Exploring Sarcopenic Obesity in the Cancer Setting: Insights from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey on Prognosis and Predictors Using Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source and Sample Collection
2.2. DXA and the Definition of SO
- Non-sarcopenia with non-obesity (nS-nO);
- Non-sarcopenia with obesity (nS-O);
- Sarcopenia with non-obesity (S-nO);
- Sarcopenia with obesity (S-O).
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Building Process and Statistical Analysis of the Machine-Learning Models for Predicting SO
2.4.1. Data Preprocessing
2.4.2. Training and Test Sets
2.4.3. Model Building Process
2.4.4. Performance Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Characteristics Among Cancer Population
3.2. SO and All-Cause Mortality in the Entire Cohort
3.3. SO and All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Different Cancer Systems
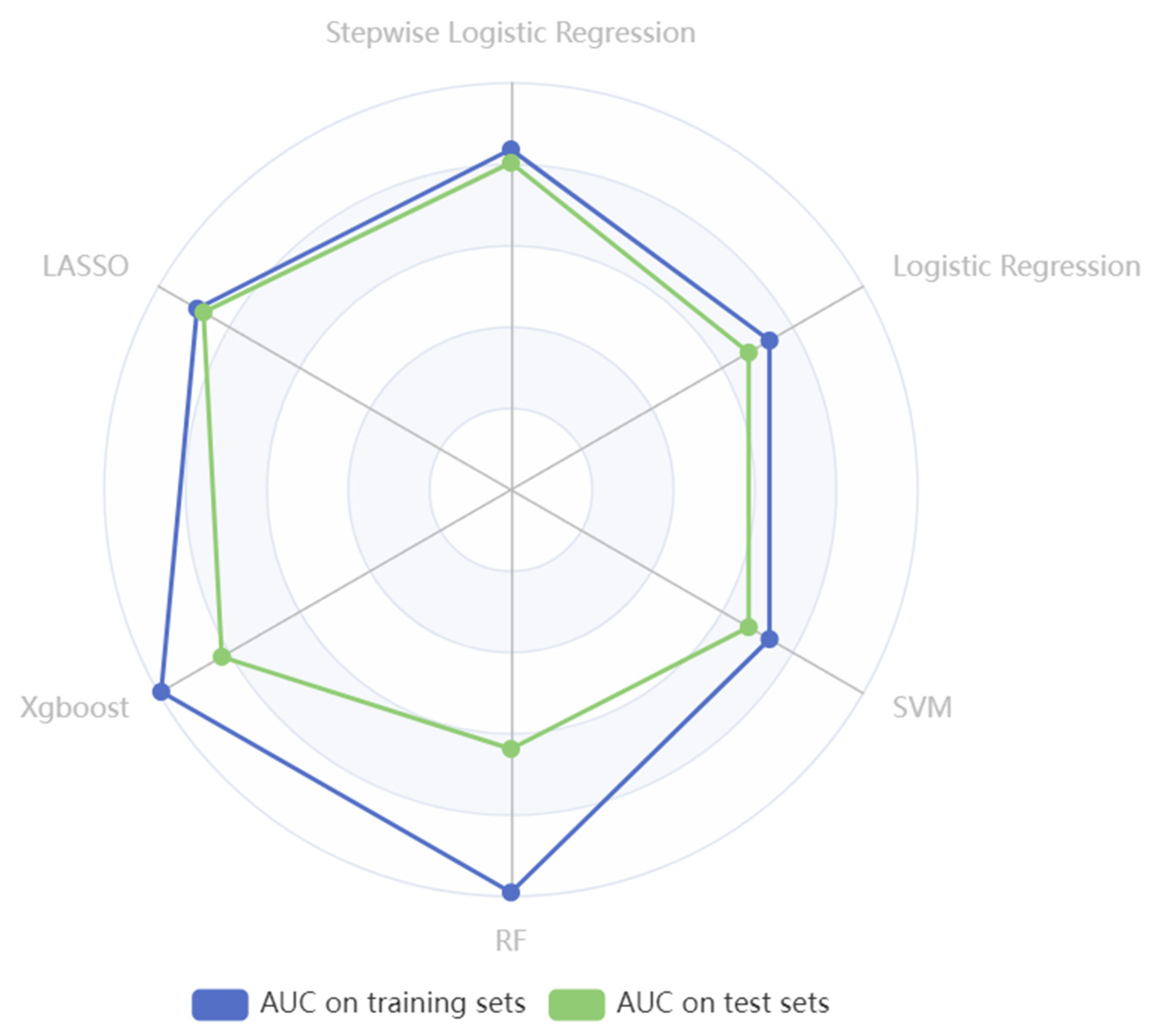
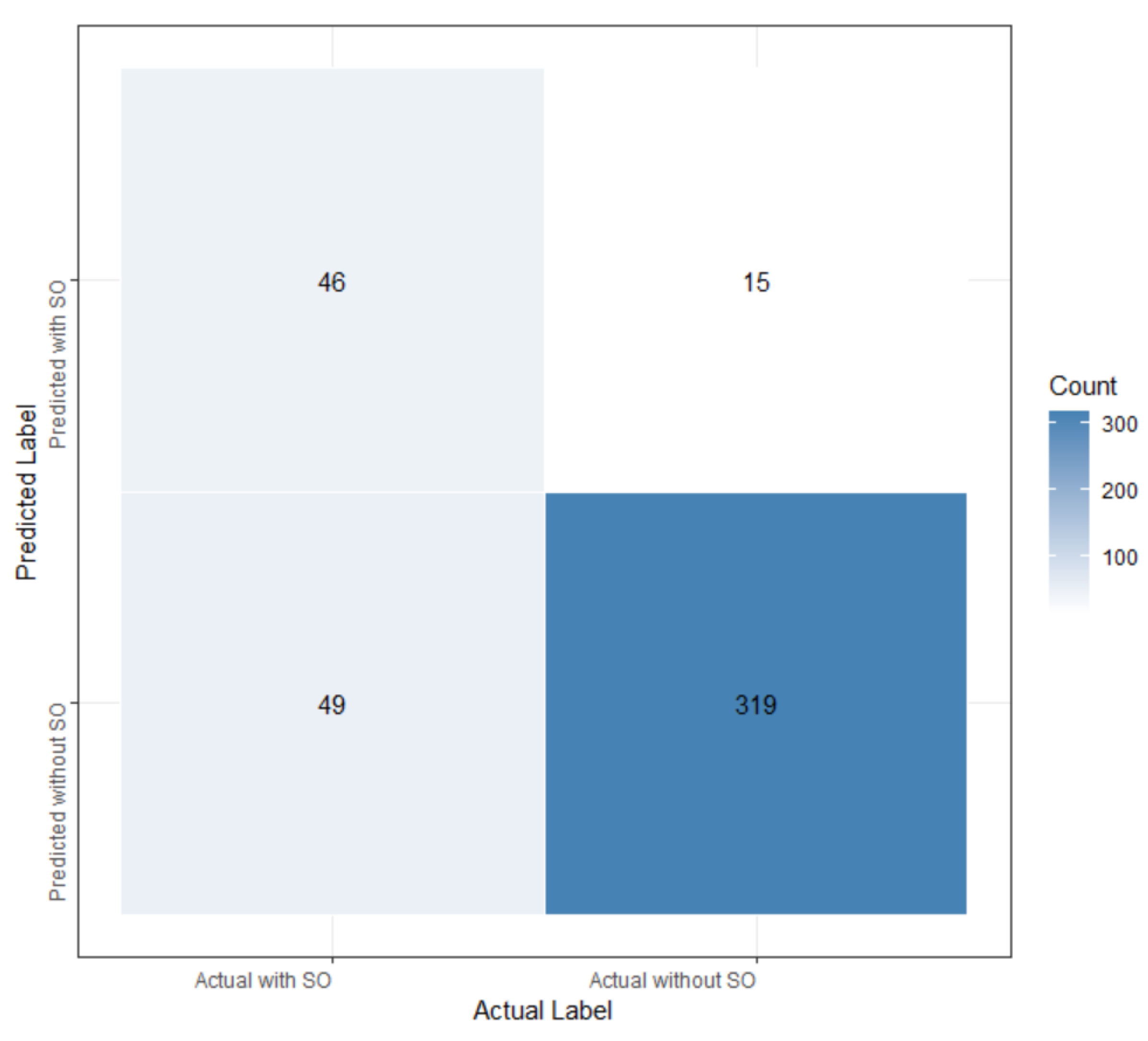
3.4. Performance of Different Machine Learning Models in Predicting SO
4. Discussion
4.1. Prediction of SO
4.2. The Mechanism of SO in the Development and Progression of Cancer
4.3. The Influence of Obesity in Cancer Patients with SO
4.4. Novelty and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Gortan, C.G.; Brasacchio, C.; Laudisio, D.; Lubrano, C.; Pivari, F.; Barrea, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Obesity Programs of Nutrition, Education, Research and Assessment (OPERA) Group. Sarcopenic obesity: What about in the cancer setting? Nutrition 2022, 98, 111624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batsis, J.A.; Villareal, D.T. Sarcopenic obesity in older adults: Aetiology, epidemiology and treatment strategies. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 513–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephen, W.C.; Janssen, I. Sarcopenic-obesity and cardiovascular disease risk in the elderly. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2009, 13, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damanti, S.; Colloca, G.F.; Ferrini, A.; Consonni, D.; Cesari, M. Sarcopenia (and sarcopenic obesity) in older patients with gynecological malignancies. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2021, 12, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, C.M.; Wells, J.C.; Smith, S.R.; Stephan, B.C.; Siervo, M. Sarcopenic obesity: A Critical appraisal of the current evidence. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 583–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamboni, M.; Rubele, S.; Rossi, A.P. Sarcopenia and obesity. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 22, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieli-Conwright, C.M.; Courneya, K.S.; Demark-Wahnefried, W.; Sami, N.; Lee, K.; Buchanan, T.A.; Spicer, D.V.; Tripathy, D.; Bernstein, L.; Mortimer, J.E. Effects of Aerobic and Resistance Exercise on Metabolic Syndrome, Sarcopenic Obesity, and Circulating Biomarkers in Overweight or Obese Survivors of Breast Cancer: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, R.; Tang, H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Luo, S.