Acid Resistance of Glass Ionomer Cement Restorative Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
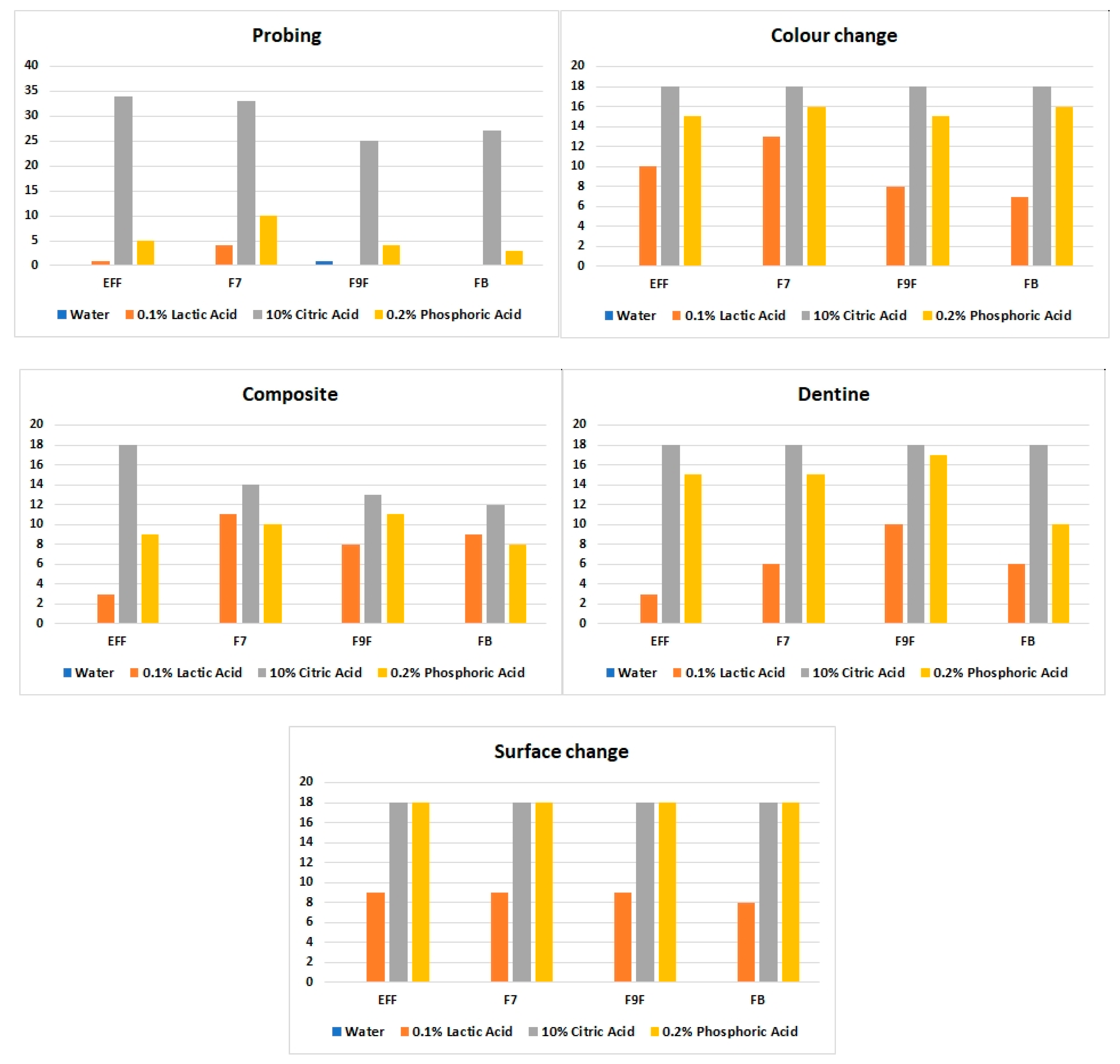
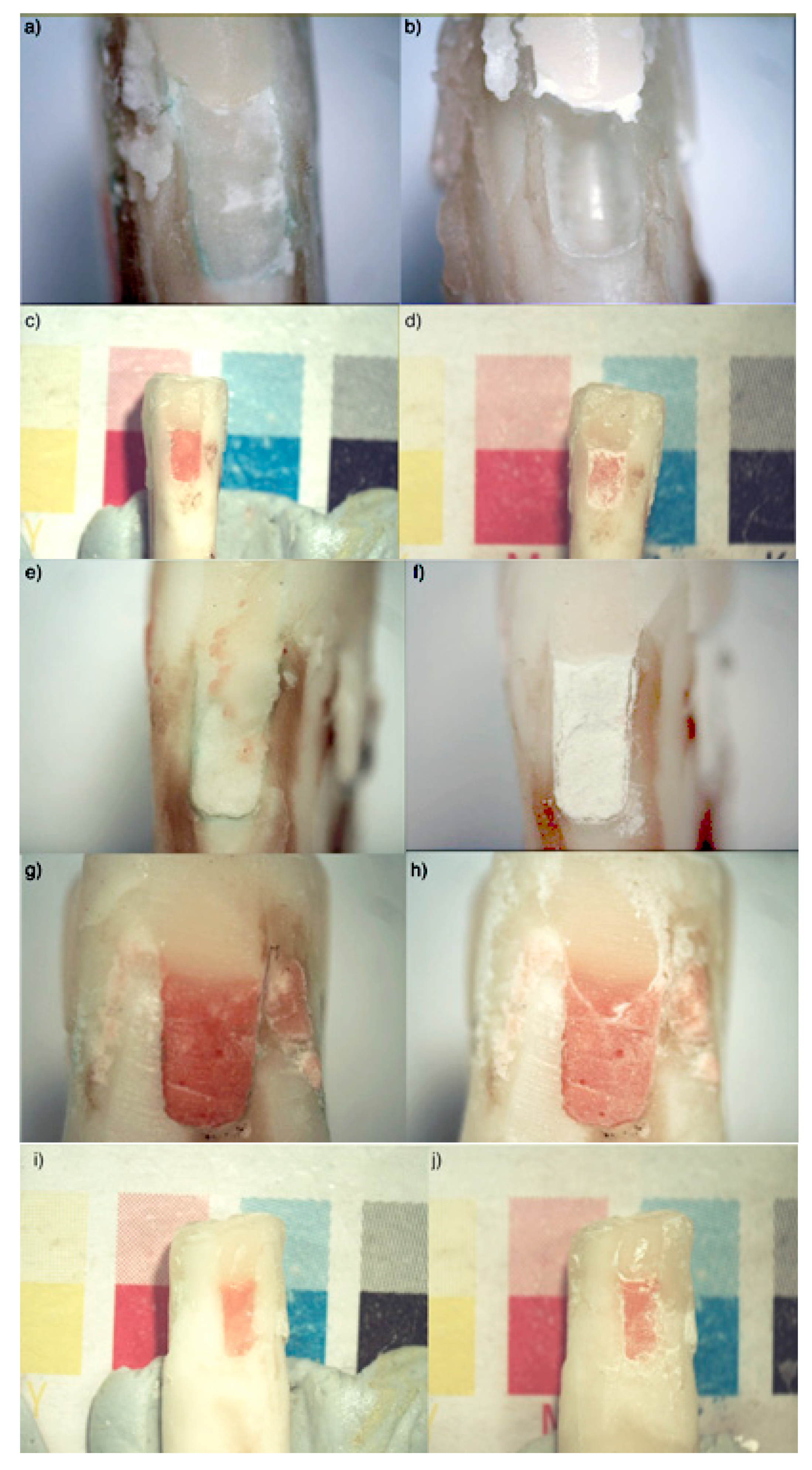
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walsh, L.J. Preventive dentistry for the general dental practitioner. Aust. Dent. J. 2000, 45, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, L.J. Minimal intervention management of the older patient. Brit. Dent. J. 2017, 223, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes-Silva, R.; Cabral, R.N.; Pascotto, R.C.; Borges, A.F.S.; Martins, C.C.; Navarro, M.F.L.; Sidhu, S.K.; Leal, S.C. Mechanical and optical properties of conventional restorative glass-ionomer cements—a systematic review. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2019, 27, e2018357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, G.M.; McIntyre, J.M.; Craig, G.G.; Mulyani; Zilm, P.S.; Gully, N.J. An in vitro investigation of marginal dentine caries abutting composite resin and glass ionomer cement restorations. Aust. Dent. J. 2007, 52, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantbirojn, D.; Rusin, R.P.; Bui, H.T.; Mitra, S.B. Inhibition of dentin demineralization adjacent to a glass-ionomer/composite sandwich restoration. Quintessence Int. 2009, 40, 287–294. [Google Scholar]
- Al Zraikat, H.; Palamara, J.E.A.; Messer, H.H.; Burrow, M.F.; Reynolds, E.C. The incorporation of casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate into a glass ionomer cement. Dent. Mater. 2011, 27, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalizniak, I.; Palamara, J.E.; Wong, R.H.; Cochrane, N.J.; Burrow, M.F.; Reynolds, E.C. Ion release and physical properties of CPP-ACP modified GIC in acid solutions. J. Dent. 2013, 41, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.; Hassan, U.; Billington, R.W.; Hill, R.G.; Anderson, P. Glass ionomer cements: Effect of strontium substitution on esthetics, radiopacity and fluoride release. Dent. Mater. 2014, 30, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourie, J.; Smit, C.F. Cervical microleakage in class II open-sandwich restorations: An in vitro study. SADJ 2011, 66, 320–324. [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu, S.K. Glass-ionomer cement restorative materials: A sticky subject? Aust. Dent. J. 2011, 56, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, S.K.; Nicholson, J.W. A review of glass-ionomer cements for clinical dentistry. J. Funct. Biomater. 