Efficacy of Ciprofloxacin and Amoxicillin Removal and the Effect on the Biochemical Composition of Chlorella vulgaris
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Algae and Incubation Conditions
2.3. Experimental Setup
2.4. Determination of Algal Growth and Biochemical Composition
2.4.1. Algal Growth
2.4.2. Biochemical Composition
2.5. Determination of Antibiotic Concentration
2.6. Determination of Antibiotic Removal Mechanisms in Algal Cells
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
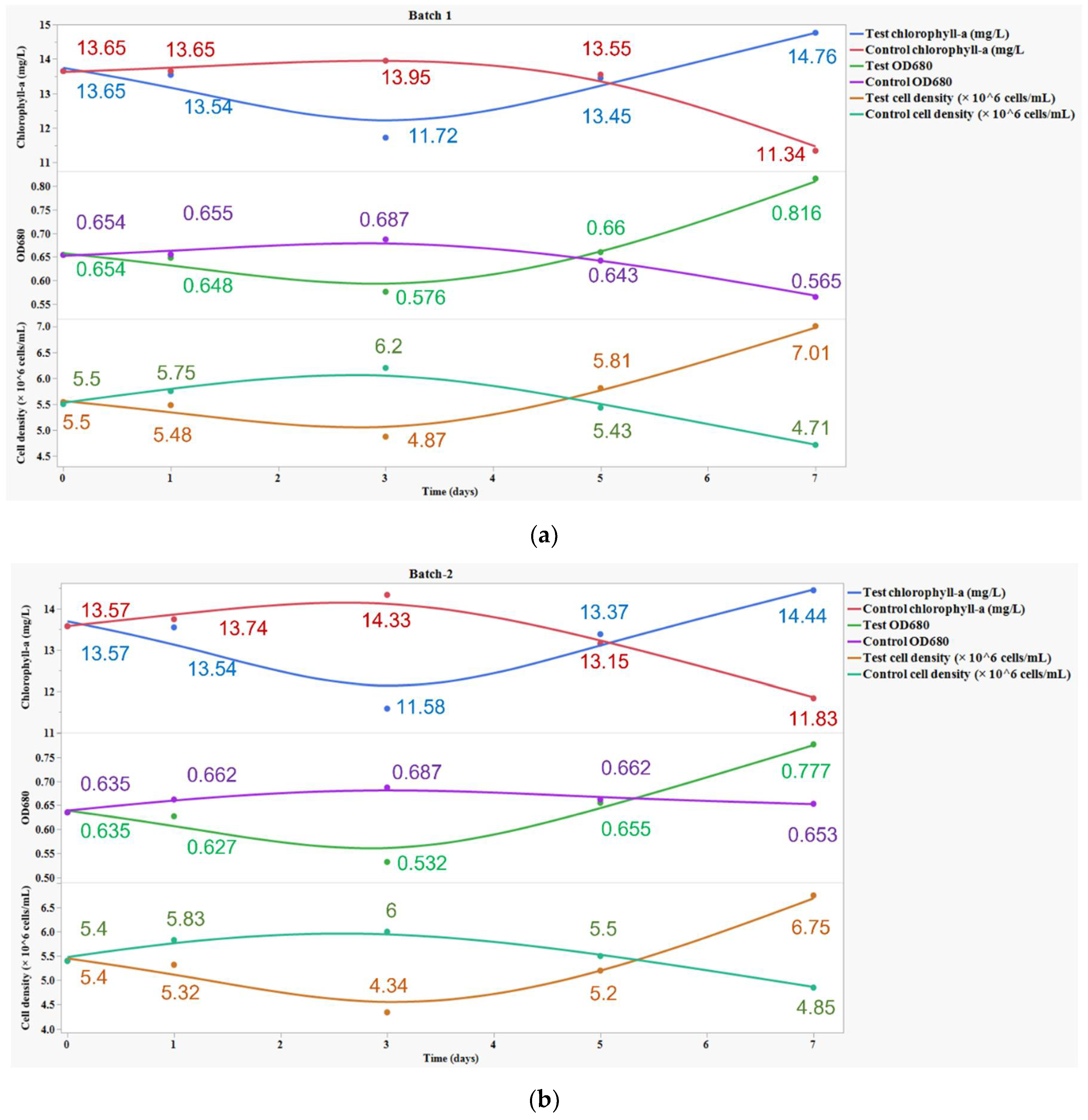
3.1. Effect of Antibiotics on Algal Growth
3.2. Effect of Antibiotics on Algal Biochemical Composition (Lipids, Carbohydrates, and Proteins)
3.3. Antibiotics Removal Mechanisms Adopted by Algae
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Danner, M.; Robertson, A.; Behrends, V.; Reiss, J. Science of the Total Environment Antibiotic pollution in surface fresh waters: Occurrence and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wu, W.; Zhang, J.; Lv, P.; Xu, L.; Yan, Y. Progress of research on the toxicology of antibiotic pollution in aquatic organisms. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Editors, P.M. Antimicrobial Resistance: Is the World UNprepared? PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, K.R.; Brooks, B.W. Global Aquatic Hazard Assessment of Ciprofloxacin: Exceedances of Antibiotic Resistance Development and Ecotoxicological Thresholds. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Teplow, D., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 159, pp. 59–77. ISBN 9780128162354. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas-Silva, J.; Silva-Oliveira, T.; Muricy, G.; Laport, M.S. Bacillus Strains Associated to Homoscleromorpha Sponges are Highly Active Against Multidrug Resistant Bacteria. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymańska, U.; Wiergowski, M.; Sołtyszewski, I.; Kuzemko, J.; Wiergowska, G.; Woźniak, M.K. Presence of antibiotics in the aquatic environment in Europe and their analytical monitoring: Recent trends and perspectives. Microchem. J. 2019, 147, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.R.; Kay, P.; Brown, L.E. Global synthesis and critical evaluation of pharmaceutical data sets collected from river systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 661–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalakova, P.; Cizmas, L.; McDonald, T.J.; Marsalek, B.; Feng, M.; Sharma, V.K. Occurrence and toxicity of antibiotics in the aquatic environment: A review. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, C.; Liu, X.; Lee, S.; Kho, Y.; Kim, W.K.; Kim, P.; Choi, K. Ecological risk assessment of amoxicillin, enrofloxacin, and neomycin: Are their current levels in the freshwater environment safe? Toxics 2021, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Välitalo, P.; Kruglova, A.; Mikola, A.; Vahala, R. Toxicological impacts of antibiotics on aquatic micro-organisms: A mini-review. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2017, 220, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leng, L.; Wei, L.; Xiong, Q.; Xu, S.; Li, W.; Lv, S.; Lu, Q.; Wan, L.; Wen, Z.; Zhou, W. Use of microalgae based technology for the removal of antibiotics from wastewater: A review. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Show, P.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Ho, S.-H. Algae-mediated antibiotic wastewater treatment: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2022, 9, 100145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollmann, F.; Dietze, S.; Ackermann, J.U.; Bley, T.; Walther, T.; Steingroewer, J.; Krujatz, F. Microalgae wastewater treatment: Biological and technological approaches. Eng. Life Sci. 2019, 19, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wirth, R.; Pap, B.; Böjti, T.; Shetty, P.; Lakatos, G.; Bagi, Z.; Kovács, K.L.; Maróti, G. Chlorella vulgaris and Its Phycosphere in Wastewater: Microalgae-Bacteria Interactions During Nutrient Removal. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Li, H.; Yu, W.; Cao, L.; He, Q. Azithromycin induces dual effects on microalgae: Roles of photosynthetic damage and oxidative stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Zitko, V.; An, T. Response of the freshwater alga Chlorella vulgaris to trichloroisocyanuric acid and ciprofloxacin. