A Concise Review on Electrospun Scaffolds for Kidney Tissue Engineering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Kidney Cells Differentiation and Development of Kidney Organoids
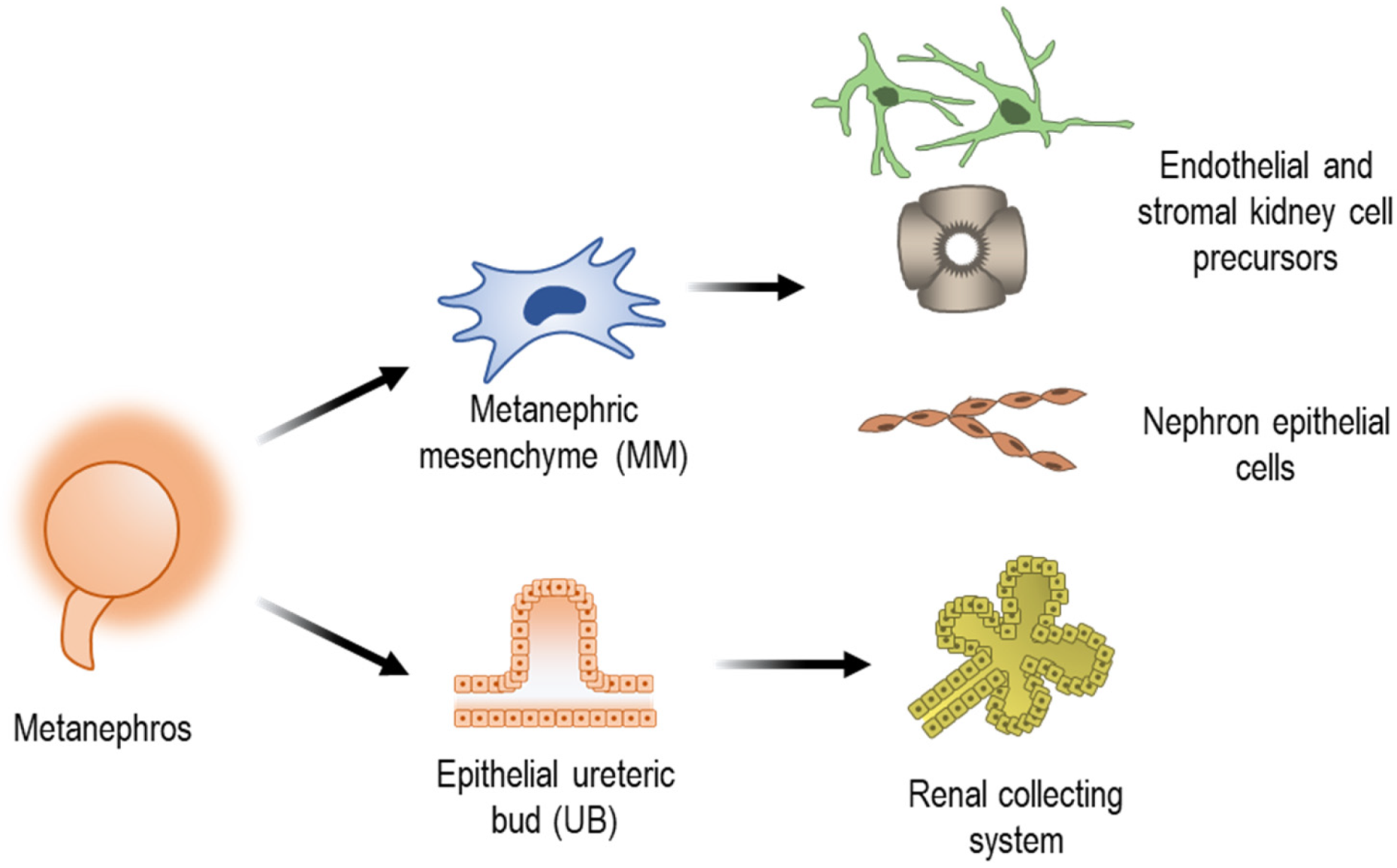
2.1. Embryonic Development of the Kidney
2.2. In Vitro Production of Human Kidney Cells and Organoids
3. Use of Electrospinning in the Development of Kidney Tissues
3.1. Overview of the Electrospinning Techniques
3.2. Electrospun Fibres Used in Kidney Tissue Engineering
3.2.1. Synthetic Polymers
3.2.2. Natural Polymers
4. Future Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kovesdy, C.P. Epidemiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: An Update 2022. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2022, 12, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, Y.; Aida, T.; Taguchi, Y. Advances in Tissue Engineering Technology for Kidney Regeneration and Construction. J. Artif. Organs 2022, 25, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerman, M.R. Tissue Engineering the Kidney. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stein, M.C.; Braun, F.; Krebs, C.F.; Bunders, M.J. Kidney Organoid Systems for Studies of Immune-Mediated Kidney Diseases: Challenges and Opportunities. Cell Tissue Res. 2021, 385, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garreta, E.; Nauryzgaliyeva, Z.; Montserrat, N. Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Kidney Organoids toward Clinical Implementations. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 20, 100346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Nam, S.A.; Yi, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, S.-Y.; Sen, T.; Choi, Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, H.L.; et al. Kidney Decellularized Extracellular Matrix Enhanced the Vascularization and Maturation of Human Kidney Organoids. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2103526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphreys, B.D. Bioprinting Better Kidney Organoids. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-H.; Castano, O.; Kim, H.-W. Electrospun Materials as Potential Platforms for Bone Tissue Engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1065–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbar, S.G.; Nukavarapu, S.P.; James, R.; Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Electrospun Poly(Lactic Acid-Co-Glycolic Acid) Scaffolds for Skin Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4100–4107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.R.; Castelo Ferreira, F.; Sanjuan-Alberte, P. Electrospun Piezoelectric Scaffolds for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 137, 212808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, K.; Castilho, M.; Aarts, S.; Kaminski, M.M.; Lienkamp, S.S.; Pichler, R.; Malda, J.; Vermonden, T.; Jansen, J.; Masereeuw, R. Fabrication of Kidney Proximal Tubule Grafts Using Biofunctionalized Electrospun Polymer Scaffolds. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 19, e1800412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskapan, B.; Callanan, A. Electrospinning Fabrication Methods to Incorporate Laminin in Polycaprolactone for Kidney Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2022, 19, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Ding, X.; Kai, D.; Ramakrishna, S. Emulsion Electrospun Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Encapsulated Poly(l-Lactic Acid-Co-ε-Caprolactone) Nanofibers for Sustained Release in Cardiac Tissue Engineering. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 3272–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junqueira, L.; Carneiro, J. Urinary System. In Junqueira’s Basic Histology: Text & Atlas; McGraw-Hill/Appleton & Lange: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 371–388. [Google Scholar]
