Radiomics for Detecting Metaplastic Histology in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Step Towards Personalized Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
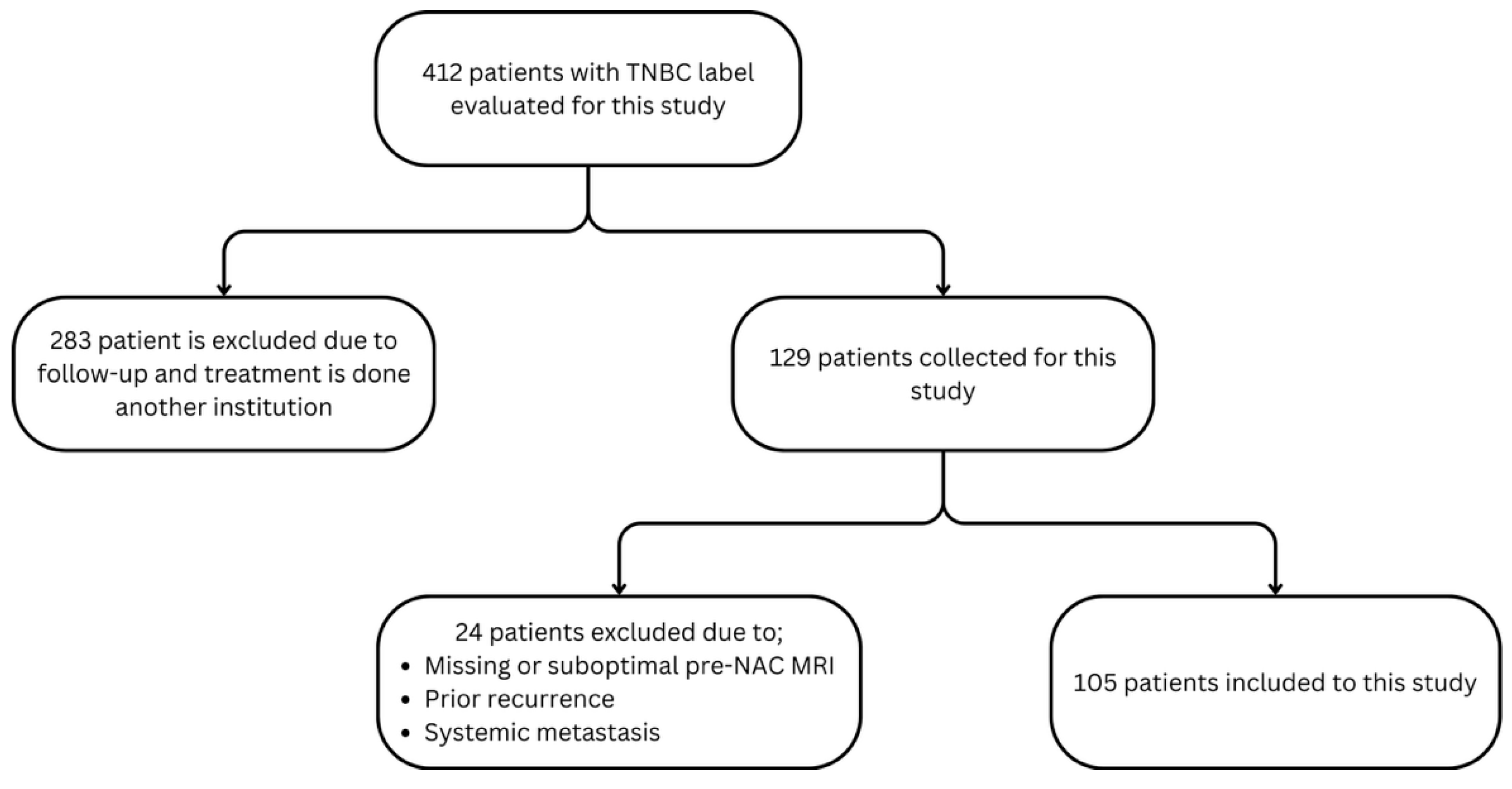
2.1. Study Design and Patient Cohort
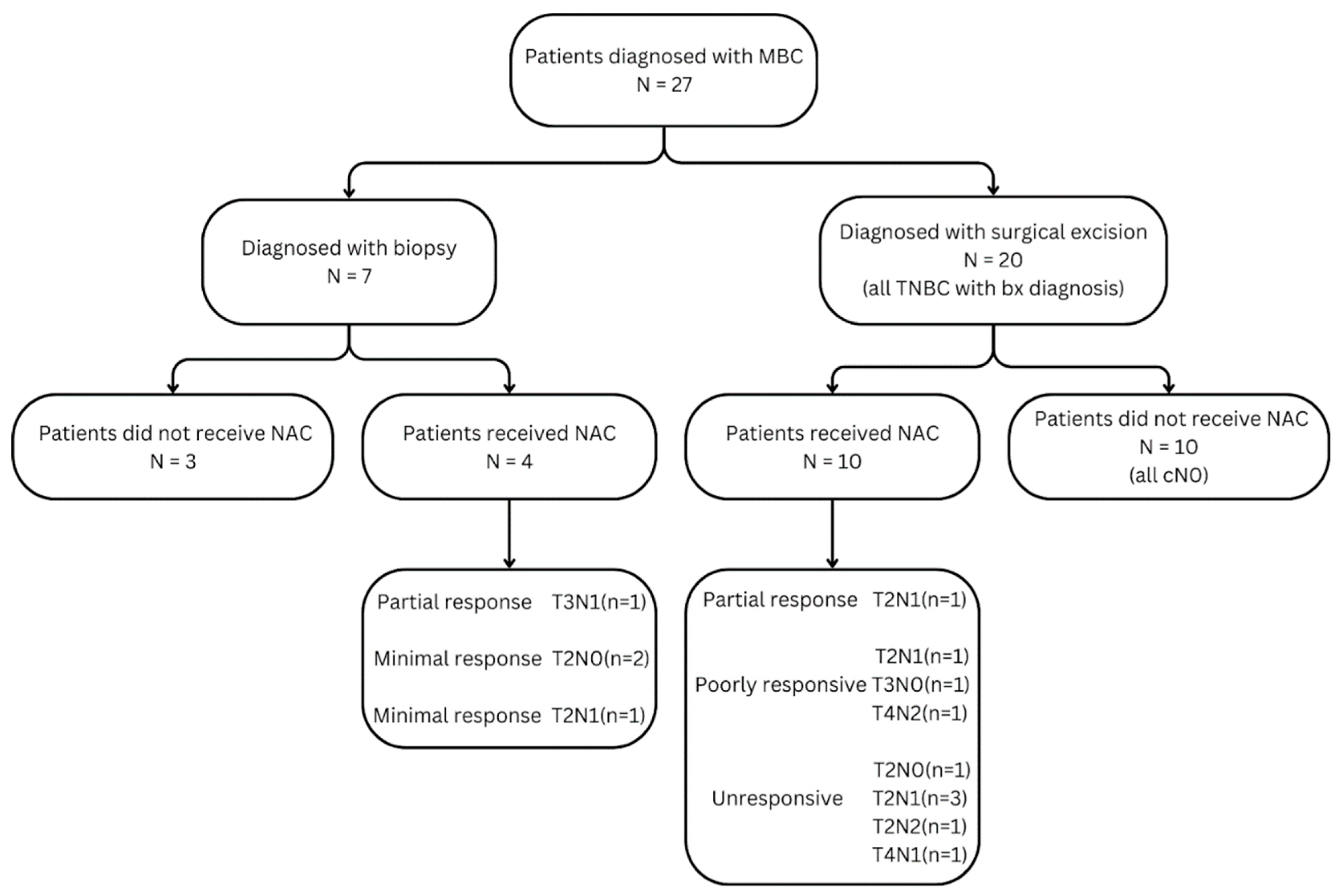
2.2. MBC Cohort
2.3. Non-Metaplastic TNBC Cohort
2.4. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Protocol
2.5. Histopathologic Evaluation
2.6. MR Image Acquisition
2.7. Ground-Truth Annotations and Inter-Observer Agreement
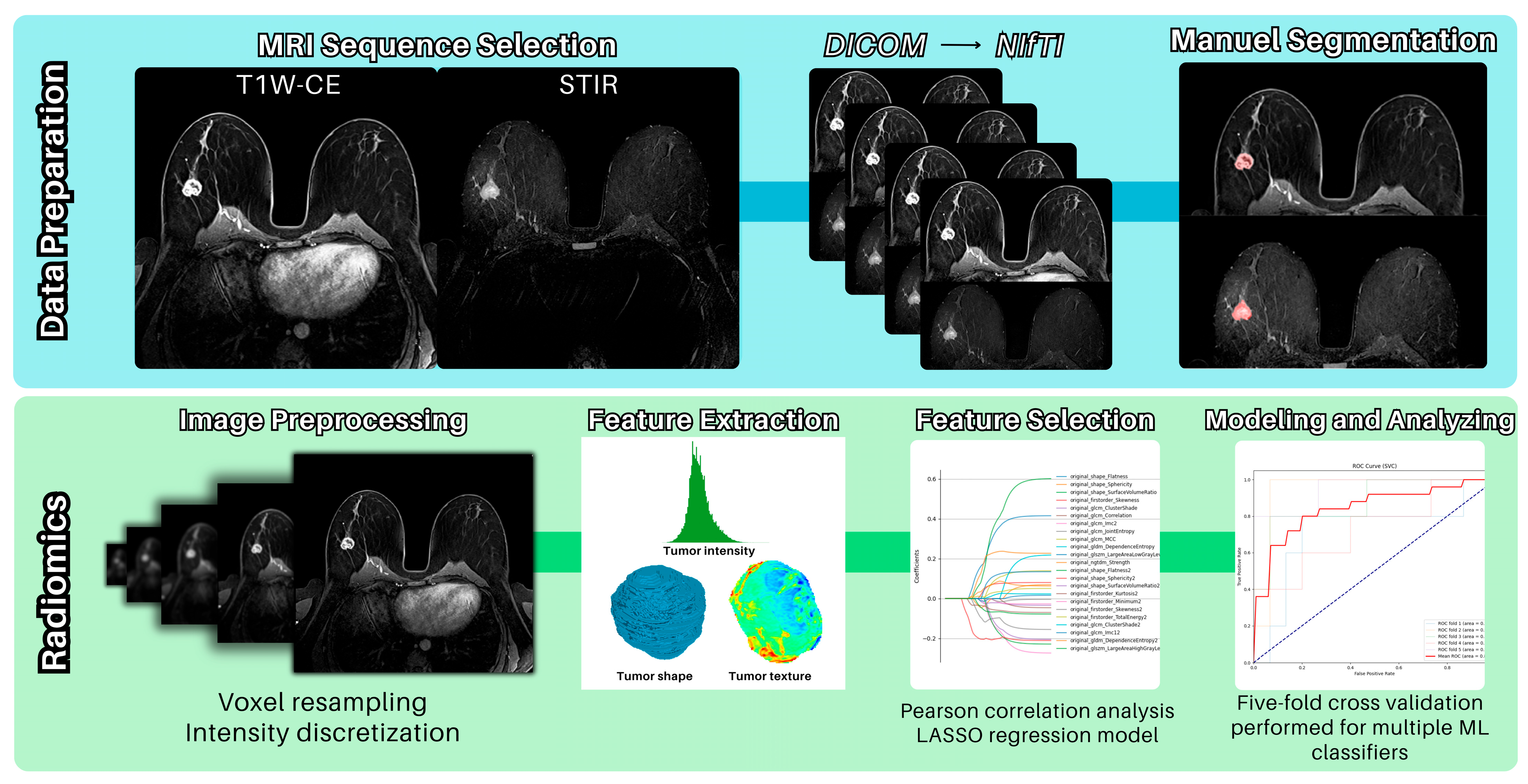
2.8. Procedure for the Radiomics Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
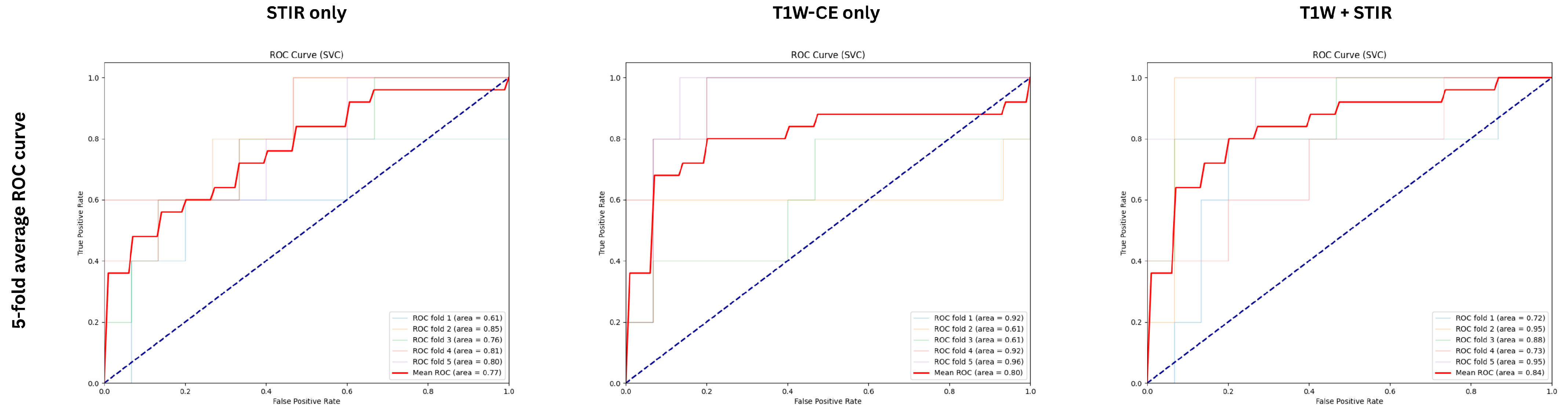
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| DWI | Diffusion-weighted imaging |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| FDG | Fluorodeoxyglucose |
| HER2 | Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| MBC | Metaplastic breast cancer |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| NAC | Neoadjuvant chemotherapy |
| pCR | Pathological complete response |
| PCTB | Post-chemotherapy tumor bed |
| PET-CT | Positron emission tomography and computed tomography |
| PR | Progesterone receptor |
| SLNB | Sentinel lymph node biopsy |
| STIR | Short tau inversion recovery |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| TNBC | Triple-negative breast cancer |
References
- Jung, S.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Nam, B.H.; Min, S.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Park, C.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, E.A.; Ko, K.L.; Shin, K.H.; et al. Worse Prognosis of Metaplastic Breast Cancer Patients than Other Patients with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 120, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.; Brogi, E.