Automated Lung-Related Pneumonia and COVID-19 Detection Based on Novel Feature Extraction Framework and Vision Transformer Approaches Using Chest X-ray Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
- This research offers a refined Chest X-ray Image Based Feature Extraction Framework for Lung Disease identification that is significantly discriminative in identifying Pneumonia, COVID-19, and Lung Cancer Diseases.
- We offer explainability-driven, medically explainable visuals that emphasize the crucial regions relevant to the model’s prediction of the input image.
- We established a novel technique for improving ensemble models by using the integration of global second-order pooling and multi-head self-attention.
- This work examined many pre-trained deep learning models, providing a unique ensemble deep learning model that acts as the suggested model backbone, tackling the problem of the requirement for large-scale data.
- We reported a well robust deep learning method in Accuracy, Specificity, Sensitivity, Precision, F1 Score, Confusion matrix, and AUC using receiver operating characteristics (ROC) for detecting Pneumonia, COVID-19, and Lung Cancer Diseases based on a detailed experimental evaluation of the proposed model and comparison with state-of-the-art results.
2. Materials and Methods
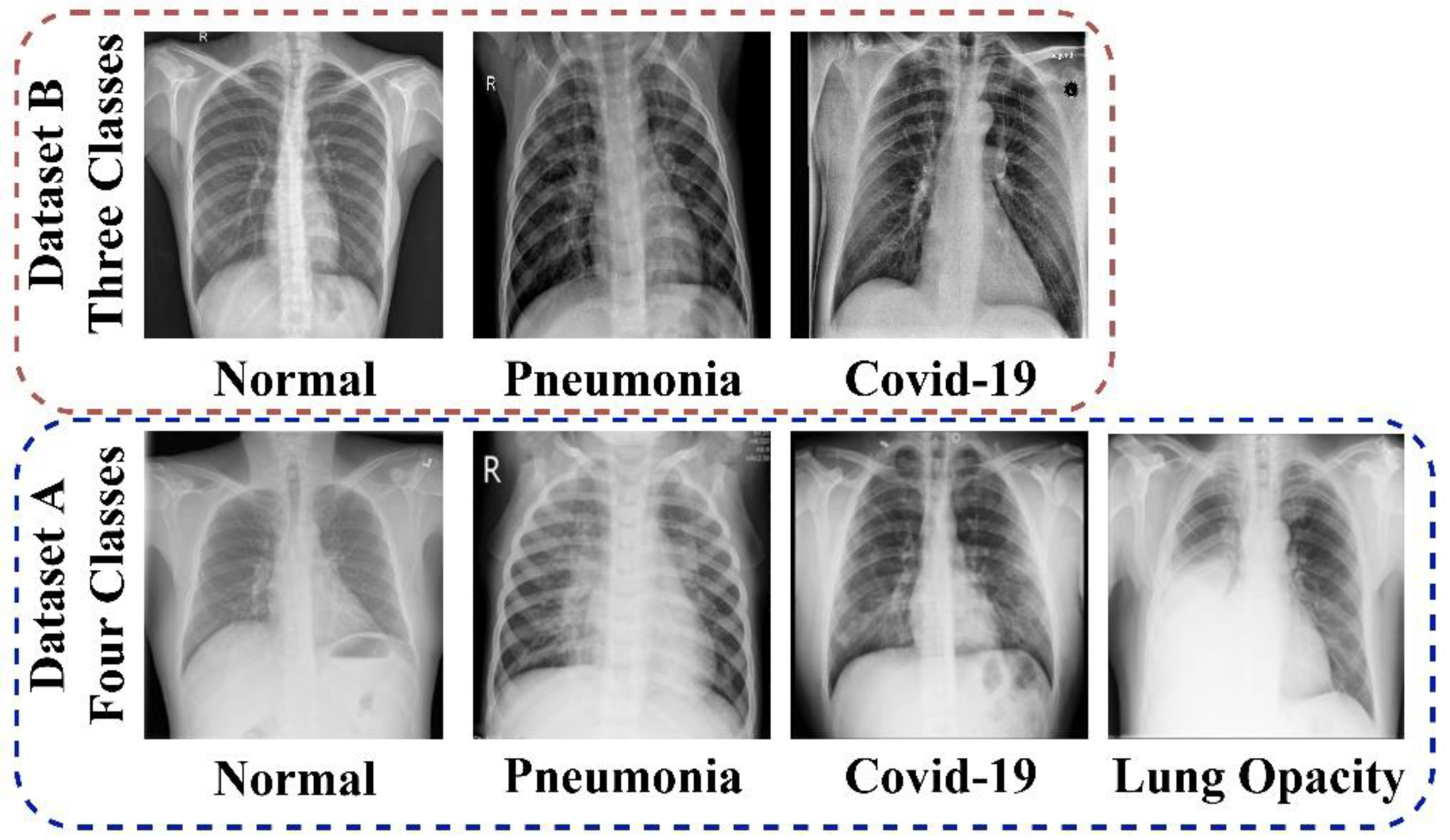
2.1. Dataset
2.1.1. Data_A
2.1.2. Data_B
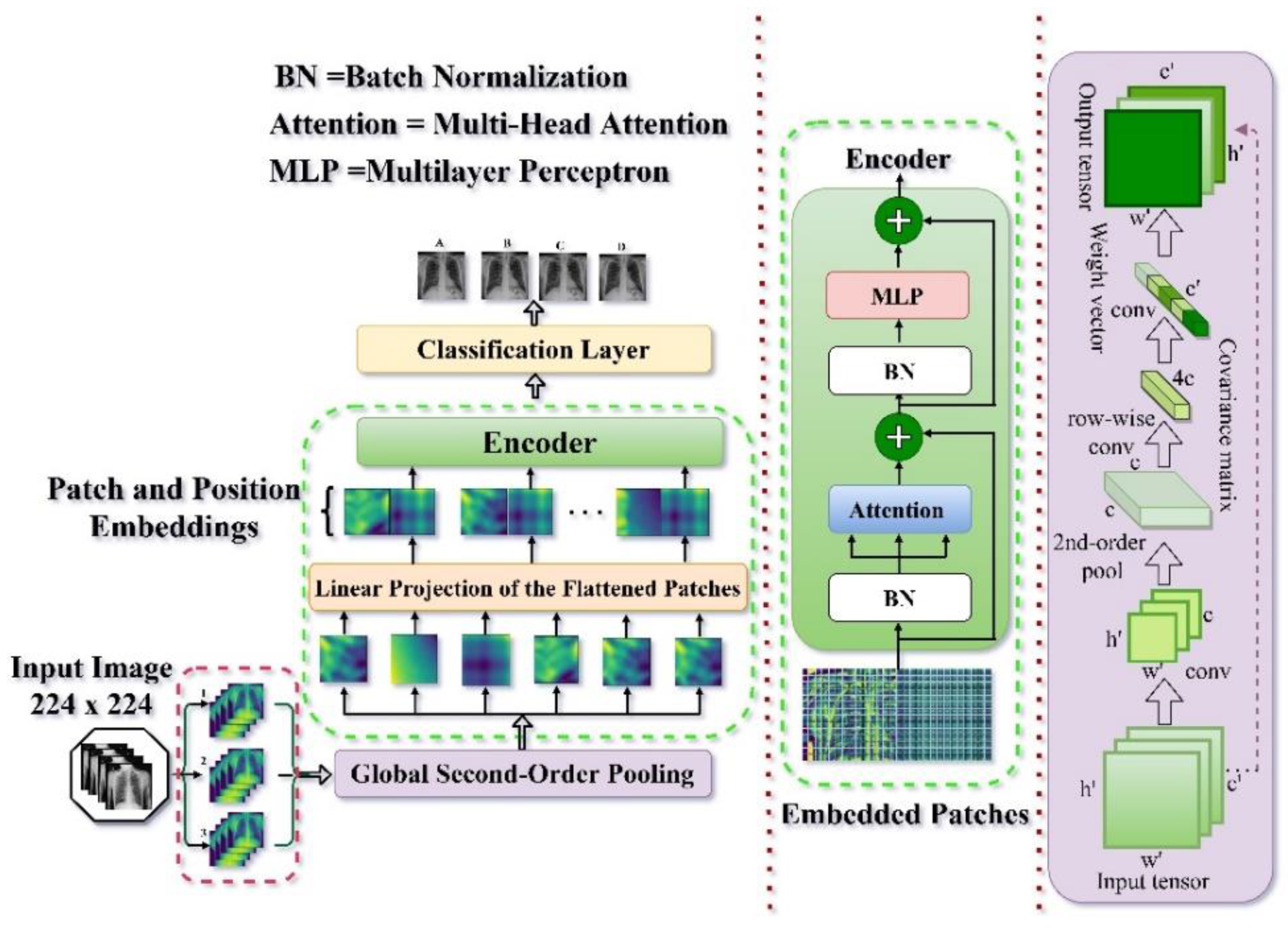
2.2. Model Architecture
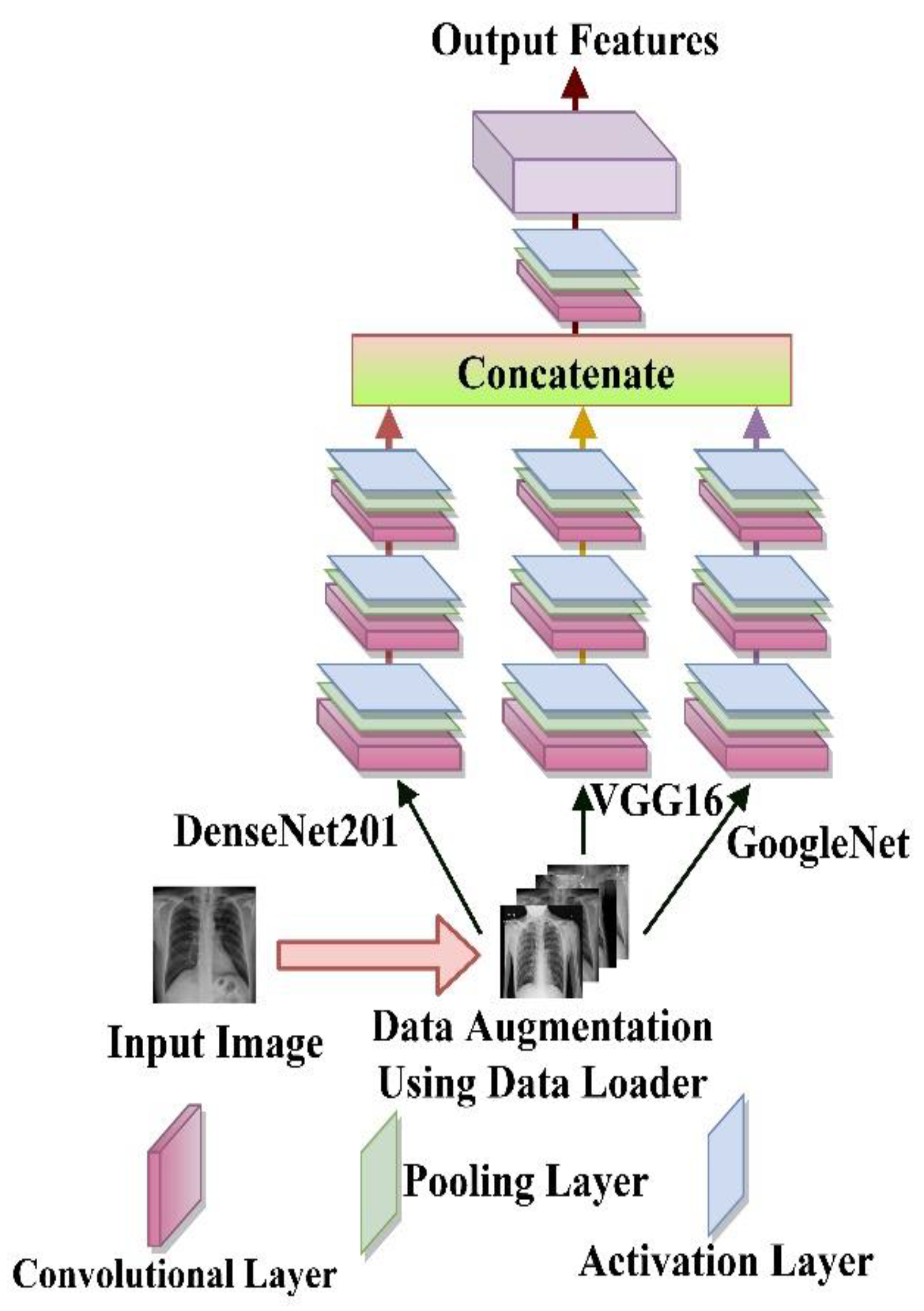
2.3. Feature Extraction
2.4. Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Classification Results
3.2.1. Backbone Model Selection
3.2.2. Classification Results Using Data_A
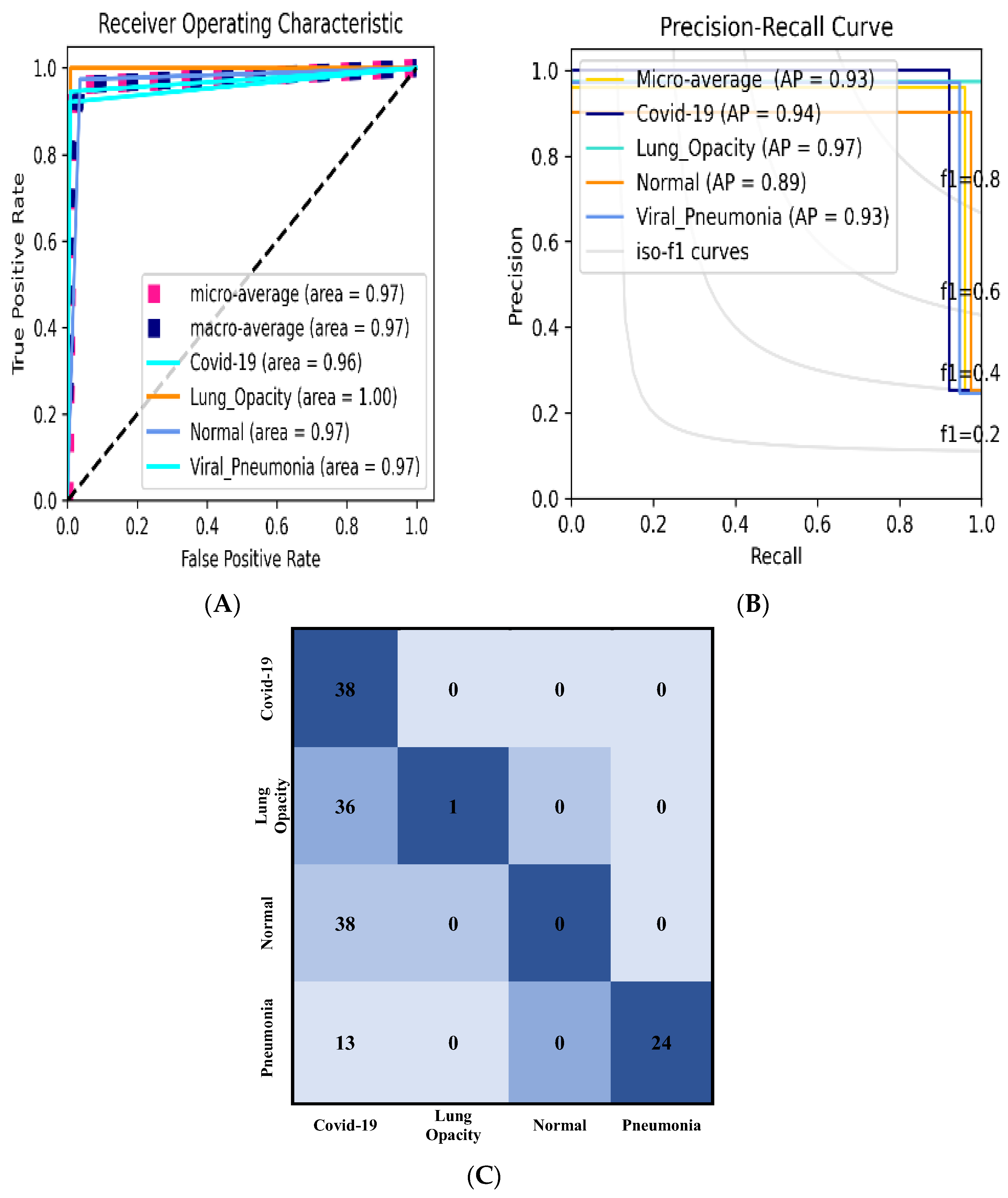
3.2.3. Classification Results Using Data_B
4. Discussion
4.1. Ablation Studies of the Proposed Model
4.2. Comparison with the State-of-the-Art Based on Deep Learning Models
4.3. Limitations and Future Works
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fong, S.J.; Dey, N.; Chaki, J. An Introduction to COVID-19. In SpringerBriefs in Applied Sciences and Technology; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Bakare, O.O.; Gokul, A.; Keyster, M. Analytical Studies of Antimicrobial Peptides as Diagnostic Biomarkers for the Detection of Bacterial and Viral Pneumonia. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padda, I.; Khehra, N.; Jaferi, U.; Parmar, M.S. The Neurological Complexities and Prognosis of COVID-19. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2020, 2, 2025–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Laurent, S.; Onur, O.A.; Kleineberg, N.N.; Fink, G.R.; Schweitzer, F.; Warnke, C. A systematic review of neurological symptoms and complications of COVID-19. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentivegna, E.; Luciani, M.; Spuntarelli, V.; Speranza, M.L.; Guerritore, L.; Sentimentale, A.; Martelletti, P. Extremely Severe Case of COVID-19 Pneumonia Recovered Despite Bad Prognostic Indicators: A Didactic Report. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2020, 2, 1204–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukwuoma, C.C.; Zhiguang, Q.; Heyat, M.B.B.; Ali, L.; Almaspoor, Z.; Monday, H.N. Recent Advancements in Fruit Detection and Classification Using Deep Learning Techniques. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 9210947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrrotraa, R.; Ansari, M.A.; Agrawal, R.; Tripathi, P.; Heyat, M.B.B.; Al-Sarem, M.; Muaad, A.Y.M.; Nagmeldin, W.A.E.; Abdelmaboud, A.; Saeed, F. Ensembling of Efficient Deep Convolutional Networks and Machine Learning Algorithms for Resource Effective Detection of Tuberculosis Using Thoracic (Chest) Radiography. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 85442–85458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawabi, A.K.; Jinfang, S.; Abbasi, R.; Iqbal, M.S.; Heyat, M.B.B.; Akhtar, F.; Wu, K.; Twumasi, B.A. Segmentation of Drug-Treated Cell Image and Mitochondrial-Oxidative Stress Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 5641727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukwuoma, C.C.; Heyat, M.B.B.; Masadeh, M.; Akhtar, F.; Zhiguang, Q.; Bondzie-Selby, E.; Alshorman, O.; Alkahtani, F. Image Inpainting and Classification Agent Training Based on Reinforcement Learning and Generative Models with Attention Mechanism. