Abstract
Imaging plays a critical role in the management of the highly complex and widely diverse central nervous system (CNS) malignancies in providing an accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, response assessment, prognosis, and surveillance. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the primary modality for CNS disease management due to its high contrast resolution, reasonable spatial resolution, and relatively low cost and risk. However, defining tumor response to radiation treatment and chemotherapy by contrast-enhanced MRI is often difficult due to various factors that can influence contrast agent distribution and perfusion, such as edema, necrosis, vascular alterations, and inflammation, leading to pseudoprogression and pseudoresponse assessments. Amino acid positron emission tomography (PET) is emerging as the method of resolving such equivocal lesion interpretations. Amino acid radiotracers can more specifically differentiate true tumor boundaries from equivocal lesions based on their specific and active uptake by the highly metabolic cellular component of CNS tumors. These therapy-induced metabolic changes detected by amino acid PET facilitate early treatment response assessments. Integrating amino acid PET in the management of CNS malignancies to complement MRI will significantly improve early therapy response assessment, treatment planning, and clinical trial design.
1. Introduction
Malignancies of the central nervous system (CNS) account for an estimated 23,000 cases and over 16,000 deaths each year [1]. Cerebral gliomas are second to meningiomas in frequency and account for the highest number of cancer mortalities in adults under the age of 35 [2]. Brain tumors arising from metastasis originating from peripheral tumors such as lymphoma, melanoma, lung, and breast cancer occur at an even a higher rate with an incidence of 9–17% [3].
The most recent 2016 World Health Organization (WHO) Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System defines CNS malignancies within four categories (grades I, II, III, and IV) based on molecular parameters and histology [4]. Grades I and II gliomas are devoid of anaplastic features and are classified as low-grade gliomas (LGG). High-grade gliomas (HGG) are classified in grades III and IV and include the most aggressive form, glioblastoma (grade IV), which has a median overall survival of 1.5 years [5].
The complexity and diversity of CNS malignancies necessitate a multifaceted approach to therapy that includes surgery, radiation treatment, chemotherapy and, more recently, immunotherapy. Historically, therapy of CNS tumors entailed surgery and radiotherapy. Improving outcomes relied on radiotherapy dose escalation and responses were measured by overall survival. With the advent of chemotherapeutics and immunotherapy (bevacizumab), radiographic assessment became necessary to assess immediate responses manifested in anatomic and molecular changes. Thus, imaging became an integral component of every stage of CNS disease management providing information that is critical to staging, formulating preoperative strategies, monitoring therapy response, surveillance, and prognosis.
2. Role of Vascularity in Magnetic Resonance Imaging of CNS Tumors
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the primary diagnostic method given its high soft tissue contrast, spatial resolution, low risk, ready availability and relatively low cost. Intensity contrast between tumor mass and surrounding brain tissue along with anatomical distortions of normal brain structures and contrast-enhanced regions typically delineate tumors in MR images although the tumor boundaries are often notoriously difficult to demonstrate accurately by imaging. T1- and T2-weighted and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) are the standard sequences utilized. Compared to healthy brain tissue, CNS tumors typically appear hypointense to myelinated white matter on T1-weighted images and hyperintense on T2. Other structural characteristics associated with tumor mass may include cysts, necrosis, hemorrhage, and calcification.
CNS tumors are generally hyper-vascularized in contrast to the highly structured and selectively permeable blood-brain barrier (BBB), which acts to protect the privileged chemical environment of the brain. The BBB is formed by tight junctions between endothelial cells supported by pericytes and astrocytic foot processes limiting permeability to the vast majority of circulating agents [6]. Although microglia within the vicinity of blood vessels can repair a transient injury to the BBB [7], pathologies of the brain can compromise the integrity of the barrier increasing permeability to large therapeutic agents such as antibody drugs [8,9,10]. Access of anti-CTLA antibodies and bevacizumab, for example, depend explicitly on a compromise of the BBB [11].
In contrast to the highly integrated nature of the BBB [12,13], tumor vascularity is irregular, leaky, and poorly structured. This abnormality gives rise to permeability, interstitial fluid pressure, hypoxia, necrosis, and edema characteristically exhibited by glioblastomas. Aberrant tumor vascularity can be established within the structured BBB environment by metastatic cancer cells that are capable of breaching and penetrating the tight junctions of the barrier through adherence and proteolytic processes that mimic leukocyte extravasation. Once established beyond the BBB, the metastatic tumor microenvironment signals the development of a new heterogenic vascular supply characterized by increased permeability due to altered pericyte composition [14]. This leaky neovasculature can favorably influence the delivery of therapeutics by way of leakiness but may also unfavorably raise interstitial pressures to resist penetration of therapeutic agents [12].
The vascular disparity between the tumor and healthy brain tissue facilitates contrast-enhanced tumor resolution with gadolinium agents for critical response assessments of CNS tumors by MRI [15,16,17]. Increased tumor vascularity is a surrogate of elevated proliferation and aggressiveness and has been employed to delineate tumors through perfusion contrast-enhancing agents to diagnose and monitor brain tumor response. Congruently, the hypervascularity of glioblastomas has also been exploited as a therapeutic target of antiangiogenic drugs such as bevacizumab. Although bevacizumab has yielded little improvement of overall survival, an undefined subset of glioma patients do receive survival benefit from this agent, and a marginal improvement of progression-free survival and quality of life has justified the use of the drug in combination with standard-of-care regimens [18].
3. Limitations of Treatment Response Assessments by MRI
The role of imaging in CNS tumor management has evolved to meet the needs of advances in therapy. Early therapeutic approaches relied primarily on resection and postoperative radiotherapy of CNS malignancies. These measures provided a survival benefit which was reflected in overall survival as the primary endpoint. Renewed efforts over the last 30 years to improve therapeutic outcomes through radiation dose escalation and adjuvant chemotherapy necessitated formulating new early response assessment parameters to provide objective and mechanistic insights into treatment response [19]. Consequently, the Macdonald criteria were established in 1990 as a means of reporting early radiographic response based on contrast-enhanced computed tomography and MRI [20]. The Macdonald criteria use contrast enhancement metrics to objectively stratify therapeutic responses into four categories: (1) complete response, (2) partial response, (3) stable disease, and (4) progressive disease [20,21].
Progression-free survival is a more immediate assessment of therapeutic efficacy and serves the needs of a more precise readout for specific therapies. This requires an accurate imaging readout at chosen intermediate time points during therapy. However, the limitations of anatomic and volumetric measurements, compounded by the subjective interpretation of equivocal lesions have hindered the ability of current imaging modalities in providing an intermediate clinical readout. These inadequacies with the Macdonald metrics became apparent with recognition of contrast-enhancing or -diminishing artifacts elicited by radiation-induced necrosis and the alteration of vascularity by chemotherapy (temozolomide) and immunotherapies (bevacizumab) leading to misinterpretation of therapeutic responses. These artifacts have introduced new caveats in the interpretation of radiological data based on the Macdonald criteria.
