstra, S.; Cerdà, A. Soil Erosion as an Environmental Concern in Vineyards: The Case Study of Celler del Roure, Eastern Spain, by Means of Rainfall Simulation Experiments. Beverages 2018, 4, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4020031
Rodrigo-Comino J, Keesstra S, Cerdà A. Soil Erosion as an Environmental Concern in Vineyards: The Case Study of Celler del Roure, Eastern Spain, by Means of Rainfall Simulation Experiments. Beverages. 2018; 4(2):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4020031
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigo-Comino, Jesús, Saskia Keesstra, and Artemi Cerdà. 2018. "Soil Erosion as an Environmental Concern in Vineyards: The Case Study of Celler del Roure, Eastern Spain, by Means of Rainfall Simulation Experiments" Beverages 4, no. 2: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4020031
APA StyleRodrigo-Comino, J., Keesstra, S., & Cerdà, A. (2018). Soil Erosion as an Environmental Concern in Vineyards: The Case Study of Celler del Roure, Eastern Spain, by Means of Rainfall Simulation Experiments. Beverages, 4(2), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4020031