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Plitas, G.; Robson, M.; Norton, L.; Morrow, M.; Wen, H.Y. Poor Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Metaplastic Breast Carcinoma. npj Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, A.M.; Pettis, J.; Rivere, A.; Elder, E.A.; Fuhrman, G. Institutional Analysis of Metaplastic Breast Cancer. Am. Surg. 2023, 89, 3579–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, G.; Cosmatos, H.; Do, T.; Lodin, K.; Varshney, D. Metaplastic Carcinoma of the Breast: A Retrospective Review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 64, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzi, C.M.; Patel-Parekh, L.; Cole, K.; Franko, J.; Klimberg, V.S.; Bland, K. Characteristics and Treatment of Metaplastic Breast Cancer: Analysis of 892 Cases from the National Cancer Data Base. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 14, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Salamat, A.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, H.; Clark, B.Z.; Dabbs, D.J.; Carter, G.J.; Brufsky, A.M.; Jankowitz, R.C.; Puhalla, S.L.; et al. Metaplastic Breast Carcinoma: A Clinical-Pathologic Study of 97 Cases with Subset Analysis of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, P. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Epidemiological Considerations and Recommendations. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, VI7–VI12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.E.; Na, Y.M.; Park, M.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lim, H.S. Prediction of Early Clinical Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Incorporating Radiomics through Breast MRI. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.T.; Campbell, B.M.; Thomas, S.M.; Rachel, A.; Hall, A.; Hyslop, T.; Hwang, E.S. Metaplastic Breast Cancer Treatment and Outcomes in 2500 Patients: A Retrospective Analysis of a National Oncology Database. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 2249–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Hoffmann, A.D.; Liu, H.; Liu, X. Organotropism: New Insights into Molecular Mechanisms of Breast Cancer Metastasis. npj Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, L.M.; Collins, L.C. Diagnostic Pitfalls in Breast Cancer Pathology with an Emphasis on Core Needle Biopsy Specimens. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2023, 147, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provenzano, E.; Pinder, S.E. Pre-Operative Diagnosis of Breast Cancer in Screening: Problems and Pitfalls. Pathology 2009, 41, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, H.; Akın, I.B.; Durak, M.G.; Balcı, P. Multimodality Imaging and Histopathology of Metaplastic Breast Cancer. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2023, 29, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hilli, Z.; Choong, G.; Keeney, M.G.; Visscher, D.W.; Ingle, J.N.; Goetz, M.P.; Jakub, J.W. Metaplastic Breast Cancer Has a Poor Response to Neoadjuvant Systemic Therapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019, 176, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology, Breast Cancer, Version 4. 2025, p. 66. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast.pdf (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- van den Ende, N.S.; Nguyen, A.H.; Jager, A.; Kok, M.; Debets, R.; van Deurzen, C.H.M. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer and Predictive Markers of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, S.; Soule, E.; Long, D.; Jasra, B.; Sharma, S. When Something Seems Amiss: Radiology-Pathology Correlation of Metaplastic Breast Cancer. Cureus 2020, 12, e8239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, A.; Beichel, R.