Biomedical Processing of Polyhydroxyalkanoates
Abstract
1. Introduction
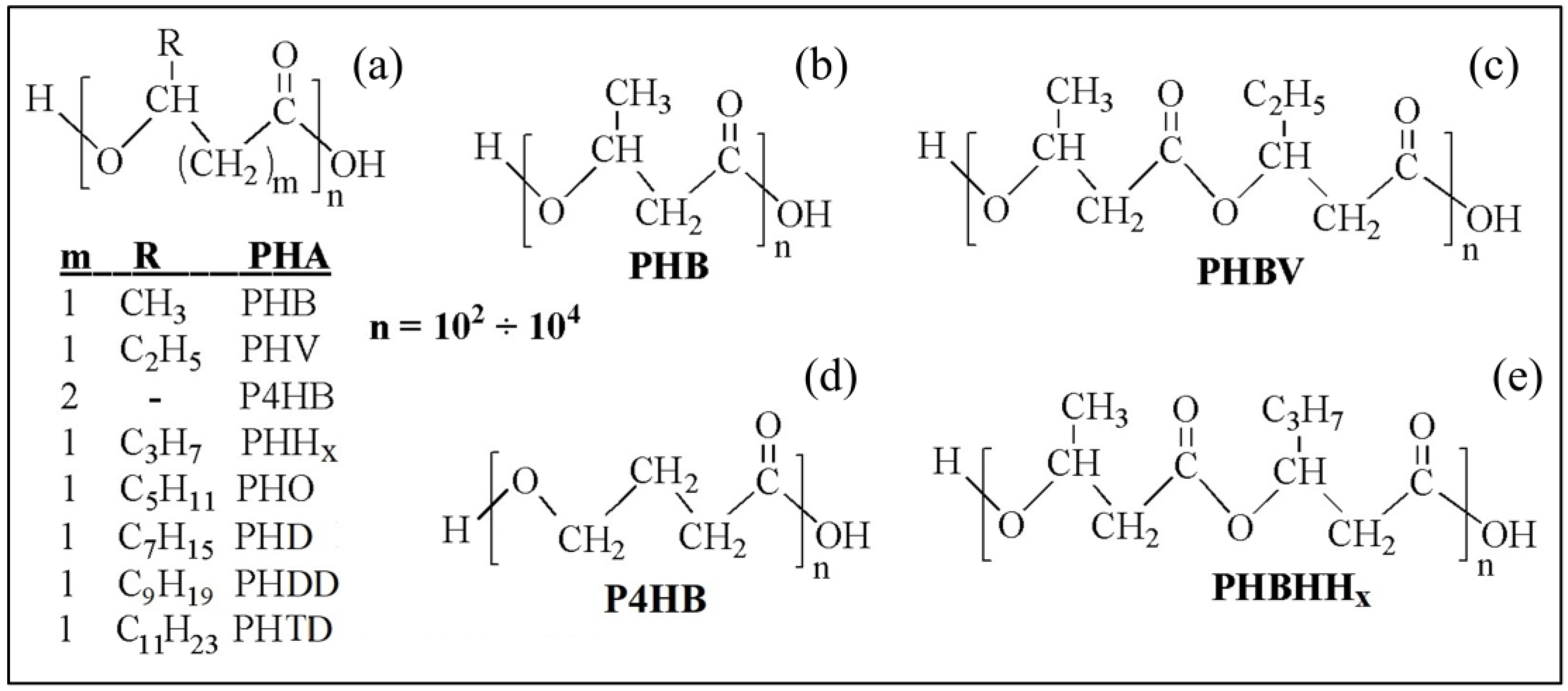
2. Physical and Processing Properties of PHA
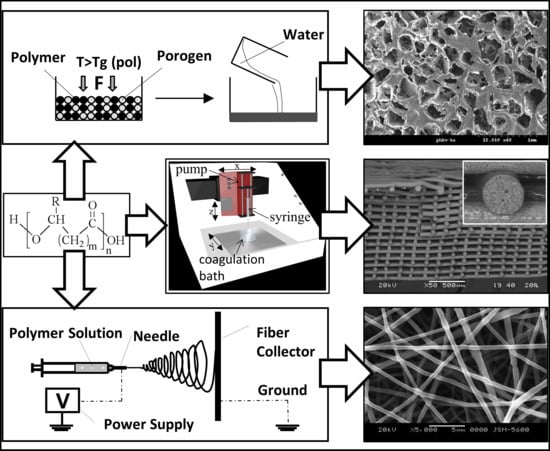
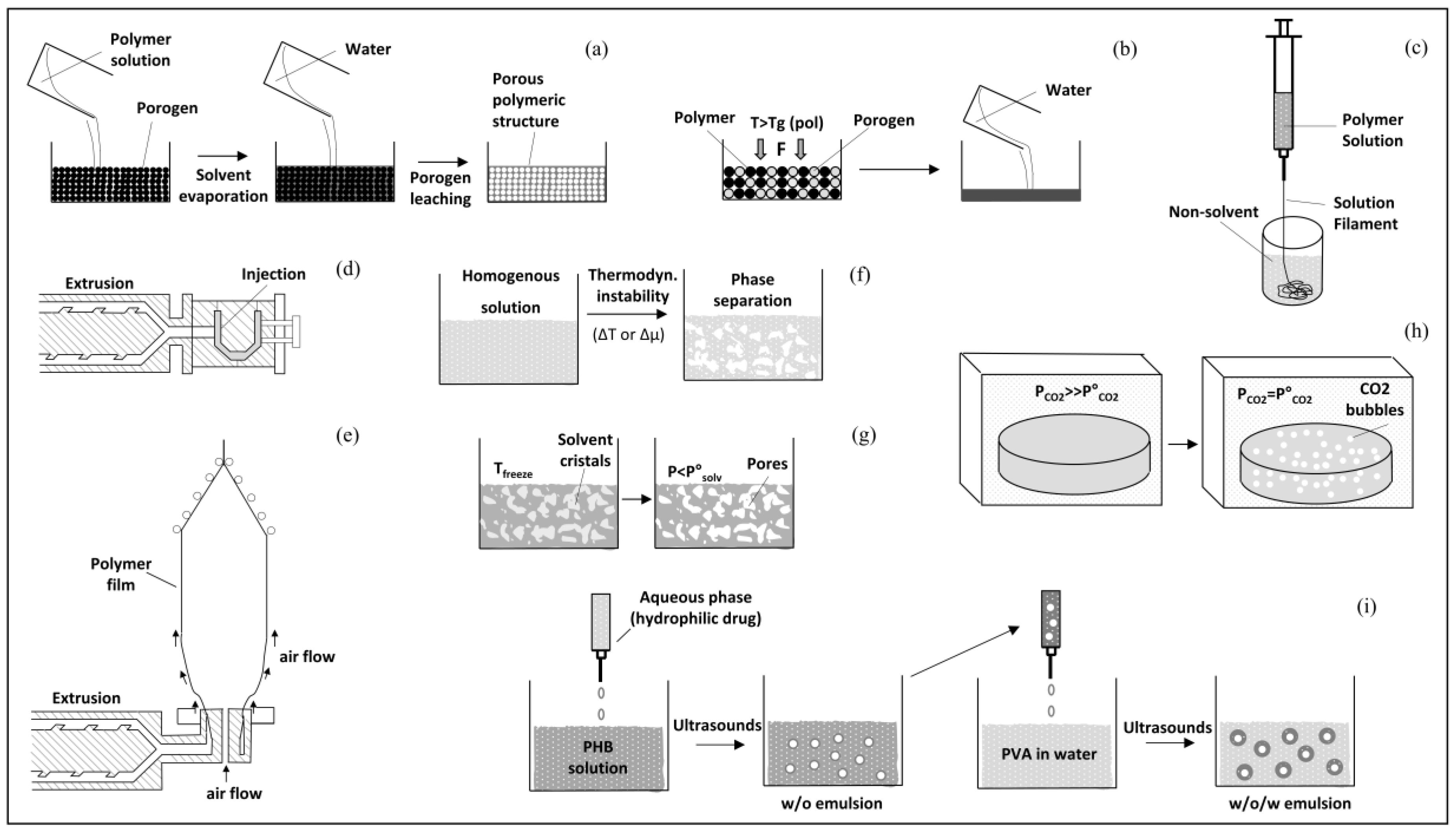
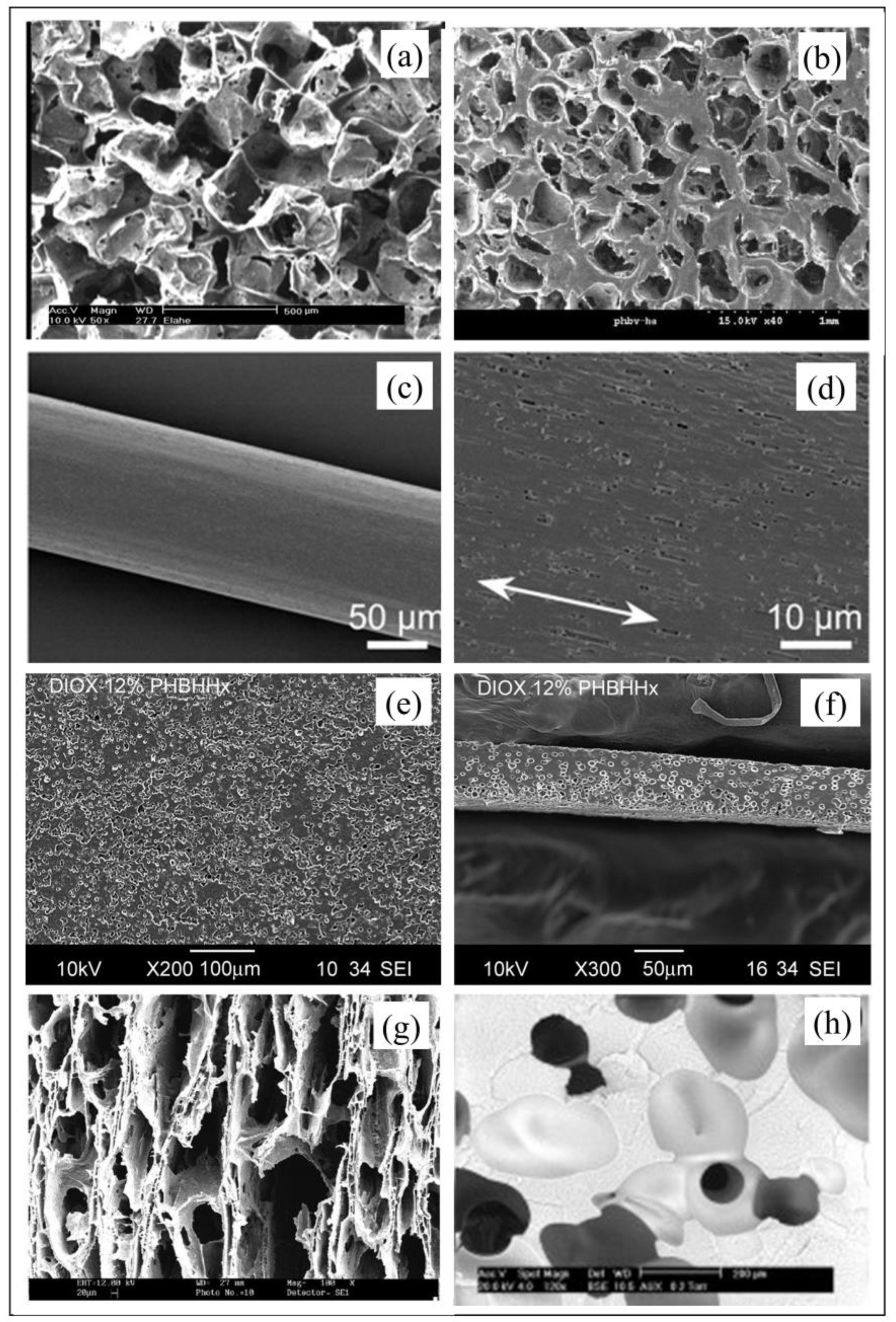
3. Biomedical Processing of PHA
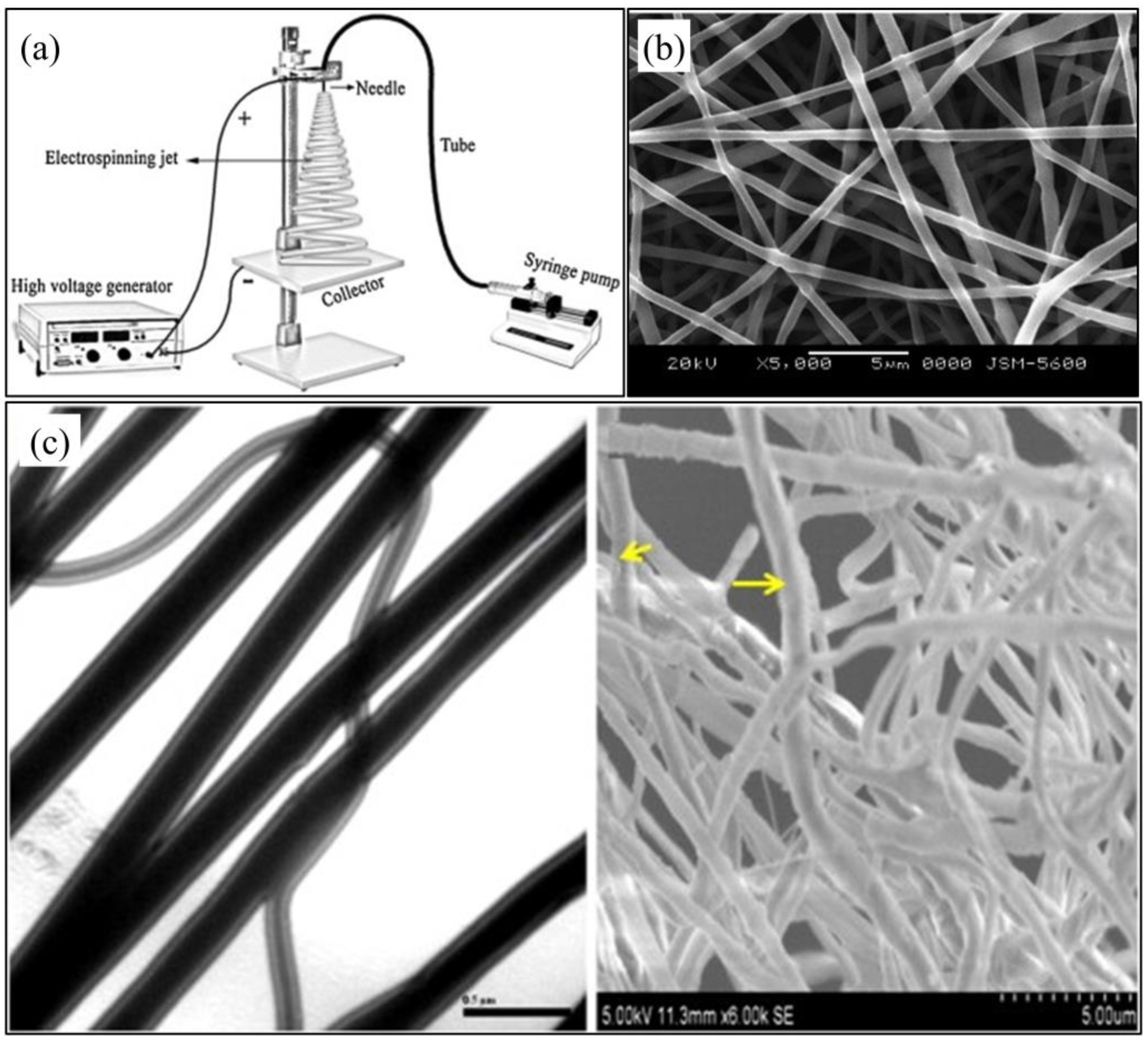
3.1. Electrospinning
3.2. Additive Manufacturing
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Puppi, D.; Chiellini, F.; Dash, M.; Chiellini, E. Biodegradable polymers for biomedical applications. In Biodegradable Polymers: Processing, Degradation & Applications; Felton, G.P., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 545–560. [Google Scholar]
- Koller, M. Advances in polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) production. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, C.T.; Tanaka, T.; Gan, Z.; Kuwabara, K.; Abe, H.; Takase, K.; Taguchi, K.; Doi, Y. Effective enhancement of short-chain-length−medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymer production by coexpression of genetically engineered 3-ketoacyl-acyl-carrier-protein synthase iii (fabh) and polyhydroxyalkanoate synthesis genes. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhu, B.; Yu, F.; Chen, G.-Q.; Inoue, Y. Polymorphic crystallization of fractionated microbial medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates. Polymer 2009, 50, 4378–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Tang, X.; Shang, G.; Peng, Q.; Wang, R.; Cai, X. The properties of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) and its applications in tissue engineering. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2014, 9, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshie, N.; Inoue, Y. Chemical composition distribution of bacterial copolyesters. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1999, 25, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoigne, M. Produits de deshydration et de polymerisation de l’acide b-oxobutyrique. Bull. Soc. Chem. Biol. 1926, 8, 770–782. [Google Scholar]
- Nigmatullin, R.; Thomas, P.; Lukasiewicz, B.; Puthussery, H.; Roy, I. Polyhydroxyalkanoates, a family of natural polymers, and their applications in drug delivery. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 90, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Contreras, A. Recent advances in the use of polyhydroyalkanoates in biomedicine. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, A.; Puppi, D.; Chiellini, F. Polymers from renewable resources. J. Renew. Mater. 2013, 1, 83–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, M. Biodegradable and biocompatible polyhydroxy-alkanoates (PHA): Auspicious microbial macromolecules for pharmaceutical and therapeutic applications. Molecules 2018, 23, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-Q.; Wu, Q. The application of polyhydroxyalkanoates as tissue engineering materials. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6565–6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manavitehrani, I.; Fathi, A.; Badr, H.; Daly, S.; Negahi Shirazi, A.; Dehghani, F. Biomedical applications of biodegradable polyesters. Polymers 2016, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galatea Surgical Scaffolds. Available online: https://www.galateasurgical.com/ (accessed on 30 October 2019).
- Tepha Medical Devices. Available online: https://www.tepha.com (accessed on 30 October 2019).
- B. Braun Italia. Available online: https://www.bbraun.it (accessed on 30 October 2019).
- Wright Medical Group N.V. Available online: http://www.wright.com (accessed on 30 October 2019).