Therapies affecting vascular permeability and perfusion give rise to the phenomena of pseudoprogression and pseudoresponse where the tumor alternately appears worse or better on imaging due to spurious effects on the vasculature. This presents a formidable challenge to the accurate and objective evaluation of therapeutic outcomes, as intermediate time points gauging progression-free survival become very difficult to interpret (Figure 1).
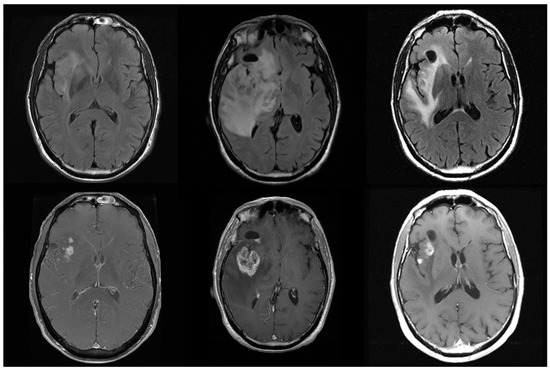
Figure 1.
Glioblastoma (WHO IV) patient at presentation (left), shows an insular tumor with islands of enhancement. Following 60 Gy of radiation with Temozolamide 75 mg/m2 daily (middle column), there is an apparent increase in both enhancement and edema with mass effect. These worsened imaging findings resolve one month later with Decadron 6 mg twice daily, with a near return to imaging baseline. This apparent worsening on imaging is known as pseudoprogression and represents an inflammatory response to therapy that is difficult to distinguish from true progression. Pseudoprogression complicates the imaging and clinical management of glioma patients.
Increased BBB permeability, necrosis, inflammation, and hemorrhage may be instigated by radiation-induced injury along with edema, and can appear mass-like on imaging. Unlike a tumor mass, however, these contrast-enhancing regions are not associated with cellular density or vascular intensity but represent a site of tissue breakdown and leakiness that mimics many of the imaging attributes of a tumor. The combination of radiotherapy and cytotoxic agents will often cause this effect and is known as pseudoprogression, which mimics the imaging appearance of tumor progression and can even cause clinical symptoms due to mass effect but is not due to true progressive disease. Checkpoint-blockade immunotherapy is also likely to present as pseudoprogression [22].
Conversely, antiangiogenic agents, such as bevacizumab, may cause short-term decreased perfusion and reduced contrast enhancement due to "normalization" of the tumor vasculature leading to a false appearance of treatment response, or pseudoresponse, not associated with a real anti-tumor effect or improved overall survival [23,24]. Bevacizumab’s effects can cause imaging to show decreased T1 contrast enhancement, edema, and mass effect. This imaging outcome, however, does not correlate with long-term benefit or improved overall survival [24].
The challenges and limitations associated with MRI limit objective assessment of timely therapy response assessment and prognostication. Contrast-enhanced MRI is mostly a function of BBB integrity and tumor vascularity and is, therefore, a nonspecific form of tumor mass characterization that is prone to equivocal interpretation. These imaging artifacts may be instigated by transient effects of therapeutic interventions enhancing contrast leading to overestimation of their therapeutic efficacy. Therefore, evaluation over multiple time points is critical to circumvent misinterpretation of the single-point transient anomaly.
4. Positron Emission Tomography of CNS Tumors
Positron emission tomography (PET) is an imaging modality that is based on the preferential uptake and retention of radiolabeled tracers by the target tissue. These radiotracers mimic or are sometimes chemically identical to, metabolites that are avidly taken up by proliferative cells to meet their energy or biomass demands. Tumor cells have a higher tendency to absorb these metabolites generating contrast in uptake between tumor mass and surrounding healthy tissue.
The development of PET radiotracers has addressed some of the limitations of structural MRI in discerning pseudoprogression from true progression. Tumor delineation based on metabolic radiotracer uptake offers a functional basis of detection that yields enhanced differentiation of tumor from equivocal lesions over MRI, improved delineation of tumor boundaries for surgery and radiotherapy planning, differentiation between tumor progression and treatment-related responses, and monitoring of tumor response to therapy.
Over the last four decades, PET with 2-deoxy-2-[18F]-fluoro-D-glucose (18F-FDG PET) combined with computed tomography has emerged as a standard-of-care imaging modality for the detection of tumors based on their elevated glucose metabolic rate (Warburg effect). The utility of 18F-FDG PET in imaging brain tumors, however, is hindered by the elevated background uptake level of glucose by normal brain tissue generating little discernable contrast. Moreover, immune cell activation within inflammatory responses also exhibits elevated glucose metabolism further obscuring distinction from brain or tumor tissue [25]. While metabolic contrast between tumor and healthy brain for FDG is low, there are considerable differences for amino acid and nucleotide metabolism. Tumor cell division (DNA replication) and growth (biomass generation) demand amino acid and nucleotide building blocks to meet the needs of the rapidly proliferating cells.
Accordingly, elevated DNA replication of tumor cells can be readily discerned using 3′-deoxy-3′-18F-fluorothymidine (18F-FLT) PET against the background of the relatively quiescent normal brain cells. Importantly, 18F-FLT does not readily accumulate in inflammatory lesions, as is the case with 18F-FDG, and is, therefore, able to report on cellular proliferation. Inflammatory immune cells primarily undergo aerobic glycolysis during activation, and are, therefore, not detected by 18F-FLT. The specificity of 18F-FLT for cellular proliferation facilitates its utility in reporting on tumor response to therapy [26] and has been shown to a better predictor of overall survival than MRI following treatment of recurrent gliomas with bevacizumab and irinotecan [27]. Moreover, 18F-FLT uptake detects treatment response early and is highly predictive of overall and progression-free survival following bevacizumab treatment [28,29]. However, the need for BBB breakdown for 18F-FLT limits its reliability in reporting on brain tumor treatment response [30].
4.1. Amino Acid PET
Amino acid PET has been evaluated extensively for detecting tumor mass based on metabolic tumor volume and is playing an increasingly important role in the management of CNS tumors. Ambiguous brain lesions that may complicate an accurate diagnosis of brain malignancies include hemorrhage, necrosis, edema, infarctions, abscesses, and inflammation. These extraneous lesions may be caused by a response to radio- and chemotherapy (inflammation and necrosis) or secondary anatomical disruptions caused by tumor outgrowth. In contrast to structural MRI, which cannot accurately differentiate lesion traits, amino acid radiotracer accumulation is a function of tumor avidity for the carbon source to meet its high demands for biomass and energy generation. This differential uptake of amino acid tracers can be exploited to specifically delineate cellular mass and tumor boundaries from surrounding normal tissue. Analogs of methionine, tyrosine, phenylalanine, alanine, and leucine have been evaluated for their specificity in delineating CNS tumors yielding nearly equally effective outcomes.