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Finet, J.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pujol, S.; Bauer, C.; Jennings, D.; Fennessy, F.; Sonka, M.; et al. 3D Slicer as an Image Computing Platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibshiranit, R. Regression Shrinkage and Selection via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Society. Ser. B 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, J.R. Induction of Decision Trees. Mach. Learn. 1986, 1, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, T.M.; Hart, P.E. Nearest Neighbor Pattern Classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1967, 13, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-Vector Networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rish, I. An Empirical Study of the Naïve Bayes Classifier. Work Empir Methods Artif Intell. 2001, 3, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, S.H.; Duncan, D.B. Biometrika Trust. Biometrika 2025, 54, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy Function Approximation: A Gradient Boosting Machine. Ann. Statist. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Du, S.; Gao, S.; Guo, L.; Zhao, R.; Bian, X.; Xie, L.; Zhang, L. Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer Identified by Dynamically Enhanced MRI Radiomics: The Delayed Phase Cannot Be Ignored. Insights Imaging 2024, 15, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.Y.; Zhang, H.T.; Gao, S.; Li, G.; Sun, Z.Y.; Tang, Z.; Cai, J.M.; Tian, N.; Zhou, J.; Dong, J.H.; et al. Predicting Breast Cancer Subtypes Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging Based Radiomics with Automatic Segmentation. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2023, 47, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, M.