An Automated Hardware-in-Loop Testbed for Evaluating Hemorrhagic Shock Resuscitation Controllers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
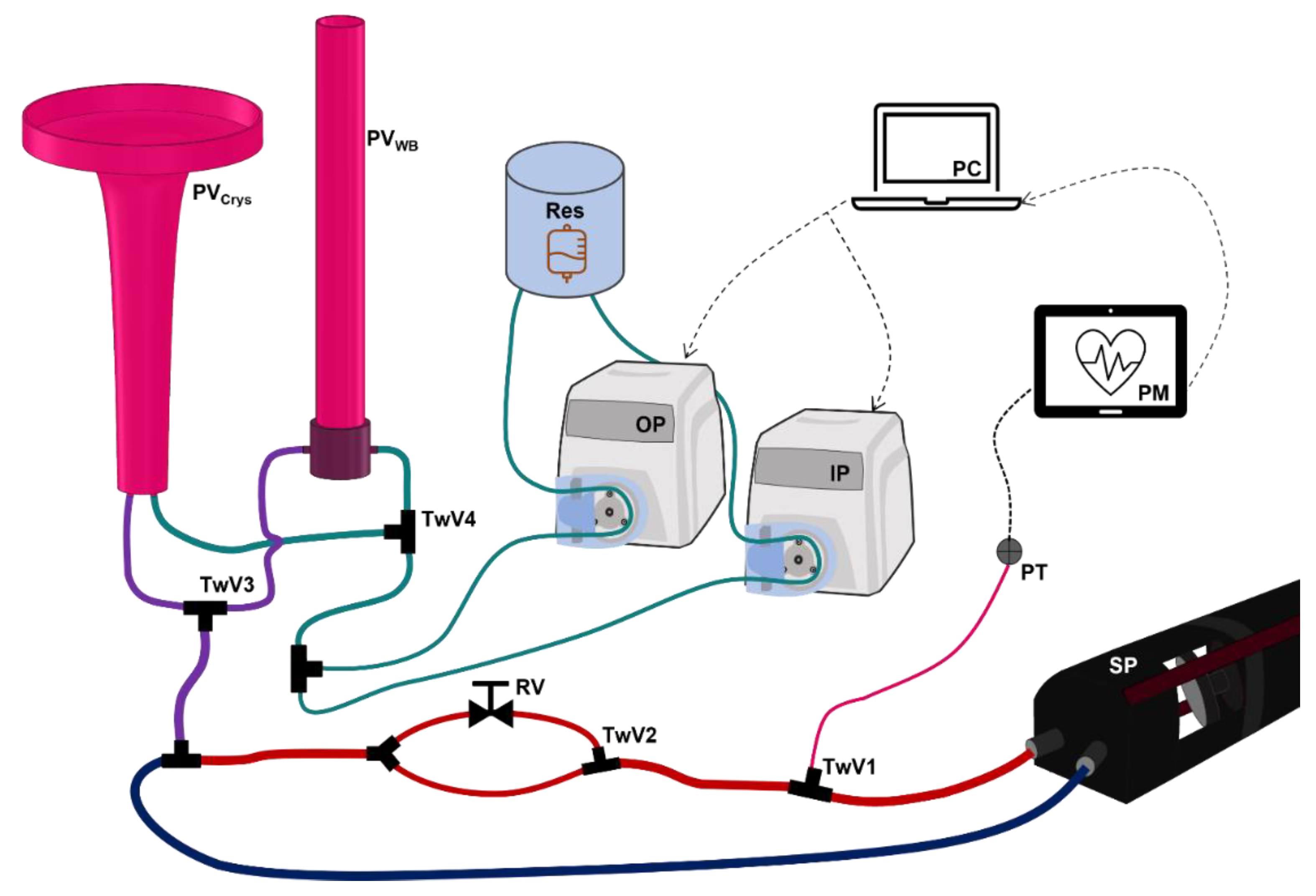
2.1. Overview of Hardware-in-Loop Automated Testbed for Resuscitation Controllers
2.2. PhysioVessel Modifications
2.3. HATRC Experimental Setup
2.4. Hemorrhage Test Scenarios
2.5. Closed-Loop Resuscitation
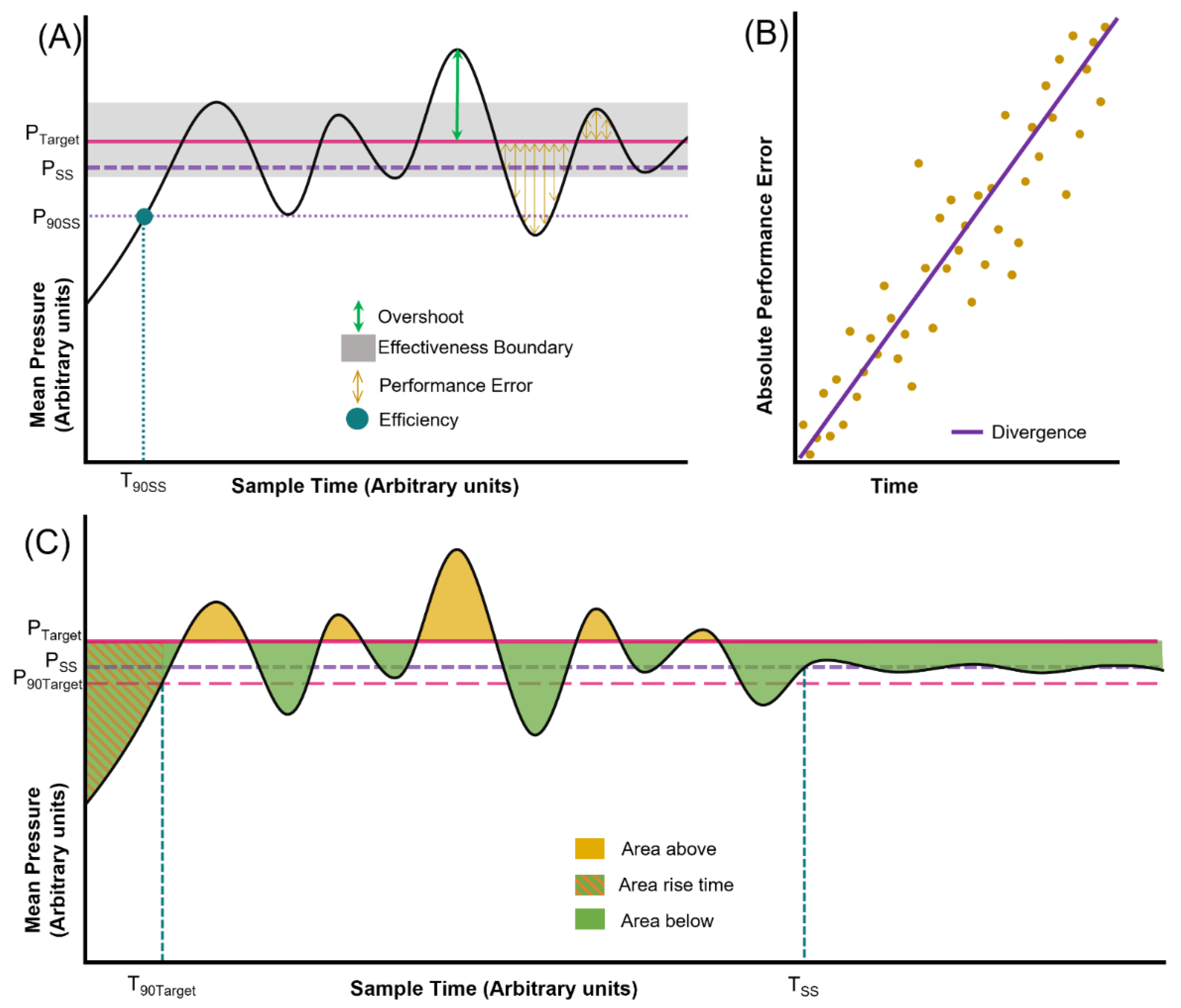
2.6. Performance Calculations
3. Results
3.1. PhysioVessel Modification and Modeling Subject Variability