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, J.; Yang, M. Development and multi-center cross-setting validation of an explainable prediction model for sarcopenic obesity: A machine learning approach based on readily available clinical features. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2025, 37, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, I.P.; Mazurak, V.C.; Prado, C.M. Clinical Implications of Sarcopenic Obesity in Cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 18, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Han, S.H.; Kim, H.I. Detection of sarcopenic obesity and prediction of long-term survival in patients with gastric cancer using preoperative computed tomography and machine learning. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 124, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, M.; Sammarco, R.; De Lorenzo, A.; Iellamo, F.; Siervo, M.; Pietrobelli, A.; Donini, L.M.; Santarpia, L.; Cataldi, M.; Pasanisi, F.; et al. Assessment of Body Composition in Health and Disease Using Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) and Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA): A Critical Overview. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2019, 2019, 3548284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiel, F.; Persson, C.; Furness, J.; Simas, V.; Pope, R.; Climstein, M.; Hing, W.; Schram, B. Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry positioning protocols in assessing body composition: A systematic review of the literature. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2018, 21, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollough, C.H.; Schueler, B.A.; Atwell, T.D.; Braun, N.N.; Regner, D.M.; Brown, D.L.; LeRoy, A.J. Radiation exposure and pregnancy: When should we be concerned? Radiographics 2007, 27, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studenski, S.A.; Peters, K.W.; Alley, D.E.; Cawthon, P.M.; McLean, R.R.; Harris, T.B.; Ferrucci, L.; Guralnik, J.M.; Fragala, M.S.; Kenny, A.M.; et al. The FNIH sarcopenia project: Rationale, study description, conference recommendations, and final estimates. J. Gerontol. A-Biol. 2014, 69, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, R.R.; Shardell, M.D.; Alley, D.E.; Cawthon, P.M.; Fragala, M.S.; Harris, T.B.; Kenny, A.M.; Peters, K.W.; Ferrucci, L.; Guralnik, J.M.; et al. Criteria for clinically relevant weakness and low lean mass and their longitudinal association with incident mobility impairment and mortality: The foundation for the National Institutes of Health (FNIH) sarcopenia project. J. Gerontol. A-Biol. 2014, 69, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolcott, O.O.; Bergman, R.N. Relative fat mass (RFM) as a new estimator of whole-body fat percentage ─ A cross-sectional study in American adult individuals. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasson, A.; Carlsson, A.C.; Önnerhag, K.; Hagström, H. Predictive Capacity for Mortality and Severe Liver Disease of the Relative Fat Mass Algorithm. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 2619–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolcott, O.O.; Bergman, R.N. Defining cutoffs to diagnose obesity using the relative fat mass (RFM): Association with mortality in NHANES 1999–2014. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagasabai, T.; Thakkar, N.A.; Kuk, J.L.; Churilla, J.R.; Ardern, C.I. Differences in physical activity domains, guideline adherence, and weight history between metabolically healthy and metabolically abnormal obese adults: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2015, 12, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biolo, G.; Di Girolamo, F.G.; Breglia, A.; Chiuc, M.; Baglio, V.; Vinci, P.; Toigo, G.; Lucchin, L.; Jurdana, M.; Pražnikar, Z.J.; et al. Inverse relationship between “a body shape index” (ABSI) and fat-free mass in women and men: Insights into mechanisms of sarcopenic obesity. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Simon, F.; Achiardi, O.; Vilos, C.; Cabrera, D.; Cabello-Verrugio, C. The Critical Role of Oxidative Stress in Sarcopenic Obesity. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 4493817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, V.; Tuli, H.S.; Varol, A.; Thakral, F.; Yerer, M.B.; Sak, K.; Varol, M.; Jain, A.; Khan, M.A.; Sethi, G. Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Cancer Progression: Molecular Mechanisms and Recent Advancements. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, A.E.; Goodwin, P.J.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Pan, K.; Stambolic, V.; Dowling, R.J. Association of Obesity-Related Metabolic Disruptions With Cancer Risk and Outcome. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4249–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.C.; Yang, W.V. Hyperglycemia, tumorigenesis, and chronic inflammation. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 108, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayers, J.R.; Torrence, M.E.; Danai, L.V.; Papagiannakopoulos, T.; Davidson, S.M.; Bauer, M.R.; Lau, A.N.; Ji, B.W.; Dixit, P.D.; Hosios, A.M.; et al. Tissue of origin dictates branched-chain amino acid metabolism in mutant Kras-driven cancers. Science 2016, 353, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasor, J.; Danes, J.M.; Komm, B.; Chang, K.C.; Lyttle, C.R.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S. Profiling of estrogen up- and down-regulated gene expression in human breast cancer cells: Insights into gene networks and pathways underlying estrogenic control of proliferation and cell phenotype. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 4562–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, E.A.; da Silva Filho, R.R.; Spexoto, M.C.B.; Haghighatdoost, F.; Sarrafzadegan, N.; de Oliveira, C. The Role of Sarcopenic Obesity in Cancer and Cardiovascular Disease: A Synthesis of the Evidence on Pathophysiological Aspects and Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köylü, B.; Sulu, C.; Yumuk, V.D.; Yumuk, P.F. The impact of sarcopenic obesity on cancer clinical outcomes. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2025, 114, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgerinos, K.I.; Spyrou, N.