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Yu, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z. Prediction of the Clinicopathological Subtypes of Breast Cancer Using a Fisher Discriminant Analysis Model Based on Radiomic Features of Diffusion-Weighted MRI. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, R.M.; Panthi, B.; Adrada, B.E.; Boge, M.; Candelaria, R.P.; Chen, H.; Guirguis, M.S.; Hunt, K.K.; Huo, L.; Hwang, K.P.; et al. Multiparametric MRI–Based Radiomic Models for Early Prediction of Response to Neoadjuvant Systemic Therapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, T.; Wu, Z.; Lin, Q.; Wang, H.; Ge, Y.; Duan, S.; Fu, G.; Cui, C.; Su, X. Radiomic Signatures Derived from Multiparametric MRI for the Pretreatment Prediction of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20200287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Fan, W.; Yang, Z. Combining Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Maps for a Radiomics Nomogram to Predict Pathological Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2020, 44, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Metaplastic Breast Cancer (TNBC) | Non-Metaplastic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) | |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | Rare (<1% of all breast cancers) | Accounts for 10–20% of all breast cancers |
| Histology | Heterogeneous, with epithelial and mesenchymal differentiation; may include spindle cells, squamous cells, or chondroid/osteoid elements | Homogeneous histology; lacks the diverse cellular differentiation seen in MBC |
| Receptor Status | Usually triple-negative (ER-, PR-, HER2-), though rare exceptions exist | Defined by triple-negative receptor status |
| Aggressiveness | Highly aggressive; disease-free survival is lower | An aggressive tumor profile |
