Dose Reduction and Image Quality Optimization of Pediatric Chest Radiography Using a Tungsten Filter
Abstract
1. Introduction
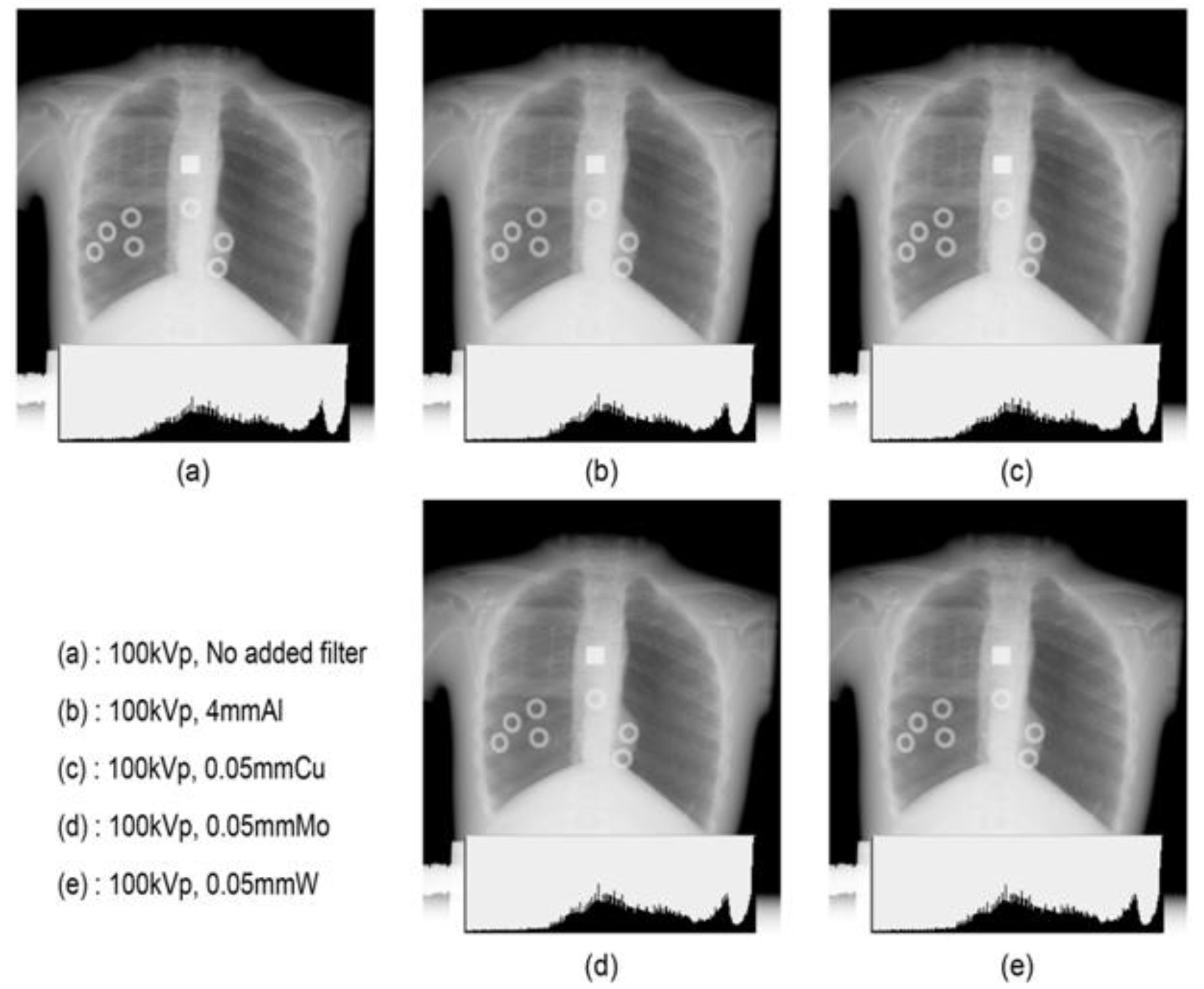
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Communicating Radiation Risks in Paediatric Imaging: Information to Support Healthcare Discussions about Benefit and Risk; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tapiovaara, M.J.; Sandborg, M.; Dance, D.R. A search for improved technique factors in paediatric fluoroscopy. Phys. Med. Biol. 1999, 44, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Boyd, B. Diagnostic Imaging of Pregnant Women and Fetuses: Literature Review. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, G.A.; Chan, H.P. Commentary: Progress in optimization of patient dose and image quality in X-ray diagnostics. Phys. Med. Biol. 1999, 44, 001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagran, J.E.; Hobbs, B.B.; Taylor, K.W. Reduction of patient exposure by use of heavy elements as radiation filters in diagnostic radiology. Radiology 1978, 127, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR). Annex A. Epidemiological Studies of Radiation and Cancer. In 2008a UNSCEAR 2006 Report; UNSCEAR: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Little, M.P. Cancer and non-cancer effects in Japanese atomic bomb survivors. J. Radiol. Prot. 2009, 29, A43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, M.P. Comparison of the risks of cancer incidence and mortality following radiation therapy for benign and malignant disease with the cancer risks observed in the Japanese A-bomb survivors. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2001, 77, 431–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The National Academics. Health Effects of Exposure to Low Levels of Ionizing Radiation: BEIR V Board on Radiation Effects Research; National Research Council of the National Academies: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- The National Academics. Health Risks from Exposure to Low Levels of Ionizing Radiation: BEIR VII Phase 2. Board on Radiation Effects Research; National Research Council of the National Academies: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hamer, O.W.; Sirlin, C.B.; Strotzer, M.; Borisch, I.; Zorger, N.; Feuerbach, S.; Völk, M. Chest radiography with a flat-panel detector: Image quality with dose reduction after copper filtration. Radiology 2005, 237, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrimpton, P.C.; Jones, D.G.; Wall, B.F. The influence of tube filtration and potential on patient dose during X-ray examinations. Phys. Med. Biol. 1988, 33, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, A.; Yamada, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Nishino, M.; Hida, K.; Hino, T.; Ueyama, M.; Yanagawa, M.; Kamitani, T.; Kurosaki, A. Dynamic Chest X-ray Using a Flat-Panel Detector System: Technique and Applications. Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 634–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berfer, M.J.; Motz, J.W. X-rays from thick tungsten targets irradiated by 500–50 keV electrons. Sci. Direct 2004, 226, 324–344. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, C.; Yamamoto, T.; Terada, H.; Akisada, M. Effect of tungsten absorption edge filter on diagnostic X-ray spectra, image quality and absorbed dose to the patient. Phys. Med. Biol. 1983, 28, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y. A study on the reduction of exposure dose and contrast improvement by use of heavy elements filter. J. Orient. Technol. 