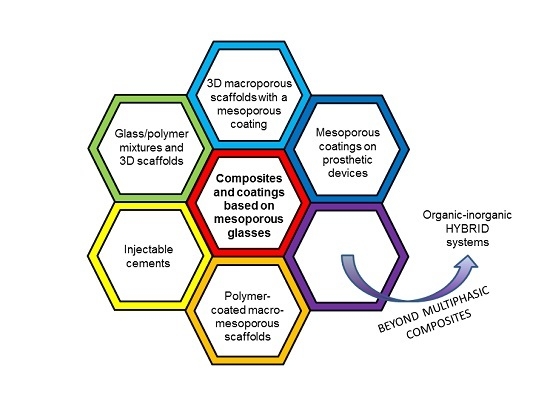
Composite Biomaterials Based on Sol-Gel Mesoporous Silicate Glasses: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Hierarchical Glass-Based Composites Produced by “Mixing Strategies”
3. Macroporous Scaffolds Provided with a Mesoporous Glass Coating
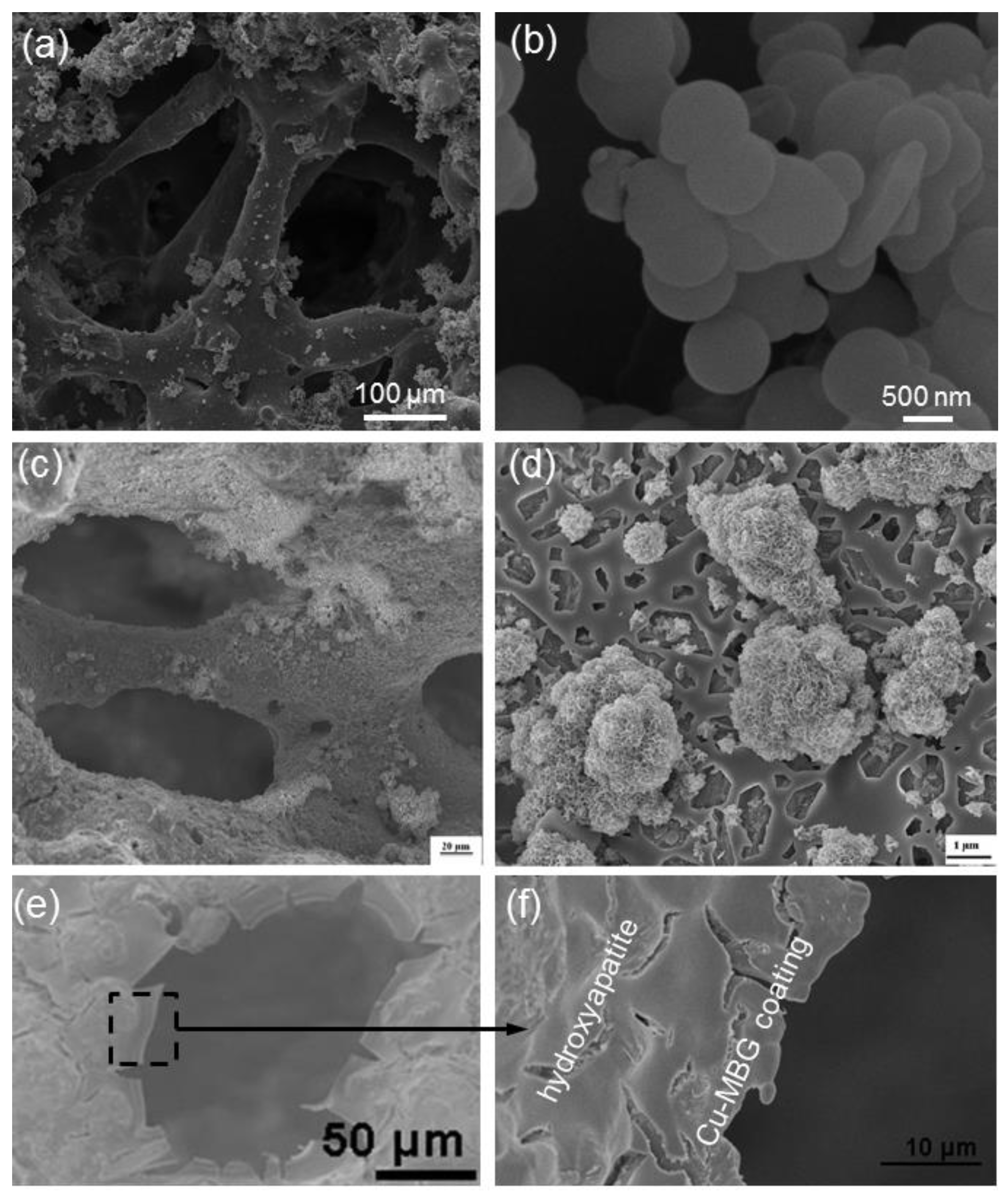
4. Sol-Gel Glass Coatings on Prosthetic Devices
5. Injectable Cements Containing Mesoporous Silicate Materials
6. Other Types of Composites and Coatings
7. Beyond Multiphasic Composite Materials: Hybrid Systems
8. Conclusions
9. Methods of Literature Search
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahaman, M.N.; Day, D.E.; Bal, B.S.; Fu, Q.; Jung, S.B.; Bonewald, L.F.; Tomsia, A.P. Bioactive glass in tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2355–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hench, L.L.; Splinter, R.J.; Allen, W.C.; Greenlee, T.K. Bonding mechanisms at the interface of ceramic prosthetic materials. J. Biomed. Mater. 1971, 5, 117–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, L.L. The story of bioglass®. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med. 2006, 7, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokubo, T.; Takadama, H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.; Pigott, G.H.; Schoen, F.J.; Hench, L.L. Toxicology and biocompatibility of bioglasses. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1981, 15, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Clark, A.E.; Hench, L.L. An investigation of bioactive glass powders by sol-gel processing. J. Appl. Biomater. 1991, 2, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.R.; Lee, P.D.; Hench, L.L. Hierarchical porous materials for tissue engineering. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2006, 364, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresge, T.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Roth, W.J.; Vartuli, J.C.; Beck, J.S. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 1992, 359, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regi, M.; Ramila, A.; Del Real, R.P.; Perez-Pariente, J. A new property of MCM-41: Drug delivery system. J. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcos, D.; Vallet-Regí, M. Bioceramics for drug delivery. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 890–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chang, J. Multifunctional mesoporous bioactive glasses for effective delivery of therapeutic ions and drug/growth factors. J. Control. Release 2014, 193, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Everett, D.; Haul, R.A.W.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 77, 603–619. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Yu, C.; Zhou, X.; Tang, J.; Zhao, D. Highly ordered mesoporous bioactive glasses with superior in vitro bone-forming bioactivities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2004, 43, 5980–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Regi, M.; Ragel, C.V.; Salinas, A.J. Glasses with medical applications. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 2003, 1029–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, G.J.; Singh, R.K.; Foroutan, F.; Alqaysi, M.; Han, C.M.; Mahapatra, C.; Kim, H.W.; Knowles, J.C. Sol-gel based materials for biomedical applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 77, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Gentile, P.; Chiono, V.; Ciardelli, G. Collagen for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 3191–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Fiqi, A.