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Microelectronics, ICM, New Cairo City, Egypt, 25–26 September 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Ukwuoma, C.C.; Qin, Z.; Heyat, M.B.B.; Akhtar, F.; Bamisile, O.; Muaad, A.Y.; Addo, D.; Al-antari, M.A. A hybrid explainable ensemble transformer encoder for pneumonia identification from chest X-ray images. J. Adv. Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, A.; Jain, R.; Vashista, H.; Mittal, N.; Ranjan, P.; Janardhanan, R. Pneumonia identification in chest X-ray images using EMD. Trends Commun. Cloud Big Data 2020, 99, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Angeline, R.; Mrithika, M.; Raman, A.; Warrier, P. Pneumonia Detection and Classification Using Chest X-Ray Images with Convolutional Neural Network. In New Trends in Computational Vision and Bio-Inspired Computing—Selected Works Presented at the ICCVBIC 2018; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switherland, 2020; pp. 701–709. ISBN 9783030418618. [Google Scholar]
- Rousan, L.A.; Elobeid, E.; Karrar, M.; Khader, Y. Chest X-ray findings and temporal lung changes in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asuntha, A.; Srinivasan, A. Deep learning for lung Cancer detection and classification. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 7731–7762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, C.; Ponsiglione, A.M.; Scala, A.; Borrelli, A.; Misasi, M.; Romano, G.; Russo, G.; Triassi, M.; Improta, G. Machine Learning and Regression Analysis to Model the Length of Hospital Stay in Patients with Femur Fracture. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, A.; Begum, W.; Saeedi, R.; Rahman, K.; Bin Heyat, M.B.; Akhtar, F.; Son, N.T.; Ullah, H. Experimental and Computational Approaches for the Classification and Correlation of Temperament (Mizaj) and Uterine Dystemperament (Su’-I-Mizaj Al-Rahim) in Abnormal Vaginal Discharge (Sayalan Al-Rahim) Based on Clinical Analysis Using Support Vector Machine. Complexity 2022, 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teelhawod, B.N.; Akhtar, F.; Heyat, M.B.B.; Tripathi, P.; Mehrotra, R.; Asfaw, A.B.; Shorman, O.A.; Masadeh, M. Machine Learning in E-health: A Comprehensive Survey of Anxiety. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Data Analytics for Business and Industry, ICDABI, Online, 25–26 October 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, F.; Heyat, M.B.B.; Li, J.P.; Patel, P.K.; Guragai, B. Role of Machine Learning in Human Stress: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2020 17th International Computer Conference on Wavelet Active Media Technology and Information Processing, ICCWAMTIP, Chengdu, China, 18–20 December 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 170–174. [Google Scholar]
- Guragai, B.; Alshorman, O.; Masadeh, M.; Heyat, M.B. Bin A Survey on Deep Learning Classification Algorithms for Motor Imagery. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Microelectronics, ICM, Aqaba, Jordan, 14–17 December 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; Volume 2020, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Heyat, M.B.B.; Lai, D.; Khan, F.I.; Zhang, Y. Sleep Bruxism Detection Using Decision Tree Method by the Combination of C4-P4 and C4-A1 Channels of Scalp EEG. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 102542–102553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Heyat, M.B.; Akhtar, F.; Abbas, S.J.; Al-Sarem, M.; Alqarafi, A.; Stalin, A.; Abbasi, R.; Muaad, A.Y.; Lai, D.; Wu, K. Wearable Flexible Electronics Based Cardiac Electrode for Researcher Mental Stress Detection System Using Machine Learning Models on Single Lead Electrocardiogram Signal. Biosensors 2022, 12, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, A.; Rahman, K.; Heyat, M.B.B.; Sumbul; Akhtar, F.; Muaad, A.Y. Role of Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Mitochondrial Changes in Premenstrual Psychosomatic Behavioral Symptoms with Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant Herbs, and Nutritional Supplements. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 3599246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyat, M.B.B.; Akhtar, F.; Khan, M.H.; Ullah, N.; Gul, I.; Khan, H.; Lai, D. Detection, Treatment Planning, and Genetic Predisposition of Bruxism: A Systematic Mapping Process and Network Visualization Technique. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 20, 755–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyat, M.B.B.; Akhtar, F.; Khan, A.; Noor, A.; Benjdira, B.; Qamar, Y.; Abbas, S.J.; Lai, D. A novel hybrid machine learning classification for the detection of bruxism patients using physiological signals. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyat, M.B.B.; Akhtar, F.; Ansari, M.A.; Khan, A.; Alkahtani, F.; Khan, H.; Lai, D. Progress in Detection of Insomnia Sleep Disorder: A Comprehensive Review. Curr. Drug Targets 2020, 22, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 2017, pp. 5999–6009. [Google Scholar]