2000, 23, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, J.C.; Galvin, J.M.; Lockett, P.; Bloch, P. Use of a tungsten filter to improve beam uniformity. Med. Phys. 1981, 8, 520–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, H.D. Comparison of performance characteristics of conventional and K-edge filters in general diagnostic radiology. Phys. Med. Biol. 1989, 34, 1269–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.S.; Kim, S.C. Comparison of image quality and effective dose by additional filtration on digital chest tomosynthesis. J. Radiol. Sci. Technol. 2015, 38, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, H.L.; Fairchild, R.G.; Robertson, J.S.; Greenberg, D. Effect of absorption edge filters on diagnostic X-ray spectra. Radiol. 1975, 115, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McParland, B.J.; Boyd, M.M. X-ray image intensifier performance and patient doses for combinations of supplemental beam filters and vascular contrast agents. Phys. Med. Biol. 2001, 46, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagel, H.D. Limitation in the determination of total filtration of X-ray tube assemblies. Phys. Med. Biol. 1988, 33, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toroi, P.; Zanca, F.; Young, K.C.; Ongeval, C.; Marchal, G.; Bosmans, G.H. Experimental investigation on the choice of the tungsten/rhodium anode/filter combination for an amorphous selenium-based digital mammography system. Eur. Radiol. 2007, 17, 2368–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onnasch, D.G.W.; Schemm, A.; Kramer, H. Optimization of radiographic parameters for paediatric cardiac angiography. Br. J. Radiol. 2004, 77, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, R.J. A method for comparing beam-hardening filter materials for diagnostic radiology. Med. Phys. 1988, 15, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koedooder, K.; Venema, H.W. Filter materials for dose reduction in screen-film radiography. Phys. Med. Biol. 1986, 31, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakoumakis, E.; Dimitriadis, A.; Makri, T.; Karlatira, M.; Karavasilis, E.; Gialousis, G. Verification of radiation dose calculations during pediatric cystourethrography examinations using MCNP5 and PCXMC 2.0 Monte Carlo codes. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2013, 157, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosi, P.; Stuessi, A.; Verdun, F.R.; Vock, P.; Wolf, R. Copper filtration in pediatric digital X-ray imaging: Its impact on image quality and dose. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2011, 4, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapiovaara, M.; Siiskonen, T. PCXMC, a Monte Carlo program for calculating patient doses in medical X-ray examinations. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2008, 40, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Smans, K.; Struelens, L.; Smet, M.; Bosmans, H.; Vanhavere, H.F. Cu filtration for dose reduction in neonatal chest imaging. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2010, 139, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iramina, H.; Hamaguchi, T.; Nakamura, M.; Minzowaki, T.; Kanno, I. Metal artifact reduction by filter-based dual-energy cone-beam computed tomography on a bench-top micro-CBCT system: Concept and demonstration. J. Radiat. Res. 2018, 59, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego, D.; Lowe, E.M.; Kitahara, C.M.; Lee, C. Assessment of PCXMC for patients with different body size in chest and abdominal X-ray examinations: A Monte Carlo simulation study. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 065015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection. The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection; ICRP Publication 103: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Aichinger, H.; Dierker, J.; Joite-Barfuß, S.; Säbel, M. Radiation Exposure and Image Quality in X-ray Diagnostic Radiology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dobbins, J.T.; Samei, E.; Chotas, H.J.; Warp, R.J.; Baydush, A.H.; Floyd, C.E., Jr.; Ravin, C.E. Chest radiography: Optimization of X-ray spectrum for cesium iodide-amorphous silicon flat-panel detector. Radiology 2003, 226, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Choi, J.H. Analysis of effectiveness of spectrum of energy and image quality evaluation by aluminium filter in the added compound filtration. J. Radiol. Sci. Technol. 2015, 38, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, P.; Martin, C.J.; Gentle, D. Application of contrast-to-noise ratio in optimizing beam quality for digital chest radiography: Comparison of experimental measurements and theoretical simulations. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006, 51, 2953–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regano, L.J.; Sutton, R.A. Radiation dose reduction in diagnostic X-ray procedures. Phys. Med. Biol. 1992, 37, 1773–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, S.T.; Park, O.S.; Jeon, C.W.; Kim, H.J. Survey of technical parameters for pediatric chest X-ray imaging by using effective DQE and dose. Korean Soc. Med. Phys. 2011, 22, 163–171. [Google Scholar]




| Filter Material | K-Edge (keV) | Equivalent Thickness (mm) (Effective Energy (keV)) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Work (70 keV) | Nagel, H (30 keV) | Jennings (65 keV) | Koedooder/Venema (70 keV) | ||
| Aluminium (Al) | 0.56 | 6.1 | 7.1 | 7.2 | 5.77 |
| Coppper (Cu) | 8.98 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 20 | 0.076 | 0.076 | ||
| Tungsten (W) | 69.5 | 0.045 | 0.046 | 0.046 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, E.; Muroi, K.; Koike, T.; Kim, J. Dose Reduction and Image Quality Optimization of Pediatric Chest Radiography Using a Tungsten Filter. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100583
Kim E, Muroi K, Koike T, Kim J. Dose Reduction and Image Quality Optimization of Pediatric Chest Radiography Using a Tungsten Filter. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(10):583. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100583
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Eunhye, Kenzo Muroi, Takahisa Koike, and Jungmin Kim. 2022. "Dose Reduction and Image Quality Optimization of Pediatric Chest Radiography Using a Tungsten Filter" Bioengineering 9, no. 10: 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100583
APA StyleKim, E., Muroi, K., Koike, T., & Kim, J. (2022). Dose Reduction and Image Quality Optimization of Pediatric Chest Radiography Using a Tungsten Filter. Bioengineering, 9(10), 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100583