The ability of amino acid tracers to cross the BBB is a crucial advantage that transcends the limitations of contrast-enhanced MRI, which relies on leaky vascularity or compromise of the barrier for delivery of contrast enhancing agents. Compromise of the BBB by tumor growth does not appear to be a requirement for amino acid tracer permeability [31,32]. The intracellular uptake of amino acid tracers by the tumor cells is an active process facilitated by the L (large) transport system with subtypes LAT1 and LAT2 and is, therefore, more specific in reporting on live proliferating cells rather than structural changes [33,34,35,36]. This is further evidenced by dexamethasone or antiangiogenic treatment with bevacizumab not affecting amino acid uptake by brain tumors [37,38]. Prior or ongoing treatment with temozolomide, however, may impact the tumor-to-background ratio of amino acid uptake and must be considered in therapy response assessments [39].
The PET radiotracer [11C-methyl]-l-methionine (11C-MET) is the most well-established and utilized amino acid probe. 11C-MET PET has been shown to be useful in delineating ependymomas, medulloblastoma, and astrocytomas in pediatric patients and can also effectively differentiate between radiation-induced brain tissue injury and tumor recurrence [40,41,42,43]. It is superior to MRI in differentiating tumor necrosis following gamma knife radiosurgery from recurrent tumor [44] and offers accurate tumor size correlation of WHO grades II and III meningiomas [45].
The short 20-min half-life of the 11C, however, limits the practical implementation of 11C-MET PET to highly specialized imaging centers with onsite cyclotron facilities. Consequently, 18F-labeled amino acid tracers (with a half-life of 110 min), such as O-(2-18F-fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine (18F-FET), 3,4-dihydroxy-6-18F-fluoro-l-phenylalanine (18F-FDOPA), and anti-1-amino-3-18F-fluorocyclobutane-1-carboxylic acid (18F-FACBC, fluciclovine, a non-natural amino acid) have been developed among many others to overcome this logistical limitation. Amino acid radiotracers, such as 18F-FET, also exhibit tumor type-specific kinetics that can facilitate differential diagnosis of CNS tumors [46,47,48,49,50,51] (Figure 2). Metabolic changes in response to bevacizumab treatment of glioblastoma identified by 18F-FET PET imaging occur earlier than morphologic changes providing a more immediate indication of tumor progression than changes detected by MRI [52]. Both 11C-MET and 18F-FACBC were able to differentiate tumor from equivocal lesions (edema) [53].
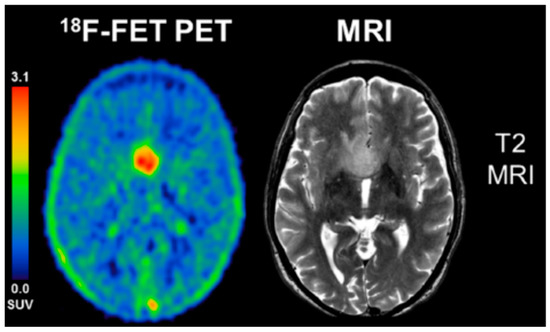
Figure 2.
18F-FET PET summation image from 5–15 min is contrasted to a T2 MR image in this patient with a WHO III astrocytoma, IDH-wild-type, without 1p/19q co-deletion. This was a non-enhancing tumor on MRI. Note excellent tumor to background contrast for the FET PET image, with standard uptake values (SUV) of up to 3. Adapted from Unterrainer et al. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 1242 with permission [51].
Although 18F-FDOPA exhibits differential tumor uptake, its similarity to dopamine results in preferential accumulation in the striatum presenting an obstacle to accurately demarcating gliomas involving this region of the brain [54]. In comparison to 11C-MET, 18F-FACBC yields lower background accumulation levels (i.e., higher tumor-to-brain signal ratios) and, hence, higher detection sensitivity and specificity. 18F-FDOPA PET metabolic tumor volume measurements at two weeks following antiangiogenic treatment are highly predictive of outcome. A first follow-up scan at two weeks predicted increased overall survival and progression-free survival. Responders identified based on 18F-FDOPA-PET survived 3.5 times longer in contrast to responders identified by MRI who lived 1.5 times longer. 18F-FDOPA PET is more accurate at identifying responders only two weeks following antiangiogenic treatment [55].
4.2. Response to Therapy
Specific detection of early responses to therapy is a significant advantage of amino acid PET as it can specifically differentiate the cellular component of a tumor mass from inflammatory and necrotic lesions. Amino acid PET detects metabolic changes, which occur earlier than morphological changes detected by MRI in response to chemotherapy, radiation treatment, or antiangiogenic treatment. Favorable outcomes following three cycles of temozolomide treatment can be predicted by reduced 11C-MET uptake in high-grade glioma patients [56,57]. Furthermore, the tumor-associated breakdown of the BBB does not appear to be a requirement for amino acid tracer permeability resulting in more accurate tumor boundary delineation even after vascular normalization by bevacizumab [31,32]. 18F-FET and 18F-FDOPA can be used to detect response to bevacizumab treatment before the appearance of morphological changes and thus provide a much earlier prediction of response [52,55,58]. In preclinical glioma models, 18F-FET PET reports on early response to combination therapy with temozolomide, interferon-beta, or bevacizumab [59]. Management of recurrent high-grade glioma patients treated with bevacizumab and radiotherapy using 18F-FET PET and MRI is cost effective and may potentially enhance the treatment quality. These outcomes are realized by the avoidance of unnecessary costs associated with overtreatment and unnecessary side effects [60].
4.3. Grade Differentiation
Differentiation between low and high-grade gliomas by imaging is a potentially beneficial diagnostic tool that would enhance the management of CNS tumors. Generally, WHO grade I and II tumors and a significant number of WHO grade III gliomas are contrast non-enhancing on MRI limiting tumor burden and therapy response assessments. Furthermore, differentiation between LGG and HGG by MRI remains challenging.
The utility of amino acid PET to differentiate between LGG and HGG based on the level of radiotracer uptake has been assessed in a limited number of studies. Generally, amino acid uptake is higher in grade III/IV gliomas compared to grade I/II [61,62,63]. [N-methyl-11C] alpha-Methylaminoisobutyric acid (11C-MeAIB), an amino acid analog, can differentiate between low-grade and high-grade astrocytoma as determined by the tumor to normal brain uptake ratio [64]. Differential uptake of alpha-[11C] methyl-l-tryptophan (11C-AMT) can be used to identify LGGs, even if they are not contrast-enhancing on MRI, and distinguish them from HGGs based on tumor-to-cortex radiotracer uptake [65].
Despite differential LGG/HGG imaging in many studies, a recent systematic review of amino acid PET of LGGs has revealed a difficulty in interpretation due to inconsistencies in radiotracer uptake and different correlations between uptake ratios and LGG molecular status [66]. Radiotracer uptake intensities for each group can vary widely resulting in overlap and unreliable preoperative grading [67].