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Dalamaga, M. Obesity and cancer risk: Emerging biological mechanisms and perspectives. Metabolism 2019, 92, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D.; Sen, A.; Prasad, M.; Norat, T.; Janszky, I.; Tonstad, S.; Romundstad, P.; Vatten, L.J. BMI and all cause mortality: Systematic review and non-linear dose-response meta-analysis of 230 cohort studies with 3.74 million deaths among 30.3 million participants. BMJ 2016, 353, i2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, F.; Cortellini, A.; Indini, A.; Tomasello, G.; Ghidini, M.; Nigro, O.; Salati, M.; Dottorini, L.; Iaculli, A.; Varricchio, A.; et al. Association of Obesity With Survival Outcomes in Patients With Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e213520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schetz, M.; De Jong, A.; Deane, A.M.; Druml, W.; Hemelaar, P.; Pelosi, P.; Pickkers, P.; Reintam-Blaser, A.; Roberts, J.; Sakr, Y.; et al. Obesity in the critically ill: A narrative review. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 45, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.B.; Langouche, L. Endocrine, metabolic, and morphologic alterations of adipose tissue during critical illness. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 41, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacharasint, P.; Boyd, J.H.; Russell, J.A.; Walley, K.R. One size does not fit all in severe infection: Obesity alters outcome, susceptibility, treatment, and inflammatory response. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipoor, E.; Mohammad, H.F.; Hosseinzadeh-Attar, M.J. Adipokines in critical illness: A review of the evidence and knowledge gaps. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1739–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantuzzi, G. Adipose tissue, adipokines, and inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immun. 2005, 115, 911–919, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strulov, S.S.; Williams, G.R. The Obesity Paradox in Cancer-Moving Beyond BMI. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. 2017, 26, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, N.; Bauer, J.; Boltong, A.; Brown, T.; Isenring, L.; Loeliger, J.; Steer, B.; Findlay, M. Awareness, perceptions and practices regarding cancer-related malnutrition and sarcopenia: A survey of cancer clinicians. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 5263–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Overall (n = 1432) | Non-SO (n = 1221) | SO (n = 211) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (median (IQR)) | 62 (50–73) | 60 (49–72) | 71 (58–79.5) | <0.001 |
| Sex = Male (%) | 621 (43.4) | 520 (42.6) | 101 (47.9) | 0.176 |
| Race (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Mexican American | 112 (7.8) | 69 (5.7) | 43 (20.4) | |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 187 (13.1) | 180 (14.7) | 7 (3.3) | |
| Non-Hispanic White | 1044 (72.9) | 895 (73.3) | 149 (70.6) | |
| Other | 89 (6.2) | 77 (6.3) | 12 (5.7) | |
| Education (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Under high school | 324 (22.6) | 252 (20.7) | 72 (34.1) | |