- Ott, M.; Edunov, S.; Grangier, D.; Auli, M. Scaling Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the WMT 2018—3rd Conference on Machine Translation, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–1 November 2018; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2018; Volume 1, pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Fedus, W.; Zoph, B.; Shazeer, N. Switch Transformers: Scaling to Trillion Parameter Models with Simple and Efficient Sparsity. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhari, S.; Mithal, V.; Polatkan, G.; Ramanath, R. An Attentive Survey of Attention Models. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albahli, S.; Rauf, H.T.; Arif, M.; Nafis, M.T.; Algosaibi, A. Identification of thoracic diseases by exploiting deep neural networks. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2020, 66, 3139–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshennawy, N.M.; Ibrahim, D.M. Deep-Pneumonia Framework Using Deep Learning Models Based on Chest X-ray Images. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Peng, Y.; Lu, L.; Lu, Z.; Bagheri, M.; Summers, R.M. ChestX-ray8: Hospital-scale chest X-ray database and benchmarks on weakly-supervised classification and localization of common thorax diseases. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3462–3471. [Google Scholar]
- Talo, M. Pneumonia detection from radiography images using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 27th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference, SIU, Sivas, Turkey, 9–11 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Varshni, D.; Thakral, K.; Agarwal, L.; Nijhawan, R.; Mittal, A. Pneumonia Detection Using CNN based Feature Extraction. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd IEEE International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Technologies, ICECCT, Coimbatore, India, 20–22 February 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Stephen, O.; Sain, M.; Maduh, U.J.; Jeong, D.U. An Efficient Deep Learning Approach to Pneumonia Classification in Healthcare. J. Healthc. Eng. 2019, 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoudi, K.; Benhabiles, H.; Melkemi, M.; Dornaika, F.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Collard, D.; Scherpereel, A. Deep Learning on Chest X-ray Images to Detect and Evaluate Pneumonia Cases at the Era of COVID-19. J. Med. Syst. 2021, 45, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirazitdinov, I.; Kholiavchenko, M.; Mustafaev, T.; Yixuan, Y.; Kuleev, R.; Ibragimov, B. Deep neural network ensemble for pneumonia localization from a large-scale chest x-ray database. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2019, 78, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Zheng, L. A transfer learning method with deep residual network for pediatric pneumonia diagnosis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 187, 104964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, V.; Singh, S.K.; Khamparia, A.; Gupta, D.; Tiwari, P.; Moreira, C.; Damaševičius, R.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C. A novel transfer learning based approach for pneumonia detection in chest X-ray images. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, R. Automated pneumonia diagnosis using a customized sequential convolutional neural network. In ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Deep Learning Technologies, Xiamen, China, 5–7 July 2019; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, R.; Nagrath, P.; Kataria, G.; Kaushik, V.S.; Hemanth, D.J. Pneumonia detection in chest X-ray images using convolutional neural networks and transfer learning. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2020, 165, 108046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.R.; Nayak, D.R.; Sinha, U.; Arora, V.; Pachori, R.B. Application of deep learning techniques for detection of COVID-19 cases using chest X-ray images: A comprehensive study. Biomed. Signal. Process. Control. 