Kinetic PET imaging, however, may offer a better differentiating parameter based on the differing rate of radiotracer uptake by LGG and HGG. Time-activity curves of grade II tumors exhibit a slow, steady increase compared to the rapid uptake of amino acid radiotracers by grade III/IV tumors. Thus, LGG and HGG can be more reliably differentiated based on a dynamic or dual-time-point PET than static or endpoint imaging [47,48,61,68,69,70].
4.4. Prognostication
As an extension to its capacity to report on the early response to therapy, amino acid PET has proven to be a reliable prognostic tool in predicting overall and progression-free survival. Decreased 18F-FET uptake following radiochemotherapy was associated with overall survival compared to increased or stable uptake [71,72]. True responders to bevacizumab treatment following recurrent glioma identified by 11C-MET PET at eight weeks were predicted to have more favorable prognoses [73]. Determination of metabolic tumor volume of 11C-MET-PET is prognostic of progression-free survival in high-grade glioma patients [74] and predictive of patients developing recurrent malignant glioma [75].
Amino acid uptake may also serve as a reliable predictor of survival in patients with LGGs. 18F-FET PET combined with anatomic MRI predicted outcome and progression-free survival [76]. Kinetics of amino acid uptake have also been demonstrated to be useful in predicting regions of malignant transformation and progression within LGG [70,77]. Detection of metabolic abnormalities in LGGs by amino acid PET following treatment may also serve as a predictor of tumor recurrence [78].
4.5. Biopsy Guidance
Diagnostic inaccuracies based on image interpretation carry risk and compromise CNS tumor therapy outcomes. Biopsy provides diagnostic accuracy at a higher rate than neuroimaging and is essential to tumor grading and treatment planning. Therefore, image-guided stereotactic biopsy of tumor volumes is crucial to achieving higher diagnostic yields. Delineation of tumor extent and identification of regions of higher grade and density with 18F-FET and 18F-DOPA PET proved useful for biopsy guidance and resection planning in most cerebral glioma cases compared to 18F-FDG [67,79,80,81]. Needle guidance to hypermetabolic foci by PET produce a higher diagnostic yield than MRI reducing sampling to a single trajectory. Reducing sampling frequency through accurate image data is particularly important to minimize the risks associated with a biopsy of intrinsic infiltrative brainstem malignancies [82].
4.6. Case Studies Validating Amino Acid PET
Some case studies illustrate the advantages of amino acid PET over MRI in delineating tumor extent, informing on response to therapy, and detecting disease recurrence. Amino acid uptake has also been shown to be consistent with exhibited symptoms and biopsy results. A unique case study involving a 37-year old woman with a “butterfly” glioblastoma exemplifies tumor extent delineation by amino acid PET. MRI findings were equivocal and imprecise, indicating bifocal growth with slight contrast enhancement despite the large extent of the bilateral tumor mass. 11C-MET PET was more diagnostically precise than contrast-enhanced MRI in delineating a broad and continuous tumor mass [83].
Amino acid PET has also proved valuable in detecting recurrence and differentiating it from pseudoprogression as confirmed by biopsy. Detection of recurrence by PET was illustrated by high 18F-DOPA uptake in the left parietal lobe of a 46-year-old patient, where resection of a glioma had taken place two years earlier. 18F-FDG uptake was not elevated and did not indicate any abnormalities. Recurrence of the tumor in this patient was confirmed by biopsy demonstrating the accuracy of amino acid PET in detecting metabolic tumor volume [84]. Similarly, pseudoprogression has been reliably determined by amino acid PET in other case studies. Morphological changes on MRI suggested recurrent tumor eight months following radiochemotherapy in a glioblastoma patient. 18F-FET PET, however, was negative for focal uptake and, indeed, histopathology of the resected tumor revealed necrotic tissue consistent with pseudoprogression. The lesion regressed in follow-up MRI further confirming the diagnosis [85].
In contrast to MRI, consistency of amino acid uptake with patient symptoms has been demonstrated in a number of case studies. Vision problems exhibited by 16-year old female optic pathway glioma patient correlated with an increase in 11C-AMT uptake indicating recurrence. 11C-AMT uptake decreased upon chemotherapy and radiotherapy and correlated with a symptomatic improvement [86]. Likewise, 18F-MET PET was able to detect recurrence of a benign oligodendroglioma in a patient exhibiting recurrent temporal epileptic seizures 15 months following resection. 18F-MET PET uptake was high in the region of the previous tumor. Secondary resection and biopsy confirmed recurrence as predicted by PET [87]. In both of these cases, MRI did not reveal morphological changes indicating tumor recurrence and was inconsistent with exhibited patient symptoms.
5. Combined PET/MRI for the Management of CNS Tumors
The strength of MRI in providing high anatomical resolution of soft brain tissue coupled with the specificity of amino acid PET in delineating CNS tumors promote combining the modalities to improve diagnostic specificity in the management of CNS malignancies. When combined with MRI, 11C-MET-PET has been shown to be a reliable identifier of true responders to bevacizumab therapy with favorable prognoses [73,88,89]. Furthermore, improved diagnostic confidence of primary low-grade astrocytoma and high-grade astrocytomas [90] and reliable early differentiation between tumor recurrence and radionecrosis in high-grade glioma patients have been demonstrated [91]. The benefits of combined PET/MRI have also been extended to pediatric patient management and found to be well-tolerated and have been recommended for early prediction of response [92].
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Metabolic changes detected by amino acid PET occur in response to therapy sooner than morphological and structural changes providing an earlier response to therapy assessment and prognosis. Moreover, metabolic uptake of radiolabeled amino acids is specific to the proliferating cellular component of the tumor, occurs independently of the status of the blood-brain barrier, and excludes non-cellular lesions created by necrosis, edema, and inflammation. As summarized in Figure 3, these advantages offered by amino acid PET translate into precise tumor boundary delineation and early treatment response assessments that transcend MRI-based limitations of pseudoprogression and pseudoresponse.
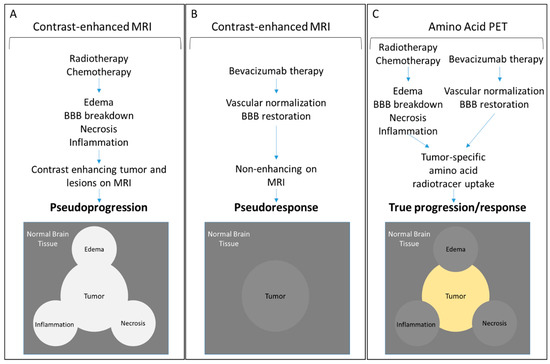
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of MRI and PET outcomes following treatment of CNS tumors. (A) Radiotherapy and chemotherapy of CNS tumors can lead to edema, necrosis, inflammation, and breakdown of the BBB creating contrast-enhancing lesions that obscure tumor boundaries and lead to pseudoprogression. (B) Conversely, vascular normalization following bevacizumab treatment, without an associated anti-tumor response, can diminish contrast enhancement yielding a false appearance of treatment response or pseudoresponse. (C) Amino acid PET reports specifically on the accumulation of the radiotracers within the cellular component of the tumor mass reflecting correct tumor boundaries and immediate metabolic changes in response to therapy.