| Lymph Node Involvement | Less common compared to non-metaplastic TNBC | More frequent compared to MBC |
| Metastasis Pattern | More likely to metastasize to lungs, bone, and distant sites; lower rates of lymphatic spread | Commonly metastasizes to lungs, brain, higher rate of lymphatic spread |
| Prognosis | Poorer prognosis than non-metaplastic TNBC due to treatment resistance; lower survival rates, especially in metastatic disease | Poor prognosis compared to hormone receptor-positive breast cancers, but slightly better than MBC |
| Response to NAC | Frequently resistant to standard NAC | Chemo-sensitive, partial and complete pathologic response rates were remarkably high |
| Clinical Trials | Heavily reliant on clinical trials due to lack of standardized therapies | Clinical trials also recommended but more established guidelines exist |
| Characteristics | Metaplastic Breast Cancer (MBC) | Non-Metaplastic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial patients | 40 | 89 | |
| Exclusions | 13 (lack of perioperative MRI, lack of pre-NAC imaging, suboptimal MRI sequencing, recurrence, or systemic metastases) | 11 (systemic metastases: 3, suboptimal MRI sequencing: 5, lack of pre-NAC imaging: 3) | |
| Patients analyzed | 27 | 78 | |
| Age | 0.090 | ||
| Mean ± SD (years) | 44.2 ± 10.1 | 48.2 ± 11.0 | |
| Median (IQR) (years) | 45 [37–48] | 48 [40–55] | |
| Tumor size | 0.560 | ||
| Mean ± SD (mm) | 39.5 ± 25.0 | 39.0 ± 18.3 | |
| Median (IQR) (mm) | 32 [26–42] | 33 [28–48] | |
| Hormone receptor profiles | 40% ER+ (1 case), HER2+ (1 case), 5% ER/5% PR+ (1 case), others TN | All TN | |
| NAC response | Non-responders: 6 (42.9%) Poor responders: 6 (42.9%) Partial responders: 2 (14.2%) | Complete response: 38 (48.7%) Partial response: 27 (34.6%) Poor response: 11 (14.1%) No response: 2 (2.5%) | |