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, H.W. Collagen hydrogels incorporated with surface-aminated mesoporous nanobioactive glass: Improvement of physicochemical stability and mechanical properties is effective for hard tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 9508–9521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Kady, A.M.; Ali, A.F.; Farag, M.M. Development, characterization, and in vitro bioactivity studies of sol-gel bioactive glass/poly(L-lactide) nanocomposite scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Shi, J. MBG/PLGA composite microspheres with prolonged drug release. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2009, 89, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Shi, J.; Dong, X.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, H. A mesoporous bioactive glass/polycaprolactone composite scaffold and its bioactivity behavior. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 84, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Chang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y. Bioactive inorganic-materials/alginate composite microspheres with controllable drug-delivery ability. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2010, 94, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Ramaswamy, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, R.; Appleyard, R.; Howard, A.; Zreiqat, H. The effect of mesoporous bioactive glass on the physiochemical, biological and drug-release properties of poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) films. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2199–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Cao, L.; Yu, B.; Song, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, M. Composite scaffolds of mesoporous bioactive glass and polyamide for bone repair. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 1255–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, H.S.; Kim, S.E.; Park, E.K. Bioactive glass-poly(ε-caprolactone) composite scaffolds with 3-dimensionally hierarchical pore networks. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.X.; Wu, C.T.; Lode, A.; Gelinsky, M. Hierarchical mesoporous bioactive glass/alginate composite scaffolds fabricated by three-dimensional plotting for bone tissue engineering. Biofabrication 2013, 5, 015005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekaran, A.; Novajra, G.; Carmagnola, I.; Gentile, P.; Fiorilli, S.; Miola, M.; Boregowda, M.; Dakshinamoorthy, A.; Ciardelli, G.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Physico-chemical and biological studies on three-dimensional porous silk/spray-dried mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 13761–13772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, W.; Xiao, Y. A comparative study of mesoporous-glass/silk and nonmesoporous-glass/silk scaffolds: physiochemistry and in vivo osteogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2229–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, X.; Gu, X.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C.; Shi, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Preparation of an rhBMP-2 loaded mesoporous bioactive glass/calcium phosphate cement porous composite scaffold for rapid bone tissue regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 8558–8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.B.; Chen, J.Y.; Feng, X.X.; Chang, J. Fabrication and characterization of chitosan/mesoporous bioactive glasses porous films. J. Clin. Rehabil. Tissue Eng. Res. 2011, 15, 7877–7880. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Chen, X.; Jing, X.; Fan, H.; Guo, B.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, X. Preparation, bioactivity, and drug release of hierarchical nanoporous bioactive glass ultrathin fibers. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Chen, X.; Jing, X.; Fan, H.