The advantages provided by amino acid PET justify its future implementation as a standard procedure in defining biopsy sites, planning surgical resection and radiotherapy, prognostication, and treatment response assessment [93,94]. These tangible benefits have been realized leading to the recommendation by the Response Assessment Neuro-Oncology (RANO) working group for the inclusion of amino acid PET in the management and diagnosis of brain tumors in conjunction with conventional MRI [95]. Complementing the limitations of MRI with the strengths of amino acid PET will lead to significant improvements in all aspects of CNS tumor management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: A.M.N., J.M.J., and D.S.; writing—original draft preparation: A.M.N.; writing—review, and editing: A.M.N., J.M.J., and D.S.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cancer Facts & Figures 2018. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/cancer-facts-figures-2018.html (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Liao, P.; Vecchione-Koval, T.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2010–2014. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19 (Suppl. S5), v1–v88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, L.; Lee, E.Q.; Wen, P.Y. Epidemiology of brain metastases. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 14, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohgaki, H.; Kleihues, P. Population-based studies on incidence, survival rates, and genetic alterations in astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 64, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, N.J. Blood-brain barrier structure and function and the challenges for CNS drug delivery. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2013, 36, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Fonseca, A.C.; Matias, D.; Garcia, C.; Amaral, R.; Geraldo, L.H.; Freitas, C.; Lima, F.R. The impact of microglial activation on blood-brain barrier in brain diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, N.J.; Ronnback, L.; Hansson, E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, D.C. Blood-brain barrier breakdown in septic encephalopathy and brain tumours. J. Anat. 2002, 200, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, M.C.; Saadoun, S.; Davies, D.C.; Bell, B.A. Emerging molecular mechanisms of brain tumour oedema. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2001, 15, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margolin, K.; Ernstoff, M.S.; Hamid, O.; Lawrence, D.; McDermott, D.; Puzanov, I.; Wolchok, J.D.; Clark, J.I.; Sznol, M.; Logan, T.F.; et al. Ipilimumab in patients with melanoma and brain metastases: An open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet. Oncol. 2012, 13, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Griffith, B.; Alotaibi, F.; Zagzag, D.; Fine, H.; Golfinos, J.; Schultz, L. Glioma Angiogenesis and Perfusion Imaging: Understanding the Relationship between Tumor Blood Volume and Leakiness with Increasing Glioma Grade. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 2030–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.K.; di Tomaso, E.; Duda, D.G.; Loeffler, J.S.; Sorensen, A.G.; Batchelor, T.T. Angiogenesis in brain tumours. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyle, L.T.; Lockman, P.R.; Adkins, C.E.; Mohammad, A.S.; Sechrest, E.; Hua, E.; Palmieri, D.; Liewehr, D.J.; Steinberg, S.M.; Kloc, W.; et al. Alterations in Pericyte Subpopulations Are Associated with Elevated Blood-Tumor Barrier Permeability in Experimental Brain Metastasis of Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5287–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, S.M.; Elliott, R.; Forshaw, D.; Golfinos, J.G.; Nelson, P.K.; Kelly, P.J. Glioma vascularity correlates with reduced patient survival and increased malignancy. Surg. Neurol. 2009, 72, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, S.P.; Folkerth, R.D.; Black, P.M. Microvessel density is a prognostic indicator for patients with astroglial brain tumors. Cancer 1996, 77, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesseling, P.; van der Laak, J.A.; Link, M.; Teepen, H.L.; Ruiter, D.J. Quantitative analysis of microvascular changes in diffuse astrocytic neoplasms with increasing grade of malignancy. Hum. Pathol. 1998, 29, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinot, O.L.; Wick, W.; Mason, W.; Henriksson, R.; Saran, F.; Nishikawa, R.; Carpentier, A.F.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Kavan, P.; Cernea, D.; et al. Bevacizumab plus radiotherapy-temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamborn, K.R.; Yung, W.K.; Chang, S.M.; Wen, P.Y.; Cloughesy, T.F.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Robins, H.I.; Lieberman, F.S.; Fine, H.A.; Fink, K.L.; et al. Progression-free survival: An important end point in evaluating therapy for recurrent high-grade gliomas. Neuro-Oncology 2008, 10, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, D.R.; Cascino, T.L.; Schold, S.C., Jr.; Cairncross, J.G. Response criteria for phase II studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 1990, 8, 1277–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinot, O.L.; Macdonald, D.R.; Abrey, L.E.; Zahlmann, G.; Kerloeguen, Y.; Cloughesy, T.F. Response assessment criteria for glioblastoma: Practical adaptation and implementation in clinical trials of antiangiogenic therapy. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2013, 13, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, V.L.; Burotto, M. Pseudoprogression and Immune-Related Response in Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3541–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.K. Antiangiogenic therapy for cancer: Current and emerging concepts. Oncology 2005, 19, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hygino da Cruz, L.C., Jr.; Rodriguez, I.; Domingues, R.C.; Gasparetto, E.L.; Sorensen, A.G. Pseudoprogression and pseudoresponse: Imaging challenges in the assessment of posttreatment glioma. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbel, C.; Patsoukis, N.; Bardhan, K.; Seth, P.; Weaver, J.D.; Boussiotis, V.A. Clinical significance of T cell metabolic reprogramming in cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollineni, V.R.; Kramer, G.M.; Jansma, E.P.; Liu, Y.; Oyen, W.J. A systematic review on [(18)F]FLT-PET uptake as a measure of treatment response in cancer patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 55, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Delaloye, S.; Silverman, D.H.; Geist, C.; Czernin, J.; Sayre, J.; Satyamurthy, N.; Pope, W.; Lai, A.; Phelps, M.E.; et al. Predicting treatment response of malignant gliomas to bevacizumab and irinotecan by imaging proliferation with [18F] fluorothymidine positron emission tomography: A pilot study. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4714–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenberg, J.; Czernin, J.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Ellingson, B.M.; Pope, W.B.; Geist, C.; Dahlbom, M.; Silverman, D.H.; Satyamurthy, N.; Phelps, M.E.; et al. 3′-deoxy-3′-18F-fluorothymidine PET and MRI for early survival predictions in patients with recurrent malignant glioma treated with bevacizumab. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardak, M.; Schiepers, C.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Dahlbom, M.; Phelps, M.E.; Huang, S.C. (1)(8)F-FLT and (1)(8)F-FDOPA PET kinetics in recurrent brain tumors. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowosielski, M.; DiFranco, M.D.; Putzer, D.; Seiz, M.; Recheis, W.; Jacobs, A.H.; Stockhammer, G.; Hutterer, M. An intra-individual comparison of MRI, [18F]-FET and [18F]-FLT PET in patients with high-grade gliomas. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapp, M.; Floeth, F.W.; Felsberg, J.; Steiger, H.J.; Sabel, M.; Langen, K.J.; Galldiks, N. Clinical value of O-(2-[(18)F]-fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine positron emission tomography in patients with low-grade glioma. Neurosurg. Focus 2013, 34, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unterrainer, M.; Schweisthal, F.; Suchorska, B.; Wenter, V.; Schmid-Tannwald, C.; Fendler, W.P.; Schuller, U.; Bartenstein, P.; Tonn, J.C.; Albert, N.L. Serial 18F-FET PET Imaging of Primarily 18F-FET-Negative Glioma: Does It Make Sense? J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okubo, S.; Zhen, H.N.; Kawai, N.; Nishiyama, Y.; Haba, R.; Tamiya, T. Correlation of l-methyl-11C-methionine (MET) uptake with L-type amino acid transporter 1 in human gliomas. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2010, 99, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youland, R.S.; Kitange, G.J.; Peterson, T.E.; Pafundi, D.H.; Ramiscal, J.A.; Pokorny, J.L.; Giannini, C.; Laack, N.N.; Parney, I.F.; Lowe, V.J.; et al. The role of LAT1 in (18)F-DOPA uptake in malignant gliomas. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2013, 111, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habermeier, A.; Graf, J.; Sandhofer, B.F.; Boissel, J.P.; Roesch, F.; Closs, E.I. System L amino acid transporter LAT1 accumulates O-(2-fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine (FET). Amino Acids 2015, 47, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadone-Montaudie, B.; Ambrosetti, D.; Dufour, M.; Darcourt, J.; Almairac, F.; Coyne, J.; Virolle, T.; Humbert, O.; Burel-Vandenbos, F. [18F] FDOPA standardized uptake values of brain tumors are not exclusively dependent on LAT1 expression. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegmayr, C.; Bandelow, U.; Oliveira, D.; Lohmann, P.; Willuweit, A.; Filss, C.; Galldiks, N.; Lubke, J.H.; Shah, N.J.; Ermert, J.; et al. Influence of blood-brain barrier permeability on O-(2-(18)F-fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine uptake in rat gliomas. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegmayr, C.; Oliveira, D.; Niemietz, N.; Willuweit, A.; Lohmann, P.; Galldiks, N.; Shah, N.J.; Ermert, J.; Langen, K.J. Influence of Bevacizumab on Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability and O-(2-(18)F-Fluoroethyl)-l-Tyrosine Uptake in Rat Gliomas. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 700–705. [Google Scholar]
- Carideo, L.; Minniti, G.; Mamede, M.; Scaringi, C.; Russo, I.; Scopinaro, F.; Cicone, F. (18)F-DOPA uptake parameters in glioma: Effects of patients’ characteristics and prior treatment history. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20170847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Tuama, L.A.; Phillips, P.C.; Strauss, L.C.; Carson, B.C.; Uno, Y.; Smith, Q.R.; Dannals, R.F.; Wilson, A.A.; Ravert, H.T.; Loats, S.; et al. Two-phase [11C]l-methionine PET in childhood brain tumors. Pediatric Neurol. 1990, 6, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kits, A.; Martin, H.; Sanchez-Crespo, A.; Delgado, A.F. Diagnostic accuracy of (11)C-methionine PET in detecting neuropathologically confirmed recurrent brain tumor after radiation therapy. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2018, 32, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Gao, L.; Shao, A.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J. The performance of 11C-Methionine PET in the differential diagnosis of glioma recurrence. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 91030–91039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yomo, S.; Oguchi, K. Prospective study of (11)C-methionine PET for distinguishing between recurrent brain metastases and radiation necrosis: Limitations of diagnostic accuracy and long-term results of salvage treatment. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomura, N.; Kokubun, M.; Saginoya, T.; Mizuno, Y.; Kikuchi, Y. Differentiation between Treatment-Induced Necrosis and Recurrent Tumors in Patients with Metastatic Brain Tumors: Comparison among (11)C-Methionine-PET, FDG-PET, MR Permeability Imaging, and MRI-ADC-Preliminary Results. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 1520–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomura, N.; Saginoya, T.; Goto, H. 11C-Methionine Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography Versus 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography in Evaluation of Residual or Recurrent World Health Organization Grades II and III Meningioma After Treatment. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2018, 42, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratochwil, C.; Combs, S.E.; Leotta, K.; Afshar-Oromieh, A.; Rieken, S.; Debus, J.; Haberkorn, U.; Giesel, F.L. Intra-individual comparison of (1)(8)F-FET and (1)(8)F-DOPA in PET imaging of recurrent brain tumors. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calcagni, M.L.; Galli, G.; Giordano, A.; Taralli, S.; Anile, C.; Niesen, A.; Baum, R.P. Dynamic O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine (F-18 FET) PET for glioma grading: Assessment of individual probability of malignancy. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2011, 36, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popperl, G.; Kreth, F.W.; Mehrkens, J.H.; Herms, J.; Seelos, K.; Koch, W.; Gildehaus, F.J.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Tonn, J.C.; Tatsch, K. FET PET for the evaluation of untreated gliomas: Correlation of FET uptake and uptake kinetics with tumour grading. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2007, 34, 1933–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weckesser, M.; Langen, K.J.; Rickert, C.H.; Kloska, S.; Straeter, R.; Hamacher, K.; Kurlemann, G.; Wassmann, H.; Coenen, H.H.; Schober, O. O-(2-[18F]fluorethyl)-l-tyrosine PET in the clinical evaluation of primary brain tumours. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2005, 32, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulin-Romsee, G.; D’Hondt, E.; de Groot, T.; Goffin, J.; Sciot, R.; Mortelmans, L.; Menten, J.; Bormans, G.; Van Laere, K. Non-invasive grading of brain tumours using dynamic amino acid PET imaging: Does it work for 11C-methionine? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2007, 34, 2082–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unterrainer, M.; Winkelmann, I.; Suchorska, B.; Giese, A.; Wenter, V.; Kreth, F.W.; Herms, J.; Bartenstein, P.; Tonn, J.C.; Albert, N.L. Correction to: Biological tumour volumes of gliomas in early and standard 20-40 min (18)F-FET PET images differ according to IDH mutation status. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galldiks, N.; Rapp, M.; Stoffels, G.; Dunkl, V.; Sabel, M.; Langen, K.J. Earlier diagnosis of progressive disease during bevacizumab treatment using O-(2-18F-fluorethyl)-l-tyrosine positron emission tomography in comparison with magnetic resonance imaging. Mol. Imaging 2013, 12, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuyuguchi, N.; Terakawa, Y.; Uda, T.; Nakajo, K.; Kanemura, Y. Diagnosis of Brain Tumors Using Amino Acid Transport PET Imaging with (18)F-fluciclovine: A Comparative Study with l-methyl-(11)C-methionine PET Imaging. Asia Ocean. J. Nucl. Med. Boil. 2017, 5, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Cicone, F.; Filss, C.P.; Minniti, G.; Rossi-Espagnet, C.; Papa, A.; Scaringi, C.; Galldiks, N.; Bozzao, A.; Shah, N.J.; Scopinaro, F.; et al. Volumetric assessment of recurrent or progressive gliomas: Comparison between F-DOPA PET and perfusion-weighted MRI. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 42, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenberg, J.; Czernin, J.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Ellingson, B.M.; Pope, W.B.; Grogan, T.; Elashoff, D.; Geist, C.; Silverman, D.H.; Phelps, M.E.; et al. Treatment response evaluation using 18F-FDOPA PET in patients with recurrent malignant glioma on bevacizumab therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3550–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galldiks, N.; Kracht, L.W.; Burghaus, L.; Thomas, A.; Jacobs, A.H.; Heiss, W.D.; Herholz, K. Use of 11C-methionine PET to monitor the effects of temozolomide chemotherapy in malignant gliomas. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2006, 33, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galldiks, N.; Kracht, L.W.; Burghaus, L.; Ullrich, R.T.; Backes, H.; Brunn, A.; Heiss, W.D.; Jacobs, A.H. Patient-tailored, imaging-guided, long-term temozolomide chemotherapy in patients with glioblastoma. Mol. Imaging 2010, 9, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galldiks, N.; Dunkl, V.; Ceccon, G.; Tscherpel, C.; Stoffels, G.; Law, I.; Henriksen, O.M.; Muhic, A.; Poulsen, H.S.; Steger, J.; et al. Early treatment response evaluation using FET PET compared to MRI in glioblastoma patients at first progression treated with bevacizumab plus lomustine. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 45, 2377–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, T.; Sasajima, T.; Doi, Y.; Oka, S.; Ono, M.; Kanagawa, M.; Baden, A.; Mizoi, K.; Shimizu, H. Amino acid PET tracers are reliable markers of treatment responses to single-agent or combination therapies including temozolomide, interferon-beta, and/or bevacizumab for glioblastoma. Nucl. Med. Boil. 2015, 42, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinzel, A.; Muller, D.; Langen, K.J.; Blaum, M.; Verburg, F.A.; Mottaghy, F.M.; Galldiks, N. The use of O-(2-18F-fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine PET for treatment management of bevacizumab and irinotecan in patients with recurrent high-grade glioma: a cost-effectiveness analysis. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, N.L.; Graute, V.; Armbruster, L.; Suchorska, B.; Lutz, J.; Eigenbrod, S.; Cumming, P.; Bartenstein, P.; Tonn, J.C.; Kreth, F.W.; et al. MRI-suspected low-grade glioma: Is there a need to perform dynamic FET PET? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2012, 39, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, W.O.; Cordeiro, J.G.; Albicker, U.; Doostkam, S.; Nikkhah, G.; Kirch, R.D.; Trippel, M.; Reithmeier, T. Correlation of (18)F-fluoroethyl tyrosine positron-emission tomography uptake values and histomorphological findings by stereotactic serial biopsy in newly diagnosed brain tumors using a refined software tool. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 8, 3803–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicuendez, M.; Lorenzo-Bosquet, C.; Cuberas-Borros, G.; Martinez-Ricarte, F.; Cordero, E.; Martinez-Saez, E.; Castell-Conesa, J.; Sahuquillo, J. Role of [(11)C] methionine positron emission tomography in the diagnosis and prediction of survival in brain tumours. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2015, 139, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishii, R.; Higashi, T.; Kagawa, S.; Arimoto, M.; Kishibe, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Yamada, S.; Saiki, M.; Arakawa, Y.; Yamauchi, H.; et al. Differential Diagnosis between Low-Grade and High-Grade Astrocytoma Using System A Amino Acid Transport PET Imaging with C-11-MeAIB: A Comparison Study with C-11-Methionine PET Imaging. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2018, 2018, 1292746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhasz, C.; Muzik, O.; Chugani, D.C.; Chugani, H.T.; Sood, S.; Chakraborty, P.K.; Barger, G.R.; Mittal, S. Differential kinetics of alpha-[(1)(1)C]methyl-l-tryptophan on PET in low-grade brain tumors. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2011, 102, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naslund, O.; Smits, A.; Forander, P.; Laesser, M.; Bartek, J., Jr.; Gempt, J.; Liljegren, A.; Daxberg, E.L.; Jakola, A.S. Amino acid tracers in PET imaging of diffuse low-grade gliomas: A systematic review of preoperative applications. Acta Neurochir. 2018, 160, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauleit, D.; Stoffels, G.; Bachofner, A.; Floeth, F.W.; Sabel, M.; Herzog, H.; Tellmann, L.; Jansen, P.; Reifenberger, G.; Hamacher, K.; et al. Comparison of (18)F-FET and (18)F-FDG PET in brain tumors. Nucl. Med. Boil. 2009, 36, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmann, P.; Herzog, H.; Rota Kops, E.; Stoffels, G.; Judov, N.; Filss, C.; Galldiks, N.; Tellmann, L.; Weiss, C.; Sabel, M.; et al. dual-time-point O-(2-[(18)F]fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine PET for grading of cerebral gliomas. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 3017–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, N.L.; Winkelmann, I.; Suchorska, B.; Wenter, V.; Schmid-Tannwald, C.; Mille, E.; Todica, A.; Brendel, M.; Tonn, J.C.; Bartenstein, P.; et al. Early static (18)F-FET-PET scans have a higher accuracy for glioma grading than the standard 20–40 min scans. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, N.L.; Suchorska, B.; Wenter, V.; Eigenbrod, S.; Schmid-Tannwald, C.; Zwergal, A.; Niyazi, M.; Drexler, M.; Bartenstein, P.; Schnell, O.; et al. Dynamic 18F-FET PET in newly diagnosed astrocytic low-grade glioma identifies high-risk patients. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piroth, M.D.; Holy, R.; Pinkawa, M.; Stoffels, G.; Kaiser, H.J.; Galldiks, N.; Herzog, H.; Coenen, H.H.; Eble, M.J.; Langen, K.J. Prognostic impact of postoperative, pre-irradiation (18)F-fluoroethyl-l-tyrosine uptake in glioblastoma patients treated with radiochemotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2011, 99, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galldiks, N.; Langen, K.J.; Holy, R.; Pinkawa, M.; Stoffels, G.; Nolte, K.W.; Kaiser, H.J.; Filss, C.P.; Fink, G.R.; Coenen, H.H.; et al. Assessment of treatment response in patients with glioblastoma using O-(2-18F-fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine PET in comparison to MRI. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beppu, T.; Terasaki, K.; Sasaki, T.; Sato, Y.; Tomabechi, M.; Kato, K.; Sasaki, M.; Ogasawara, K. MRI and 11C-methyl-l-methionine PET Differentiate Bevacizumab True Responders After Initiating Therapy for Recurrent Glioblastoma. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2016, 41, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, M.Y.; Paeng, J.C.; Cheon, G.J.; Lee, D.S.; Chung, J.K.; Kim, E.E.; Kang, K.W. Prognostic Value of Metabolic Tumor Volume on (11)C-Methionine PET in Predicting Progression-Free Survival in High-Grade Glioma. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 49, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, T.Y.; Min, J.J.; Bom, H.S.; Jung, S.; Kim, I.Y.; Lim, S.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Kwon, S.Y. Prognostic value of post-treatment metabolic tumor volume from (11)C-methionine PET/CT in recurrent malignant glioma. Neurosurg. Rev. 2017, 40, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floeth, F.W.; Sabel, M.; Stoffels, G.; Pauleit, D.; Hamacher, K.; Steiger, H.J.; Langen, K.J. Prognostic value of 18F-fluoroethyl-l-tyrosine PET and MRI in small nonspecific incidental brain lesions. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galldiks, N.; Stoffels, G.; Ruge, M.I.; Rapp, M.; Sabel, M.; Reifenberger, G.; Erdem, Z.; Shah, N.J.; Fink, G.R.; Coenen, H.H.; et al. Role of O-(2-18F-fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine PET as a diagnostic tool for detection of malignant progression in patients with low-grade glioma. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 2046–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morana, G.; Piccardo, A.; Garre, M.L.; Nozza, P.; Consales, A.; Rossi, A. Multimodal magnetic resonance imaging and 18F-l-dihydroxyphenylalanine positron emission tomography in early characterization of pseudoresponse and nonenhancing tumor progression in a pediatric patient with malignant transformation of ganglioglioma treated with bevacizumab. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, e1–e5. [Google Scholar]
- Pirotte, B.; Goldman, S.; David, P.; Wikler, D.; Damhaut, P.; Vandesteene, A.; Salmon, L.; Brotchi, J.; Levivier, M. Stereotactic brain biopsy guided by positron emission tomography (PET) with [F-18]fluorodeoxyglucose and [C-11]methionine. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 1997, 68, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pirotte, B.; Goldman, S.; Massager, N.; David, P.; Wikler, D.; Vandesteene, A.; Salmon, I.; Brotchi, J.; Levivier, M. Comparison of 18F-FDG and 11C-methionine for PET-guided stereotactic brain biopsy of gliomas. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2004, 45, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Pafundi, D.H.; Laack, N.N.; Youland, R.S.; Parney, I.F.; Lowe, V.J.; Giannini, C.; Kemp, B.J.; Grams, M.P.; Morris, J.M.; Hoover, J.M.; et al. Biopsy validation of 18F-DOPA PET and biodistribution in gliomas for neurosurgical planning and radiotherapy target delineation: Results of a prospective pilot study. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirotte, B.J.; Lubansu, A.; Massager, N.; Wikler, D.; Goldman, S.; Levivier, M. Results of positron emission tomography guidance and reassessment of the utility of and indications for stereotactic biopsy in children with infiltrative brainstem tumors. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 107 (Suppl. S5), 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galldiks, N.; Schroeter, M.; Fink, G.R.; Kracht, L.W. Interesting image. PET imaging of a butterfly glioblastoma. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2010, 35, 49–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabria, F.; Schillaci, O. Recurrent glioma and crossed cerebellar diaschisis in a patient examined with 18F-DOPA and 18F-FDG PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2012, 37, 878–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kebir, S.; Rauschenbach, L.; Gielen, G.H.; Schafer, N.; Tzaridis, T.; Scheffler, B.; Giordano, F.A.; Lazaridis, L.; Herrlinger, U.; Glas, M. Recurrent pseudoprogression in isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 mutant glioblastoma. J. Clin. Neurosci. Off. J. Neurosurg. Soc. Australas 2018, 53, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.; Juhasz, C.; Bhambhani, K.; Wu, D.; Chugani, D.C.; Chugani, H.T. Assessment of progression and treatment response of optic pathway glioma with positron emission tomography using alpha-[(11)C]methyl-l-tryptophan. Mol. Imaging Boil. MIB Off. Publ. Acad. Mol. Imaging 2007, 9, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viader, F.; Derlon, J.M.; Petit-Taboue, M.C.; Shishido, F.; Hubert, P.; Houtteville, J.P.; Courtheoux, P.; Chapon, F. Recurrent oligodendroglioma diagnosed with 11C-l-methionine and pet: A case report. Eur. Neurol. 1993, 33, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Halloran, P.J.; Viel, T.; Murray, D.W.; Wachsmuth, L.; Schwegmann, K.; Wagner, S.; Kopka, K.; Jarzabek, M.A.; Dicker, P.; Hermann, S.; et al. Mechanistic interrogation of combination bevacizumab/dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor response in glioblastoma implementing novel MR and PET imaging biomarkers. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deuschl, C.; Moenninghoff, C.; Goericke, S.; Kirchner, J.; Koppen, S.; Binse, I.; Poeppel, T.D.; Quick, H.H.; Forsting, M.; Umutlu, L.; et al. Response assessment of bevacizumab therapy in GBM with integrated 11C-MET-PET/MRI: A feasibility study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deuschl, C.; Goericke, S.; Grueneisen, J.; Sawicki, L.M.; GOEBEL, J.; El Hindy, N.; Wrede, K.; Binse, I.; Poeppel, T.; Quick, H.; et al. Simultaneous 11C-Methionine Positron Emission Tomography/Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Suspected Primary Brain Tumors. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J.R.; Cozar, M.; Baquero, M.; Fernandez Barrionuevo, J.M.; Jaramillo, A.; Rubio, J.; Maida, G.; Soler, M.; Riera, E. The value of (11)C-methionine PET in the early differentiation between tumour recurrence and radionecrosis in patients treated for a high-grade glioma and indeterminate MRI. Rev. Esp. Med. Nucl. Imagen Mol. 2017, 36, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gauvain, K.; Ponisio, M.R.; Barone, A.; Grimaldi, M.; Parent, E.; Leeds, H.; Goyal, M.; Rubin, J.; McConathy, J. (18)F-FDOPA PET/MRI for monitoring early response to bevacizumab in children with recurrent brain tumors. Neuro-Oncol. Pract. 2018, 5, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filss, C.P.; Cicone, F.; Shah, N.J.; Galldiks, N.; Langen, K.J. Amino acid PET and MR perfusion imaging in brain tumours. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2017, 5, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muoio, B.; Giovanella, L.; Treglia, G. Recent Developments of 18F-FET PET in Neuro-oncology. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 3061–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, N.L.; Weller, M.; Suchorska, B.; Galldiks, N.; Soffietti, R.; Kim, M.M.; la Fougere, C.; Pope, W.; Law, I.; Arbizu, J.; et al. Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology working group and European Association for Neuro-Oncology recommendations for the clinical use of PET imaging in gliomas. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).