- VanPutte, C.; Regan, J.; Russo, A.; Seeley, R.; Stephens, T.; Tate, P. Urinary System. In Seeley´s Anatomy & Physiology; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 958–981. [Google Scholar]
- Treuting, P.M.; Kowalewska, J. Urinary System. In Comparative Anatomy and Histology; Treuting, P.M., Dintzis, S.M., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 229–251. ISBN 9780123813619. [Google Scholar]
- Little, M.H. Kidney Development in the Mammal. In Kidney Transplantation, Bioengineering, and Regeneration: Kidney Transplantation in the Regenerative Medicine Era; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 787–799. [Google Scholar]
- Moritz, K.M.; Wintour-Coghlan, M.; Black, M.J.; Bertram, J.F.; Caruana, G. Morphological Development of the Mammalian Kidney. In Factors Influencing Mammalian Kidney Development: Implications for Health in Adult Life. Advances in Anatomy Embryology and Cell Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 196, pp. 1–9. ISBN 9783540777670. [Google Scholar]
- McMahon, A.P. Development of the Mammalian Kidney. In Current Topics in Developmental Biology; Wassarman, P.M., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 117, pp. 31–64. [Google Scholar]
- Little, M.H.; Kumar, S.V.; Forbes, T. Recapitulating Kidney Development: Progress and Challenges. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 91, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, S.F.; Barresi, M.J.F. Developmental Biology, 11th ed.; Meyers, R., Ed.; Sinauer Associates, Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum, N.D. Developmental Biology of the Human Kidney. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2008, 13, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshdel Rad, N.; Aghdami, N.; Moghadasali, R. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Kidney Development: From the Embryo to the Kidney Organoid. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faa, G.; Gerosa, C.; Fanni, D.; Monga, G.; Zaffanello, M.; Van Eyken, P.; Fanos, V. Morphogenesis and Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Human Kidney Development. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morizane, R.; Miyoshi, T.; Bonventre, J.V. Concise Review: Kidney Generation with Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 2209–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yengej, F.A.Y.; Jansen, J.; Rookmaaker, M.B.; Verhaar, M.C.; Clevers, H. Kidney Organoids and Tubuloids. Cells 2020, 9, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, M.H.; Combes, A.N. Kidney Organoids: Accurate Models or Fortunate Accidents. Genes Dev. 2019, 33, 1319–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, K.; Schumacher, K.M.; Tasnim, F.; Kandasamy, K.; Schumacher, A.; Ni, M.; Gao, S.; Gopalan, B.; Zink, D.; Ying, J.Y. Human Embryonic Stem Cells Differentiate into Functional Renal Proximal Tubular–like Cells. Kidney Int. 2013, 83, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Han, Y.-M. Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells into Nephron Progenitor Cells in a Serum and Feeder Free System. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, A.Q.; Freedman, B.S.; Morizane, R.; Lerou, P.H.; Valerius, M.T.; Bonventre, J.V. Rapid and Efficient Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells into Intermediate Mesoderm That Forms Tubules Expressing Kidney Proximal Tubular Markers. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 1211–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Sancho-Martinez, I.; Nivet, E.; Rodriguez Esteban, C.; Campistol, J.M.; Izpisua Belmonte, J.C. The Generation of Kidney Organoids by Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Cells to Ureteric Bud Progenitor–like Cells. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 2693–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasato, M.; Er, P.X.; Chiu, H.S.; Maier, B.; Baillie, G.J.; Ferguson, C.; Parton, R.G.; Wolvetang, E.J.; Roost, M.S.; Chuva de Sousa Lopes, S.M.; et al. Kidney Organoids from Human IPS Cells Contain Multiple Lineages and Model Human Nephrogenesis. Nature 2015, 526, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morizane, R.; Lam, A.Q.; Freedman, B.S.; Kishi, S.; Valerius, M.T.; Bonventre, J.V. Nephron Organoids Derived from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Model Kidney Development and Injury. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampi, O.; Iacone, R.; Longaretti, L.; Benedetti, V.; Graf, M.; Magnone, M.C.; Patsch, C.; Xinaris, C.; Remuzzi, G.; Benigni, A.; et al. Generation of Functional Podocytes from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cell Res. 2016, 17, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combes, A.N.; Zappia, L.; Er, P.X.; Oshlack, A.; Little, M.H. Single-Cell Analysis Reveals Congruence between Kidney Organoids and Human Fetal Kidney. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, F.M.; Driskell, R.R. The Therapeutic Potential of Stem Cells. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasato, M.; Er, P.X.; Chiu, H.S.; Little, M.H. Generation of Kidney Organoids from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1681–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, V.; Carta, G.; da Costa Pereira, D.; Gupta, R.; Murphy, C.; Feifel, E.; Kern, G.; Lechner, J.; Cavallo, A.L.; Gupta, S.; et al. Generation and Characterization of IPSC-Derived Renal Proximal Tubule-like Cells with Extended Stability. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musah, S.; Mammoto, A.; Ferrante, T.C.; Jeanty, S.S.F.; Hirano-Kobayashi, M.; Mammoto, T.; Roberts, K.; Chung, S.; Novak, R.; Ingram, M.; et al. Mature Induced-Pluripotent-Stem-Cell-Derived Human Podocytes Reconstitute Kidney Glomerular-Capillary-Wall Function on a Chip. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, T.; Diogo, M.; Cabral, J.M.S. Stem Cell Bioprocessing for Cellular Therapy, Diagnostics and Drug Development, 1st ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lund, A.W.; Yener, B.; Stegemann, J.P.; Plopper, G.E. The Natural and Engineered 3D Microenvironment as a Regulatory Cue During Stem Cell Fate Determination. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2009, 15, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumbar, S.G.; James, R.; Nukavarapu, S.P.; Laurencin, C.T. Electrospun Nanofiber Scaffolds: Engineering Soft Tissues. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 3, 34002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robb, B.; Lennox, B. 3-The Electrospinning Process, Conditions and Control. In Electrospinning for Tissue Regeneration; Bosworth, L.A., Downes, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Biomaterials; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2011; pp. 51–66. ISBN 978-1-84569-741-9. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, T.C.; Amanah, A.Y.; Gluck, J.M. Electrospun Scaffolds and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes for Cardiac Tissue Engineering Applications. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, T.P.; Corcoran, A.; Callanan, A. The Effect of Electrospun Polycaprolactone Scaffold Morphology on Human Kidney Epithelial Cells. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 13, 15006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, M.F.; Chan, W.Y.; Chian, K.S. Cryogenic Electrospinning: Proposed Mechanism, Process Parameters and Its Use in Engineering of Bilayered Tissue Structures. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, M.F.; Rasheed, M.Z.; Lim, T.C.; Chian, K.S. In Vitro Cell Infiltration and in Vivo Cell Infiltration and Vascularization in a Fibrous, Highly Porous Poly(D,L-Lactide) Scaffold Fabricated by Cryogenic Electrospinning Technique. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2009, 91, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Steckl, A.J. Coaxial Electrospinning Formation of Complex Polymer Fibers and Their Applications. Chempluschem 2019, 84, 1453–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque Sánchez, L.; Brack, N.; Postma, A.; Pigram, P.J.; Meagher, L. Surface Modification of Electrospun Fibres for Biomedical Applications: A Focus on Radical Polymerization Methods. Biomaterials 2016, 106, 24–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, B.; Lv, Y. Dual-Delivery of VEGF and NGF by Emulsion Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffold for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 82, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasinghe, S.N. Cell Electrospinning: A Novel Tool for Functionalising Fibres, Scaffolds and Membranes with Living Cells and Other Advanced Materials for Regenerative Biology and Medicine. Analyst 2013, 138, 2215–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosoudi, N.; Hart, C.; McKnight, I.; Esmaeilpour, M.; Ghomian, T.; Zadeh, A.; Raines, R.; Ramirez Vick, J.E. Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells to Chondrocytes Using Electrospraying. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzgo, M.; Mickova, A.; Rampichova, M.; Doupnik, M. 11-Blend Electrospinning, Coaxial Electrospinning, and Emulsion Electrospinning Techniques. In Core-Shell Nanostructures for Drug Delivery and Theranostics; Focarete, M.L., Tampieri, A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Biomaterials; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 325–347. ISBN 978-0-08-102198-9. [Google Scholar]
- Lannutti, J.; Reneker, D.; Ma, T.; Tomasko, D.; Farson, D. Electrospinning for Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2007, 27, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.Z.; Zhou, Y. Electrospinning of Biomimetic Fibrous Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering: A Review. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2020, 69, 947–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, M.; Mills, D.K.; Urbanska, A.M.; Saeb, M.R.; Venugopal, J.R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Mozafari, M. Electrospinning for Tissue Engineering Applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 117, 100721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadalizadeh, Z.; Bahremandi-Toloue, E.; Karbasi, S. Synthetic-Based Blended Electrospun Scaffolds in Tissue Engineering Applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 4020–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turunen, S.; Kaisto, S.; Skovorodkin, I.; Mironov, V.; Kalpio, T.; Vainio, S.; Rak-Raszewska, A. 3D Bioprinting of the Kidney—Hype or Hope? AIMS Cell Tissue Eng. 2018, 2, 119–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransen, M.F.J.; Addario, G.; Bouten, C.V.C.; Halary, F.; Moroni, L.; Mota, C. Bioprinting of Kidney in Vitro Models: Cells, Biomaterials, and Manufacturing Techniques. Essays Biochem. 