2021, 64, 102365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, T.; Talo, M.; Yildirim, E.A.; Baloglu, U.B.; Yildirim, O.; Acharya, U.R. Automated detection of COVID-19 cases using deep neural networks with X-ray images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 121, 103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.K.; Kalam, S.; Kumar, C.; Sinha, D. TLCoV—An automated COVID-19 screening model using Transfer Learning from chest X-ray images. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 144, 110713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monshi, M.M.A.; Poon, J.; Chung, V.; Monshi, F.M. CovidXrayNet: Optimizing data augmentation and CNN hyperparameters for improved COVID-19 detection from CXR. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 133, 104375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajpal, S.; Lakhyani, N.; Singh, A.K.; Kohli, R.; Kumar, N. Using handpicked features in conjunction with ResNet-50 for improved detection of COVID-19 from chest X-ray images. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 145, 110749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Tripathi, A.R.; Satapathy, S.C.; Zhang, Y.D. SARS-Net: COVID-19 detection from chest x-rays by combining graph convolutional network and convolutional neural network. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 122, 108255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narin, A.; Kaya, C.; Pamuk, Z. Automatic detection of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) using X-ray images and deep convolutional neural networks. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2021, 24, 1207–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, Z.Q.; Wong, A. COVID-Net: A tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of COVID-19 cases from chest X-ray images. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, A.; Yu, Z.; Nutini, A. COVID-19 Variants and Transfer Learning for the Emerging Stringency Indices. Neural Process. Lett. 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, R.; Song, S.; Huang, Z.; Huang, G. Not All Images are Worth 16x16 Words: Dynamic Transformers for Efficient Image Recognition. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 15, 11960–11973. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Xie, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, P. Global Second-Order Pooling Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3019–3028. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Rahman, T.; Khandakar, A.; Mazhar, R.; Kadir, M.A.; Mahbub, Z.B.; Islam, K.R.; Khan, M.S.; Iqbal, A.; Emadi, N.A.; et al. Can AI Help in Screening Viral and COVID-19 Pneumonia? IEEE Access 2020, 8, 132665–132676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A.; Elgazzar, K. Detecting Coronavirus from Chest X-rays Using Transfer Learning. COVID 2021, 1, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; Volume 1, pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; Volume 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, H.; Heyat, M.B.B.; Akhtar, F.; Sumbul; Muaad, A.Y.; Islam, M.S.; Abbas, Z.; Pan, T.; Gao, M.; Lin, Y.; et al. An End-to-End Cardiac Arrhythmia Recognition Method with an Effective DenseNet Model on Imbalanced Datasets Using ECG Signal. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurohive. VGG16—Convolutional Network for Classification and Detection. 2018. Available online: https://neurohive.io/en/popular-networks/vgg16/ (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going Deeper with Convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, L.; He, Z.; Cao, W.; Rauf, H.T.; Imrana, Y.; Bin Heyat, M.B. MMDD-Ensemble: A Multimodal Data–Driven Ensemble Approach for Parkinson’s Disease Detection. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, P.; Ansari, M.A.; Gandhi, T.K.; Mehrotra, R.; Heyat, M.B.B.; Akhtar, F.; Ukwuoma, C.C.; Muaad, A.Y.; Kadah, Y.M.; Al-Antari, M.A.; et al. Ensemble Computational Intelligent for Insomnia Sleep Stage Detection via the Sleep ECG Signal. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 108710–108721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Bin Heyat, M.B.; Alsalman, H.; Khan, H.M.; Akhtar, F.; Gumaei, A.; Mehdi, A.; Muaad, A.Y.; Islam, M.S.; Ali, A.; et al. An Effective and Lightweight Deep Electrocardiography Arrhythmia Recognition Model Using Novel Special and Native Structural Regularization Techniques on Cardiac Signal. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 3408501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.S.; Abbasi, R.; Heyat, M.B.B.; Akhtar, F.; Abdelgeliel, A.S.; Albogami, S.; Fayad, E.; Iqbal, M.A. Recognition of mRNA N4 Acetylcytidine (ac4C) by Using Non-Deep vs. Deep Learning. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlShorman, O.; Masadeh, M.; Heyat, M.B.B.; Akhtar, F.; Almahasneh, H.; Ashraf, G.M.; Alexiou, A. Frontal lobe real-time EEG analysis using machine learning techniques for mental stress detection. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2022, 21, 020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, P.; Ansari, M.A.; Akhtar, F.; Bin Heyat, M.B.; Mehrotra, R.; Yatoo, A.H.; Teelhawod, B.N.; Asfaw, A.B.; Baig, A.A. Automatic Epileptic Seizure Detection Based on the Discrete Wavelet Transform Approach Using an Artificial Neural Network Classifier on the Scalp Electroencephalogram Signal. Comput. Intell. Healthc. Appl. 2022, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukwuoma, C.C.; Urama, G.C.; Qin, Z.; Bin Heyat, M.B.; Mohammed Khan, H.; Akhtar, F.; Masadeh, M.S.; Ibegbulam, C.S.; Delali, F.L.; AlShorman, O. Boosting Breast Cancer Classification from Microscopic Images Using Attention Mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Decision Aid Sciences and Applications (DASA), Chiangrai, Thailand, 23 March 2022; pp. 258–264. [Google Scholar]
- Ukwuoma, C.C.; Zhiguang, Q.; Bin Heyat, M.B.; Mohammed Khan, H.; Akhtar, F.; Masadeh, M.S.; Bamisile, O.; AlShorman, O.; Nneji, G.U. Detection of Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma from Normal Epithelium of the Oral Cavity Using Microscopic Images. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Decision Aid Sciences and Applications (DASA), Chiangrai, Thailand, 23 March 2022; pp. 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Chola, C.; Muaad, A.Y.; Bin Heyat, M.B.; Benifa, J.V.B.; Naji, W.R.; Hemachandran, K.; Mahmoud, N.F.; Samee, N.A.; Al-Antari, M.A.; Kadah, Y.M.; et al. BCNet: A Deep Learning Computer-Aided Diagnosis Framework for Human Peripheral Blood Cell Identification. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.I.; Shah, J.L.; Bhat, M.M. CoroNet: A deep neural network for detection and diagnosis of COVID-19 from chest x-ray images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 196, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Jin, Q.; Sun, L. Multiscale Attention Guided Network for COVID-19 Diagnosis Using Chest X-Ray Images. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 25, 1336–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, A.K. COVID-19 prognosis using limited chest X-ray images. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 122, 108867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Tong, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, M.D. COVID-19 Automatic Diagnosis with Radiographic Imaging: Explainable Attention Transfer Deep Neural Networks. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 25, 2376–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, E.; Rehman, M.Z.U.; Ahmed, F.; Alfouzan, F.A.; Alzahrani, N.M.; Ahmad, J. Chest X-ray Classification for the Detection of COVID-19 Using Deep Learning Techniques. Sensors 2022, 22, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naralasetti, V.; Shaik, R.K.; Katepalli, G.; Bodapati, J.D. Deep learning models for Pneumonia identification and classification based on X-ray images. Trait. du Signal. 2021, 38, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darici, M.B.; Dokur, Z.; Olmez, T. Pneumonia detection and classification using deep learning on chest x-ray images. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. Eng. 2020, 8, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widodo, C.S.; Naba, A.; Mahasin, M.M.; Yueniwati, Y.; Putranto, T.A.; Patra, P.I. UBNet: Deep learning-based approach for automatic X-ray image detection of pneumonia and COVID-19 patients. J. Xray. Sci. Technol. 2022, 30, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermany, D.S.; Goldbaum, M.; Cai, W.; Valentim, C.C.S.; Liang, H.; Baxter, S.L.; McKeown, A.; Yang, G.; Wu, X.; Yan, F.; et al. Identifying Medical Diagnoses and Treatable Diseases by Image-Based Deep Learning. Cell 2018, 172, 1122–1131.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.U.; Ozsoz, M.; Serte, S.; Al-Turjman, F.; Yakoi, P.S. Pneumonia Classification Using Deep Learning from Chest X-ray Images During COVID-19. Cognit. Comput. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, H.; Gupta, P.K.; Siddiqui, M.K.; Morales-Menendez, R.; Singh, V. Application of deep learning for fast detection of COVID-19 in X-Rays using nCOVnet. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 138, 109944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Ref. | Architecture | Type | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| [34] | Residual Blocks and Dilated Convolution | Pneumonia detection | Recall = 96.7% F1_score = 92.7% |
