Purification and Characterization of Polyhydroxyalkanoate Synthase from Extremely Halophilic Archaeon Haloferax mediterranei: Key Enzyme of Biodegradable Plastic Synthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagent and Standards
2.2. Microorganisms and Growth Conditions
2.3. Production and Purification of PHA Synthase
2.4. Determination of PHA Synthase Activity
2.5. Characterization of PHA Synthase
3. Results
3.1. Purification of PHA Synthase
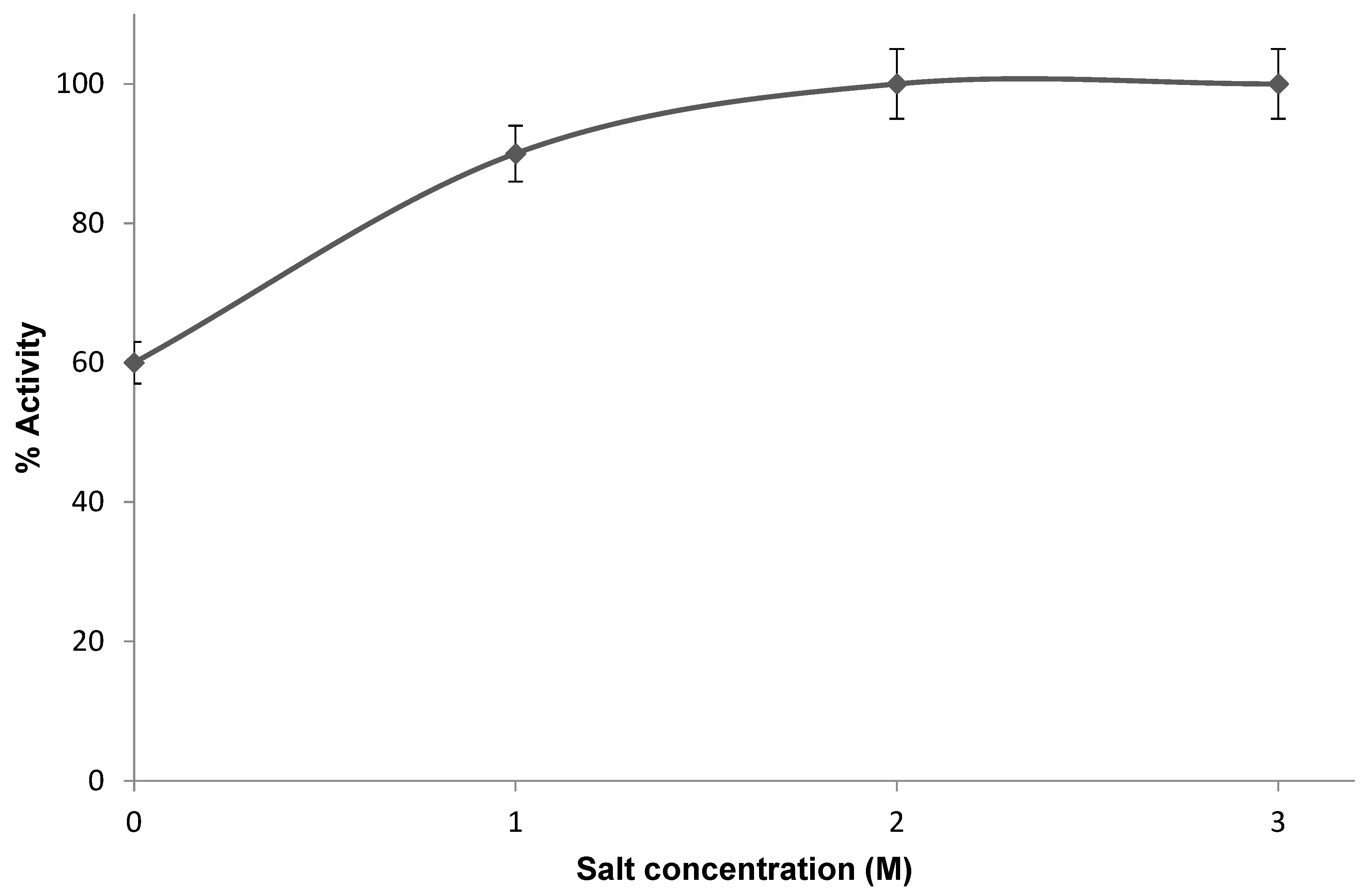
3.2. Characterizationof PHA Synthase
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nayanathara Thathsarani Pilapitiya, P.G.C.; Ratnayake, A.S. The world of plastic waste: A review. Clean. Mater. 2024, 11, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, R.; Chandra, A.; Sen, S.; Konyukhov, Y.; Fuentes, E.; Burmistrov, I.; Kravchenko, M. Microplastics and Nanoplastics as Environmental Contaminants of Emerging Concern: Potential Hazards for Human Health. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.; Khan, M.T.; Moholkar, V.S. Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs): Mechanistic Insights and Contributions to Sustainable Practices. Encyclopedia 2024, 4, 1933–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obruča, S.; Dvořák, P.; Sedláček, P.; Koller, M.; Sedlář, K.; Pernicová, I.; Šafránek, D. Polyhydroxyalkanoates synthesis by halophiles and thermophiles: Towards sustainable production of microbial bioplastics. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 58, 107906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsafadi, D.; Al-Mashaqbeh, O.; Mansour, A.; Alsaad, M. Optimization of Nitrogen Source Supply for Enhanced Biosynthesis and Quality of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-3-Hydroxyvalerate) by Extremely Halophilic Archaeon Haloferax mediterranei. Microbiologyopen 2020, 9, e1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novackova, I.; Kourilova, X.; Mrazova, K.; Sedlacek, P.; Kalina, M.; Krzyzanek, V.; Koller, M.; Obruca, S. Combination of Hypotonic Lysis and Application of Detergent for Isolation of Polyhydroxyalkanoates from Extremophiles. Polymers 2022, 14, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, R.; Xu, T.; Xiang, H.; Han, J. Current developments on polyhydroxyalkanoates synthesis by using halophiles as a promising cell factory. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.I.; Alsafadi, D.; Alamry, K.A.; Hussein, M.A. Properties and Applications of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Biocomposites. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 1010–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Bergsma, S.; Colpa, D.I.; Euverink, G.-J.W.; Krooneman, J. Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) synthesis and degradation by microbes and applications towards a circular economy. J. Environ. Manage. 2023, 341, 118033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozejko-Ciesielska, J.; Szacherska, K.; Marciniak, P. Pseudomonas Species as Producers of Eco-friendly Polyhydroxyalkanoates. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 1151–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonio, R.V.; Steinbüchel, A.; Rehm, B.H.A. Analysis of in vivo substrate specificity of the PHA synthase from Ralstonia eutropha: Formation of novel copolyesters in recombinant Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 182, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Shi, M.; Zhang, T.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Xian, M. Natural and engineered polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthase: Key enzyme in biopolyester production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 7417–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, B.H.A.; Krüger, N.; Steinbüchel, A. A New Metabolic Link between Fatty Acid Synthesis and Polyhydroxyalkanoic Acid Synthesis. The PHAG gene from Pseudomonas putida KT2440 encodes a 3-hydroxyacyl-acyl carrier protein-coenzyme a transferase. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 24044–24051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Lu, Q.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, J.; Xiang, H. Molecular Characterization of the phaECHm Genes, Required for Biosynthesis of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) in the Extremely Halophilic Archaeon Haloarcula marismortui. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 6058–6065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool Gabriel, J.; Cannon Maura, C. PhaC and PhaR Are Required for Polyhydroxyalkanoic Acid Synthase Activity in Bacillus megaterium. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 4235–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simica, A.; Segovia, Y.; Navarro-Sempere, A.; Martínez-Espinosa, R.M.; Pire, C. Advanced Strategies for Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Production: PHA Synthase Homologous Overexpression in the Extremophile Haloferax mediterranei. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Li, M.; Hou, J.; Wu, L.; Zhou, J.; Xiang, H. Comparison of four phaC genes from Haloferax mediterranei and their function in different PHBV copolymer biosyntheses in Haloarcula hispanica. Saline Syst. 2010, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Han, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, J.; Xiang, H. Genetic and Biochemical Characterization of the Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-co-3-Hydroxyvalerate) Synthase in Haloferax mediterranei. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 4173–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, F.; Wang, M.; Huang, H.; Kim, Y.; Lansing, S.; Wang, Z. Haloferax mediterranei for bioplastics production from wasted materials: Potential, opportunities, and challenges. Adv. Bioenergy 2025, 10, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsafadi, D.; Al-Mashaqbeh, O. A one-stage cultivation process for the production of poly-3-(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) from olive mill wastewater by Haloferax mediterranei. New Biotechnol. 2017, 34, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsafadi, D.; Al-Mashaqbeh, O.; Oqdeh, S.; Mansour, A. Dead Sea water as a sustainable source for the production of microbial bioplastics polyhydroxyalkanoates by halophiles. Bior. Technol. Rep. 2024, 28, 101989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, H.E.; Steinbüchel, A. Application of enzymatically synthesized short-chain-length hydroxy fatty acid coenzyme A thioesters for assay of polyhydroxyalkanoic acid synthases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1994, 40, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Hou, J.; Liu, H.; Cai, S.; Feng, B.; Zhou, J.; Xiang, H. Wide Distribution among Halophilic Archaea of a Novel Polyhydroxyalkanoate Synthase Subtype with Homology to Bacterial Type III Synthases. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7811–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantazaki, A.A.; Tambaka, M.G.; Langlois, V.; Guerin, P.; Kyriakidis, D.A. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) biosynthesis in Thermus thermophilus: Purification and biochemical properties of PHA synthase. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 254, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkateswar Reddy, M.; Mawatari, Y.; Onodera, R.; Nakamura, Y.; Yajima, Y.; Chang, Y.-C. Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) production from synthetic waste using Pseudomonas pseudoflava: PHA synthase enzyme activity analysis from P. pseudoflava and P. palleronii. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 234, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhubalan, K.; Chuah, J.A.; Shozui, F.; Brigham, C.J.; Taguchi, S.; Sinskey, A.J.; Rha, C.; Sudesh, K. Characterization of the highly active polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase of Chromobacterium sp. strain USM2. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2926–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, K.; Han, X.; Hashimoto, Y.; Satoh, Y.; Satoh, T.; Taguchi, S. In vitro synthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates using thermostable acetyl-CoA synthetase, CoA transferase, and PHA synthase from thermotorelant bacteria. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 122, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, M.; Kataoka, K.; Shirai, M.; Asada, Y. Control of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate synthase mediated by acetyl phosphate in cyanobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 5009–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Jia, Y.; Tian, J.; Snell, K.D.; Müh, U.; Sinskey, A.J.; Lambalot, R.H.; Walsh, C.T.; Stubbe, J. Class I and III Polyhydroxyalkanoate Synthases from Ralstonia eutropha and Allochromatium vinosum: Characterization and Substrate Specificity Studies. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 394, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duangsri, C.; Salminen, T.A.; Alix, M.; Kaewmongkol, S.; Akrimajirachoote, N.; Khetkorn, W.; Jittapalapong, S.; Mäenpää, P.; Incharoensakdi, A.; Raksajit, W. Characterization and Homology Modeling of Catalytically Active Recombinant PhaCAp Protein from Arthrospira platensis. Biology 2023, 12, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siglioccolo, A.; Paiardini, A.; Piscitelli, M.; Pascarella, S. Structural adaptation of extreme halophilic proteins through decrease of conserved hydrophobic contact surface. BMC Struct. Biol. 2011, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esclapez, J.; Pire, C.; Bautista, V.; Martínez-Espinosa, R.M.; Ferrer, J.; Bonete, M.J. Analysis of acidic surface of Haloferax mediterranei glucose dehydrogenase by site-directed mutagenesis. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferre-Guell, A.; Winterburn, J. Increased production of polyhydroxyalkanoates with controllable compositionand consistent material properties by fed-batch fermentation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2019, 141, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alsafadi, D.; Ghalawinji, Y.; Khalili, F.I. Purification and Characterization of Polyhydroxyalkanoate Synthase from Extremely Halophilic Archaeon Haloferax mediterranei: Key Enzyme of Biodegradable Plastic Synthesis. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12091003
Alsafadi D, Ghalawinji Y, Khalili FI. Purification and Characterization of Polyhydroxyalkanoate Synthase from Extremely Halophilic Archaeon Haloferax mediterranei: Key Enzyme of Biodegradable Plastic Synthesis. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(9):1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12091003
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlsafadi, Diya, Yomen Ghalawinji, and Fawwaz I. Khalili. 2025. "Purification and Characterization of Polyhydroxyalkanoate Synthase from Extremely Halophilic Archaeon Haloferax mediterranei: Key Enzyme of Biodegradable Plastic Synthesis" Bioengineering 12, no. 9: 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12091003
APA StyleAlsafadi, D., Ghalawinji, Y., & Khalili, F. I. (2025). Purification and Characterization of Polyhydroxyalkanoate Synthase from Extremely Halophilic Archaeon Haloferax mediterranei: Key Enzyme of Biodegradable Plastic Synthesis. Bioengineering, 12(9), 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12091003