| High school or equivalent | 345 (24.1) | 294 (24.1) | 51 (24.2) | |
| Above high school | 762 (53.2) | 674 (55.2) | 88 (41.7) | |
| Marital status (%) | 0.079 | |||
| Widowed/divorced/separated | 419 (29.8) | 358 (29.8) | 61 (29.6) | |
| Married/cohabiting | 899 (63.8) | 760 (63.2) | 139 (67.5) | |
| Never married | 90 (6.4) | 84 (7.0) | 6 (2.9) | |
| Poverty to income ratio (median (IQR)) | 2.4 (1.2–4.3) | 2.9 (1.4–5) | 2 (1.2–3.2) | <0.001 |
| BMI (median (IQR)) | 27.4 (24.1–31.7) | 26.9 (23.8–31.0) | 30.6 (27.2–34.6) | <0.001 |
| RFM (median (IQR)) | 35.7 (30.3–43.3) | 35.2 (29.4–42.7) | 41.9 (33.5–46.5) | <0.001 |
| Smoking status (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Former | 563 (39.3) | 454 (37.2) | 109 (51.7) | |
| Never | 599 (41.9) | 514 (42.1) | 85 (40.3) | |
| Now | 269 (18.8) | 252 (20.7) | 17 (8.1) | |
| Alcohol consumption status (%) | 0.198 | |||
| Heavy | 152 (18.5) | 139 (19.0) | 13 (14.0) | |
| Mild | 505 (61.4) | 440 (60.3) | 65 (69.9) | |
| Moderate | 166 (20.2) | 151 (20.7) | 15 (16.1) | |
| Glycemic control (%) | <0.001 | |||
| DM | 269 (18.8) | 200 (16.4) | 69 (32.7) | |
| IFG | 66 (4.6) | 56 (4.6) | 10 (4.7) | |
| IGT | 19 (1.3) | 18 (1.5) | 1 (0.5) | |
| Normal | 1078 (75.3) | 947 (77.6) | 131 (62.1) |
| nS-nO (n = 574) | nS-O (n = 613) | S-O (n = 211) | S-nO (n = 34) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (median (IQR)) | 59 (48–72) | 60 (49–70) | 71 (58–79.5) | 76.5 (71–81.75) | <0.001 |
| Sex = Male (%) | 301 (52.4) | 193 (31.5) | 101 (47.9) | 26 (76.5) | <0.001 |
| Race (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| Mexican American | 27 (4.7) | 40 (6.5) | 43 (20.4) | 2 (5.9) | |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 73 (12.7) | 106 (17.3) | 7 (3.3) | 1 (2.9) | |
| Non-Hispanic White | 439 (76.5) | 427 (69.7) | 149 (70.6) | 29 (85.3) | |
| Other | 35 (6.1) | 40 (6.5) | 12 (5.7) | 2 (5.9) | |
| Education (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| Under high school | 101 (17.6) | 139 (22.7) | 72 (34.1) | 12 (35.3) | |
| High school or equivalent | 136 (23.7) | 145 (23.7) | 51 (24.2) | 13 (38.2) | |
| Above high school | 336 (58.6) | 329 (53.7) | 88 (41.7) | 9 (26.5) | |
| Marital status (%) | 0.008 | ||||
| Widowed/divorced/separated | 142 (25.4) | 205 (33.7) | 61 (29.6) | 11 (32.4) | |
| Married/cohabiting | 371 (66.2) | 367 (60.4) | 139 (67.5) | 22 (64.7) | |
| Never married | 47 (8.4) | 36 (5.9) | 6 (2.9) | 1 (2.9) | |
| Poverty to income ratio (median (IQR)) | 3.4 (1.6–5) | 2.6 (1.3–4.3) | 2 (1.2–3.2) | 2 (1.3–3.3) | <0.001 |
| BMI (median (IQR)) | 23.9 (21.7–25.7) | 30.9 (28.2–34.9) | 30.6 (27.2–34.6) | 24.1 (23.5–25.3) | <0.001 |
| RFM (median (IQR)) | 29.4 (26.8–35.7) | 42.6 (34.2–45.7) | 41.9 (33.5–46.5) | 29.2 (27.3–30.0) | <0.001 |
| Smoking status (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| Former | 204 (35.6) | 235 (38.3) | 109 (51.7) | 15 (44.1) | |
| Never | 233 (40.7) | 266 (43.4) | 85 (40.3) | 15 (44.1) | |
| Now | 136 (23.7) | 112 (18.3) | 17 (8.1) | 4 (11.8) | |
| Alcohol consumption status (%) | 0.232 | ||||
| Heavy | 65 (16.9) | 72 (21.6) | 13 (14.0) | 2 (15.4) | |
| Mild | 240 (62.5) | 190 (57.1) | 65 (69.9) | 10 (76.9) | |