2016, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GC Australasia Dental Pty Ltd. Equia® Forte Glass Hybrid Restorative System [Pamphlet]; GC Australasia Dental Pty Ltd.: Banksmeadow, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- GC Australasia Dental Pty Ltd. Fuji BULK: Rapid, Robust, Remarkable [Pamphlet]; GC Australasia Dental Pty Ltd.: Banksmeadow, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hengtrakool, C.; Pearson, G.J.; Wilson, M. Interaction Between GIC and S. sanguis biofilms: Antibacterial properties and changes of surface hardness. J. Dent. 2006, 34, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan Bakar, W.Z.; McIntyre, J. Susceptibility of selected tooth-coloured dental materials to damage by common erosive acids. Aust. Dent. J. 2006, 53, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy-Gutekunst, L. Hidden phosphorus in popular beverages. Nephrol. Nurs. J. 2005, 32, 443–445. [Google Scholar]
- Penniston, K.L.; Nakada, S.Y.; Holmes, R.P.; Assimos, D.G. Quantitative assessment of citric acid in lemon juice, lime juice, and commercially-available fruit juice products. J. Endourol. 2008, 22, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poornima, P.; Koley, P.; Kenchappa, M.; Nagaveni, N.B.; Bharath, K.P.; Neena, I.E. Comparative evaluation of compressive strength and surface microhardness of EQUIA Forte, resin-modified glass-ionomer cement with conventional glass-ionomer cement. J. Indian Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2019, 37, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshaverinia, M.; Navas, A.; Jahedmanesh, N.; Shah, K.C.; Moshaverinia, A.; Ansari, S. Comparative evaluation of the physical properties of a reinforced glass ionomer dental restorative material. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 122, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beech, D.R.; Bandyopadhyay, S. A new laboratory method for evaluating the relative solubility and erosion of dental cements. J. Oral Rehabil. 1983, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukazawa, M.; Matsuya, S.; Yamane, M. Mechanism for erosion of glass-ionomer cements in an acidic buffer solution. J. Dent. Res. 1987, 66, 1770–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.W.; Amiri, M.A. The interaction of dental cements with aqueous solutions of varying pH. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1998, 9, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.W.; Czarnecka, B.; Limanowska-Shaw, H. The long-term interaction of dental cements with lactic acid solutions. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1999, 10, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, J.W.; Czarnecka, B.; Limanowska-Shaw, H. A preliminary study of the effect of glass-ionomer and related dental cements on the pH of lactic acid storage solutions. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Tawfik, H.; Myint, Y.; Brocklehurst, D.; Nicholson, J.W. Factors affecting the ability of dental cements to alter the pH of lactic acid solutions. J. Oral Rehabil. 2000, 27, 1030–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps, J.; Pashley, D. Reliability of dye penetration studies. J. Endod. 2003, 29, 592–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarnecka, B.; Nicholson, J.W. Ion release by resin-modified glass-ionomer cements into water and lactic acid solutions. J. Dent. 2006, 34, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, R.; Tyas, M.J.; Burrow, M.F. Comparison of the effect of storage media on hardness and shear punch strength of tooth-colored restorative materials. Am. J. Dent. 2007, 20, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prabhakar, A.R.; Raja Sekhar, V.; Kurthukoti, A.J. Leaching of ions from materials used in alternative restorative technique under neutral and acidic conditions: A comparative evaluation. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2009, 34, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cefaly, D.F.G.; Santos, J.L.D.; Santos, J.R.D.; Lauris, J.R.P.; Mondelli, R.F.L.; Atta, M.T. In vitro interactions between lactic acid solution and Art glass-ionomer cements. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2009, 17, 274–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- GC Australasia Dental Pty Ltd. Fuji IX GP Extra: Extra Translucency, Extra Fast, Extra Fluoride [Pamphlet]; GC Australasia Dental Pty Ltd.: Banksmeadow, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Arbabzadeh-Zavareh, F.; Gibbs, T.; Meyers, I.A.; Bouzari, M.; Mortazavi, S.; Walsh, L.J. Recharge pattern of contemporary glass ionomer restoratives. Dent. Res. J. 2012, 9, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, J.; Walsh, L.J.; Naser-ud Din, S.; Ngo, H.; Manton, D.J. Evaluation of a novel approach in the prevention of white spot lesions around orthodontic brackets. Aust. Dent. J. 2014, 59, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, R.B.W.; de Farias, J.F.G.; Andrade, A.K.M.; Silva, F.B.S.; Duarte, R.M. Water sorption and solubility of glass ionomer cements indicated for atraumatic restorative treatment considering the time and the pH of the storage solution. Rev. Gaúch. Odontol. 2018, 66, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.W. Maturation processes in glass-ionomer dental cements. Acta Biomater. Odontol. Scand. 