3.2. Controller Evaluation Using the Automated Bleed Logic Test Platform
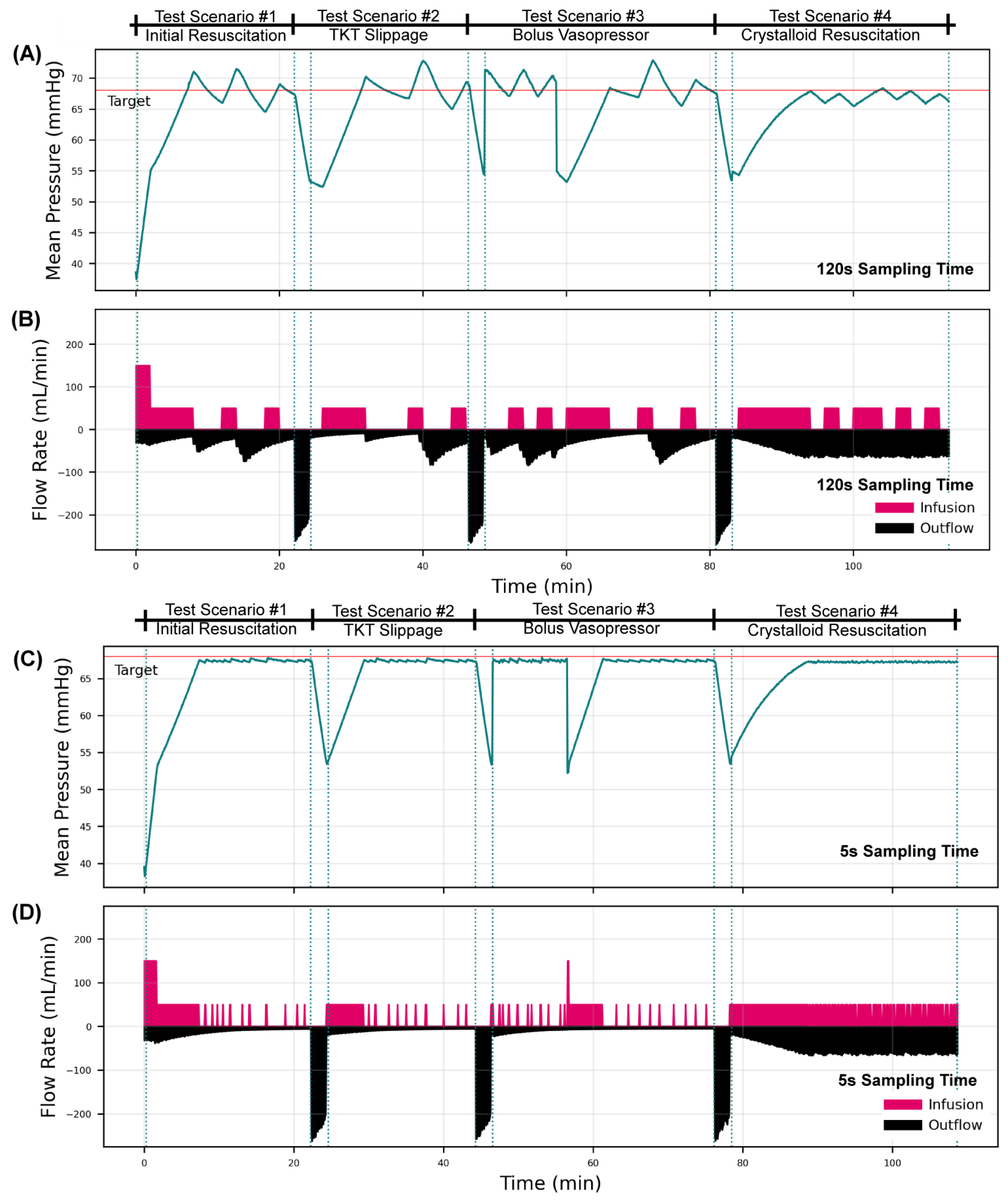
3.2.1. Overall Testing Scenario Results for a Decision Table Controller
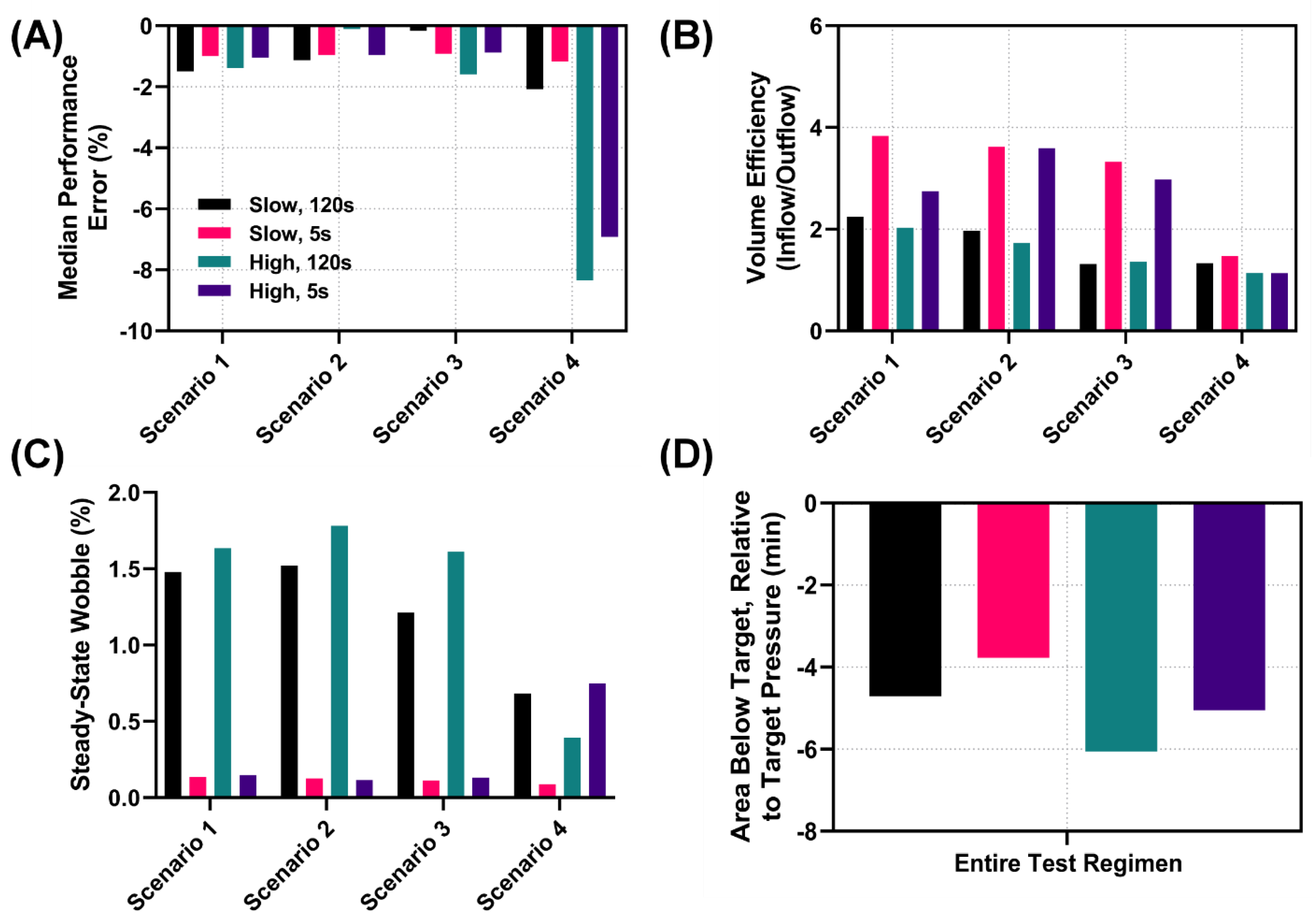
3.2.2. Performance Metric Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
DoD Disclaimer
References
- Kleber, C.; Giesecke, M.T.; Tsokos, M.; Haas, N.P.; Buschmann, C.T. Trauma-Related Preventable Deaths in Berlin 2010: Need to Change Prehospital Management Strategies and Trauma Management Education. World J. Surg. 2013, 37, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastridge, B.J.; Mabry, R.L.; Seguin, P.; Cantrell, J.; Tops, T.; Uribe, P.; Mallett, O.; Zubko, T.; Oetjen-Gerdes, L.; Rasmussen, T.E.; et al. Death on the Battlefield (2001–2011): Implications for the Future of Combat Casualty Care. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012, 73, S431–S437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackbourne, L.H.; Baer, D.G.; Cestero, R.F.; Inaba, K.; Rasmussen, T.E. Exsanguination Shock: The next Frontier in Prevention of Battlefield Mortality. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2011, 71, S1–S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, N.J.; Ward, K.R.; Pati, S.; Strandenes, G.; Cap, A.P. Hemorrhagic Blood Failure: Oxygen Debt, Coagulopathy and Endothelial Damage. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017, 82, S41–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, T.J.; De Pasquale, M.; Strandenes, G.; Sunde, G.; Ward, K.R. Challenges and Possibilities in Forward Resuscitation. Shock 2014, 41 (Suppl. 1), 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, D.H.; Rappold, J.F.; Badloe, J.F.; Berséus, O.; Blackbourne, L.; Brohi, K.H.; Butler, F.K.; Cap, A.P.; Cohen, M.J.; Davenport, R.; et al. THOR Position Paper on Remote Damage Control Resuscitation: Definitions, Current Practice and Knowledge Gaps. Shock 2014, 41, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Surgeons Committee on Trauma. Advanced Trauma Life Support Student Course Manual, 10th ed.; American College of Surgeons: Chicago, IL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- TCCC Guidelines. Available online: https://books.allogy.com/web/tenant/8/books/b729b76a-1a34-4bf7-b76b-66bb2072b2a7/ (accessed on 23 February 2022).