| [32] | Transfer Learning Via VGG-16 And Xception Models | Accuracy = 87%(VGG) and 82% (Xception) | |
| [33] | Transfer Learning Via Resnet152 Model | Accuracy = 97.4% | |
| [35] | Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) | Accuracy = 93.73%. | |
| [37] | RetinaNet And Mask R-CNN | Accuracy = 79.3% | |
| [38] | Transfer Learning | Recall Rate = 96.7% F1_score = 92.7%. | |
| VGG16 | Accuracy = 90.5%, Precision = 89.1%, Recall = 96.7%, and F1_score = 92.7% | ||
| [39] | Transfer Learning | Accuracy = 96.4% | |
| [40] | 18-Layer CNN | Accuracy = 93.75% | |
| [41] | CNN-Based Transfer Learning | Accuracy = 95.62%, Recall = 95%, and Precision = 96% | |
| [42] | Resnet34 | COVID-19 | Accuracy = 98.33% |
| [43] | CNN-Based Transfer Learning | Accuracy = 96% | |
| [44] | VGG-16 | Accuracy = 97.67% | |
| [45] | COVIDXrayNet | Accuracy = 95.82% | |
| [46] | Resnet-50 With TL+ PCA + Ensemble | Accuracy = 98% | |
| [47] | SARS-Net | Accuracy = 97.60% | |
| [48] | ResNet50 | Accuracy = 98% | |
| [49] | COVID-Net | Accuracy = 92% |
| Partition | Normal | Pneumonia | COVID-19 | Lung Opacity | Total | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data_A | Training | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 | 12,000 | 14,400 |
| Validation | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 1200 | ||
| Testing | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 1200 | ||
| Data_B | Training | 3500 | 3500 | 3500 | 10,500 | ||
| Validation | 500 | 500 | 500 | 1500 | 1500 | ||
| Testing | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 3000 |
| Loss Function | Categorical Smooth Loss, Categorical Cross-Entropy |
|---|---|
| Optimizers | Adam |
| Learning rate | 0.0001/0.001 |
| Batch size | 8 |
| Reduce Learning Rate | 0.2 |
| Epsilon | 0.001 |
| Patience | 10 |
| Verbose | 1 |
| Es-Callback (Patience) | 10 |
| Clip Value | 0.2 |
| Epoch | 100 |
| Patch Size | (2, 2) |
| Drop Rate | 0.01 |
| Number of Heads | 8 |
| Embed_dim | 64 |
| Num_MLP | 256 |
| Window Size | Window Size//2 |
| Input Size | (224 × 224) |
| Models | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Precision (%) | F1 Score | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Rate: 10−4 | ||||||
| DenseNet201 | 0.9600 | 0.91981 | 0.97325 | 0.92453 | 0.92088 | 0.94651 |
| EfficientNetB7 | 0.87333 | 0.74787 | 0.91542 | 0.83094 | 0.73639 | 0.83164 |
| GoogleNet | 0.9300 | 0.86024 | 0.95322 | 0.86795 | 0.86188 | 0.90673 |
| InceptResNetV2 | 0.94667 | 0.89385 | 0.96434 | 0.90298 | 0.89398 | 0.9291 |
| VGG16 | 0.9100 | 0.81988 | 0.93985 | 0.87301 | 0.82008 | 0.87986 |
| Xception | 0.9000 | 0.80032 | 0.93315 | 0.83420 | 0.80144 | 0.86674 |
| Learning Rate: 10−3 | ||||||
| DenseNet201 | 0.92333 | 0.84691 | 0.94880 | 0.86073 | 0.84883 | 0.8976 |
| EfficientNetB7 | 0.85667 | 0.71337 | 0.90408 | 0.77687 | 0.72241 | 0.80872 |
| GoogleNet | 0.89000 | 0.78094 | 0.92666 | 0.80353 | 0.78311 | 0.8538 |
| InceptResNetV2 | 0.92667 | 0.85331 | 0.95097 | 0.86683 | 0.85618 | 0.90214 |
| VGG16 | 0.89667 | 0.79374 | 0.93100 | 0.81953 | 0.79527 | 0.86237 |
| Xception | 0.88667 | 0.77400 | 0.92428 | 0.80688 | 0.77546 | 0.84914 |
| ROC (Area) | Macro-Average | Micro-Average | COVID-19 | Lung Opacity | Normal | Pneumonia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Rate: 10−4 | ||||||
| DenseNet201 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95583 | 0.95061 | 0.93374 | 0.94595 |
| EfficientNetB7 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.69737 | 0.93339 | 0.84445 | 0.85135 |
| GoogleNet | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.90296 | 0.93734 | 0.86772 | 0.91892 |
| InceptResNetV2 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.86819 | 0.97321 | 0.92904 | 0.94595 |
| VGG16 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.85526 | 0.97345 | 0.87993 | 0.81081 |
| Xception | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.78477 | 0.90588 | 0.8844 | 0.89189 |
| Learning Rate: 10−3 | ||||||
| DenseNet201 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.86372 | 0.91497 | 0.8938 | 0.91892 |