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, X. Fabrication and drug delivery of ultrathin mesoporous bioactive glass hollow fibers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 1503–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X. Modification of porous alumina ceramics with bioinert and bioactive glass coatings. Adv. Mater. Res. 2008, 32, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dong, Z.; Miao, X. Porous alumina/zirconia composite scaffold with bioactive glass 58S33C coating. J. Biomim. Biomater. Tissue Eng. 2010, 6, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, S.I.R.; Nouri-Khorasani, S.; Lu, Z.F.; Appleyard, R.C.; Zreiqat, H. Effects of bioactive glass nanoparticles on the mechanical and biological behavior of composite coated scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esfahani, S.I.R.; Tavangarian, F.; Emadi, R. Nanostructured bioactive glass coating on porous hydroxyapatite scaffold for strength enhancement. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3428–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauda, V.; Fiorilli, S.; Onida, B.; Verné, E.; Vitale-Brovarone, C.; Viterbo, D.; Croce, G.; Milanesio, M.; Garrone, E. SBA-15 ordered mesoporous silica inside a bioactive glass-ceramic scaffold for local drug delivery. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 3303–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortera, R.; Onida, B.; Fiorilli, S.; Cauda, V.; Vitale-Brovarone, C.; Baino, F.; Verné, E.; Garrone, E. Synthesis of MCM-41 spheres inside bioactive glass-ceramic scaffold. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 137, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale-Brovarone, C.; Baino, F.; Miola, M.; Mortera, R.; Onida, B.; Verné, E. Glass-ceramic scaffolds containing silica mesophases for bone grafting and drug delivery. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortera, R.; Baino, F.; Croce, G.; Fiorilli, S.; Vitale-Brovarone, C.; Verné, E.; Onida, B. Monodisperse mesoporous silica spheres inside a bioactive macroporous glass-ceramic scaffold. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2010, 12, B256–B259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccardi, E.; Philippart, A.; Juhasz-Bortuzzo, J.; Beltran, A.; Novajra, G.; Vitale-Brovarone, C.; Spiecker, E.; Boccaccini, A.R. Uniform surface modification of 3D Bioglass®-based scaffolds with mesoporous silica particles (MCM-41) for enhancing drug delivery capability. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horcajada, P.; Ramila, A.; Boulahya, K.; Gonzalez-Calbet, J.; Vallet-Regi, M. Bioactivity in ordered mesoporous materials. Solid State Sci. 2004, 6, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Ruiz-Gonzalez, L.; Doadrio, J.C.; Gonzalez-Calbet, J.M.; Vallet-Regi, M. Tissue regeneration: A new property of mesoporous materials. Solid State Sci. 2005, 7, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Vallet-Regi, M. Mesoporous bioactive glasses: relevance of their porous structure compared to that of classical bioglasses. Biomed. Glasses 2015, 1, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baino, F.; Fiorilli, S.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Bioactive glass-based materials with hierarchical porosity for medical applications: review of recent advances. Acta Biomater. 2016, 42, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorilli, S.; Baino, F.; Cauda, V.; Crepaldi, M.; Vitale-Brovarone, C.; Demarchi, D.; Onida, B. Electrophoretic deposition of mesoporous bioactive glass on glass-ceramic foam scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 26, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molino, G.; Bari, A.; Baino, F.; Fiorilli, S.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Electrophoretic deposition of spray-dried Sr-containing mesoporous bioactive glass spheres on glass-ceramic scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration. J. Mater. Sci. under review.