- Rinehart, J.; Alexander, B.; Manach, Y.L.; Hofer, C.K.; Tavernier, B.; Kain, Z.N.; Cannesson, M. Evaluation of a Novel Closed-Loop Fluid-Administration System Based on Dynamic Predictors of Fluid Responsiveness: An In Silico Simulation Study. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hundeshagen, G.; Kramer, G.C.; Ribeiro Marques, N.; Salter, M.G.; Koutrouvelis, A.K.; Li, H.; Solanki, D.R.; Indrikovs, A.; Seeton, R.; Henkel, S.N.; et al. Closed-Loop- and Decision-Assist-Guided Fluid Therapy of Human Hemorrhage. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, e1068–e1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, N.R.; Ford, B.J.; Khan, M.N.; Kinsky, M.; Deyo, D.J.; Mileski, W.J.; Ying, H.; Kramer, G.C. Automated Closed-Loop Resuscitation of Multiple Hemorrhages: A Comparison between Fuzzy Logic and Decision Table Controllers in a Sheep Model. Disaster Mil. Med. 2017, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joosten, A.; Delaporte, A.; Ickx, B.; Touihri, K.; Stany, I.; Barvais, L.; Van Obbergh, L.; Loi, P.; Rinehart, J.; Cannesson, M.; et al. Crystalloid versus Colloid for Intraoperative Goal-Directed Fluid Therapy Using a Closed-Loop System: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Controlled Trial in Major Abdominal Surgery. Anesthesiology 2018, 128, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menger, J.; Fischer, A.; Mouhieddine, M.; Seidel, M.; Edlinger-Stanger, M.; Bevilacqua, M.; Hiesmayr, M.; Dworschak, M. Evaluation of an Active Decision Support System for Hemodynamic Optimization during Elective Major Vascular Surgery. Minerva Anestesiol. 2019, 85, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libert, N.; Chenegros, G.; Harrois, A.; Baudry, N.; Cordurie, G.; Benosman, R.; Vicaut, E.; Duranteau, J. Performance of Closed-Loop Resuscitation of Haemorrhagic Shock with Fluid Alone or in Combination with Norepinephrine: An Experimental Study. Ann. Intensive Care 2018, 8, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingert, W.; Peter, J.; Thiel, C.; Thiel, K.; Rosenstiel, W.; Klingert, K.; Grasshoff, C.; Königsrainer, A.; Schenk, M. Fully Automated Life Support: An Implementation and Feasibility Pilot Study in Healthy Pigs. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2018, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Bighamian, R.; Hahn, J.-O. Development and In Silico Evaluation of a Model-Based Closed-Loop Fluid Resuscitation Control Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng 2018, 66, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snider, E.J.; Berard, D.; Vega, S.J.; Avital, G.; Boice, E.N. Evaluation of a Proportional–Integral–Derivative Controller for Hemorrhage Resuscitation Using a Hardware-in-Loop Test Platform. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, B.; Haddad, W.M.; Bailey, J.M.; Geist, B.; Ueyama, Y.; Muir, W.W. A Pilot Study Evaluating Adaptive Closed-Loop Fluid Resuscitation during States of Absolute and Relative Hypovolemia in Dogs. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2018, 28, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsalti, M.; Tivay, A.; Jin, X.; Kramer, G.C.; Hahn, J.-O. Design and In Silico Evaluation of a Closed-Loop Hemorrhage Resuscitation Algorithm with Blood Pressure as Controlled Variable. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2021, 144, 021001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berard, D.; Vega, S.J.; Torres, S.I.H.; Polykratis, I.A.; Salinas, J.; Ross, E.; Avital, G.; Boice, E.N.; Snider, E.J. Development of the PhysioVessel: A Customizable Platform for Simulating Physiological Fluid Resuscitation. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2022, 8, 035017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackelford, S.A.; Gurney, J.M.; Taylor, A.L.; Keenan, S.; Corley, J.B.; Cunningham, C.W.; Drew, B.G.; Jensen, S.D.; Kotwal, R.S.; Montgomery, H.R.; et al. Joint Trauma System, Defense Committee on Trauma, and Armed Services Blood Program Consensus Statement on Whole Blood. Transfusion 2021, 61, S333–S335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Valkinburgh, D.; Kerndt, C.C.; Hashmi, M.F. Inotropes and Vasopressors; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Åneman, A.; Wilander, P.; Zoerner, F.; Lipcsey, M.; Chew, M.S. Vasopressor