2021, 65, 587–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhvi, M.S.; Zinjarde, S.S.; Gokhale, D. V Polylactic Acid: Synthesis and Biomedical Applications. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 1612–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, T.P.; Callanan, A. A Non-Woven Path: Electrospun Poly(Lactic Acid) Scaffolds for Kidney Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 15, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, H.F.; Luqman, M.; Khalil, K.A.; Elnakady, Y.A.; Abd-Elkader, O.H.; Rady, A.M.; Alharthi, N.H.; Karim, M.R. Fabrication of Core-Shell Structured Nanofibers of Poly (Lactic Acid) and Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) by Coaxial Electrospinning for Tissue Engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 98, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.A.; Amorim, M.T.P.; Felgueiras, H.P. Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)-Based Nanofibrous Electrospun Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Cai, J.; Lin, S.; Li, F.; Tian, F. Controlled Release of Monodisperse Silver Nanoparticles via in Situ Cross-Linked Polyvinyl Alcohol as Benign and Antibacterial Electrospun Nanofibers. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2021, 197, 111370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, X.; Shah, J.; Bhattacharya, R.; Kalejaiye, T.D.; Sun, B.; Hsu, P.-C.; Musah, S. A Biomimetic Electrospun Membrane Supports the Differentiation and Maturation of Kidney Epithelium from Human Stem Cells. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobreiro-Almeida, R.; Melica, M.E.; Lasagni, L.; Romagnani, P.; Neves, N.M. Co-Cultures of Renal Progenitors and Endothelial Cells on Kidney Decellularized Matrices Replicate the Renal Tubular Environment in Vitro. Acta Physiol. 2020, 230, e13491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.Y.C.; Homan, K.A.; Robinson, S.S.; Kolesky, D.B.; Duarte, N.; Moisan, A.; Lewis, J.A. Renal Reabsorption in 3D Vascularized Proximal Tubule Models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 5399–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Cui, K.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qin, J. Advances in Hydrogels in Organoids and Organs-on-a-Chip. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1902042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miranda, C.C.; Gomes, M.R.; Moço, M.; Cabral, J.M.S.; Ferreira, F.C.; Sanjuan-Alberte, P. A Concise Review on Electrospun Scaffolds for Kidney Tissue Engineering. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100554
Miranda CC, Gomes MR, Moço M, Cabral JMS, Ferreira FC, Sanjuan-Alberte P. A Concise Review on Electrospun Scaffolds for Kidney Tissue Engineering. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(10):554. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100554
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiranda, Cláudia C., Mariana Ramalho Gomes, Mariana Moço, Joaquim M. S. Cabral, Frederico Castelo Ferreira, and Paola Sanjuan-Alberte. 2022. "A Concise Review on Electrospun Scaffolds for Kidney Tissue Engineering" Bioengineering 9, no. 10: 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100554
APA StyleMiranda, C. C., Gomes, M. R., Moço, M., Cabral, J. M. S., Ferreira, F. C., & Sanjuan-Alberte, P. (2022). A Concise Review on Electrospun Scaffolds for Kidney Tissue Engineering. Bioengineering, 9(10), 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9100554