| Moderate | 79 (20.6) | 71 (21.3) | 15 (16.1) | 1 (7.7) | |
| Glycemic control (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| DM | 62 (10.8) | 134 (21.9) | 69 (32.7) | 4 (11.8) | |
| IFG | 20 (3.5) | 33 (5.4) | 10 (4.7) | 3 (8.8) | |
| IGT | 5 (0.9) | 13 (2.1) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Normal | 487 (84.8) | 433 (70.6) | 131 (62.1) | 27 (79.4) |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95%CIs Lower | 95%CIs Upper | p | HR | 95%CIs Lower | 95%CIs Upper | p | HR | 95%Cis Lower | 95%CIs Upper | p | |
| Dichotomous taxonomy of SO | ||||||||||||
| Non-SO | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||||||||
| SO | 1.476 | 1.211 | 1.799 | <0.001 | 1.367 | 1.122 | 1.666 | 0.002 | 1.368 | 1.107 | 1.690 | 0.004 |
| Quadruple taxonomy of SO | ||||||||||||
| nS-nO | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||||||||
| nS-O | 0.812 | 0.677 | 0.974 | 0.025 | 0.898 | 0.747 | 1.080 | 0.255 | 0.858 | 0.711 | 1.036 | 0.110 |
| S-O | 1.364 | 1.097 | 1.698 | 0.005 | 1.326 | 1.066 | 1.651 | 0.011 | 1.298 | 1.028 | 1.640 | 0.028 |
| S-nO | 2.002 | 1.335 | 3.004 | <0.001 | 1.714 | 1.142 | 2.572 | 0.009 | 1.565 | 1.038 | 2.362 | 0.033 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95%CIs Lower | 95%CIs Upper | p | HR | 95%CIs Lower | 95%CIs Upper | p | HR | 95%CIs Lower | 95%CIs Upper | p | |
| Dichotomous taxonomy of SO | ||||||||||||
| Non-SO | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||||||||
| SO | 1.562 | 1.036 | 2.357 | 0.034 | 1.459 | 0.965 | 2.206 | 0.073 | 1.345 | 0.847 | 2.137 | 0.209 |
| Quadruple taxonomy of SO | ||||||||||||
| nS-nO | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||||||||
| nS-O | 1.265 | 0.845 | 1.893 | 0.254 | 1.200 | 0.801 | 1.797 | 0.376 | 1.117 | 0.742 | 1.682 | 0.595 |
| S-O | 1.836 | 1.124 | 2.999 | 0.015 | 1.661 | 1.014 | 2.721 | 0.044 | 1.464 | 0.855 | 2.506 | 0.321 |
| S-nO | 1.892 | 0.668 | 5.360 | 0.230 | 1.685 | 0.594 | 4.781 | 0.326 | 1.736 | 0.585 | 5.153 | 0.165 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95%CIs Lower | 95%CIs Upper | p | HR | 95%CIs Lower | 95%CIs Upper | p | HR | 95%Cis Lower | 95%CIs Upper | p | |
| Dichotomous taxonomy of SO | ||||||||||||
| Non-SO | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||||||||
| SO | 1.612 | 1.102 | 2.359 | 0.014 | 1.520 | 1.038 | 2.226 | 0.031 | 1.318 | 0.882 | 1.970 | 0.178 |
| Quadruple taxonomy of SO | ||||||||||||
| nS-nO | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||||||||
| nS-O | 1.036 | 0.746 | 1.439 | 0.834 | 1.055 | 0.756 | 1.474 | 0.752 | 0.960 | 0.673 | 1.370 | 0.822 |
| S-O | 1.633 | 1.080 | 2.470 | 0.020 | 1.554 | 1.028 | 2.349 | 0.037 | 1.287 | 0.823 | 2.012 | 0.268 |
| S-nO | 0.665 | 0.092 | 4.799 | 0.686 | 0.684 | 0.095 | 4.947 | 0.707 | 0.861 | 0.118 | 6.283 | 0.883 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95%CIs Lower | 95%CIs Upper | p | HR | 95%CIs Lower | 95%CIs Upper | p | HR | 95%CIs Lower | 95%CIs Upper | p | |
| Dichotomous taxonomy of SO | ||||||||||||
| Non-SO | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||||||||
| SO | 1.083 | 0.587 | 1.999 | 0.797 | 1.081 | 0.586 | 1.993 | 0.804 | 1.554 | 0.776 | 3.112 | 0.213 |