Responsiveness Beyond Arterial Pressure: A Conceptual Systematic Review Using Venous Return Physiology. Shock 2021, 56, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondeen, J.L.; Dubick, M.A.; Holcomb, J.B.; Wade, C.E. Uncontrolled Hemorrhage Differs from Volume- or Pressure-Matched Controlled Hemorrhage in Swine. Shock 2007, 28, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, E.E.; Moore, H.B.; Kornblith, L.Z.; Neal, M.D.; Hoffman, M.; Mutch, N.J.; Schöchl, H.; Hunt, B.J.; Sauaia, A. Trauma-Induced Coagulopathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhondt, L.; Croubels, S.; De Paepe, P.; Wallis, S.C.; Pandey, S.; Roberts, J.A.; Lipman, J.; De Cock, P.; Devreese, M. Conventional Pig as Animal Model for Human Renal Drug Excretion Processes: Unravelling the Porcine Renal Function by Use of a Cocktail of Exogenous Markers. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirshberg, A.; Dugas, M.; Banez, E.I.; Scott, B.G.; Wall, M.J.; Mattox, K.L. Minimizing Dilutional Coagulopathy in Exsanguinating Hemorrhage: A Computer Simulation. J. Trauma 2003, 54, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondeen, J.L.; Coppes, V.G.; Holcomb, J.B. Blood Pressure at Which Rebleeding Occurs after Resuscitation in Swine with Aortic Injury. J. Trauma 2003, 54, S110–S117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Râdegran, G. Ultrasound Doppler Estimates of Femoral Artery Blood Flow during Dynamic Knee Extensor Exercise in Humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1997, 83, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvel, J.R.; Donoho, D.L.; Shafer, S.L. Measuring the Predictive Performance of Computer-Controlled Infusion Pumps. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 1992, 20, 63–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirinejad, H.; Parvinian, B.; Ricks, M.; Zhang, Y.; Weininger, S.; Hahn, J.-O.; Scully, C.G. Evaluation of Fluid Resuscitation Control Algorithms via a Hardware-in-the-Loop Test Bed. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 67, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 60601-1-10:2007; Medical Electrical Equipment—Part 1–10: General Requirements for Basic Safety and Essential Performance—Collateral Standard: Requirements for the Development of Physiologic Closed-Loop Controllers. IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- Avital, G.; Snider, E.J.; Berard, D.; Vega, S.J.; Hernandez-Torres, S.I.; Convertino, V.A.; Salinas, J.; Boice, E.N. Closed-Loop Controlled Fluid Administration Systems: A Comprehensive Review. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, E.J.; Berard, D.; Vega, S.J.; Ross, E.; Knowlton, Z.J.; Avital, G.; Boice, E.N. Hardware-in-Loop Comparison of Physiological Closed-Loop Controllers for the Automonous Management of Hypotension. Bioengineering 2022. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Wafaisade, A.; Wutzler, S.; Lefering, R.; Tjardes, T.; Banerjee, M.; Paffrath, T.; Bouillon, B.; Maegele, M. Trauma Registry of DGU Drivers of Acute Coagulopathy after Severe Trauma: A Multivariate Analysis of 1987 Patients. Emerg. Med. J. 2010, 27, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Snider, E.J.; Berard, D.; Vega, S.J.; Hernandez Torres, S.I.; Avital, G.; Boice, E.N. An Automated Hardware-in-Loop Testbed for Evaluating Hemorrhagic Shock Resuscitation Controllers. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080373
Snider EJ, Berard D, Vega SJ, Hernandez Torres SI, Avital G, Boice EN. An Automated Hardware-in-Loop Testbed for Evaluating Hemorrhagic Shock Resuscitation Controllers. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(8):373. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080373
Chicago/Turabian StyleSnider, Eric. J., David Berard, Saul J. Vega, Sofia I. Hernandez Torres, Guy Avital, and Emily N. Boice. 2022. "An Automated Hardware-in-Loop Testbed for Evaluating Hemorrhagic Shock Resuscitation Controllers" Bioengineering 9, no. 8: 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080373
APA StyleSnider, E. J., Berard, D., Vega, S. J., Hernandez Torres, S. I., Avital, G., & Boice, E. N. (2022). An Automated Hardware-in-Loop Testbed for Evaluating Hemorrhagic Shock Resuscitation Controllers. Bioengineering, 9(8), 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080373