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, L.; Zhai, D.; Shi, M.; Luo, Y.; Feng, C.; Fang, B.; Yin, J.; Chang, J.; Wu, C. Mesoporous bioactive glass nanolayer-functionalized 3D-printed scaffolds for accelerating osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 19207–19221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Zhai, D.; Zhao, L.; Wu, C.; Chang, J. Nanosized mesoporous bioactive glass/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) composite-coated CaSiO3 scaffolds with multifunctional properties for bone tissue engineering. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 323046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; He, J.; Wang, C.; Yao, K.; Gou, Z. copper-containing mesoporous bioactive glass coatings on orbital implants for improving drug delivery capacity and antibacterial activity. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 36, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novajra, G.; Boetti, N.G.; Lousteau, J.; Fiorilli, S.; Milanese, D.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Phosphate glass fibre scaffolds: Tailoring of the properties and enhancement of the bioactivity through mesoporous glass particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 67, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezwan, K.; Chen, Q.Z.; Blaker, J.J.; Boccaccini, A.R. Biodegradable and bioactive porous polymer/inorganic composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3413–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad Yunos, D.; Bretcanu, O.; Boccaccini, A.R. Polymer-bioceramic composites for tissue engineering scaffolds. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 4433–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zhang, L.X.; He, Q.J.; Zhao, J.J.; Guo, L.M.; Shi, J.L. Mesoporous bioactive glass-coated poly(L-lactic acid) scaffolds: A sustained antibiotic drug release system for bone repairing. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Tang, L.; Ao, H.; Tan, H.; Tang, T.; Liu, C. Mesoporous bioactive glass doped-poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) composite scaffolds with 3-dimensionally hierarchical pore networks for bone regeneration. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 116, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabanas-Polo, S.; Philippart, A.; Boccardi, E.; Hazur, J.; Boccaccini, A.R. Facile production of porous bioactive glass scaffolds by the foam replica technique combined with sol-gel/electrophoretic deposition. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 5772–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdimamaghani, M.; Razavi, M.; Vashaee, D.; Raveendra Pothineni, V.; Rajadas, J.; Tayebi, L. Significant degradability enhancement in multilayer coating of polycaprolactone-bioactive glass/gelatin-bioactive glass on magnesium scaffold for tissue engineering applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 338, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEntire, B.J.; Bal, B.S.; Rahaman, M.N.; Chevalier, J.; Pezzotti, G. Ceramics and ceramic coatings in orthopaedics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 4327–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Barrio, J.A.; Sanchez-Herraez, S.; Fernandez-Hernandez, O.; Betegon-Nicolas, J.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, J.J.; Lopez-Sastre, A. Bioglass-coated femoral stem. J. Bone Joint Surg. 2004, 86B (Suppl. II), 138. [Google Scholar]