| EfficientNetB7 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.73167 | 0.87862 | 0.80028 | 0.82432 |
| GoogleNet | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.80663 | 0.87515 | 0.82801 | 0.90541 |
| InceptResNetV2 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.89427 | 0.92825 | 0.88064 | 0.90541 |
| VGG16 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.81978 | 0.91521 | 0.84962 | 0.86486 |
| Xception | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.78031 | 0.91964 | 0.83177 | 0.86486 |
| Precision-Recall (AP) | Micro-Average | COVID-19 | Lung Opacity | Normal | Pneumonia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Rate: 10−4 | |||||
| DenseNet201 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.81 | 0.92 |
| EfficientNetB7 | 0.62 | 0.55 | 0.74 | 0.55 | 0.78 |
| GoogleNet | 0.77 | 0.75 | 0.82 | 0.68 | 0.88 |
| InceptResNetV2 | 0.82 | 0.75 | 0.90 | 0.75 | 0.92 |
| VGG16 | 0.72 | 0.78 | 0.86 | 0.61 | 0.71 |
| Xception | 0.69 | 0.62 | 0.76 | 0.62 | 0.84 |
| Learning Rate: 10−3 | |||||
| DenseNet201 | 0.76 | 0.73 | 0.76 | 0.69 | 0.88 |
| EfficientNetB7 | 0.58 | 0.49 | 0.76 | 0.49 | 0.74 |
| GoogleNet | 0.66 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.60 | 0.86 |
| InceptResNetV2 | 0.76 | 0.75 | 0.82 | 0.67 | 0.86 |
| VGG16 | 0.68 | 0.65 | 0.73 | 0.60 | 0.80 |
| Xception | 0.65 | 0.60 | 0.75 | 0.56 | 0.80 |
| Model | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Precision (%) | F1 Score | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Rate: 10−4, Loss Function: categorical_smooth_loss | ||||||
| Backbone | 0.95333 | 0.90701 | 0.96891 | 0.91419 | 0.90736 | 0.93796 |
| Proposed Method | 0.96000 | 0.91945 | 0.97325 | 0.92783 | 0.91934 | 0.94635 |
| Learning Rate: 10−3, Loss Function: categorical_smooth_loss | ||||||
| Backbone | 0.94000 | 0.87909 | 0.95986 | 0.89431 | 0.88056 | 0.91948 |
| Proposed Method | 0.96667 | 0.93314 | 0.97772 | 0.93895 | 0.93391 | 0.95543 |
| Learning Rate: 10−4, Loss Function: categorical cross-entropy | ||||||
| Backbone | 0.96333 | 0.92656 | 0.97551 | 0.93172 | 0.92677 | 0.95104 |
| Proposed Method | 0.98000 | 0.96017 | 0.98665 | 0.96209 | 0.9603 | 0.97341 |
| Learning Rate: 10−3, Loss Function: categorical cross-entropy | ||||||
| Backbone | 0.83667 | 0.67372 | 0.89098 | 0.78304 | 0.65383 | 0.78235 |
| Proposed Method | 0.98000 | 0.94965 | 0.98992 | 0.95508 | 0.95216 | 0.96976 |
| ROC (Area) | Macro-Average | Micro-Average | COVID-19 | Lung Opacity | Normal | Pneumonia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimizer: Adaptive Moment Estimation, Learning Rate: 10−4, Loss Function: categorical_smooth_loss | ||||||
| Backbone | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94737 | 0.96903 | 0.90742 | 0.92801 |
| Proposed Method | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.99107 | 0.97764 | 0.92481 | 0.89189 |
| Learning Rate: 10−3, Loss Function: categorical_smooth_loss | ||||||
| Backbone | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.94690 | 0.89656 | 0.92904 | 0.90541 |
| Proposed Method | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.95606 | 0.98206 | 0.95559 | 0.92801 |
| Learning Rate: 10−4, Loss Function: categorical cross-entropy | ||||||
| Backbone | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95606 | 0.99115 | 0.94243 | 0.91449 |
| Proposed Method | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.96053 | 0.99558 | 0.96898 | 0.96855 |
| Learning Rate: 10−3, Loss Function: categorical cross-entropy | ||||||
| Backbone | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.67975 | 0.89333 | 0.8266 | 0.72973 |
| Proposed Method | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.90158 | 0.97534 | 0.94884 | 0.94354 |
| Precision-Recall (AP) | Micro-Average | COVID-19 | Lung Opacity | Normal | Pneumonia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Rate: 10−4, Loss Function: categorical_smooth_loss | |||||
| Backbone | 0.85 | 0.92 | 0.84 | 0.77 | 0.87 |
| Proposed Method | 0.87 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.77 | 0.84 |
| Learning Rate: 10−3, Loss Function: categorical_smooth_loss | |||||
| Backbone | 0.80 | 0.83 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.86 |
| Proposed Method | 0.89 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.83 | 0.87 |
| Learning Rate: 10−4, Loss Function: categorical cross-entropy | |||||
| Backbone | 0.88 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.81 | 0.85 |