- Leroy, E.; Petit, I.; Audic, J.L.; Colomines, G.; Deterre, R. Rheological characterization of a thermally unstable bioplastic in injection molding conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 1915–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda De Sousa Dias, M.; Koller, M.; Puppi, D.; Morelli, A.; Chiellini, F.; Braunegg, G. Fed-batch synthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) from sucrose and 4-hydroxybutyrate precursors by burkholderia sacchari strain dsm 17165. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkour, M.H.; Heinrich, D.; Alghamdi, M.A.; Shabbaj, I.I.; Steinbüchel, A. PHA recovery from biomass. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 2963–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanhueza, C.; Acevedo, F.; Rocha, S.; Villegas, P.; Seeger, M.; Navia, R. Polyhydroxyalkanoates as biomaterial for electrospun scaffolds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppi, D.; Chiellini, F. Additive manufacturing of PHA. In Handbook of Polyhydroxyalkanoates; Koller, M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Puppi, D.; Chiellini, F.; Piras, A.M.; Chiellini, E. Polymeric materials for bone and cartilage repair. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 403–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnett, P.; Ching, K.Y.; Stolz, M.; Knowles, J.C.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Smith, C.; Locke, I.C.; Keshavarz, T.; Roy, I. Novel poly(3-hydroxyoctanoate)/poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) blends for medical applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.-Y.; Xing, Z.-C.; Kwak, G.; Yoon, K.-B.; Park, S.-Y.; Park, L.S.; Kang, I.-K. Fabrication and characterization of collagen-immobilized porous PHBV/HA nanocomposite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 171804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Fujita, M.; Takeuchi, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Uesugi, K.; Ito, K.; Fujisawa, T.; Doi, Y.; Iwata, T. Formation of highly ordered structure in poly[(r)-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-(r)-3-hydroxyvalerate] high-strength fibers. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 2940–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.-W.; Zou, X.-H.; Chen, G.-Q. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) as an injectable implant system for prevention of post-surgical tissue adhesion. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3075–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, N.; Khan, T.H. In vitro degradation of PHBV scaffolds and nHA/PHBV composite scaffolds containing hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 190950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Moigne, N.; Sauceau, M.; Benyakhlef, M.; Jemai, R.; Benezet, J.-C.; Rodier, E.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.-M.; Fages, J. Foaming of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/organo-clays nano-biocomposites by a continuous supercritical co2 assisted extrusion process. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 61, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaeli, E.; Morshed, M.; Rasekhian, P.; Karbasi, S.; Karbalaie, K.; Karamali, F.; Abedi, D.; Razavi, S.; Jafarian-Dehkordi, A.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H.; et al. Does the tissue engineering architecture of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) scaffold affects cell-material interactions? J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2012, 100, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, H.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, M. Melt-spun microbial poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) fibers with enhanced toughness: Synergistic effect of heterogeneous nucleation, long-chain branching and drawing process. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagoz, A.S.; Rodriguez-Cabello, J.C.; Hasirci, V. PHBV wet-spun scaffold coated with ELR-REDV improves vascularization for bone tissue engineering. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 13, 055010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeisdasteh Hokmabad, V.; Davaran, S.; Ramazani, A.; Salehi, R. Design and fabrication of porous biodegradable scaffolds: A strategy for tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2017, 28, 1797–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashter, S.A. 7-processing biodegradable polymers. In Introduction to Bioplastics Engineering; Ashter, S.A., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 179–209. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.-T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.-Q. Nanofibrous polyhydroxyalkanoate matrices as cell growth supporting materials. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3720–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, T.; Hosoda, N.; Uyama, H. Fabrication of porous poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) monoliths via thermally induced phase separation. Polymers 2016, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppi, D.; Piras, A.M.; Chiellini, F.; Chiellini, E.; Martins, A.; Leonor, I.B.; Neves, N.; Reis, R. Optimized electro- and wet-spinning techniques for the production of polymeric fibrous scaffolds loaded with bisphosphonate and hydroxyapatite. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2011, 5, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, N.; Wang, M. Fabrication of HA/PHBV composite scaffolds through the emulsion freezing/freeze-drying process and characterisation of the scaffolds. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 19, 2555–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, N.; Wang, M. PHBV/PLLA-based composite scaffolds fabricated using an emulsion freezing/freeze-drying technique for bone tissue engineering: Surface modification andin vitrobiological evaluation. Biofabrication 2012, 4, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Q.; Tsui, A.; Billington, S.; Frank, C.W. Extruded foams from microbial poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and its blends with cellulose acetate butyrate. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2012, 52, 1495–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, Z.C.; Frank, C.W. Increasing cell homogeneity of semicrystalline, biodegradable polymer foams with a narrow processing window via rapid quenching. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2014, 54, 2877–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, H.; Laguna-Gutiérrez, E.; Rodriguez-Perez, M.A.; Ardanuy, M. Effect of chain extender and water-quenching on the properties of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) foams for its production by extrusion foaming. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 85, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastav, A.; Kim, H.-Y.; Kim, Y.-R. Advances in the applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate nanoparticles for novel drug delivery system. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 581684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barouti, G.; Jaffredo, C.G.; Guillaume, S.M. Advances in drug delivery systems based on synthetic poly(hydroxybutyrate) (co)polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 73, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errico, C.; Bartoli, C.; Chiellini, F.; Chiellini, E. Poly(hydroxyalkanoates)-based polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2009, 2009, 571702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althuri, A.; Mathew, J.; Sindhu, R.; Banerjee, R.; Pandey, A.; Binod, P. Microbial synthesis of poly-3-hydroxybutyrate and its application as targeted drug delivery vehicle. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 145, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano, L.; Camposeo, A.; Tekmen, C.; Pisignano, D. Industrial upscaling of electrospinning and applications of polymer nanofibers: A review. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 504–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, W.E.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on electrospinning design and nanofibre assemblies. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, R89–R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almuhamed, S.; Bonne, M.; Khenoussi, N.; Brendle, J.; Schacher, L.; Lebeau, B.; Adolphe, D.C. Electrospinning composite nanofibers of polyacrylonitrile/synthetic na-montmorillonite. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 35, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.-L.; Chen, P.-Y.; Lan, C.-H.; Sun, Y.-M. Structure, mechanical properties and degradation behaviors of the electrospun fibrous blends of phbhhx/pdlla. Polymer 2011, 52, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagiah, N.; Madhavi, L.; Anitha, R.; Anandan, C.; Srinivasan, N.T.; Sivagnanam, U.T. Development and characterization of coaxially electrospun gelatin coated poly (3-hydroxybutyric acid) thin films as potential scaffolds for skin regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 4444–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puppi, D.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Chiellini, F.; Sun, X.; Chiellini, E. Nano/microfibrous polymeric constructs loaded with bioactive agents and designed for tissue engineering applications: A review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2014, 102, 1562–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puppi, D.; Chiellini, F. 12-drug release kinetics of electrospun fibrous systems. In Core-Shell Nanostructures for Drug Delivery and Theranostics; Focarete, M.L., Tampieri, A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK; Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 349–374. [Google Scholar]
- Sombatmankhong, K.; Suwantong, O.; Waleetorncheepsawat, S.; Supaphol, P. Electrospun fiber mats of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate), poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate), and their blends. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 2923–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sombatmankhong, K.; Sanchavanakit, N.; Pavasant, P.; Supaphol, P. Bone scaffolds from electrospun fiber mats of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate), poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and their blend. Polymer 2007, 48, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramier, J.; Grande, D.; Bouderlique, T.; Stoilova, O.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Langlois, V.; Albanese, P.; Renard, E. From design of bio-based biocomposite electrospun scaffolds to osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2014, 25, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, D.; Ramier, J.; Versace, D.L.; Renard, E.; Langlois, V. Design of functionalized biodegradable PHA-based electrospun scaffolds meant for tissue engineering applications. New Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, M. Study on the morphologies and formational mechanism of poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) ultrafine fibers by dry-jet-wet-electrospinning. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 525419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppi, D.; Piras, A.M.; Detta, N.; Dinucci, D.; Chiellini, F. Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) electrospun fibrous meshes for the controlled release of retinoic acid. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daranarong, D.; Chan, R.T.H.; Wanandy, N.S.; Molloy, R.; Punyodom, W.; Foster, L.J.R. Electrospun polyhydroxybutyrate and poly(L-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) composites as nanofibrous scaffolds. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 741408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hadi, A.M. Improvement of the miscibility by combination of poly(3-hydroxy butyrate) phb and poly(propylene carbonate) ppc with additives. J. Polym. Environ. 