- Schrooten, J.; Helsen, J.A. Adhesion of bioactive glass coating to Ti6Al4V oral implant. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, S.I.R.; Ebrahimi-Kahrizsangi, R.; Saleh, D.M.; Karbasi, S. Bonding strength, hardness and bioactivity of nano bioglass-titania nanocomposite coating deposited on NiTi nails. Curr. Nanosci. 2011, 7, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasuriya, R.L.; Buckley, S.C.; Hamer, A.J.; Kerry, R.M.; Stockley, I.; Tomouk, M.W.; Wilkinson, J.M. Effect of sliding-taper compared with composite-beam cemented femoral prosthesis loading regime on proximal femoral bone remodeling. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2013, 95, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ormsby, R.; McNally, T.; O’Hare, P.; Burke, G.; Mitchell, C.; Dunne, N. Fatigue and biocompatibility properties of a poly(methyl methacrylate) bone cement with multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaled, S.M.; Charpentier, P.A.; Rizkalla, A.S. Physical and mechanical properties of PMMA bone cement reinforced with nano-sized titania fibers. J. Biomater. Appl. 2011, 25, 515–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennon, A.B. Fracture toughness and fatigue characteristics of bone cements. In Orthopaedic Bone Cements; Deb, S., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Sawston, Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 265–310. [Google Scholar]
- Shadjou, N.; Hasanzadeh, M. Bone tissue engineering using silica-based mesoporous nanobiomaterials: recent progress. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 55, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slane, J.; Vivanco, J.; Meyer, J.; Ploeg, H.L.; Squire, M. Modification of acrylic bone cement with mesoporous silica nanoparticles: effects on mechanical, fatigue and absorption properties. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 29, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slane, J.; Vivanco, J.; Ebenstein, D.; Squire, M.; Ploeg, H.L. Multiscale characterization of acrylic bone cement modified with functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 37, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Gu, J.; Ali Shah, L.; Siddiq, M.; Hu, J.; Cai, X.; Yang, D. Bone cement based on vancomycin loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticle and calcium sulfate composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 49, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallia, F.; Gallo, M.; Pontiroli, L.; Baino, F.; Fiorilli, S.; Onida, B.; Anselmetti, G.C.; Manca, A.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Zirconia-containing radiopaque mesoporous bioactive glasses. Mater. Lett. 2014, 130, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale-Brovarone, C.; Verné, E.; Bergui, M.; Onida, B.; Ferraris, S.; Miola, M.; Baino, F.; Tallia, F. Injectable Osteoinductive Bone Cements. Patent No. EP2569025, 29 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dadkhah, M.; Pontiroli, L.; Fiorilli, S.; Manca, A.; Tallia, F.; Tcacencu, I.