2018, 4, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO. ISO 9917–1: Dentistry—Water-Based Cements—Part 1: Powder/Liquid Acid-Base Cements; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Alm, L. Effect of fermentation on L(+) and D(-) lactic acid in milk. J. Dairy Sci. 1982, 65, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, E. Phosphorus content in commonly consumed beverages. J. Ren. Nutrit. 2014, 24, e1–e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickenautsch, S.; Mount, G.J.; Yengopal, V. Therapeutic effect of glass ionomers: An overview of evidence. Aust. Dent. J. 2011, 56, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukazawa, M.; Matsuya, S.; Yamane, M. The mechanism for erosion of glass-ionomer cements in organic-acid buffer solutions. J. Dent. Res. 1990, 69, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumdahl, S.; DeCoste, D.J. Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation, 6th ed.; Houghton Mifflin Custom Publishing: Boston, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bruice, P.Y. Organic Chemistry, 5th ed.; Pearson/Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; Narasimhan, J.; Nammalwar, R.B. The effect of capsulated glass ionomer cements on the pH of a lactic acid solution: An in-vitro study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2012, 6, 316–318. [Google Scholar]
- Kaga, N.; Nagano-Takebe, F.; Nezu, T.; Matsuura, T.; Endo, K.; Kaga, M. Protective effects of GIC and S-PRG filler restoratives on demineralization of bovine enamel in lactic acid solution. Materials 2020, 13, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, N.J.; Cai, F.; Yuan, Y.; Reynolds, E.C. Erosive potential of beverages sold in Australian schools. Aust. Dent. J. 2009, 54, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, N.J.; Yuan, Y.; Walker, G.D.; Shen, P.; Chang, C.H.; Reynolds, C.; Reynolds, E.C. Erosive potential of sports beverages. Aust. Dent. J. 2012, 57, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perera, D.; Yu, S.C.H.; Zeng, H.; Meyers, I.A.; Walsh, L.J. Acid Resistance of Glass Ionomer Cement Restorative Materials. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7040150
Perera D, Yu SCH, Zeng H, Meyers IA, Walsh LJ. Acid Resistance of Glass Ionomer Cement Restorative Materials. Bioengineering. 2020; 7(4):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7040150
Chicago/Turabian StylePerera, Dinuki, Sean C. H. Yu, Henry Zeng, Ian A. Meyers, and Laurence J. Walsh. 2020. "Acid Resistance of Glass Ionomer Cement Restorative Materials" Bioengineering 7, no. 4: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7040150
APA StylePerera, D., Yu, S. C. H., Zeng, H., Meyers, I. A., & Walsh, L. J. (2020). Acid Resistance of Glass Ionomer Cement Restorative Materials. Bioengineering, 7(4), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7040150