| Histological subtypes | Undifferentiated n = 12 (44.4%), Matrix-producing n = 6 (22.2%), Squamous differentiation n = 9 (33.3%), Apocrine/spindle sarcomatous features n = 1 (3.7%) | Non-specific invasive carcinoma Squamous-differentiated invasive ductal carcinoma (1 case among poor responders) Papillary-differentiated invasive ductal carcinoma (1 case among non-responders) |
| ML Model | AUC | Prec (%) | Sens (%) | Spec (%) | F1 (%) | Acc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decision Tree | 0.700 | 73.00 | 48.00 | 92.00 | 55.30 | 0.81 |
| Random Forest | 0.724 | 45.21 | 60.00 | 68.00 | 49.68 | 0.66 |
| KNeighbors | 0.641 | 53.56 | 48.00 | 80.00 | 49.54 | 0.72 |
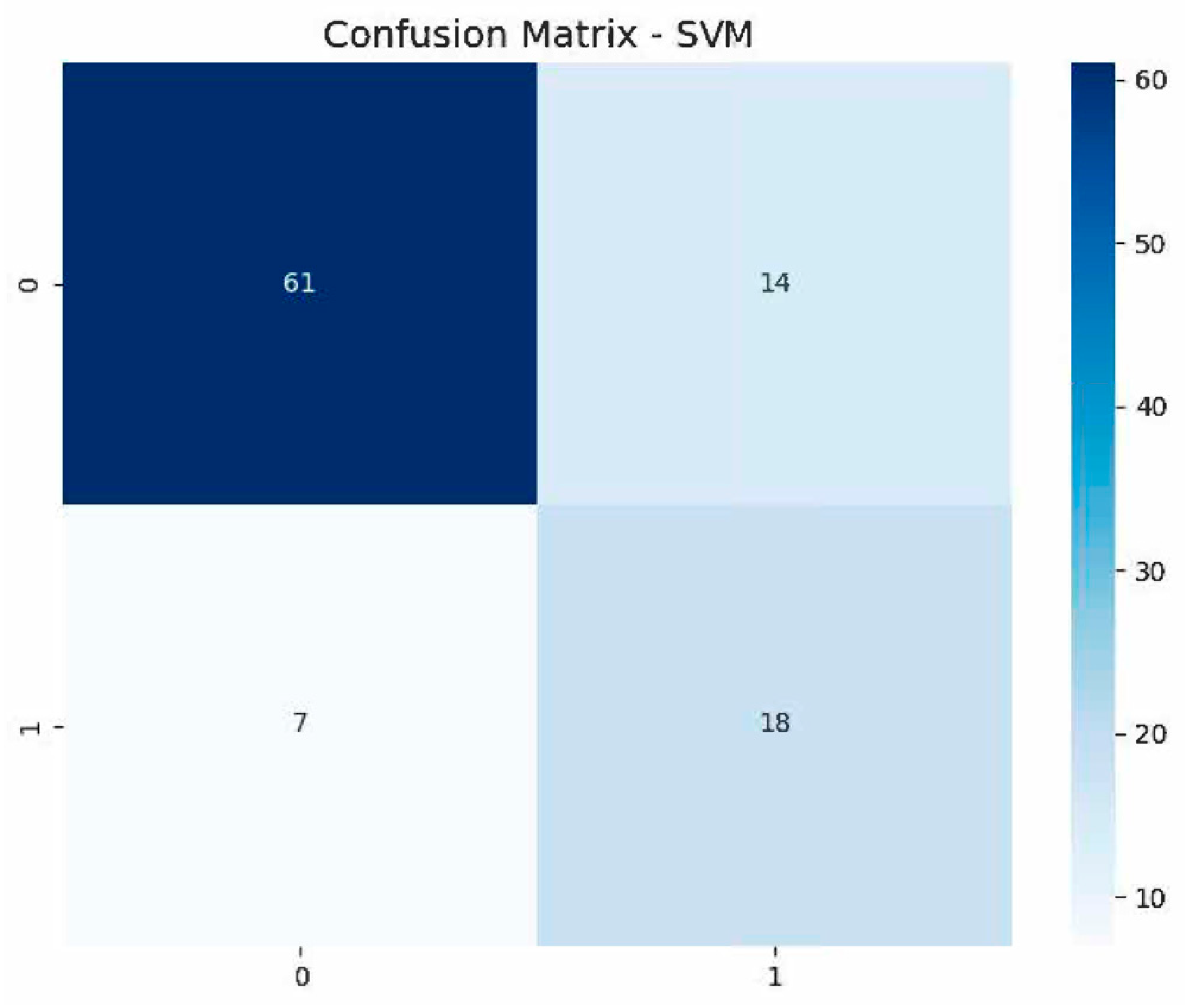
| SVM | 0.845 | 59.33 | 72.00 | 81.33 | 64.12 | 0.79 |
| GaussianNB | 0.629 | 25.08 | 72.00 | 32.00 | 36.48 | 0.42 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.832 | 61.09 | 76.00 | 81.33 | 66.32 | 0.80 |
| Gradient Boosting | 0.811 | 59.39 | 60.00 | 81.33 | 56.99 | 0.76 |
| ML Model | AUC | Prec (%) | Sens (%) | Spec (%) | F1 (%) | Acc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decision Tree | 0.687 | 59.76 | 56.00 | 81.33 | 53.22 | 0.75 |
| Random Forest | 0.663 | 39.17 | 52.00 | 65.33 | 42.56 | 0.62 |
| KNeighbors | 0.540 | 38.00 | 24.00 | 80.00 | 25.26 | 0.66 |
| SVM | 0.805 | 68.43 | 68.00 | 84.00 | 65.67 | 0.80 |
| GaussianNB | 0.467 | 17.45 | 56.00 | 26.67 | 26.58 | 0.34 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.779 | 60.50 | 68.00 | 81.33 | 62.05 | 0.78 |
| Gradient Boosting | 0.664 | 58.00 | 56.00 | 78.67 | 52.49 | 0.73 |
| ML Model | AUC | Prec (%) | Sens (%) | Spec (%) | F1 (%) | Acc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decision Tree | 0.680 | 58.00 | 56.00 | 80.00 | 50.93 | 0.74 |
| Random Forest | 0.713 | 44.96 | 60.00 | 72.00 | 49.23 | 0.69 |