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Preparation and characterisation of an innovative injectable calcium sulphate based bone cement for vertebroplasty application. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.T.; Potes, J.; Queiroga, M.C.; Castro, J.L.; Pereira, A.F.; Rehman, S.; Dalgarno, K.; Ramos, A.; Vitale-Brovarone, C.; Reis, J.C. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: A new animal model. Spine J. 2016, 16, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Friis, T.; Xiao, Y. Structure-property relationships of silk-modified mesoporous bioglass scaffolds. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3429–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Lin, H.; Li, X.; Bian, C.; Xiang, D.; Han, X.; Wu, X.; Qu, F. Hierarchical porous bioactive glasses/PLGA-magnetic SBA-15 for dual-drug release. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 39, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaker, J.J.; Nazhat, S.N.; Boccaccini, A.R. Development and characterisation of silver-doped bioactive glass-coated sutures for tissue engineering and wound healing applications. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratten, J.; Nazhat, S.N.; Blaker, J.J.; Boccaccini, A.R. In vitro attachment of Staphylococcus epidermidis to surgical sutures with and without Ag-containing bioactive glass coating. J. Biomater. Appl. 2004, 19, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, B.M. Hybrid nanocomposite materials—Between inorganic glasses and organic polymers. Adv. Mater. 1993, 5, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valliant, E.M.; Jones, J.R. Softening bioactive glass for bone regeneration: sol-gel hybrid materials. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 5083–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.R. New trends in bioactive scaffolds: the importance of nanostructure. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 29, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.R. Review of bioactive glass: from Hench to hybrids. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 4457–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.P.V.; Vasconcelos, W.L.; Orefice, R.L. Novel multicomponent silicate-poly(vinyl alcohol) hybrids with controlled reactivity. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2000, 273, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, A.I.; Salinas, A.J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Bioactive and degradable organic-inorganic hybrids. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 25, 3533–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Teng, S.H.; Jang, T.S.; Wang, P.; Yook, S.W.; Kim, H.E.; Koh, Y.H. Nanostructured poly(ε-caprolactone)-silica xerogel fibrous membrane for guided bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3557–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.H.; Koh, Y.H.; Kim, H.E. Synthesis and characterization of drug-loaded poly(epsilon-caprolactone)/silica hybrid nanofibrous scaffolds. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Yoon, B.H.; Kim, H.E.; Kim, H.W. Bioactive and degradable hybridized nanofibers of gelatin-siloxane for bone regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 84, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.J.; Shin, D.S.; Kim, H.E.; Kim, H.W.; Koh, Y.H.; Jang, J.H. Membrane of hybrid chitosan-silica xerogel for guided bone regeneration. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.J.; Jun, S.H.; Kim, H.E.; Kim, H.W.; Koh, Y.H.; Jang, J.H. Silica xerogel-chitosan nano-hybrids for use as drug eluting bone replacement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xie, Q.R.; Zhang, J.; Xia, W.; Gu, H. The packaging of siRNA within the mesoporous structure of silica nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9546–9556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabuta, T.; Bescher, E.P.; Mackenzie, J.D.; Tsuru, K.; Hayakawa, S.; Osaka, A. Synthesis of PDMS-based porous materials for biomedical applications. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2003, 26, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Miyamoto, T.; Kokubo, T.; Nakamura, T. Preparation of polymer-silicate hybrid materials bearing silanol groups and the apatite formation on/in the hybrid materials. Polym. Bull. 1998, 40, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, K.; Hashizume, M.; Ariga, K.; Terashima, T.; Kikuchi, J. Preparation and characterization of a novel organic-inorganic nanohybrid “cerasome” formed with a liposomal membrane and silicate surface. Chemistry 2007, 13, 5272–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Hitzky, E.; Letaief, S.; Prevot, V. Novel organic-inorganic mesophases: self-templating synthesis and intratubular swelling. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Dai, Z. Recent advances in liposomal nanohybrid cerasomes as promising drug nanocarriers. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 207, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzano, M.; Arcos, D.; Delgado, M.R.; Ruiz, E.; Gil, F.J.; Vallet-Regi, M. Bioactive star gels. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 5696–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regi, M.; Salinas, A.J.; Arcos, D. From the bioactive glasses to the star gels. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.J.; Li, S.; Stevens, M.M.; Georgiou, T.K.; Jones, J.R. Tailoring mechanical properties of sol-gel hybrids for bone regeneration through polymer structure. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 6127–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Bennet, A.E. Synthesis, toxicology and potential of ordered mesoporous materials in nanomedicine. Nanomedicine (Lond.) 2011, 6, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.S.; Hurley, K.R.; Haynes, C.L. Critical considerations in the biomedical use of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, S.P.; Padera, R.F.; Langer, R.; Kohane, D.S. The biocompatibility of mesoporous silicates. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4045–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidi, P.; Nigro, M.; Bernardeschi, M.; Scarcelli, V.; Lucchesi, P.; Onida, B.; Mortera, R.; Frenzilli, G. Genotoxicity of amorphous silica particles with different structure and dimension in human and murine cell lines. Mutagenesis 2013, 28, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

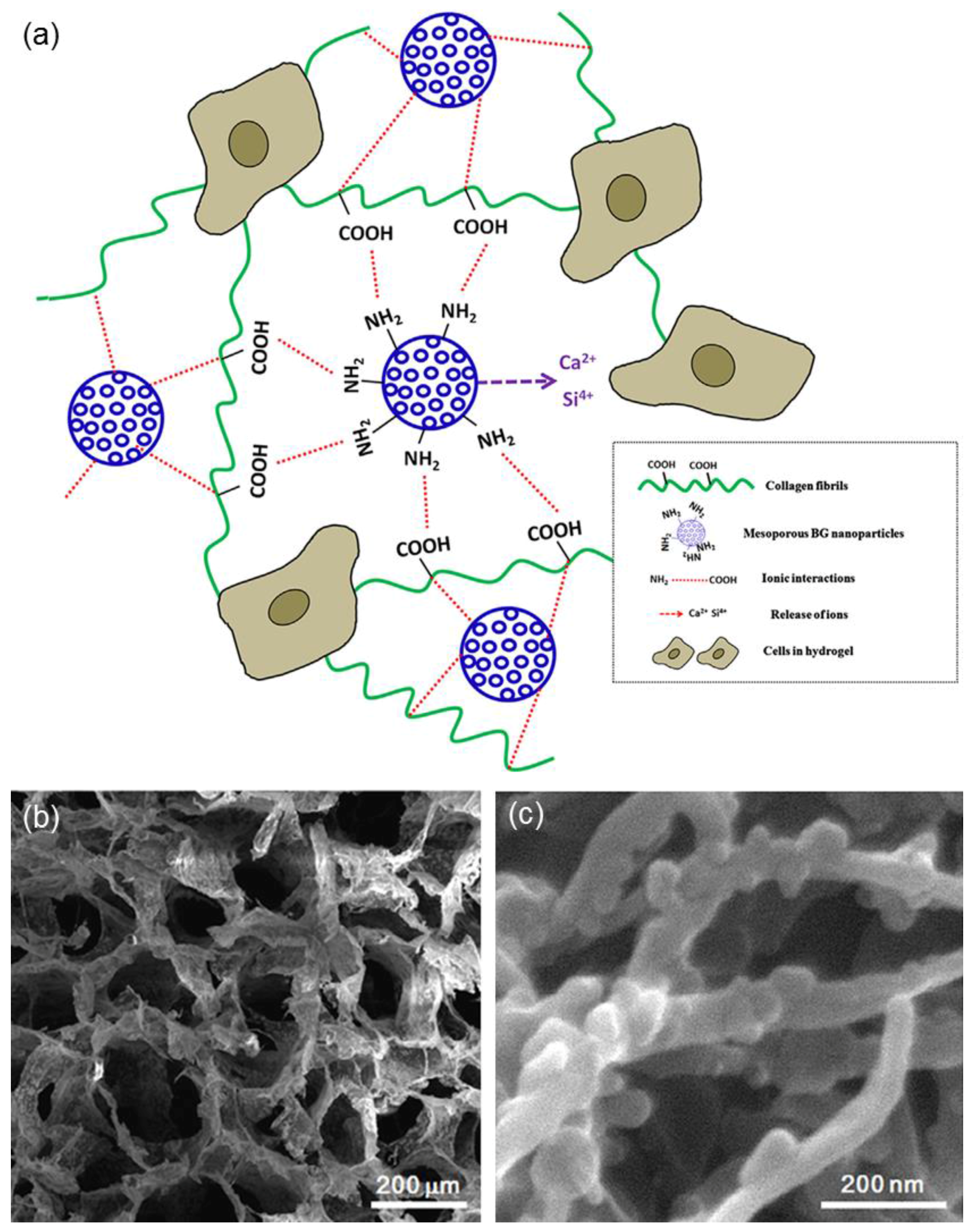

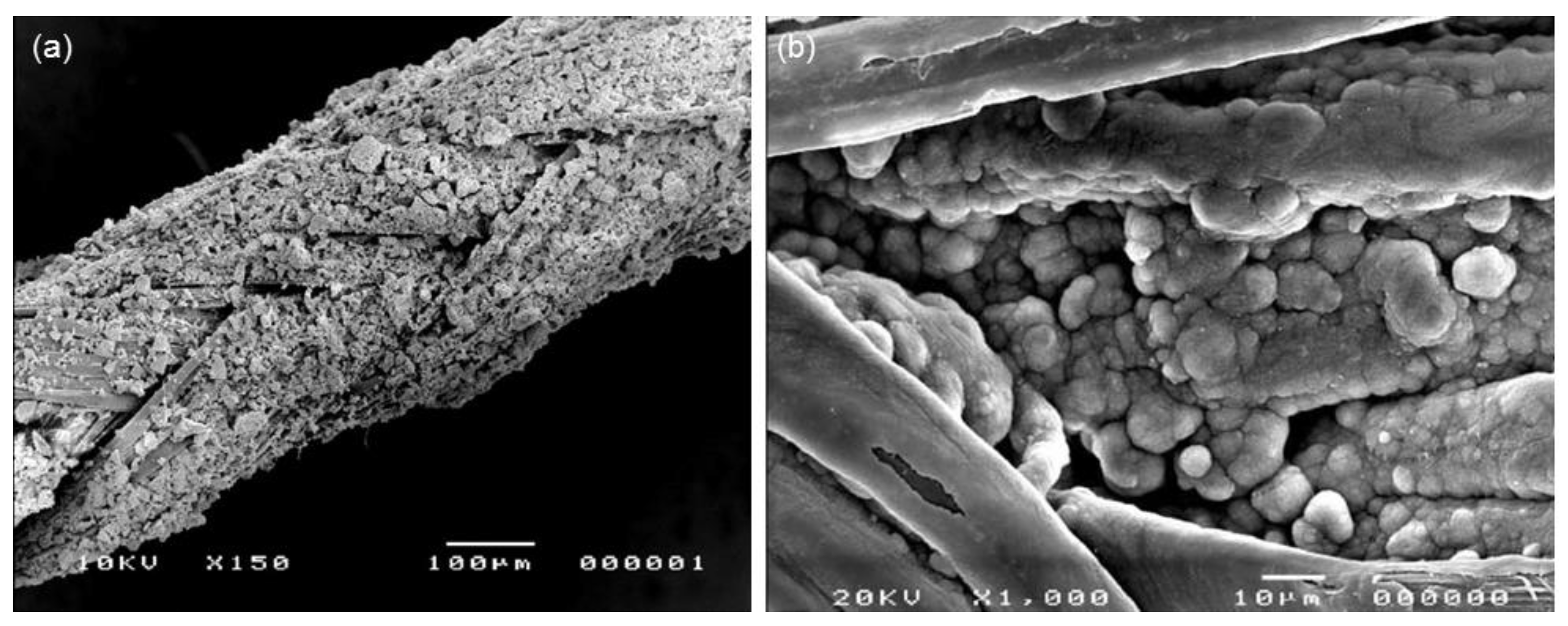
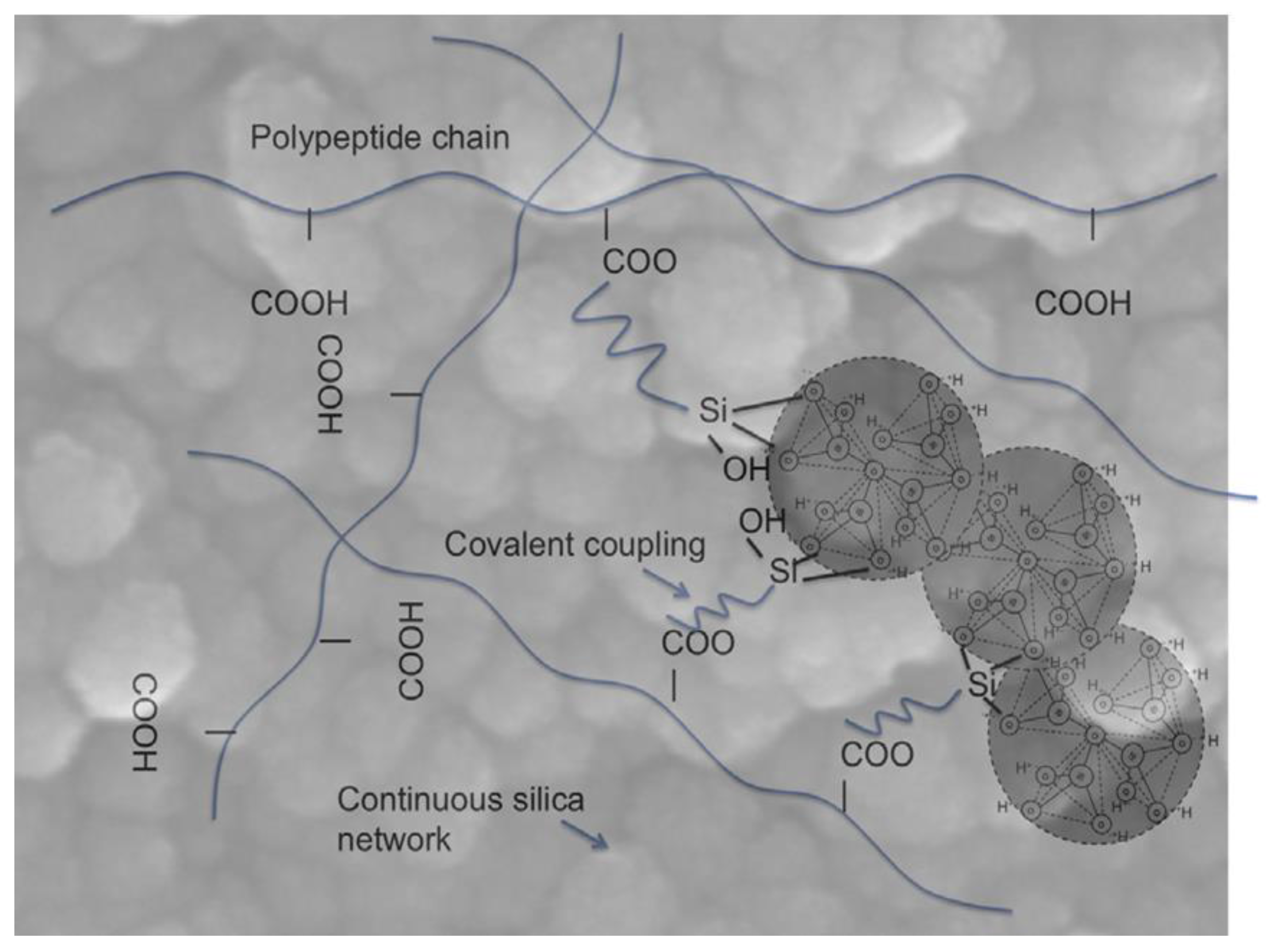
| Mesoporous Phase | Matrix | Processing | Effect | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBG | Collagen | Mixing | Improved bioactivity in vitro and mechanical properties | [17] |