| Proposed Method | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.89 | 0. 93 |
| Learning Rate: 10−3, Loss Function: categorical cross-entropy | |||||
| Backbone | 0.54 | 0.50 | 0.64 | 0.52 | 0.59 |
| Proposed Method | 0.90 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.80 | 0.87 |
| Models | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Precision (%) | F1_score | AUC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Rate: 10−4, Loss Function: categorical_smooth_loss | ||||||||||||
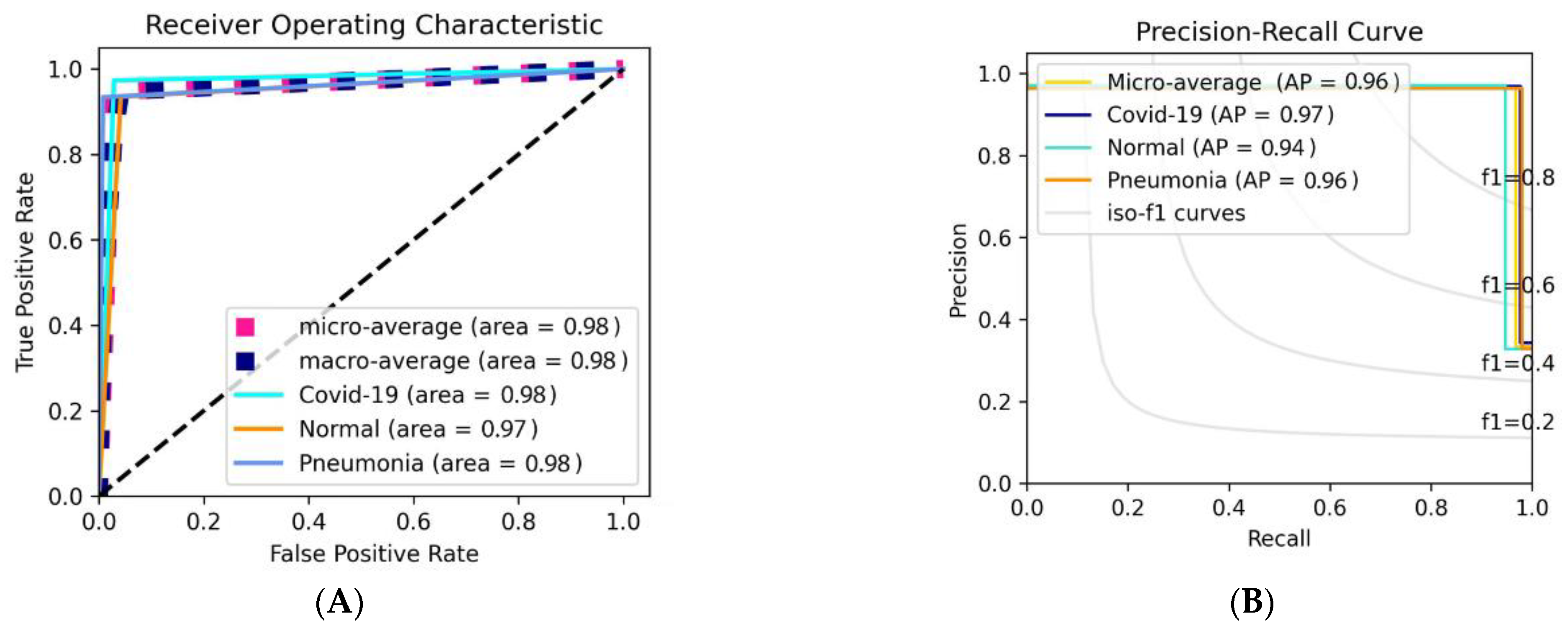
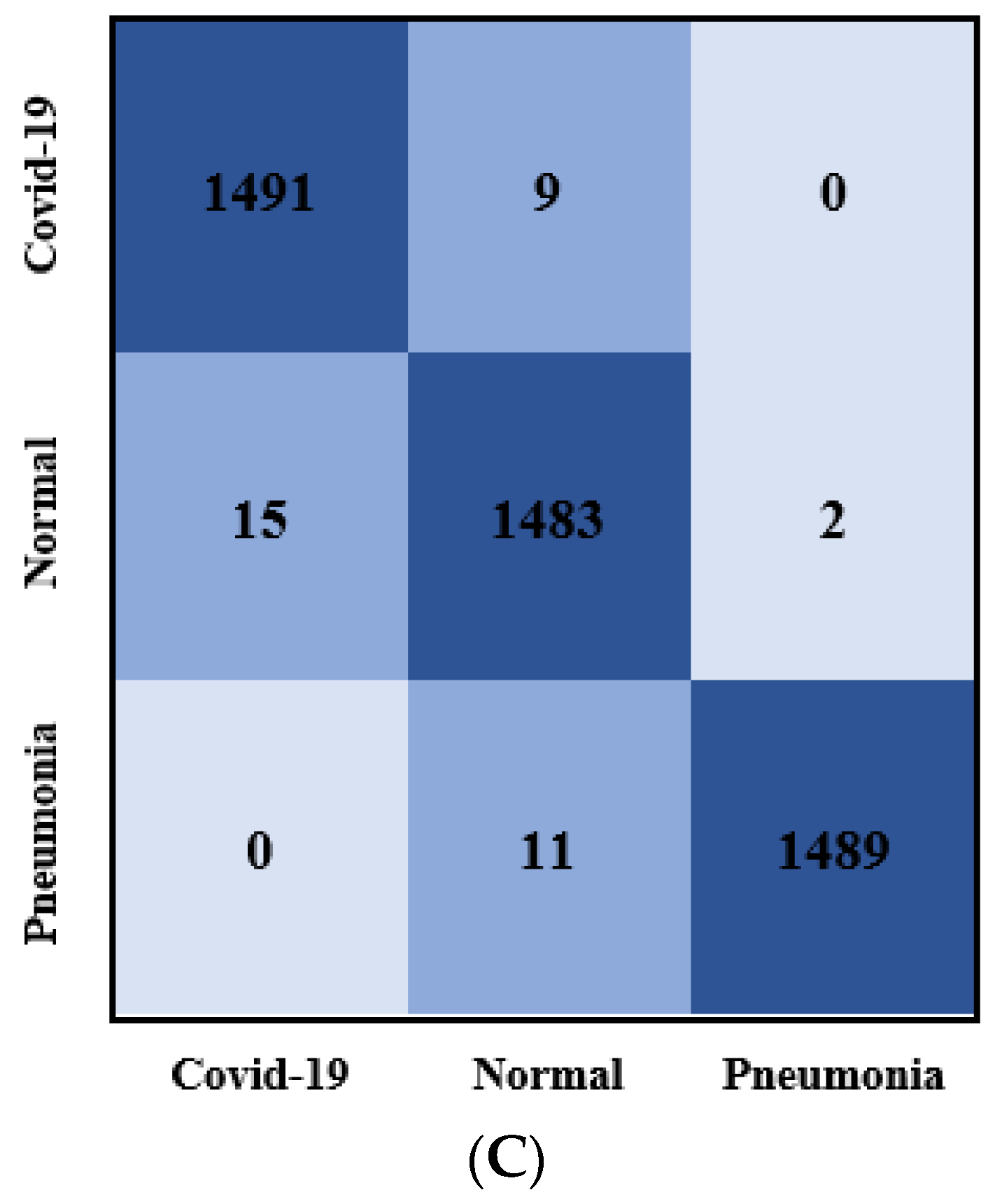
| Proposed Model | 0.9819 | 0.9729 | 0.9864 | 0.9729 | 0.9729 | 0.9810 | ||||||
| Backbone | 0.9720 | 0.9580 | 0.9790 | 0.9583 | 0.9580 | 0.9686 | ||||||
| ROC | Macro-Average Area | Micro-Average Area | Class 0 Area | Class 1 Area | Class 2 Area | |||||||
| Proposed Model | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.9842 | 0.9700 | 0.9848 | |||||||
| Backbone | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.9771 | 0.9541 | 0.9741 | |||||||
| Average Precision | Micro-Average Precision-Recall | Class 0 AP | Class 1 AP | Class 2 AP | ||||||||
| Proposed Model | 0.96 | 0.9796 | 0.9606 | 0.9785 | ||||||||
| Backbone | 0.93 | 0.9461 | 0.9077 | 0.9574 | ||||||||
| Reference | Year | Model | Accuracy | Precision | Sensitivity | F1_score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Khan et al. (Strategy 1) [73] | 2022 | EfficientNetB1 | 92 | 91.75 | 94.50 | 92.75 |
| NasNetMobile | 89.30 | 89.25 | 91.75 | 91 | ||
| MobileNetV2 | 90.03 | 92.25 | 92 | 91.75 | ||
| Khan et al. (Strategy 2) [73] | 2022 | EfficientNetB1 | 96.13 | 97.25 | 96.50 | 97.50 |
| NasNetMobile | 94.81 | 95.50 | 95 | 95.25 | ||
| MobileNetV2 | 93.96 | 94.50 | 95 | 94.50 | ||
| Mondal et al. [71] | 2022 | Local Global Attention Network | 95.87 | 95.56 | 95.99 | 95.74 |
| Shi et al. [72] | 2021 | Teacher Student Attention | 91.38 | 91.65 | 90.86 | 91.24 |
| Li et al. [70] | 2021 | Mag-SD | 92.35 | 92.50 | 92.20 | 92.34 |
| Khan et al. [69] | 2020 | CoroNet | 89.6 | 90.0 | 96.4 | 89.8 |
| Shi et al. [72] | 2020 | COVIDNet | 90.78 | 91.1 | 90.56 | 90.81 |
| Ours | 2022 | 98.00 | 96.21 | 96.02 | 96.03 |
| Reference | Year | Architecture | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1_score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naralasetti et al. [74] | 2021 | Deep CNN | 91% | - | - | - |
| Dokur et al. [75] | 2020 | CNN Ensemble | 78% 75% | 80% 77% | 78% 75% | 78% 75% |
| Hammoudi et al. [36] | 2020 | VGG19 ResNet+RNN1 ResNet+RNN2 DenseNet169 | 83% 78% 80% 96% | - - - - | - - - - | - - - - |
| Windodo et al. [76] | 2021 | UBNetV1 UBNetV2 | 88% 88% | 89% 89% | 86% 85% | 86% 86% |
| Kermany et al. [77] | 2021 | AutoML | 86% | 82% | 84% | 84% |
| Ibrahim et al. [78] | 2020 | AlexNet | 97.40% | - | - | - |
| Ours | 2022 | 98.19% | 97.29% | 97.29% | 97.29% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ukwuoma, C.C.; Qin, Z.; Heyat, M.B.B.; Akhtar, F.; Smahi, A.; Jackson, J.K.; Furqan Qadri, S.; Muaad, A.Y.; Monday, H.N.; Nneji, G.U. Automated Lung-Related Pneumonia and COVID-19 Detection Based on Novel Feature Extraction Framework and Vision Transformer Approaches Using Chest X-ray Images. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110709
Ukwuoma CC, Qin Z, Heyat MBB, Akhtar F, Smahi A, Jackson JK, Furqan Qadri S, Muaad AY, Monday HN, Nneji GU. Automated Lung-Related Pneumonia and COVID-19 Detection Based on Novel Feature Extraction Framework and Vision Transformer Approaches Using Chest X-ray Images. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(11):709. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110709
Chicago/Turabian StyleUkwuoma, Chiagoziem C., Zhiguang Qin, Md Belal Bin Heyat, Faijan Akhtar, Abla Smahi, Jehoiada K. Jackson, Syed Furqan Qadri, Abdullah Y. Muaad, Happy N. Monday, and Grace U. Nneji. 2022. "Automated Lung-Related Pneumonia and COVID-19 Detection Based on Novel Feature Extraction Framework and Vision Transformer Approaches Using Chest X-ray Images" Bioengineering 9, no. 11: 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110709
APA StyleUkwuoma, C. C., Qin, Z., Heyat, M. B. B., Akhtar, F., Smahi, A., Jackson, J. K., Furqan Qadri, S., Muaad, A. Y., Monday, H. N., & Nneji, G. U. (2022). Automated Lung-Related Pneumonia and COVID-19 Detection Based on Novel Feature Extraction Framework and Vision Transformer Approaches Using Chest X-ray Images. Bioengineering, 9(11), 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110709