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, R.; Caprio, V.; Ciniglia, C.; De Champdoré, M.; Lo Giudice, R.; Marotta, R.; Zuccato, E. Antibiotics in the environment: Occurrence in Italian STPs, fate, and preliminary assessment on algal toxicity of amoxicillin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 6832–6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hena, S.; Gutierrez, L.; Croué, J.P. Removal of metronidazole from aqueous media by C. vulgaris. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M. Microalgae—Biotechnology and Microbiology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; Volume 183, ISBN 0521350204. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Ballardo, D.U.; Rossi, S.; Hernández, V.; Gómez, R.V.; del Carmen Rendón-Unceta, M.; Caro-Corrales, J.; Valdez-Ortiz, A. A simple spectrophotometric method for biomass measurement of important microalgae species in aquaculture. Aquaculture 2015, 448, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Vaidyanathan, S. Simultaneous assay of pigments, carbohydrates, proteins and lipids in microalgae. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 776, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, C.B.V.N.; Sharma, H.K.; Rao, S.C.; Rao, G. RP-HPLC method for analysis of related substances in amoxicillin drug substance. Acta Chromatogr. 2009, 21, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistos, C.; Tsantili-Kakoulidou, A.; Koupparis, M. Investigation of the retention/pH profile of zwitterionic fluoroquinolones in reversed-phase and ion-interaction high performance liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 39, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Acharya, K. Removal of trimethoprim, sulfamethoxazole, and triclosan by the green alga Nannochloris sp. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 315, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.-Q.; Kurade, M.B.; Abou-Shanab, R.A.I.; Ji, M.-K.; Choi, J.; Kim, J.O.; Jeon, B.-H. Biodegradation of carbamazepine using freshwater microalgae Chlamydomonas mexicana and Scenedesmus obliquus and the determination of its metabolic fate. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 205, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, T.; Yang, M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; Lin, K.; Li, J.; Gan, J. Toxicity, degradation and metabolic fate of ibuprofen on freshwater diatom Navicula sp. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 330, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.Q.; Kurade, M.B.; Jeon, B.H. Biodegradation of levofloxacin by an acclimated freshwater microalga, Chlorella vulgaris. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wei, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Qi, Y.; Li, Y.; Kitamura, Y. Biodegradability and mechanism of florfenicol via Chlorella sp. UTEX1602 and L38: Experimental study. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 272, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hom-Diaz, A.; Jaén-Gil, A.; Rodríguez-Mozaz, S.; Barceló, D.; Vicent, T.; Blánquez, P. Insights into removal of antibiotics by selected microalgae (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Chlorella sorokiniana, Dunaliella tertiolecta and Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata). Algal Res. 2022, 61, 102560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathasivam, R.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Hashem, A.; Abd_Allah, E.F. Microalgae metabolites: A rich source for food and medicine. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.M.; Cheng, L.H.; Xu, X.H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.L. Enhanced lipid production of Chlorella vulgaris by adjustment of cultivation conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6797–6804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, S.; Zhou, D. Could co-substrate sodium acetate simultaneously promote Chlorella to degrade amoxicillin and produce bioresources? J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, C.; Bandyopadhyay, T.K.; Bhunia, B.; Mishra, U.; Narayanasamy, S.; Muthuraj, M. Microalgae: Sustainable resource of carbohydrates in third-generation biofuel production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 150, 111464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alishah Aratboni, H.; Rafiei, N.; Garcia-Granados, R.; Alemzadeh, A.; Morones-Ramírez, J.R. Biomass and lipid induction strategies in microalgae for biofuel production and other applications. Microb. Cell Fact. 2019, 18, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiong, Q.; Hu, L.X.