| Quadruple taxonomy of SO | ||||||||||||
| nS-nO | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||||||||
| nS-O | 0.653 | 0.367 | 1.163 | 0.148 | 0.655 | 0.365 | 1.176 | 0.156 | 0.635 | 0.347 | 1.164 | 0.142 |
| S-O | 0.843 | 0.432 | 1.647 | 0.618 | 0.842 | 0.430 | 1.648 | 0.616 | 1.177 | 0.554 | 2.501 | 0.671 |
| S-nO | 0.502 | 0.151 | 1.663 | 0.259 | 0.502 | 0.151 | 1.663 | 0.259 | 0.455 | 0.131 | 1.582 | 0.216 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95%CIs Lower | 95%CIs Upper | p | HR | 95%CIs Lower | 95%CIs Upper | p | HR | 95%CIs Lower | 95%CIs Upper | p | |
| Dichotomous taxonomy of SO | ||||||||||||
| Non-SO | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||||||||
| SO | 1.024 | 0.687 | 1.527 | 0.908 | 1.117 | 0.747 | 1.668 | 0.590 | 0.968 | 0.614 | 1.526 | 0.889 |
| Quadruple taxonomy of SO | ||||||||||||
| nS-nO | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||||||||
| nS-O | 0.737 | 0.493 | 1.103 | 0.138 | 0.782 | 0.522 | 1.172 | 0.233 | 0.806 | 0.534 | 1.215 | 0.302 |
| S-O | 0.940 | 0.609 | 1.453 | 0.782 | 1.051 | 0.679 | 1.626 | 0.824 | 0.928 | 0.566 | 1.524 | 0.768 |
| S-nO | 1.473 | 0.808 | 2.687 | 0.207 | 1.430 | 0.783 | 2.609 | 0.245 | 1.577 | 0.855 | 2.908 | 0.144 |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95%CIs Lower | 95%CIs Upper | p | HR | 95%CIs Lower | 95%CIs Upper | p | HR | 95%CIs Lower | 95%CIs Upper | p | |
| Dichotomous taxonomy of SO | ||||||||||||
| Non-SO | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||||||||
| SO | 2.743 | 1.353 | 5.558 | 0.005 | 1.839 | 0.845 | 4.005 | 0.125 | 1.822 | 0.688 | 4.824 | 0.227 |
| Quadruple taxonomy of SO | ||||||||||||
| nS-nO | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||||||||
| nS-O | 1.598 | 0.683 | 3.742 | 0.280 | 1.330 | 0.543 | 3.259 | 0.533 | 0.762 | 0.257 | 2.258 | 0.623 |
| S-O | 3.521 | 1.480 | 8.377 | 0.004 | 2.098 | 0.853 | 5.160 | 0.107 | 1.565 | 0.503 | 4.871 | 0.439 |
| S-nO | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Model | Selected Features | Train | Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| XGBoost | All features | 0.993 | 0.821 |
| RF | All features | 0.990 | 0.637 |
| SVM | All features | 0.742 | 0.633 |
| Top 10 features | 0.622 | 0.605 | |
| Top 15 features | 0.615 | 0.587 | |
| Top 20 features | 0.624 | 0.587 | |
| Logistic Regression | All features | 0.941 | 0.785 |
| Top 10 features | 0.673 | 0.588 | |
| Top 15 features | 0.720 | 0.675 | |
| Top 20 features | 0.734 | 0.675 | |
| Stepwise Logistic Regression | All features | 0.928 | 0.809 |
| Top 10 features | 0.699 | 0.627 | |
| Top 15 features | 0.762 | 0.682 | |
| Top 20 features | 0.837 | 0.804 | |
| LASSO | All features | 0.915 | 0.832 |
| Top 10 features | 0.842 | 0.818 | |
| Top 11 features | 0.846 | 0.815 | |
| Top 12 features | 0.846 | 0.815 | |
| Top 13 features | 0.846 | 0.815 | |
| Top 14 features | 0.855 | 0.843 | |
| Top 15 features | 0.862 | 0.847 | |
| Top 16 features | 0.889 | 0.852 | |
| Top 17 features | 0.891 | 0.873 | |
| Top 18 features | 0.892 | 0.869 | |
| Top 19 features | 0.890 | 0.863 | |
| Top 20 features | 0.891 | 0.858 |