| KNeighbors | 0.660 | 42.71 | 52.00 | 77.33 | 46.44 | 0.71 |
| SVM | 0.768 | 59.14 | 60.00 | 82.67 | 57.91 | 0.77 |
| GaussianNB | 0.555 | 25.92 | 60.00 | 42.67 | 36.14 | 0.47 |
| Logistic Regression | 0.757 | 55.24 | 52.00 | 78.67 | 47.06 | 0.72 |
| Gradient Boosting | 0.755 | 47.83 | 56.00 | 76.00 | 49.69 | 0.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Comert, R.G.; Durak, G.; Yilmaz, R.; Aktas, H.E.; Tuz, Z.; Pan, H.; Zeng, J.; Bayram, A.; Mollavelioglu, B.; Erturk, S.M.; et al. Radiomics for Detecting Metaplastic Histology in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Step Towards Personalized Therapy. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090973
Comert RG, Durak G, Yilmaz R, Aktas HE, Tuz Z, Pan H, Zeng J, Bayram A, Mollavelioglu B, Erturk SM, et al. Radiomics for Detecting Metaplastic Histology in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Step Towards Personalized Therapy. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(9):973. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090973
Chicago/Turabian StyleComert, Rana Gunoz, Gorkem Durak, Ravza Yilmaz, Halil Ertugrul Aktas, Zeynep Tuz, Hongyi Pan, Jun Zeng, Aysel Bayram, Baran Mollavelioglu, Sukru Mehmet Erturk, and et al. 2025. "Radiomics for Detecting Metaplastic Histology in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Step Towards Personalized Therapy" Bioengineering 12, no. 9: 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090973
APA StyleComert, R. G., Durak, G., Yilmaz, R., Aktas, H. E., Tuz, Z., Pan, H., Zeng, J., Bayram, A., Mollavelioglu, B., Erturk, S. M., & Bagci, U. (2025). Radiomics for Detecting Metaplastic Histology in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Step Towards Personalized Therapy. Bioengineering, 12(9), 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090973