| Sol-gel glass | PLLA | Solid–liquid phase separation + solvent extraction | Improved bioactivity in vitro | [18] |
| MBG | PLGA | Mixing | Improved bioactivity in vitro, drug release | [19,22] |
| MBG | Polyamide | Solvent casting/particulate leaching | Improved bioactivity in vitro and bone regeneration in vivo | [23] |
| MBG | PCL | Solvent casting/particulate leaching | Improved bioactivity in vitro, drug release | [20] |
| Robocasting + salt leaching | Improved bioactivity in vitro and mechanical properties, pliability | [24] | ||
| MBG | Alginate | Mixing | Improved bioactivity in vitro, drug release | [21] |
| 3D plotting | Improved bioactivity in vitro, drug release | [25] | ||
| MBG | Silk fibroin | Freeze-drying | Improved bioactivity in vitro and mechanical properties | [26,27] |
| MBG | Calcium phosphate | Mixing + freeze-drying | Adequate mechanical properties and bone regeneration in vivo | [28] |
| MBG | Chitosan | Freeze-drying | Hemostasis to promote wound healing | [29] |
| Coating | Base scaffold | Processing | Effect | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 58S | Al2O3 | Dip-coating | Improved bioactivity in vitro | [32] |
| 58S | Al2O3/ZrO2 | Dip-coating | Improved bioactivity in vitro | [33] |
| 58S/PCL | Calcium phosphate | Dipping | Improved mechanical properties | [34] |
| 58S | Bovine hydroxyapatite | Dipping | Improved mechanical properties | [35] |
| SBA-15 | Glass–ceramic | Dipping | Drug release | [36] |
| MCM-41 | Glass–ceramic | Dipping | Drug release | [37,38,39] |
| MBG | Glass–ceramic | Electrophoretic deposition | Improved bioactivity in vitro | [45,46] |
| MBG | β-TCP | Spin coating | Improved bioactivity in vitro | [47] |
| MBG/PLGA | CaSiO3 | Dipping | Improved bioactivity in vitro and mechanical properties, drug release | [48] |
| Cu-doped MBG | Hydroxyapatite | Dipping | Drug release and antibacterial effect due to the release of Cu2+ ions | [49] |
| MBG | Phosphate glass fibers | Thermal bonding | Improved bioactivity in vitro, drug release | [50] |
| MBG | PLLA | Dip-coating | Improved bioactivity in vitro, drug release | [53] |
| PCL/gelatin/sol-gel glass | Magnesium | Freeze-drying | Improved bioactivity in vitro, reduction of magnesium dissolution | [56] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baino, F.; Fiorilli, S.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Composite Biomaterials Based on Sol-Gel Mesoporous Silicate Glasses: A Review. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering4010015
Baino F, Fiorilli S, Vitale-Brovarone C. Composite Biomaterials Based on Sol-Gel Mesoporous Silicate Glasses: A Review. Bioengineering. 2017; 4(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering4010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaino, Francesco, Sonia Fiorilli, and Chiara Vitale-Brovarone. 2017. "Composite Biomaterials Based on Sol-Gel Mesoporous Silicate Glasses: A Review" Bioengineering 4, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering4010015
APA StyleBaino, F., Fiorilli, S., & Vitale-Brovarone, C. (2017). Composite Biomaterials Based on Sol-Gel Mesoporous Silicate Glasses: A Review. Bioengineering, 4(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering4010015