2017, 25, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagiah, N.; Madhavi, L.; Anitha, R.; Srinivasan, N.T.; Sivagnanam, U.T. Electrospinning of poly (3-hydroxybutyric acid) and gelatin blended thin films: Fabrication, characterization, and application in skin regeneration. Polym. Bull. 2013, 70, 2337–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhijiang, C.; Yi, X.; Haizheng, Y.; Jia, J.; Liu, Y. Poly(hydroxybutyrate)/cellulose acetate blend nanofiber scaffolds: Preparation, characterization and cytocompatibility. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, D.; Karbasi, S.; Razavi, S.; Mohammadi, S.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Bonakdar, S. Electrospun poly(hydroxybutyrate)/chitosan blend fibrous scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramier, J.; Boubaker, M.B.; Guerrouache, M.; Langlois, V.; Grande, D.; Renard, E. Novel routes to epoxy functionalization of PHA-based electrospun scaffolds as ways to improve cell adhesion. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2014, 52, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemechko, P.; Ramier, J.; Versace, D.L.; Guezennec, J.; Simon-Colin, C.; Albanese, P.; Renard, E.; Langlois, V. Designing exopolysaccharide-graft-poly(3-hydroxyalkanoate) copolymers for electrospun scaffolds. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versace, D.-L.; Ramier, J.; Babinot, J.; Lemechko, P.; Soppera, O.; Lalevee, J.; Albanese, P.; Renard, E.; Langlois, V. Photoinduced modification of the natural biopolymer poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) microfibrous surface with anthraquinone-derived dextran for biological applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 4834–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versace, D.-L.; Ramier, J.; Grande, D.; Andaloussi, S.A.; Dubot, P.; Hobeika, N.; Malval, J.-P.; Lalevee, J.; Renard, E.; Langlois, V. Versatile photochemical surface modification of biopolyester microfibrous scaffolds with photogenerated silver nanoparticles for antibacterial activity. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Tobías, H.; Morales, G.; Ledezma, A.; Romero, J.; Saldívar, R.; Langlois, V.; Renard, E.; Grande, D. Electrospinning and electrospraying techniques for designing novel antibacterial poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)/zinc oxide nanofibrous composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 8593–8609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramier, J.; Bouderlique, T.; Stoilova, O.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I.; Langlois, V.; Renard, E.; Albanese, P.; Grande, D. Biocomposite scaffolds based on electrospun poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) nanofibers and electrosprayed hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 38, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangeon, C.; Mahouche-Chergui, S.; Versace, D.L.; Guerrouache, M.; Carbonnier, B.; Langlois, V.; Renard, E. Poly(3-hydroxyalkanoate)-grafted carbon nanotube nanofillers as reinforcing agent for PHAs-based electrospun mats. React. Funct. Polym. 2015, 89, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.-Y.; Chen, P.-Y.; Sun, Y.-M.; Lee, Y.-T.; Young, T.-H. Response of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) to the topographic variation of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) (PHBHHx) films. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2012, 23, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.-W.; Wang, M. Electrospinning of aligned biodegradable polymer fibers and composite fibers for tissue engineering applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2007, 7, 3834–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.-W.; Wang, M.; Lu, W.W. Electrospun poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) fibrous membranes consisting of parallel-aligned fibers or cross-aligned fibers: Characterization and biological evaluation. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2011, 22, 2475–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, R.; Wang, P.-P.; Jian, J.; Jiang, X.-L.; Yan, C.; Lin, X.; Wu, L.; Chen, G.-Q.; Wu, Q. The differential effects of aligned electrospun phbhhx fibers on adipogenic and osteogenic potential of mscs through the regulation of pparγ signaling. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volova, T.; Goncharov, D.; Sukovatyi, A.; Shabanov, A.; Nikolaeva, E.; Shishatskaya, E. Electrospinning of polyhydroxyalkanoate fibrous scaffolds: Effects on electrospinning parameters on structure and properties. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2014, 25, 370–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslantunali, D.; Dursun, T.; Yucel, D.; Hasirci, N.; Hasirci, V. Peripheral nerve conduits: Technology update. Med. Devices (Auckl.) 2014, 7, 405–424. [Google Scholar]
- Awad, N.K.; Niu, H.; Ali, U.; Morsi, Y.S.; Lin, T. Electrospun fibrous scaffolds for small-diameter blood vessels: A review. Membranes 2018, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard F2792-12a. Standard terminology for additive manufacturing technologies (Withdrawn 2015); ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mota, C.; Puppi, D.; Chiellini, F.; Chiellini, E. Additive manufacturing techniques for the production of tissue engineering constructs. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2015, 9, 174–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chartrain, N.A.; Williams, C.B.; Whittington, A.R. A review on fabricating tissue scaffolds using vat photopolymerization. Acta Biomater. 2018, 74, 90–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.M.; Adewunmi, A.; Schek, R.M.; Flanagan, C.L.; Krebsbach, P.H.; Feinberg, S.E.; Hollister, S.J.; Das, S. Bone tissue engineering using polycaprolactone scaffolds fabricated via selective laser sintering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 4817–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butscher, A.; Bohner, M.; Hofmann, S.; Gauckler, L.; Müller, R. Structural and material approaches to bone tissue engineering in powder-based three-dimensional printing. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 907–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, B.N.; Strong, R.; Gold, S.A. A review of melt extrusion additive manufacturing processes: I. Process design and modeling. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2014, 20, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppi, D.; Chiellini, F. Wet-spinning of biomedical polymers: From single-fibre production to additive manufacturing of three-dimensional scaffolds. Polym. Int. 2017, 66, 1690–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppi, D.; Morelli, A.; Bello, F.; Valentini, S.; Chiellini, F. Additive manufacturing of poly(methyl methacrylate) biomedical implants with dual-scale porosity. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1800247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.F.; Maia, I.A.; Noritomi, P.Y.; Nargi, G.C.; Silva, J.V.L.; Ferreira, B.M.P.; Duek, E.A.R. Construção de scaffolds para engenharia tecidual utilizando prototipagem rápida. Matéria 2007, 12, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.F.; Silva, M.A.C.; Oliveira, M.F.; Maia, I.A.; Silva, J.V.L.; Costa, M.F.; Thiré, R.M.S.M. Effect of process parameters on the properties of selective laser sintered poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2012, 7, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.F.; Oliveira, M.F.; Maia, I.A.; Silva, J.V.L.; Costa, M.F.; Thiré, R.M.S.M. 3d printing of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) porous structures using selective laser sintering. Macromol. Symp. 2012, 319, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Wang, M.; Zhou, W.Y.; Cheung, W.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Lu, W.W. Three-dimensional nanocomposite scaffolds fabricated via selective laser sintering for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 4495–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, B.; Wang, M. Customized Ca–P/PHBV nanocomposite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: Design, fabrication, surface modification and sustained release of growth factor. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, S615–S629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, B.; Cheung, W.L.; Wang, M. Optimized fabrication of Ca–P/PHBV nanocomposite scaffolds via selective laser sintering for bone tissue engineering. Biofabrication 2011, 3, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosorn, W.; Sakulsumbat, M.; Uppanan, P.; Kaewkong, P.; Chantaweroad, S.; Jitsaard, J.; Sitthiseripratip, K.; Janvikul, W. PCL/PHBV blended three dimensional scaffolds fabricated by fused deposition modeling and responses of chondrocytes to the scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105B, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota, C.; Wang, S.Y.; Puppi, D.; Gazzarri, M.; Migone, C.; Chiellini, F.; Chen, G.Q.; Chiellini, E. Additive manufacturing of poly[(r)-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-(r)-3-hydroxyhexanoate] scaffolds for engineered bone development. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2017, 11, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menčík, P.; Přikryl, R.; Stehnová, I.; Melčová, V.; Kontárová, S.; Figalla, S.; Alexy, P.; Bočkaj, J. Effect of selected commercial plasticizers on mechanical, thermal, and morphological properties of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)/poly(lactic acid)/plasticizer biodegradable blends for three-dimensional (3d) print. Materials 2018, 11, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-S.; Liao, H.-T.; Cai, Y.-X. Characterisation, biodegradability and application of palm fibre-reinforced polyhydroxyalkanoate composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 140, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-S.; Liao, H.-T. Fabrication, characterization, and application of polyester/wood flour composites. J. Polym. Eng. 2017, 37, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.S.; Liao, H.T. Interface design of environmentally friendly carbon nanotube-filled polyester composites: Fabrication, characterisation, functionality and application. Express Polym. Lett. 2017, 11, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppi, D.; Mota, C.; Gazzarri, M.; Dinucci, D.; Gloria, A.; Myrzabekova, M.; Ambrosio, L.; Chiellini, F. Additive manufacturing of wet-spun polymeric scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomed. Microdevices 2012, 14, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppi, D.; Pirosa, A.; Morelli, A.; Chiellini, F. Design, fabrication and characterization of tailored poly[(r)-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-(r)-3-hydroxyexanoate] scaffolds by computer-aided wet-spinning. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2018, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppi, D.; Morelli, A.; Chiellini, F. Additive manufacturing of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate)/poly(ε-caprolactone) blend scaffolds for tissue engineering. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puppi, D.; Pirosa, A.; Lupi, G.; Erba, P.A.; Giachi, G.; Chiellini, F. Design and fabrication of novel polymeric biodegradable stents for small caliber blood vessels by computer-aided wet-spinning. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 12, 035011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller, M.; Maršálek, L.; de Sousa Dias, M.M.; Braunegg, G. Producing microbial polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) biopolyesters in a sustainable manner. New Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puppi, D.; Pecorini, G.; Chiellini, F. Biomedical Processing of Polyhydroxyalkanoates. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering6040108
Puppi D, Pecorini G, Chiellini F. Biomedical Processing of Polyhydroxyalkanoates. Bioengineering. 2019; 6(4):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering6040108
Chicago/Turabian StylePuppi, Dario, Gianni Pecorini, and Federica Chiellini. 2019. "Biomedical Processing of Polyhydroxyalkanoates" Bioengineering 6, no. 4: 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering6040108
APA StylePuppi, D., Pecorini, G., & Chiellini, F. (2019). Biomedical Processing of Polyhydroxyalkanoates. Bioengineering, 6(4), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering6040108