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhao, J.L.; He, L.Y.; Ying, G.G. Microalgae-based technology for antibiotics removal: From mechanisms to application of innovational hybrid systems. Environ. Int. 2021, 155, 106594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Liang, W.; Sun, J.; Zhao, C.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced production of microalgae-originated photosensitizer by integrating photosynthetic electrons extraction and antibiotic induction towards photocatalytic degradation of antibiotic: A novel complementary treatment process for antibiotic removal from effluent of conventional biological wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 308, 114527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petsas, A.S.; Vagi, M.C. Effects on the Photosynthetic Activity of Algae after Exposure to Various Organic and Inorganic Pollutants: Review. In Chlorophyll; Jacob-Lopez, E., Queiroz Zepka, L., Queiroz, M.I., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; Chapter 4; ISBN 978-953-51-3108-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, P.; Tong, S. Comparative sensitivity of eight freshwater phytoplankton species to isoprocarb, propargite, flumetralin and propiconazol. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2008, 17, 525–529. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, H.R. Sources, behaviour and fate of organic contaminants during sewage treatment and in sewage sludges. Sci. Total Environ. 1996, 185, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjali, R.; Shanthakumar, S. Insights on the current status of occurrence and removal of antibiotics in wastewater by advanced oxidation processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Torres, O.L.; Guo, R.; Chen, J. Investigation of the removal mechanism of antibiotic ceftazidime by green algae and subsequent microbic impact assessment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, P.; Chen, C.; Zhang, C.; Su, G.; Ren, N.; Ho, S.H. Revealing the role of adsorption in ciprofloxacin and sulfadiazine elimination routes in microalgae. Water Res. 2020, 172, 115475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xue, R.; Fu, L.; Chen, C.; Ndayisenga, F.; Zhou, D. Carbon dots enhance the recovery of microalgae bioresources from wastewater containing amoxicillin. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 335, 125258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Batch 1—CIP | Experimental Condition | Culture | Antibiotic | Illumination |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | CIP Test | Algae | + | + |
| B | CIP Control | Algae | - | + |
| C | CIP Abiotic light | - | + | + |
| D | CIP Abiotic Dark | - | + | - |
| Batch 2—AMX | Experimental Condition | Culture | Antibiotic | Illumination |
| A | AMX Test | Algae | + | + |
| B | AMX Control | Algae | - | + |
| C | AMX Abiotic light | - | + | + |
| D | AMX Abiotic Dark | - | + | - |
| Antibiotic | Total Removal | Photodegradation | Bioadsorption | Bioaccumulation | Biodegradation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIP | 36.9 ± 1.1 | 0.54 ± 0.02 | 15.4 ± 0.4 | 7.92 ± 0.06 | 76.09 ± 0.55 |
| AMX | 24. 7 ± 1.0 | 24.44 ± 9.71 | 18.48 ± 5.64 | 10.84 ± 9.56 | 46.23 ± 5.89 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ricky, R.; Chiampo, F.; Shanthakumar, S. Efficacy of Ciprofloxacin and Amoxicillin Removal and the Effect on the Biochemical Composition of Chlorella vulgaris. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9040134
Ricky R, Chiampo F, Shanthakumar S. Efficacy of Ciprofloxacin and Amoxicillin Removal and the Effect on the Biochemical Composition of Chlorella vulgaris. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(4):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9040134
Chicago/Turabian StyleRicky, Rajamanickam, Fulvia Chiampo, and Subramaniam Shanthakumar. 2022. "Efficacy of Ciprofloxacin and Amoxicillin Removal and the Effect on the Biochemical Composition of Chlorella vulgaris" Bioengineering 9, no. 4: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9040134
APA StyleRicky, R., Chiampo, F., & Shanthakumar, S. (2022). Efficacy of Ciprofloxacin and Amoxicillin Removal and the Effect on the Biochemical Composition of Chlorella vulgaris. Bioengineering, 9(4), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9040134