| Variable | Type | Coding and Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Epilepsy (x1) | Categorical | 1 = had history of epilepsy; 0 = no history of epilepsy |
| Anemia, Moderate (x2) | Categorical | 1 = moderate anemia; 0 = mild anemia, non-anemia, or missing data |
| Race, Mexican American (x3) | Categorical | 1 = Mexican American; 0 = Non-Hispanic Black, Non-Hispanic White, other |
| Parkinson (x4) | Categorical | 1 = had history of Parkinson; 0 = no history of Parkinson |
| No history of heart attack (x5) | Categorical | 1 = no history of heart attack; 0 = had history of heart attack or missing data |
| Race, Non-Hispanic Black (x6) | Categorical | 1 = Non-Hispanic Black; 0 = Mexican American, Non-Hispanic White, other |
| Waist circumference (x7) | Continuous | Measured in centimeters (cm) |
| Stroke (x8) | Categorical | 1 = no stroke history; 0 = had stroke or missing data |
| Upper arm length (x9) | Continuous | Measured in centimeters (cm) |
| MAO (x10) | Categorical | 1 = diagnosed as metabolically abnormal obese; 0 = no metabolically abnormal obese or missing data |
| Congestive heart failure (x11) | Categorical | 1 = had congestive heart failure; 0 = no congestive heart failure or missing data |
| Age (x12) | Continuous | Measured in years, integer |
| Upper leg length (x13) | Continuous | Measured in centimeters (cm) |
| Smoke now (x14) | Categorical | 1 = current smoker; 0 = former smoker, never smoked, or missing data |
| Military (x15) | Categorical | 1 = participant has prior service in the armed forces; 0 = participant has no prior service in the armed forces |
| ABSI (x16) | Continuous | ABSI = (waist circumference / hip circumference) ÷ BMI |
| Heart attack (x17) | Categorical | 1 = had history of heart attack; 0 = no history of heart attack or missing data |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Wang, Q.; Wei, T.; Chan, L.W.C. Exploring Sarcopenic Obesity in the Cancer Setting: Insights from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey on Prognosis and Predictors Using Machine Learning. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090921
Jiang Y, Jiang W, Wang Q, Wei T, Chan LWC. Exploring Sarcopenic Obesity in the Cancer Setting: Insights from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey on Prognosis and Predictors Using Machine Learning. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(9):921. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090921
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Yinuo, Wenjie Jiang, Qun Wang, Ting Wei, and Lawrence Wing Chi Chan. 2025. "Exploring Sarcopenic Obesity in the Cancer Setting: Insights from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey on Prognosis and Predictors Using Machine Learning" Bioengineering 12, no. 9: 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090921
APA StyleJiang, Y., Jiang, W., Wang, Q., Wei, T., & Chan, L. W. C. (2025). Exploring Sarcopenic Obesity in the Cancer Setting: Insights from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey on Prognosis and Predictors Using Machine Learning. Bioengineering, 12(9), 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090921







